ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cross-Sectional Study
2.2. Longitudinal Study
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Clinical Examination and Blood Sampling
2.5. Biochemical Assays
2.6. ANGPTL-4 Pre-Adsorption
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
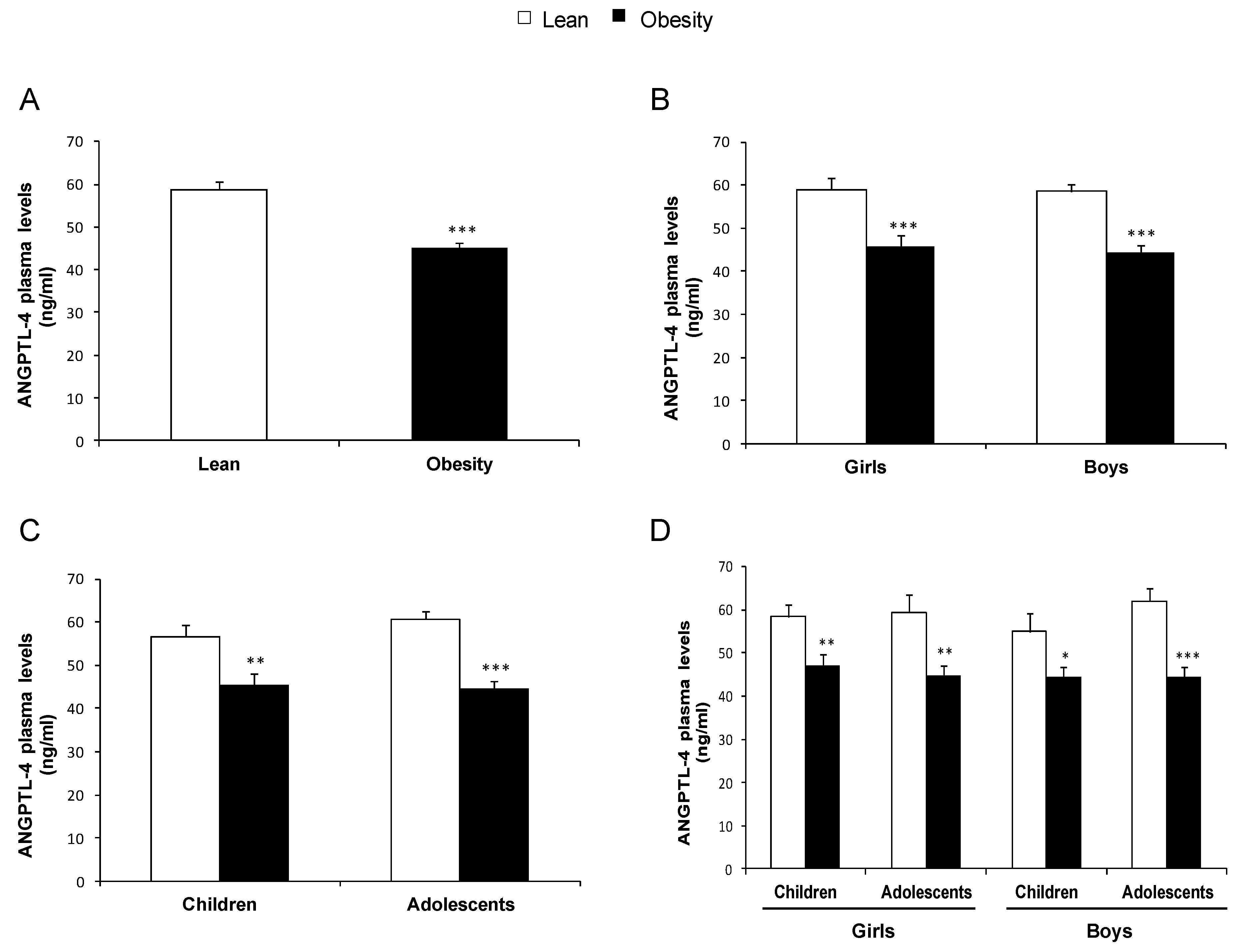
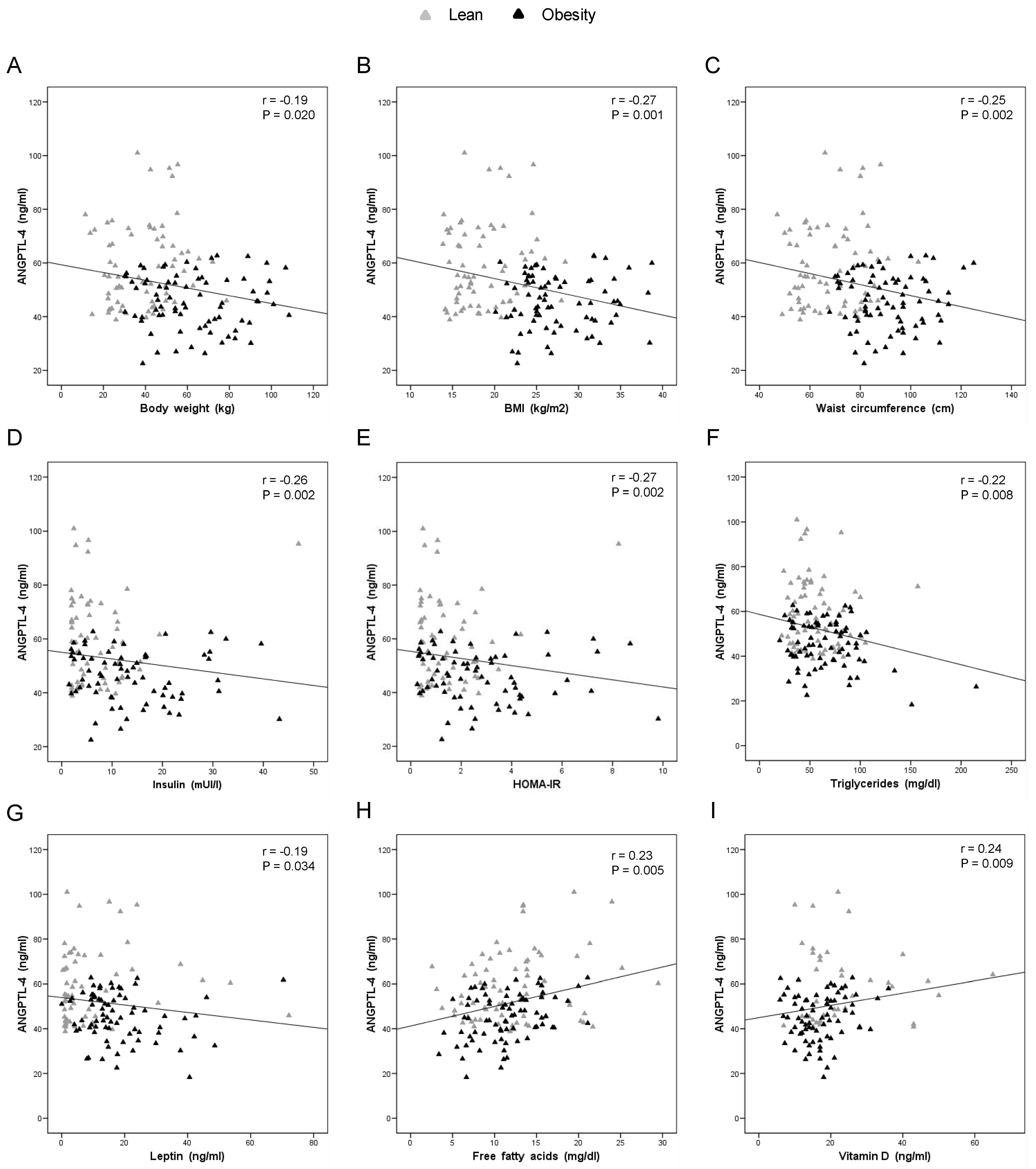
3.1. Plasma ANGPTL-4 Levels Are Reduced in Children and Adolescents with Obesity and Associated with Obesity-Related Parameters
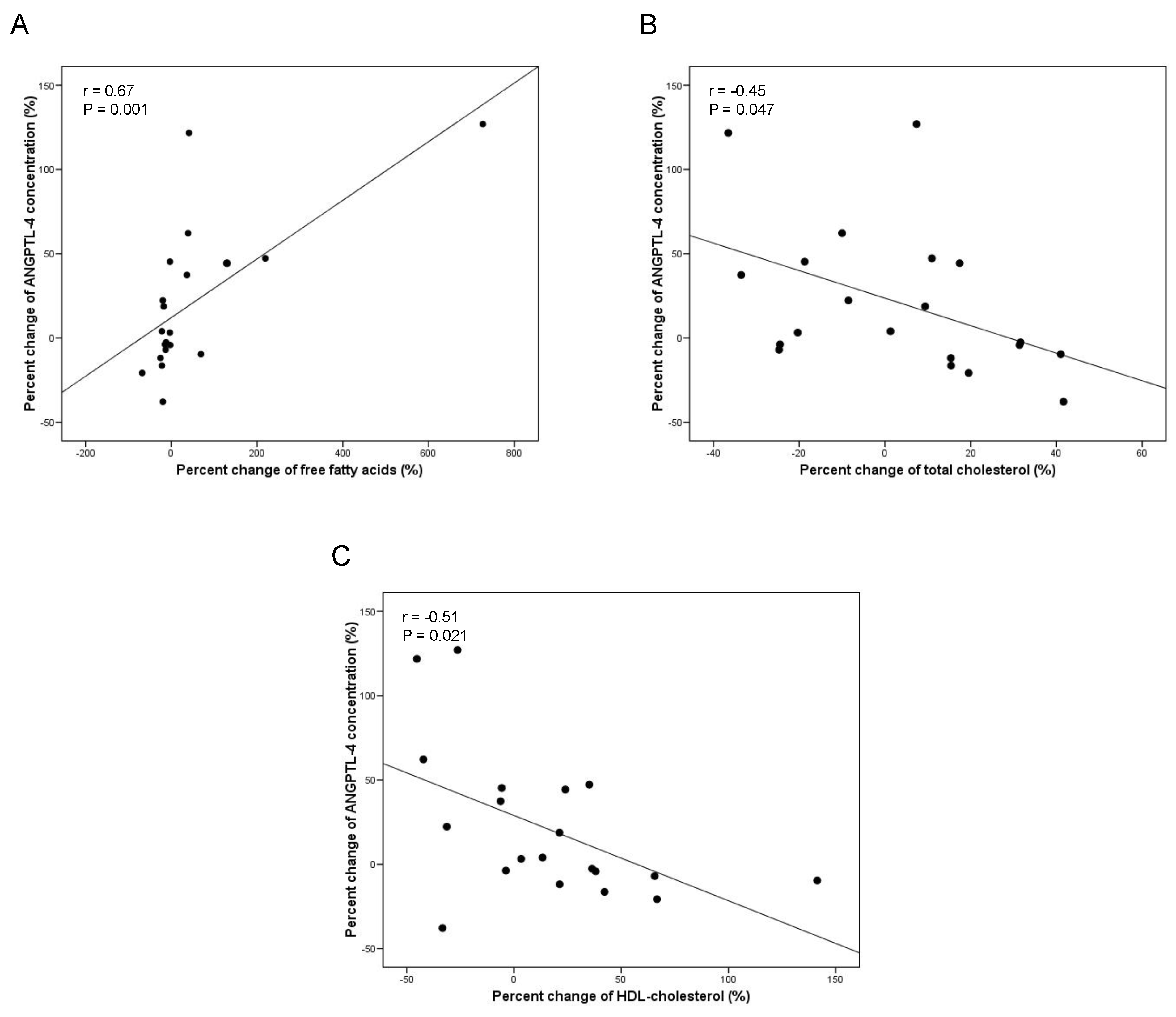
3.2. Impact of BMI Loss and Plasma Lipid Changes on ANGPTL-4 Circulating Levels
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, I.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.H.; Park, S.K.; Uhm, C.S.; Lee, Z.H.; Koh, G.Y. Hepatic expression, synthesis and secretion of a novel fibrinogen/angiopoietin-related protein that prevents endothelial-cell apoptosis. Biochem. J. 2000, 346, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Mandard, S.; Tan, N.S.; Escher, P.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Characterization of the fasting-induced adipose factor FIAF, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28488–28493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandard, S.; Zandbergen, F.; van Straten, E.; Wahli, W.; Kuipers, F.; Muller, M.; Kersten, S. The fasting-induced adipose factor/angiopoietin-like protein 4 is physically associated with lipoproteins and governs plasma lipid levels and adiposity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, S.; Lichtenstein, L.; Steenbergen, E.; Mudde, K.; Hendriks, H.F.; Hesselink, M.K.; Schrauwen, P.; Müller, M. Caloric restriction and exercise increase plasma ANGPTL4 levels in humans via elevated free fatty acids. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Youn, B.S.; Shin, M.S.; Namkoong, C.; Park, K.H.; Baik, J.H.; Baik, J.H.; Kim, J.B.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; et al. Hypothalamic Angptl4/Fiaf is a novel regulator of food intake and body weight. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijk, W.; Kersten, S. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase by Angptl4. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Goh, Y.Y.; Chin, H.F.; Kersten, S.; Tan, N.S. Angiopoietin-like 4: A decade of research. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Shi, F.; Basu, D.; Huq, A.; Routhier, S.; Day, R.; Jin, W. Proteolytic processing of angiopoietin-like protein 4 by proprotein convertases modulates its inhibitory effects on lipoprotein lipase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15747–15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandard, S.; Zandbergen, F.; Tan, N.S.; Escher, P.; Patsouris, D.; Koenig, W.; Kleemann, R.; Bakker, A.; Veenman, F.; Wahli, W.; et al. The direct peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target fasting-induced adipose factor (FIAF/PGAR/ANGPTL4) is present in blood plasma as a truncated protein that is increased by fenofibrate treatment. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 34411–34420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robciuc, M.R.; Tahvanainen, E.; Jauhiainen, M.; Ehnholm, C. Quantitation of serum angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 in a Finnish population sample. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattijssen, F.; Kersten, S. Regulation of triglyceride metabolism by Angiopoietin-like proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Tan, M.J.; Huang, R.L.; Tan, C.K.; Chong, H.C.; Pal, M.; Lam, C.R.; Boukamp, P.; Pan, J.Y.; Tan, S.H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 protein elevates the prosurvival intracellular O2(-):H2O2 ratio and confers anoikis resistance to tumors. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen, A.E.; Kanamaluru, D.; Yan, K.; Gray, N.E.; Wu, L.; Li, M.L.; Chang, A.; Hasan, A.; Stifler, D.; Koliwad, S.K.; et al. The C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain of angiopoietin-like 4 stimulates adipose tissue lipolysis and promotes energy expenditure. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16122–16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, H.; Haas, C.; Machann, J.; Werner, R.; Weisser, M.; Schick, F.; Machicao, F.; Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.U. Muscle-derived angiopoietin-like protein 4 is induced by fatty acids via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-delta and is of metabolic relevance in humans. Diabetes 2009, 58, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, J.T.; Smit, J.W.; Hammer, S.; Snel, M.; van der Meer, R.W.; Lamb, H.J.; Mattijssen, F.; Mudde, K.; Jazet, I.M.; Dekkers, O.M.; et al. Dietary modulation of plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 concentrations in healthy volunteers and in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catoire, M.; Alex, S.; Paraskevopulos, N.; Mattijssen, F.; Evers-van Gogh, I.; Schaart, G.; Jeppesen, J.; Kneppers, A.; Mensink, M.; Voshol, P.J.; et al. Fatty acid-inducible ANGPTL4 governs lipid metabolic response to exercise. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1043–E1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robciuc, M.R.; Naukkarinen, J.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Tyynismaa, H.; Raivio, T.; Rissanen, A.; Kaprio, J.; Ehnholm, C.; Jauhiainen, M.; Pietiläinen, K.H. Serum angiopoietin-like 4 protein levels and expression in adipose tissue are inversely correlated with obesity in monozygotic twins. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart-Halajko, M.C.; Robciuc, M.R.; Cooper, J.A.; Jauhiainen, M.; Kumari, M.; Kivimaki, M.; Khaw, K.T.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Wareham, N.J.; Gaunt, T.R.; et al. The relationship between plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 levels, angiopoietin-like protein 4 genotype, and coronary heart disease risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legry, V.; Bokor, S.; Cottel, D.; Beghin, L.; Catasta, G.; Nagy, E.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Spinneker, A.; Stehle, P.; Molnár, D.; et al. Associations between common genetic polymorphisms in angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 and lipid metabolism and adiposity in European adolescents and adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5070–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Fu, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yin, R.X.; Cao, X.L.; Huang, F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Chen, W.X. ANGPTL4 variants and their haplotypes are associated with serum lipid levels, the risk of coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke and atorvastatin cholesterol-lowering responses. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2018, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Khairi, I.; Cherian, P.; Chandy, B.; Sriraman, D.; Alhubail, A.; Al-Refaei, F.; AlTerki, A.; Abubaker, J. Increased ANGPTL3, 4 and ANGPTL8/betatrophin expression levels in obesity and T2D. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barja-Fernandez, S.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Folgueira, C.; Xifra, G.; Sabater, M.; Castelao, C.; FernØ, J.; Leis, R.; Diéguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. Plasma ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Glucose Tolerance: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Findings. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.E.; Lam, L.N.; Yang, K.; Zhou, A.Y.; Koliwad, S.; Wang, J.C. Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) protein is a physiological mediator of intracellular lipolysis in murine adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8444–8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Gastaldelli, A. The Subtle Balance between Lipolysis and Lipogenesis: A Critical Point in Metabolic Homeostasis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9453–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Aryal, B.; Chaube, B.; Rotllan, N.; Varela, L.; Horvath, T.L.; Suárez, Y.; Fernández-Hernando, C. Brown adipose tissue derived ANGPTL4 controls glucose and lipid metabolism and regulates thermogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinkajzlova, A.; Mraz, M.; Lacinova, Z.; Klouckova, J.; Kavalkova, P.; Kratochvilova, H.; Trachta, P.; Křížová, J.; Haluzíková, D.; Škrha, J.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 3 and 4 in obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and malnutrition: The effect of weight reduction and realimentation. Nutr. Diabetes 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Y.; Yu, C.G.; Wang, X.H.; Yuan, S.S.; Zhang, L.J.; Lang, J.N.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y.M. Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4 Is a High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Component for HDL Metabolism and Function in Nondiabetic Participants and Type-2 Diabetic Patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgueira, C.; Beiroa, D.; Callon, A.; Al-Massadi, O.; Barja-Fernandez, S.; Senra, A.; Fernø, J.; López, M.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. Uroguanylin Action in the Brain Reduces Weight Gain in Obese Mice via Different Efferent Autonomic Pathways. Diabetes 2016, 65, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanian, S.; Suprasongsin, C.; Kalhan, S.C.; Drash, A.L.; Brna, R.; Janosky, J.E. Plasma leptin in children: Relationship to puberty, gender, body composition, insulin sensitivity, and energy expenditure. Metabolism 1998, 47, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghabadi, Z.A.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Alaee, M.; Larijani, B.; Razzaghy-Azar, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and angiopoietin-like protein 4 levels in obese children and adolescents. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenau, T.; Vest, R.; Gissel, T.N.; Poulsen, C.S.; Erlandsen, M.; Mosekilde, L.; Vestergaard, P. Global vitamin D levels in relation to age, gender, skin pigmentation and latitude: An ecologic meta-regression analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barja-Fernandez, S.; Aguilera, C.M.; Martinez-Silva, I.; Vazquez, R.; Gil-Campos, M.; Olza, J.; Bedoya, J.; Cadarso-Suárez, C.; Gil, Á.; Seoane, L.M.; et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels of children are inversely related to adiposity assessed by body mass index. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Lean (n = 73) | Obesity (n = 77) | p | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 10.53 (3.45) | 11.16 (3.07) | 0.24 | $ |
| Sex (girl:boy) | 38:35 | 40:37 | 0.99 | |
| Sexual development (prepuberty:puberty) | 34:39 | 38:39 | 0.73 | |
| Birth weight (kg) | 3.24 (0.63) | 3.25 (0.55) | 0.91 | $ |
| Weight (kg) | 38.70 (15.03) | 62.64 (20.86) | <0.001 | # |
| Height (cm) | 140.85 (18.46) | 148.39 (16.03) | 0.01 | $ |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.64 (3.63) | 27.56 (4.59) | <0.001 | # |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 67.89 (12.47) | 91.15 (13.27) | <0.001 | $ |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 83.86 (9.02) | 79.12 (11.76) | 0.007 | $ |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 6.72 (6.68) | 13.83 (9.69) | <0.001 | # |
| HOMA index | 1.40 (1.29) | 2.76 (2.12) | <0.001 | # |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | 298.95 (184.69) | 327.26 (189.30) | 0.51 | $ |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 55.14 (23.84) | 65.24 (31.55) | 0.03 | $ |
| Free fatty acids (mg/dL) | 12.37 (5.40) | 11.37 (3.94) | 0.41 | # |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 171.15 (36.25) | 160.49 (31.07) | 0.06 | $ |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 102.26 (35.13) | 97.24 (29.72) | 0.37 | $ |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 59.57 (13.55) | 46.60 (12.05) | <0.001 | $ |
| Leptin (ng) | 9.65 (14.28) | 18.30 (12.26) | <0.001 | $ |
| TSH (mUI/L) | 2.39 (1.18) | 2.68 (1.15) | 0.14 | $ |
| fT4 (ng/dL) | 1.08 (0.22) | 1.16 (0.13) | 0.03 | # |
| fT3 (pg/mL) | 4.26 (0.46) | 4.19 (0.40) | 0.47 | $ |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | 31.12 (36.35) | 26.13 (33.16) | 0.41 | $ |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 0.73 (1.43) | 0.46 (0.67) | 0.14 | # |
| FSH (UI/L) | 2.48 (2.16) | 2.96 (2.55) | 0.57 | # |
| Vitamin-D (ng/mL) | 23.37 (12.38) | 16.97 (6.59) | 0.006 | # |
| β (SE) | t Statistic | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 59.65 (8.87) | 6.72 | <0.001 |
| Obesity diagnostic | −14.86 (2.75) | −5.39 | <0.001 |
| Free fatty acids | 0.75 (0.27) | 2.77 | 0.007 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.15 (0.07) | 2.15 | 0.03 |
| Vitamin-D | 0.04 (0.13) | 0.28 | 0.77 |
| Total-cholesterol | −0.15 (0.07) | −2.18 | 0.03 |
| Baseline | Follow-up | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 20 | ||
| Age (year) | 10.9 (2.6) | 13.11 (2.6) | 0.01 |
| Sex (girl:boy) | 11:9 | ||
| Sexual development (prepuberty:puberty) | 9:11 | 4:16 | 0.09 |
| Weight (kg) | 60.2 (18.2) | 55.8 (12.3) | 0.37 |
| Height (cm) | 147.8 (15.6) | 156.9 (13.1) | 0.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 (3.4) | 22.3 (2.2) | <0.001 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 27.2 (10.0) | 19.6 (6.3) | 0.01 |
| Non-fat mass (kg) | 29.5 (8.5) | 32.9 (9.3) | 0.27 |
| Percent Fat mass | 45.3 (4.5) | 32.7 (7.1) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 89.4 (12.5) | 81.7 (9.0) | 0.03 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 81.4 (9.0) | 82.25 (7.9) | 0.77 |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 9.0 (5.2) | 9.5 (6.7) | 0.74 |
| HOMA index | 1.8 (1.0) | 2.0 (1.4) | 0.71 |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | 367.4 (197.2) | 362.2 (179.3) | 0.94 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 68.9 (55.8) | 69.3 (32.0) | 0.98 |
| Free fatty acids (mg/dL) | 13.5 (6.4) | 14.9 (7.0) | 0.52 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 166.8 (25.4) | 168.3 (30.4) | 0.86 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 102.6 (21.5) | 101.6 (26.9) | 0.90 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 44.3 (8.7) | 48.6 (12.5) | 0.21 |
| T-cholesterol/HDL | 3.9 (1.2) | 3.6 (1.0) | 0.44 |
| LDL/HDL | 2.4 (0.9) | 2.2 (0.9) | 0.47 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 18.2 (20.9) | 14.3 (17.4) | 0.55 |
| TSH (mUI/L) | 2.7 (1.4) | 2.5 (1.1) | 0.63 |
| fT4 (ng/dL) | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) | 0.11 |
| fT3 (pg/mL) | 4.1 (0.3) | 4.1 (0.4) | 0.86 |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | 37.6 (56.3) | 48.4 (79.4) | 0.64 |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 0.6 (1.1) | 0.6 (0.8) | 0.93 |
| FSH (UI/L) | 3.3 (2.7) | 3.1 (2.5) | 0.80 |
| Vitamin-D (ng/mL) | 26.4 (16.5) | 23.1 (14.7) | 0.52 |
| ANGPTL4 (ng/mL) | 59.7 (4.0) | 67.7 (4.1) | 0.16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barja-Fernández, S.; Folgueira, C.; Castelao, C.; Pena-León, V.; González-Saenz, P.; Vázquez-Cobela, R.; Aguilera, C.M.; Gil-Campos, M.; Bueno, G.; Gil, Á.; et al. ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061340
Barja-Fernández S, Folgueira C, Castelao C, Pena-León V, González-Saenz P, Vázquez-Cobela R, Aguilera CM, Gil-Campos M, Bueno G, Gil Á, et al. ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061340
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarja-Fernández, Silvia, Cintia Folgueira, Cecilia Castelao, Verónica Pena-León, Patricia González-Saenz, Rocío Vázquez-Cobela, Concepción M. Aguilera, Mercedes Gil-Campos, Gloria Bueno, Ángel Gil, and et al. 2019. "ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061340
APA StyleBarja-Fernández, S., Folgueira, C., Castelao, C., Pena-León, V., González-Saenz, P., Vázquez-Cobela, R., Aguilera, C. M., Gil-Campos, M., Bueno, G., Gil, Á., Moreno, L. A., Ruiz-Piñon, M., García-Palacios, M., Casanueva, F. F., Diéguez, C., Nogueiras, R., Leis, R., & Seoane, L. M. (2019). ANGPTL-4 is Associated with Obesity and Lipid Profile in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients, 11(6), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061340









