Development of a Choline Database to Estimate Australian Population Intakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of an Australian Choline Database
2.1.1. Systematic Literature Review
2.1.2. Assigning Food Composition Data
2.2. Australian Choline Intakes Using the Australian Health Survey
3. Results
3.1. Australian Choline Database
- 1.
- 2.
- USDA database for the choline content (4530 foods).
- Substitutions were made based on similar energy contributions and conceptual descriptions of food appearance (2576 substitutions).
- Recipe calculations were used (105 new recipes were created).
- Analytical data was used for 26 data points. This included several varieties of pulses (chickpeas, black beans and lima beans), shellfish and seafood (shrimp).
- In total, 2707 foods matches came from a USDA source
- 3.
- In total, 5597 foods were aligned with a choline value (97.51% of the AUSNUT 2011-13 database). The database can be sourced by contacting the corresponding author of this study. Where a zero value was provided, no values were identified. While traditionally zero values are reserved for foods without any trace amounts of a nutrient i.e., theoretical zero, for the purpose of the subsequent analyses in this study, zero was used. Many of these foods may also contain trace or values below the limits of quantification.
- 4.
- Betaine and choline were commonly reported together. Where this occurred, betaine data was also added to the database (3910 foods in total).
3.2. Australian Population Intakes of Choline
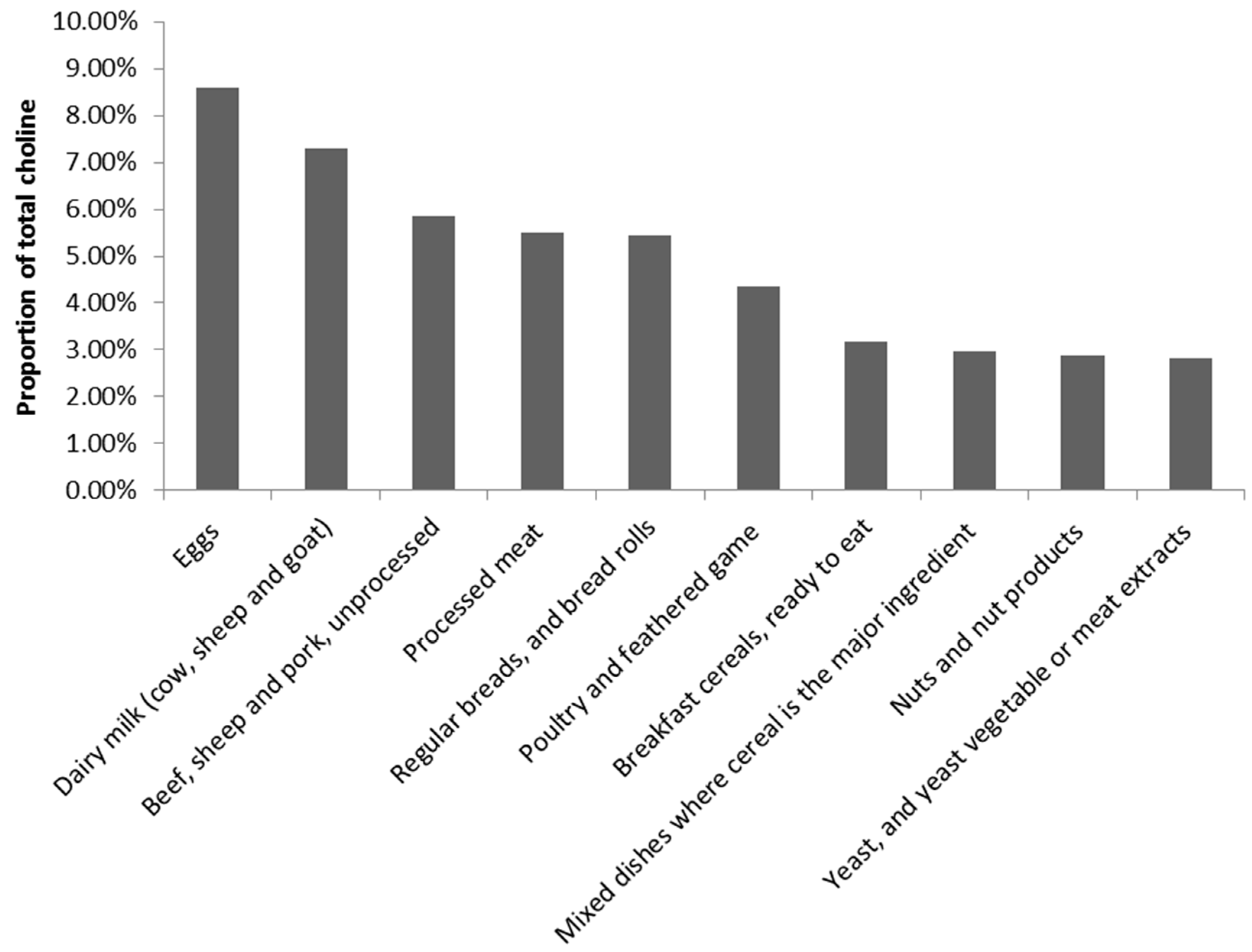
3.2.1. Food Sources of Choline for the Australian Population
3.2.2. Food Groups Associated with High Choline Intake
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2006.
- Zeisel, S.H. A brief history of choline. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, L.M.; Dacosta, K.A.; Kwock, L.; Stewart, P.W.; Lu, T.-S.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; Zeisel, S.H. Sex and menopausal status influence human dietary requirements for the nutrient choline. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resseguie, M.E.; da Costa, K.-A.; Galanko, J.A.; Patel, M.; Davis, I.J.; Zeisel, S.H. Aberrant estrogen regulation of PEMT results in choline deficiency-associated liver dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline: Critical role during fetal development and dietary requirements in adults. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, C.D.; Cifasd, T.; Kable, J.A.; Keen, C.L.; Jones, K.L.; Wertelecki, W.; Granovska, I.V.; Pashtepa, A.O.; Chambers, C.D. Dose and timing of prenatal alcohol exposure and maternal nutritional supplements: Developmental effects on 6-month-old infants. Matern. Child Heal. J. 2015, 19, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.G.; Hunter, S.K.; McCarthy, L.; Beuler, J.; Hutchison, A.K.; Wagner, B.D.; Leonard, S.; Stevens, K.E.; Freedman, R. Perinatal choline effects on neonatal pathophysiology related to later schizophrenia risk. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.D. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, D.E.; Castro, R.; Loscalzo, J. Epigenetic modifications: Basic mechanisms and role in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2011, 123, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaie, S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary choline and betaine intakes and risk of cardiovascular diseases: Review of epidemiological evidence. ARYA Atheroscler. 2011, 7, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blusztajn, J.K.; Slack, B.E.; Mellott, T.J. Neuroprotective Actions of Dietary Choline. Nutrients 2017, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherriff, J.L.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; Properzi, C.; Oddo, J.-L.; A Adams, L. Choline, Its potential role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and the case for human and bacterial genes. Adv. Nutr. Int. J. 2016, 7, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, A.K.; Woods, K.; McMahon, A.; Probst, Y. Food composition database format and structure: A user focused approach. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Neale, E.P.; Tapsell, L.C.; Martin, A.; Batterham, M.J.; Wibisono, C.; Probst, Y.C. Impact of providing walnut samples in a lifestyle intervention for weight loss: a secondary analysis of the HealthTrack trial. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1344522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, Y.C.; Cunningham, J. An overview of the influential developments and stakeholders within the food composition program of Australia. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. USDA Table of Nutrient Retention Factors, Release 6; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. The Australian Health Survey 2011–13. Available online: http://www.abs.gov.au/australianhealthsurvey (accessed on 17 April 2019).
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. AUSNUT 2011–13—Australian Food, Supplement and Nutrient Database for Estimation of Population Nutrient Intakes; FSANZ: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Galea, L.M.; Dalton, S.M.; Beck, E.J.; Cashman, C.J.; Probst, Y.C. Update of a database for estimation of whole grain content of foods in Australia. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2016, 50, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, E.; Neale, E.; Charlton, K.E.; Morton, K.; Probst, Y.C. First stage development of an Australian anthocyanin food composition database for dietary studies—a systematic process and its challenges. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2017, 64, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. USDA Database for the Choline Content of Common Foods, Release 2. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400525/Data/Choline/Choln02.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2018).
- Food and Agriculture Organization. FAO/INFOODS Guidelines for Food Matching; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. AUSNUT 2011–13 Food Recipe File. Available online: http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/science/monitoringnutrients/ausnut/ausnutdatafiles/Pages/foodrecipe.aspx (accessed on 17 December 2018).
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Australian Health Survey: Users’ Guide, 2011–13; ABS: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Lewis, E.D.; Kosik, S.J.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Jacobs, R.L.; Curtis, J.M.; Field, C.J. Total Choline and Choline-Containing Moieties of Commercially Available Pulses. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.D.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Richard, C.; Bruce, H.L.; Jacobs, R.L.; Field, C.; Curtis, J.M. Measurement of the abundance of choline and the distribution of choline-containing moieties in meat. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, C.; Lewis, E.D.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Asomaning, J.; Jacobs, R.L.; Field, C.J.; Curtis, J.M. Measurement of the total choline content in 48 commercial dairy products or dairy alternatives. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2016, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Nutrient Intakes from Food: Mean Amounts Consumed Per Individual, by Gender and Age, What We Eat in America, NHANES 2013–2014. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400530/pdf/1314/Table_1_NIN_GEN_13.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Vennemann, F.B.C.; Ioannidou, S.; Valsta, L.M.; Dumas, C.; Ocké, M.C.; Mensink, G.B.M.; Lindtner, O.; Virtanen, S.M.; Tlustos, C.; D’Addezio, L.; et al. Dietary intake and food sources of choline in European populations. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mygind, V.L.; Evans, S.E.; Peddie, M.C.; Miller, J.C.; Houghton, L.A. Estimation of usual intake and food sources of choline and betaine in New Zealand reproductive age women. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 22, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, E.D.; Subhan, F.B.; Bell, R.C.; McCargar, L.J.; Curtis, J.M.; Jacobs, R.L.; Field, C.J.; The APrON Team. Estimation of choline intake from 24 h dietary intake recalls and contribution of egg and milk consumption to intake among pregnant and lactating women in Alberta. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.C.; Fulgoni, V.L. Assessment of Total Choline Intakes in the United States. J. Am. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonemori, K.M.; Lim, U.; Koga, K.R.; Wilkens, L.R.; Au, D.; Boushey, C.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Kolonel, L.N.; Murphy, S.P. Dietary Choline and Betaine Intakes Vary in an Adult Multiethnic Population. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Mar, M.-H.; Howe, J.C.; Holden, J.M. Concentrations of choline-containing compounds and betaine in common foods. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSW Food Authority. Mercury and Fish. Available online: http://www.foodauthority.nsw.gov.au/foodsafetyandyou/life-events-and-food/pregnancy/mercury-and-fish (accessed on 21 February 2019).
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. AUSNUT 2011–13 Food Measures Database File. Available online: http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/science/monitoringnutrients/ausnut/classificationofsupps/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 18 April 2019).
- Hiza, H.A.; Casavale, K.O.; Guenther, P.M.; Davis, C.A. Diet Quality of Americans Differs by Age, Sex, Race/Ethnicity, Income, and Education Level. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Leung, C.W.; Li, Y.; Ding, E.L.; Chiuve, S.E.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Trends in dietary quality among adults in the United States, 1999 through 2010. JAMA Int. Med. 2014, 174, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Choline, mg | n | Population Equivalent. 1 | Mean | SE | 95% CI | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | AI 2, Mg/Day | Intake ≥ AI 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % (n =) | Population Equivalent. 1 | |||||||||||
| Total intake | 12,153 | 21,526,456 | 265.18 | 1.30 | 262.58–267.77 | 0.00–198.09 | 198.09–249.90 | 249.90–315.64 | 315.64–578.57 | NA | - | - |
| Children | ||||||||||||
| 2–3 years | 464 | 561,399.4 | 185.36 | 3.43 | 178.50–192.22 | 0.00–148.97 | 148.97–178.91 | 178.91–212.40 | 212.40–380.50 | 200 | 67.03% (311) | 382,817.22 |
| 4–8 years | 789 | 1,372,102 | 203.37 | 2.92 | 197.530–209.21 | 0.00– 154.78 | 154.78–189.68 | 189.68–232.29 | 232.29–411.17 | 250 | 20.03% (158) | 261,468.33 |
| Male | ||||||||||||
| 9-13 years | 392 | 770,917.54 | 244.17 | 5.17 | 233.82–254.52 | 0.00–195.99 | 195.99–240.21 | 240.21–284.74 | 284.74–464.58 | 375 | 7.14% (28) | 54,114.994 |
| 14–18 years | 403 | 660,624.57 | 275.37 | 6.24 | 262.89–287.85 | 0.00–215.43 | 215.43–251.69 | 251.69–327.02 | 327.02–569.06 | 550 | 1.99% (8) | 11,233.998 |
| 19–64 years | 3372 | 6,899,404 | 310.54 | 2.49 | 305.56–315.51 | 0.00–232.12 | 232.12–293.67 | 293.67–367.42 | 367.42–676.34 | 550 | 3.74% (126) | 246,086.08 |
| 65–85 years | 910 | 1,374,767 | 281.29 | 3.28 | 274.73–287.86 | 0.00–222.38 | 222.38–271.42 | 271.42–329.75 | 329.75–541.46 | 550 | 1.21% (11) | 12,317.192 |
| Female | ||||||||||||
| 9–13 years | 395 | 755,088.81 | 228.06 | 4.50 | 219.05–237.06 | 0.00–175.76 | 175.76–222.25 | 222.25–267.81 | 267.81–443.44 | 375 | 4.30% (17) | 27,728.827 |
| 14–18 years | 367 | 645,741.25 | 229.02 | 6.28 | 216.46–241.59 | 0.00–173.31 | 173.30–214.51 | 214.51–274.77 | 274.77–493.26 | 400 | 1.91% (7) | 10,866.495 |
| Pregnant (14–18 years) | 2 | 4,220.548 | 151.50 | 26.94 | 97.60–205.40 | - | - | - | - | 415 | 0 | 0 |
| 19–64 years | 3640 | 6,521,097 | 247.65 | 1.92 | 243.82–251.49 | 0.00–191.10 | 191.10–236.41 | 236.41–291.21 | 291.21–510.75 | 425 | 3.32% (121) | 237,729.29 |
| Pregnant (19–50 years) | 116 | 213,030.18 | 252.91 | 10.32 | 232.25–273.57 | 0.00–193.15 | 193.15–250.72 | 250.72–304.46 | 304.46–428.67 | 440 | 0.86% (1) | 1,658.7132 |
| Lactating (19–50 years) | 110 | 202,643.04 | 253.86 | 8.01 | 237.84–269.88 | 0.00–195.44 | 195.44–256.93 | 256.93–295.00 | 295.00–478.55 | 550 | 0.91% (1) | 166.809503 |
| 65–85 years | 1193 | 1,545,421 | 249.00 | 2.59 | 243.80–254.18 | 0.00–198.49 | 198.49–239.17 | 239.17–287.35 | 287.35–479.60 | 425 | 3.02% (36) | 46,117.23 |
| Childbearing age (16–44 years) 3 | 2210 | 4,073,867 | 243.63 | 2.09 | 246.01–254.71 | 0.00–187.43 | 187.43–233.12 | 233.12–290.76 | 290.76–511.08 | 425, 19–44 years 4 | 4.75% (102, 19–44 years 5) | 195,107.54 19–44 years 6 |
| Coefficient | Jackknife Standard Error | T | P > |t| | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choline | 48.245 | 1.388 | 34.76 | 0.000 |
| Energy | −0.001 | 0.001 | −0.86 | 0.378 |
| Physical activity 2 | 0.542 | 0.715 | 0.76 | 0.451 |
| Gender | −9.131 | 2.174 | −4.20 | 0.000 |
| Age | −0.098 | 0.071 | −1.38 | 0.172 |
| Education level 3 | 2.174 | 0.563 | 3.86 | 0.000 |
| Coefficient | Jackknife Standard Error | T | P > |t| | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choline | 30.558 | 1.374 | 22.25 | 0.000 |
| Energy | −0.005 | 0.001 | −7.73 | 0.000 |
| Physical activity 2 | −1.128 | 0.640 | −1.76 | 0.083 |
| Gender | 2.114 | 1.712 | 1.23 | 0.222 |
| Age | 0.023 | 0.534 | 0.42 | 0.673 |
| Education level 3 | 0.321 | 0.447 | 0.72 | 0.475 |
| Coefficient | Jackknife Standard Error | T | P > |t| | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choline | 2.882 | 0.917 | 3.14 | 0.003 |
| Energy | 0.008 | 0.001 | 12.53 | 0.000 |
| Physical activity 2 | 0.991 | 0.534 | 1.86 | 0.069 |
| Gender | –0.402 | 1.403 | –0.29 | 0.776 |
| Age | 0.693 | 0.048 | –8.77 | 0.000 |
| Education level 3 | -6.667 | 0.335 | 2.07 | 0.043 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Probst, Y.; Guan, V.; Neale, E. Development of a Choline Database to Estimate Australian Population Intakes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040913
Probst Y, Guan V, Neale E. Development of a Choline Database to Estimate Australian Population Intakes. Nutrients. 2019; 11(4):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040913
Chicago/Turabian StyleProbst, Yasmine, Vivienne Guan, and Elizabeth Neale. 2019. "Development of a Choline Database to Estimate Australian Population Intakes" Nutrients 11, no. 4: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040913
APA StyleProbst, Y., Guan, V., & Neale, E. (2019). Development of a Choline Database to Estimate Australian Population Intakes. Nutrients, 11(4), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040913





