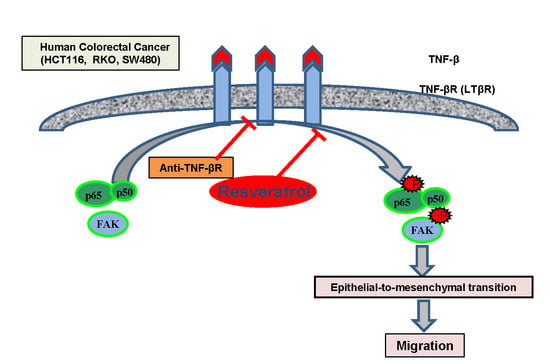
Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human TNF-β (Lymphotoxin) and its Reversal by Resveratrol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies, Cytokines, and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Immunofluorescence Investigations
2.5. Three Dimensional Alginate Culture
2.6. Invasion and Colony Forming Assay
2.7. Cell Viability Investigation from Alginate Culture
2.8. Ultrastructural Investigations
2.9. Pre-Embedding for Ultrastructural Immunoelectron Microscopy
2.10. Immunoblotting Investigations
2.11. Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
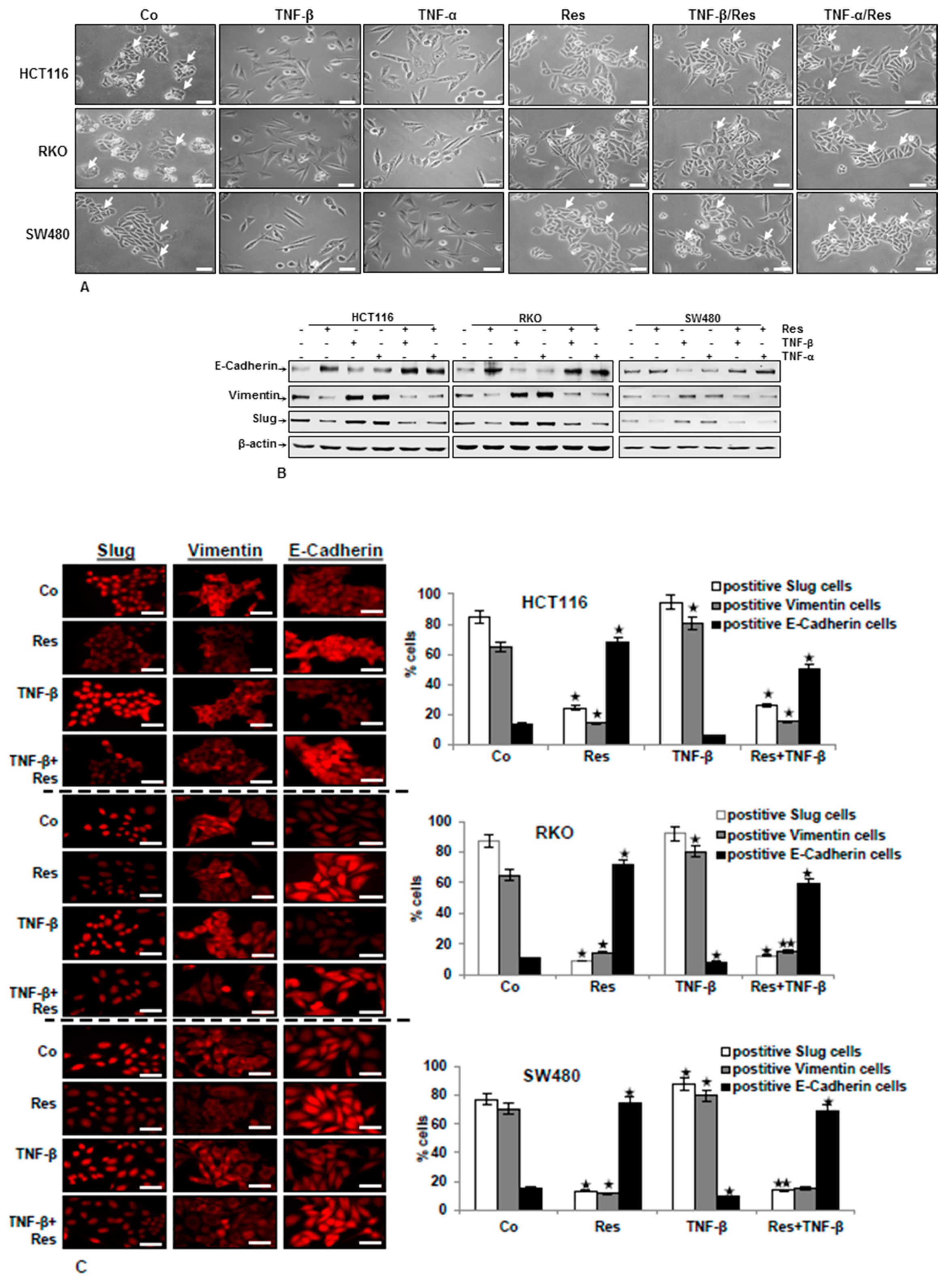
3.1. TNF-β Induces EMT in CRC Cells and Resveratrol Reverses That
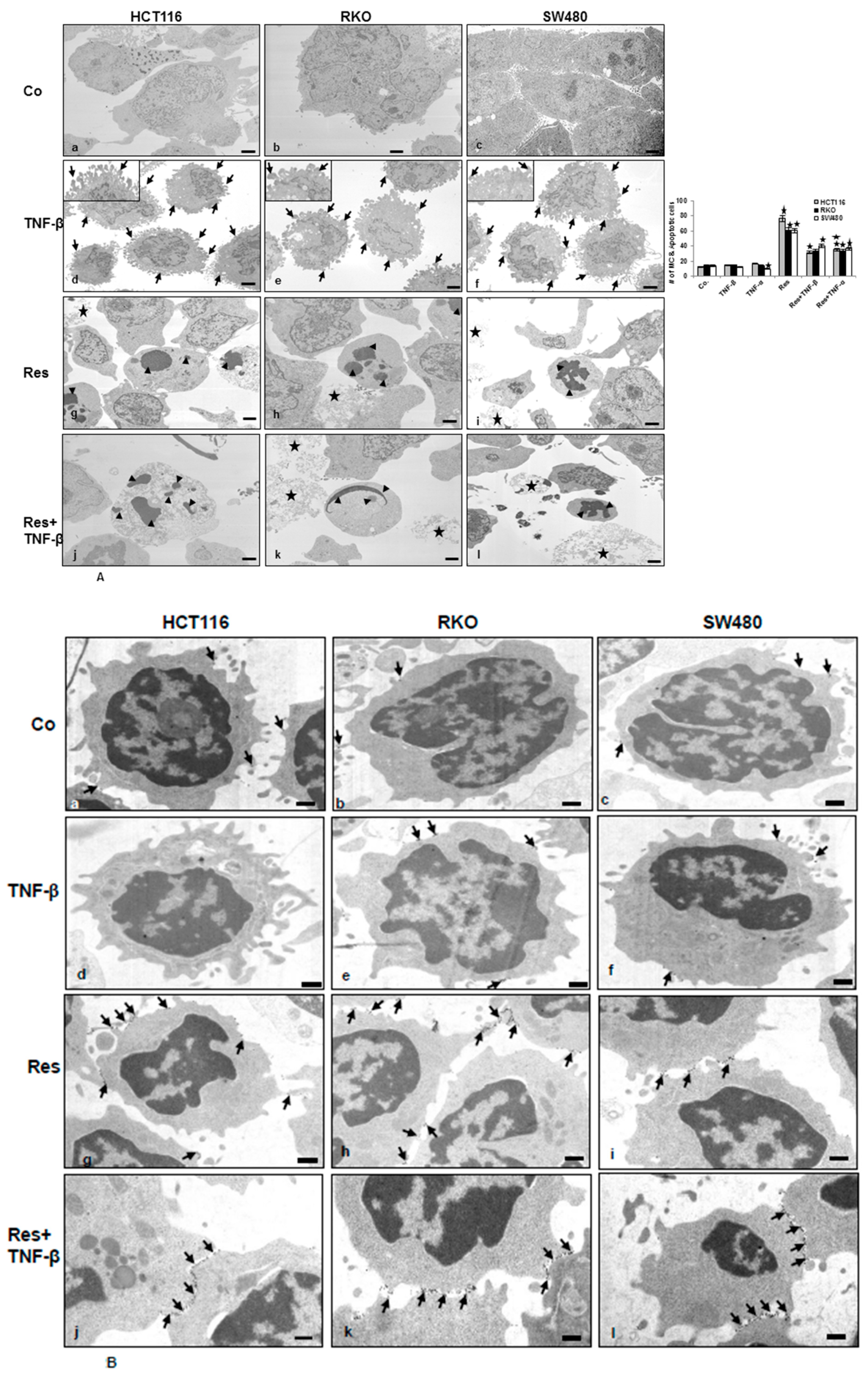
3.2. Resveratrol Suppresses CRC Cell Malignancy by Modifying the Ultrastructure of the Cell Surface Protein
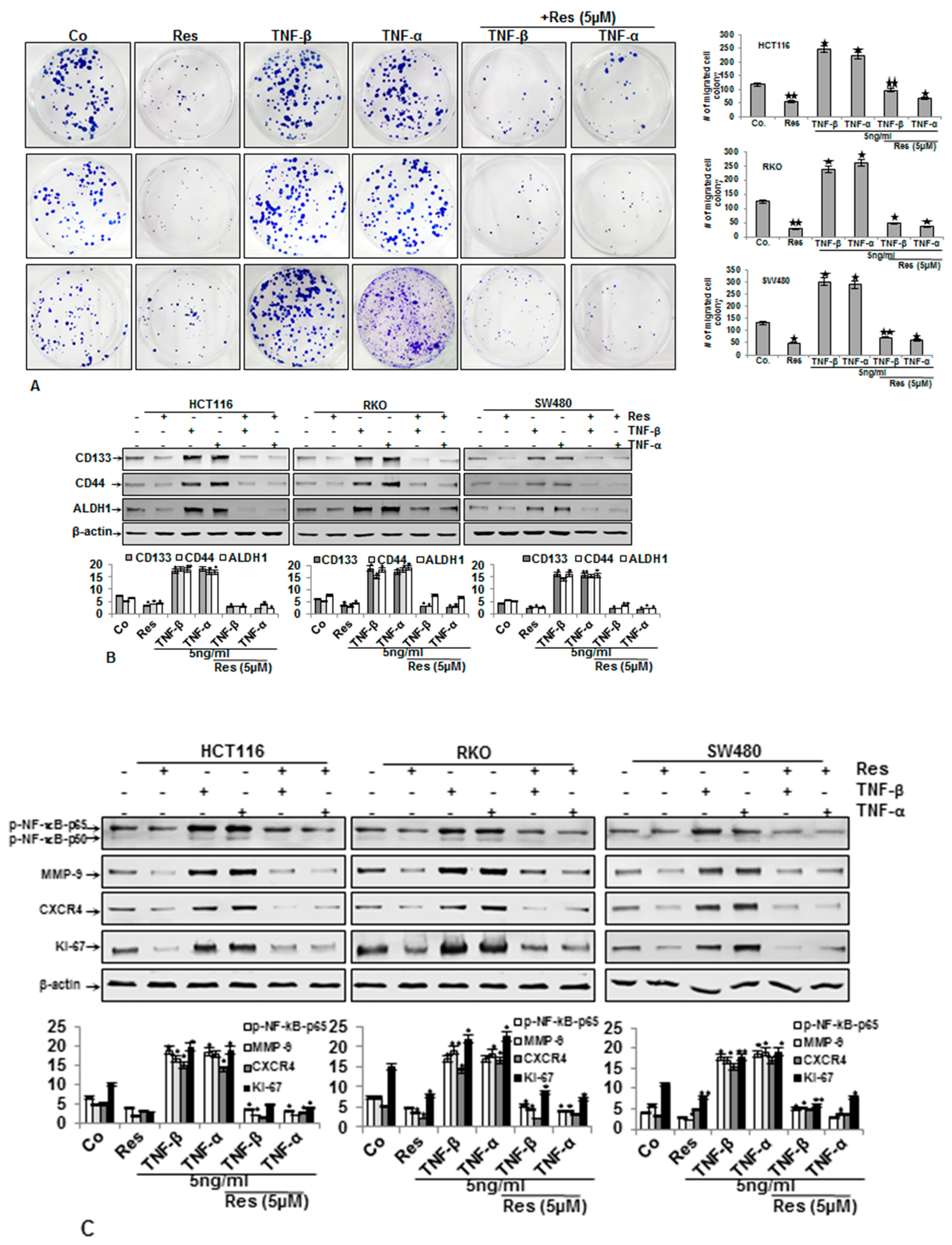
3.3. Resveratrol Suppresses TNF-β-Promoted Migration, Colon Cancer Stem Cell Markers, NF-κΒ Activation, and NF-κB-Regulated Gene Products Involved in Proliferation and Metastasis
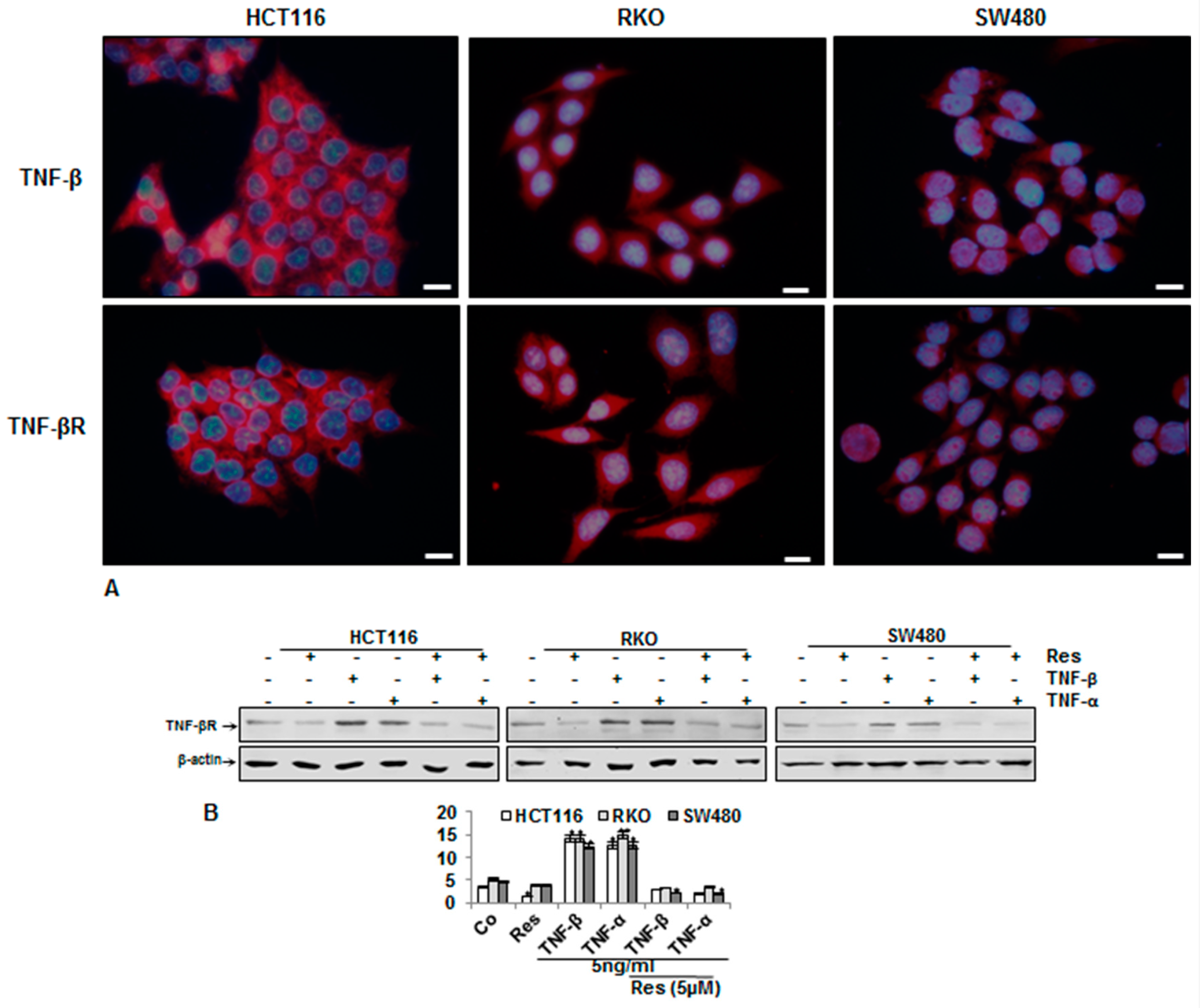
3.4. Endogenous Demonstration of TNF-β and of TNF-βR on the CRC Cell Membrane
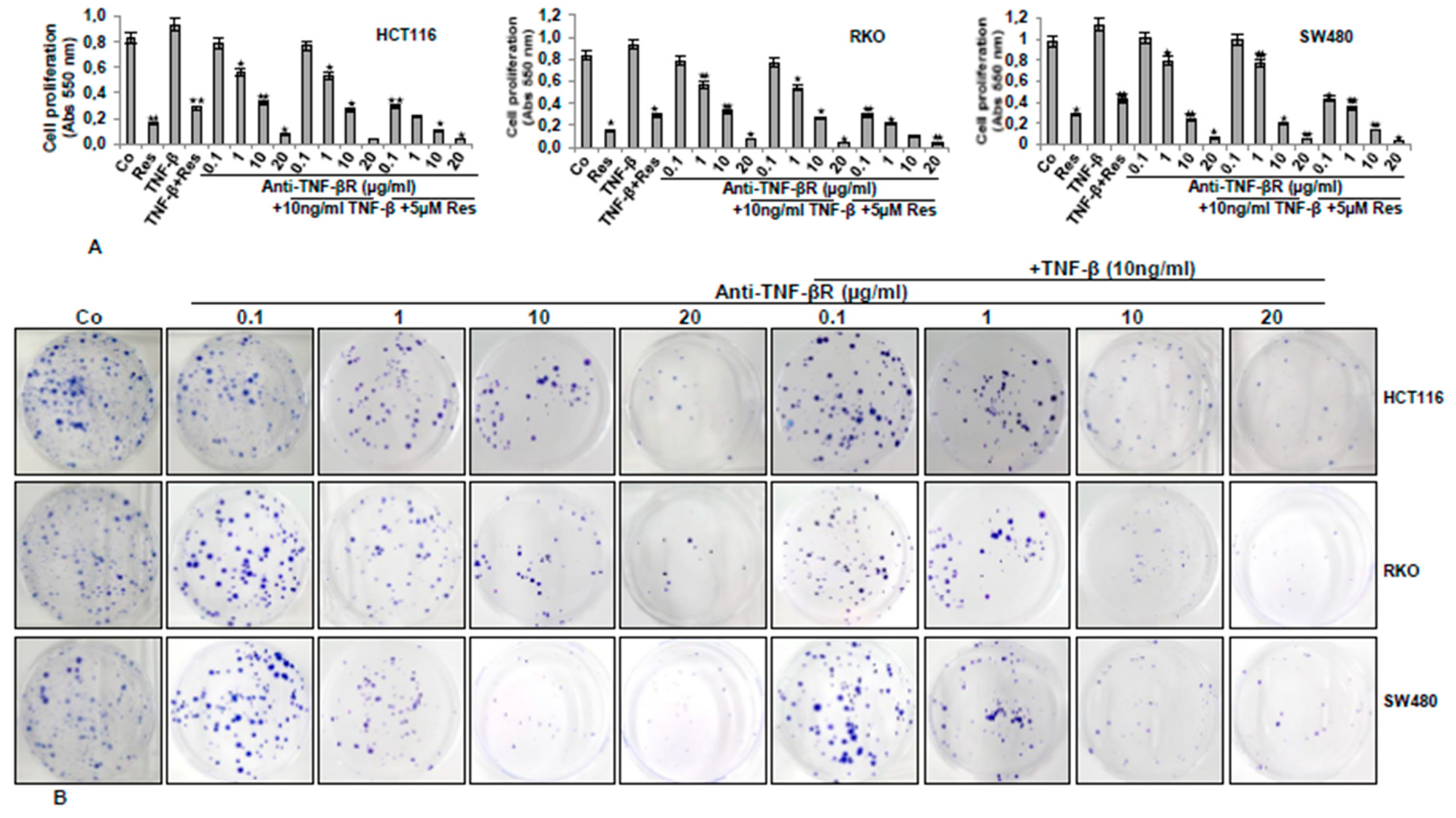
3.5. Anti-TNF-βR or Resveratrol Down-Modulates TNF-β-Promoted Proliferation, Invasion, and Colony Formation
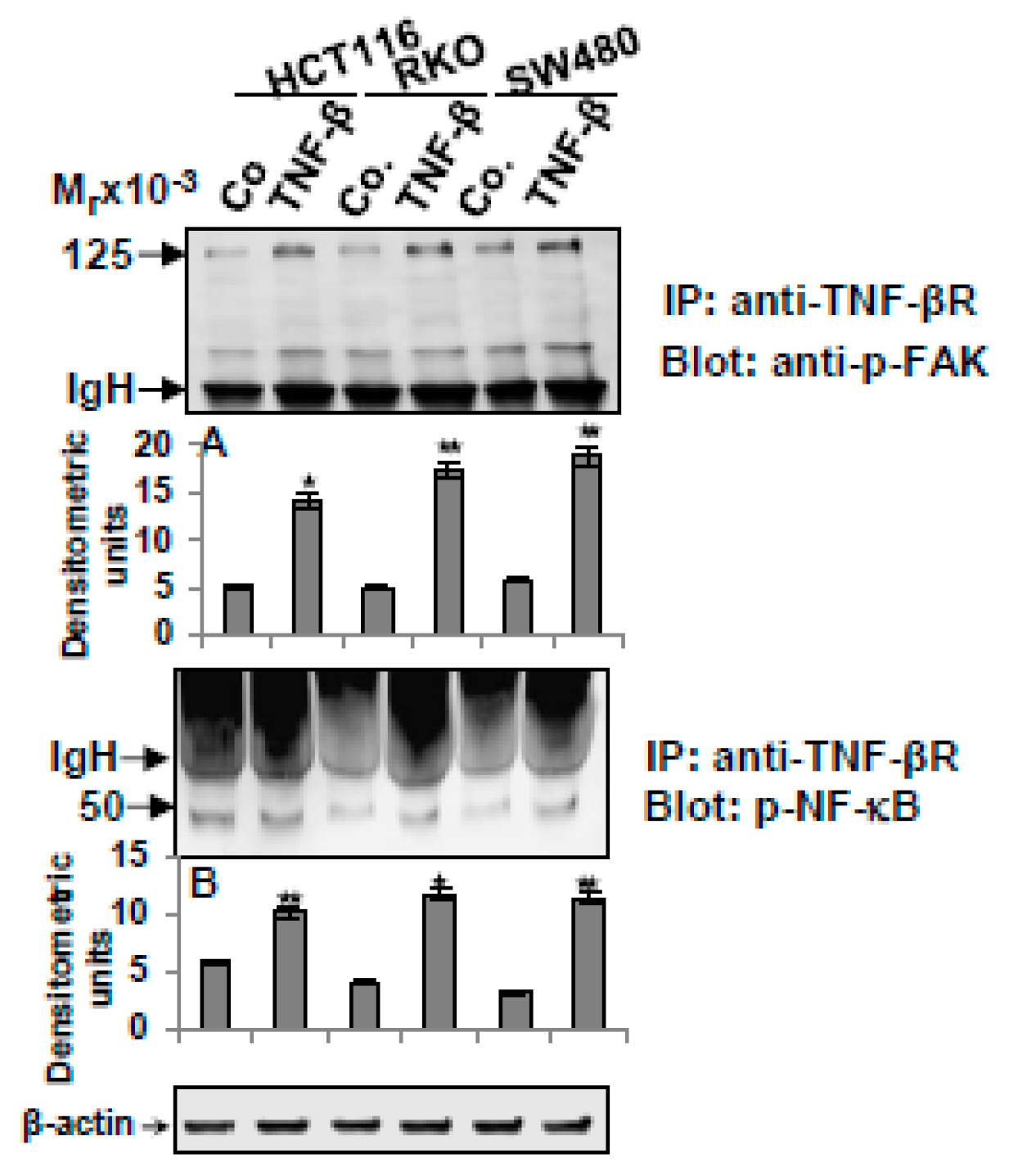
3.6. TNF-β-Promoted TNF-βR Expression Interacts with FAK and NF-κB in CRC Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araghi, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jenkins, M.; Brierley, J.; Morris, E.; Bray, F.; Arnold, M. Global trends in colorectal cancer mortality: Projections to the year 2035. Int. J. Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttridge, D.C.; Albanese, C.; Reuther, J.Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 5785–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Achieving transcriptional specificity with NF-kappa B. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 29, 1433–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Kumar, A.P.; Tergaonkar, V. Multifaceted link between cancer and inflammation. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Sethi, G. Inflammation and cancer: How hot is the link? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, C.; Larghi, P.; Rimoldi, M.; Totaro, M.G.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A.; Sica, A. Cellular and molecular pathways linking inflammation and cancer. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, T.S.; Chung, T.K.; Cheung, T.H.; Chan, L.K.; Cheung, L.W.; Yim, S.F.; Siu, N.S.; Lo, K.W.; Yu, M.M.; Kulbe, H.; et al. Cancer cell-derived lymphotoxin mediates reciprocal tumour-stromal interactions in human ovarian cancer by inducing CXCL11 in fibroblasts. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Chemosensitizes TNF-beta-Induced Survival of 5-FU-Treated Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejardin, E.; Droin, N.M.; Delhase, M.; Haas, E.; Cao, Y.; Makris, C.; Li, Z.W.; Karin, M.; Ware, C.F.; Green, D.R. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity 2002, 17, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.R.; Siebenlist, U. Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces sequential activation of distinct NF-kappa B factors via separate signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12006–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupedo, T.; Mebius, R.E. Cellular Interactions in Lymph Node Development. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Majeau, G.R.; Hochman, P.S.; Browning, J.L. Lymphotoxin beta receptor triggering induces activation of the nuclear factor kappaB transcription factor in some cell types. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24934–24938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.; Potter, K.G.; Ware, C.F. Lymphotoxin and LIGHT signaling pathways and target genes. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanArsdale, T.L.; VanArsdale, S.L.; Force, W.R.; Walter, B.N.; Mosialos, G.; Kieff, E.; Reed, J.C.; Ware, C.F. Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling complex: Role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 recruitment in cell death and activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2460–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Liang, X. Inflammation linking EMT and cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.A. The role of tight junctions in cancer metastasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepass, U.; Truong, K.; Godt, D.; Ikura, M.; Peifer, M. Cadherins in embryonic and neural morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Garcia, E.; Diaz-Garcia, C.V.; Garcia-Ruiz, I.; Agullo-Ortuno, M.T. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in tumor progression. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Targeting the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: The Case for Differentiation-Based Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2016, 81, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Ichwan, S.J.; Soundharrajan, I.; Govindan, N. Nutraceuticals as potential therapeutic agents for colon cancer: A review. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesalma, S.; Sudhandiran, G. Differential inhibitory effects of the polyphenol ellagic acid on inflammatory mediators NF-kappaB, iNOS, COX-2, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colon carcinogenesis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 107, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cell Invasion by Modulation of Focal Adhesion Molecules. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cal, C.; Garban, H.; Jazirehi, A.; Yeh, C.; Mizutani, Y.; Bonavida, B. Resveratrol and cancer: Chemoprevention, apoptosis, and chemo-immunosensitizing activities. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents 2003, 3, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Kraehe, P.; Popper, B.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Resveratrol induces chemosensitization to 5-fluorouracil through up-regulation of intercellular junctions, Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Evidence that TNF-beta induces proliferation in colorectal cancer cells and resveratrol can down-modulate it. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringman, T.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Monoclonal antibodies to human tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta: Application for affinity purification, immunoassays, and as structural probes. Hybridoma 1987, 6, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaei, M.; Kraehe, P.; Popper, B.; Shayan, P.; Goel, A.; Buhrmann, C. Curcumin potentiates antitumor activity of 5-fluorouracil in a 3D alginate tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakibaei, M.; De Souza, P. Differentiation of mesenchymal limb bud cells to chondrocytes in alginate beads. Cell Biol. Int. 1997, 21, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhrmann, C.; Busch, F.; Shayan, P.; Shakibaei, M. Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) is required for promoting chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22048–22062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifacino, J.S.; Dell’Angelica, E.C.; Springer, T.A. Immunoprecipitation. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shen, B.; Jiang, F.; Xia, L.; Fan, T.; Qin, M.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; et al. TRPP2 Enhances Metastasis by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramudo, L.; Yubero, S.; Manso, M.A.; Vicente, S.; De Dios, I. Signal transduction of MCP-1 expression induced by pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid in pancreatic acinar cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, A.M.; Clarke, D.L.; Bradbury, D.A.; Corbett, L.M.; Patel, J.A.; Knox, A.J. Transcriptional regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 release by endothelin-1 in human airway smooth muscle cells involves NF-kappaB and AP-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Helfand, B.T.; Jang, T.L.; Zhu, L.J.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.J.; Kozlowski, J.; Smith, N.; Kundu, S.D.; Yang, G.; et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated transforming growth factor-beta-induced expression of vimentin is an independent predictor of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hauck, C.R.; Sieg, D.J. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 71, 435–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.L.; Guan, J.L. Differential regulation of cell migration and cell cycle progression by FAK complexes with Src, PI3K, Grb7 and Grb2 in focal contacts. FEBS Lett. 2001, 499, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.A.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase in integrin-mediated signaling. Front. Biosci. 1999, 4, D102–D113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-kappaB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.Y.; Tang, S.J.; Chuang, M.J.; Cha, T.L.; Li, J.Y.; Sun, G.H.; Sun, K.H. TNF-alpha induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells via a GSK3beta-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Huo, L.; Lim, S.O.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Chao, C.H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yang, N.K.; Ding, Q.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TNF-alpha requires NF-kappaB-mediated transcriptional upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtanski, D.; Poretsky, L. Phyto-polyphenols as potential inhibitors of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Sarkar, N.; Bishayee, A.; Sinha, D. Dietary phytochemicals in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and associated enzymes: A promising anticancer therapeutic approach. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Gupta, S.C.; Nabavizadeh, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Regulation of cell signaling pathways by dietary agents for cancer prevention and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 46, 158–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrmann, C.; Shayan, P.; Popper, B.; Goel, A.; Shakibaei, M. Sirt1 Is Required for Resveratrol-Mediated Chemopreventive Effects in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2016, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Dedhar, S.; Kalluri, R.; Thompson, E.W. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, G.; Ofri-Shahak, M.; Haas, I.; Yaal-Hahoshen, N.; Leider-Trejo, L.; Leibovich-Rivkin, T.; Weitzenfeld, P.; Meshel, T.; Shabtai, E.; Gutman, M.; et al. Inflammatory mediators in breast cancer: Coordinated expression of TNFalpha & IL-1beta with CCL2 & CCL5 and effects on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Csiszar, A.; Szentes, T.; Haraszti, B.; Zou, W.; Emilie, D.; Petranyi, G.; Pocsik, E. Characterisation of cytokine mRNA expression in tumour-infiltrating mononuclear cells and tumour cells freshly isolated from human colorectal carcinomas. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2001, 12, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nantajit, D.; Lin, D.; Li, J.J. The network of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Potential new targets for tumor resistance. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalay, I.; Janji, B.; Hasmim, M.; Noman, M.Z.; Andre, F.; De Cremoux, P.; Bertheau, P.; Badoual, C.; Vielh, P.; Larsen, A.K.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in breast carcinoma promote escape from T-cell-mediated lysis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Ford, H.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.L.; Sun, Z.J.; Yu, L.; Meng, K.W.; Qin, X.L.; Pan, C.E. Effect of resveratrol and in combination with 5-FU on murine liver cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3048–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, J.C.; Lambert, P.D.; Schenk, S.; Carney, D.P.; Smith, J.J.; Gagne, D.J.; Jin, L.; Boss, O.; Perni, R.B.; Vu, C.B.; et al. Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature 2007, 450, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.P.; Gao, Z.L.; Zhou, M.L.; He, M.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Tao, D.T.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, L.K. Snail interacts with Id2 in the regulation of TNF-alpha-induced cancer cell invasion and migration in OSCC. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, J.S.; Mok, J.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, H.K.; Kim, C.H.; Byun, D.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Jin, S.Y.; et al. Increased expression of focal adhesion kinase in thyroid cancer: Immunohistochemical study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2004, 19, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Chen, F.; Sima, N.I. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells via Src and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, L.H.; Varadharajan, T.; Tsai, M.J.; Chia, Y.C.; Yuan, T.C.; Sung, P.J.; Weng, C.F. Resveratrol inhibits glucose-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells mediated by focal adhesion kinase. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanamala, J.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Reddivari, L.; Bhat, V.B.; Ptitsyn, A. Resveratrol suppresses human colon cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via targeting the pentose phosphate and the talin-FAK signaling pathways-A proteomic approach. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.R.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Ahn, S.; Jeong, E.; Park, H. FERM domain promotes resveratrol-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells via inhibition of NO production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condeelis, J.S.; Wyckoff, J.B.; Bailly, M.; Pestell, R.; Lawrence, D.; Backer, J.; Segall, J.E. Lamellipodia in invasion. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2001, 11, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, J.V.; Stradal, T.; Vignal, E.; Rottner, K. The lamellipodium: Where motility begins. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buhrmann, C.; Yazdi, M.; Popper, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Shakibaei, M. Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human TNF-β (Lymphotoxin) and its Reversal by Resveratrol. Nutrients 2019, 11, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030704
Buhrmann C, Yazdi M, Popper B, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB, Shakibaei M. Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human TNF-β (Lymphotoxin) and its Reversal by Resveratrol. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030704
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuhrmann, Constanze, Mina Yazdi, Bastian Popper, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara, Bharat B. Aggarwal, and Mehdi Shakibaei. 2019. "Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human TNF-β (Lymphotoxin) and its Reversal by Resveratrol" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030704
APA StyleBuhrmann, C., Yazdi, M., Popper, B., Kunnumakkara, A. B., Aggarwal, B. B., & Shakibaei, M. (2019). Induction of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Human Colorectal Cancer by Human TNF-β (Lymphotoxin) and its Reversal by Resveratrol. Nutrients, 11(3), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030704