Analysis of 2009–2012 Nutrition Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) Data to Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting Hydration Criteria for Individuals Aged 12–80 Years in the US Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Demographic Data
2.3.2. Anthropometric Data
2.3.3. Dietary Intake Data
2.3.4. Laboratory Data
2.3.5. Hydration Criteria
2.3.6. Physical Activity
2.3.7. Cigarette Smoking
2.3.8. Self-Reported Health Conditions
2.3.9. Prescription Medication Use
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Descriptive Analysis
2.4.2. Determine If the Hydration Classification Varied by Water Intake
2.4.3. Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting the Hydration Classification
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Variation in Hydration Classification by Water Intake
3.3. Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting the Hydration Criteria
4. Discussion
4.1. Did Hydration Classification Vary by Water Intake?
4.2. Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting the Hydration Criteria
4.3. Analysis Strengths
4.4. Analysis Limitations
4.4.1. Choice of Datasets
4.4.2. Choice of Study Population and Sub-Group
4.4.3. Choice of Hydration Criteria
4.4.4. Choice of Water Intake Specification
4.4.5. Choice of Multivariable Model Specification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Age 12–18 years | Age 19–50 years | Age 51–70 years | Age 71–80 years | Pregnant | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Weighted % (SE) | n | Weighted % (SE) | n | Weighted % (SE) | n | Weighted % (SE) | n | Weighted% (SE) | ||
| US Population | |||||||||||
| Male | 978 | 2703 | 1551 | 713 | - | ||||||
| Body weight, kg | <70 | 574 | 56.4 (2.8) | 520 | 15.4 (1.2) | 264 | 11.1 (1.3) | 155 | 19.1 (1.7) | - | - |
| 70–79 | 180 | 17.8 (1.7) | 595 | 21.2 (1.2) | 315 | 17.8 (1.3) | 184 | 25.7 (2.1) | - | - | |
| 80–94 | 126 | 16.6 (1.7) | 818 | 33.4 (1.5 | 498 | 34.8 (2.6) | 232 | 35.7 (1.9) | - | - | |
| ≥95 | 98 | 9.2 (1.3) | 770 | 30.0 (1.2) | 474 | 36.2 (2.3) | 142 | 19.5 (1.7) | - | - | |
| Race–ethnicity | White | 283 | 55.9 (3.9) | 1092 | 62.6 (2.7) | 634 | 76.2 (2.4) | 479 | 81.5 (2.5) | - | - |
| Hispanic | 336 | 22.3 (2.9) | 746 | 18.8 (2.4) | 399 | 8.8 (1.6) | 81 | 6.4 (1.4) | - | - | |
| Black | 240 | 13.2 (1.9) | 530 | 10.9 (1.2) | 389 | 9.4 (1.3) | 107 | 7.4 (1.4) | - | - | |
| Other | 119 | 8.5 (1.9) | 335 | 7.8 (0.8) | 129 | 5.6 (0.9) | 46 | 4.7 (1.1) | - | - | |
| Activity METs, min/week | <1000 | 210 | 19.9 (2.2) | 789 | 25.9 (1.5) | 763 | 42.9 (1.7) | 457 | 61.5 (2.3) | - | - |
| 1000–4999 | 492 | 49.9 (3.2) | 939 | 37.0 (1.6) | 470 | 35.4 (1.6) | 192 | 29.5 (2.3) | - | - | |
| ≥5000 | 276 | 30.2 (3.6) | 975 | 37.1 (1.9) | 318 | 21.7 (1.8) | 64 | 9.0 (1.6) | - | - | |
| Dietary solute, mOsm/day | <500 | 253 | 24.2 (2.5) | 391 | 13.1 (0.6) | 326 | 15.9 (1.6) | 212 | 24.1 (2.1) | - | - |
| 500–999 | 528 | 52.4 (2.4) | 1479 | 54.4 (1.3) | 910 | 60.0 (1.9) | 447 | 68.5 (1.9) | - | - | |
| 1000–1499 | 163 | 19.1 (2.8) | 667 | 25.7 (1.2) | 269 | 20.7 (1.5) | 50 | 7.0 (1.2) | - | - | |
| ≥1500 | 34 | 4.3 (0.9) | 166 | 6.8 (0.8) | 46 | 3.4 (0.7) | 4 | 0.4 (0.2) | - | - | |
| Current cigarette smoker | Yes | - | - | 742 | 24.6 (1.6) | 369 | 21.8 (1.8) | 66 | 7.1 (0.9) | - | - |
| No | - | - | 1810 | 71.5 (1.3) | 1182 | 78.2 (1.8) | 647 | 92.9 (0.9) | - | - | |
| Unknown | 978 | 100 | 151 | 3.9 (0.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | |
| Prescription medication | Yes | 202 | 22.5 (1.9) | 788 | 33.8 (1.4) | 1072 | 72.4 (1.6) | 641 | 89.6 (1.5) | - | - |
| No | 776 | 77.5 (1.9) | 1915 | 66.2 (1.4) | 479 | 27.6 (1.6) | 72 | 10.4 (1.5) | - | - | |
| MEC visit timing | Winter | 482 | 43.4 (5.7) | 1270 | 44.3 (4.7) | 735 | 37.9 (4.6) | 299 | 42.8 (6.1) | - | - |
| Summer | 496 | 56.6 (5.7) | 1433 | 55.7 (4.7) | 816 | 62.1 (4.6) | 414 | 57.2 (6.1) | - | - | |
| 8-hour fasted | Yes | 462 | 43.0 (2.9) | 1252 | 42.1 (1.9) | 726 | 45.1 (2.1) | 307 | 43.6 (2.1) | - | - |
| No | 516 | 57.0 (2.9) | 1451 | 57.9 (1.9) | 825 | 54.9 (2.1) | 406 | 56.4 (2.1) | - | - | |
| One or more chronic disease risk factor * | Yes | 229 | 48.7 (3.1) | 1012 | 81.1 (1.8) | 623 | 85.4 (1.5) | 277 | 89.4 (2.7) | - | - |
| No | 233 | 51.3 (3.1) | 240 | 18.9 (1.8) | 101 | 14.6 (1.5) | 28 | 10.6 (2.7) | - | - | |
| Female | 882 | 2849 | 1526 | 722 | 108 | ||||||
| Body weight, kg | <60 | 483 | 57.0 (2.3) | 658 | 22.2 (1.1) | 249 | 18.4 (1.6) | 208 | 27.2 (2.0) | 17 | 12.7 (4.0) |
| 60–69 | 184 | 20.8 (2.2) | 659 | 24.5 (1.0) | 318 | 24.1 (2.4) | 196 | 29.5 (2.1) | 23 | 19.8 (5.7) | |
| 70–84 | 133 | 13.7 (1.9) | 739 | 27.0 (1.6) | 478 | 27.7 (1.6) | 180 | 24.4 (1.8) | 28 | 27.8 (4.9) | |
| ≥85 | 82 | 8.4 (1.1) | 793 | 26.3 (1.1) | 481 | 29.8 (1.8) | 138 | 18.8 (1.6) | 40 | 39.7 (6.0) | |
| Race-ethnicity | White | 243 | 59.5 (3.3) | 1151 | 60.9 (3.3) | 591 | 74.0 (2.5) | 488 | 82.8 (2.0) | 36 | 55.4 (6.3) |
| Hispanic | 316 | 20.3 (2.4) | 773 | 17.4 (2.4) | 424 | 9.5 (1.7) | 96 | 6.2 (1.3) | 31 | 20.8 (5.3) | |
| Black | 207 | 12.5 (1.8) | 604 | 13.4 (1.6) | 391 | 11.4 (1.6). | 105 | 6.6 (1.0) | 27 | 14.0 (3.1) | |
| Other | 116 | 7.8 (1.2) | 321 | 8.3 (0.8) | 120 | 5.2 (0.8) | 33 | 4.4 (0.9) | 14 | 9.7 (3.3) | |
| Activity METs, min/wk | <1000 | 385 | 38.4 (2.1) | 1430 | 47.4 (1.9) | 972 | 58.5 (2.0) | 551 | 72.2 (2.2) | 73 | 64.9 (6.6) |
| 1000–4999 | 390 | 47.4 (2.4) | 985 | 47.4 (1.9) | 405 | 32.3 (1.7) | 140 | 22.6 (2.1) | 24 | 26.3 (5.7) | |
| ≥5000 | 107 | 14.2 (2.3) | 434 | 16.2 (1.1) | 149 | 9.2 (0.9 | 31 | 5.2 (1.0) | 11 | 8.8 (4.4) | |
| Dietary solute, mOsm/d | <500 | 398 | 46.0 (2.5) | 1040 | 37.1 (1.1) | 631 | 38.4 (1.9) | 394 | 51.5 (2.1) | 23 | 24.1 (6.4) |
| 500–999 | 441 | 50.6 (2.5) | 1601 | 56.9 (1.4) | 825 | 58.1 (1.9) | 309 | 45.7 (1.9) | 73 | 67.6 (5.5) | |
| 1000–1499 | 40 | 2.7 (0.8) | 194 | 3.3 (0.6) | 67 | 5.6 (0.7) | 17 | 3.2 (0.8) | 11 | 7.3 (3.2) | |
| ≥1500 | 3 | 0.2 (0.1) | 14 | 0.4 (0.1) | 3 | 0.1 (0.0) | 2 | 0.1 (0.0) | 1 | 1.0 (1.0) | |
| Current cigarette smoker | Yes | - | - | 599 | 21.7 (1.4) | 226 | 14.5 (1.4) | 40 | 5.6 (0.9) | 15 | 10.7 (3.0) |
| No | - | - | 2136 | 75.5 (1.4) | 1300 | 85.5 (1.4) | 682 | 94.4(0.9) | 93 | 89.3 (3.0) | |
| Unknown | 882 | 100 | 114 | 2.8 (0.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Prescription medication | Yes | 215 | 27.9 (2.9) | 1300 | 51.8 (1.9) | 1172 | 76.6 (1.3) | 671 | 92.9 (1.1) | 27 | 29.5 (6.7) |
| No | 667 | 72.1 (2.9) | 1549 | 48.2 (1.9) | 354 | 23.4 (1.3) | 51 | 7.1 (1.1) | 81 | 70.5 (6.7) | |
| MEC visit timing | Winter | 437 | 38.6 (5.3) | 1463 | 45.7 (4.6) | 811 | 39.2 (5.1) | 412 | 41.9 (5.5) | 47 | 36.7 (7.4) |
| Summer | 445 | 61.4 (5.3) | 1386 | 54.3(4.6) | 715 | 60.8 (5.1) | 310 | 58.1(5.5) | 61 | 63.3 (7.4) | |
| 8-hour fasted | Yes | 421 | 44.1 (4.1) | 1341 | 41.4 (1.4) | 757 | 47.5 (1.5) | 338 | 46.6 (2.0) | 46 | 30.8 (5.2) |
| No | 461 | 55.9 (4.1) | 1508 | 58.6 (1.4) | 769 | 52.5 (1.5) | 384 | 53.4 (2.0) | 62 | 69.2 (5.2) | |
| One or more chronic disease risk factor * | Yes | 242 | 54.4 (3.7) | 988 | 70.4 (2.1) | 643 | 81.3 (1.6) | 288 | 84.9 (2.2) | 37 | 89.2 (4.2) |
| No | 179 | 45.6 (3.7) | 353 | 29.6 (2.1) | 114 | 18.7 (1.6) | 50 | 15.1(2.2) | 9 | 10.8 (4.2) | |
| Sub-group without selected chronic disease risk factors | |||||||||||
| Male | 201 | 234 | 96 | - | - | ||||||
| Body weight, kg | <70 | 168 | 84.2 (3.8) | 140 | 51.9 (4.5) | 55 | 41.0 (7.7) | - | - | - | - |
| 70–79 | 32 | 14.8 (3.5) | 74 | 35.8 (4.3) | 30 | 45.4 (6.7) | - | - | - | - | |
| 80–94 | 1 | 1.0 (1.0) | 20 | 12.3 (3.0) | 11 | 13.6 (5.5) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Race–ethnicity | White | 60 | 57.1 (4.7) | 89 | 62.3 (4.4) | 40 | 72.4 (4.9) | - | - | - | - |
| Hispanic | 60 | 18.9 (3.2) | 50 | 13.1 (2.6) | 19 | 6.4 (1.9) | - | - | - | - | |
| Black | 55 | 16.7 (2.9) | 47 | 13.7 (2.6) | 23 | 13.1 (3.4) | - | - | - | - | |
| Other | 26 | 7.3 (1.9) | 48 | 11.0 (2.7) | 14 | 8.1 (3.6) | - | - | - | - | |
| Activity METs, min/wk | <1000 | 35 | 15.3 (4.3) | 66 | 28.7 (2.7) | 41 | 30.0 (5.5) | - | - | - | - |
| 1000–4999 | 110 | 56.3 (5.3) | 76 | 29.9 (3.5) | 27 | 37.0 (7.2) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥5000 | 56 | 28.4 (5.2) | 92 | 41.3 (4.0) | 28 | 33.0 (8.3) | - | - | - | - | |
| Dietary solute, mOsm/d | <500 | 54 | 29.3 (5.1) | 30 | 14.1 (4.0) | 17 | 15.2 (4.6) | - | - | - | - |
| 500–999 | 111 | 55.8 (4.7) | 144 | 57.1 (4.2) | 56 | 58.9 (6.8) | - | - | - | - | |
| 1000–1499 | 34 | 14.3 (2.7) | 51 | 24.7 (4.1) | 21 | 23.6 (5.0) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥1500 | 2 | 0.7 (0.5) | 9 | 4.2 (1.7) | 2 | 2.2 (1.8) | - | - | - | - | |
| Current cigarette smoker | Yes | - | 66 | 26.7 (3.9) | 24 | 29.7 (7.9) | - | - | - | - | |
| No | - | 139 | 64.6 (3.8) | 72 | 70.3 (7.9) | - | - | - | - | ||
| Unknown | 201 | 100 | 29 | 8.7 (2.0) | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Prescription medication | Yes | 38 | 15.7 (3.4) | 38 | 19.9 (3.2) | 59 | 75.5 (4.6) | - | - | - | - |
| No | 163 | 84.3 (3.4) | 196 | 80.1 (3.2) | 37 | 24.5 (4.6) | - | - | - | - | |
| MEC visit timing | Winter | 95 | 43.0 (6.3) | 115 | 45.3 (6.8) | 43 | 38.4 (7.5) | - | - | - | - |
| Summer | 106 | 57.0 (6.3) | 119 | 54.7 (6.8) | 53 | 61.6 (7.5) | - | - | - | - | |
| Female | 132 | 305 | 98 | - | - | ||||||
| Body weight, kg | <70 | 116 | 83.2 (4.3) | 166 | 44.9 (4.1) | 60 | 49.5 (6.5) | - | - | - | - |
| 70–79 | 15 | 16.4 (4.3) | 127 | 49.4 (4.5) | 37 | 48.9 (6.7) | - | - | - | - | |
| 80–94 | 1 | 0.4 (0.4) | 12 | 5.7 (2.0) | 1 | 1.6 (1.6) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Race–ethnicity | White | 47 | 65.3 (5.2) | 139 | 69.4 (4.2) | 52 | 82.1 (3.8) | - | - | - | - |
| Hispanic | 40 | 15.9 (3.7) | 68 | 10.7 (1.8) | 13 | 3.5 (1.0) | - | - | - | - | |
| Black | 28 | 11.4 (3.1) | 40 | 7.2 (1.6) | 16 | 6.2 (1.8) | - | - | - | - | |
| Other | 17 | 7.4 (2.6) | 58 | 12.7 (2.7) | 17 | 8.3 (3.4) | - | - | - | - | |
| Activity METs, min/wk | <1000 | 48 | 26.7 (5.0) | 120 | 32.9 (2.5) | 51 | 40.3 (6.5) | - | - | - | - |
| 1000–4999 | 65 | 54.5 (5.4) | 130 | 47.4 (3.9) | 39 | 53.3 (7.3) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥5000 | 19 | 18.8 (4.2) | 55 | 20.0 (2.8) | 8 | 6.3 (2.8) | - | - | - | - | |
| Dietary solute, mOsm/d | <500 | 55 | 39.4 (5.0) | 99 | 29.2 (2.9) | 44 | 39.1 (5.6) | - | - | - | - |
| 500–999 | 69 | 56.5 (5.0) | 185 | 65.1 (3.5) | 46 | 54.4 (6.0) | - | - | - | - | |
| 1000–1499 | 8 | 4.1 (1.9) | 20 | 5.5 (1.4) | 8 | 6.5 (1.6) | - | - | - | - | |
| ≥1500 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Current cigarette smoker | Yes | - | - | 39 | 14.3 (2.6) | 12 | 13.1 (6.2) | - | - | - | - |
| No | - | - | 249 | 83.2 (3.1) | 86 | 86.9 (6.2) | - | - | - | - | |
| Unknown | 132 | 100 | 17 | 2.4 (0.9) | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| Prescription medication | Yes | 38 | 33.6 (6.2) | 130 | 52.1 (3.3) | 68 | 72.8 (7.1) | - | - | - | - |
| No | 94 | 66.4 (6.2) | 175 | 47.9 (3.3) | 30 | 27.2 (7.1) | - | - | - | - | |
| MEC visit timing | Winter | 61 | 31.2 (6.5) | 126 | 36.0 (5.3) | 39 | 37.6 (5.8) | - | - | - | - |
| Summer | 71 | 68.8 (6.5) | 179 | 64.0 (5.3) | 59 | 62.4 (5.8) | - | - | - | - | |
References
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W. Am I Drinking Enough? Yes, No, and Maybe. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, E.T.; Buendia-Jimenez, I.; Vecchio, M.; Armstrong, L.E.; Tack, I.; Klein, A. Twenty-four-hour urine osmolality as a physiological index of adequate water intake. Dis. Markers 2015, 231063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, E.T.; Armstrong, L.E.; Daudon, M.; Kavouras, S.; Lafontan, M.; Lang, F.; Péronnet, F.; Stookey, J.D.; Tack, I.; Klein, A. From state to process: Defining hydration. Obes. Facts 2014, 7 (Suppl. 2), 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W.; Charkoudian, N.; Sawka, M.N. Physiologic basis for understanding quantitative dehydration assessment. Am. J. L. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, L.E. Assessing hydration status: The elusive gold standard. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26 (Suppl. 5), 575S–584S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, S.M.; Aylward, L.L.; Blount, B.C. Variation in urinary flow rates according to demographic characteristics and body mass index in NHANES: Potential confounding of associations between health outcomes and urinary biomarker concentratation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinger, A.Y.; Lawman, H.G.; Akinbami, L.J.; Ogden, C.L. The role of obesity in the relation between total water intake and urine osmolality in US adults, 2009–2012. AJCN 2016, 104, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, K.M.; Schubert, M.M.; Desbrow, B.; Byrne, N.M.; King, N.A. Acute exercise and gastric emptying: A meta-analysis and implications for appetite control. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.H.; Shirreffs, S.M.; Maughan, R.J. The effects of repeated ingestion of high and low glucose-electrolyte solutions on gastric emptying and blood 2H2O concentration after an overnight fast. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, M.A.; Charest, A.F.; Cheema-Dhadli, S.; Glick, D.N.; Napolova, O.; Roozbeh, J.; Semenova, E.; Sharman, A.; Halperin, M.L. Defining conditions that lead to the retention of water: The importance of the arterial sodium concentration. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Watson, P.; Cordery, P.A.; Walsh, N.P.; Oliver, S.J.; Dolci, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, N.; Galloway, S.D. A randomized trial to assess the potential of different beverages to affect hydration status: Development of a beverage hydration index. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollanek, K.J.; Tsurumoto, M.; Vidyasagar, S.; Kenefick, R.W.; Cheuvront, S.N. Neither body mass nor sex influences beverage hydration index outcomes during randomized trial when comparing 3 commercial beverages. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbrow, B.; Jansen, S.; Barrett, A.; Leveritt, M.D.; Irwin, C. Comparing the rehydration potential of different milk-based drinks to a carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, D.J.; Evans, G.H.; James, L.J. Effect of drink carbohydrate content on postexercise gastric emptying, rehydration, and the calculation of net fluid balance. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.; Irwin, C.; Cox, G.R.; Desbrow, B. Fluid, energy, and nutrient recovery via ad libitum intake of different commercial beverages and food in female athletes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnolo, N.; Iudakhina, E.; Irwin, C.; Schubert, M.; Cox, G.R.; Leveritt, M.; Desbrow, B. Fluid, energy and nutrient recovery via ad libitum intake of different fluids and food. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 171, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J. Negative, Null and Beneficial Effects of Drinking Water on Energy Intake, Energy Expenditure, Fat Oxidation and Weight Change in Randomized Trials: A Qualitative Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.A.; Ganio, M.S.; Adams, J.D.; Brown, L.A.; Ridings, C.B.; Burchfield, J.M.; Robinson, F.B.; McDermott, J.L.; Schreiber, B.A.; Moyen, N.E.; et al. Hydration Status over 24-H Is Not Affected by Ingested Beverage Composition. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, A.C.; Reimer, K.J.; Haven, M.C.; Curtis, G.L. The effect on hydration of two diets, one with and one without plain water. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merson, S.J.; Maughan, R.J.; Shirreffs, S.M. Rehydration with drinks differing in sodium concentration and recovery from moderate exercise-induced hypohydration in man. Eur. J Appl. Physiol. 2008, 103, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, S. Osmolality and pH of sport and other drinks available in Switzerland. Schweiz. Z. Fur Sportmed. Und Sporttraumatologie 2006, 54, 92–95. Available online: https://sgsm.ch/fileadmin/user_upload/Zeitschrift/54-2006-3/Osmolality_54_3_06.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Keller, U.; Szinnai, G.; Bilz, S.; Berneis, K. Effects of changes in hydration on protein, glucose and lipid metabolism in man: Impact on health. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57 (Suppl. 2), S69–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berneis, K.; Ninnis, R.; Häussinger, D.; Keller, U. Effects of hyper- and hypoosmolality on whole body protein and glucose kinetics in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276 Pt 1, E188–E195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Busch, G.L.; Ritter, M.; Völkl, H.; Waldegger, S.; Gulbins, E.; Häussinger, D. Functional significance of cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 247–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, P.H.; Clark, M.E.; Hand, S.C.; Bowlus, R.D.; Somero, G.N. Living with water stress: Evolution of osmolyte systems. Science 1982, 217, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliess, F.; Häussinger, D. Cell volume and insulin signaling. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2003, 225, 187–228. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, C.; Gehrmann, T.; Richter, L.; Keitel, V.; Köhrer, K.; Häussinger, D.; Schliess, F. Modulation of gene expression profiles by hyperosmolarity and insulin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, D. The role of cellular hydration in the regulation of cell function. Biochem. J. 1996, 313 Pt 3, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoer, E.; Ng, C.W.; De Matteo, R. Glutamatergic input in the PVN is important in renal nerve response to elevations in osmolality. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2003, 285, F640–F650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathai, J.C.; Sauna, Z.E.; John, O.; Sitaramam, V. Rate-limiting step in electron transport. Osmotically sensitive diffusion of quinones through voids in the bilayer. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15442–15454. [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger, D.; Stoll, B.; Morimoto, Y.; Lang, F.; Gerok, W. Anisoosmostic liver perfusion: Redox shifts and modulation of alpha-ketoisocaproate and glycine metabolism. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1992, 373, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschmann, M.; Steiniger, J.; Franke, G.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Luft, F.C.; Jordan, J. Water drinking induces thermogenesis through osmosensitive mechanisms. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3334–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubnov-Raz, G.; Constantini, N.W.; Yariv, H.; Nice, S.; Shapira, N. Influence of water drinking on resting energy expenditure in overweight children. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parretti, H.M.; Aveyard, P.; Blannin, A.; Clifford, S.J.; Coleman, S.J.; Roalfe, A.; Daley, A.J. Efficacy of water preloading before main meals as a strategy for weight loss in primary care patients with obesity: RCT. Obesity 2015, 23, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Dengo, A.L.; Comber, D.L.; Flack, K.D.; Savla, J.; Davy, K.P.; Davy, B.M. Water consumption increases weight loss during a hypocaloric diet intervention in middle-aged and older adults. Obesity 2010, 18, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stookey, J.D.; Constant, F.; Popkin, B.M.; Gardner, C.D. Drinking water is associated with weight loss in overweight dieting women independent of diet and activity. Obesity 2008, 16, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J.D.; Del Toro, R.; Hamer, J.; Medina, A.; Higa, A.; Ng, V.; TinajeroDeck, L.; Juarez, L. Qualitative and/or quantitative drinking water recommendations for pediatric obesity treatment. J. Obes. Weight Loss 2014, 4, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stookey, J.D.; Pieper, C.F.; Cohen, H.J. Hypertonic hyperglycemia progresses to diabetes faster than normotonic hyperglycemia. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, R.; Fezeu, L.; Bouby, N.; Balkau, B.; Lantieri, O.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Marre, M.; Bankir, L.; DESIR Study Group. Low water intake and risk for new-onset hyperglycemia. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2551–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasevska, I.; Enhörning, S.; Christensson, A.; Persson, M.; Nilsson, P.M.; Melander, O. Increased Levels of Copeptin, a Surrogate Marker of Arginine Vasopressin, Are Associated with an Increased Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease in a General Population. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankir, L.; Bouby, N.; Ritz, E. Vasopressin: A novel target for the prevention and retardation of kidney disease? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.F.; Devuyst, O.; Roussel, R. The vasopressin system: New insights for patients with kidney diseases. J. Int. Med. 2017, 282, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, O. Vasopressin: Novel roles for a new hormone—Emerging therapies in cardiometabolic and renal diseases. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontrop, J.M.; Huang, S.H.; Garg, A.X.; Moist, L.; House, A.A.; Gallo, K.; Clark, W.F. Effect of increased water intake on plasma copeptin in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results from a pilot randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbeling, C.B.; Feldman, H.A.; Chomitz, V.R.; Antonelli, T.A.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Osganian, S.K.; Ludwig, D.S. A randomized trial of sugar-sweetened beverages and adolescent body weight. N Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichieri, R.; Paula Trotte, A.; de Souza, R.A.; Veiga, G.V. School randomised trial on prevention of excessive weight gain by discouraging students from drinking sodas. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnberg, K.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Jensen, S.M.; Trolle, E.; Larnkjær, A. Skim milk, whey, and casein increase body weight and whey and casein increase the plasma C-peptide concentration in overweight adolescents. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Malik, V.S.; Schulze, M.B.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Plain-water intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in young and middle-aged women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.M.; Barstow, C.H.; Pyzocha, N.J. Diagnosis and management of sodium disorders: Hyponatremia and Hypernatremia. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Spasovski, G.; Vanholder, R.; Allolio, B.; Annane, D.; Ball, S.; Bichet, D.; Decaux, G.; Fenske, W.; Hoorn, E.J.; Hyponatraemia Guideline Development Group; et al. Clinical practice guideline on diagnosis and treatment of hyponatraemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, G1–G47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczynski, C.; Staros, E.B. Urine Osmolality. MedScape, 13 May 2014. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2088250-overview (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC), National Center for Health Statistics. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, NHANES Survey Methods and Analytic Guidelines. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/analyticguidelines.aspx (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC), National Center for Health Statistics. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, NHANES 2009–2010. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/default.aspx?BeginYear=2009 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC), National Center for Health Statistics. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, NHANES 2011–2012. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/default.aspx?BeginYear=2011 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Anthropometry Procedures Manual. 2009. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2009-2010/manuals/bodymeasures_09.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Recommended BMI-For-Age Cutoffs. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpao/growthcharts/training/bmiage/page4.html (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Laboratory Procedures Manual. 2009. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_09_10/lab.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Laboratory Procedures Manual. 2011. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_11_12/2011-12_Laboratory_Procedures_Manual.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Urine Flow Rate (UCFLOW_F) Data File: UCFLOW_F.xpt. First Published: September 2011. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2009-2010/UCFLOW_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Urine Flow Rate (UCFLOW_G) Data File: UCFLOW_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/UCFLOW_G.htm#Description_of_Laboratory_Methodology (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Pregnancy Test—Urine (UCPREG_F) Data File: UCPREG_F.xpt. First Published: September 2011. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/UCPREG_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Pregnancy Test—Urine (UCPREG_G) Data File: UCPREG_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/UCPREG_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Albumin & Creatinine—Urine (ALB_CR_F) Data File: ALB_CR_F.xpt. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/ALB_CR_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Albumin & Creatinine—Urine (ALB_CR_G) Data File: ALB_CR_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/ALB_CR_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Middleton, D.R.S.; Watts, M.J.; Lark, R.M.; Milne, C.J.; Polya, D.A. Assessing urinary flow rate, creatinine, osmolality and other hydration adjustment methods for urinary biomonitoring using NHANES arsenic, iodine, lead and cadmium data. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Chronic kidney Disease Surveillance System, Tracking Kidney Disease in the United States/Methods. Available online: https://nccd.cdc.gov/ckd/Methods.aspx?QNum=Q634 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Glycohemoglobin (GHB_F) Data File: GHB_F.xpt. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/GHB_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Glycohemoglobin (GHB_G), Data File: GHB_G.xpt. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2011-2012/GHB_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- American Diabetes Association (ADA). Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Sec. 2. In Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016. Diabetes Care 2016, 39 (Suppl. 1), S13–S22. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Standard Biochemistry Profile (BIOPRO_F). Data File: BIOPRO_F.xpt. First Published: September 2011. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2009-2010/BIOPRO_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Standard Biochemistry Profile (BIOPRO_G) Data File: BIOPRO_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2011-2012/BIOPRO_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, T.; Matsushita, K.; Selvin, E.; Sang, Y.; Astor, B.C.; Inker, L.A.; Coresh, J. Comparing the association of GFR estimated by the CKD-EPI and MDRD study equations and mortality: The third national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES III). BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. CKD-EPI Creatinine Equation. 2009. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/content/ckd-epi-creatinine-equation-2009 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Kidney Foundation. Glomerular Filtration Rate. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/gfr (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Fox, C.; Bernardino, L.; Cochran, J.; Essig, M.; Bridges, K.G. Inappropriate use of Homeostasis Model Assessment Cutoff values for diagnosing insulin resistance in pediatric studies. J. Am. Osteopath Assoc. 2017, 117, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.C.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Keast, D.R.; Rains, T.M.; Park, K.M.; Rubin, M.R. Vitamin D intake and status are associated with Vitamin D intake and status are associated with lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome in U.S. adults: National Health and Nutrition Examinations Surveys 2003–2006. Metab. Syn. Relat. Disord. 2012, 10, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavey, R.E.; Daniels, S.R.; Lauer, R.M.; Atkins, D.L.; Hayman, L.L.; Taubert, K.; American Heart Association. American Heart Association guidelines for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease beginning in childhood. Circulation 2003, 107, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, P.S.; Handelsman, Y.; Rosenblit, P.D.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Fonseca, V.A.; Garber, A.J.; Grunberger, G.; Guerin, C.K.; Bell, D.S.H.; Mechanick, J.I.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr. Pract. 2017, 23 (Suppl. 2), 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents: Summary Report. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/node/80308 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for water. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1459–1506.
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Physical Activity (PAQ_F) Data File: PAQ_F.xpt. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/PAQ_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Physical Activity (PAQ_G) Data File: PAQ_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/PAQ_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Smoking—Cigarette Use (SMQ_F). Data File: SMQ_F.xpt. First Published: September 2011. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/SMQ_F.htm#SMQ040 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Smoking—Cigarette Use (SMQ_G). Data File: SMQ_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2011-2012/SMQ_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Diabetes (DIQ_F). First published: September 2011. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/DIQ_F.htm (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies—Diabetes (DIQ_G) Data File: DIQ_G.xpt. First Published: September 2013. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/DIQ_G.htm (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies—Kidney Conditions—Urology (KIQ_U_F) Data File: KIQ_U_F.xpt. First Published: January 2012. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/KIQ_U_F.htm (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies—Kidney Conditions—Urology (KIQ_U_G) Data File: KIQ_U_G.xpt. First Published: November 2014. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2011-2012/KIQ_U_G.htm (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2010 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Prescription Medications (RXQ_RX_F). Data File: RXQ_RX_F.xpt First Published: May 2012. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2009-2010/RXQ_RX_F.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2012 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Prescription Medications (RXQ_RX_G) Data File: RXQ_RX_G.xpt. First Published: July 2014. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/2011-2012/RXQ_RX_G.htm (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Module 3: Weighting. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/tutorials/module3.aspx (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Lindquist, K. How Can I Estimate Relative Risk Using Glm for Common Outcomes in Cohort Studies? Stata FAQ. UCLA Institute for Digital Research and Education. Available online: https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stata/faq/how-can-i-estimate-relative-risk-using-glm-for-common-outcomes-in-cohort-studies/ (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Nose, H.; Mack, G.W.; Shi, X.R.; Nadel, E.R. Role of osmolality and plasma volume during rehydration in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 65, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stookey, J.D.; Klein, A.; Hamer, J.; Chi, C.; Higa, A.; Ng, V.; Arieff, A.; Kuypers, F.A.; Larkin, S.; Perrier, E.; et al. RBC deformability and amino acid concentrations after hypo-osmotic challenge may reflect chronic cell hydration status in healthy young men. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, e00117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J.D.; Hamer, J.; Killilea, D.W. Change in hydration indices associated with an increase in total water intake of more than 0.5 L/day, sustained over 4 weeks, in healthy young men with initial total water intake below 2 L/day. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M.B.; Owen, J.A.; Raymond-Barker, P.; Bishop, C.; Elghenzai, S.; Oliver, S.J.; Walsh, N.P. Is this elderly patient dehydrated? Diagnostic accuracy of hydration assessment using physical signs, urine, and saliva markers. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Bunn, D.K.; Abdelhamid, A.; Gillings, R.; Jennings, A.; Maas, K.; Potter, J.F. Water-loss (intracellular) dehydration assessed using urinary tests: How well do they work? Diagnostic accuracy in older people. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, J.D.; Brass, B.; Holliday, A.; Arieff, A. What is the cell hydration status of healthy children in the USA? Preliminary data on urine osmolality and water intake. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.J.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Long, M.W.; Cradock, A.L.; Kenney, E.L. Racial/Ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in hydration status among US adults and the role of tap water and other beverage intake. Am. J. Public Health 2017, 107, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Ravi, N.; Plegue, M.A.; Sonneville, K.R.; Davis, M.M. Inadequate Hydration, BMI, and Obesity Among US Adults: NHANES 2009-2012. Ann. FAM. Med. 2016, 14, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, N.; Van den Bussche, K.; Vande Walle, J.; De Henauw, S. Belgian primary school children’s hydration status at school and its personal determinants. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.M.; Bragg, D.; Watson, P.; Neal, K.; Sahota, O.; Maughan, R.J.; Lobo, D.N. Hydration amongst nurses and doctors on-call (the HANDS on prospective cohort study). Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, Z.; Zarea, M.; El-Hennawy, U.; Viltard, M.; Lepicard, E.; Hawili, N.; Constant, F. Hydration Deficit in 9- to 11-Year-Old Egyptian Children. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2015, 2, 2333794X15611786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-David, Y.; Urkin, J.; Landau, D.; Bar-David, Z.; Pilpel, D. Voluntary dehydration among elementary school children residing in a hot arid environment. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2009, 22, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Johnson, E.C. Water Intake, Water Balance, and the Elusive Daily Water Requirement. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berl, T. Impact of solute intake on urine flow and water excretion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Agriculture; US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010, 7th ed.; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- What We Eat in America, NHANES 2007–2008. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400530/pdf/1516/Table_1_NIN_GEN_15.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Valtin, H. “Drink at least eight glasses of water a day.” Really? Is there scientific evidence for “8 x 8”? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
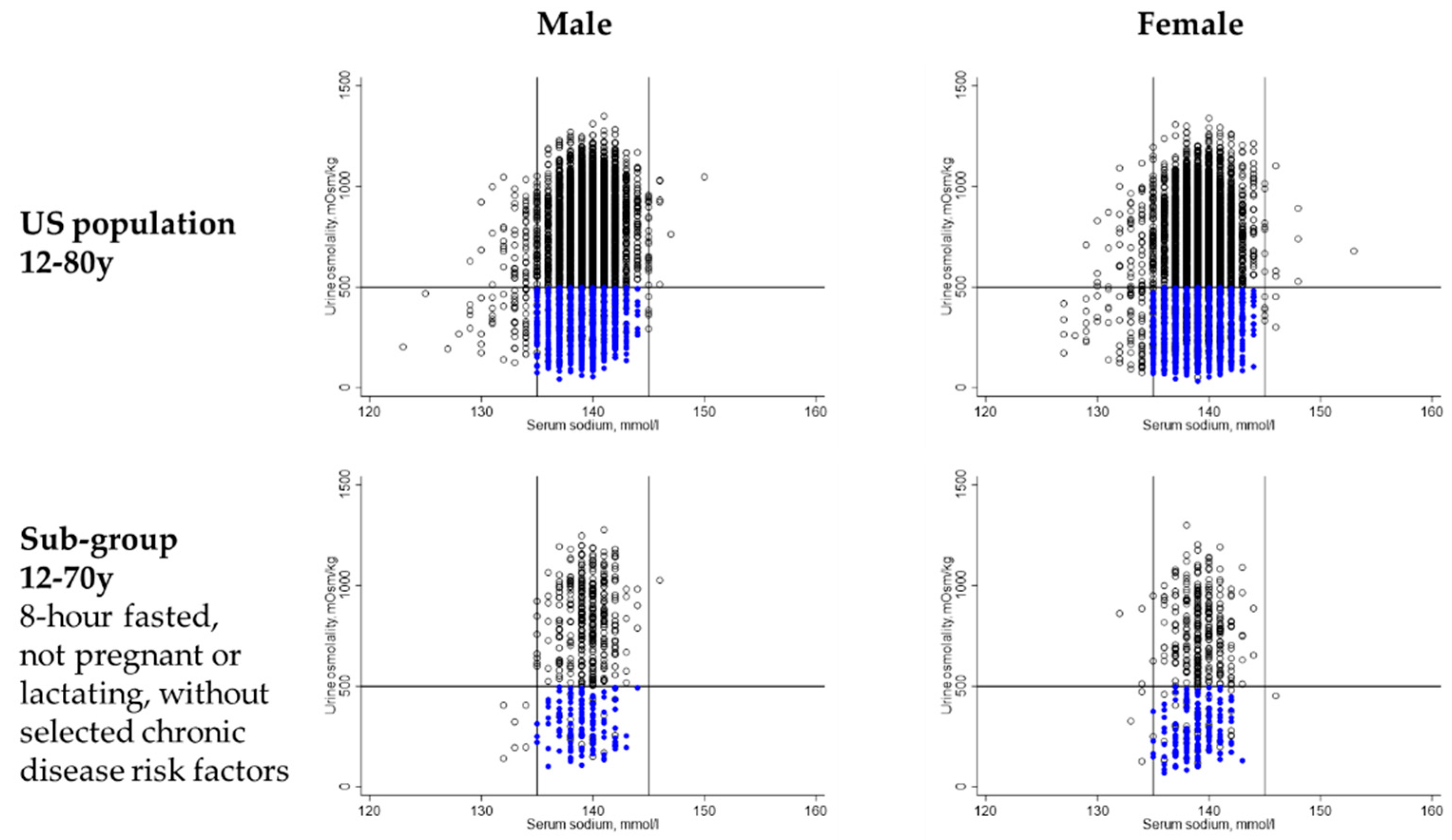
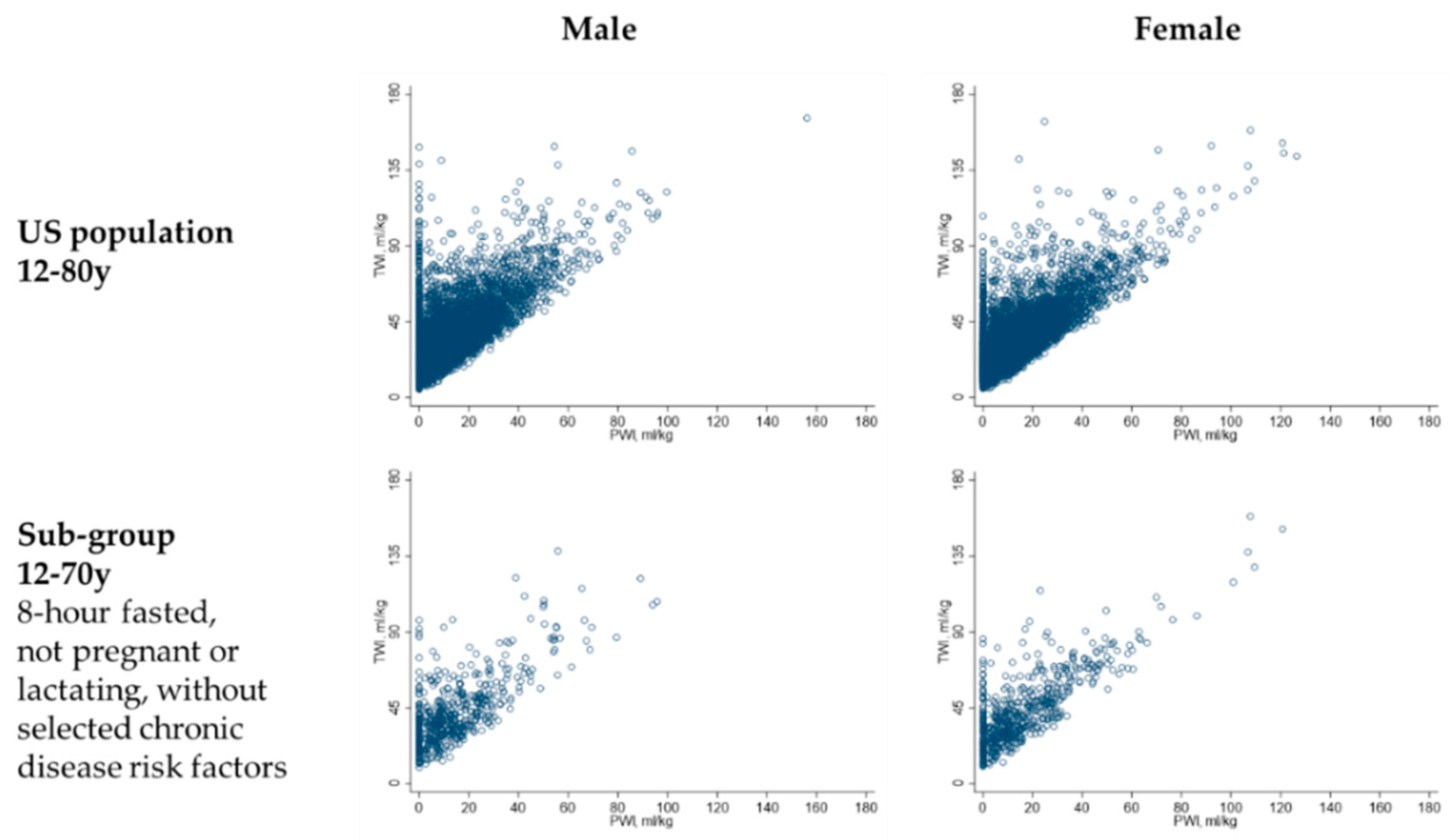
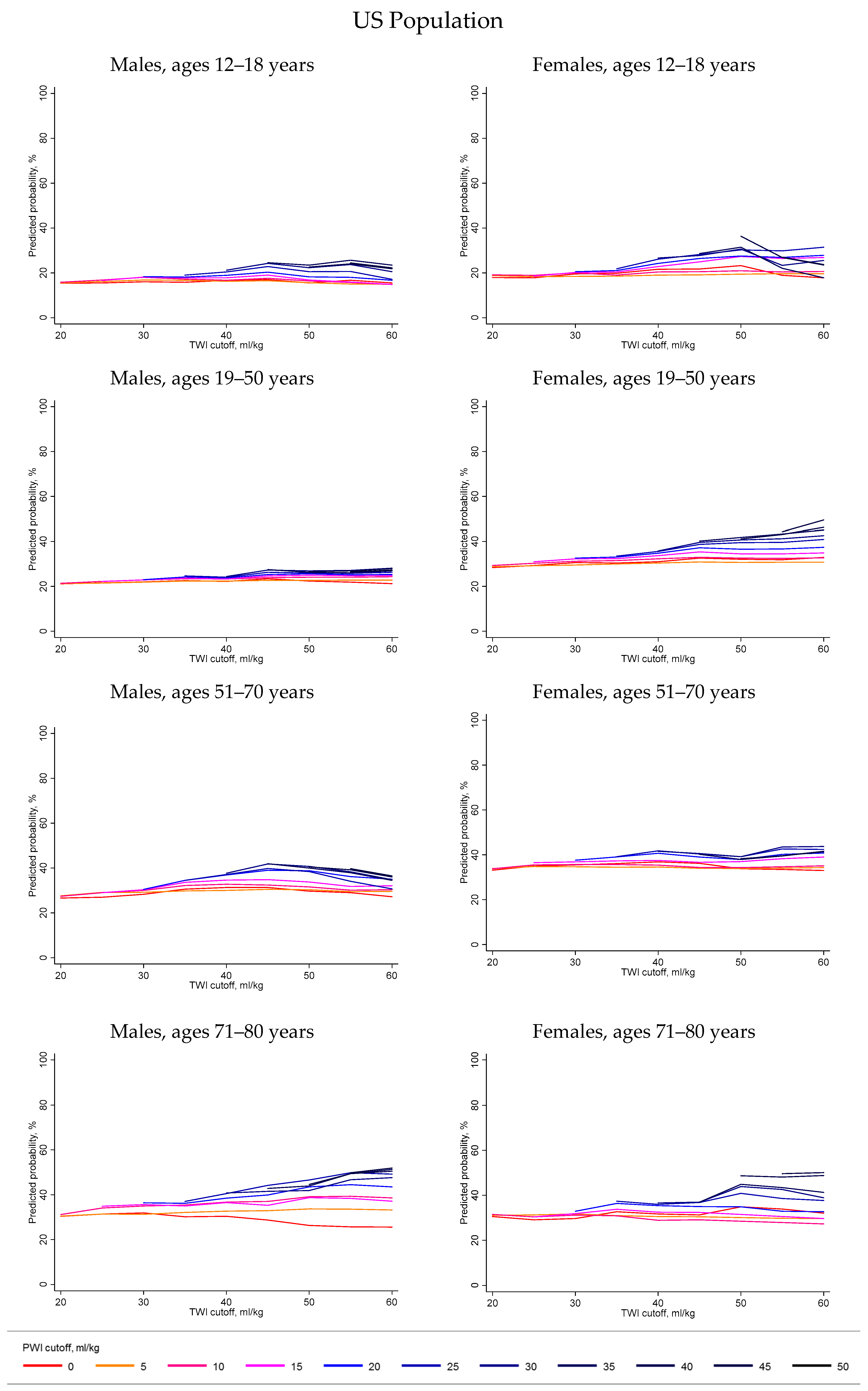
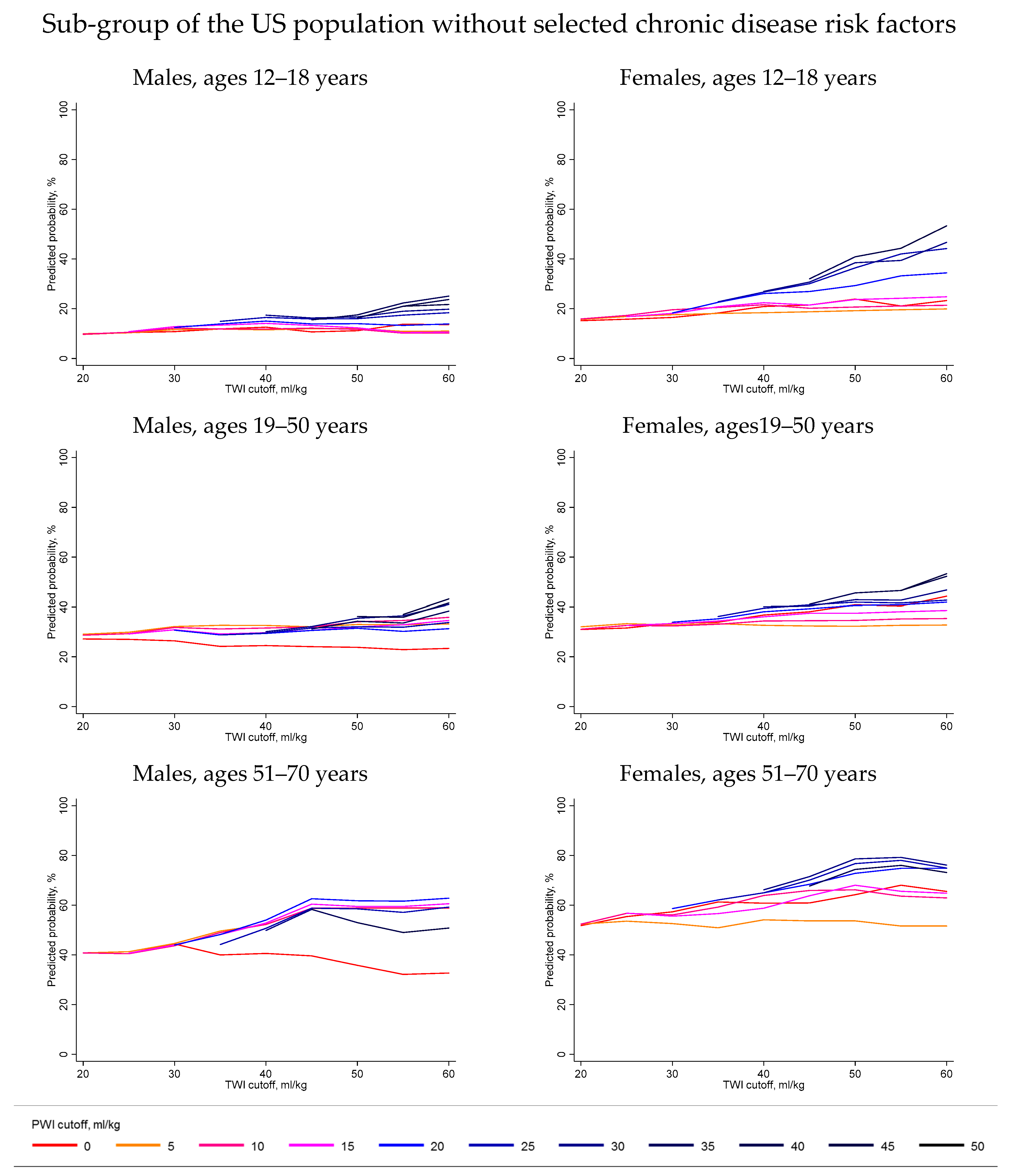
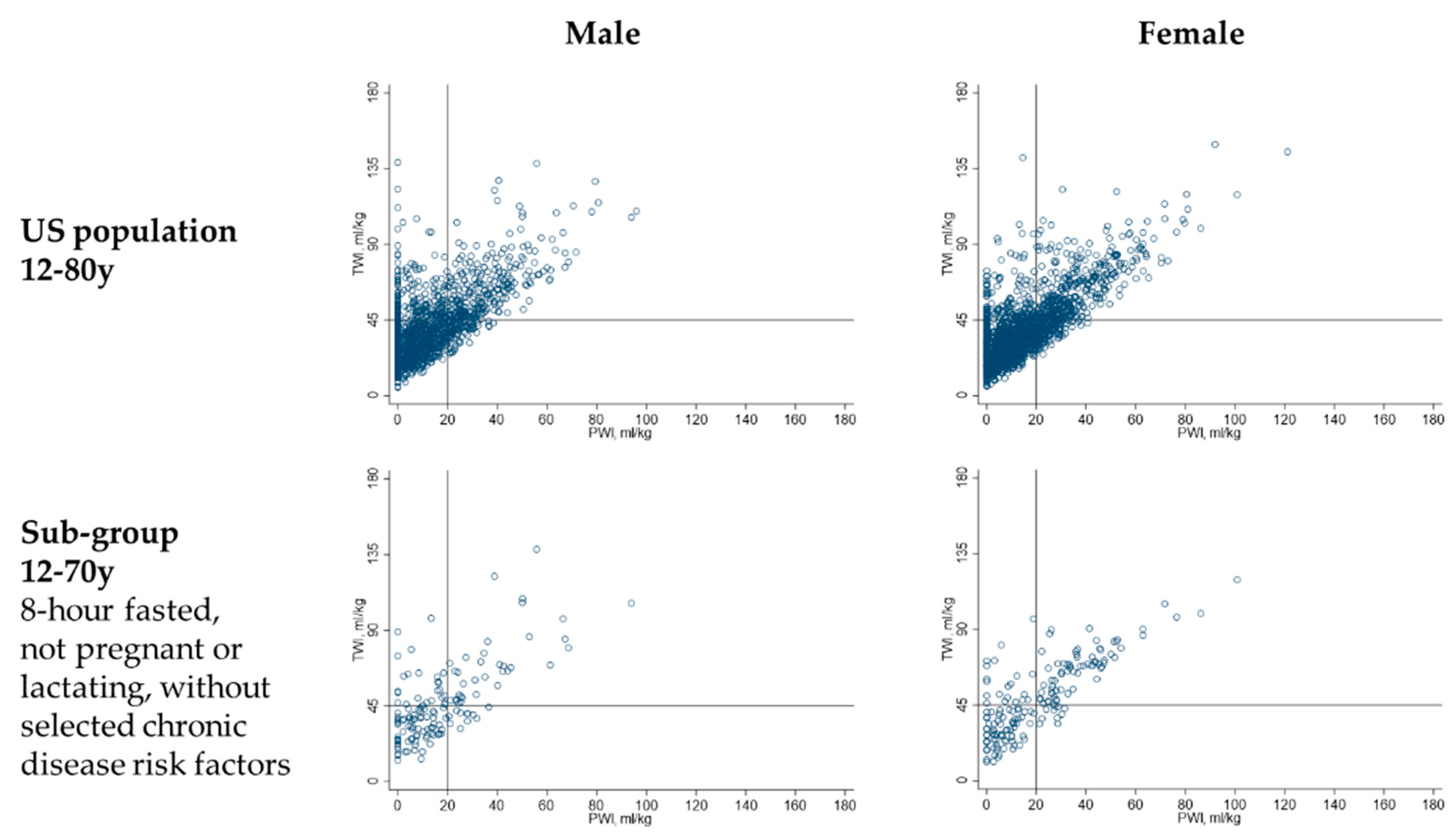
| Age 12–18 Years | Age 19–50 Years | Age 51–70 Years | Age 71–80 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Mean (SE) | Weighted Mean (SE) | Weighted Mean (SE) | Weighted Mean (SE) | |
| Male | (n = 978) | (n = 2703) | (n = 1551) | (n = 713) |
| Body weight, kg | 66.8 (0.9) | 86.4 (0.5) | 89.0 (0.8) | 81.9 (0.5) |
| Height, cm | 170.0 (0.5) | 176.5 (0.3) | 175.7 (0.4) | 172.1 (0.3) |
| BMI | 23.1 (0.3) | 27.7 (0.2) | 28.8 (0.3) | 27.6 (0.2) |
| Serum Na, mmol/L | 139.4 (0.1) | 139.2 (0.1) | 139.1 (0.1) | 139.5 (0.1) |
| Urine Volume, mL | 99.3 (4.8) | 113.7 (2.9) | 100.1 (3.2) | 77.4 (2.9) |
| Urine Osmolality, mmol/kg | 721 (24) | 618 (10) | 566 (9) | 550 (8) |
| Urine Albumin:Creatinine | 7.7 (0.5) | 5.4 (0.2) | 7.9 (0.4) | 15.6 (0.9) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 135.8 (1.1) | 102.3 (0.5) | 81.5 (0.7) | 62.5 (0.9) |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.01) | 0.9 (0.01) | 1.0 (0.01) | 1.1 (0.01) |
| HgA1c, % | 5.2 (0.01) | 5.4 (0.01) | 5.8 (0.03) | 5.9 (0.03) |
| Female | (n = 882) | (n = 2849) | (n = 1526) | (n = 722) |
| Body weight, kg | 59.4 (0.8) | 73.3 (0.5) | 74.9 (0.8) | 68.7 (0.8) |
| Height, cm | 161.0 (0.3) | 163.0 (0.3) | 161.5 (0.3) | 157.7 (0.3) |
| BMI | 22.9 (0.3) | 27.6 (0.2) | 28.7 (0.3) | 27.7 (0.3) |
| Serum Na, mmol/L | 139.2 (0.1) | 138.6 (0.1) | 139.5 (0.1) | 139.2 (0.1) |
| Urine Volume, mL | 74.3 (3.6) | 78.6 (2.1) | 73.7 (3.3) | 54.4 (2.3) |
| Urine Osmolality, mmol/kg | 620.5 (15.1) | 521.9 (12.2) | 455.2 (11.5) | 455.9 (8.9) |
| Urine Albumin:Creatinine | 12.0 (0.9) | 7.7 (0.1) | 9.0 (0.4) | 16.3 (1.0) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 128.3 (2.3) | 106.3 (0.5) | 82.9 (0.7) | 60.9 (0.9) |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.01) | 0.7 (0.004) | 0.8 (0.01) | 0.9 (0.01) |
| HgA1c, % | 5.3 (0.02) | 5.3 (0.01) | 5.8 (0.02) | 5.9 (0.03) |
| Age 12–18 Years | Age 19–50 Years | Age 51–70 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Mean (SE) | Weighted Mean (SE) | Weighted Mean (SE) | |
| Male | (n = 201) | (n = 233) | (n = 96) |
| Body Weight, kg | 58.7 (0.9) | 69.4 (0.7) | 70.7 (1.0) |
| Height, cm | 170.6 (0.8) | 176.4 (0.5) | 176.8 (0.9) |
| BMI | 20.2 (0.2) | 22.3 (0.2) | 22.6 (0.2) |
| Serum Na, mmol/L | 139.7 (0.1) | 139.2 (0.2) | 138.9 (0.3) |
| Urine Volume, mL | 77.2 (7.6) | 110.3 (9.4) | 86.5 (15.3) |
| Urine Osmolality, mmol/kg | 731 (28) | 561 (32) | 508 (27) |
| Urine Albumin:Creatinine | 6.7 (0.6) | 5.1 (0.2) | 5.5 (0.3) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 137.3 (1.1) | 108.3 (1.3) | 86.7 (1.4) |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.01) | 0.9 (0.01) | 0.9 (0.02) |
| HgA1c, % | 5.2 (0.03) | 5.3 (0.03) | 5.5 (0.04) |
| Fasting HOMA-IR | 0.8 (0.04) | 0.6 (0.03) | 0.6 (0.03) |
| Fasting Glucose, mg/dL | 93.3 (0.5) | 94.0 (0.7) | 97.1 (1.6) |
| Fasting Triglyceride, mg/dL | 57.3 (2.0) | 78.0 (2.4) | 82.8 (3.9) |
| Fasting HDL, mg/dL | 53.7 (0.7) | 55.0 (0.9) | 58.8 (2.3) |
| Female | (n = 132) | (n = 305) | (n = 98) |
| Body Weight, kg | 53.0 (0.6) | 59.8 (0.5) | 59.4 (0.8) |
| Height, cm | 161.5 (0.5) | 165.0 (0.5) | 162.7 (0.8) |
| BMI | 20.3 (0.2) | 22.0 (0.1) | 22.4 (0.2) |
| Serum Na, mmol/L | 138.9 (0.3) | 138.7 (0.1) | 139.8 (0.2) |
| Urine Volume, mL | 71.6 (9.8) | 76.5 (5.6) | 75.1 (11.0) |
| Urine Osmolality, mmol/kg | 561 (45) | 459 (22) | 382 (32) |
| Urine Albumin:Creatinine | 7.7 (0.6) | 6.5 (0.3) | 7.7 (0.4) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 128.3 (1.8) | 104.7 (1.2) | 89.4 (1.4) |
| Serum Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.01) | 0.7 (0.01) | 0.7 (0.01) |
| HgA1c, % | 5.2 (0.03) | 5.2 (0.02) | 5.5 (0.03) |
| Fasting HOMA-IR | 0.8 (0.05) | 0.5 (0.02) | 0.5 (0.06) |
| Fasting Glucose, mg/dL | 90.8 (0.7) | 89.7 (0.5) | 95.6 (0.9) |
| Fasting Triglyceride, mg/dL | 64.0 (2.4) | 68.5 (1.5) | 83.2 (3.8) |
| Fasting HDL, mg/dL | 62.4 (0.7) | 66.0 (1.0) | 70.5 (1.9) |
| US Population | Sub-Group without Selected Chronic Disease Risk Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Met Hydration Criteria | Total | Met Hydration Criteria | |||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | |||
| n | Weighted % (95% CI) | Weighted % (95% CI) | n | Weighted % (95% CI) | Weighted % (95% CI) | |
| Male | ||||||
| 12–18 years | 978 | 16.5 (11.9–22.5) | 83.5 (77.5–88.1) | 201 | 12.8 (8.1–19.5) | 87.2 (80.5–91.8) |
| 19–50 years | 2703 | 22.7 (20.1–25.6) | 77.3 (74.4–80.0) | 234 | 29.9 (23.6–37.2) | 70.1 (62.8–76.4) |
| 51–70 years | 1551 | 27.9 (24.5–31.6) | 72.1 (68.4–75.5) | 96 | 43.2 (27.5–60.4) | 56.8 (39.6–72.5) |
| 71–80 years | 713 | 28.9 (25.7–32.4) | 71.1 (67.6–74.3) | |||
| Female | ||||||
| 12–18 years | 882 | 19.8 (15.7–24.6) | 80.2 (75.4–84.3) | 132 | 18.2 (11.5–27.5) | 81.8 (72.5–88.5) |
| 19–50 years | 2849 | 28.7 (25.6–31.9) | 71.3 (68.1–74.4) | 305 | 32.7 (26.7–39.4) | 67.3 (60.6–73.3) |
| 51–70 years | 1526 | 34.1 (29.4–39.0) | 65.9 (61.0–70.6) | 98 | 51.0 (36.0–65.8) | 49.0 (34.2–64.0) |
| 71–80 years | 722 | 30.8 (26.3–35.7) | 69.2 (64.3–73.7) | |||
| Pregnant | 108 | 24.9 (15.3–37.9) | 75.1 (62.1–84.7) | |||
| Water Intake | Total | Percent Hydrated | Relative Risk of Meeting the Hydration Criteria | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | ||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||
| TWI ≥ 45 mL/kg or PWI ≥ 20 mL/kg | n | Weighted % (95% CI) | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | |
| US Population | |||||||||
| Male | |||||||||
| 12–18 years | No | 683 | 12.8 (9.5–17.1) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 295 | 24.6 (14.6–38.3) | 1.92 (1.16–3.19)) | 0.013 | 1.77 (1.21–2.59) | 0.005 | 1.58 (1.09–2.30) | 0.018 | |
| 19–50 years | No | 1623 | 19.2 (16.2–22.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 1080 | 27.6 (23.6–31.9) | 1.43 (1.16–1.77) | 0.001 | 1.50 (1.22–1.84) | 0.000 | 1.36 (1.10–1.68) | 0.006 | |
| 51–70 years | No | 1123 | 21.8 (18.5–25.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 428 | 41.7 (33.9–49.9) | 1.91 (1.49–2.46) | 0.000 | 1.96 (1.52–2.53) | 0.000 | 1.76 (1.36–2.28) | 0.000 | |
| 71–80 years | No | 583 | 26.3 (22.4–30.7) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 130 | 40.8 (29.8–52.9) | 1.55 (1.06–2.26) | 0.02 | 1.48 (1.01–2.17) | 0.045 | 1.47 (0.96–2.24) | 0.074 | |
| Female | |||||||||
| 12–18 years | No | 664 | 15.4 (11.5–20.3) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 218 | 30.0 (22.0–39.4) | 1.94 (1.35–2.79) | 0.001 | 1.85 (1.25–2.74) | 0.003 | 1.75 (1.19–2.58) | 0.006 | |
| 19–50 years | No | 1759 | 21.2 (18.1–24.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 1090 | 39.8 (35.5–44.3) | 1.88 (1.63–2.17) | 0.000 | 1.79 (1.56–2.05) | 0.000 | 1.70 (1.49–1.95) | 0.000 | |
| 51–70 years | No | 1038 | 29.4 (24.4–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 488 | 42.4 (34.5–50.6) | 1.44 (1.12–1.86) | 0.006 | 1.42 (1.07–1.88) | 0.016 | 1.29 (1.00–1.66) | 0.051 | |
| 71–80 years | No | 570 | 29.3 (24.1–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 152 | 36.2 (27.6–45.8) | 1.24 (0.91–1.69) | 0.172 | 1.28 (0.93–1.77) | 0.128 | 1.22 (0.87–1.71) | 0.234 | |
| Pregnant | No | 62 | 15.3 (7.3–29.4) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 46 | 38.2 (22.7–56.5) | 2.50 (1.10–5.66) | 0.030 | 2.08 (0.87–4.93) | 0.095 | 1.78 (0.81–3.90) | 0.145 | |
| Sub-group without selected chronic disease risk factors | |||||||||
| Male | |||||||||
| 12–18 years | No | 122 | 9.7 (5.4–16.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 79 | 17.3 (8.7–31.3) | 1.79 (0.79–4.05) | 0.155 | 1.99 (0.87–4.54) | 0.098 | 1.83 (0.78–4.29) | 0.156 | |
| 19–50 years | No | 129 | 30.4 (21.4–41.1) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 105 | 29.4 (21.2–39.2) | 0.97 (0.62–1.51) | 0.885 | 1.18 (0.69–2.03) | 0.536 | 1.16 (0.67–1.99) | 0.587 | |
| 51–70 years | No | 65 | 30.8 (17.7–48.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 31 | 62.7 (34.3–84.4) | 2.04 (1.09–3.82) | 0.028 | 1.92 (1.07–3.46) | 0.030 | 2.20 (1.15–4.18) | 0.018 | |
| Female | |||||||||
| 12–18 years | No | 84 | 14.1 (5.5–31.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 48 | 23.9 (14.5–36.7) | 1.70 (0.57–5.07) | 0.333 | 1.97 (0.66–5.84) | 0.214 | 3.36 (1.23–9.21) | 0.020 | |
| 19–50 years | No | 158 | 24.4 (16.1–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 147 | 41.2 (35.5–47.2) | 1.69 (1.15–2.50) | 0.010 | 1.56 (1.04–2.35) | 0.032 | 1.56 (1.05–2.34) | 0.031 | |
| 51–70 years | No | 47 | 39.7 (21.4–61.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| Yes | 51 | 61.9 (43.4–77.5) | 1.56 (0.90–2.71) | 0.112 | 1.88 (1.12–3.17) | 0.019 | 2.00 (1.18–3.40) | 0.011 | |
| Water Intake | Total | Percent Hydrated | Relative Risk of Meeting Hydration Criteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | |||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||
| mL/kg | n | Weighted % (95% CI) | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | Weighted RR (95% CI) | p | ||
| US Population | ||||||||||
| Male | 12–18 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 683 | 12.8 (9.4–17.1) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 67 | 8.7 (5.3–13.9) | 0.68 (0.40–1.15) | 0.145 | 0.61 (0.33–1.14) | 0.118 | 0.62 (0.32–1.17) | 0.135 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 93 | 37.5 (17.3–63.2) | 2.92 (1.51–5.66) | 0.002 | 2.83 (1.64–4.88) | 0.000 | 2.48 (1.39–4.42) | 0.003 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 135 | 18.7 (10.2–31.6) | 1.46 (0.75–2.81) | 0.253 | 1.45 (0.72–2.90) | 0.285 | 1.33 (0.67–2.61) | 0.408 | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 1623 | 19.2 (16.2–22.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 185 | 19.6 (13.6–27.4) | 1.02 (0.69–1.51) | 0.926 | 0.97 (0.66–1.43) | 0.886 | 0.97 (0.66–1.42) | 0.867 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 379 | 26.6 (18.7–36.2) | 1.38 (0.98–1.94) | 0.062 | 1.50 (1.07–2.10) | 0.020 | 1.29 (0.92–1.81) | 0.129 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 516 | 31.3 (25.7–37.6) | 1.63 (1.27–2.09) | 0.000 | 1.75 (1.38–2.22) | 0.000 | 1.58 (1.25–2.01) | 0.000 | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 1123 | 21.8 (18.5–25.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 88 | 25.7 (15.3–39.9) | 1.18 (0.69–2.01) | 0.532 | 1.18 (0.69–1.99) | 0.534 | 1.23 (0.74–2.03) | 0.414 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 170 | 47.5 (33.2–62.3) | 2.18 (1.55–3.07) | 0.000 | 2.31 (1.57–3.40) | 0.000 | 1.98 (1.35–2.90) | 0.001 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 170 | 41.5 (31.3–52.3) | 1.90 (1.39–2.60) | 0.000 | 1.99 (1.48–2.69) | 0.000 | 1.80 (1.31–2.48) | 0.001 | ||
| 71–80 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 583 | 26.3 (22.4–30.7) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 39 | 32.5 (14.6–57.6) | 1.23 (0.57–2.65) | 0.579 | 1.20 (0.61–2.37) | 0.580 | 1.21 (0.62–2.34) | 0.564 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 35 | 38.4 (22.0–58.0) | 1.46 (0.83–2.56) | 0.180 | 1.36 (0.78–2.35) | 0.269 | 1.34 (0.73–2.47) | 0.332 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 56 | 49.1 (34.7–63.7) | 1.87 (1.33–2.63) | 0.001 | 1.80 (1.22–2.67) | 0.004 | 1.79 (1.15–2.79) | 0.012 | ||
| Female | 12–18 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 664 | 15.4 (11.5–20.3) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 55 | 20.6 (10.4–36.8) | 1.34 (0.66–2.71) | 0.408 | 1.31 (0.61–2.80) | 0.480 | 1.34 (0.63–2.84) | 0.431 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 53 | 28.3 (13.6–50.0) | 1.83 (0.85–3.93) | 0.116 | 1.85 (0.86–3.97) | 0.114 | 1.71 (0.75–3.89) | 0.191 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 110 | 34.7 (21.3–51.1) | 2.25 (1.46–3.48) | 0.001 | 2.12 (1.27–3.53) | 0.005 | 1.99 (1.17–3.37) | 0.012 | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 1759 | 21.2 (18.1–24.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 290 | 28.5 (21.9–36.3) | 1.35 (1.06–1.71) | 0.016 | 1.35 (1.06–1.71) | 0.016 | 1.36 (1.06–1.73) | 0.016 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 237 | 43.7 (35.2–52.4) | 2.06 (1.67–2.55) | 0.000 | 2.04 (1.62–2.57) | 0.000 | 1.91 (1.51–2.41) | 0.000 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 563 | 42.8 (37.0–48.7) | 2.03 (1.70–2.41) | 0.000 | 1.88 (1.59–2.22) | 0.000 | 1.79 (1.51–2.12) | 0.000 | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 1038 | 29.4 (24.4–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 128 | 33.3 (21.5–47.7) | 1.13 (0.72–1.78) | 0.585 | 1.16 (0.74–1.84) | 0.487 | 1.14 (0.72–1.78) | 0.569 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 131 | 34.2 (24.5–45.4) | 1.16 (0.83–1.62) | 0.363 | 1.13 (0.77–1.65) | 0.513 | 1.01 (0.70–1.45) | 0.957 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 229 | 50.9 (39.9–61.7) | 1.73 (1.32–2.27) | 0.000 | 1.69 (1.27–2.27) | 0.001 | 1.52 (1.17–1.98) | 0.003 | ||
| 71–80 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 570 | 29.3 (24.1–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 41 | 31.2 (19.0–46.6) | 1.07 (0.64–1.77) | 0.802 | 1.07 (0.62–1.83) | 0.813 | 1.05 (0.61–1.80) | 0.849 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 41 | 47.3 (29.1–66.3) | 1.62 (1.03–2.53) | 0.036 | 1.67 (1.00–2.79) | 0.050 | 1.56 (0.88–2.75) | 0.121 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 70 | 32.5 (23.5–43.1) | 1.11 (0.80–1.54) | 0.514 | 1.20 (0.84–1.72) | 0.311 | 1.14 (0.80–1.63) | 0.448 | ||
| Pregnant | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 62 | 15.3 (7.3–29.4) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 12 | 66.5 (32.2–89.2) | 4.34 (1.85–10.18) | 0.001 | 3.11 (1.13–8.57) | 0.030 | 3.22 (1.13–9.22) | 0.030 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 27 | 32.2 (17.1–52.3) | 2.11 (0.83–5.34) | 0.112 | 1.95 (0.72–5.29) | 0.183 | 1.53 (0.61–3.81) | 0.350 | ||
| Sub-group without selected chronic disease risk factors | ||||||||||
| Male | 12–18 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 122 | 9.7 (5.4–16.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 13 | 20.6 (6.0–51.4) | 2.13 (0.74–6.16) | 0.156 | 1.59 (0.70–3.63) | 0.262 | 1.64 (0.71–3.82) | 0.241 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 26 | 20.0 (7.7–43.0) | 2.08 (0.80–5.42) | 0.130 | 2.21 (0.67–7.29) | 0.185 | 1.83 (0.56–6.04) | 0.310 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥20 | 40 | 14.6 (4.07–37.5) | 1.52 (0.42–5.44) | 0.512 | 2.09 (0.61–7.13) | 0.230 | 1.96 (0.55–6.91) | 0.287 | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 129 | 30.4 (21.4–41.1) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 14 | 26.0 (6.9–62.5) | 0.85 (0.25–2.97) | 0.799 | 1.08 (0.28–4.18) | 0.914 | 1.09 (0.27–4.33) | 0.903 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 43 | 29.9 (14.3–52.2) | 0.99 (0.50–1.95) | 0.965 | 1.29 (0.62–2.67) | 0.489 | 1.26 (0.60–2.65) | 0.538 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI ≥ 20 | 48 | 30.3 (17.5–47.2) | 1.00 (0.54–1.85) | 0.995 | 1.14 (0.57–2.28) | 0.710 | 1.11 (0.56–2.17) | 0.763 | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 65 | 30.8 (17.7–48.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 5 | 80.7 (34.5–97.1) | 2.62 (1.30–5.27) | 0.008 | 3.21 (1.20–8.54) | 0.021 | 3.49 (1.11–11.0) | 0.034 | ||
| TWI ≥ 45 PWI < 20 | 10 | 44.4 (11.5–83.1) | 1.44 (0.50–4.19) | 0.489 | 0.98 (0.43–2.27) | 0.968 | 1.12 (0.45–2.78) | 0.797 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 16 | 75.9 (41.0–93.4) | 2.46 (1.34–4.52) | 0.005 | 3.91 (1.59–9.62) | 0.004 | 4.21 (1.64–10.77) | 0.004 | ||
| Female | 12–18 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 84 | 14.1 (5.5–31.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 11 | 12.1 (2.0–48.3) | 0.86 (0.10–7.14) | 0.888 | 1.55 (0.20–12.10) | 0.666 | 1.71 (0.21–14.18) | 0.607 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 12 | 7.3 (2.3–21.1) | 0.52 (0.11–2.37) | 0.386 | 0.37 (0.09–1.51) | 0.161 | 0.71 (0.19–2.62) | 0.593 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 25 | 36.6 (19.9–57.4) | 2.61 (0.92–7.38) | 0.070 | 4.40 (1.99–9.70) | 0.001 | 7.49 (2.72–20.62) | 0.000 | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 158 | 24.4 (16.1–35.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 21 | 27.3 (11.9–51.1) | 1.12 (0.54–2.34) | 0.757 | 1.08 (0.53–2.19) | 0.830 | 1.08 (0.53–2.21) | 0.833 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 38 | 37.3 (21.5–56.3) | 1.53 (0.83–2.81) | 0.163 | 1.38 (0.75–2.53) | 0.284 | 1.38 (0.77–2.50) | 0.272 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 88 | 44.9 (37.1–52.9) | 1.84 (1.21–2.82) | 0.006 | 1.71 (1.10–2.68) | 0.020 | 1.71 (1.10–2.68) | 0.020 | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI < 45 PWI < 20 | 47 | 39.7 (21.3–61.6) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| TWI < 45 PWI ≥20 | 4 | 64.7 (13.5–95.5) | 1.63 (0.60–4.42) | 0.328 | 2.30 (0.84–6.32) | 0.102 | 2.03 (0.68–6.00) | 0.194 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI < 20 | 14 | 21.9 (3.9–66.0) | 0.55 (0.11–2.85) | 0.466 | 0.78 (0.17–3.59) | 0.738 | 0.80 (0.18–3.63) | 0.767 | ||
| TWI ≥45 PWI ≥20 | 33 | 71.7 (48.9–87.0) | 1.80 (1.03–3.17) | 0.041 | 2.07 (1.19–3.60) | 0.011 | 2.27 (1.34–3.86) | 0.004 | ||
| US Population | Sub-Group without Selected Chronic Disease Risk Factors | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS Regression Coefficients | Predicted Difference in TWI mL/kg | OLS Regression Coefficients | Predicted Difference in TWI mL/kg | |||||||||||
| Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | |||||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||
| B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | Mean (SE) | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | Mean (SE) | |
| Male | ||||||||||||||
| 12–18 years | 11.2 (4.6) | 0.020 | 8.9 (2.5) | 0.001 | 7.1 (2.3) | 0.003 | 7.1 (2.3) | 8.8 (5.2) | 0.099 | 9.5 (4.5) | 0.042 | 8.2 (4.4) | 0.069 | 8.2 (4.4) |
| 19–50 years | 5.0 (1.4) | 0.001 | 5.5 (1.2) | 0.000 | 3.5 (1.2) | 0.005 | 3.5 (1.2) | 2.7 (3.7) | 0.474 | 4.9 (3.1) | 0.130 | 4.3 (3.0) | 0.159 | 4.3 (3.0) |
| 51–70 years | 8.1 (1.8) | 0.000 | 7.7 (1.2) | 0.000 | 5.7 (1.3) | 0.000 | 5.7 (1.3) | 11.5 (9.0) | 0.212 | 10.4 (6.6) | 0.127 | 11.3 (6.6) | 0.098 | 11.3 (6.6) |
| 71–80 years | 5.6 (1.4) | 0.000 | 4.6 (1.4) | 0.002 | 4.4 (1.4) | 0.005 | 4.4 (1.4) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Female | ||||||||||||||
| 12–18 years | 6.2 (2.6) | 0.024 | 5.2 (2.2) | 0.024 | 3.9 (2.0) | 0.056 | 3.9 (2.0) | 11.9 (5.3) | 0.033 | 11.2 (5.5) | 0.050 | 14.3 (5.1) | 0.009 | 14.3 (5.1) |
| 19–50 years | 10.7 (1.2) | 0.000 | 9.6 (1.1) | 0.000 | 8.1 (0.9) | 0.000 | 8.1 (0.9) | 9.0 (3.1) | 0.006 | 7.2 (3.3) | 0.036 | 7.1 (3.2) | 0.031 | 7.1 (3.2) |
| 51–70 years | 7.4 (2.1) | 0.001 | 7.1 (2.2) | 0.003 | 5.2 (1.9) | 0.009 | 5.2 (1.9) | 7.9 (5.6) | 0.167 | 11.4 (5.0) | 0.030 | 11.8 (4.8) | 0.019 | 11.8 (4.8) |
| 71–80 years | 2.8 (1.5) | 0.064 | 3.5 (1.3) | 0.012 | 2.8 (1.2) | 0.029 | 2.8 (1.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pregnant | 7.6 (4.1) | 0.075 | 5.0 (3.4) | 0.151 | 1.0 (3.3) | 0.764 | 1.0 (3.3) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| US Population | Sub-group without Selected Chronic Disease Risk Factors | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZINB Model Coefficients | Predicted Difference in PWI mL/kg | ZINB Model Coefficients | Predicted Difference in PWI mL/kg | |||||||||||
| Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | Unadjusted | Multivariable Adjusted | |||||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||
| B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | Mean (SE) | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | B (SE) | p | Mean (SE) | |
| Male | ||||||||||||||
| 12–18 years | −0.01 (0.19) | 0.979 | 0.01 (0.18) | 0.946 | −0.02 (0.18) | 0.917 | −0.2 (2.1) | 0.23 (0.25) | 0.368 | 0.40 (0.24) | 0.101 | 0.41 (0.24) | 0.103 | 7.1 (4.6) |
| 19–50 years | 0.15 (0.06) | 0.020 | 0.16 (0.06) | 0.009 | 0.12 (0.06) | 0.035 | 1.9 (0.9) | 0.03 (0.13) | 0.815 | 0.12 (0.15) | 0.441 | 0.09 (0.15) | 0.548 | 1.4 (2.3) |
| 51–70 years | 0.24 (0.09) | 0.012 | 0.21 (0.08) | 0.015 | 0.16 (0.09) | 0.069 | 1.8 (1.0) | 0.78 (0.29) | 0.011 | 0.72 (0.24) | 0.005 | 0.73 (0.25) | 0.006 | 8.1 (3.0) |
| 71–80 years | 0.22 (0.10) | 0.040 | 0.19 (0.11) | 0.102 | 0.18 (0.11) | 0.107 | 1.6 (1.0) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Female | ||||||||||||||
| 12–18 years | 0.23 (0.09) | 0.011 | 0.22 (0.11) | 0.054 | 0.16 (0.09) | 0.081 | 2.1 (1.2) | 0.41 (0.26) | 0.131 | 0.42 (0.26) | 0.113 | 0.52 (0.19) | 0.011 | 8.7 (3.8) |
| 19–50 years | 0.29 (0.05) | 0.000 | 0.27 (0.05) | 0.000 | 0.23 (0.04) | 0.000 | 3.8 (0.7) | 0.21 (0.14) | 0.144 | 0.19 (0.15) | 0.202 | 0.20 (0.15) | 0.188 | 3.9 (3.0) |
| 51–70 years | 0.24 (0.09) | 0.010 | 0.21 (0.08) | 0.016 | 0.15 (0.07) | 0.034 | 2.0 (0.9) | 0.40 (0.18) | 0.035 | 0.53 (0.18) | 0.007 | 0.51 (0.19) | 0.010 | 9.6 (4.2) |
| 71–80 years | 0.02 (0.08) | 0.849 | 0.02 (0.07) | 0.777 | 0.00 (0.08) | 0.993 | 0.0 (0.9) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pregnant | 0.39 (0.17) | 0.028 | 0.49 (0.18) | 0.010 | 0.49 (0.21) | 0.026 | 10.0 (4.7) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Percentiles of the TWI and PWI Distributions | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did Not Meet Hydration Criteria | Met Hydration Criteria | |||||||||||
| 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | |||
| Weighted Estimate (SE) | Weighted Estimate (SE) | |||||||||||
| US Population | ||||||||||||
| Male | 12–18 years | TWI, L/d | 1.2 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.1) | 2.9 (0.1) | 3.9 (0.2) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.8 (0.1) | 2.8 (0.3) | 3.5 (0.5) | 5.1 (0.4) |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.04) | 1.2 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | 0.4 (0.2) | 1.0 (0.4) | 2.3 (0.6) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 17.5 (0.8) | 23.9 (0.9) | 32.4 (1.3) | 42.7 (2.5) | 58.2 (2.5) | 21.3 (2.7) | 31.2 (2.1) | 41.5 (3.4) | 57.1 (4.7) | 74.7 (15.1) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 1.9 (0.9) | 8.5 (0.7) | 17.6 (1.6) | 28.6 (2.6) | 0 | 0 | 6.6 (2.2) | 17.5 (6.6) | 34.6 (7.8) | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI, L/d | 1.8 (0.05) | 2.4 (0.1) | 3.2 (0.1) | 4.3 (0.1) | 5.8 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.1) | 2.7 (0.1) | 3.5 (0.1) | 4.5 (0.1) | 5.6 (0.2) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.1) | 3.0 (0.1) | 0 | 0.4 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.1) | 3.2 (0.1) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 20.2 (0.6) | 27.0 (0.6) | 36.6 (0.8) | 48.8 (1.4) | 67.0 (2.5) | 23.3 (0.9) | 31.7 (1.4) | 41.9 (1.6) | 55.6 (1.9) | 73.4 (2.9) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 2.7 (0.9) | 10.0 (0.6) | 20.8 (1.1) | 33.9 (1.2) | 0 | 4.4 (0.7) | 13.7 (1.1) | 25.4 (0.8) | 39.9 (2.5) | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI, L/d | 1.7 (0.1) | 2.3 (0.1) | 2.9 (0.1) | 4.0 (0.2) | 5.0 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.1) | 2.6 (0.1) | 3.4 (0.1) | 4.3 (0.3) | 5.6 (0.5) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.1 (0.05) | 0.6 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.2) | 0 | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.1) | 2.6 (0.4) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 18.2 (0.7) | 24.6 (0.6) | 32.8 (1.1) | 42.3 (1.2) | 55.5 (2.1) | 22.9 (1.1) | 29.1 (1.4) | 41.5 (1.4) | 51.1 (2.4) | 67.8 (6.2) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 0.7 (0.5) | 6.6 (0.7) | 15.4 (1.1) | 24.6 (1.1) | 0 | 1.5 (0.7) | 8.5 (1.3) | 19.3 (1.9) | 30.3 (5.4) | ||
| 71–80 years | TWI, L/d | 1.3 (0.04) | 1.7 (0.05) | 2.2 (0.1) | 3.0 (0.1) | 3.7 (0.2) | 1.7 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.1) | 2.5 (0.1) | 3.3 (0.2) | 4.2 (0.2) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.5 (0.04) | 0.9 (0.04) | 1.7 (0.1) | 0 | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.2) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 15.2 (40.8) | 20.0 (0.6) | 26.7 (0.9) | 35.7 (0.9) | 45.1 (1.7) | 18.5 (1.5) | 24.5 (1.1) | 31.6 (1.5) | 42.2 (2.2) | 52.3 (4.7) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 0.2 (0.4) | 5.2 (0.5) | 11.1 (0.9) | 19.7 (1.0) | 0 | 2.4 (0.9) | 7.2 (1.1) | 13.4 (1.8) | 24.2 (1.9) | ||
| Female | 12–18 years | TWI, L/d | 0.9 (0.04) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.8 (0.1) | 2.4 (0.1) | 3.0 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.2) | 2.9 (0.3) | 3.7 (0.6) |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.01) | 1.0 (0.1) | 1.8 (0.2) | 0 | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.2) | 2.1 (0.3) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 14.8 (0.6) | 20.0 (1.0) | 30.3 (1.3) | 42.8 (2.0) | 51.2 (3.1) | 17.2 (1.5) | 22.9 (2.6) | 34.9 (5.3) | 53.2 (4.8) | 60.9 (3.6) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 1.5 (0.8) | 9.2 (0.5) | 16.2 (1.7) | 29.0 (3.9) | 0 | 2.7 (2.0) | 11.0 (2.5) | 27.1 (3.3) | 32.2 (1.8) | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI, L/d | 1.4 (0.03) | 1.8 (0.03) | 2.5 (0.04) | 3.3 (0.1) | 4.2 (0.1) | 1.7 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.1) | 3.0 (0.1) | 4.0 (0.1) | 5.2 (0.2) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.2 (0.04) | 0.8 (0.04) | 1.6 (0.1) | 2.5 (0.1) | 0 | 0.5 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) | 2.0 (0.2) | 3.0 (0.2) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 17.5 (0.4) | 23.2 (0.6) | 33.2 (0.7) | 44.9 (0.8) | 58.4 (1.1) | 23.3 (1.0) | 30.4 (1.1) | 42.5 (1.5) | 60.5 (2.5) | 78.7 (3.0) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 3.0 (0.5) | 10.2 (0.6) | 21.5 (1.1) | 32.9 (1.3) | 0 | 6.7 (0.7) | 16.2 (1.3) | 29.6 (1.7) | 45.6 (2.4) | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI, L/d | 1.4 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.03) | 2.5 (0.04) | 3.4 (0.1) | 4.3 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.1) | 2.7 (0.1) | 3.6 (0.2) | 4.6 (0.3) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.2 (0.05) | 0.7 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.1) | 0 | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.7 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.2) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 18.4 (0.6) | 23.4 (0.4) | 32.3 (0.6) | 44.7 (1.4) | 57.4 (2.7) | 20.3 (1.6) | 29.0 (1.2) | 39.8 (1.7) | 52.4 (2.5) | 70.3 (7.4) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 2.9 (0.5) | 10.0 (0.7) | 17.8 (0.8) | 27.3 (1.6) | 0 | 3.9 (0.9) | 13.5 (1.9) | 23.3 (2.3) | 33.7 (2.3) | ||
| 71–80 years | TWI, L/d | 1.1 (0.03) | 1.5 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.1) | 2.7 (0.1) | 3.3 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.7 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.1) | 2.8 (0.2) | 3.5 (0.2) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.2 (0.05) | 0.6 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.1) | 0 | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.03) | 1.0 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.1) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 16.6 (0.9) | 21.9 (0.8) | 30.1 (0.8) | 38.3 (1.2) | 48.7 (0.8) | 18.1 (1.2) | 23.9 (0.9) | 32.1 (2.0) | 42.2 (2.0) | 56.2 (2.1) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 2.9 (0.8) | 8.4 (0.8) | 15.0 (0.7) | 24.3 (1.4) | 0 | 2.9 (1.0) | 8.2 (0.6) | 14.2 (1.7) | 26.0 (2.7) | ||
| Pregnant | TWI, L/d | 1.5 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.1) | 2.8 (0.2) | 4.0 (0.2) | 4.8 (0.3) | 2.3 (0.3) | 2.8 (0.4) | 3.2 (0.2) | 3.7 (0.7) | 4.7 (0.5) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.4) | 3.0 (0.6) | 0.5 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.4) | 1.8 (0.4) | 2.7 (0.5) | 3.6 (0.4) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 15.3 (3.9) | 23.7 (2.4) | 37.3 (2.9) | 52.7 (3.8) | 64.7 (6.3) | 23.7 (3.6) | 35.4 (5.0) | 42.0 (4.6) | 53.7 (12.5) | 60.5 (5.6) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0.9 (0.8) | 5.3 (1.5) | 10.8 (2.0) | 25.8 (5.3) | 40.2 (5.7) | 5.7 (2.2) | 12.6 (4.9) | 25.1 (6.4) | 38.0 (8.8) | 45.6 (3.8) | ||
| Sub-group without selected chronic disease risk factors | ||||||||||||
| Male | 12–18 years | TWI, L/d | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.2) | 2.9 (0.1) | 3.8 (0.8) | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.3) | 2.6 (0.2) | 3.0 (0.8) | 5.0 (1.0) |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.2) | 2.1 (1.2) | 0 | 0 | 0.6 (0.4) | 1.8 (0.9) | 2.8 (0.2) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 20.0 (1.3) | 25.8 (1.1) | 35.2 (1.7) | 50.0 (2.3) | 60.6 (8.1) | 24.5 (4.4) | 34.1 (4.7) | 43.9 (6.2) | 60.4 (8.4) | 79.6 (9.6) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 3.0 (1.6) | 11.9 (2.1) | 21.7 (2.9) | 33.4 (9.5) | 0 | 0 | 10.0 (6.6) | 31.8 (14.1) | 42.3 (3.0) | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI, L/d | 1.5 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.2) | 2.8 (0.1) | 3.6 (0.2) | 4.5 (0.6) | 1.6 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.2) | 2.9 (0.2) | 4.0 (0.3) | 4.9 (0.5) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.7 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.2) | 2.2 (0.3) | 0 | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.3) | 2.4 (0.5) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 21.8 (2.4) | 30.0 (1.8) | 40.2 (2.0) | 49.3 (2.7) | 67.2 (6.9) | 23.9 (2.5) | 31.9 (2.8) | 39.7 (3.6) | 51.8 (7.1) | 73.9 (19.0) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 1.8 (1.2) | 9.4 (1.2) | 22.2 (3.0) | 35.2 (6.8) | 0 | 6.2 (2.1) | 13.6 (1.7) | 20.6 (3.8) | 33.4 (7.1) | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI, L/d | 1.8 (0.3) | 2.1 (0.1) | 2.6 (0.2) | 3.1 (0.2) | 4.3 (0.4) | 1.9 (0.3) | 2.3 (0.2) | 2.8 (0.4) | 3.9 (1.5) | 7.7 (1.9) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0 | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.6 (0.2) | 1.3 (0.3) | 0 | 0.4 (0.2) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.9 (0.4) | 3.8 (1.0) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 27.0 (3.9) | 31.2 (2.3) | 35.9 (3.2) | 44.7 (5.5) | 61.4 (8.7) | 23.7 (4.3) | 31.1 (3.5) | 41.9 (4.2) | 64.0 (13.1) | 108.8 (22.4) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 0 | 3.6 (2.2) | 9.3 (2.9) | 17.8 (5.6) | 0 | 6.4 (3.6) | 14.3 (5.2) | 25.4 (5.6) | 45.5 (10.2) | ||
| Female | 12–18 years | TWI, L/d | 1.0 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.1) | 2.5 (0.3) | 3.2 (0.2) | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.4) | 2.5 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.9) | 4.4 (0.3) |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0 | 0.5 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.3) | 0 | 0 | 0.7 (0.5) | 1.9 (1.1) | 2.8 (0.5) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 21.2 (1.7) | 26.9 (1.6) | 34.3 (3.6) | 49.5 (5.4) | 58.8 (4.8) | 23.2 (3.6) | 30.7 (6.0) | 47.7 (10.9) | 65.3 (12.8) | 77.7 (6.2) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 0 | 10.3 (2.2) | 19.5 (2.4) | 31.3 (6.3) | 0 | 0 | 16.6 (10.0) | 36.7 (21.1) | 45.9 (4.6) | ||
| 19–50 years | TWI, L/d | 1.4 (0.1) | 1.8 (0.1) | 2.4 (0.1) | 3.3 (0.2) | 4.2 (0.4) | 1.6 (0.2) | 2.0 (0.1) | 3.0 (0.4) | 4.4 (0.2) | 4.9 (0.2) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.8 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) | 2.2 (0.2) | 0 | 0.4 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.2) | 2.1 (0.2) | 3.0 (0.4) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 23.9 (1.4) | 29.5 (1.1) | 38.4 (1.9) | 54.0 (2.8) | 72.1 (4.6) | 27.0 (3.1) | 33.8 (3.0) | 48.3 (6.0) | 70.8 (2.9) | 82.8 (3.3) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 5.3 (1.5) | 12.2 (1.5) | 25.3 (2.5) | 37.2 (3.2) | 0 | 5.8 (1.9) | 19.0 (3.5) | 33.7 (3.7) | 47.3 (5.4) | ||
| 51–70 years | TWI, L/d | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.8 (0.2) | 2.2 (0.2) | 3.0 (0.3) | 4.3 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.3) | 2.7 (0.3) | 3.8 (0.5) | 4.8 (0.5) | |
| PWI, L/d | 0 | 0 | 0.7 (0.2) | 1.2 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.7) | 0 | 0.4 (0.3) | 1.3 (0.4) | 2.2 (0.4) | 3.1 (0.5) | ||
| TWI, mL/kg | 23.7 (3.1) | 31.1 (2.3) | 37.7 (3.3) | 52.1 (4.6) | 70.1 (7.3) | 23.4 (4.2) | 31.8 (5.9) | 45.9 (4.8) | 68.2 (7.5) | 78.2 (5.0) | ||
| PWI, mL/kg | 0 | 0 | 12.6 (3.4) | 20.0 (3.3) | 34.9 (10.1) | 0 | 6.5 (5.3) | 22.7 (6.0) | 37.7 (7.8) | 51.5 (6.9) | ||
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stookey, J.D. Analysis of 2009–2012 Nutrition Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) Data to Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting Hydration Criteria for Individuals Aged 12–80 Years in the US Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030657
Stookey JD. Analysis of 2009–2012 Nutrition Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) Data to Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting Hydration Criteria for Individuals Aged 12–80 Years in the US Population. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030657
Chicago/Turabian StyleStookey, Jodi Dunmeyer. 2019. "Analysis of 2009–2012 Nutrition Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) Data to Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting Hydration Criteria for Individuals Aged 12–80 Years in the US Population" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030657
APA StyleStookey, J. D. (2019). Analysis of 2009–2012 Nutrition Health and Examination Survey (NHANES) Data to Estimate the Median Water Intake Associated with Meeting Hydration Criteria for Individuals Aged 12–80 Years in the US Population. Nutrients, 11(3), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030657





