Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Dietary Assessment
2.4. Self-Reported Questionnaires
2.4.1. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI)
2.4.2. Morningness–Eveningness Questionnaire (MEQ)
2.4.3. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics
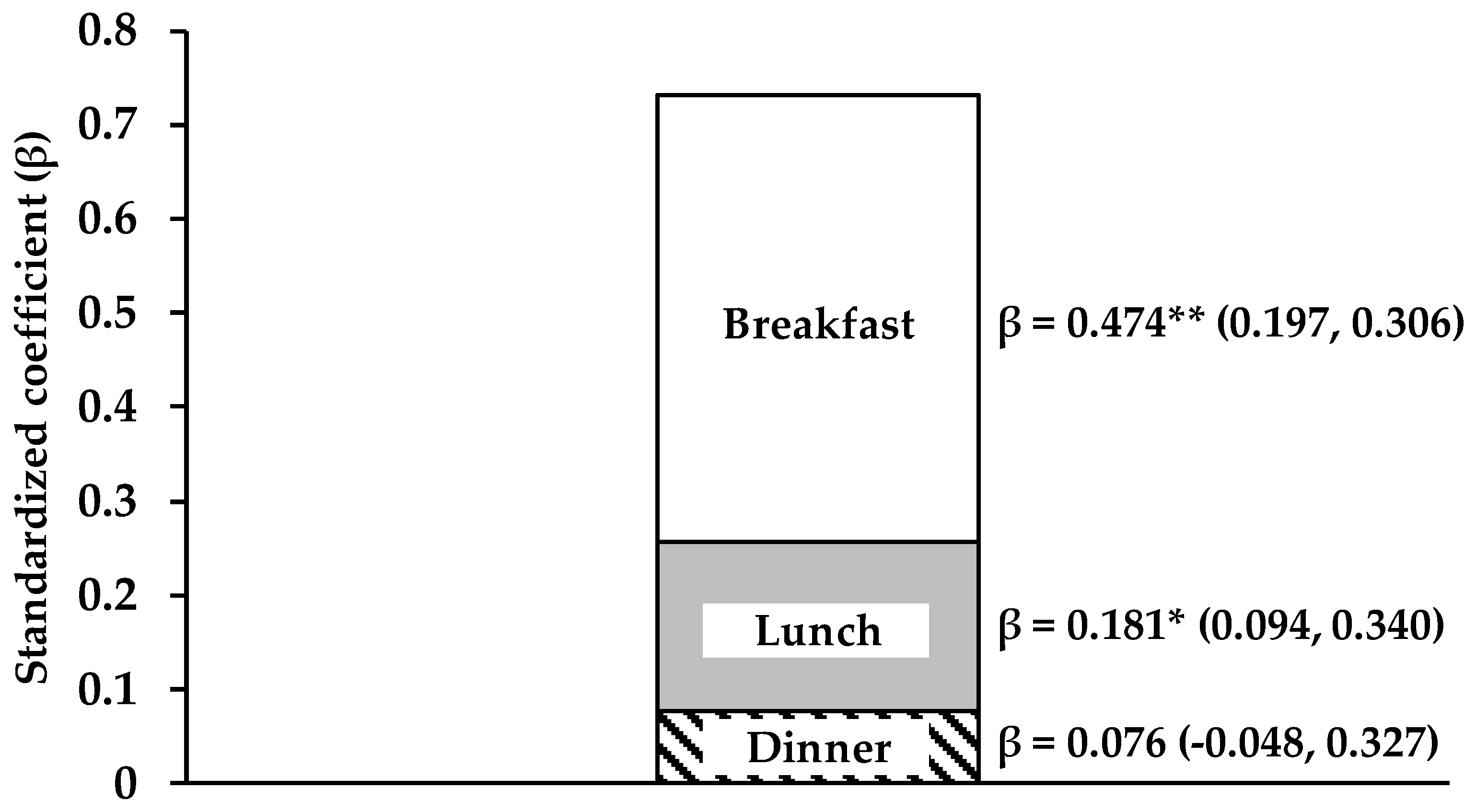
3.2. Protein Intake per Meal for Maximization of MPS
3.3. Contribution of Achieving 0.24 g/kg BW of Protein Intake at Each Meal to Total Protein Intake
3.4. Association between FFM and RDA for Protein Intake
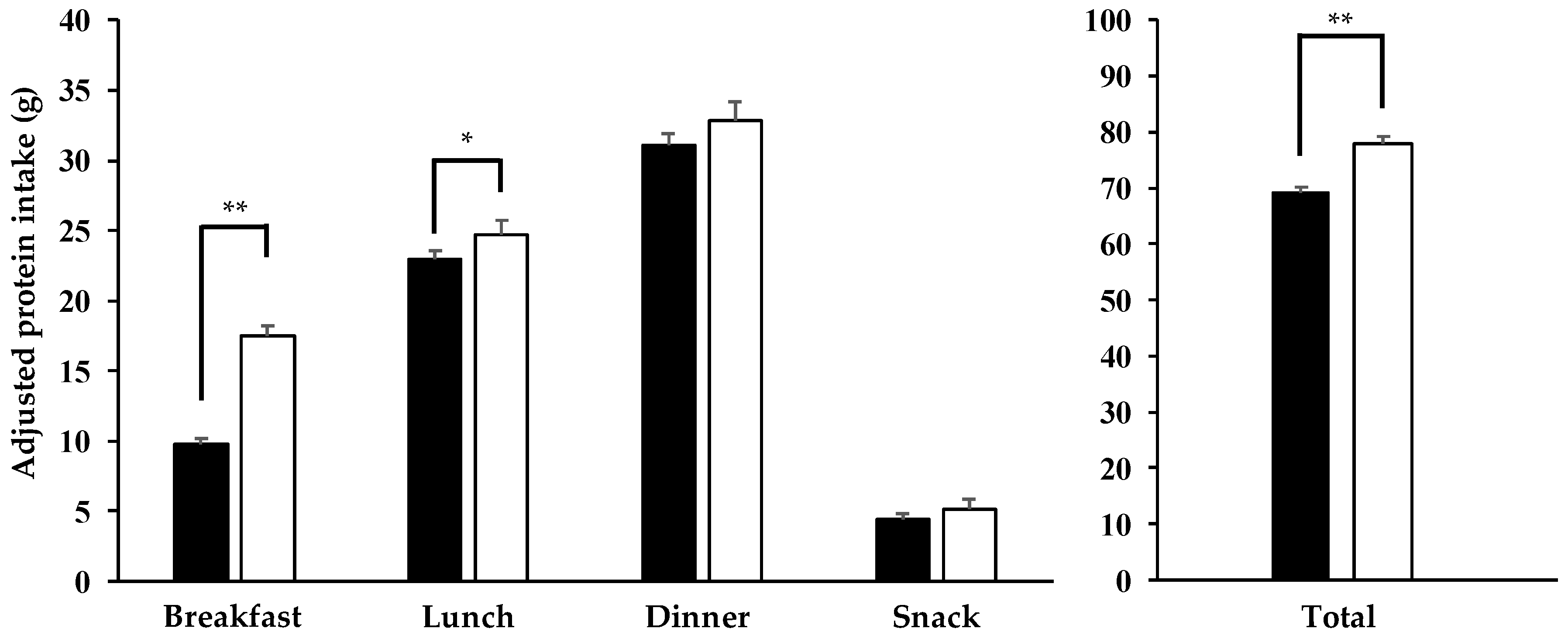
3.5. Comparison of Adjusted Protein Intake between AP and NP Groups
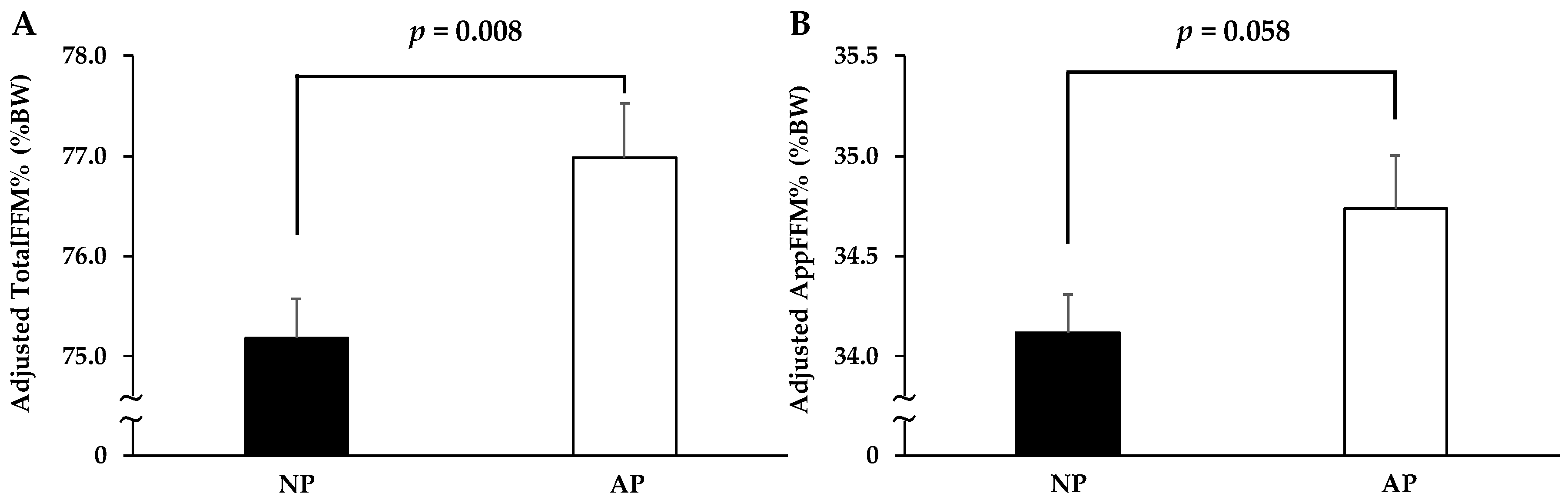
3.6. Comparison of FFM between AP and NP Groups with Total Protein Intake More Than the RDA
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Confounding Factors on Outcomes
4.2. Importance of Protein Intake More Than the RDA for Regulation of Muscle Mass
4.3. Effect of Achieving Protein Intake 0.24 g/kg BW at All Three Meals on Muscle Mass
4.4. Importance of Protein Intake at Breakfast for the Regulation of Muscle Mass
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, D.; Park, M.S.; Kim, T.N.; Ryu, J.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Jones, G.; Choi, K.M. Associations of low muscle mass and the metabolic syndrome in Caucasian and Asian middle-aged and older Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.W.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.R.; Yoo, S.J.; Cha, B.Y.; Son, H.Y.; Cho, N.H. Low muscle mass and risk of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older adults: Findings from the KoGES. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokata, H.; Ando, F.; Yuki, A.; Otsuka, R. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle mass among community-dwelling Japanese: A 12-year longitudinal study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2014, 14 (Suppl. 1), 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Dankel, S.J.; Buckner, S.L.; Jessee, M.B.; Mattocks, K.T.; Mouser, J.G.; Bell, Z.W.; Loenneke, J.P. Differences in 100-m sprint performance and skeletal muscle mass between elite male and female sprinters. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujika, I.; Ronnestad, B.R.; Martin, D.T. Effects of increased muscle strength and muscle mass on endurance-cycling performance. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Noohu, M.M. Correlation of percentage body fat and muscle mass with anaerobic and aerobic performance in collegiate soccer players. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 60, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, S.; Mangano, K.M.; Hannan, M.T.; Kiel, D.P.; McLean, R.R. Higher protein intake is associated with higher lean mass and quadriceps muscle strength in adult men and women. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Smith, S.R.; de Jonge, L.; Xie, H.; Rood, J.; Martin, C.K.; Most, M.; Brock, C.; Mancuso, S.; Redman, L.M. Effect of dietary protein content on weight gain, energy expenditure, and body composition during overeating: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012, 307, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Milan, A.M.; Mitchell, S.M.; Zeng, N.; Ramzan, F.; Sharma, P.; Knowles, S.O.; Roy, N.C.; Sjodin, A.; Wagner, K.H.; et al. The effects of dietary protein intake on appendicular lean mass and muscle function in elderly men: A 10-wk randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurka, J.M.; Vezina, J.; Brown, D.D.; Schumacher, J.; Cullen, R.W.; Laurson, K.R. Combined increases in muscle-strengthening activity frequency and protein intake reveal graded relationship with fat-free mass percentage in U.S. adults, NHANES (1999-2004). J. Frailty Aging 2015, 4, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, J.M.; Deierlein, A.L.; Morland, K.B.; Granieri, E.C.; Spark, A. Is meeting the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein related to body composition among older adults?: Results from the Cardiovascular Health of Seniors and Built Environment Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsdottir, O.G.; Arnarson, A.; Ramel, A.; Jonsson, P.V.; Thorsdottir, I. Dietary protein intake is associated with lean body mass in community-dwelling older adults. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.R.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Witard, O.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Tipton, K.D.; Phillips, S.M. Protein ingestion to stimulate myofibrillar protein synthesis requires greater relative protein intakes in healthy older versus younger men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Smith, R.; Aulet, M.; Bensen, B.; Lichtman, S.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N., Jr. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: Measurement by dual-photon absorptiometry. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmueller, S.E.; Corriveau, A.; Sharma, S. Differences in dietary quality and adequacy by smoking status among a Canadian Aboriginal population. Public Health 2012, 126, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetts, B.M.; Jackson, A.A. Interactions between people’s diet and their smoking habits: The dietary and nutritional survey of British adults. BMJ 1993, 307, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmueller, S.E.; Corriveau, A.; Sharma, S. Dietary quality and adequacy among Aboriginal alcohol consumers in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2012, 71, 17341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S. Relationship between alcohol intake and dietary pattern: Findings from NHANES III. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4055–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, R.; Asakura, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Suga, H.; Sasaki, S. Low intake of vegetables, high intake of confectionary, and unhealthy eating habits are associated with poor sleep quality among middle-aged female Japanese workers. J. Occup. Health 2014, 56, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato-Mito, N.; Shibata, S.; Sasaki, S.; Sato, K. Dietary intake is associated with human chronotype as assessed by both morningness-eveningness score and preferred midpoint of sleep in young Japanese women. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanovec, M.; Lakkakula, A.P.; Johnson, L.G.; Turri, G. Physical activity is associated with percent body fat and body composition but not body mass index in white and black college students. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2009, 2, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Minowa, M.; Uchiyama, M.; Okawa, M.; Kim, K.; Shibui, K.; Kamei, Y. Psychometric assessment of subjective sleep quality using the Japanese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J) in psychiatric disordered and control subjects. Psychiatry Res. 2000, 97, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, J.A.; Ostberg, O. A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms. Int. J. Chronobiol. 1976, 4, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, K.; Miyashita, A.; Inugami, M.; Fukuda, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Miyata, Y. The results of investigation by the Japanese version of Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire. Shinrigaku Kenkyu 1986, 57, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, N.; Katsumura, T.; Ueda, C.; Inoue, S.; Shimomitsu, T. Validity and reliability of Japanese version of International Physical Activity Questionnaire. J. Health Welf. Stat. 2002, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjostrom, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, M.; Muto, T.; Minakawa, T.; Shibata, T. The combined unhealthy behaviors of breakfast skipping and smoking are associated with the prevalence of diabetes mellitus. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 218, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Evers, S.; Manske, S.; Bercovitz, K.; Edward, H.G. Smoking, physical activity and breakfast consumption among secondary school students in a southwestern Ontario community. Can. J. Public Health 2003, 94, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Patte, K.A.; Leatherdale, S.T. A cross-sectional analysis examining the association between dieting behaviours and alcohol use among secondary school students in the COMPASS study. J. Public Health 2017, 39, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Martin, J.L.; Galan, I.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F. The association between alcohol consumption patterns and adherence to food consumption guidelines. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, Y.; Narisawa, H.; Ueda, F.; Saito, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Mitarai, M.; Suzuki, R.; Tamura, N.; Inoue, S.; Inoue, Y. Relationship between Self-Reported Dietary Nutrient Intake and Self-Reported Sleep Duration among Japanese Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H.; Shih, C.C.; Lee, I.H.; Hou, Y.W.; Chen, K.C.; Chen, K.T.; Yang, Y.K.; Yang, Y.C. A study on the sleep quality of incoming university students. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 197, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakade, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Kurotani, M.; Harada, T. Effects of meal habits and alcohol/cigarette consumption on morningness-eveningness preference and sleep habits by Japanese female students aged 18–29. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2009, 28, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, D.K.; Anthony, T.G.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Adams, S.H.; Lynch, C.J.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Davis, T.A. Defining meal requirements for protein to optimize metabolic roles of amino acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 1330S–1338S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasiakos, S.M.; Cao, J.J.; Margolis, L.M.; Sauter, E.R.; Whigham, L.D.; McClung, J.P.; Rood, J.C.; Carbone, J.W.; Combs, G.F., Jr.; Young, A.J. Effects of high-protein diets on fat-free mass and muscle protein synthesis following weight loss: A randomized controlled trial. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3837–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Takimoto, H. Current protein and amino acid intakes among Japanese people: Analysis of the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Agricultural Research Service. Energy intakes: Percentages of energy from protein, carbohydrate, fat, and alcohol, by gender and age, what we eat in America, NHANES 2009–2010. 2012. Available online: www.ars.usda.gov/ba/bhnrc/fsrg (accessed on 25 August 2018).
- Mamerow, M.M.; Mettler, J.A.; English, K.L.; Casperson, S.L.; Arentson-Lantz, E.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Layman, D.K.; Paddon-Jones, D. Dietary protein distribution positively influences 24-h muscle protein synthesis in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.Y.; Schutzler, S.; Schrader, A.M.; Spencer, H.J.; Azhar, G.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. Protein intake distribution pattern does not affect anabolic response, lean body mass, muscle strength or function over 8 weeks in older adults: A randomized-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollwein, J.; Diekmann, R.; Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Uter, W.; Sieber, C.C.; Volkert, D. Distribution but not amount of protein intake is associated with frailty: A cross-sectional investigation in the region of Nurnberg. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.W.; Murphy, K.T.; McKellar, S.R.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Henselmans, M.; Helms, E.; Aragon, A.A.; Devries, M.C.; Banfield, L.; Krieger, J.W.; et al. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in healthy adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Aragon, A.A.; Krieger, J.W. The effect of protein timing on muscle strength and hypertrophy: A meta-analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2013, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.Y.; Schutzler, S.; Schrader, A.; Spencer, H.; Kortebein, P.; Deutz, N.E.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. Quantity of dietary protein intake, but not pattern of intake, affects net protein balance primarily through differences in protein synthesis in older adults. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E21–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genaro Pde, S.; Pinheiro Mde, M.; Szejnfeld, V.L.; Martini, L.A. Dietary protein intake in elderly women: Association with muscle and bone mass. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.H.; Hector, A.J.; Phillips, S.M. Considerations for protein intake in managing weight loss in athletes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.L.; Matias, C.N.; Santos, D.A.; Morgado, J.P.; Monteiro, C.P.; Sousa, M.; Minderico, C.S.; Rocha, P.M.; St-Onge, M.P.; Sardinha, L.B.; et al. Characterization and Comparison of Nutritional Intake between Preparatory and Competitive Phase of Highly Trained Athletes. Medicina 2018, 54, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deldicque, L.; Francaux, M. Recommendations for Healthy Nutrition in Female Endurance Runners: An Update. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, N.; Sato, K.; Ogasawara, R.; Kurihara, T.; Hamaoka, T.; Fujita, S. Relationship between Dietary Protein or Essential Amino Acid Intake and Training-Induced Muscle Hypertrophy among Older Individuals. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2017, 63, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, S.; Patureau Mirand, P.; Brandolini, M.; Martin, J.F.; Boirie, Y. Daily protein intakes and eating patterns in young and elderly French. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemming, L.; Ni Mhurchu, C. Dietary under-reporting: What foods and which meals are typically under-reported? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| All (n = 266) | Men (n = 149) | Women (n = 117) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 21.4 ± 2.4 | 21.4 ± 2.3 | 21.4 ± 2.6 | 0.381 |
| Drinking habit | 79 (29.7) | 53 (35.6) | 26 (22.2) | 0.022 |
| Smoking habit | 8 (3.0) | 7 (4.7) | 1 (0.9) | 0.082 |
| Living condition (alone) | 163 (61.3) | 98 (65.8) | 65 (55.6) | 0.100 |
| BW (kg) | 59.7 ± 10.2 | 65.8 ± 8.7 | 52.0 ± 5.9 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.6 ± 2.5 | 22.4 ± 2.6 | 20.5 ± 1.8 | <0.001 |
| TotalFFM (kg) | 45.0 ± 9.9 | 52.5 ± 5.8 | 35.4 ± 3.7 | <0.001 |
| AppFFM (kg) | 20.5 ± 5.2 | 24.4 ± 3.2 | 15.5 ± 1.9 | <0.001 |
| TotalFFM% (%BW) | 74.9 ± 7.8 | 79.7 ± 6.2 | 68.9 ± 4.8 | <0.001 |
| AppFFM% (%BW) | 33.9 ± 4.3 | 36.9 ± 3.0 | 30.1 ± 2.3 | <0.001 |
| Body fat percentage (%) | 21.6 ± 8.2 | 16.6 ± 6.7 | 28.0 ± 5.1 | <0.001 |
| Sleep condition | ||||
| Waking time (h:min) | 7:39 ± 1:27 | 7:54 ± 1:28 | 7:20 ± 1:24 | 0.010 |
| Bedtime (h:min) | 0:39 ± 1:04 | 0:45 ± 1:06 | 0:32 ±1:01 | 0.143 |
| Sleep latency (min) | 25.5 ± 20.9 | 25.8 ± 20.4 | 25.1 ± 21.7 | 0.509 |
| Sleep duration (hour) | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.3 | 6.1 ± 1.3 | 0.055 |
| Sleep quality (%) | 75.6 ± 17.5 | 75.2 ± 17.8 | 76.3 ± 17.2 | 0.514 |
| PSQI (score) | 7.3 ± 2.8 | 7.0 ± 2.7 | 7.5 ± 2.9 | 0.153 |
| MEQ (score) | 53.5 ± 7.6 | 52.7 ± 7.5 | 54.5 ± 7.6 | 0.056 |
| IPAQ (MET-min/week) | 2721 ± 2438 | 3298 ± 2571 | 1987 ± 2044 | <0.001 |
| Meal time | ||||
| Breakfast time (h:min) | 8:45 ± 1:19 | 8:51 ± 1:23 | 8:38 ± 1:15 | 0.478 |
| Lunch time (h:min) | 12:51 ± 1:00 | 12:52 ± 1:07 | 12:50 ± 0:50 | 0.968 |
| Dinner time (h:min) | 20:21 ± 1:31 | 20:35 ± 1:35 | 20:03 ± 1:23 | 0.004 |
| All (n = 266) | Men (n = 149) | Women (n = 117) | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total dietary intake | ||||
| Energy (kcal/day) | 1933 ± 528 | 2177 ± 493 | 1623 ± 393 | <0.001 |
| Protein (g/day) | 70.2 ± 22.5 | 80.0 ± 21.6 | 57.8 ± 16.8 | <0.001 |
| Fat (g/day) | 66.0 ± 20.4 | 72.9 ± 21.2 | 57.2 ± 15.6 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate (g/day) | 255.5 ± 76.7 | 288.4 ± 75.0 | 213.8 ± 55.8 | <0.001 |
| Protein (g/kg/day) | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.043 |
| Fat (g/kg/day) | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.871 |
| Carbohydrate (g/kg/day) | 4.3 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 1.3 | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 0.121 |
| Breakfast | ||||
| Energy (kcal/meal) | 358.5 ± 218.5 | 380.1 ± 245.8 | 331.1 ± 175.0 | 0.118 |
| Protein (g/meal) | 12.1 ± 8.6 | 13.0 ± 9.6 | 11.0 ± 7.2 | 0.129 |
| Fat (g/meal) | 11.8 ± 8.6 | 12.3 ± 9.6 | 11.1 ± 7.1 | 0.585 |
| Carbohydrate (g/meal) | 50.7 ± 31.1 | 53.6 ± 34.8 | 46.9 ± 25.3 | 0.109 |
| Lunch | ||||
| Energy (kcal/meal) | 647.7 ± 225.8 | 727.5 ± 211.1 | 546.0 ± 202.4 | <0.001 |
| Protein (g/meal) | 23.0 ± 8.9 | 25.6 ± 8.8 | 19.8 ± 8.0 | <0.001 |
| Fat (g/meal) | 21.1 ± 9.3 | 23.1 ± 9.3 | 18.6 ± 8.6 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate (g/meal) | 88.0 ± 33.3 | 100.1 ± 32.4 | 72.7 ± 27.6 | <0.001 |
| Dinner | ||||
| Energy (kcal/meal) | 750.2 ± 305.8 | 898.6 ± 283.5 | 561.1 ± 216.3 | <0.001 |
| Protein (g/meal) | 30.6 ± 13.7 | 36.5 ± 13.1 | 23.1 ± 10.4 | <0.001 |
| Fat (g/meal) | 27.0 ± 13.1 | 31.9 ± 13.1 | 20.6 ± 10.0 | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrate (g/meal) | 90.7 ± 40.6 | 109.1 ± 39.4 | 67.2 ± 28.1 | <0.001 |
| Snack | ||||
| Energy (kcal/meal) | 177.0 ± 170.1 | 171.2 ± 180.6 | 184.5 ± 156.1 | 0.130 |
| Protein (g/meal) | 4.5 ± 5.7 | 4.9 ± 6.7 | 3.9 ± 4.0 | 0.450 |
| Fat (g/meal) | 6.1 ± 7.1 | 5.5 ± 7.5 | 6.9 ± 6.5 | 0.002 |
| Carbohydrate (g/meal) | 26.2 ± 25.5 | 25.5 ± 27.2 | 27.0 ± 23.3 | 0.144 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasuda, J.; Asako, M.; Arimitsu, T.; Fujita, S. Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030612
Yasuda J, Asako M, Arimitsu T, Fujita S. Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030612
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasuda, Jun, Mai Asako, Takuma Arimitsu, and Satoshi Fujita. 2019. "Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030612
APA StyleYasuda, J., Asako, M., Arimitsu, T., & Fujita, S. (2019). Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 11(3), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030612





