Diabetic Retinopathy as a Risk Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Case–Control Study in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
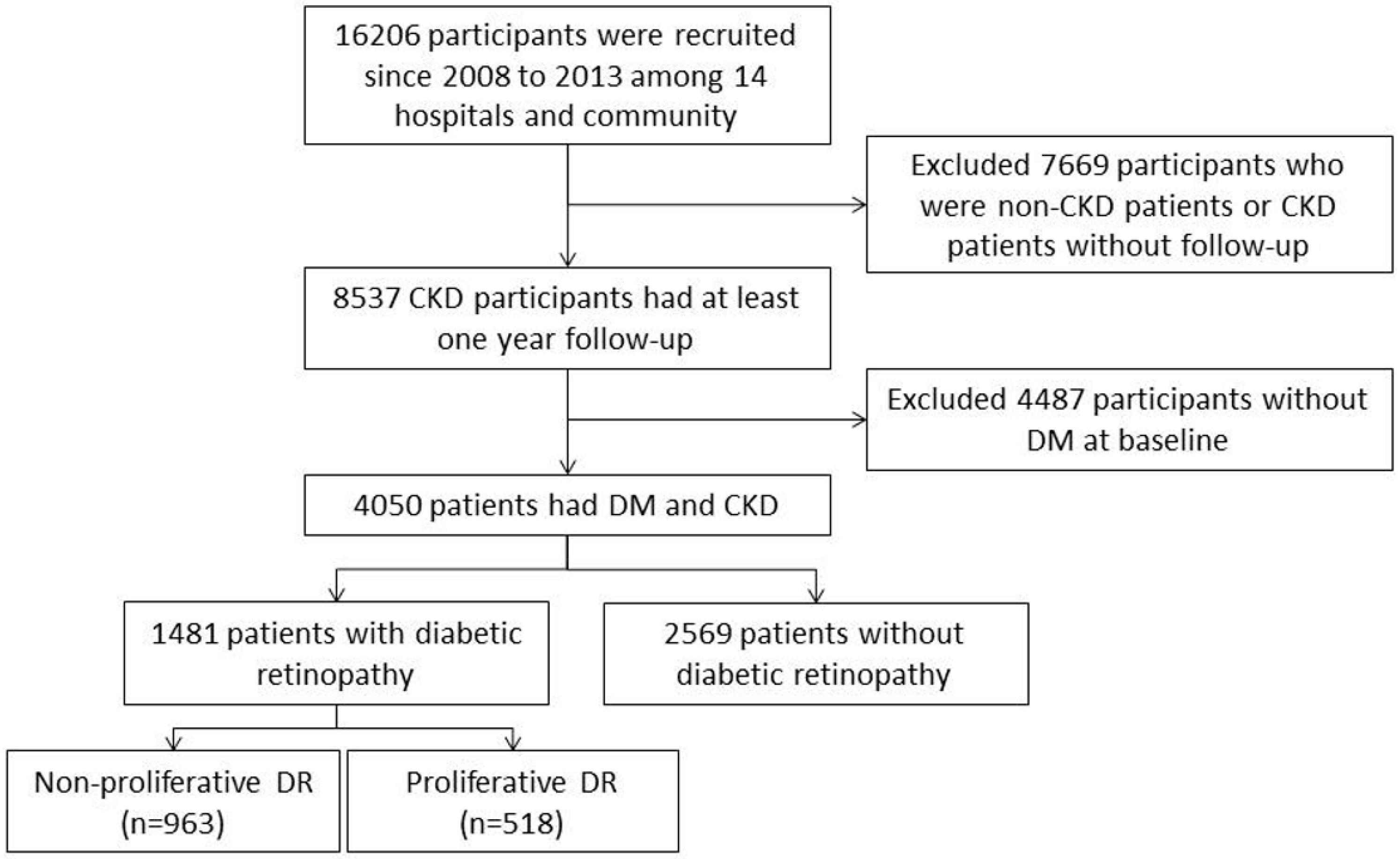
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Measurements and Variable Definitions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Analysis of CKD Progression among the DR and Non-DR Groups
3.3. Association between DR and CKD Progression in Different CKD Stages
3.4. Assoiciation between DR and CKD Progression According to Different DR Severity Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.W.; Tsai, S.S.; Tiao, M.M.; Yang, C.Y. Epidemiological features of CKD in Taiwan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, R.N.; Collins, A.J. The USRDS: What you need to know about what it can and can’t tell us about ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.L.; Lin, C.; Kao, S.; Wu, C.C.; Lu, K.C.; Lai, C.H.; Yang, H.Y.; Chiu, Y.L.; Chen, J.S.; Sung, F.C.; et al. Risk factors and their interaction on chronic kidney disease: A multi-centre case control study in Taiwan. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebovitz, H.E. Glycaemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes: New observations and clinical significance. J. Indian Med. Assoc 2008, 106, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, N.; Sasson, S.; Feener, E.P.; Boukobza-Vardi, N.; Higashi, S.; Moller, D.E.; Davidheiser, S.; Przybylski, R.J.; King, G.L. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes 1993, 42, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, M.; Kern, T.S.; Lorenzi, M. Accelerated death of retinal microvascular cells in human and experimental diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin Investig. 1996, 97, 2883–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, H.P.; Federoff, H.J.; Brownlee, M. Nerve growth factor prevents both neuroretinal programmed cell death and capillary pathology in experimental diabetes. Mol. Med. 1995, 1, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dronavalli, S.; Duka, I.; Bakris, G.L. The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parving, H.H.; Gall, M.A.; Skott, P.; Jorgensen, H.E.; Lokkegaard, H.; Jorgensen, F.; Nielsen, B.; Larsen, S. Prevalence and causes of albuminuria in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.M.; Lewis, E.J.; Leonard-Martin, T.; Lewis, J.B.; Batlle, D. Renal pathology patterns in type II diabetes mellitus: Relationship with retinopathy. The Collaborative Study Group. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998, 13, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, M.; Bolignano, D.; Tesar, V.; Pisano, A.; Biesen, W.V.; Tripepi, G.; D’Arrigo, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Group E-EIW. Renal biopsy in patients with diabetes: A pooled meta-analysis of 48 studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Guo, R.; Yin, Q.; Yang, L.; Yue, R.; Su, B.; Huang, S.; et al. Renal pathological implications in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with renal involvement. J. Diabetes Complications 2017, 31, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.W.; Kim, S.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.W.; Kim, S.; Jin, D.C.; Chin, H.J. Clinical implications of pathologic diagnosis and classification for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Poncelas, A.; Mundet-Tuduri, X.; Miravet-Jimenez, S.; Casellas, A.; Barrot-De la Puente, J.F.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Coll-de Tuero, G. Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications (DCCT) Research Group. Effect of intensive therapy on the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Kidney Int. 1995, 47, 1703–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998, 352, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, E.R.; Ronn, B.; Storm, B.; Foght, H.; Deckert, T. The natural course of microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes: A 10-year prospective study. Diabet. Med. 1995, 12, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehey, D.J.; Kramer, H.J.; Daoud, T.M.; Chatha, M.P.; Isreb, M.A. Progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes—Beyond blood pressure control: An observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2005, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaviat, M.R.; Afkhami, M.; Shoja, M.R. Retinopathy and microalbuminuria in type II diabetic patients. BMC Ophthalmol. 2004, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.S.; Wilson, D.B.; Craven, T.E.; Stafford, J.; Fried, L.F.; Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Burke, G.L.; Hansen, K.J. Associations between retinal microvascular abnormalities and declining renal function in the elderly population: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Coresh, J.; Klein, R.; Muntner, P.; Couper, D.J.; Sharrett, A.R.; Klein, B.E.; Heiss, G.; Hubbard, L.D.; Duncan, B.B. Retinal microvascular abnormalities and renal dysfunction: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, R.; Vedovato, M.; Mazzon, C.; Coracina, A.; Iori, E.; Tiengo, A.; Del Prato, S. Concomitance of diabetic retinopathy and proteinuria accelerates the rate of decline of kidney function in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Sobrin, L.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, M.H.; Seong, M.; Cho, H. The relationship between diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in a population-based study in Korea (KNHANES V-2, 3). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6547–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Ying, G.S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Z. Diabetic retinopathy and renal function in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Kidney, F. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, S1–S266. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group, M. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penno, G.; Solini, A.; Zoppini, G.; Orsi, E.; Zerbini, G.; Trevisan, R.; Gruden, G.; Cavalot, F.; Laviola, L.; Morano, S.; et al. Rate and determinants of association between advanced retinopathy and chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Renal Insufficiency and Cardiovascular Events (RIACE) Italian multicenter study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, N.A.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Skali, H.; McGill, J.B.; Rossert, J.; Olson, K.A.; Weinrauch, L.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Rossing, P.; et al. Retinopathy and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and anemia. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2014, 2, e000011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parving, H.H.; Mogensen, C.E.; Thomas, M.C.; Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E. Poor prognosis in proteinuric type 2 diabetic patients with retinopathy: Insights from the RENAAL study. QJM 2005, 98, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Alexander, J.; Maguire, M.; Whittock, R.; Parker, C.; McWilliams, K.; Lo, J.C.; Townsend, R.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Lash, J.P.; et al. Prevalence of ocular fundus pathology in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Zhu, L.; Pan, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Ocular fundus pathology and chronic kidney disease in a Chinese population. BMC Nephrol. 2011, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.W.; Xie, J.; Kawasaki, R.; Kramer, H.; Shlipak, M.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.; Cotch, M.F.; Wong, T.Y. Retinal arteriolar narrowing and subsequent development of CKD Stage 3: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.; Moss, S.E.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Brazy, P.C. The 10-year incidence of renal insufficiency in people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorhofer, L.; Lammert, A.; Krane, V.; Gorski, M.; Banas, B.; Wanner, C.; Kramer, B.K.; Heid, I.M.; Boger, C.A.; Group, D.S. Study design of DIACORE (DIAbetes COhoRtE)—A cohort study of patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lash, J.P.; Go, A.S.; Appel, L.J.; He, J.; Ojo, A.; Rahman, M.; Townsend, R.R.; Xie, D.; Cifelli, D.; Cohan, J.; et al. Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study: Baseline characteristics and associations with kidney function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, H.I.; Appel, L.J.; Chertow, G.M.; Cifelli, D.; Cizman, B.; Daugirdas, J.; Fink, J.C.; Franklin-Becker, E.D.; Go, A.S.; Hamm, L.L.; et al. The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study: Design and Methods. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, S148–S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coresh, J.; Selvin, E.; Stevens, L.A.; Manzi, J.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Levey, A.S. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2007, 298, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Xia, X.; Wu, X.F.; Yu, X.Q.; Huang, F.X. Diabetic retinopathy in predicting diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease: A meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Islam, F.M.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.; Cotch, M.F.; Castro, C.; Sharrett, A.R.; Shahar, E. Retinal vascular caliber, cardiovascular risk factors, and inflammation: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.E.; Knudtson, M.D.; Tsai, M.Y.; Klein, R. The relation of markers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction to the prevalence and progression of diabetic retinopathy: Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Riva, C.E.; Brucker, A.J.; Sinclair, S.H.; Petrig, B.L. Altered retinal vascular response to 100% oxygen breathing in diabetes mellitus. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, J.E.; Riva, C.E.; Sinclair, S.H.; Brucker, A.J.; Petrig, B.L. Laser Doppler velocimetry study of retinal circulation in diabetes mellitus. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1986, 104, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group; Lachin, J.M.; Genuth, S.; Cleary, P.; Davis, M.D.; Nathan, D.M. Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arar, N.H.; Freedman, B.I.; Adler, S.G.; Iyengar, S.K.; Chew, E.Y.; Davis, M.D.; Satko, S.G.; Bowden, D.W.; Duggirala, R.; Elston, R.C.; et al. Heritability of the severity of diabetic retinopathy: The FIND-Eye study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.Y.; Majeed, A.; Kuo, K.N. An overview of the healthcare system in Taiwan. Lond. J. Prim. Care (Abingdon) 2010, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.K.; Alrukhaimi, M.; Ashuntantang, G.E.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Benghanem Gharbi, M.; Braam, B.; Feehally, J.; Harris, D.C.; Jha, V.; Jindal, K.; et al. Global overview of health systems oversight and financing for kidney care. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Diabetic Retinopathy n = 1481 (%) | Without Diabetic Retinopathy n = 2569 (%) | p-Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), y | 64.95 ± 11.22 | 66.57 ± 12.11 | <0.01 | ||
| Male Sex | 819 | (55.30) | 1477 | (57.49) | 0.18 |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 25.90 ± 4.09 | 26.02 ± 4.30 | 0.41 | ||
| Waist, mean (SD), cm | 90.03 ± 10.80 | 90.09 ± 11.65 | 0.88 | ||
| Exercise | 487 | (34.71) | 825 | (34.01) | 0.66 |
| Smoking | 385 | (26.00) | 704 | (27.40) | 0.33 |
| Alcohol | 125 | (8.44) | 268 | (10.43) | 0.04 |
| Betel Nut | 102 | (6.89) | 166 | (6.46) | 0.60 |
| CKD progression | 321 | (21.67) | 350 | (13.62) | <0.01 |
| Hypertension | 1408 | (95.07) | 2251 | (87.62) | <0.01 |
| Blood pressure | <0.01 | ||||
| Less than 130/85 | 445 | (44.41) | 828 | (50.36) | |
| Over 130/85 | 557 | (55.59) | 816 | (49.64) | |
| HbA1C, mean (SD), % | 7.85 ± 4.97 | 7.29 ± 4.02 | <0.01 | ||
| HbA1C (<7%) | 460 | (41.18) | 840 | (56.04) | <0.01 |
| HbA1C (≥7%) | 657 | (58.82) | 659 | (43.96) | |
| Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR), mean (SD), g/dL | 1.94 ± 2.96 | 0.91 ± 2.11 | <0.01 | ||
| UPCR (<150) | 241 | (21.16) | 871 | (43.21) | <0.01 |
| UPCR (150–1000) | 406 | (35.65) | 720 | (35.71) | |
| UPCR (1000–3500) | 276 | (24.23) | 284 | (14.09) | |
| UPCR (>3500) | 216 | (18.96) | 141 | (6.99) | |
| Baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), mean (SD), mL/min/1.73 m2 | 39.17 ± 30.36 | 54.38 ± 33.67 | <0.01 | ||
| Cholesterol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 183.41 ± 50.19 | 183.15 ± 43.57 | 0.88 | ||
| Triglyceride, mean (SD), mg/dL | 159.25 ± 104.13 | 159.73 ± 115.46 | 0.90 | ||
| Uric Acid, mean (SD), mg/dL | 8.56 ± 41.07 | 10.09 ± 74.78 | 0.44 | ||
| Glucose (AC), mean (SD), mg/dL | 142.85 ± 64.63 | 129.09 ± 46.62 | <0.01 | ||
| Na, mean (SD), mmol/L | 139.79 ± 40.07 | 139.16 ± 5.04 | 0.64 | ||
| K, mean (SD), mmol/L | 4.66 ± 4.26 | 4.55 ± 4.04 | 0.54 | ||
| Ca, mean (SD), mmol/L | 8.87 ± 0.92 | 9.10 ± 2.30 | <0.01 | ||
| P, mean (SD), mg/dL | 4.30 ± 1.11 | 4.11 ± 4.59 | 0.17 | ||
| Hb, mean (SD), g/dL | 11.22 ± 2.43 | 12.39 ± 3.85 | <0.01 | ||
| Hct, mean (SD), % | 32.84 ± 6.43 | 36.49 ± 6.48 | <0.01 | ||
| Albumin, mean (SD), g/dL | 3.88 ± 0.95 | 4.16 ± 1.74 | <0.01 | ||
| Variables | Without Diabetic Retinopathy | Diabetic Retinopathy |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Univariate Model | 1.00 | 1.75 (1.48–2.07) * |
| Multivariate Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.28 (1.07–1.52) * |
| Multivariate Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.32 (1.06–1.65) * |
| Multivariate Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.37 (1.08–1.73) * |
| Variables | Without Diabetic Retinopathy | With Diabetic Retinopathy |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| CKD stage | ||
| Stage 1–3a | ||
| Univariate Model | 1.00 | 0.80 (0.54–1.19) |
| Multivariate Model 1 | 1.00 | 0.80 (0.54–1.19) |
| Multivariate Model 2 | 1.00 | 0.76 (0.47–1.25) |
| Multivariate Model 3 | 1.00 | 0.74 (0.44–1.24) |
| Stage 3b–5 | ||
| Univariate Model | 1.00 | 1.66 (1.36–2.02) * |
| Multivariate Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.32 (1.06–1.63) * |
| Multivariate Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.40 (1.07–1.83) * |
| Multivariate Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.47 (1.10–1.98) * |
| Severity of DR | ||
| Non-proliferative DR | ||
| Univariate Model | 1.00 | 1.57 (1.29–1.91) * |
| Multivariate Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.25 (1.02–1.53) * |
| Multivariate Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.26 (0.98–1.62) |
| Multivariate Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.25 (0.96–1.65) |
| Proliferative DR | ||
| Univariate Model | 1.00 | 2.18 (1.71–2.78) * |
| Multivariate Model 1 | 1.00 | 1.46 (1.13–1.88) * |
| Multivariate Model 2 | 1.00 | 1.64 (1.21–2.22) * |
| Multivariate Model 3 | 1.00 | 1.82 (1.31–2.54) * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-T.; Zheng, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-T.; Liang, C.-M.; Chang, T.-J.; Zheng, J.-Q.; Tai, M.-C.; Lin, Y.-F. Diabetic Retinopathy as a Risk Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Case–Control Study in Taiwan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030509
Lin H-T, Zheng C-M, Wu Y-C, Chang Y-H, Chen J-T, Liang C-M, Chang T-J, Zheng J-Q, Tai M-C, Lin Y-F. Diabetic Retinopathy as a Risk Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Case–Control Study in Taiwan. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hsin-Ting, Cai-Mei Zheng, Yun-Chun Wu, Yun-Hsiang Chang, Jiann-Torng Chen, Chang-Min Liang, Tian-Jong Chang, Jing-Quan Zheng, Ming-Cheng Tai, and Yuh-Feng Lin. 2019. "Diabetic Retinopathy as a Risk Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Case–Control Study in Taiwan" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030509
APA StyleLin, H.-T., Zheng, C.-M., Wu, Y.-C., Chang, Y.-H., Chen, J.-T., Liang, C.-M., Chang, T.-J., Zheng, J.-Q., Tai, M.-C., & Lin, Y.-F. (2019). Diabetic Retinopathy as a Risk Factor for Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Case–Control Study in Taiwan. Nutrients, 11(3), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030509





