Curcumae Radix Extract Decreases Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis via Suppression of C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Curcumae Radix Extract
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of Marker Compounds in Curcumae Radix Extract
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Animal Studies
2.5. Animal Treatment and Excision of Organs
2.6. Histological Analysis of Tumor and Lung Tissue
2.7. RNA Analysis and Reverse Transcription-PCR
2.8. Protein Analysis and Western Blotting
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Scratch Wound Healing Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
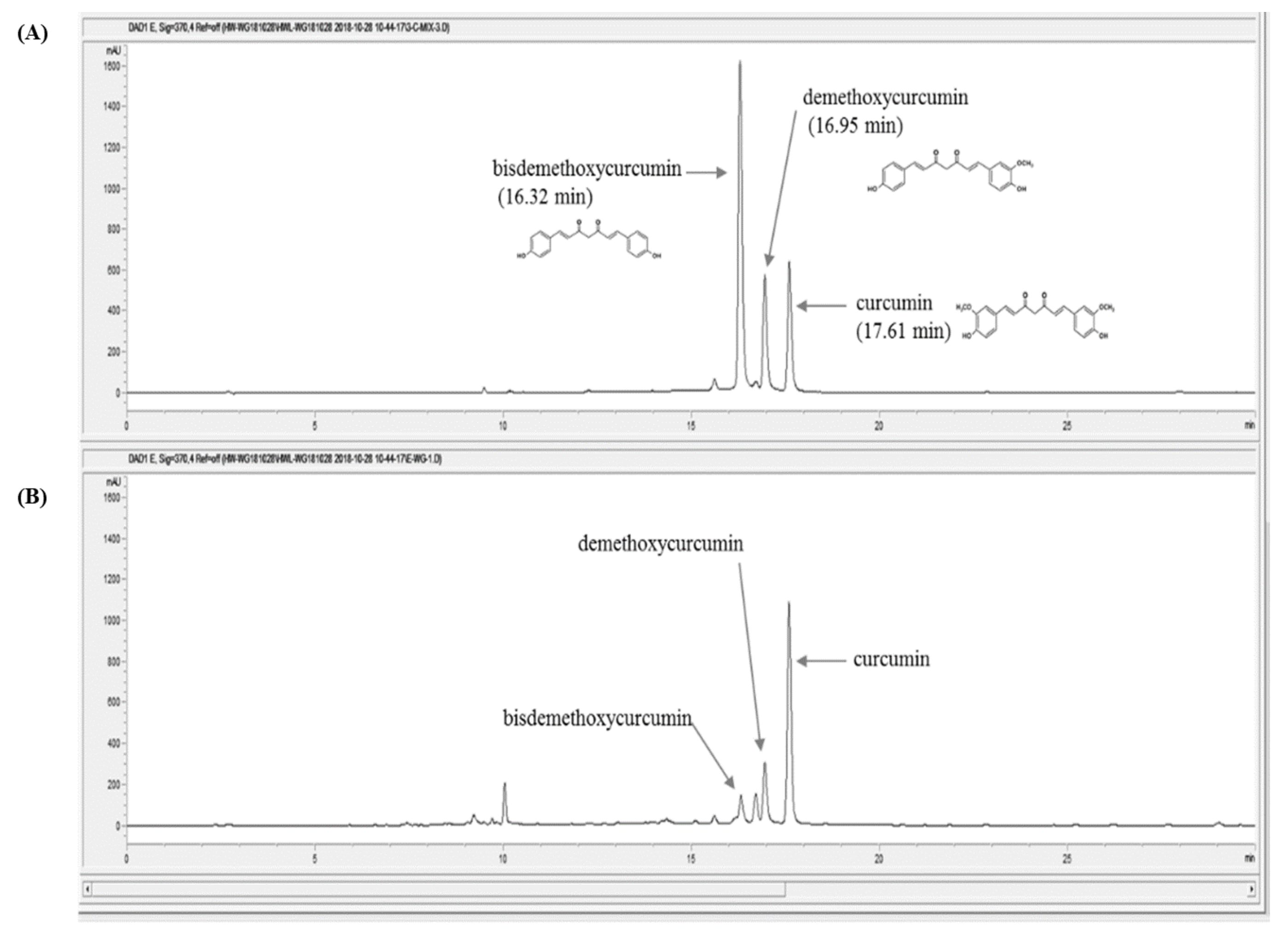
3.1. Quantitative Analysis of Marker Compounds in Curcumae Radix Extract
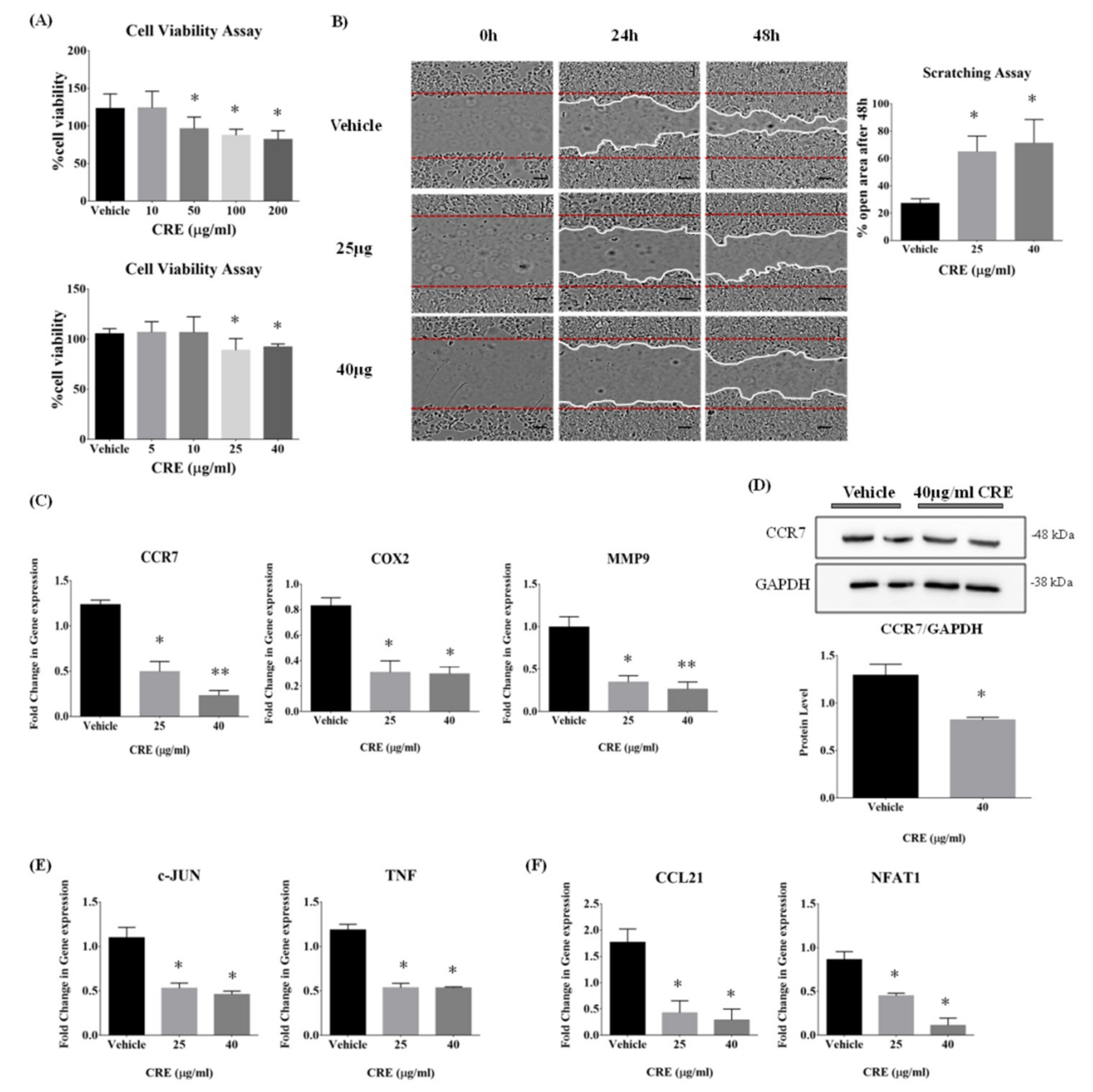
3.2. Curcumae Radix Extract Inhibits Cell Growth, Cell Motility, and Cell Migration of MCF7 Cells
3.3. Curcumae Radix Extract Inhibits CCR7, MMP9, and COX2 Gene Expression in MCF7 Cells
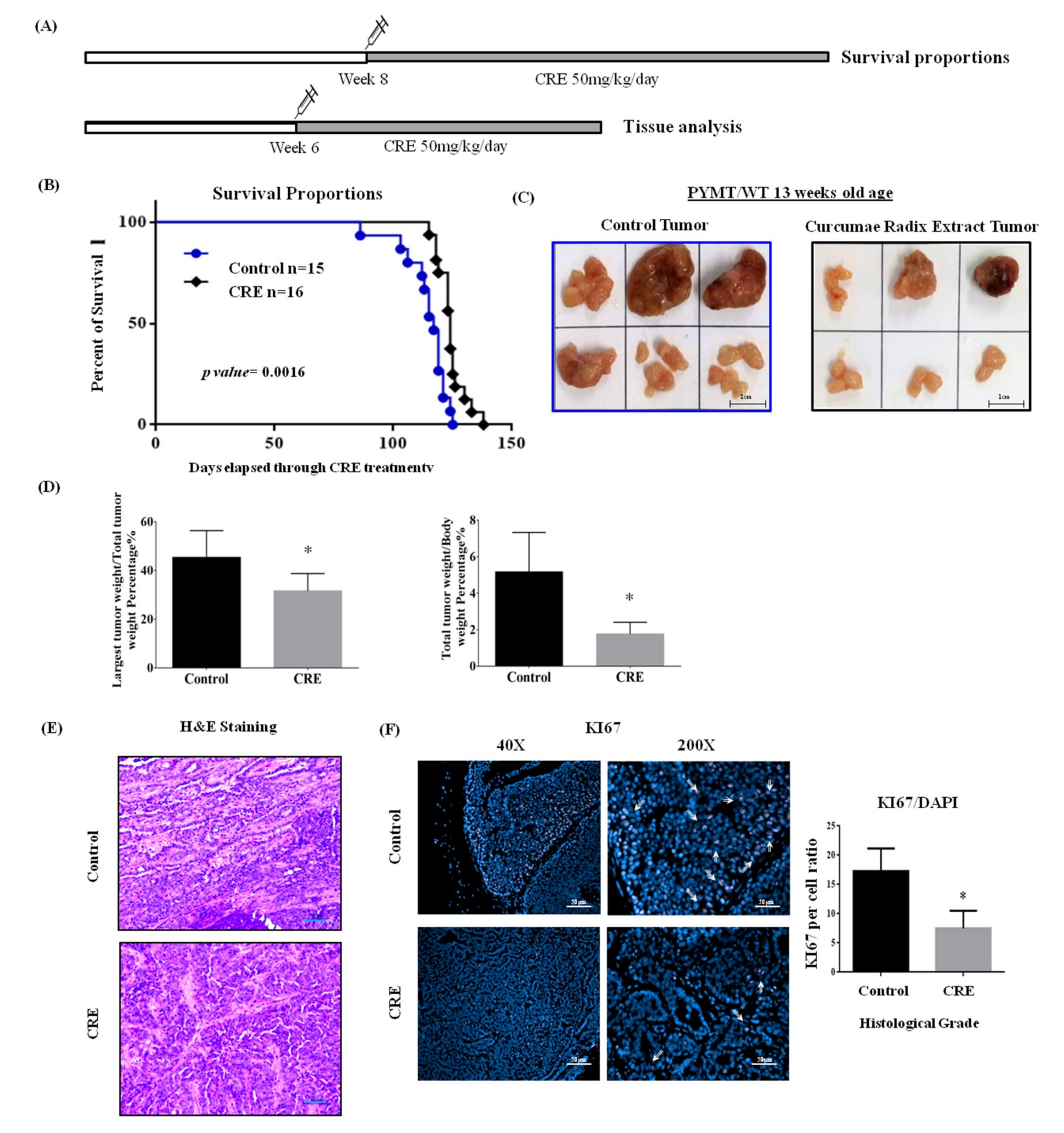
3.4. Ethanol Extract of Curcumae Radix Significantly Enhances the Survival of MMTV-PyMT Female Transgenic Mice
3.5. Curcumae Radix Extract Treatment Decreases Tumor Burden and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Primary Tumor in PyMT Transgenic Mice
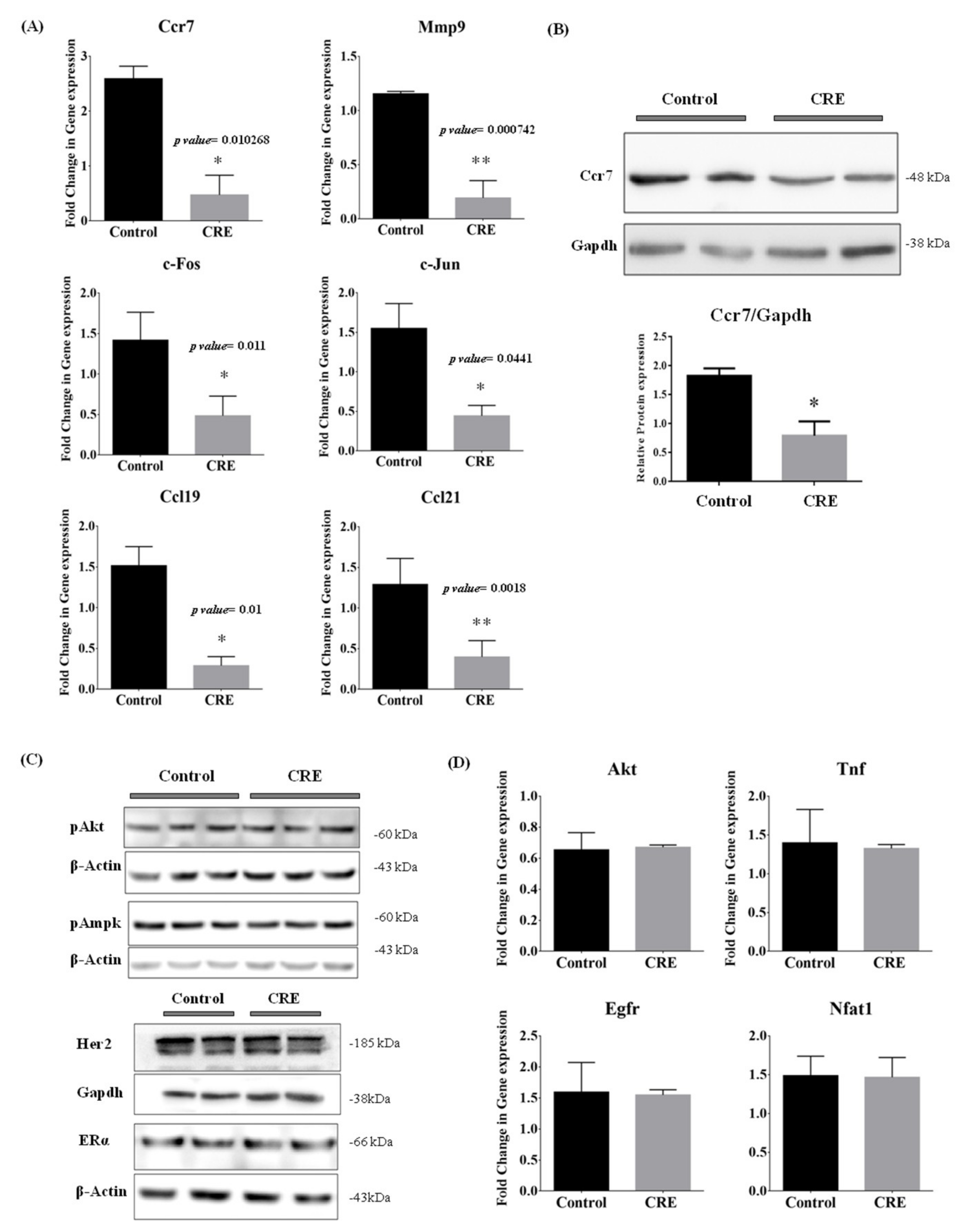
3.6. Curcumae Radix Extract Treatment Interferes with Ccr7, Mmp9, c-Jun and c-Fos Expression Levels in Primary Tumor in PyMT Transgenic Mice
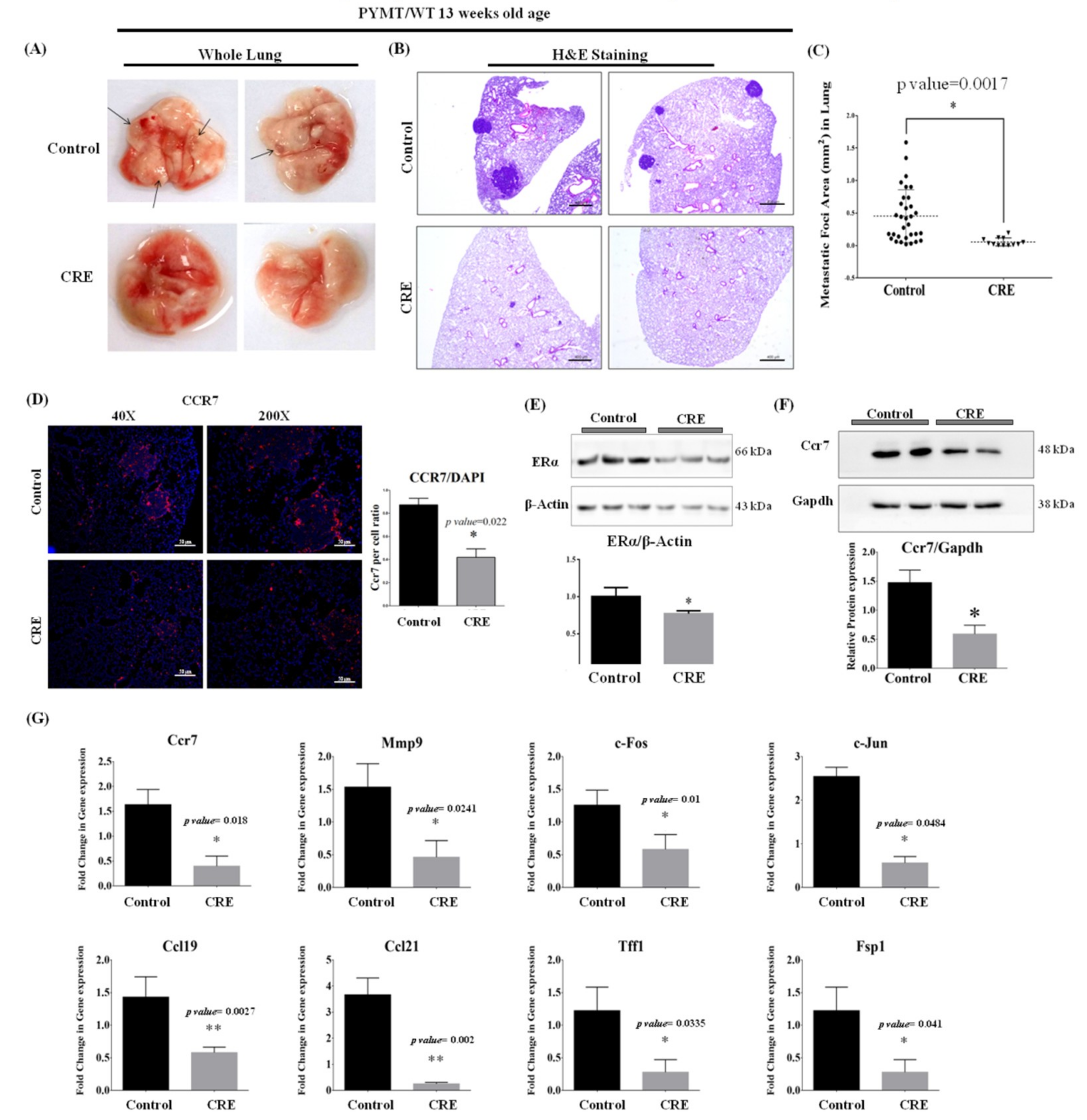
3.7. Curcumae Radix Extract Inhibits Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis in PyMT Transgenic Mice
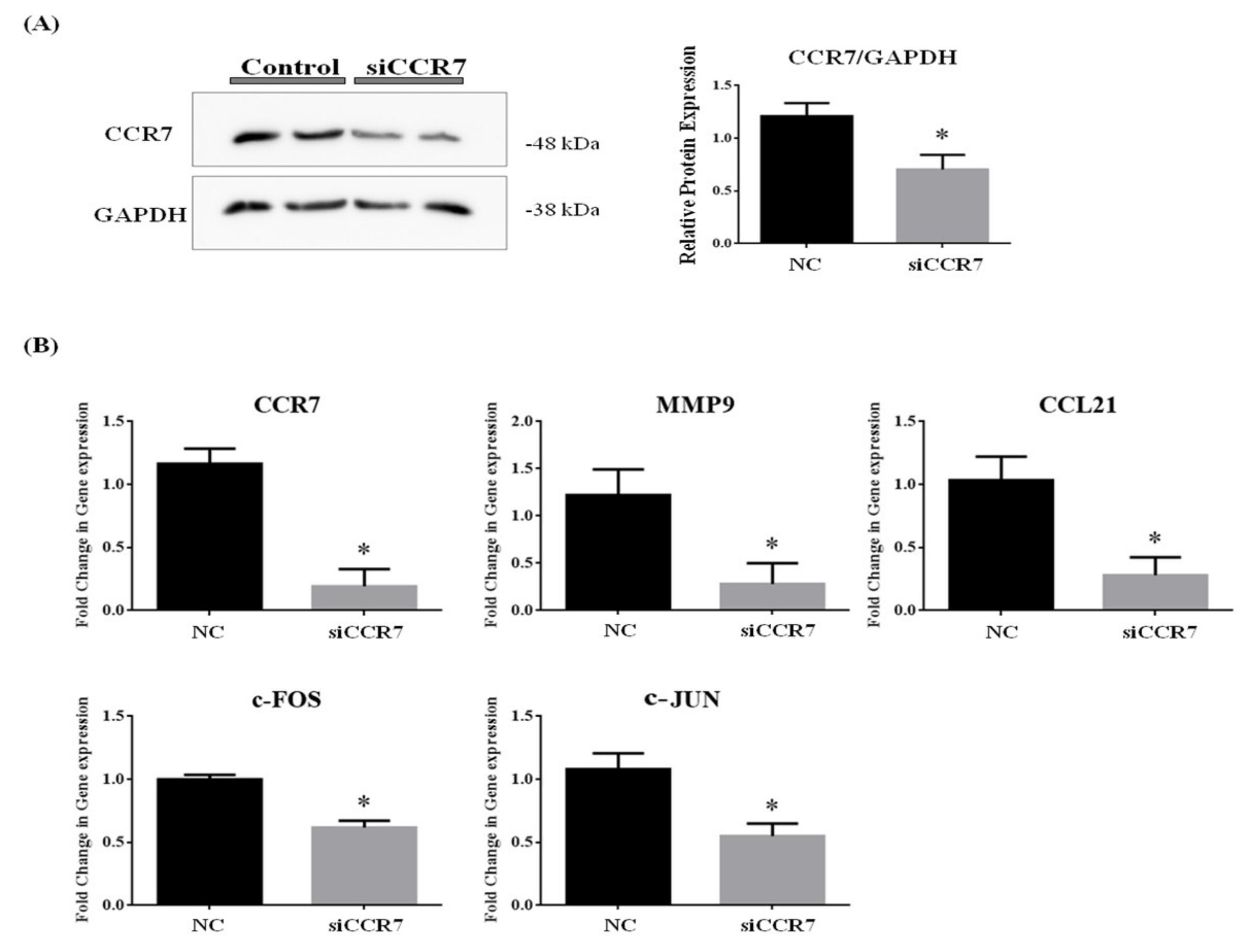
3.8. CCR7 Regulates the Gene Expression of CCL21, MMP9 and AP1 Complex (c-FOS and c-JUN)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.-T.; Lan, Q.; Lorusso, G.; Duffey, N.; Rüegg, C. The matricellular protein CYR61 promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by facilitating tumor cell extravasation and suppressing anoikis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 9200–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minn, A.J.; Gupta, G.P.; Siegel, P.M.; Bos, P.D.; Shu, W.; Giri, D.D.; Viale, A.; Olshen, A.B.; Gerald, W.L.; Massagué, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 2005, 436, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecorino, L. Molecular Biology of Cancer: Mechanisms, Targets, and Therapeutics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 197–199. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Two Traditional Chinese Medicines Curcumae Radix and Curcumae Rhizoma: An Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology Review. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 4973128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.-R.; Liu, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chou, S.-H.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Hwang, J.-J.; Chong, I.-W. Curcumin Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Metastasis through the Adiponectin/NF-κb/MMPs Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-K.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y. Turmeric (Curcumin). In Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Spices; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009; pp. 403–424. ISBN 978-981-283-790-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Hassandarvish, P.; Tajik, H.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 186864. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, C.; Rodriguez, S.; Ramachandran, R.; Nair, P.K.R.; Fonseca, H.; Khatib, Z.; Escalon, E.; Melnick, S.J. Expression Profiles of Apoptotic Genes Induced by Curcumin in Human Breast Cancer and Mammary Epithelial Cell Lines. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3293–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.P.; Salamone, E.; Goldin, B. Curcumin and Genistein, Plant Natural Products, Show Synergistic Inhibitory Effects on the Growth of Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells Induced by Estrogenic Pesticides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 233, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, K.; Aleck, K.; Dwyer, B.; Lloyd, V.; Quigley, M.; Sitto, N.; Siebert, A.E.; Dinda, S. The effects of turmeric (curcumin) on tumor suppressor protein (p53) and estrogen receptor (ERα) in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer 2017, 9, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yue, G.G.-L.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Fung, K.-P.; Lau, C.B.-S. Turmeric extract, with absorbable curcumin, has potent anti-metastatic effect in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2018, 46, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, F.-Q.; Li, S.-P.; Hu, G.; Lee, S.-M.-Y.; Wang, Y.-T. Essential oil of Curcuma wenyujin induces apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 4309–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.-B.; Ky, N.; Ng, H.-M.; Hamza, M.S.; Zhao, Y. Curcuma wenyujin Extract Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Human Cervical Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Cui, R.; Lin, J.; Ding, X. Curcumin in Treating Breast Cancer: A Review. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, C.; Fonseca, H.B.; Jhabvala, P.; Escalon, E.A.; Melnick, S.J. Curcumin inhibits telomerase activity through human telomerase reverse transcritpase in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Cancer Lett. 2002, 184, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodkeeree, S.; Ampasavate, C.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Limtrakul, P. Demethoxycurcumin suppresses migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 627, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei Koohpar, Z.; Entezari, M.; Movafagh, A.; Hashemi, M. Anticancer Activity of Curcumin on Human Breast Adenocarcinoma: Role of Mcl-1 Gene. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, e2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.-M.; Shen, Z.-Z.; Liu, C.-H.; Sartippour, M.R.; Go, V.L.; Heber, D.; Nguyen, M. Curcumin exerts multiple suppressive effects on human breast carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 98, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Chen, O.; Luan, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhao, J.-J.; Liu, L.; Jia, H.-Y. Curcumin inhibits MCF-7 cells by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5581–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S.; Takada, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Newman, R.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Price, J.E. Curcumin Suppresses the Paclitaxel-Induced Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells and Inhibits Lung Metastasis of Human Breast Cancer in Nude Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7490 LP-7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, G.S.; Mohanty, S.; Hossain, D.M.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Banerjee, S.; Chakraborty, J.; Saha, S.; Ray, P.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Mandal, D.; et al. Curcumin enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy by tailoring p65NFκB-p300 cross-talk in favor of p53-p300 in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42232–42247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.-J. Diterpenoid C of Radix Curcumae: An inhibitor of proliferation and inducer of apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma cells acting via inhibiting MAPK signaling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Zeng, L.; Zeng, Y. The Effects of Radix Curcumae Extract on Expressions of VEGF, COX-2 and PCNA in Gastric Mucosa of Rats Fed with MNNG. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L. Extract of Radix Curcumae Prevents Gastric Cancer in Rats. Digestion 2008, 77, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Muller, W.J. Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: A transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, L.; Kuang, S.-Q.; Tien, J.C.-Y.; O’Malley, B.W.; Xu, J. Disruption of the SRC-1 gene in mice suppresses breast cancer metastasis without affecting primary tumor formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.M.; Medina, F.; Badano, I.; Hazan, R.B.; Hutchinson, J.; Muller, W.J.; Chopra, N.G.; Scherer, P.E.; Pestell, R.G.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 Gene Disruption Promotes Mammary Tumorigenesis and Dramatically Enhances Lung Metastasis in Vivo: Role of CAV-1 in Cell Invasiveness and Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP-2/9) Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51630–51646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.; Lee, E.; Liu, Y.; Lee, D.; Ideker, T. Network-based classification of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Gadakh, S.; Gopal, P.; George, B.; Advani, J.; Soman, S.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Girijadevi, R. Differential ligand-signaling network of CCL19/CCL21-CCR7 system. Database 2015, 2015, bav106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, G.K.; Toker, A. NFAT Induces Breast Cancer Cell Invasion by Promoting the Induction of Cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12210–12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Anver, M.R.; Gusterson, B.A.; Hennighausen, L.; Jensen, R.A.; Merino, M.J.; Rehm, S.; Russo, J.; Tavassoli, F.A.; Wakefield, L.M.; et al. The mammary pathology of genetically engineered mice: The consensus report and recommendations from the Annapolis meeting. Oncogene 2000, 19, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juríková, M.; Danihel, Ľ.; Polák, Š.; Varga, I. Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.K.; Smith, L.M.; Gebhardt, D.K.; Birrer, M.J.; Brown, P.H. Activation and inhibition of the AP-1 complex in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 1996, 15, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.-I.; Eguchi, H.; Tanimoto, K.; Yoshida, T.; Omoto, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yoshida, N.; Yamaguchi, Y. The Expression and Function of Estrogen Receptor Alpha and Beta in Human Breast Cancer and Its Clinical Application. Endocr. -Relat. Cancer 2003, 10, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Liao, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Q.; Liang, H.; Ai, B.; Fu, S.; Zhou, S. Estrogen promotes tumor metastasis via estrogen receptor beta-mediated regulation of matrix-metalloproteinase-2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56443–56459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, F.; Qu, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. S100A4 in cancer progression and metastasis: A systematic review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73219–73239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnagdy, M.H.; Farouk, O.; Seleem, A.K.; Nada, H.A. TFF1 and TFF3 mRNAs Are Higher in Blood from Breast Cancer Patients with Metastatic Disease than Those without. J. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 4793498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlings, S.J.; Kalman, D.S. Curcumin: A Review of Its’ Effects on Human Health. Foods 2017, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Yuan, W.; Li, S.; Gupta, S.C. Curcumin-free turmeric exhibits anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities: Identification of novel components of turmeric. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, R.C.; Chen, G.J.; Solyom, A.M.; Jolad, S.D.; Timmermann, B.N. The effect of turmeric extracts on inflammatory mediator production. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porschen, R.; Classen, S.; Piontek, M.; Borchard, F. Vascularization of Carcinomas of the Esophagus and Its Correlation with Tumor Proliferation. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riol-Blanco, L.; Sánchez-Sánchez, N.; Torres, A.; Tejedor, A.; Narumiya, S.; Corbí, A.L.; Sánchez-Mateos, P.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J.L. The Chemokine Receptor CCR7 Activates in Dendritic Cells Two Signaling Modules That Independently Regulate Chemotaxis and Migratory Speed. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4070–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M.-F.; Georgoudaki, A.-M.; Lambut, L.; Johansson, J.; Tabor, V.; Hagikura, K.; Jin, Y.; Jansson, M.; Alexander, J.S.; Nelson, C.M.; et al. TGF-β1-induced EMT promotes targeted migration of breast cancer cells through the lymphatic system by the activation of CCR7/CCL21-mediated chemotaxis. Oncogene 2015, 35, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legler, D.F.; Uetz-von Allmen, E.; Hauser, M.A. CCR7: Roles in cancer cell dissemination, migration and metastasis formation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 54, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabioglu, N.; Yazici, M.S.; Arun, B.; Broglio, K.R.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Price, J.E.; Sahin, A. CCR7 and CXCR4 as Novel Biomarkers Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in T1 Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5686–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Song, L.; Wang, Z. CCR7: A metastasis and prognosis indicator of postoperative patients with esophageal carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013, 60, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Feng, D.; Jiang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. CCL21/CCR7 interaction promotes cellular migration and invasion via modulation of the MEK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway and correlates with lymphatic metastatic spread and poor prognosis in urinary bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mburu, Y.K.; Egloff, A.M.; Walker, W.H.; Wang, L.; Seethala, R.R.; van Waes, C.; Ferris, R.L. Chemokine Receptor 7 (CCR7) Gene Expression Is Regulated by NF-κB and Activator Protein 1 (AP1) in Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Head and Neck (SCCHN). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3581–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; He, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; She, F.; Chen, Y. CCR7 mediates the TNF-α-induced lymphatic metastasis of gallbladder cancer through the “ERK1/2-AP-1” and “JNK-AP-1” pathways. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Muñoz, J.; José Terol, M.; García-Marco, J.A.; García-Pardo, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is up-regulated by CCL21/CCR7 interaction via extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 signaling and is involved in CCL21-driven B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell invasion and migration. Blood 2008, 111, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, N.; Yamada, A.; Nitta, T.; Arakaki, R.; Lipp, M.; Takahama, Y.; Hayashi, Y. CCR7 with S1P1 Signaling through AP-1 for Migration of Foxp3+ Regulatory T-Cells Controls Autoimmune Exocrinopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCR7 | TGA GGT CAC GGA CGA TTA CAT | GTA GGC CCA CGA AAC AAA TGA T | Human |
| c-JUN | TCC AAG TGC CGA AAA AGG AAG | CGA GTT CTG AGC TTT CAA GGT | Human |
| c-FOS | CCG GGG ATA GCC TCT CTT ACT | CCA GGT CCG TGC AGA AGT C | Human |
| HER2 | TGT GAC TGC CTG TCC CTA CAA | CCA GAC CAT AGC ACA CTC GG | Human |
| MMP9 | TGT ACC GCT ATG GTT ACA CTC G | GGC AGG GAC AGT TGC TTC T | Human |
| CCL19 | CTG CTG GTT CTC TGG ACT TCC | AGG GAT GGG TTT CTG GGT CA | Human |
| CCL21 | GTT GCC TCAA GTA CAG CCA AA | AGA ACA GGA TAG CTG GGA TGG | Human |
| NFAT1 | GAG CCG AAT GCA CAT AAG GTC | CCA GAG AGA CTA GCA AGG GG | Human |
| COX-2 | CTG GCG CTC AGC CAT ACA G | CGC ACT TAT ACT GGT CAA ATC CC | Human |
| TNF | CCT CTC TCT AAT CAG CCC TCT G | GAG GAC CTG GGA GTA GAT GAG | Human |
| Ccr7 | TGT ACG AGT CGG TGT GCT TC | GGT AGG TAT CCG TCA TGG TCT TG | Mouse |
| c-Fos | CGG GTT TCA ACG CCG ACT A | CGG GTT TCA ACG CCG ACT A | Mouse |
| c-Jun | CCT TCT ACG ACG ATG CCC TC | GGT TCA AGG TCA TGC TCT GTT T | Mouse |
| Her2 | ACC GAC ATG AAG TTG CGA CTC | AGG TAA GCT CCA AAT TGC CCT | Mouse |
| Mmp9 | CTG GAC AGC CAG ACA CTA AAG | CTC GCG GCA AGT CTT CAG AG | Mouse |
| Ccl19 | GGG GTG CTA ATG ATG CGG AA | CCT TAG TGT GGT GAA CAC AAC A | Mouse |
| Ccl21 | GTG ATG GAG GGG GTC AGG A | GGG ATG GGA CAG CCT AAA CT | Mouse |
| Fsp1 | TCC ACA AAT ACT CAG GCA AAG AG | GCA GCT CCC TGG TCA GTA G | Mouse |
| Ps2 | AGC ACA AGG TGA TCT GTG TCC | GGA AGC CAC AAT TTA TCC TCT CC | Mouse |
| Tnf | CCT GTA GCC CAC GTC GTA G | GGG AGT AGA CAA GGT ACA ACC C | Mouse |
| Akt | ATG AAC GAC GTA GCC ATT GTG | TTG TAG CCA ATA AAG GTG CCA T | Mouse |
| Cox-2 | TTC AAC ACA CTC TAT CAC TGG C | AGA AGC GTT TGC GGT ACT CAT | Mouse |
| β-ACTIN | CAT GTA CGT TGC TAT CCA GGC | CTC CTT AAT GTC ACG CAC GAT | Human |
| GAPDH | GGA GCG AGA TCC CTC CAA AAT | GGC TGT TGT CAT ACT TCT CAT GG | Human |
| Hprt | AGG CCC CAA AAT GGT TAA GGT T | CAA GGG CAT ATC CAA CAA CAA A | Mouse |
| β-Actin | GGC TGT ATT CCC CTC CAT CG | CCA GTT GGT AAC AAT GCC ATG T | Mouse |
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Linear Range (μg/mL) | Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | Amount (μg/mg) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| curcumin | 17.60 | 3.125–400 | y = 20.2393x − 30.2014 | 0.999 | 15.28 ± 0.097 |
| demethoxycurcumin | 16.95 | 3.125–400 | y = 22.7311x − 39.6534 | 0.999 | 3.82 ± 0.037 |
| bisdemethoxycurcumin | 16.32 | 3.125–400 | y = 59.2165x − 27.5719 | 0.999 | 0.63 ± 0.010 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaya, P.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, Y.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Yang, H.; Lee, H.W.; Hong, E.-J. Curcumae Radix Extract Decreases Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis via Suppression of C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 Expression. Nutrients 2019, 11, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020410
Kaya P, Lee SR, Lee YH, Kwon SW, Yang H, Lee HW, Hong E-J. Curcumae Radix Extract Decreases Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis via Suppression of C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 Expression. Nutrients. 2019; 11(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaya, Pelin, Sang R. Lee, Young Ho Lee, Sun Woo Kwon, Hyun Yang, Hye Won Lee, and Eui-Ju Hong. 2019. "Curcumae Radix Extract Decreases Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis via Suppression of C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 Expression" Nutrients 11, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020410
APA StyleKaya, P., Lee, S. R., Lee, Y. H., Kwon, S. W., Yang, H., Lee, H. W., & Hong, E.-J. (2019). Curcumae Radix Extract Decreases Mammary Tumor-Derived Lung Metastasis via Suppression of C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 Expression. Nutrients, 11(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020410





