New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger During a 24 h Water Only Fast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design, Supplements and Protocol
2.3. Appetite Measures
2.4. Characterization of Hops Acid Compounds
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
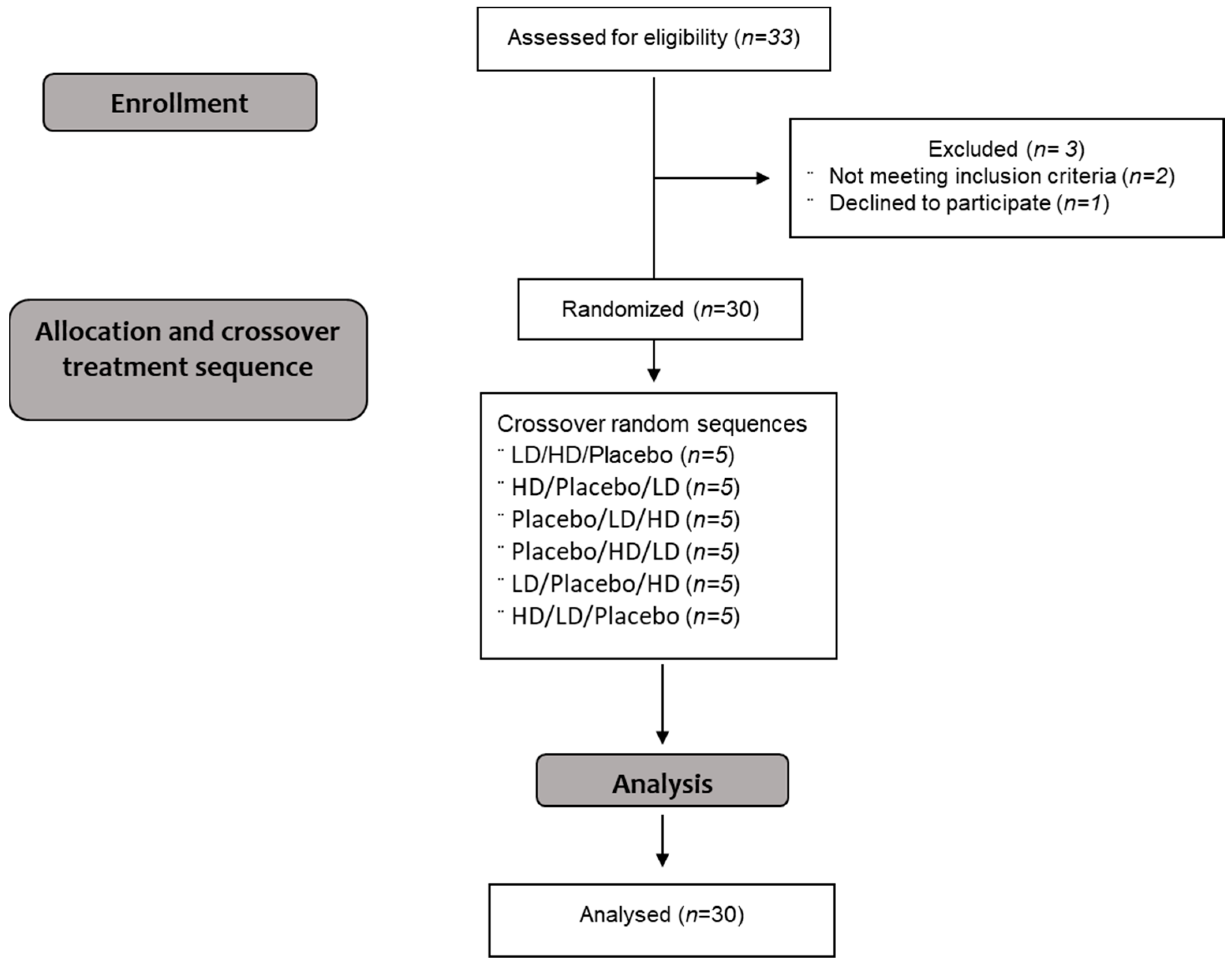
3.1. Participants
3.2. Composition of the Treatments
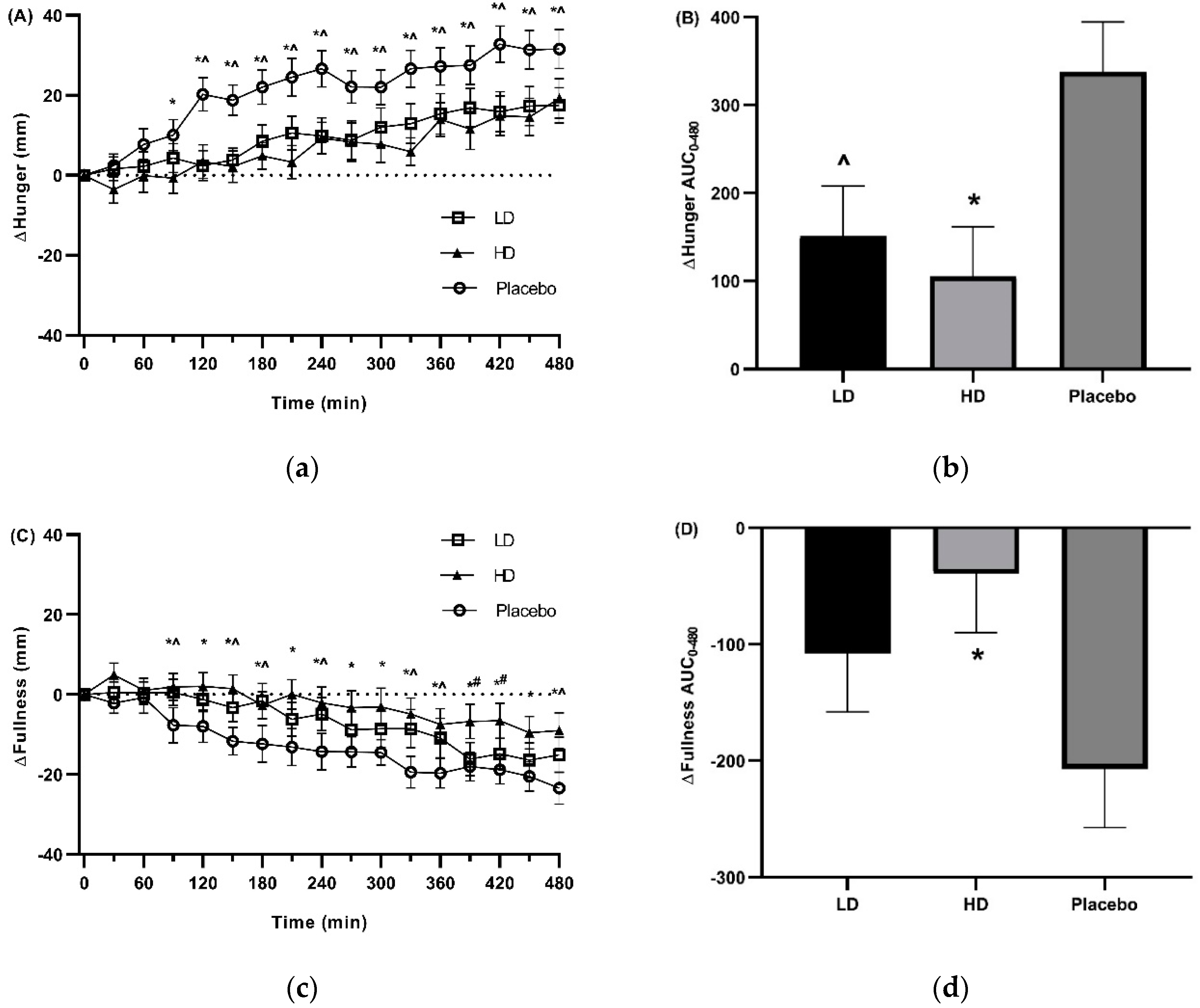
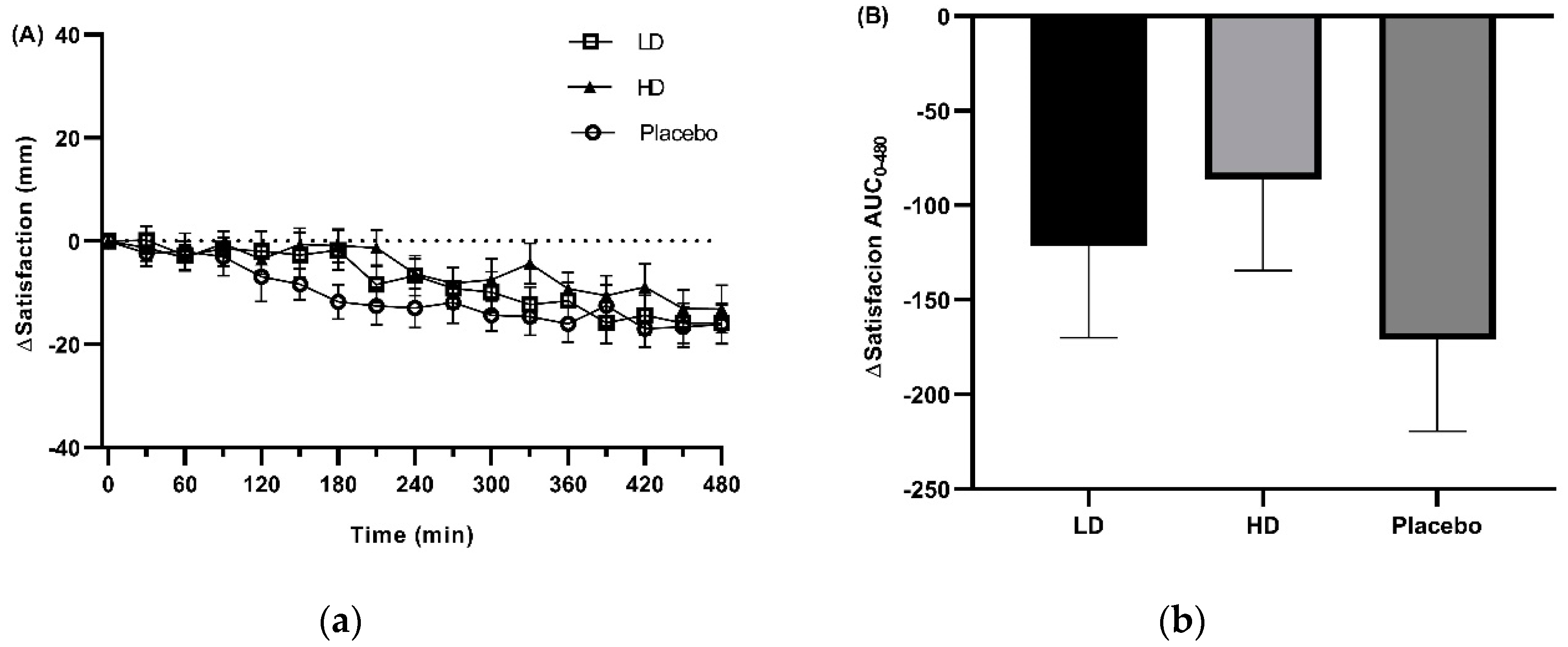
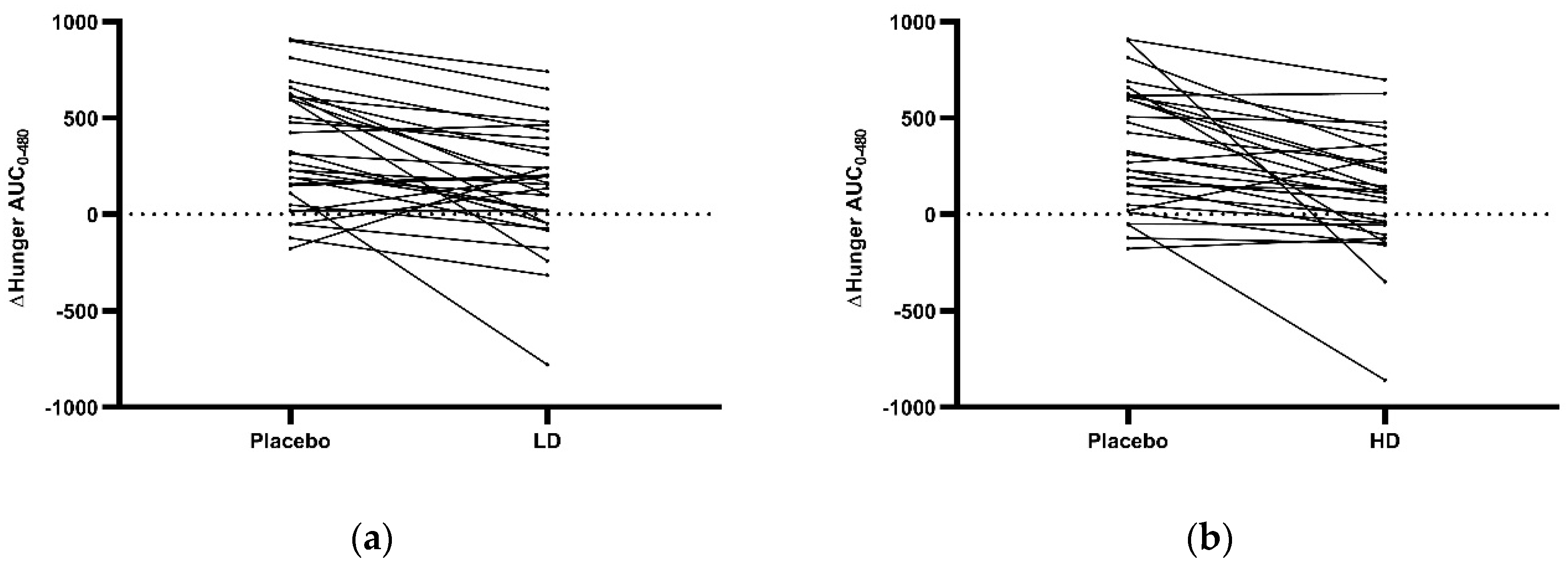
3.3. Appetite Ratings
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sotos-Prieto, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Mattei, J.; Fung, T.T.; Li, Y.; Pan, A.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. Association of Changes in Diet Quality with Total and Cause-Specific Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 37, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarantos, E.; Martinez, A.; Dwyer, J. Nutrition and quality of life in older adults. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Caterson, I.; Seidell, J.C.; James, W.P. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B. Globalization of diabetes: The role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, R.; Peto, R. The causes of cancer: Quantitative estimates of avoidable risks of cancer in the United States today. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1981, 66, 1191–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, T.T.; Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Dietary patterns and the risk of coronary heart disease in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F.N.; Pasco, J.A.; Mykletun, A.; Williams, L.J.; Hodge, A.M.; O′Reilly, S.L.; Nicholson, G.C.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Berk, M. Association of Western and traditional diets with depression and anxiety in women. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Russell, J.; Flood, V.M.; Burlutsky, G.; Mitchell, P. Adherence to dietary guidelines positively affects quality of life and functional status of older adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Pagoto, S.L.; Griffith, J.A.; Merriam, P.A.; Ockene, I.S.; Hafner, A.R.; Olendzki, B.C. A dietary quality comparison of popular weight-loss plans. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoto, S.L.; Appelhans, B.M. A call for an end to the diet debates. JAMA 2013, 310, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansinger, M.L.; Gleason, J.A.; Griffith, J.L.; Selker, H.P.; Schaefer, E.J. Comparison of the Atkins, Ornish, Weight Watchers, and Zone diets for weight loss and heart disease risk reduction: A randomized trial. JAMA 2005, 29, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, S.D.; Lee, S.A.; Donahoo, W.T.; McLaren, C.; Manini, T.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Pahor, M. The Effects of Time Restricted Feeding on Overweight, Older Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnosky, A.R.; Hoddy, K.K.; Unterman, T.G.; Varady, K.A. Intermittent fasting vs. daily calorie restriction for type 2 diabetes prevention: A review of human findings. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley, B.T.; Carroll, R.W.; Hall, R.M.; Weatherall, M.; Parry-Strong, A.; Krebs, J.D. Intermittent fasting in Type 2 diabetes mellitus and the risk of hypoglycaemia: A randomized controlled trial. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvie, M.N.; Pegington, M.; Mattson, M.P.; Frystyk, J.; Dillon, B.; Evans, G.; Cuzick, J.; Jebb, S.A.; Martin, B.; Cutler, R.G.; et al. The effects of intermittent or continuous energy restriction on weight loss and metabolic disease risk markers: A randomized trial in young overweight women. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2011, 35, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Longo, V.D.; Harvie, M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbidi, S.; Daiber, A.; Korac, B.; Li, H.; Essop, M.F.; Laher, I. Health Benefits of Fasting and Caloric Restriction. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, B.D.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Lappe, D.L.; May, H.T.; Carlquist, J.F.; Galenko, O.; Brunisholz, K.D.; Anderson, J.L. Randomized cross-over trial of short-term water-only fasting: Metabolic and cardiovascular consequences. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Summer, W.; Cutler, R.G.; Martin, B.; Hyun, D.H.; Dixit, V.D.; Pearson, M.; Nassar, M.; Telljohann, R.; Maudsley, S.; et al. Alternate day calorie restriction improves clinical findings and reduces markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in overweight adults with moderate asthma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempel, M.C.; Kroeger, C.M.; Bhutani, S.; Trepanowski, J.F.; Varady, K.A. Intermittent fasting combined with calorie restriction is effective for weight loss and cardio-protection in obese women. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, Y.; Ozkan, G.; Ulusoy, S.; Arici, M.; Derici, U.; Sengul, S.; Sindel, S.; Erturk, S.; Turkish Society of Hypertension and Renal Diseases. The effect of intermittent fasting on blood pressure variability in patients with newly diagnosed hypertension or prehypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilbronn, L.K.; Smith, S.R.; Martin, C.K.; Anton, S.D.; Ravussin, E. Alternate-day fasting in nonobese subjects: Effects on body weight, body composition, and energy metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksungar, F.B.; Topkaya, A.E.; Akyildiz, M. Interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and biochemical parameters during prolonged intermittent fasting. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 51, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshed, H.; Beyl, R.A.; Della Manna, D.L.; Yang, E.S.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves 24-Hour Glucose Levels and Affects Markers of the Circadian Clock, Aging, and Autophagy in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adawi, M.; Watad, A.; Brown, S.; Aazza, K.; Aazza, H.; Zouhir, M.; Sharif, K.; Ghanayem, K.; Farah, R.; Mahagna, H.; et al. Ramadan Fasting Exerts Immunomodulatory Effects: Insights from a Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, N.L.; Sellami, M.; Salem, I.; Conic, R.; Kimak, M.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Damiani, G. Fasting and Its Impact on Skin Anatomy, Physiology, and Physiopathology: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Watad, A.; Bridgewood, C.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Pacifico, A.; Malagoli, P.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Adawi, M. The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on the Reduction of PASI Score, in Moderate-To-Severe Psoriatic Patients: A Real-Life Multicenter Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Mahroum, N.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Pacifico, A.; Malagoli, P.; Tiodorovic, D.; Conic, R.R.; Amital, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Watad, A.; et al. The Safety and Impact of a Model of Intermittent, Time-Restricted Circadian Fasting (“Ramadan Fasting”) on Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Insights from a Multicenter, Observational, Cross-Over, Pilot, Exploratory Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adawi, M.; Damiani, G.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Bridgewood, C.; Pacifico, A.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Morrone, A.; Malagoli, P.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Amital, H.; et al. The Impact of Intermittent Fasting (Ramadan Fasting) on Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity, Enthesitis, and Dactylitis: A Multicentre Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinac, C.R.; Nelson, S.H.; Breen, C.I.; Hartman, S.J.; Natarajan, L.; Pierce, J.P.; Flatt, S.W.; Sears, D.D.; Patterson, R.E. Prolonged Nightly Fasting and Breast Cancer Prognosis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltaief, K.; Bouida, W.; Trabelsi, I.; Baccouche, H.; Sassi, M.; Dridi, Z.; Chakroun, T.; Hellara, I.; Boukef, R.; Hassine, M.; et al. Metabolic effects of Ramadan fasting in patients at high risk of cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2019, 12, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelmi de Toledo, F.; Grundler, F.; Bergouignan, A.; Drinda, S.; Michalsen, A. Safety, health improvement and well-being during a 4 to 21-day fasting period in an observational study including 1422 subjects. PLoS ONE 2019, 1, e0209353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solianik, R.; Sujeta, A.; Cekanauskaite, A. Effects of 2-day calorie restriction on cardiovascular autonomic response, mood, and cognitive and motor functions in obese young adult women. Exp. Brain. Res. 2018, 236, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Moore, M.L.; Graybeal, A.J. Reliability of hunger-related assessments during 24-hour fasts and their relationship to body composition and subsequent energy compensation. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 188, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogels, N.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Categorical strategies based on subject characteristics of dietary restraint and physical activity, for weight maintenance. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2005, 29, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasman, W.J.; Saris, W.H.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Predictors of weight maintenance. Obes. Res. 1999, 7, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, A. Fasting for weight loss: An effective strategy or latest dieting trend? Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.F.; Geiselman, P.J.; Williamson, D.A.; Champagne, C.M.; Bray, G.A.; Ryan, D.H. Association of dietary restraint and disinhibition with eating behavior, body mass, and hunger. Eat. Weight Disord. 1998, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marloth, R. The Flora of South Africa with Synopsis of the South African Genera of Phanerogamous Plant; Wheldon and Wesley: Buckinghamshire, UK, 1932; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M.; Weiss, E. Domestication of Plants in the Old World: The Origin and Spread of Domesticated Plants in Southwest Asia, Europe, and the Mediterranean Basin, 4th ed.; University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Deloose, E.; Janssen, P.; Corsetti, M.; Biesiekierski, J.; Masuy, I.; Rotondo, A.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Intragastric infusion of denatonium benzoate attenuates interdigestive gastric motility and hunger scores in healthy female volunteers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iven, J.; Biesiekierski, J.R.; Zhao, D.; Deloose, E.; O’Daly, O.G.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J.; Van Oudenhove, L. Intragastric quinine administration decreases hedonic eating in healthy women through peptide-mediated gut-brain signaling mechanisms. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 22, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, H.; Ikeshima, E.; Shiraki, M.; Kanaya, T.; Fujiwara, D.; Odai, H.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; Ezaki, O.; Oikawa, S.; Kondo, K. Isohumulones, bitter acids derived from hops, activate both peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and gamma and reduce insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33456–33462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kok, B.P.; Galmozzi, A.; Littlejohn, N.K.; Albert, V.; Godio, C.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.M.; Bland, J.S.; Grayson, N.; Fang, M.; et al. Intestinal bitter taste receptor activation alters hormone secretion and imparts metabolic benefits. Mol. Metab. 2018, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, P.A.; Finlin, B.S.; Ross, D.; Boyechko, T.; Zhu, B.; Grayson, N.; Sims, R.; Bland, J.S. Effects of KDT501 on Metabolic Parameters in Insulin-Resistant Prediabetic Humans. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amo, R. DRcaps® Capsules Achieve Delayed Release Properties for Nutritional Ingredients in Human Clinical Study. Available online: https://www.capsugel.com/knowledge-center/drcaps-achieve-delayed-release-properties-for-nutritional-ingredients-in-hu (accessed on 8 July 2019).
- Krofta, K.; Vrabcová, S.; Mikyska, A.; Jurková, M.; Cajka, T.; Hajslová, J. Stability of hops beta acids and their decomposition products during natural aging. Acta Hortic. 2013, 1010, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, N.; Tirunagari, M.; Qureshi, H.K.; Anitha, N.; Rao, J. Drug-excipient interaction and its importance in dosage form development. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Thivel, D.; Finlayson, G.; Miguet, M.; Pereira, B.; Duclos, M.; Boirie, Y.; Doucet, E.; Blundell, J.E.; Metz, L. Energy depletion by 24-h fast leads to compensatory appetite responses compared with matched energy depletion by exercise in healthy young males. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blundell, J.; de Graaf, C.; Hulshof, T.; Jebb, S.; Livingstone, B.; Lluch, A.; Mela, D.; Salah, S.; Schuring, E.; van der Knaap, H.; et al. Appetite control: Methodological aspects of the evaluation of foods. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharafi, M.; Alamdari, N.; Wilson, M.; Leidy, H.J.; Glynn, E.L. Effect of a High-Protein, High-Fiber Beverage Preload on Subjective Appetite Ratings and Subsequent Ad Libitum Energy Intake in Overweight Men and Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2018, 2, nzy022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belza, A.; Ritz, C.; Sorensen, M.Q.; Holst, J.J.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Astrup, A. Contribution of gastroenteropancreatic appetite hormones to protein-induced satiety. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstenbach-Waelen, A.; Veldhorst, M.A.; Nieuwenhuizen, A.G.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Westerterp, K.R. Comparison of 2 diets with either 25% or 10% of energy as casein on energy expenditure, substrate balance, and appetite profile. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 8, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, C.J.; Chu, Y.F.; Johnson, W.D.; Martin, C.K.; Han, H.; Bordenave, N.; Shi, Y.; O′Shea, M.; Greenway, F.L. The role of meal viscosity and oat beta-glucan characteristics in human appetite control: A randomized crossover trial. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, A. Involvement of the gut chemosensory system in the regulation of colonic anion secretion. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Neve, B.; Foltz, M.; Daniel, H.; Gouka, R. The steroid glycoside Hg.-12 from Hoodia gordonii activates the human bitter receptor TAS2R14 and induces CCK release from HuTu-80 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G1368–G1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, P.; Sarnelli, G.; Pesce, M.; Zito, F.P.; Alessandro, A.D.; Verlezza, V.; Palumbo, I.; Turco, F.; Esposito, K.; Cuomo, R. The Bitter Taste Receptor Agonist Quinine Reduces Calorie Intake and Increases the Postprandial Release of Cholecystokinin in Healthy Subjects. J. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015, 21, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deloose, E.; Corsetti, M.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Intragastric infusion of the bitter tastant quinine suppresses hormone release and antral motility during the fasting state in healthy female volunteers. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018, 30, e13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flint, A.; Raben, A.; Blundell, J.E.; Astrup, A. Reproducibility, power and validity of visual analogue scales in assessment of appetite sensations in single test meal studies. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayer, R.D.; Peters, J.C.; Pan, Z.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O. Hunger, Food Cravings, and Diet Satisfaction are Related to Changes in Body Weight During a 6-Month Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention: The Beef WISE Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapeau, V.; King, N.; Hetherington, M.; Doucet, E.; Blundell, J.; Tremblay, A. Appetite sensations and satiety quotient: Predictors of energy intake and weight loss. Appetite 2007, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, D.E.; Purnell, J.Q.; Frayo, R.S.; Schmidova, K.; Wisse, B.E.; Weigle, D.S. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, K.; Tasali, E.; Leproult, R.; Scherberg, N.; Van Cauter, E. Twenty-four-hour profiles of acylated and total ghrelin: Relationship with glucose levels and impact of time of day and sleep. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natalucci, G.; Riedl, S.; Gleiss, A.; Zidek, T.; Frisch, H. Spontaneous 24-h ghrelin secretion pattern in fasting subjects: Maintenance of a meal-related pattern. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 152, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Degen, L.; Drewe, J.; Piccoli, F.; Grani, K.; Oesch, S.; Bunea, R.; D′Amato, M.; Beglinger, C. Effect of CCK-1 receptor blockade on ghrelin and PYY secretion in men. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1391–R1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Degen, L.; Oesch, S.; Casanova, M.; Graf, S.; Ketterer, S.; Drewe, J.; Beglinger, C. Effect of peptide YY3-36 on food intake in humans. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennella, I.; Fogliano, V.; Ferracane, R.; Arlorio, M.; Pattarino, F.; Vitaglione, P. Microencapsulated bitter compounds (from Gentiana lutea) reduce daily energy intakes in humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutzwiller, J.P.; Goke, B.; Drewe, J.; Hildebrand, P.; Ketterer, S.; Handschin, D.; Winterhalder, R.; Conen, D.; Beglinger, C. Glucagon-like peptide-1: A potent regulator of food intake in humans. Gut 1999, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cowley, M.A.; Small, C.J.; Herzog, H.; Cohen, M.A.; Dakin, C.L.; Wren, A.M.; Brynes, A.E.; Low, M.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Gut hormone PYY(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 2002, 418, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzwiller, J.P.; Drewe, J.; Ketterer, S.; Hildebrand, P.; Krautheim, A.; Beglinger, C. Interaction between CCK and a preload on reduction of food intake is mediated by CCK-A receptors in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R189–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.; Poppitt, S.D. How Satiating Are the ‘Satiety’ Peptides: A Problem of Pharmacology versus Physiology in the Development of Novel Foods for Regulation of Food Intake. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, Y.; Koseki, J.; Sekine, H.; Fujitsuka, N.; Kobayashi, H. Role of Bitter Taste Receptors in Regulating Gastric Accommodation in Guinea Pigs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 369, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.P.; Zhang, G.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qing, J.; Hui, L. Effect of weekend fasting therapy on blood pressure in overweight or obese patients with hypertension. J. Integr. Cardiol. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous III, A.G.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Romijn, J.A.; Carroll, R.M. Progressive alterations in lipid and glucose metabolism during short-term fasting in young adult men. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, E801–E806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, H.A.; Zibellini, J.; Harris, R.A.; Seimon, R.V.; Sainsbury, A. Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Weight and Body Composition in Healthy Non-Athlete Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
 = VAS measurements.
= VAS measurements.
 = VAS measurements.
= VAS measurements.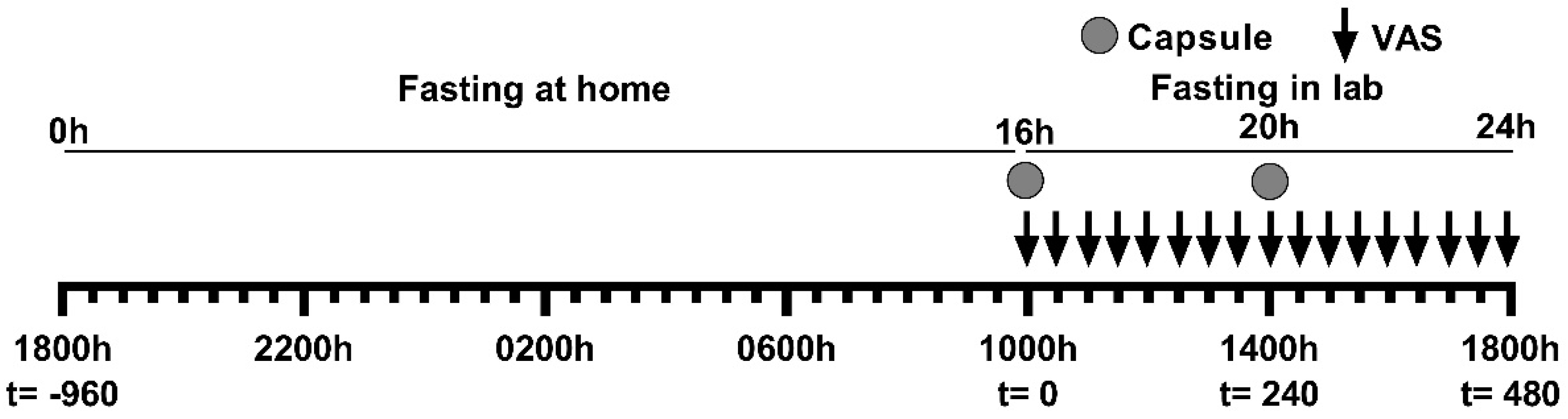
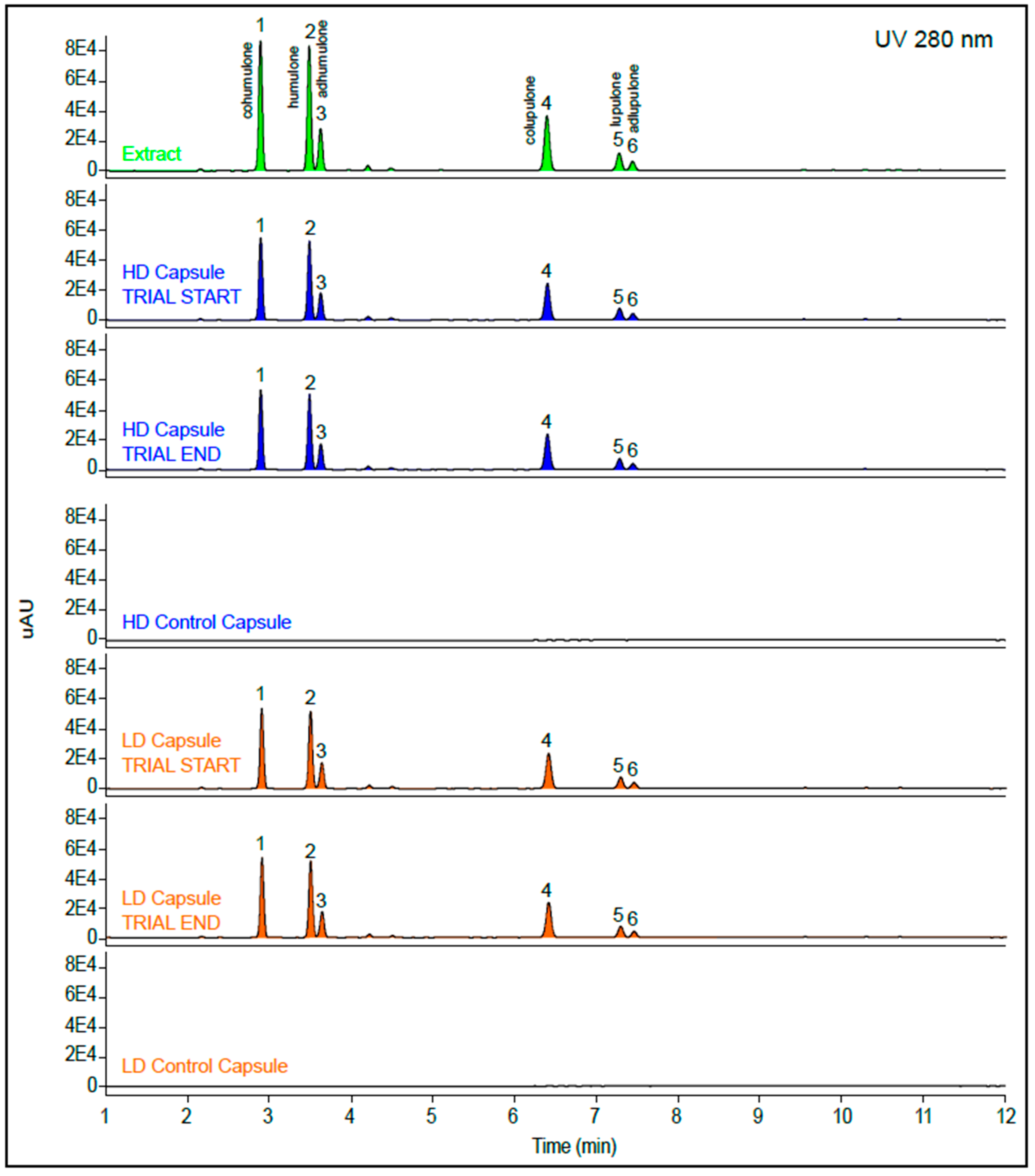

| Placebo | HD | LD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amarasate® Hops Extract (mg) | 0 | 500 | 200 |
| Canola Oil (µL) | 250 | 250 | 100 |
| Characteristics of Participants | |
|---|---|
| Age, y (mean ± s.d, range, median (IQR)) | 24 ± 6, 18–40, 22 (8) |
| Ethnicity, Caucasian | 19/30 |
| Chinese | 3/30 |
| Persian | 2/30 |
| South American | 2/30 |
| New Zealand Maori | 1/30 |
| Sri Lankan | 1/30 |
| Filipino | 1/30 |
| Malaysian | 1/30 |
| Body weight, kg (mean ± s.d, median (IQR)) | 72 ± 7, 74 (8.5) |
| BMI, kg/m2 (mean ± s.d, median (IQR)) | 23.1 ± 1.4, 23.6 (2.2) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walker, E.; Lo, K.; Tham, S.; Pahl, M.; Lomiwes, D.; Cooney, J.; Wohlers, M.; Gopal, P. New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger During a 24 h Water Only Fast. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2754. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112754
Walker E, Lo K, Tham S, Pahl M, Lomiwes D, Cooney J, Wohlers M, Gopal P. New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger During a 24 h Water Only Fast. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2754. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112754
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalker, Edward, Kim Lo, Sze Tham, Malcolm Pahl, Dominic Lomiwes, Janine Cooney, Mark Wohlers, and Pramod Gopal. 2019. "New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger During a 24 h Water Only Fast" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2754. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112754
APA StyleWalker, E., Lo, K., Tham, S., Pahl, M., Lomiwes, D., Cooney, J., Wohlers, M., & Gopal, P. (2019). New Zealand Bitter Hops Extract Reduces Hunger During a 24 h Water Only Fast. Nutrients, 11(11), 2754. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112754






