Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options?
Abstract
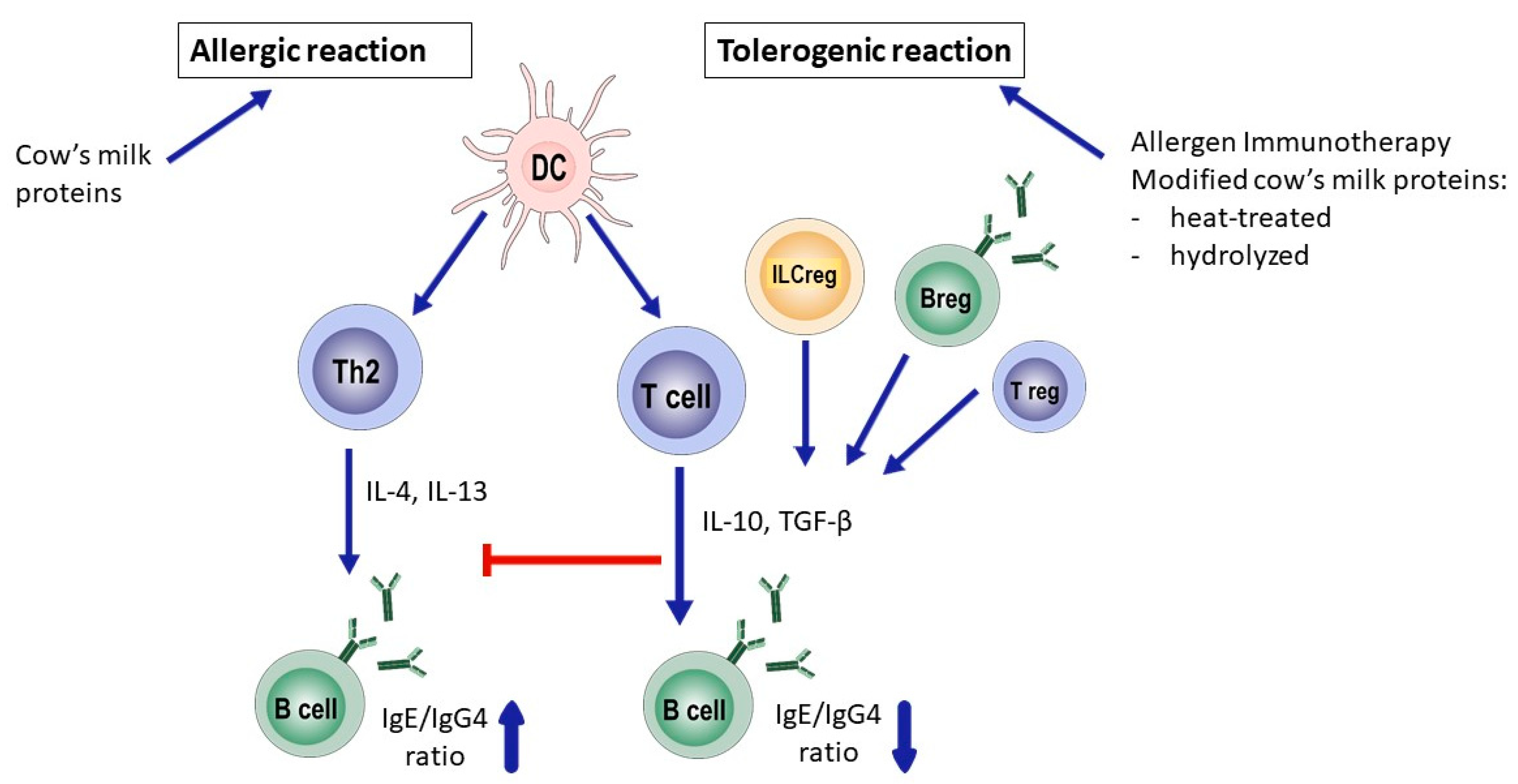
:1. Immunological Aspects of Cow’s Milk Allergy
2. Cow’s Milk Formula, Including Hydrolysate in Cow’s-Milk-Allergic Patients
3. Baked Milk in the Treatment of Cow’s Milk Allergy
4. Allergen Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Cow’s Milk Allergy
5. Which Immune Cells Are Involved in Immunotherapy for Cow’s Milk Allergy?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Host, A.; Halken, S.; Jacobsen, H.P.; Christensen, A.E.; Herskind, A.M.; Plesner, K. Clinical course of cow’s milk protein allergy/intolerance and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 13 (Suppl. 15), 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Host, A.; Halken, S. Hypoallergenic formulas—When, to whom and how long: After more than 15 years we know the right indication! Allergy 2004, 59 (Suppl. 78), 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchi, A.; Schunemann, H.J.; Brozek, J.; Restani, P.; Beyer, K.; Troncone, R.; Martelli, A.; Terracciano, L.; Bahna, S.L.; Rancé, F.; et al. Diagnosis and Rationale for Action Against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA): A summary report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, H.A. Food allergy. Part 1: Immunopathogenesis and clinical disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.-Y.; Van Hoffen, E.; Michelsen, A.; Guikers, K.; Van Der Tas, C.H.W.; Knulst, A.C.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M. Cow’s milk allergy in adults is rare but severe: Both casein and whey proteins are involved. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, R.P.; Dijk, A.G.V.I.-V.; Van Reijsen, F.C.; Versluis, C.; Kimpen, J.L.; Knol, E.F.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Van Hoffen, E. Differences in antigen-specific T-cell responses between infants with atopic dermatitis with and without cow’s milk allergy: Relevance of TH2 cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiter, B.; Knol, E.F.; Van Neerven, R.J.J.; Garssen, J.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Knulst, A.C.; Van Hoffen, E. Maintenance of tolerance to cow’s milk in atopic individuals is characterized by high levels of specific immunoglobulin G4. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.; Hahn, Y.S. Increased cow’s milk protein-specific IgG4 levels after oral desensitization in 7-to 12-month-old infants. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiter, B.; Trégoat, V.; M’Rabet, L.; Garssen, J.; Knol, E.F.; Hoffen, E.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M. Characterization of T cell epitopes in alphas1-casein in cow’s milk allergic, atopic and non-atopic children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouw, J.W.; Jo, J.; Meulenbroek, L.A.P.M.; Heijjer, T.S.; Kremer, E.; Sandalova, E.; Knulst, A.C.; Jeurink, P.V.; Garssen, J.; Rijnierse, A.; et al. Identification of peptides with tolerogenic potential in a hydrolysed whey-based infant formula. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knol, E.F. Requirements for effective IgE cross-linking on mast cells and basophils. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl-Hajek, R.; Spangfort, M.D.; Schou, C.; Breiteneder, H.; Yssel, H.; Joost van Neerven, R.J. Identification of a highly promiscuous and an HLA allele-specific T-cell epitope in the birch major allergen Bet v 1: HLA restriction, epitope mapping and TCR sequence comparisons. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, L.; Beyer, K.; Jarvinen, K.M.; Chatchatee, P.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H.A. Role of conformational and linear epitopes in the achievement of tolerance in cow’s milk allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatchatee, P.; Jarvinen, K.M.; Bardina, L.; Beyer, K.; Sampson, H.A. Identification of IgE- and IgG-binding epitopes on alpha(s1)-casein: Differences in patients with persistent and transient cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, S.K.; Sampson, H.A. Allergenic properties of ovomucoid in man. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Roberts, G.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.; Dutoit, G.; Eigenmann, P.; et al. EAACI food allergy and anaphylaxis guidelines: Diagnosis and management of food allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terheggen-Lagro, S.W.; Khouw, I.M.; Schaafsma, A.; Wauters, E.A. Safety of a new extensively hydrolysed formula in children with cow’s milk protein allergy: A double blind crossover study. BMC Pediatr. 2002, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, D.A.; Sinn, J.K.; Jones, L.J. Infant formulas containing hydrolysed protein for prevention of allergic disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochwallner, H.; Schulmeister, U.; Swoboda, I.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Reininger, R.; Civaj, V.; Campana, R.; Thalhamer, J.; Scheiblhofer, S.; Balic NHorak, F. Infant milk formulas differ regarding their allergenic activity and induction of T-cell and cytokine responses. Allergy 2017, 72, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knipping, K.; Van Esch, B.C.; Dijk, A.G.V.I.-V.; Van Hoffen, E.; Van Baalen, T.; Knippels, L.M.; Van Der Heide, S.; Dubois, A.E.; Garssen, J.; Knol, E.F. Enzymatic treatment of whey proteins in cow’s milk results in differential inhibition of IgE-mediated mast cell activation compared to T-cell activation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 159, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenbroek, L.A.P.M.; Oliveira, S.; Jager, C.F.D.H.; Klemans, R.J.B.; Lebens, A.F.M.; Van Baalen, T.; Knulst, A.C.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Garssen, J.; Knippels, L.M.J.; et al. The degree of whey hydrolysis does not uniformly affect in vitro basophil and T cell responses of cow’s milk-allergic patients. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedler, J.; Braun-Fahrlander, C.; Eder, W.; Schreuer, M.; Waser, M.; Maisch, S.; Carr, D.; Schierl, R.; Nowak, D.; Von Mutius, E. Exposure to farming in early life and development of asthma and allergy: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet 2001, 358, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Neerven, R.J.; Knol, E.F.; Heck, J.M.; Savelkoul, H.F. Which factors in raw cow’s milk contribute to protection against allergies? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozanska, B. Raw Cow’s Milk and Its Protective Effect on Allergies and Asthma. Nutrients 2019, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, O.; Mowat, A.M. Oral tolerance to food protein. Mucosal Immunol. 2012, 5, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wopereis, H.; Oozeer, R.; Knipping, K.; Belzer, C.; Knol, J. The first thousand days—Intestinal microbiology of early life: Establishing a symbiosis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 25, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canani, R.B.; Nocerino, R.; Terrin, G.; Coruzzo, A.; Cosenza, L.; Leone LTroncone, R. Effect of Lactobacillus GG on tolerance acquisition in infants with cow’s milk allergy: A randomized trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Sicherer, S.H.; Noone, S.; Moshier, E.L.; Sampson, H.A. Dietary baked milk accelerates the resolution of cow’s milk allergy in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Host, A.; Halken, S. A prospective study of cow milk allergy in Danish infants during the first 3 years of life. Clinical course in relation to clinical and immunological type of hypersensitivity reaction. Allergy 1990, 45, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, R.; Grimshaw, K.E.C.; Ellis, B.; Jaitly, J.; Roberts, G. Evidence that eating baked egg or milk influences egg or milk allergy resolution: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.A.; Caubet, J.C.; Kim, J.S.; Groetch, M.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A. Baked milk and egg-containing diet in the management of milk and egg allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol Pract. 2015, 3, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak-Węgrzyn, A.; Bloom, K.A.; Sicherer, S.H.; Shreffler, W.G.; Noone, S.; Wanich, N.; Sampson, H.A. Tolerance to extensively heated milk in children with cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caubet, J.C.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Moshier, E.; Godbold, J.; Wang, J.; Sampson, H.A. Utility of casein-specific IgE levels in predicting reactivity to baked milk. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keet, C.A.; Seopaul, S.; Knorr, S.; Narisety, S.; Skripak, J.; Wood, R.A. Long-term follow-up of oral immunotherapy for cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nurmatov, U.; Dhami, S.; Arasi, S.; Pajno, G.B.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; Muraro, A.; Roberts, G.; Akdis, C.; Alvaro-Lozano, M.; Beyer, K.; et al. Allergen immunotherapy for IgE-mediated food allergy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2017, 72, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.A. Food allergen immunotherapy: Current status and prospects for the future. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gernez, Y.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A. Immunotherapy for Food Allergy: Are We There Yet? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajno, G.B.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; Arasi, S.; Roberts, G.; Akdis, C.A.; Alvaro-Lozano, M.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Burks, W.; Ebisawa, M.; et al. EAACI Guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: IgE-mediated food allergy. Allergy 2018, 73, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inuo, C.; Tanaka, K.; Suzuki, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Yamawaki, K.; Tsuge, I.; Urisu, A.; Kondo, Y. Oral Immunotherapy Using Partially Hydrolyzed Formula for Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 177, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorell, A.; De La Hoz, B.; Ibáñez, M.D.; Boné, J.; Terrados, M.S.; Michavila, A.; Plaza, A.M.; Alonso, E.; Garde, J.; Nevot, S.; et al. Oral desensitization as a useful treatment in 2-year-old children with cow’s milk allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriarca, G.; Roncallo, C.; Del Ninno, M.; Pollastrini, E.; Milani, A.; De Pasquale, T.; Schiavino, D.; Nucera, E.; Buonomo, A.; Gasbarrini, G. Oral desensitisation in cow milk allergy: Immunological findings. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2002, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiemessen, M.M.; Van Hoffen, E.; Knulst, A.C.; Van Der Zee, J.A.; Knol, E.F.; Taams, L.S. CD4 CD25 regulatory T cells are not functionally impaired in adult patients with IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savilahti, E.M.; Karinen, S.; Salo, H.M.; Klemetti, P.; Saarinen, K.M.; Klemola, T.; Kuitunen, M.; Hautaniemi, S.; Savilahti, E.; Vaarala, O. Combined T regulatory cell and Th2 expression profile identifies children with cow’s milk allergy. Clin Immunol. 2010, 136, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemessen, M.M.; Van Ieperen-Van Dijk, A.G.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Garssen, J.; Knol, E.F.; Van Hoffen, E. Cow’s milk-specific T-cell reactivity of children with and without persistent cow’s milk allergy: Key role for IL-10. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xia, P.; Chen, Y.; Qu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yin, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Regulatory Innate Lymphoid Cells Control Innate Intestinal Inflammation. Cell 2017, 171, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Burton, O.T.; Oettgen, H.C.; Chatila, T. IL-4 production by group 2 innate lymphoid cells promotes food allergy by blocking regulatory T-cell function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van de Veen, W.; Stanic, B.; Wirz, O.F.; Jansen, K.; Globinska, A.; Akdis, M. Role of regulatory B cells in immune tolerance to allergens and beyond. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knol, E.F.; de Jong, N.W.; Ulfman, L.H.; Tiemessen, M.M. Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112734
Knol EF, de Jong NW, Ulfman LH, Tiemessen MM. Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options? Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112734
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnol, Edward F., Nicolette W. de Jong, Laurien H. Ulfman, and Machteld M. Tiemessen. 2019. "Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options?" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112734
APA StyleKnol, E. F., de Jong, N. W., Ulfman, L. H., & Tiemessen, M. M. (2019). Management of Cow’s Milk Allergy from an Immunological Perspective: What Are the Options? Nutrients, 11(11), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112734




