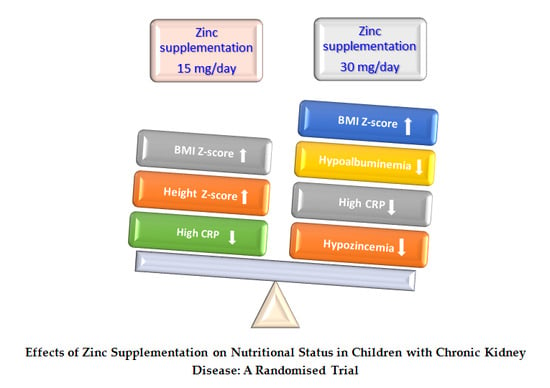
Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
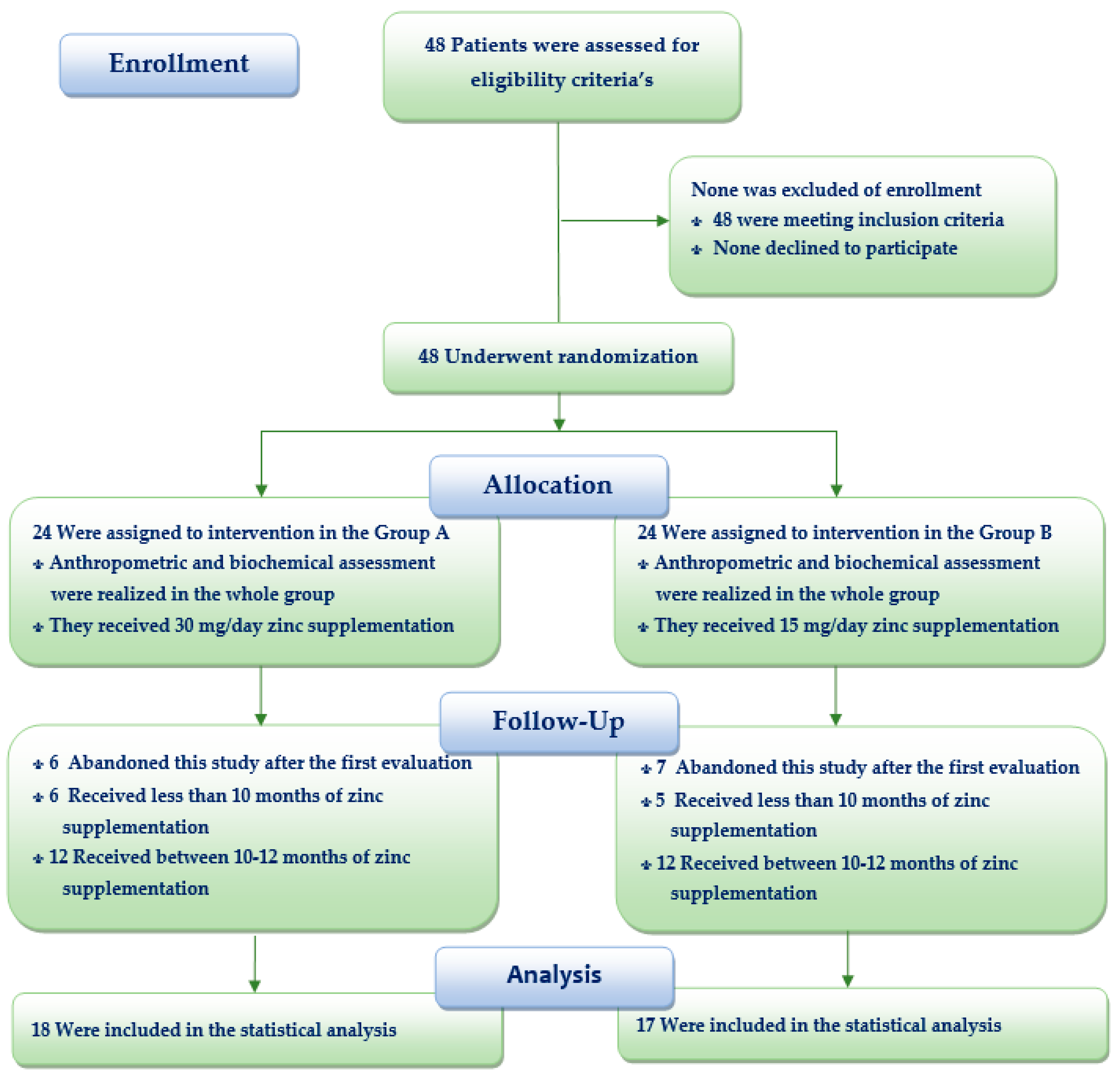
2. Materials and Methods
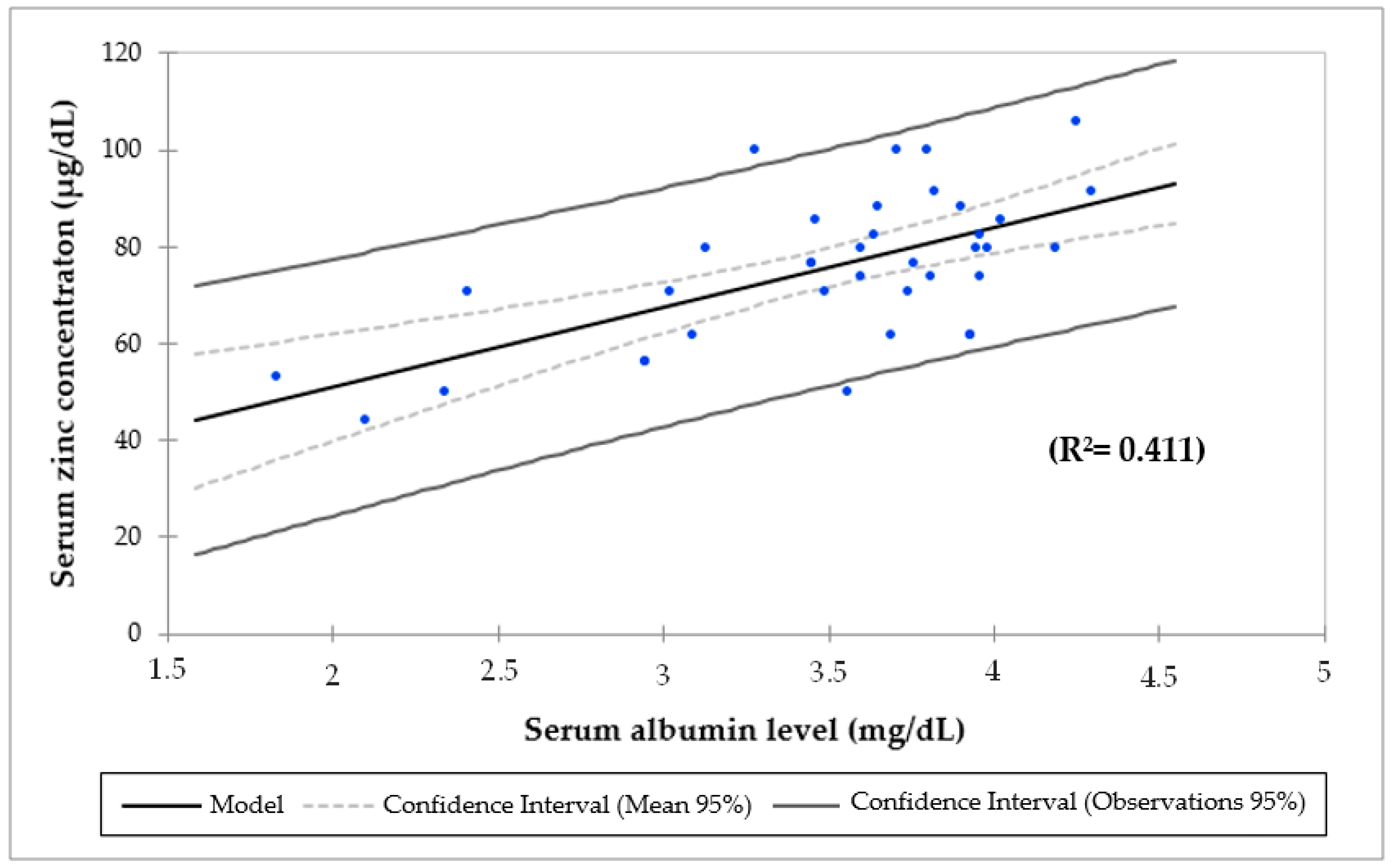
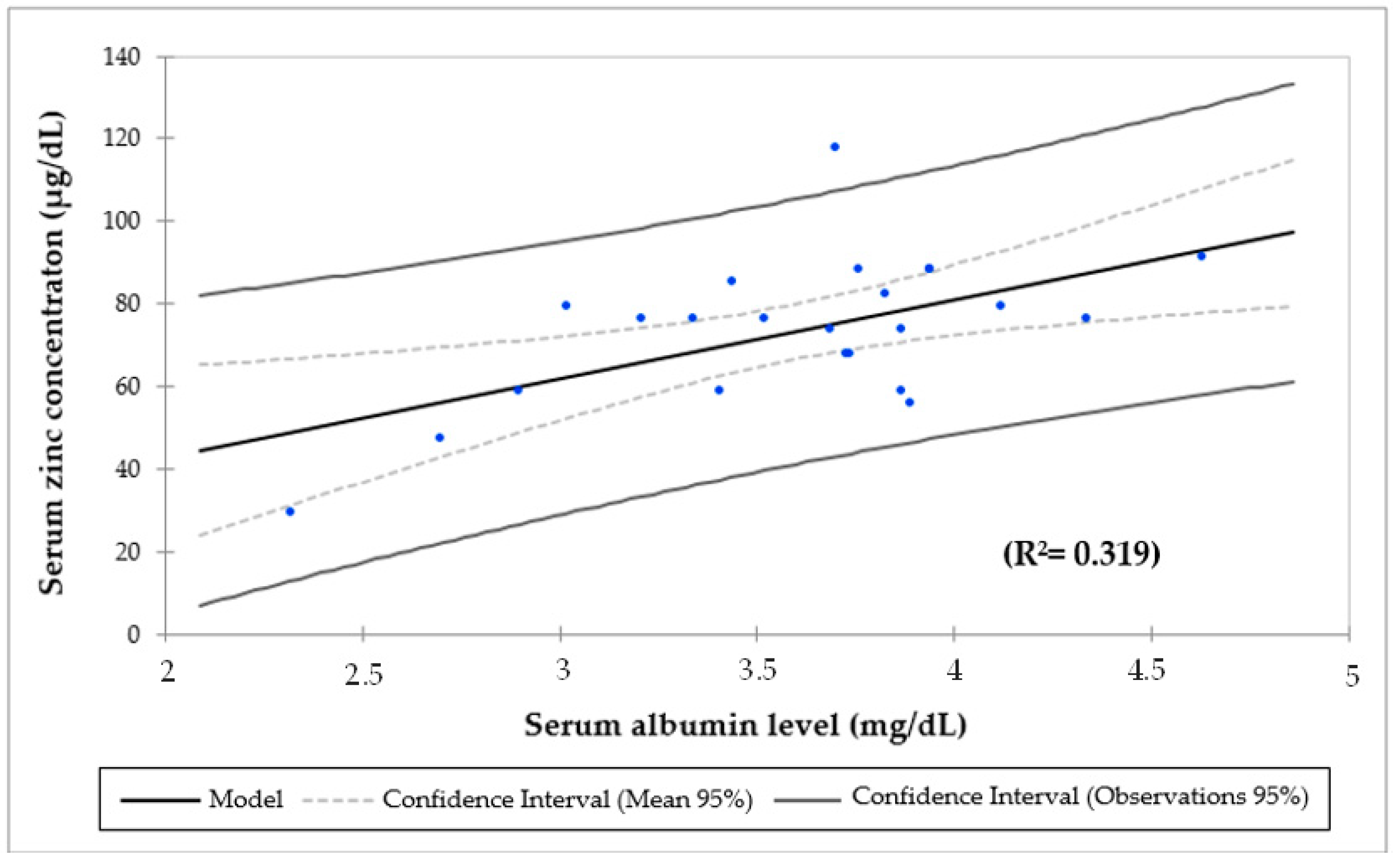
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nugent, R.A.; Fathima, S.F.; Feigl, A.B.; Chyung, D. The burden of chronic kidney disease on developing nations: A 21st century challenge in global health. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011, 118, c269–c277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Yao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liang, W.; Meng, R.; Jin, Q.; Wu, N.; Xu, F.; Ying, C.; Zuo, X. Comparative Study on Trace Element Excretions between Nonanuric and Anuric Patients Undergoing Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Tuttle, K.R.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Gharbi, M.B.; Heerspinj, G.J.L.; Johnson, D.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Massy, Z.A.; Moe, O.; Nelson, R.G.; et al. Reducing major risk factors for chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becherucci, F.; Roperto, R.M.; Materassi, M.; Romagnani, P. Chronic kidney disease in children. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikaly, M.G.; Ho, P.L.; Emmett, L.; Fine, R.N.; Tejani, A. Chronic renal insufficiency in children: The 2001 Annual Report of the NAPRTCS. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2003, 18, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDOQI Work Group. Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in Children with CKD: 2008 update. Executive summary. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, S11–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorember, F.M. Malnutrition in chronic kidney disease. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, M.; Rutkowski, B.; Debska-Slizien, A. Vitamins and microelement bioavailability in different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Consequences and therapy of the metabolic acidosis of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and human health: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, M.J.; Fazel, N. Zinc deficiency. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 25, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, P.; Vergnano, A.M.; Barbour, B.; Casado, M. Zinc at glutamatergic synapses. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastney, M.E.; Aamodt, R.L.; Rumble, W.F.; Henkin, R.I. Kinetic analysis of zinc metabolism and its regulation in normal humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 51, R398–R408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W. Zinc biochemistry, physiology, and homeostasis: Recent insights and current trends. Biometals 2001, 14, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tan, Y.; Sun, W.; Fu, Y.; Miao, L.; Cai, L. The role of zinc in the prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2013, 23, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.H.; Wang, C.L. Effects of zinc supplementation on plasma copper/zinc ratios, oxidative stress, and immunological status in hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Shames, D.M.; Woodhouse, L.R. Zinc homeostasis in humans. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1360S–1366S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Brown, K.H.; Gibson, R.S.; Krebs, N.F.; Lowe, N.M.; Siekmann, J.H.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND)—Zinc Review. J. Nutr. 2016, 9, 1S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, S.; Wenzlaff, S.; Hornig, D. Essential role of vitamin C and zinc in child immunity and health. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 386–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Di Paolo, B.; De Risio, F.; Niri, L.; Klinkmann, H.; Ivanovich, P.; Albertazzi, A. Effects of zinc supplementation in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1993, 8, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.S.; Adesina, S.E.; Ellis, C.L.; Gooch, J.L.; Hoover, R.S.; Williams, C.R. NADPH oxidase-2 mediates zinc deficiency-induced oxidative stress and kidney damage. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C47–C55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, P.C.; Diniz Ada, S.; de Arruda, I.K. Vitamin A and zinc status in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology 2005, 10, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Suen, D.; Tan, Y.; Jin, L.; Xiao, J.; Xie, R.; Rane, M.; et al. Zinc supplementation partially prevents renal pathological changes in diabetic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisancho, A.R. New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.; Sobradillo, B.; Aguirre, A.; Aresti, U.; Bilbao, A.; Fernández-Ramos, C.; Lizárraga, A.; Lorenzo, H.; Madariaga, L.; Rica, I. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento (Estudios Longitudinal y Transversal); Fundación Faustino Orbegozo: Bilbao, Spain, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Soldin, S.J.; Brugnara, C.; Hicks, J.M. Pediatric Reference Ranges, 3rd ed.; American Association for Clinical Chemistry: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.; Hess, S.; Hotz, C.; Brown, K. The indicators of zinc status in the population: A review of the evidence. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99 (Suppl. 3), S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, K.; Stel, V.S.; Fraser, S.; De Goeij, M.C.; Caskey, F.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Jager, K.J. Translational research in nephrology: Chronic kidney disease prevention and public health. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, M.Q.; Hu, R.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.S.; Xian, S.X.; Lu, L. Effect of Zinc Supplementation on Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 15 Randomized Controlled Trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1024769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, G.; Felder, S. Trace elements in dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W.; Sandstead, H.H. Zinc requirements and the risks and benefits of zinc supplementation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2006, 20, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, N.; O’connor, J.M.; Maiani, G.; Cashman, K.D.; Secker, D.L.; Ferry, M.; Roussel, A.M.; Coudray, C. Importance of zinc in the elderly: The ZENITH study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59 (Suppl. 2), S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, A.; Firinu, D.; Zavattari, P.; Valera, P. Zinc Status and Autoimmunity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/whr/2002 (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Chandel, G.; Datta, K.; Datta, S.K. Detection of genomic changes in transgenic Bt rice populations through genetic fingerprinting using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP). GM Crops 2010, 1, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benoist, B.; Darnton-Hill, I.; Davidsson, L.; Fontaine, O.; Hotz, C. Conclusions of the Joint WHO/UNICEF/IAEA/IZiNCG Interagency Meeting on Zinc Status Indicators. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, S480–S484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, C.; Ramos, W. Análisis de la Situación de la Enfermedad renal Crónica en el Perú, 2015; Ministerio de Salud, Dirección General de Epidemiología: Lima, Peru, 2016. Available online: www.dge.gob.pe (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Esfahani, S.T.; Hamidian, M.R.; Madani, A.; Ataei, N.; Mohseni, P.; Roudbari, M.; Haddadi, M. Serum zinc and copper levels in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2006, 21, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazani, M.; Argani, H.; Rashtchizadeh, N.; Ghorbanihaghjo, A.; Hamdi, A.; Asghari Estiar, M.; Nezami, N. Effects of zinc supplementation on antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in hemodialysis patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Mak, R.; Mitsnefes, M.; White, C.; Moxey-Mims, M.; Warady, B.; Furth, S.L. Protein energy wasting in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, A.; Printza, N.; Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi, T.; Dotis, J.; Papachristou, F. Nutrition assessment of children with advanced stages of chronic kidney disease-A single center study. Hippokratia 2014, 18, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.S.; Chang, J.W.; Park, Y. Nutritional status predicts 10-year mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payahoo, L.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Mobasseri, M.; Bishak, Y.K.; Farrin, N.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Ostadrahimi, A. Effects of zinc supple- mentation on the anthropometric measurements, lipid profiles and fasting blood glucose in the healthy obese adults. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo, M.A.F. Effects of the Zinc Sulphate in a Girl with Chronic Renal Failure. Acad. J. Ped. Neonatol. 2016, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, R.S. The role of zinc in growth and cell proliferation. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1500S–1508S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, T.; Hojyo, S.; Bin, B.-H. Zinc Signal in Growth Control and Bone Disease; Zinc Signals in Cellular Functions and Disorders; Kambe, T., Fukada, T., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, B.; Soremark, R. Autoradiographic studies on the distribution of zinc-65 in mice. J. Nutr. 1968, 94, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurban, C.V.; Mederle, O. The OPG/RANKL system and zinc ions are promoters of bone remodeling by osteoblast proliferation in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2011, 52, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcantara, E.H.; Lomeda, R.A.; Feldmann, J.; Nixon, G.F.; Beattie, J.H.; Kwun, I.S. Zinc deprivation inhibits extracellular matrix calcification through decreased synthesis of matrix proteins in osteoblasts. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.J.; Leonard, M.B. Measuring nutritional status in children with chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, L.; Shaw, V. Nutrition in children with CRF and on dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.; Gipson, D.S.; Gillen, D.L.; Emerson, S.; Koepsell, T.; Sherrard, D.J.; Watkins, S.L.; Stehman-Breen, C. Anthropometric measures and risk of death in children with end-stage renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.; Fothergill, H.; Seuge, L.; Zaloszyc, A. Dialysis strategies to improve growth in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henningar, S.R.; Lieberman, H.R.; Fulgoni, V.L., III; McClung, J.P. Serum Zinc Concentrations in the US Population Are Related to Sex, Age, and Time of Blood Draw but Not Dietary or Supplemental Zinc. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-shazly, A.N.; El-hady Ibrahim, S.A.; El-Mashad, G.M.; Sabry, J.H.; Sherbini, N.S. Effect of zinc supplementation on body mass index and serum levels of zinc and leptin in pediatric hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2015, 8, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Thompson, S.; Kinniburgh, D.; Klarenbach, S.W.; Walsh, M.; Bello, A.K.; Faruque, L.; Field, C.; Manns, B.J.; et al. Trace element supplementation in hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Field, C.; Manns, B.; Thadhani, R.; Gill, J.; Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Trace elements in hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2009, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, M.; Rakhshanizadeh, F. Serum Trace Elements in Children with End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2019, 29, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.M.; Nosseer, A.; Abdallah, A.M.; Aboelmagd, Y.E. Evaluation of serum zinc and copper in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Pediatr. Biochem. 2012, 2, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.P.H. Assessment of zinc status. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1991, 50, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, J.; Dean, S.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Imdad, A. Bhutta Zinc supplementation for preventing mortality and morbidity, and promoting growth, in children aged 6 months to 12 years of age (protocol). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruz, M.; Castillo-Duran, C.; Lara, X.; Codoceo, J.; Rebolledo, A.; Atalah, E. A 14-mo zinc-supplementation trial in apparently healthy Chilean preschool children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.; Millward, D.J. Growth and zinc homeostasis in severely Zn-deficient rat. Br. J. Nutr. 1984, 52, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozbeh, J.; Sharifian, M.; Sagheb, M.M.; Shabani, S.; Hamidian Jahromi, A.; Afshariani, R.; Pakfetrat, M.; Salehi, O. Comment on: Does zinc supplementation affect inflammatory markers in hemodialysis patients? Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, T.; Brown, F.C.; Wallace, D.; Reid, C.J.D.; Sinha, M.D. Trace element and vitamin concentrations in paediatric dialysis patients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Khalili, H.; Vahedi, S.M.; Lessan-Pezeshki, M. Serum zinc concentrations in patients on hemodialysis and its relationship with anemia, parathyroid hormone concentrations and pruritis severity. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2010, 21, 641–645. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.S.; Beck, F.W.J.; Bao, B.; Fitzgerald, J.T.; Snell, D.C.; Steinberg, J.D.; Cardozo, L.J. Zinc supplementation decreases incidence of infections in the elderly: Effect of zinc on generation of cytokines and oxidative stress. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, M.; Samman, S. Zinc and Regulation of inflammatory cytokines: Implications for cardiometabolic disease. Nutrients 2012, 4, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Djafarian, K.; Mojtahed, A.; Varkaneh, H.K.; Shab-Bidar, S. The effect of zinc supplementation on plasma C-reactive protein concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.; Hingorani, S.; Gillen, D.L.; Sherrard, D.J.; Watkins, S.L.; Brandt, J.R.; Ball, A.; Stehman-Breen, C.O. Hypoalbuminemia and risk of death in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.S.; Lambert, C.; Hill, C.; Kitsen, J.; Shemin, D.G. Prevalence of protein malnutrition in children maintained on peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2002, 17, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Discovery of human ZnD: Its impact on human health and disease. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshanizadeh, F.; Esmaeeli, M. Serum zinc, copper, selenium, and lead levels in children with chronic renal failure. Rev. Clin. Med. 2014, 1, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, J.W.; Delves, H.T. Albumin bound and alpha 2-macroglobulin bound zinc concentrations in the sera of healthy adults. J. Clin. Pathol. 1984, 37, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.; McClain, C.J. The effect of severe zinc deficiency on serum levels of albumin, transferrin, and prealbumin in man. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, J.B.; Dao, M.C.; Hamer, D.H.; Kandel, R.; Brandeis, G.; Wu, D.; Dallal, G.E.; Jacques, P.F.; Schreiber, R.; Kong, E.; et al. Effect of zinc supplementationon serum zinc concentration and Tcell proliferation in nursing home elderly: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Smoak, B.L.; Patterson, K.Y.; LeMay, L.G.; Veillon, C.; Deuster, P.A. Biochemical indices of selected trace minerals in men: Effect of stress. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbo, M.D.; Lam, J. Zinc deficiency and its management in the pediatric population: A literature review and proposed etiologic classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashut, R.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Kinsella, J.; Vasilaki, A.T.; Talwar, D.; Duncan, A. The effect of the systemic inflammatory response on plasma zinc and selenium adjusted for albumin. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mashad, G.M.; El-Geballya, E.I.; El-Hefnawy, S.M.; El-Sayed, A.M. Effect of zinc supplementation on serum zinc and leptin levels in children on regular hemodialysis. Menoufia Med. J. 2018, 31, 664–670. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, F.; Wuhl, E.; Feneberg, R.; Mehls, O.; Scharer, K. Assessment of body composition in children with CRF. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2000, 14, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Leonard, M.B.; Zemel, B.; Kalkwarf, H.; Foster, B. Interpretation of Body Mass Index in Children with CK. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis, H.; Ndhlovu, P.; Mduluza, T.; Kaondera, K.; Sandström, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Vennervald, B.J.; Christensen, N.O. The impact of zinc supplementation on growth and body composition: A randomized, controlled trial among rural Zimbabwean schoolchildren. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 51, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, J.E.; Lopez de Romana, D.; Penny, M.E.; Van Loan, M.D.; Brown, K.H. Additional zinc delivered in a liquid supplement, but not in a fortified porridge, increased fat-free mass accrual among young Peruvian children with mild-to-moderate stunting. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahi, Z.; Fozouni, F.; Bondarianzadeh, D. Oral zinc supplementation positively affects linear growth, but not weight, in children 6–24 months of age. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.H.; Peerson, J.M.; Baker, S.K.; Hess, S.Y. Preventive zinc supplementation among infants, pre-schoolers, and older prepubertal children. Food Nutr. Bull. 2009, 30, s12–s40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imdad, A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Effect of preventive zinc supplementation on linear growth in children under 5 years of age in developing countries: A meta-analysis of studies for input to the lives saved tool. BMC Public Health 2011, 11 (Suppl. 3), S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Zinc Nutrition Consultative Group (IZiNCG); Brown, K.H.; Rivera, J.A.; Bhutta, Z.; Gibson, R.S.; King, J.C.; Lönnerdal, B.; Ruel, M.T.; Sandtröm, B.; Wasantwisut, E.; et al. Assessment of the risk of zinc deficiency in populations and options for its control. Food Nutr. Bull. 2004, 25, S99–S203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Alarcon, M.; Reyes-Pérez, A.; Lopez-Garcia, H.; Palomares-Bayo, M.; Olalla-Herrera, M.; Lopez-Martinez, M.C. Longitudinal study of serum zinc and copper levels in hemodialysis patients and their relation to biochemical markers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2006, 113, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohinata, K.; Takemoto, M.; Kawanago, M.; Fushimi, S.; Shirakawa, H.; Goto, T.; Asakawa, A.; Komai, M. Orally administrated zinc increase food intake via vagal stimulation in rats. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, H.; Uyanik, F.; Inanç, N.; Erdem, O. Serum zinc, plasma ghrelin, leptin levels, selected biochemical parameters and nutritional status in malnourished hemodialysis patients. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 127, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority Committee on Food. Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for Vitamins and Minerals. Scientific February 2006. Parma, Italy. Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/efsa_rep/blobserver_assets/ndatolerableuil.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2019).
| Assessments | Group A (n = 24) | Group B (n = 24) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 13.5 ± 3.2 | 12 ± 4.7 | 0.206 |
| Sex (female) | 14 (58.3%) | 9 (37.5%) | 0.155 |
| Anthropometric | |||
| Weight-for-age (kg) | 32.3 ± 9.9 | 27.5 ± 12.8 | 0.146 |
| Height-for-age (cm) | 135 ± 18.3 | 126.5 ± 23.6 | 0.167 |
| Weight-for-height | 33.6 ± 12.6 | 28.9 ± 9.9 | 0.189 |
| Body mass index-for-age (kg/cm2) | 17.4 ± 2.8 | 16.2 ± 2.7 | 0.129 |
| Nutritional index | 77.2 ± 15.2 | 73.9 ± 13.6 | 0.427 |
| Mid-arm circumference (mm) | 19.7 ± 3.6 | 17.9 ± 3.4 | 0.078 |
| Triceps skinfold thickness (mm) | 9 ± 4.7 | 7.4 ± 2.8 | 0.156 |
| Mid-arm muscle area (mm3) | 23.1 ± 8.8 | 20.9 ± 9.1 | 0.417 |
| Mid-arm fat mass (mm3) | 8.4 ± 5.4 | 6 ± 2.4 | 0.066 |
| Growth rate (cm/year) | 2.6 ± 2.6 | 3.9 ± 3.4 | 0.229 |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | −2.3 ± 1.1 | −2.6 ± 1 | 0.270 |
| Height-for-age Z-score | −3.3 ± 1.8 | −3.4 ± 1.5 | 0.761 |
| Weight-for-height Z score | 0.8 ± 2.1 | −1 ± 2.9 | 0.062 |
| Body mass index Z-score | −0.8 ± 1.2 | −1.2 ± 1.1 | 0.280 |
| BMI-height-age Z-score | −0.15 ± 0.1 | −0.11 ± 0.6 | 0.744 |
| Biochemical analysis | |||
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.48 (0.58) | 3.58 (0.63) | 0.610 |
| C-reactive protein (U/L) | 12.2 (20.4) | 20 (24.9) | 0.356 |
| Serum zinc concentration (µg/dL) | 74.9 (14.9) | 75.1 (16.5) | 0.962 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |||
| Undernutrition | 8.3% (2/24) | 12.5% (3/24) | 0.500 |
| Underweight | 66.7% (16/24) | 87.5% (21/24) | 0.084 |
| Stunting | 75% (18/24) | 91.7% (22/24) | 0.122 |
| Wasting | 7.2% (1/14) | 0% (0/16) | 1.000 |
| Obesity | 4.2% (1/48) | 0% (0/24) | 1.000 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 44.4% (8/18) | 30% (6/20) | 0.279 |
| High C-reactive protein | 33.3% (5/15) | 46.7% (7/15) | 0.355 |
| Hypozincemia | 36.8% (7/19) | 44.4% (8/18) | 0.446 |
| Causes | Therapy Zinc Sulphate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | % | Group B | % | Total | % | |
| Glomerulonephritis | 9 | 18.75 | 9 | 18.75 | 12 | 37.50 |
| Obstructive uropathy | 6 | 12.5 | 7 | 14.58 | 13 | 27.08 |
| Chronic interstitial nephritis | 6 | 12.5 | 4 | 8.33 | 10 | 20.83 |
| Unknown cause | 3 | 6.25 | 4 | 8.33 | 7 | 14.58 |
| Total | 24 | 50 | 24 | 50 | 48 | 100 |
| Assessments | n | Pre-Treatment | n | Post-Treatment | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric | |||||
| Weight-for-age (kg) | 48 | 29.9 ± 11.6 | 35 | 32.6 ± 9.5 | 0.015 * |
| Height-for-age (cm) | 48 | 130.8 ± 21.3 | 35 | 137.6 ± 14.7 | 0.000 * |
| Weight-for-height | 42 | 31.3 ± 11.5 | 27 | 34.5 ± 11.1 | 0.000 * |
| Mid-arm circumference (cm) | 48 | 18.8 ± 3.6 | 35 | 20 ± 3.3 | 0.035 * |
| Triceps skinfold thickness (mm) | 45 | 8.2 ± 3.9 | 35 | 9.3 ± 3.6 | 0.093 |
| Body mass index (kg/cm2) | 47 | 16.7 ± 2.6 | 35 | 16.8 ± 2.5 | 0.543 |
| Nutritional index | 48 | 75.5 ± 14.3 | 35 | 72.53 ± 14.1 | 0.322 |
| Mid-arm muscle area (mm3) | 44 | 22 ± 8.8 | 35 | 24.3 ± 8.1 | 0.050 |
| Mid-arm fat mass (mm3) | 44 | 7.2 ± 4.3 | 35 | 8.9 ± 4.9 | 0.028 * |
| Growth rate (cm/year) | 32 | 3.2 ± 2.9 | 34 | 2.3 ± 4.1 | 0.260 |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | 48 | −2.43 ± 1.06 | 35 | −2.6 ± 1.1 | 0.036 * |
| Height-for-age Z-score | 48 | −3.34 ± 1.6 | 35 | −3.48 ± 1.72 | 0.012 * |
| Weight-for-height Z score | 30 | −0.15 ± 2.7 | 20 | 0.08 ± 1.36 | 0.469 |
| Body mass index Z-score | 48 | −1 ± 1.1 | 35 | −1.2 ± 0.9 | 0.411 |
| BMI-height-age Z-score | 35 | −0.13 ± 0.4 | 35 | −0.21 ± 0.3 | 0.323 |
| Biochemical analysis | |||||
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 23 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 23 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 0.915 |
| C-reactive protein (U/L) | 11 | 22.4 ± 28.1 | 11 | 9.3 ± 7.5 | 0.157 |
| Serum zinc concentration (µg/dL) | 37 | 75 ± 15.5 | 24 | 73.5 ± 17.4 | 0.330 |
| Comorbidities (n, %) | |||||
| Undernutrition | 48 | 5 (10.4) | 35 | 8 (22.9) | 0.083 |
| Underweight | 48 | 37 (77.1) | 35 | 28 (80) | 0.571 |
| Stunting | 48 | 40 (83.3) | 35 | 29 (82.9) | 0.571 |
| Wasting | 30 | 1 (3.33) | 20 | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Obesity | 48 | 1 (2.1) | 34 | 1 (2.9) | 1.000 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 38 | 14 (36.8) | 24 | 9 (37.5) | 0.747 |
| High C-reactive protein | 30 | 12 (40) | 11 | 6 (54.5) | 0.588 |
| Hypozincemia | 37 | 15 (40.5) | 24 | 10 (41.7) | 0.770 |
| 2º – 1º Assessments | Z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric | ||
| Weight-for-age | −1.02 | 0.305 |
| Height-for-age | −4.62 | 0.000 * |
| Weight-for-height | −4.46 | 0.000 * |
| Mid-arm circumference | −0.92 | 0.355 |
| Triceps skinfold thickness | −1.74 | 0.080 |
| Body mass index | −2.17 | 0.030 * |
| Nutritional index | −1.80 | 0.071 |
| Mid-arm muscle area | −0.61 | 0.537 |
| Mid-arm fat mass | −1.46 | 0.144 |
| Growth rate | −0.11 | 0.912 |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | −2.10 | 0.036 * |
| Height-for-age Z-score | −2.52 | 0.012 * |
| Weight-for-height Z score | −0.14 | 0.891 |
| Body mass index Z-score | −0.82 | 0.411 |
| BMI-height-age Z-score | −0.33 | 0.033 * |
| Biochemical analysis | ||
| Serum albumin | −0.00 | 1.000 |
| C-reactive protein | −1.89 | 0.059 |
| Serum zinc concentration | −0.97 | 0.330 |
| Assessments | Group A | Group B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | p-Value | Z | p-Value | |
| Anthropometric | ||||
| Weight-for-age | −1.13 | 0.257 | −0.37 | 0.705 |
| Height-for-age | −3.18 | 0.001 * | −3.41 | 0.001 * |
| Weight-for-height | −3.06 | 0.002 * | −3.24 | 0.001 * |
| Mid-arm circumference | −2.04 | 0.041 * | −0.99 | 0.319 |
| Triceps skinfold thickness | −1.19 | 0.234 | −1.31 | 0.187 |
| Nutritional index | −2.23 | 0.025 * | −0.63 | 0.527 |
| Body mass index | −2.62 | 0.009 * | −0.43 | 0.660 |
| Mid-arm muscle area | 0.00 | 1.000 | −0.55 | 0.581 |
| Mid-arm fat mass | 0.00 | 1.000 | −1.71 | 0.086 |
| Growth rate | −0.12 | 0.905 | −0.23 | 0.811 |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | −2.03 | 0.043 * | −1.02 | 0.306 |
| Height-for-age Z-score | −1.48 | 0.140 | −2.16 | 0.031 * |
| Weight-for-height Z score | −0.53 | 0.594 | −0.31 | 0.721 |
| Body mass index Z-score | −0.44 | 0.660 | −1.52 | 0.129 |
| BMI-height-age Z-score | −1.92 | 0.022 * | −1.19 | 0.210 |
| Biochemical analysis | ||||
| Serum albumin | 0.00 | 1.000 | 0.00 | 1.000 |
| C-reactive protein | −1.34 | 0.180 | −1.41 | 0.157 |
| Serum zinc concentration | −1.16 | 0.247 | −0.16 | 0.875 |
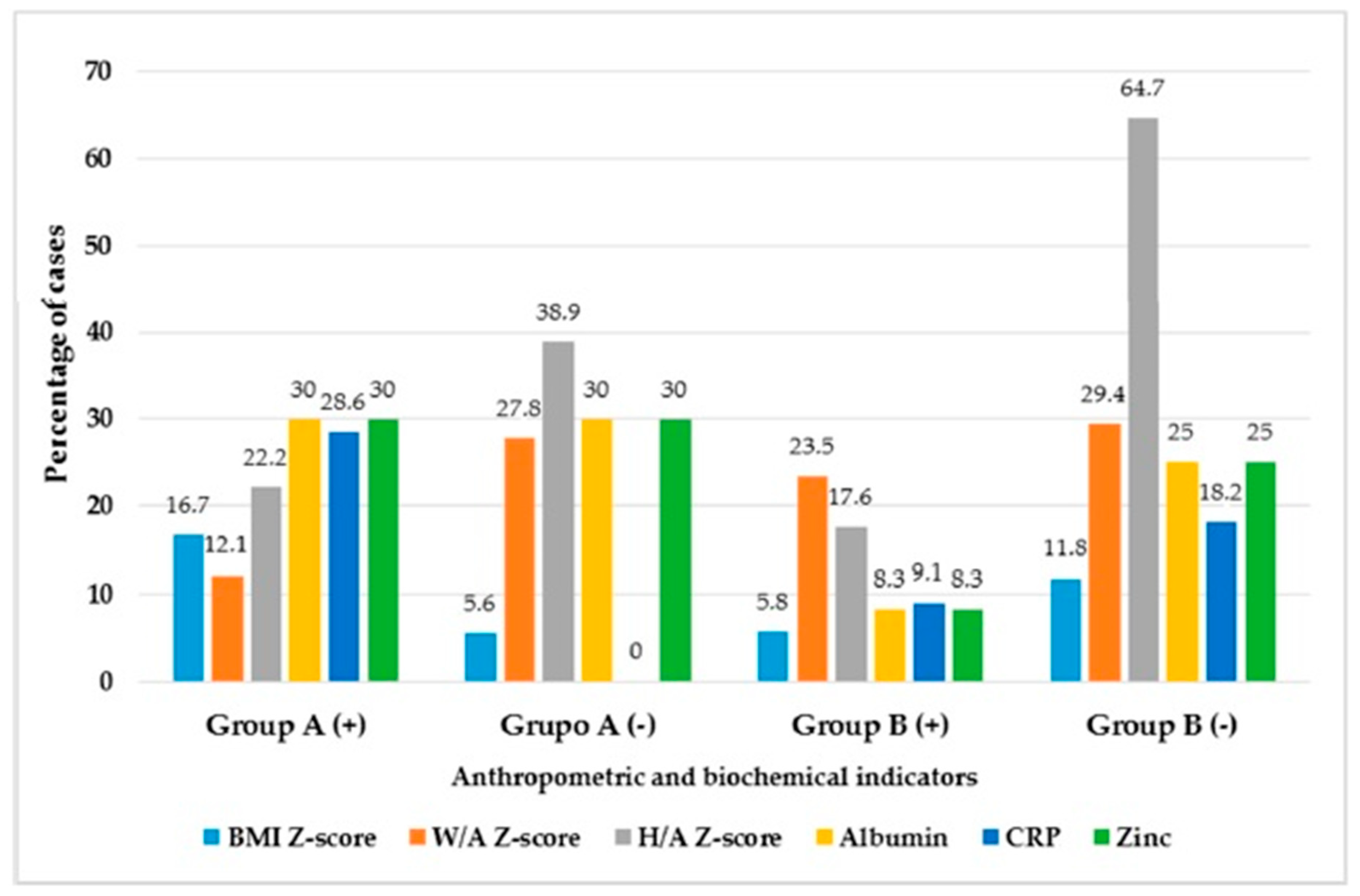
| Nutritional Assessments | Group A (+) | Group A (−) | Group B (+) | Group B (−) | X2 p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body mass index Z-score | 16.7 * | 5.6 | 5.8 | 11.8 * | 0.020 |
| Weight-for-age Z-score | 12.1 | 27.8 | 23.5 | 29.4 | 0.243 |
| Height-for-age Z-score | 22.2 | 38.9 | 17.6 | 64.7 * | 0.074 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 30 * | 30 * | 8.3 | 25 | 0.032 |
| High C-protein reactive | 28.6 * | 0 | 9.1 | 18.2 * | <0.0001 |
| Hypozincemia | 30 * | 30 * | 8.3 | 25 | 0.032 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Ayala-Macedo, G.; Sakihara, G.; Peralta, S.; Almaraz-Gómez, A.; Barrado, E.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112671
Escobedo-Monge MF, Ayala-Macedo G, Sakihara G, Peralta S, Almaraz-Gómez A, Barrado E, Marugán-Miguelsanz JM. Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112671
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscobedo-Monge, Marlene Fabiola, Guido Ayala-Macedo, Graciela Sakihara, Silvia Peralta, Ana Almaraz-Gómez, Enrique Barrado, and J. M. Marugán-Miguelsanz. 2019. "Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Trial" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112671
APA StyleEscobedo-Monge, M. F., Ayala-Macedo, G., Sakihara, G., Peralta, S., Almaraz-Gómez, A., Barrado, E., & Marugán-Miguelsanz, J. M. (2019). Effects of Zinc Supplementation on Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients, 11(11), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112671