Dietary Protein Intake, Protein Energy Wasting, and the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis from the KNOW-CKD Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurement
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Missing Values
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argiles, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borst, J.G. Protein katabolism in uraemia; effects of protein-free diet, infections, and blood-transfusions. Lancet 1948, 1, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, S.; Maggiore, Q. A Low-Nitrogen Diet with Proteins of High Biological Value for Severe Chronic Uraemia. Lancet 1964, 1, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, B.A.; Branley, P.; Bulfone, L.; Collins, J.F.; Craig, J.C.; Fraenkel, M.B.; Harris, A.; Johnson, D.W.; Kesselhut, J.; Li, J.J.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of early versus late initiation of dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosansky, S.J.; Cancarini, G.; Clark, W.F.; Eggers, P.; Germaine, M.; Glassock, R.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Harris, D.; Hwang, S.J.; Imperial, E.B.; et al. Dialysis initiation: What’s the rush? Semin. Dial. 2013, 26, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunori, G.; Viola, B.F.; Parrinello, G.; De Biase, V.; Como, G.; Franco, V.; Garibotto, G.; Zubani, R.; Cancarini, G.C. Efficacy and safety of a very-low-protein diet when postponing dialysis in the elderly: A prospective randomized multicenter controlled study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; Mitch, W.E. Low-protein diets in chronic kidney disease: Are we finally reaching a consensus? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: The role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, L.E.; Smadel, J.E. The Effect of Dietary Protein on the Course of Nephrotoxic Nephritis in Rats. J. Exp. Med. 1939, 70, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moore, L.W.; Tortorici, A.R.; Chou, J.A.; St-Jules, D.E.; Aoun, A.; Rojas-Bautista, V.; Tschida, A.K.; Rhee, C.M.; Shah, A.A.; et al. North American experience with Low protein diet for Non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahr, S.; Levey, A.S.; Beck, G.J.; Caggiula, A.W.; Hunsicker, L.; Kusek, J.W.; Striker, G. The effects of dietary protein restriction and blood-pressure control on the progression of chronic renal disease. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Kopple, J.D.; Wang, X.; Beck, G.J.; Collins, A.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Greene, T.; Levey, A.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Effect of a very low-protein diet on outcomes: Long-term follow-up of the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of protein-energy wasting in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Reconciling low protein intake with nutritional therapy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, Y.; Nakao, T.; Murai, S.; Okada, T.; Matsumoto, H. Diagnosis and Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting and Its Association with Mortality in Japanese Haemodialysis Patients. Nephrology 2017, 22, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noce, A.; Vidiri, M.F.; Marrone, G.; Moriconi, E.; Bocedi, A.; Capria, A.; Rovella, V.; Ricci, G.; De Lorenzo, A.; Di Daniele, N. Is low-protein diet a possible risk factor of malnutrition in chronic kidney disease patients? Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple, J.D.; Greene, T.; Chumlea, W.C.; Hollinger, D.; Maroni, B.J.; Merrill, D.; Scherch, L.K.; Schulman, G.; Wang, S.R.; Zimmer, G.S. Relationship between nutritional status and the glomerular filtration rate: Results from the MDRD study. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1688–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; Laville, M. Low protein diets for chronic kidney disease in non diabetic adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 3, CD001892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezu, U.; Kamiyama, H.; Kondo, Y.; Sakuma, M.; Morimoto, T.; Ueda, S. Effect of low-protein diet on kidney function in diabetic nephropathy: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneata, L.; Stancu, A.; Dragomir, D.; Stefan, G.; Mircescu, G. Ketoanalogue-Supplemented Vegetarian Very Low-Protein Diet and CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, M.; Lombardi, C.; Chiricone, D.; De Santo, N.G.; Zanchetti, A.; Bilancio, G. Protein intake and kidney function in the middle-age population: Contrast between cross-sectional and longitudinal data. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herber-Gast, G.M.; Biesbroek, S.; Verschuren, W.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.; Spijkerman, A.M. Association of dietary protein and dairy intakes and change in renal function: Results from the population-based longitudinal Doetinchem cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, J.M.; Aragaki, A.K.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Tinker, L.F.; Cauley, J.A.; Ensrud, K.E.; Jackson, R.D.; Prentice, R.L. Higher biomarker-calibrated protein intake is not associated with impaired renal function in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, R.; Lipworth, L.; Cavanaugh, K.L.; Young, B.A.; Tucker, K.L.; Carithers, T.C.; Taylor, H.A.; Correa, A.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Ikizler, T.A. Protein Intake and Long-term Change in Glomerular Filtration Rate in the Jackson Heart Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.; Yuan, W.L.; Haymann, J.P.; Flamant, M.; Houillier, P.; Thervet, E.; Boffa, J.J.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Froissart, M.; Banki, L.; et al. Association of a Low-Protein Diet With Slower Progression of CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.H.; Park, S.K.; Park, H.C.; Chin, H.J.; Chae, D.W.; Choi, K.H.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, T.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. KNOW-CKD (KoreaN cohort study for Outcome in patients With Chronic Kidney Disease): Design and methods. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 1471–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.A.; Cogswell, M.E.; Campbell, N.R.; Nowson, C.A.; Legetic, B.; Hennis, A.J.; Patel, S.M. Accuracy and Usefulness of Select Methods for Assessing Complete Collection of 24-Hour Urine: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Okamura, T.; Miura, K.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueshima, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Hashimoto, T. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a casual urine specimen. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, B.J.; Steinman, T.I.; Mitch, W.E. A method for estimating nitrogen intake of patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1985, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospective Studies Collaboration; Whitlock, G.; Lewington, S.; Sherliker, P.; Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 373, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.M.; Gallagher, D.; Nelson, M.E.; Matthews, D.E.; Heymsfield, S.B. Total-body skeletal muscle mass: Evaluation of 24-h urinary creatinine excretion by computerized axial tomography. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.N. Stable and efficient multiple smoothing parameter estimation for generalized additive models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2004, 99, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Monno, I.; Koya, D. A Low-Protein Diet for Diabetic Kidney Disease: Its Effect and Molecular Mechanism, an Approach from Animal Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Vigotti, F.N.; Leone, F.; Capizzi, I.; Daidola, G.; Cabiddu, G.; Avagnina, P. Low-protein diets in CKD: How can we achieve them? A narrative, pragmatic review. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B.; Cialkowska-Rysz, A.; Gluba-Brzozka, A. The Effect of Diet on the Survival of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Ventrella, F.; Capizzi, I.; Vigotti, F.N.; Mongilardi, E.; Grassi, G.; Loi, V.; Cabiddu, G.; Avagnina, P.; Versino, E. Low-Protein Diets in Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Patients: Are They Feasible and Worth the Effort? Nutrients 2016, 8, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, B.R.; Di Micco, L.; Marzocco, S.; De Simone, E.; De Blasio, A.; Sirico, M.L.; Nardone, L.; UBI Study Group. Very Low-Protein Diet (VLPD) Reduces Metabolic Acidosis in Subjects with Chronic Kidney Disease: The “Nutritional Light Signal” of the Renal Acid Load. Nutrients 2017, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, M.; Zingone, F.; Lombardi, C.; Cavallo, P.; Zanchetti, A.; Bilancio, G. Population-based dose-response curve of glomerular filtration rate to dietary protein intake. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, M.; Neelemaat, F.; Struijk-Wielinga, T.; Weijs, P.J.; van Jaarsveld, B.C. Physical performance and protein-energy wasting in patients treated with nocturnal haemodialysis compared to conventional haemodialysis: Protocol of the DiapriFIT study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, K.B.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Yoo, T.H.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.H.; et al. Serum adiponectin and protein-energy wasting in predialysis chronic kidney disease. Nutrition 2017, 33, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.W.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Scott Parrott, J.; Rigassio-Radler, D.; Mandayam, S.; Jones, S.L.; Mitch, W.E.; Osama Gaber, A. The mean dietary protein intake at different stages of chronic kidney disease is higher than current guidelines. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
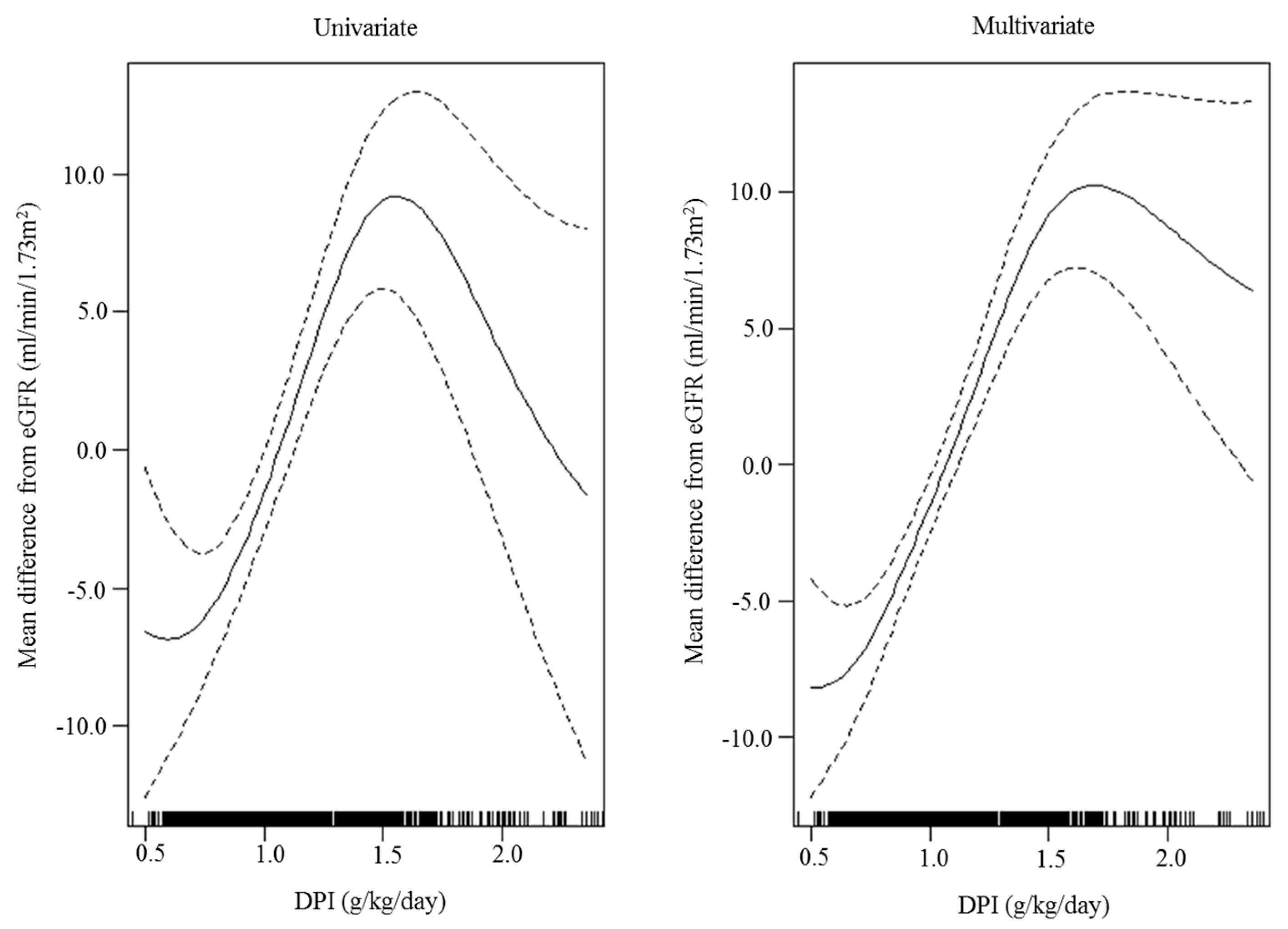
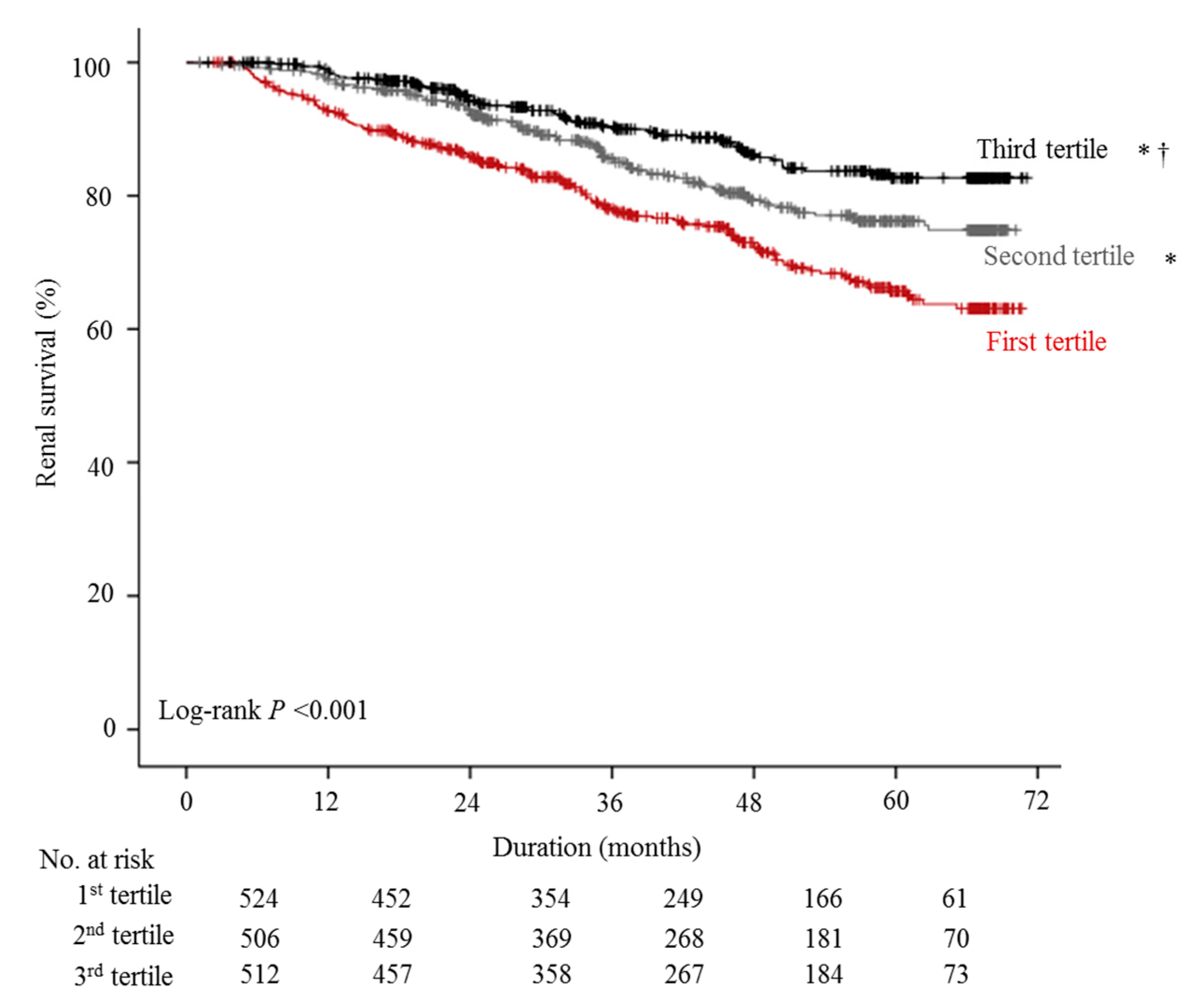
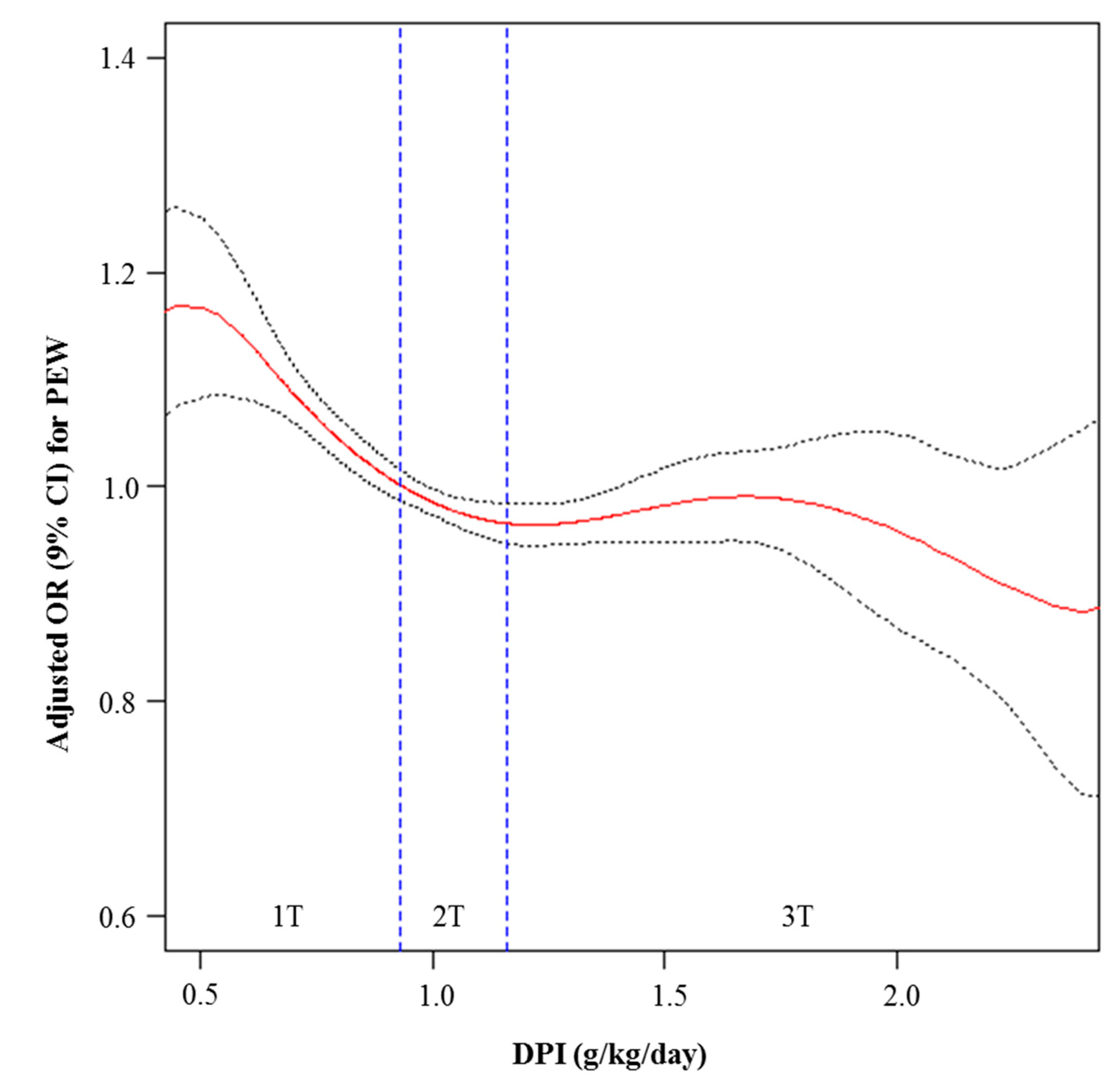
| Tertile of DPI | p-trend | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1T (n = 533) | 2T (n = 512) | 3T (n = 527) | ||
| Age (years) | 54.1 ± 12.0 | 54.0 ± 12.1 | 54.7 ± 12.0 | 0.35 |
| Male sex (%) | 58.9 | 61.3 | 69.1 *,† | 0.001 |
| Current smoking (%) | 15.6 | 16.8 | 14.1 | 0.50 |
| Alcohol drinking (%) | 39.9 | 43.7 | 53.7 *,† | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (%) | 94.9 | 94.9 | 95.6 | 0.60 |
| Diabetes (%) | 24.7 | 23.7 | 25.5 | 0.78 |
| Cause of CKD | ||||
| DMN (%) | 25.0 | 23.0 | 21.1 | 0.14 |
| HN (%) | 18.6 | 21.9 | 21.9 | 0.19 |
| GN (%) | 34.1 | 32.4 | 32.1 | 0.48 |
| Others (%) | 22.3 | 22.7 | 24.9 | 0.32 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 9.9 ± 5.9 | 9.9 ± 5.3 | 9.5 ± 4.9 | 0.19 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 175.5 ± 109.7 | 154.2 ± 86.3 * | 132.9 ± 67.4 *,† | <0.001 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 49.2 ± 30.9 | 53.9 ± 30.5 * | 60.8 ± 29.3 *,† | <0.001 |
| UPCR (g/g Cr) | 0.54 (0.17–1.63) | 0.45 (0.12–1.40) * | 0.40 (0.12–1.03) * | 0.001 |
| Advanced CKD (%) | 55.3 | 47.7 * | 36.6 *,† | <0.001 |
| DPI (g/kg/day) | 0.78 ± 0.12 | 1.04 ± 0.07 * | 1.48 ± 0.41 *,† | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) | 11.1 ± 4.8 | 11.9 ± 5.1 * | 12.3 ± 5.3 * | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.4 ± 3.2 | 24.6 ± 3.2 * | 25.4 ± 3.1 *,† | <0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.9 ± 1.8 | 6.1 ± 2.2 | 6.1 ± 1.9 | 0.17 |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 41.6 ± 4.5 | 42.3 ± 3.8 * | 42.5 ± 3.7 * | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.9 | 0.27 |
| Estimated SMM (kg) | 24.8 ± 5.6 | 28.0 ± 6.2 * | 32.0 ± 7.8 *,† | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.4 ± 2.0 | 13.0 ± 2.0 * | 13.5 ± 1.9 *,† | <0.001 |
| hsCRP (nmol/L) | 5.7 (1.9–16.2) | 5.3 (1.9–14.1) | 6.7 (2.4–16.2) | 0.39 |
| Univariate | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| DPI tertile | ||||||
| Second tertile vs. first tertile | 0.626 (0.482–0.814) | <0.001 | 0.765 (0.576–1.016) | 0.07 | 0.810 (0.600–1.094) | 0.17 |
| Third tertile vs. first tertile | 0.412 (0.306–0.556) | <0.001 | 0.685 (0.495–0.948) | 0.02 | 0.737 (0.516–1.054) | 0.10 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | - | - | - | - | 1.013 (0.966–1.062) | 0.59 |
| Estimated SMM (kg) | - | - | - | - | 0.989 (0.961–1.019) | 0.48 |
| Cholesterol < 3.8 mmol/L (yes vs. no) | - | - | - | - | 1.030 (0.777–1.364) | 0.84 |
| Serum albumin < 40.0 g/L (yes vs. no) | - | - | - | - | 1.438 (1.051–1.969) | 0.02 |
| Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| DPI tertile (vs. first tertile) | ||||||||
| Second tertile | 0.812 (0.603–1.092) | 0.17 | 0.763 (0.572–1.018) | 0.07 | 0.792 (0.591–1.063) | 0.12 | 0.828 (0.620–1.105) | 0.20 |
| Third tertile | 0.714 (0.511–0.998) | 0.05 | 0.684 (0.491–0.952) | 0.02 | 0.705 (0.506–0.983) | 0.04 | 0.725 (0.523–1.006) | 0.05 |
| No. of PEW components (vs. 0) | ||||||||
| 1 | 1.029 (0.745–1.420) | 0.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 0.913 (0.619–1.346) | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ≥3 | 1.800 (1.181–2.742) | 0.01 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PEW components ≥1 (yes vs. no) | - | - | 1.077 (0.799–1.452) | 0.63 | - | - | - | - |
| PEW components ≥2 (yes vs. no) | - | - | - | - | 1.131 (0.860–1.487) | 0.38 | - | - |
| PEW (yes vs. no) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.835 (1.297–2.596) | 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.H.; Chung, W.; Park, S.K.; Choi, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Oh, K.-H. Dietary Protein Intake, Protein Energy Wasting, and the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis from the KNOW-CKD Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010121
Lee SW, Kim Y-S, Kim YH, Chung W, Park SK, Choi KH, Ahn C, Oh K-H. Dietary Protein Intake, Protein Energy Wasting, and the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis from the KNOW-CKD Study. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sung Woo, Yong-Soo Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Wookyung Chung, Sue K. Park, Kyu Hun Choi, Curie Ahn, and Kook-Hwan Oh. 2019. "Dietary Protein Intake, Protein Energy Wasting, and the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis from the KNOW-CKD Study" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010121
APA StyleLee, S. W., Kim, Y.-S., Kim, Y. H., Chung, W., Park, S. K., Choi, K. H., Ahn, C., & Oh, K.-H. (2019). Dietary Protein Intake, Protein Energy Wasting, and the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis from the KNOW-CKD Study. Nutrients, 11(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010121






