25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Its Association with Sleep Duration in Chinese Schoolchildren
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Experimental Design
2.2. Blood Collection and Anthropometrics Measurement
2.3. Biochemistry Analysis
2.4. Sleep Duration and Healt and h-Related Behavioral Factors
2.5. Statistical Analysis
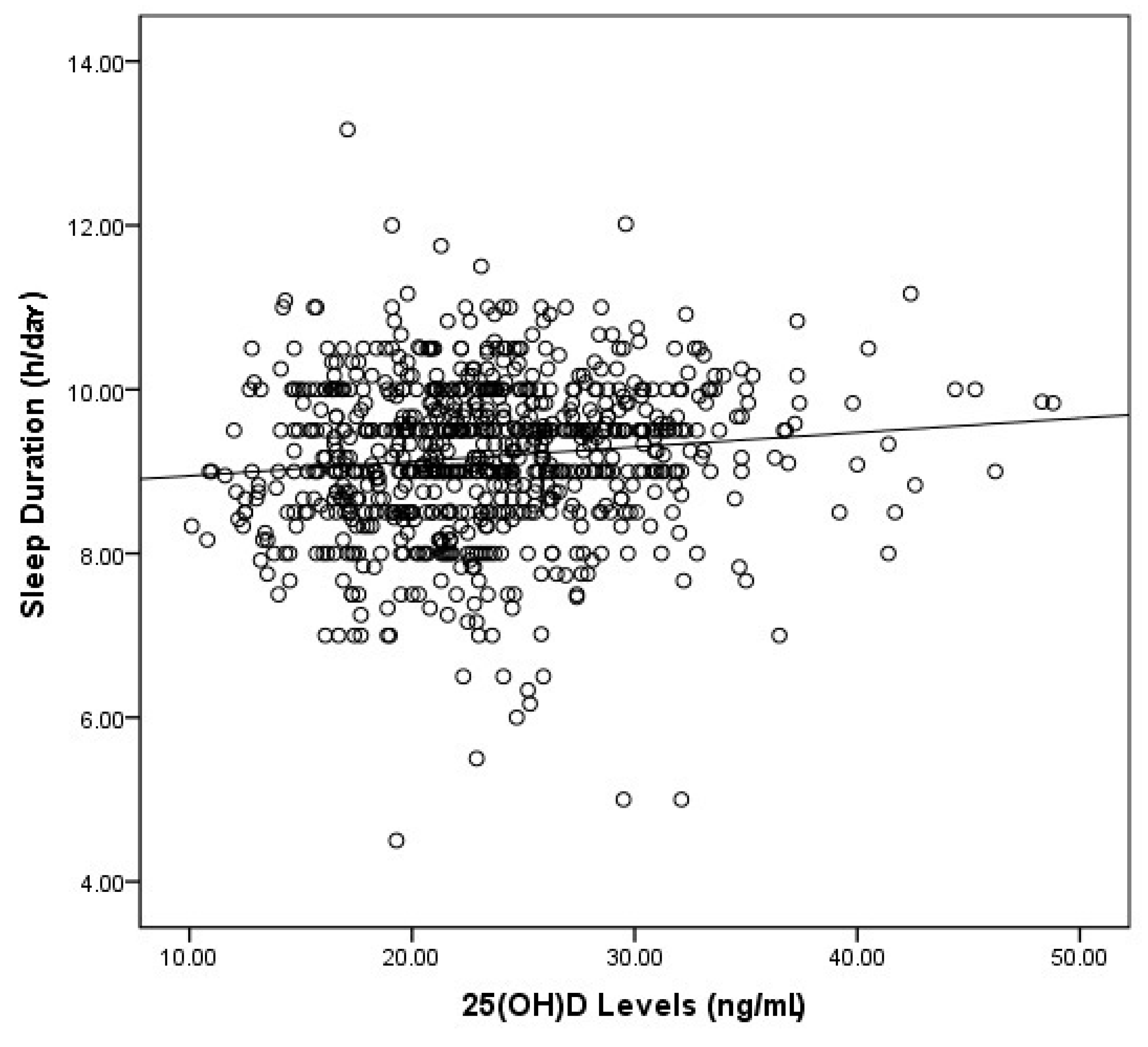
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.Y.; Wang, E.K.; Jeng, Y.J. Adequate sleep among adolescents is positively associated with health status and health-related behaviors. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zee, P.C.; Turek, F.W. Sleep and health: Everywhere and in both directions. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1686–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.L.; Larkin, E.K.; Patel, S.; Berger, N.A.; Redline, S.; Li, L. Short duration of sleep increases risk of colorectal adenoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshiko, K.; Eiji, Y.; Hiroki, S.; Yasuaki, S.; Mariko, K.; Eisaku, O.; Reiko, K. Short Sleep Duration and Poor Sleep Quality Increase the Risk of Diabetes in Japanese Workers with No Family History of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O. Short sleep and obesity: Are poor sleep, chronic stress, and unhealthy behaviors the link? Sleep 2008, 31, 1203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Keadle, S.K.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Matthews, C.E. Sleep duration and total and cause-specific mortality in a large US cohort: Interrelationships with physical activity, sedentary behavior, and body mass index. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.H.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, T.; Cui, J.; Xu, G.Z. Associations between sleep duration and physical activity and dietary behaviors in Chinese adolescents: Results from the Youth Behavioral Risk Factor Surveys of 2015. Sleep Med. 2017, 37, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaldone, A.; Honig, J.C.; Byrne, M.W. Sleepless in America: Inadequate sleep and relationships to health and well-being of our nation’s children. Pediatrics 2007, 119 (Suppl. 1), S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, J.; Group, A.S.W.; Adolescence, C.O. Insufficient sleep in adolescents and young adults: An update on causes and consequences. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmy, P.; Clausson, E.K.; Nyberg, P.; Jakobsson, U. Insufficient sleep is associated with obesity and excessive screen time amongst ten-year-old children in Sweden. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2018, 39, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D: A D-Lightful health perspective. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66 (Suppl. 2), S182–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Chen, T.C. Vitamin D deficiency: A worldwide problem with health consequences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1080S–1086S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashman, K.D.; Sheehy, T.; O’Neill, C.M. Is vitamin D deficiency a public health concern for low middle income countries? A systematic literature review. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Crocombe, S.; McGrath, M.; Berry, J.L.; Mughal, M.Z. Hypovitaminosis D among healthy adolescent girls attending an inner city school. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Wen, H.K.; Tao, H.Q.; Zhang, X.W. Vitamin D status among infants, children, and adolescents in southeastern China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2016, 17, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Pei, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, H.; Cheng, X.; Fang, F.; Sun, B.; Xiao, H.; Li, N. Low levels of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of metabolic syndrome in China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 13790–13796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Santos, M.; Costa, P.R.; Assis, A.M.; Santos, C.A.; Santos, D.B. Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, C.S.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C.; Billings, L.K.; Meigs, J.B. Association of vitamin D deficiency with incidence of type 2 diabetes in high-risk Asian subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.J.; Meenagh, G.K.; Bickle, I.; Lee, A.S.; Curran, E.S.; Finch, M.B. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with anxiety and depression in fibromyalgia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, C.; Pilz, S.; Obermayerpietsch, B.; Verduijn, M.; Tomaschitz, A.; Krane, V.; Espe, K.; Dekker, F.; Brandenburg, V.; März, W. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with sudden cardiac death, combined cardiovascular events, and mortality in haemodialysis patients. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovezan, R.D.; Hirotsu, C.; Feres, M.C.; Cintra, F.D.; Andersen, M.L.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D. Obstructive sleep apnea and objective short sleep duration are independently associated with the risk of serum vitamin D deficiency. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertisch, S.M.; Sillau, S.; de Boer, I.H.; Szklo, M.; Redline, S. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration and Sleep Duration and Continuity: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Sleep 2014, 38, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiue, I. Low vitamin D levels in adults with longer time to fall asleep: US NHANES, 2005–2006. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 5074–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunduz, S.; Kosger, H.; Aldemir, S.; Akcal, B.; Tevrizci, H.; Hizli, D.; Celik, H.T. Sleep deprivation in the last trimester of pregnancy and inadequate vitamin D: Is there a relationship? J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, A.A.; Schlicker, S.A.; Suitor, C.W. Dietary Reference Intakes: The new basis for recommendations for calcium and related nutrients, B vitamins, and choline. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1998, 98, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lau, A.; Ali, G.; Huang, P.; Geng, Y.; Xu, T.; Shan, G. Sleep duration associated with body mass index among Chinese adults. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Owens, J.A.; Hu, C. The association between sleep and injury among school-aged children in rural China: A case-control study. Sleep Med. 2008, 9, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Gill, T.K.; Tuckerman, J.; Adams, R.; Martin, J. Short sleep duration and obesity among Australian children. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.E.; Goodwin, J.L.; Parthasarathy, S.; Sherrill, D.L.; Vana, K.D.; Drescher, A.A.; Quan, S.F. Longitudinal Association between Short Sleep, Body Weight, and Emotional and Learning Problems in Hispanic and Caucasian Children. Sleep 2011, 34, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricciani, L.; Olds, T.; Petkov, J. In search of lost sleep: Secular trends in the sleep time of school-aged children and adolescents. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xian, Y.; Min, M.; Dai, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, D. Association of 25-hydroxyvitamin D Status with obesity as well as blood glucose and lipid concentrations in children and adolescents in China. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolassa, W.; Whiting, S.J.; Tefera, B. Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Overweight and/or Obesity among Schoolchildren in Central Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, J.; Stone, K.L.; Wei, E.K.; Harrison, S.L.; Barrettconnor, E.; Lane, N.E.; Paudel, M.; Redline, S.; Ancoliisrael, S.; Orwoll, E. Vitamin D and actigraphic sleep outcomes in older community-dwelling men: The MrOS sleep study. Sleep 2015, 38, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, D.E.; Chesson, A.L., Jr.; Jain, S.K.; Marino, A.A. The link between vitamin D metabolism and sleep medicine. Sleep Med. Rev. 2014, 18, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, D.; Staun-Ram, E.; Glass-Marmor, L.; Lavi, I.; Rozenberg, O.; Dishon, S.; Barak, M.; Ish-Shalom, S.; Miller, A. The influence of vitamin D supplementation on melatonin status in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 32, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiol, I.M.; Stumpf, W.E.; Bidmon, H.J.; Heiss, C.; Mayerhofer, A.; Bartke, A. Vitamin D nuclear binding toneurons of the septal, substriatal and amygdaloid area in the siberian hamster (Phodopussungorus) brain. Neuroscience 1992, 48, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, W.E.; Bidmon, H.J.; Li, L.; Pilgrim, C.; Bartke, A.; Mayerhofer, A.; Heiss, C. Nuclear receptor sitesfor vitamin D-soltriol in midbrain and hindbrain of siberian hamster (Phodopussungorus) assessed byautoradiography. Histochemistry 1992, 98, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpf, W.E.; O’Brien, L.P. 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 sites of action in the brain. Histochemistry 1987, 87, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Eguchi, N.; Kimura, K.; Kiyohara, Y.; Qu, W.M.; Huang, Z.L.; Mochizuki, T.; Lazarus, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Kaneko, T.; et al. Dominant localization of prostaglandin d receptors on arachnoid trabecular cells in mouse basal forebrain and their involvement in the regulation of non-rapid eye movement sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11674–11679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Shah, S.; Long, Q.; Crankshaw, A.K.; Tangpricha, V. Improvement of pain, sleep, and quality of life in chronic pain patients with vitamin D supplementation. Clin. J. Pain 2013, 29, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, M.S.; Ahmad, H.S.; Bizhan, H.; Mohammad Hosein, H.A.; Mohammad, A. The effect of vitamin D supplement on the score and quality of sleep in 20–50 year-old people with sleep disorders compared with control group. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, D.L.; Hirotsu, C.; Tufik, S.; Andersen, M.L. Vitamin D and Sleep Apnea: Beyond a Simple Association. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | |
|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD a) | 11.15 (1.91) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 436 (54.50) |
| Female | 364 (45.50) |
| Parents’ highest education at college level, n (%) | |
| Both had college degree | 283 (35.38) |
| Only one of them had college degree | 111 (13.88) |
| None of them had college | 406 (50.24) |
| Parents’ marriage status, n (%) | |
| Married | 754 (94.25) |
| Divorced/widowed/separated | 46 (5.75) |
| Bedtimes, mean (SD) | 21:12 (0:41) |
| Wake times, mean (SD) | 6:23 (0:36) |
| sleep duration, mean (SD) (h) | 9.17 (0.97) |
| BMI b, mean (SD) (kg/m2) | 17.61 (3.19) |
| Hipline, mean (SD) (cm) | 74.19 (14.28) |
| Waistline, mean (SD) (cm) | 65.67 (33.03) |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR), mean (SD) | 0.90 (0.30) |
| Waist-to-Heigth Ratio (WHtR), mean (SD) | 0.46 (0.26) |
| 25(OH)D, mean (SD) (ng/mL) | 22.4 (6.0) |
| Variables | Sleep Duration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <9.0 h/day (n = 262) | 9.0–9.9 h/day (n = 353) | ≥10.0 h/day (n = 185) | p | |
| Age, years, mean (SD a) | 12.22 (1.75) | 10.24 (1.73) | 9.41 (0.90) | <0.001 |
| Age group (years), n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| ≤10 | 52 (19.85) | 224 (63.46) | 148 (80.00) | |
| >10 | 210 (80.15) | 129 (36.54) | 37 (20.00) | |
| Gender | 0.071 | |||
| Male, n (%) | 128 (48.85) | 205 (58.07) | 103 (55.68) | |
| Parents’ highest education at college level, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Both had college degree | 61 (23.28) | 136 (38.53) | 86 (46.49) | |
| Only one of them had college degree | 33 (12.60) | 49 (13.88) | 29 (15.68) | |
| None of them had college | 168 (64.12) | 168 (47.59) | 70 (37.84) | |
| Parents’ marriage status, n (%) | 0.170 | |||
| Married | 252 (96.18) | 327 (92.63) | 175 (94.59) | |
| Divorced/widowed/separated | 10 (3.82) | 26 (7.37) | 10 (5.41) | |
| Bedtimes, mean (SD) | 21:44 (0:39) | 21:08 (0:23) | 20:35 (0:34) | <0.001 |
| Wake times, mean (SD) | 5:53 (0:24) | 6:29 (0:24) | 6:54 (0:35) | <0.001 |
| BMI b, mean (SD) (kg/m2) | 18.93 (3.58) | 17.18 (2.58) | 16.58 (2.57) | <0.001 |
| 25(OH)D, mean (SD) (ng/mL) | 21.9 (5.7) | 24.3 (5.8) | 23.6 (6.2) | <0.001 |
| 25(OH)D Status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Deficiency/Insufficiency (≤20 ng/mL) | 106 (40.46) | 80 (22.66) | 56 (30.27) | |
| Sufficiency (>20 ng/mL) | 156 (59.54) | 273 (77.34) | 129 (69.73) | |
| Felt sad or hopeless (yes) c,n (%) | 34 (12.98) | 40 (11.33) | 18 (9.73) | 0.564 |
| Current smoking (yes) d, n (%) | 9 (3.44) | 10 (2.83) | 4 (2.16) | 0.729 |
| Current drinking (yes) d,n (%) | 34 (12.98) | 24 (6.80) | 5 (2.70) | <0.001 |
| Breakfastskipping (breakfast consumption frequency ≤6 days/week), n (%) | 48 (18.32) | 27 (7.65) | 6 (3.24) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity e | ||||
| Moderate physical activity (≥1 day/week), n (%) | 254 (96.95) | 338 (95.75) | 178 (96.22) | 0.742 |
| Outdoor activity (≥2 days/week), n (%) | 198 (77.95) | 252 (75.68) | 135 (75.00) | 0.732 |
| Watching TV (≥2 h/day), n (%) | 44 (17.32) | 51 (15.18) | 29 (16.11) | 0.782 |
| 25(OH)D Levels (mg/mL) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep Duration Insufficiency (Less Than 9 h) | ≤20 | >20 | |
| Model 1 | 1.71 (1.17–2.49) | 1 | 0.005 |
| Model 2 | 1.07 (1.01–1.13) | 1 | 0.007 |
| Model 3 | 1.67 (1.14–2.43) | 1 | 0.009 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Q.-H.; Li, S.-X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Xu, G.-Z. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Its Association with Sleep Duration in Chinese Schoolchildren. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081013
Gong Q-H, Li S-X, Li H, Chen Q, Li X-Y, Xu G-Z. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Its Association with Sleep Duration in Chinese Schoolchildren. Nutrients. 2018; 10(8):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Qing-Hai, Si-Xuan Li, Hui Li, Qi Chen, Xiao-Yong Li, and Guo-Zhang Xu. 2018. "25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Its Association with Sleep Duration in Chinese Schoolchildren" Nutrients 10, no. 8: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081013
APA StyleGong, Q.-H., Li, S.-X., Li, H., Chen, Q., Li, X.-Y., & Xu, G.-Z. (2018). 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Status and Its Association with Sleep Duration in Chinese Schoolchildren. Nutrients, 10(8), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081013





