Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Tumor Angiogenesis, Migration, Invasion, and Sphere Formation Through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb Signaling Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
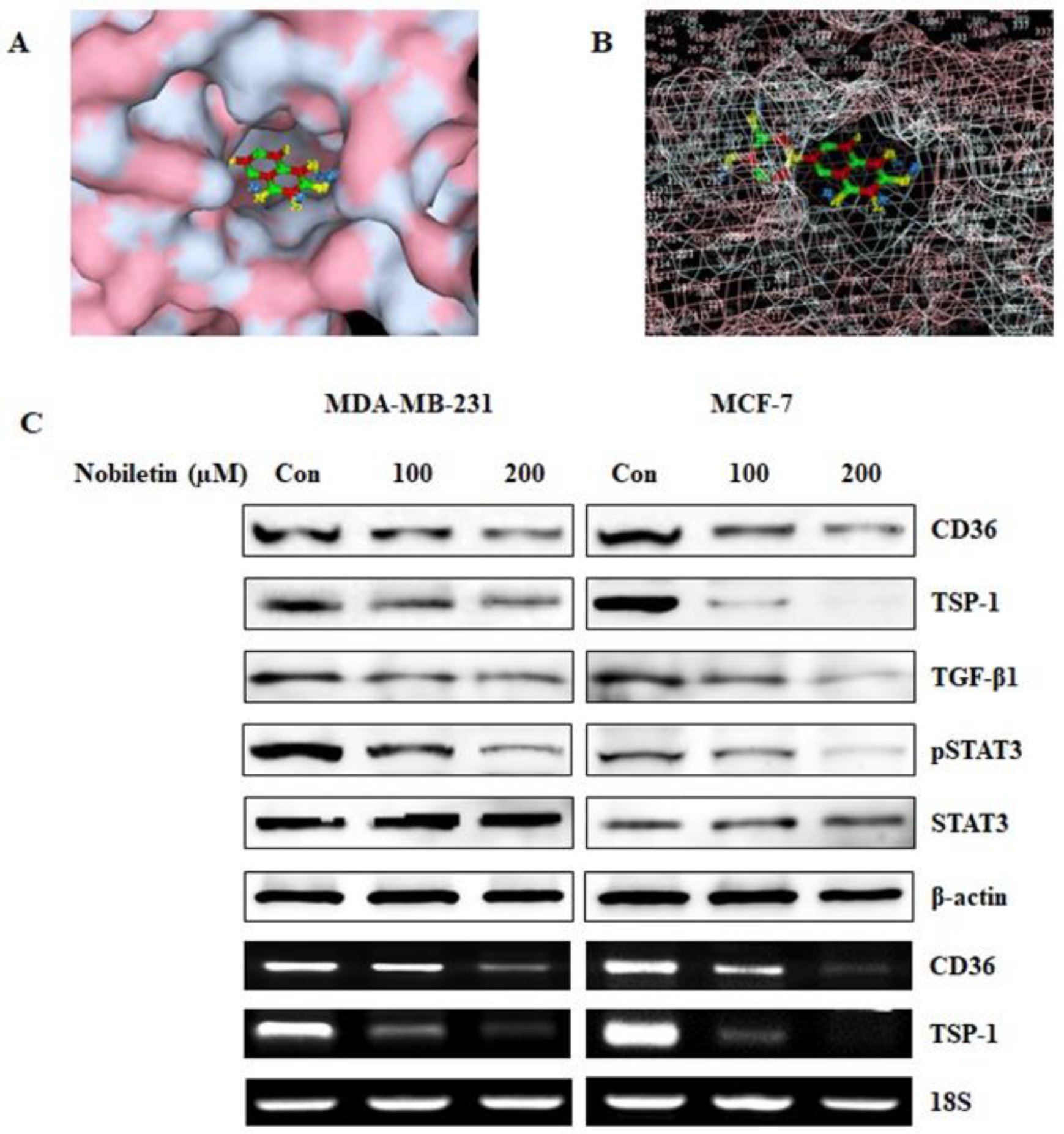
2.1. Nobiletin Binds to CD36 and Inhibits the Expression of CD36 and its Downstream Target Proteins
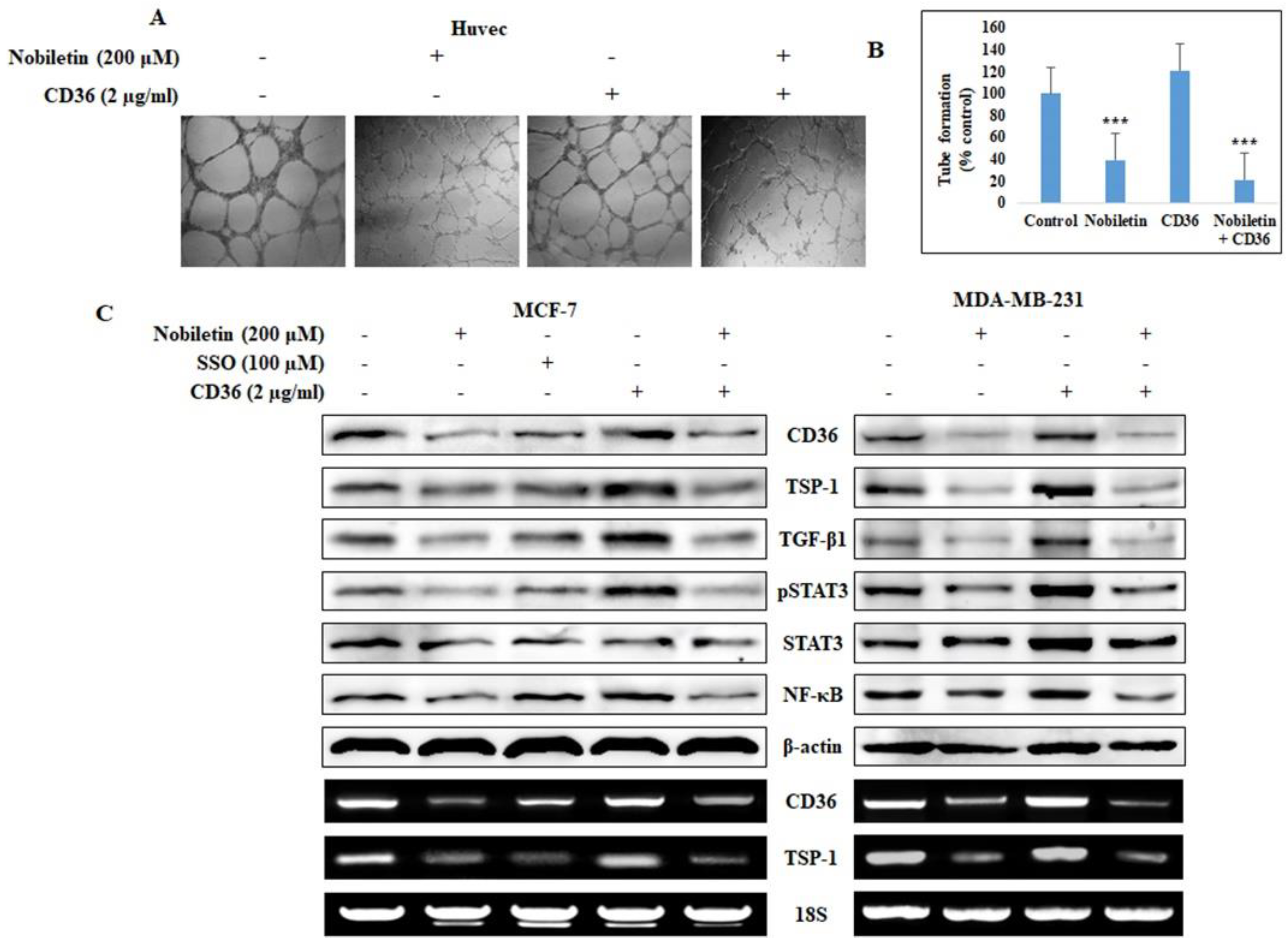
2.2. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Mediated In Vitro Angiogenesis by Regulating STAT3
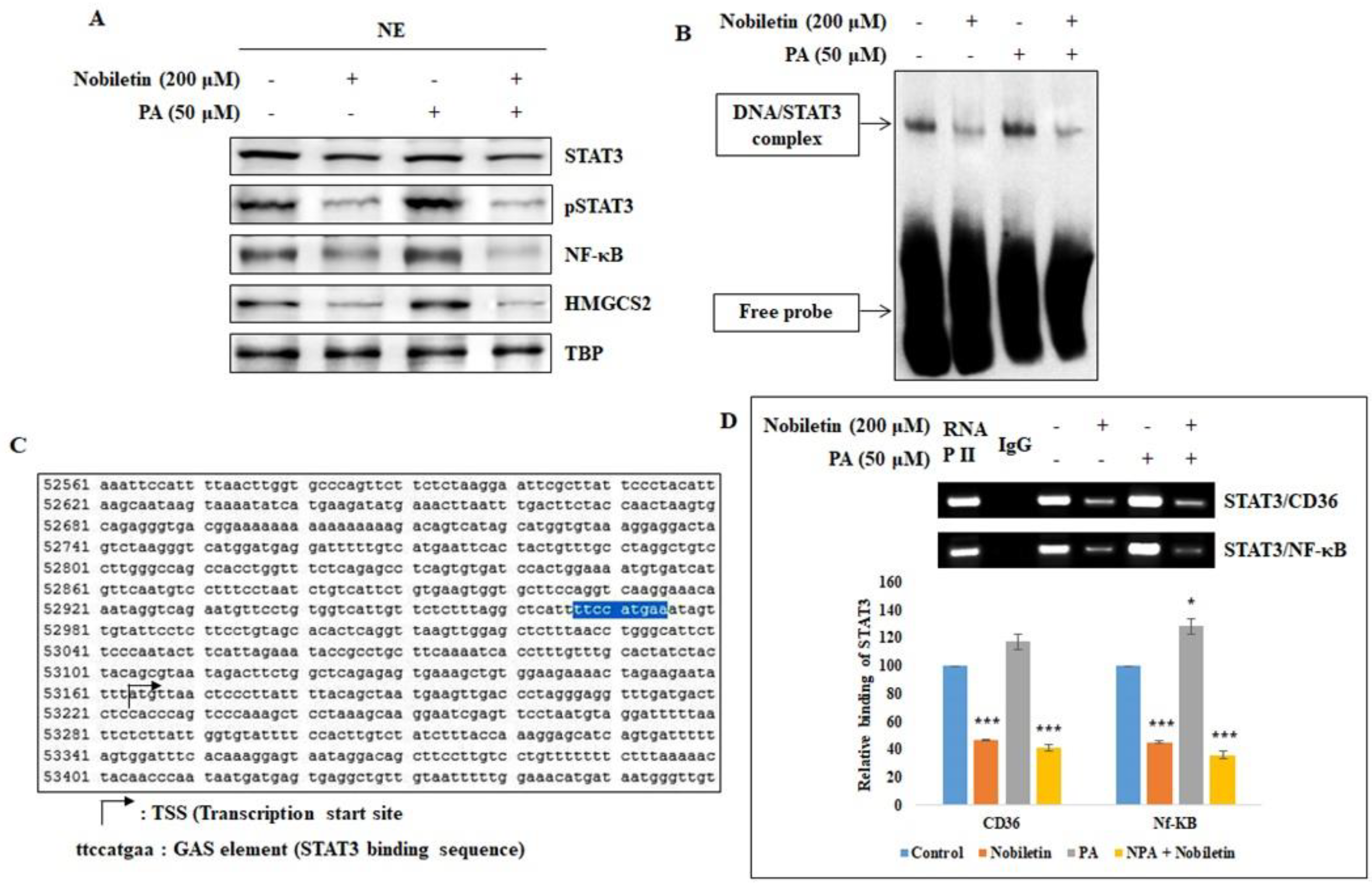
2.3. Nobiletin Inhibits the Nuclear Translocation of STAT3 and Its Binding to the CD36 Gene Promoter
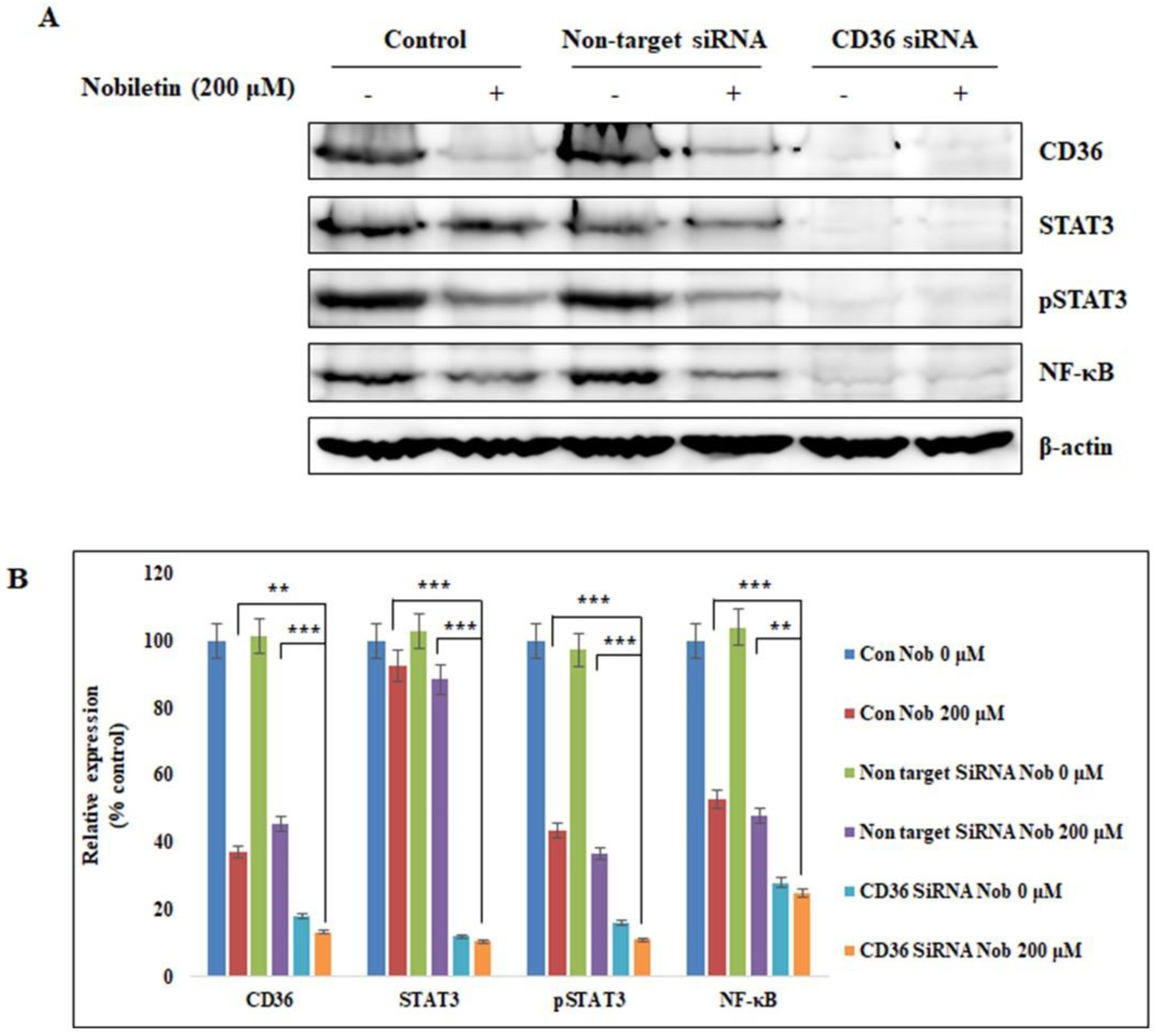
2.4. Nobiletin Suppresses STAT3 Expression in a CD36-Dependent Manner
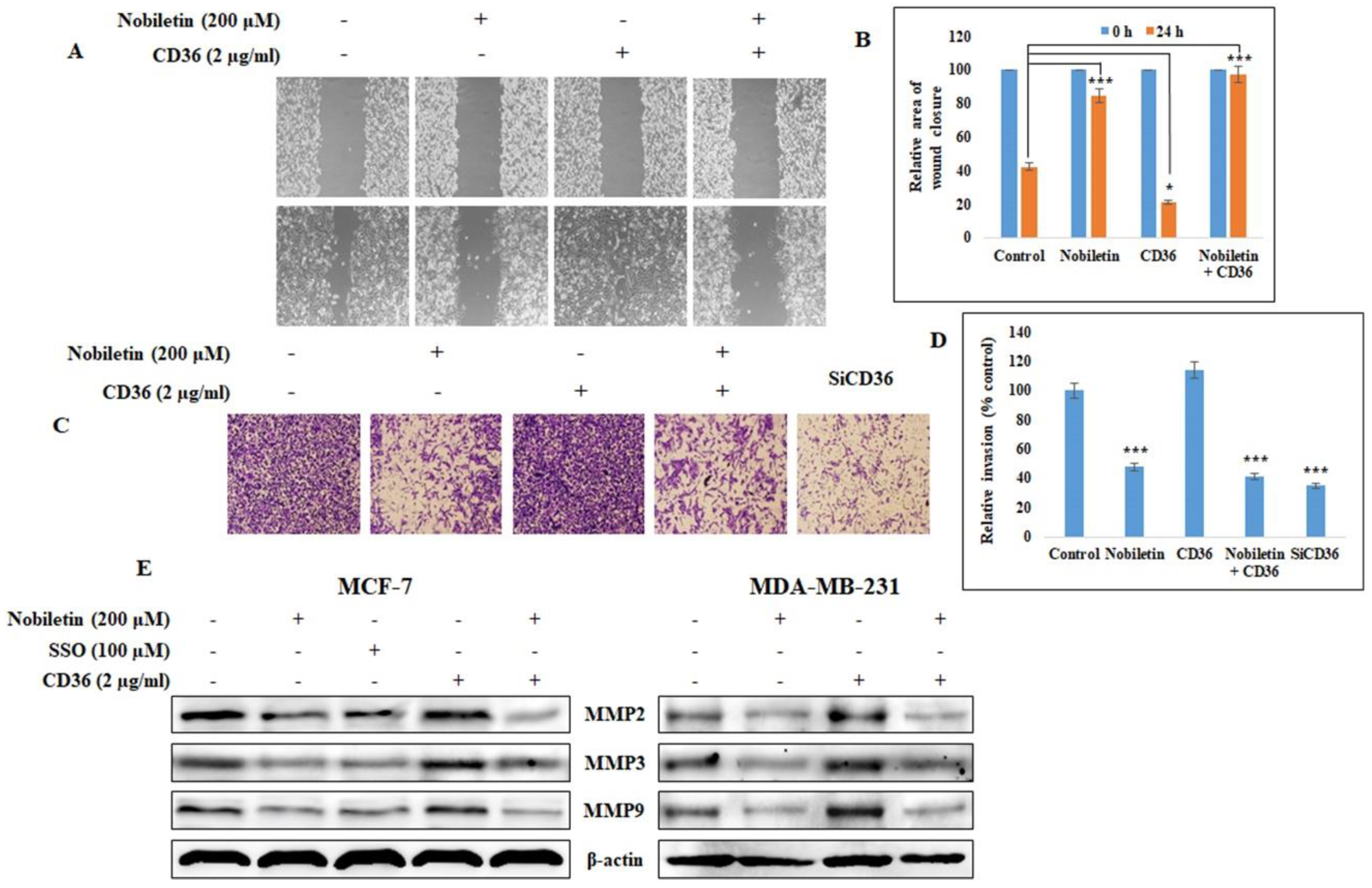
2.5. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion
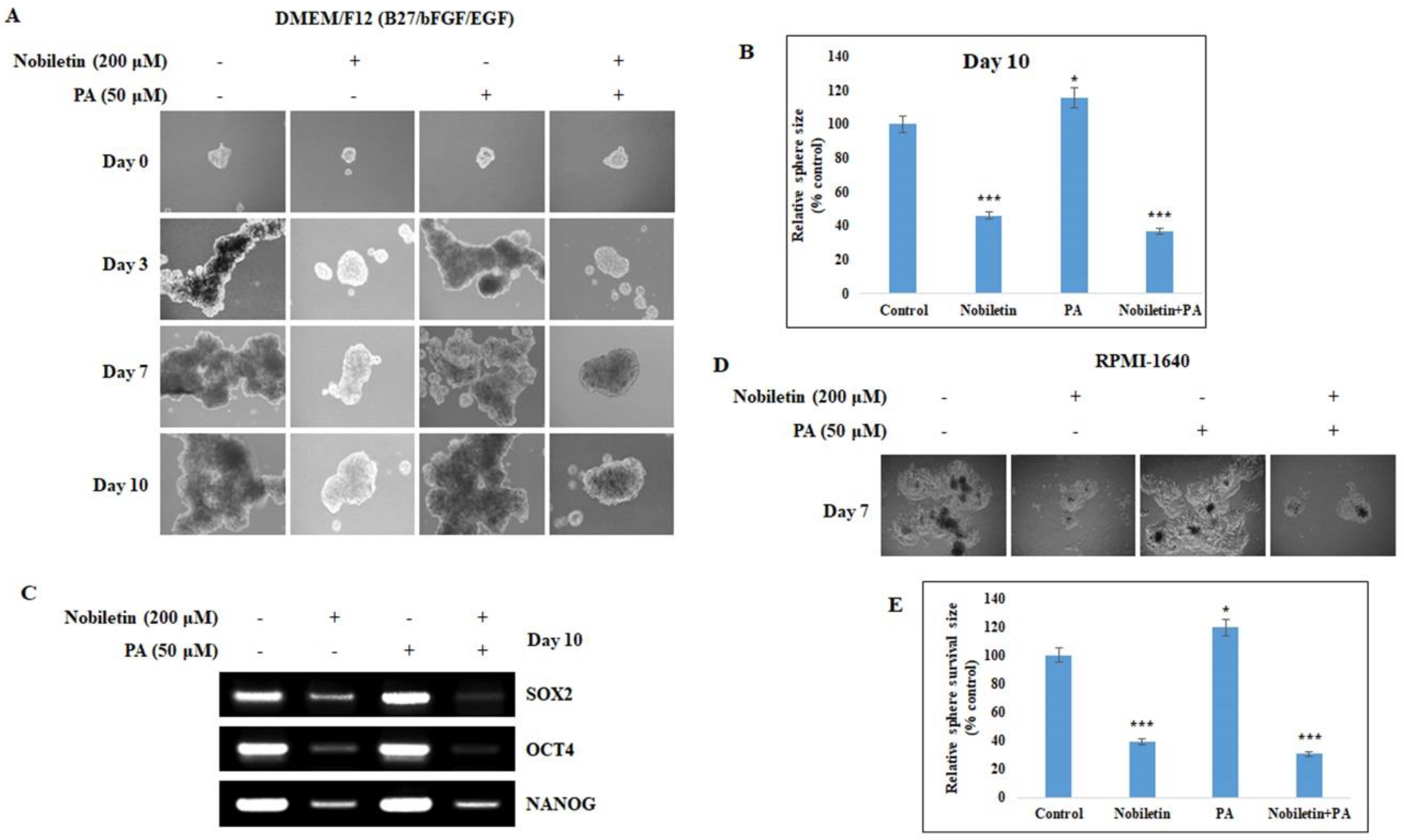
2.6. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Mediated Tumorsphere Formation and Survival
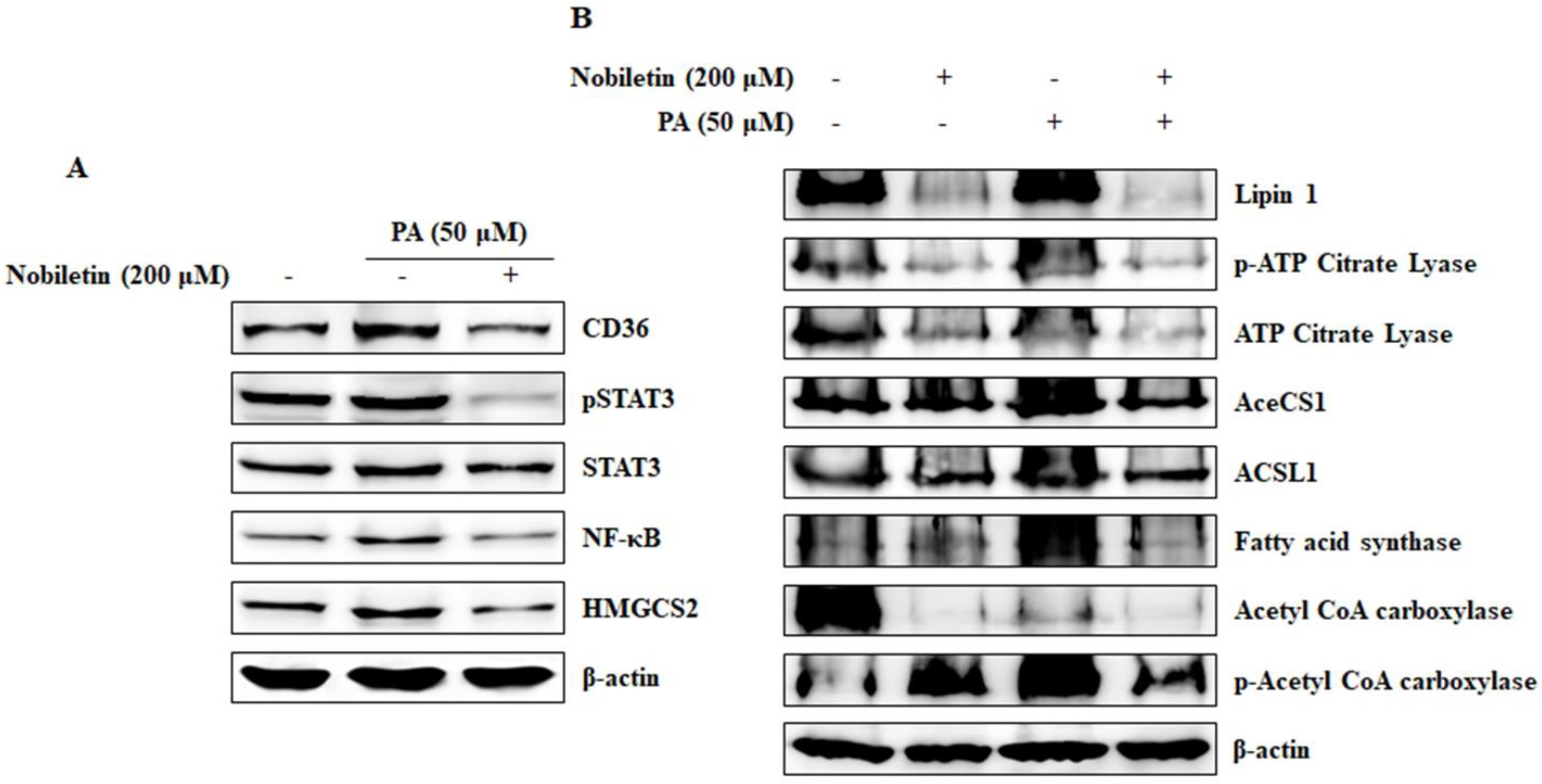
2.7. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Mediated Fatty Acid-Regulated Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies and Reagents
4.2. Molecular Docking
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. In vitro Angiogenesis Assay
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Reverse Transcription-PCR
4.7. EMSA
4.8. ChIP Assay
4.9. Wound Healing Assay
4.10. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.11. Tumor Sphere Formation Assay
4.12. Small Interference RNA (siRNA) Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, N.; Sato, T.; Takayama, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Sashida, Y.; Yano, M.; Ito, A. Novel anti-inflammatory actions of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxy flavonoid, on human synovial fibroblasts and mouse macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Sakai, S.; Yawo, H.; Nakata, N.; Moriguchi, S.; Fukunaga, K.; Yokosuka, A.; Sashida, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; et al. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid with neurotrophic action, augments protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit, GluR1, and the postsynaptic receptor response to glutamate in murine hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshitari, T.; Okuyama, Y.; Miyata, Y.; Kosano, H.; Takahashi, H.; Natsugari, H. Nobiletin metabolites: Synthesis and inhibitory activity against matrix metalloproteinase-9 production. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4540–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ono, M.; Takeshima, M.; Nakano, S. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity of nobiletin against three subtypes of human breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chien, S.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, S.F.; Chen, M.K. Nobiletin inhibits invasion and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines by involving ERK1/2 and transcriptional inhibition of MMP-2. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.D.; Liao, Y.C.; Shih, Y.W.; Tsai, L.Y. Nobiletin attenuates metastasis via both ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in HGF-treated liver cancer HepG2 cells. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surichan, S.; Arroo, R.R.; Ruparelia, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Androutsopoulos, V.P. Nobiletin bioactivation in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells by cytochrome P450 CYP1 enzymes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 113, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sp, N.; Kang, D.Y.; Joung, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, W.P.; Lee, H.K.; Song, K.D.; Park, Y.M.; Yang, Y.M. Nobiletin inhibits angiogenesis by regulating Src/FAK/STAT3-mediated signaling through PXN in ER+ breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, R.L.; Baird, M.; Lo, S.K.; Yesner, L.M. Sense and antisense cDNA transfection of CD36 (glycoprotein IV) in melanoma cells. Role of CD36 as a thrombospondin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16607–16612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Elghetany, M.T. CD36: A multiligand molecule. Lab. Hematol. 2005, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirochnik, Y.; Kwiatek, A.; Volpert, O.V. Thrombospondin and apoptosis: Molecular mechanisms and use for design of complementation treatments. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxhimer, J.B.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Ridnour, L.A.; Shih, H.B.; Degraff, W.G.; Tsokos, M.; Wink, D.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Roberts, D.D. Radioprotection in normal tissue and delayed tumor growth by blockade of CD47 signaling. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.Y.; Ramakrishnan, D.P.; Silverstein, R.L. Thrombospondin-1 modulates VEGF signaling via CD36 by recruiting SHP-1 to VEGFR2 complex in microvascular endothelial cells. Blood 2013, 122, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozovski, U.; Harris, D.M.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Jain, P.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.A.; Bose, P.; Thompson, P.A.; Jain, N.; et al. Overexpression of CD36, driven by STAT3, mediates free fatty acid uptake in CLL cells. Blood 2017, 130, 4301. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Mao, R.; Yang, J. NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, G.; Avgustinova, A.; Mejetta, S.; Martín, M.; Castellanos, A.; Attolini, C.S.; Berenguer, A.; Prats, N.; Toll, A.; Hueto, J.A.; et al. Targeting metastasis-initiating cells through the fatty acid receptor CD36. Nature 2017, 541, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladanyi, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Kenny, H.A.; Johnson, A.; Mitra, A.K.; Sundaresan, S.; Nieman, K.M.; Pascual, G.; Benitah, S.A.; Montag, A.; et al. Adipocyte-induced CD36 expression drives ovarian cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2285–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.Y.; Nipon, S.P.; Darvin, P.; Joung, Y.H.; Byun, H.J.; Do, C.H.; Park, K.D.; Park, M.N.; Cho, K.H.; Yang, Y.M. Momilactone B inhibits ketosis in vitro by regulating the ANGPTL3-LPL pathway and inhibiting HMGCS2. Anim. Biotechnol. 2016, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SP, N.; Darvin, P.; Yoo, Y.B.; Joung, Y.H.; Kang, D.Y.; Kim, D.N.; Hwang, T.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, H.K.; et al. The combination of methylsulfonylmethane and tamoxifen inhibits the Jak2/STAT5b pathway and synergistically inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in ER-positive breast cancer xenografts. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimizu, N.; Otani, Y.; Saikawa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yoshida, M.; Furukawa, T.; Kumai, K.; Kameyama, K.; Fujii, M.; Yano, M.; et al. Anti-tumour effects of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, on gastric cancer include: Antiproliferative effects, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle deregulation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Feng, S.; Yao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y. Nobiletin enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents in ABCB1 overexpression cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, K.L.; Ferguson, P.J.; Koropatnick, J. Tangeretin and nobiletin induce G1 cell cycle arrest but not apoptosis in human breast and colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osz, K.; Ross, M.; Petrik, J. The thrombospondin-1 receptor CD36 is an important mediator of ovarian angiogenesis and folliculogenesis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2014, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, J. Thrombospondin-1 as an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2002, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Chasovskikh, S.; Lonskaya, I.; Tarasova, N.I.; Khavrutskii, L.; Tarasov, S.G.; Zhang, X.; Korostyshevskiy, V.R.; Cheema, A.; Zhang, L.; et al. Mechanisms of unphosphorylated STAT3 transcription factor binding to DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 14192–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, R.; Itoh, Y. Analysis of MMP-dependent cell migration and invasion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 622, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Yu, C.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Chang, W.W. Tumorsphere as an effective in vitro platform for screening anti-cancer stem cell drugs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Tackling the cancer stem cells—What challenges do they pose? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, S.; Fathi, F.; Mobalegi, J.; Sofimajidpour, H.; Ghadimi, T. The expressions of stem cell markers: Oct4, Nanog, Sox2, nucleostemin, Bmi, Zfx, Tcl1, Tbx3, Dppa4, and Esrrb in bladder, colon, and prostate cancer, and certain cancer cell lines. Anat. Cell Biol. 2014, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reue, K. The role of lipin 1 in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism. Novartis Found. Symp. 2007, 286, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.F.; Wu, H.C.; Hsieh, W.C.; Tsai, H.W.; Su, I.J. Activation of ATP citrate lyase by mTOR signal induces disturbed lipid metabolism in hepatitis B virus pre-S2 mutant tumorigenesis. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahar, S.; Masubuchi, S.; Eckel-Mahan, K.; Vollmer, S.; Galla, L.; Ceglia, N.; Masri, S.; Barth, T.K.; Grimaldi, B.; Oluyemi, O.; et al. Circadian control of fatty acid elongation by SIRT1 protein-mediated deacetylation of acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 6091–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, H.L.; Fu, N.; Ouyang, Y.; Qing, K. Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase in fatty acid metabolism involved in liver and other diseases: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen-Urstad, A.P.; Semenkovich, C.F. Fatty acid synthase and liver triglyceride metabolism: Housekeeper or messenger? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zoubi, M.; Chipitsyna, G.; Saxena, S.; Sarosiek, K.; Gandhi, A.; Kang, C.Y.; Relles, D.; Andrelsendecki, J.; Hyslop, T.; Yeo, C.J.; et al. Overexpressing TNF-alpha in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and fibroblasts modifies cell survival and reduces fatty acid synthesis via downregulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 and activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sl No | Gene | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Product Size (bp) | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CD36 | 55 | 768 | F-ggcaccactgtgtacagacag R-ggaaaggaggctgcgtctgtgc |
| 2 | TSP-1 | 60 | 345 | F-gttgcatgtgtgtggaagcaac R-accacactgaagatctggccag |
| 3 | 18S | 58 | 490 | F-agccttcggctgactggctgg R-ctgcccatcatcatgacctgg |
| 4 | SOX2 | 55 | 165 | F-ctgcagtacaactccatgac R-gagtgggaggaagaggtaac |
| 5 | OCT4 | 55 | 190 | F-actggttcgctttctctttc R-aaggtattcagccaaacgac |
| 6 | NANOG | 55 | 202 | F-ctcctccatggatctgctta R-ggctgaggtatttctgtctc |
| 7 | CD36 (ChIP assay) | 55 | 191 | F-ttctcagagcctcagtgtga R-acctgagtgtgctacaggaa |
| 8 | NF-κB (ChIP assay) | 55 | 123 | F-tcctacctgaaggcaaagga R-ccgtttcatagaaagggcca |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sp, N.; Kang, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Darvin, P.; Park, Y.-M.; Yang, Y.M. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Tumor Angiogenesis, Migration, Invasion, and Sphere Formation Through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb Signaling Axis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060772
Sp N, Kang DY, Kim DH, Park JH, Lee HG, Kim HJ, Darvin P, Park Y-M, Yang YM. Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Tumor Angiogenesis, Migration, Invasion, and Sphere Formation Through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb Signaling Axis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(6):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060772
Chicago/Turabian StyleSp, Nipin, Dong Young Kang, Doh Hoon Kim, Jong Hwan Park, Hyo Gun Lee, Hye Jee Kim, Pramod Darvin, Yeong-Min Park, and Young Mok Yang. 2018. "Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Tumor Angiogenesis, Migration, Invasion, and Sphere Formation Through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb Signaling Axis" Nutrients 10, no. 6: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060772
APA StyleSp, N., Kang, D. Y., Kim, D. H., Park, J. H., Lee, H. G., Kim, H. J., Darvin, P., Park, Y.-M., & Yang, Y. M. (2018). Nobiletin Inhibits CD36-Dependent Tumor Angiogenesis, Migration, Invasion, and Sphere Formation Through the Cd36/Stat3/Nf-Κb Signaling Axis. Nutrients, 10(6), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060772






