Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Animal Protocol
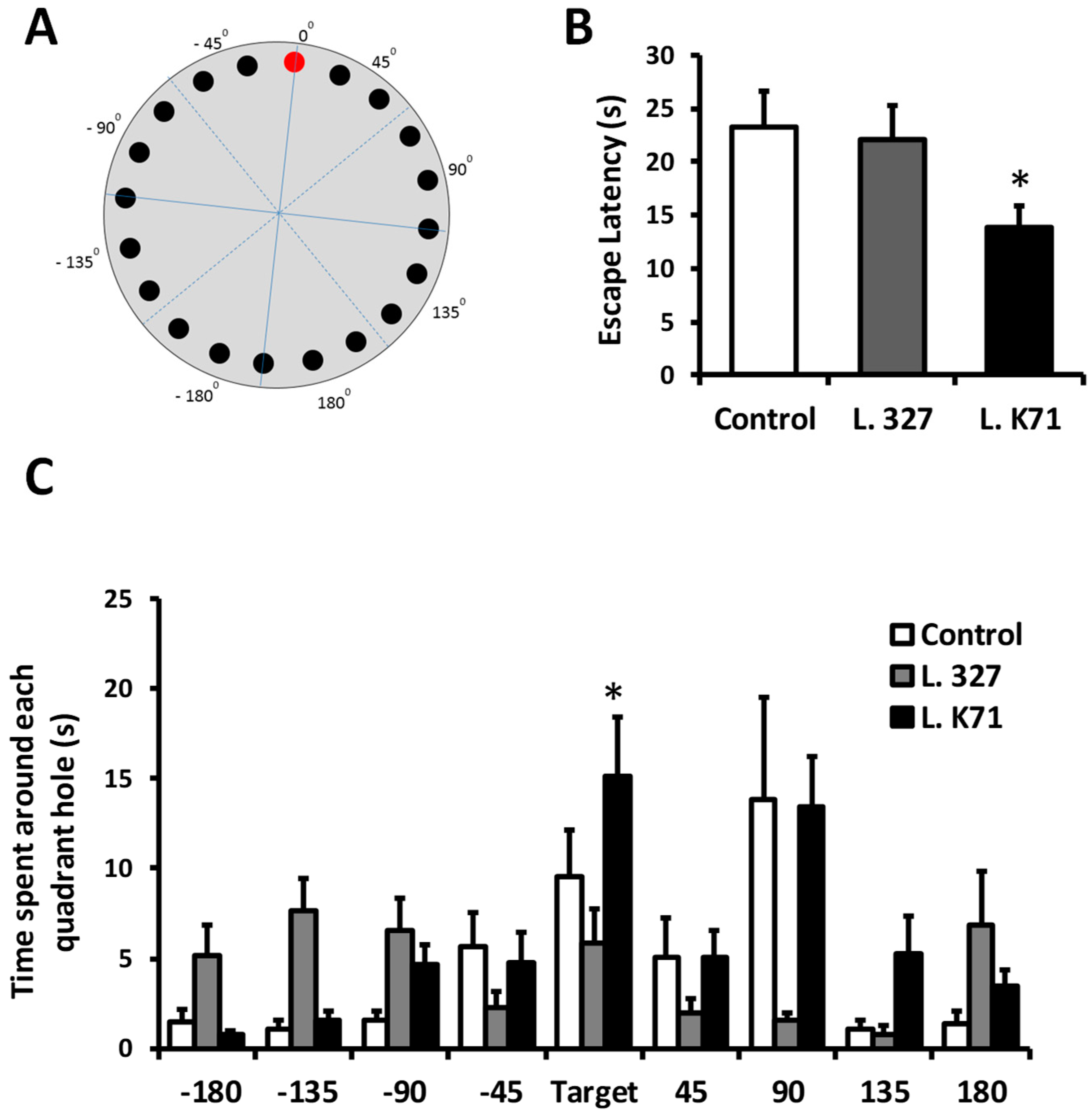
2.3. Barnes Maze Test
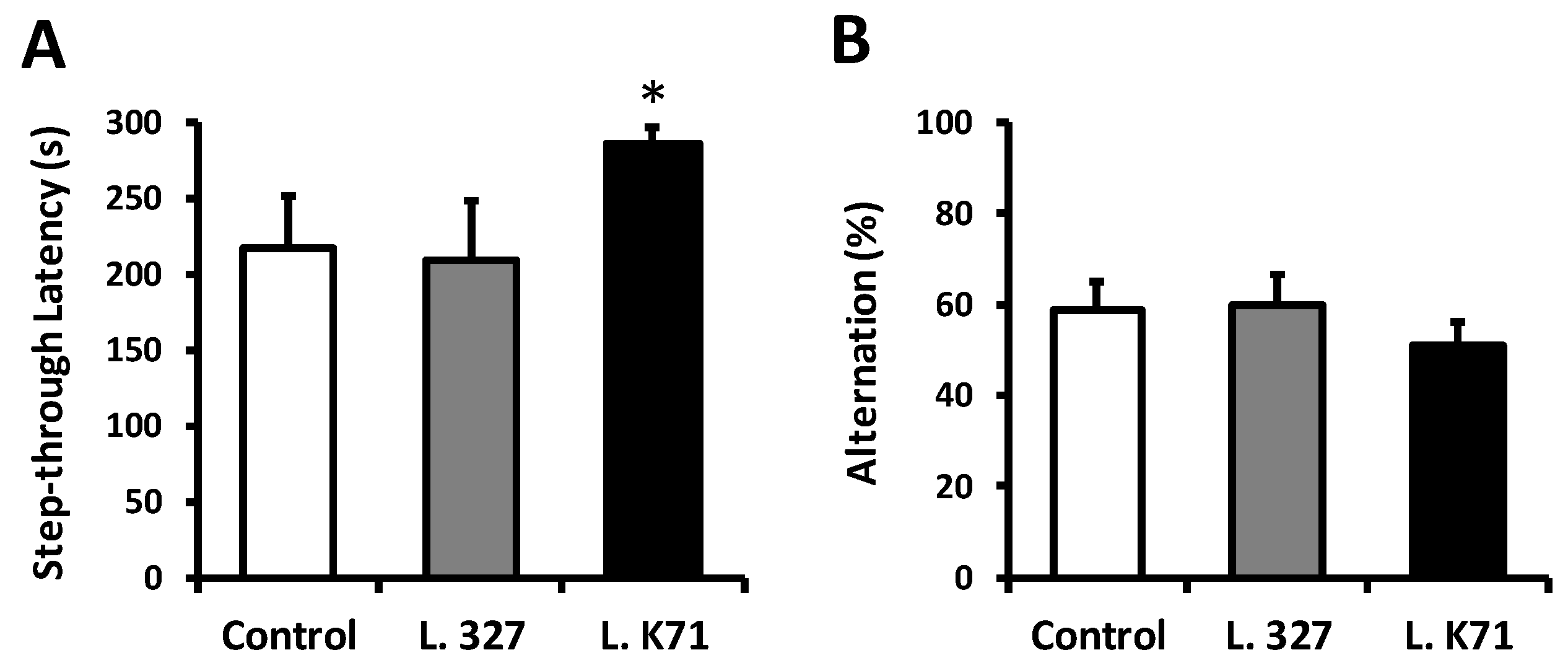
2.4. Passive Avoidance Test
2.5. Y-Maze Test
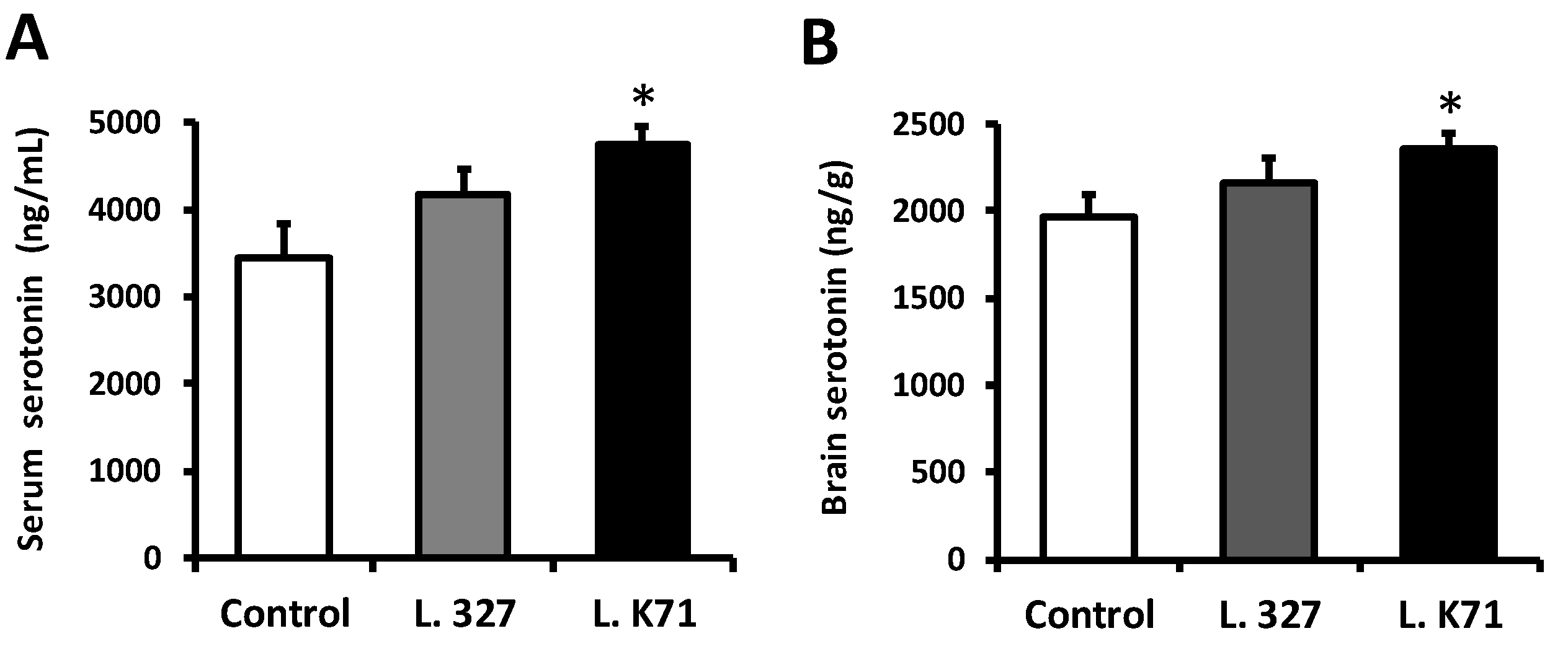
2.6. ELISA Measurement of Serotonin Levels
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. Immunostaining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Long-Term Administration of Lactobacillus Strains on Spatial Learning and Memory in SAMP8 Mice
3.2. Effect of Lactobacillus Strain Supplementation on Serotonin Levels in the Blood Serum and Brain of SAMP8 Mice
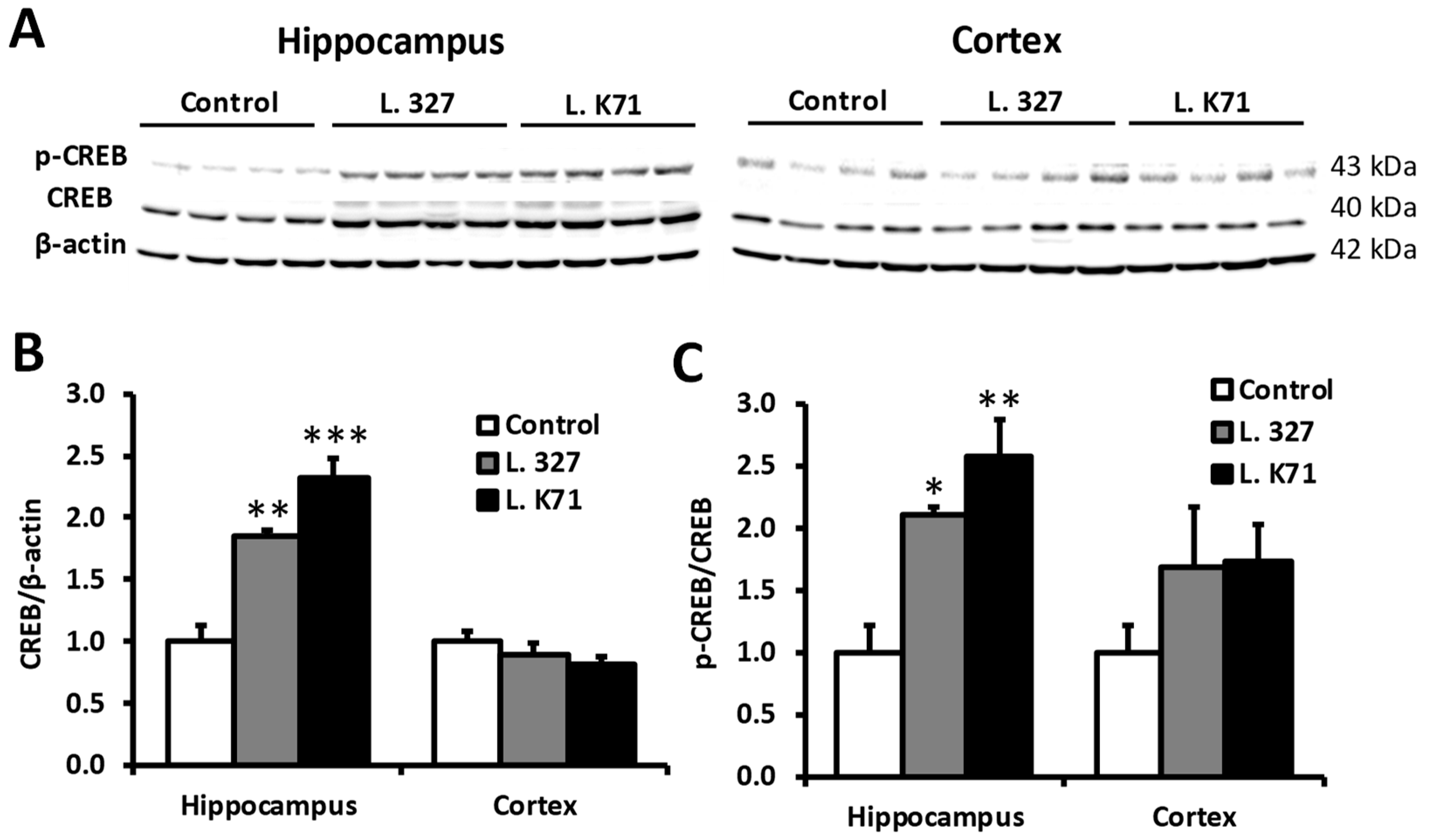
3.3. Effect of Prolonged Lactobacillus Supplementation on Serotonin Biosynthesis in the Hippocampus and Cortex
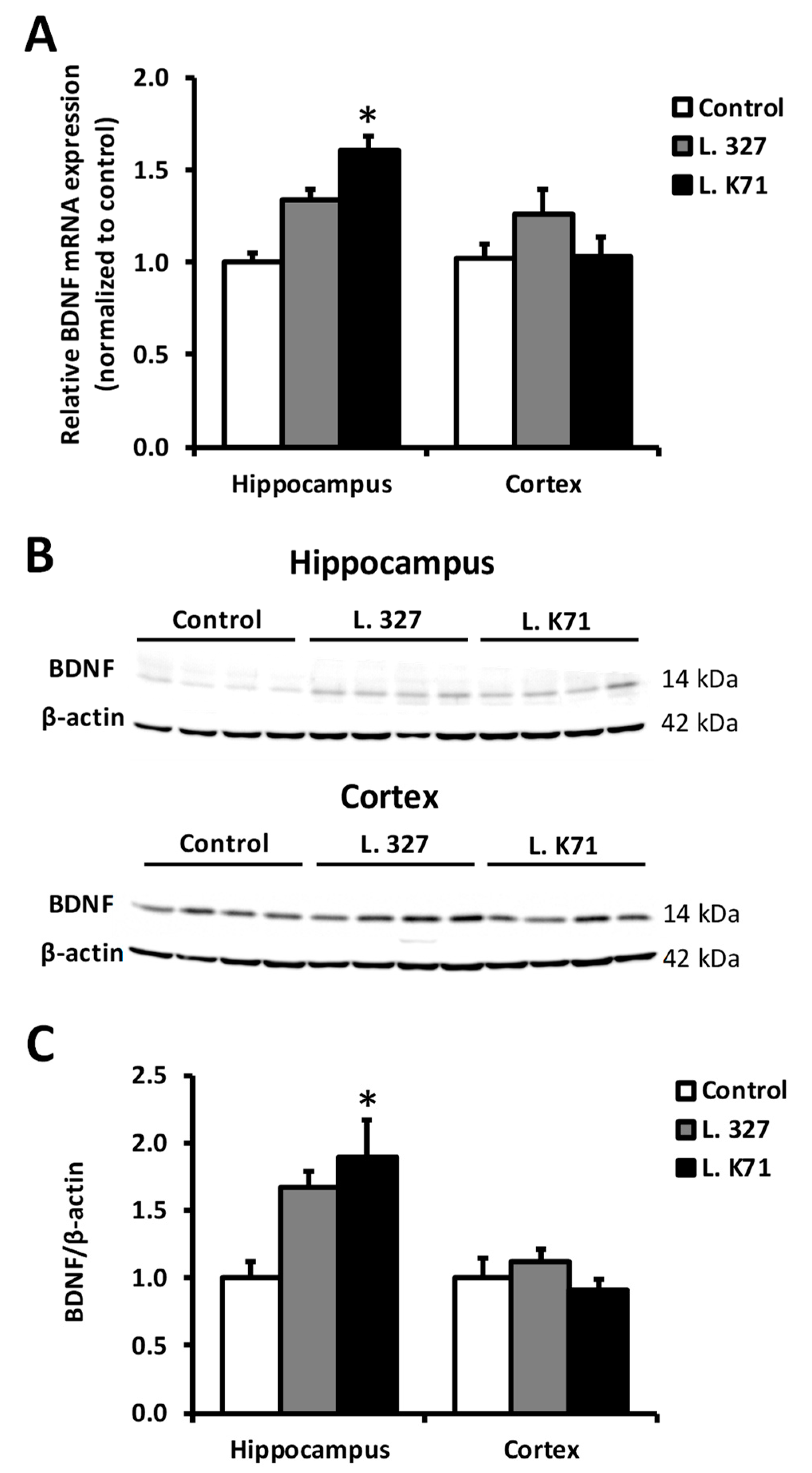
3.4. Effect of Lactobacillus Strain Supplementation on BDNF Expression in the Hippocampus and Cortex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: Mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Zeng, M.Y.; Núñez, G. The interplay between host immune cells and gut microbiota in chronic inflammatory diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. The gut microbiota: A treasure for human health. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisermana, A.M.; Koliadaa, A.K.; Marotta, F. Gut microbiota: A player in aging and a target for anti-aging intervention. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savignac, H.; Tramullas, M.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J. Bifidobacteria modulate cognitive processes in an anxious mouse strain. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 287, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distrutti, E.; O’Reilly, J.-A.; McDonald, C.; Cipriani, S.; Renga, B.; Lynch, M.A.; Fiorucci, S. Modulation of intestinal microbiota by the probiotic VSL# 3 resets brain gene expression and ameliorates the age-related deficit in LTP. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106503. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Fujii, M.; Watanabe, T.; Maruyama, K.; Kowatari, Y.; Ogata, H.; Kumagai, T. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of the effect of Lactobacillus paracasei K71 intake on salivary release of secretory immunoglobulin A. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2017, 36, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Mihara, T.; Maruyama, K.; Saito, J.; Ikeda, M.; Tomonaga, A.; Kumagai, T. Effects of intake of Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei 327 on skin conditions: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in women. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2017, 36, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Poon, H.F. The senescence-accelerated prone mouse (SAMP8): A model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to alterations of the gene expression and protein abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, J.F.; Morley, J.E. Learning and memory in the SAMP8 mouse. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.; Ilchibaeva, T.; Naumenko, V. Neurotrophic factors (BDNF and GDNF) and the serotonergic system of the brain. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2017, 82, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, A.; Constantine-Paton, M. Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB signaling in synapse maturation, plasticity, and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Cory, S.; Kidane, A.H.; Shirkey, N.J.; Marshak, S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the development of structural neuronal connectivity. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poo, M. Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M.E.; Xu, B.; Lu, B.; Hempstead, B.L. New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: Implications in CNS function. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12764–12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, G.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Castorina, S.; Imbesi, R.; Szychlinska, M.A.; Scuderi, S.; Loreto, C.; Giunta, S. Changes in serotonin (5-HT) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDFN) expression in frontal cortex and hippocampus of aged rat treated with high tryptophan diet. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 119, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štrac, D.Š.; Pivac, N.; Mück-Šeler, D. The serotonergic system and cognitive function. Transl. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, M.; Brindle, P.; Harootunian, A.; Armstrong, R.; Rivier, J.; Vale, W.; Tsien, R.; Montminy, M. Coupling of hormonal stimulation and transcription via the cyclic AMP-responsive factor CREB is rate limited by nuclear entry of protein kinase A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4852–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, S.; Imai, R.; Sugiyama, H.; Nakamura, S. Oral Administration of Soy Peptides Suppresses Cognitive Decline by Induction of Neurotrophic Factors in SAMP8 Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Long-term green tea catechin administration prevents spatial learning and memory impairment in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 mice by decreasing Aβ1-42 oligomers and upregulating synaptic plasticity–related proteins in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Huang, C.-S.; Inoue, T.; Yamashita, T.; Ishida, T.; Kang, K.-M.; Nakao, A. Drinking hydrogen water ameliorated cognitive impairment in senescence-accelerated mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Camilleri, M. Serotonin: A mediator of the brain–gut connection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 2698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bortolato, M.; Chen, K.; Shih, J.C. Monoamine oxidase inactivation: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J. Monoamine oxidase in aging human brain. In Monoamine Oxidase: Structure, Function and Altered Function; Singer, T.P., Von Korff, R.W., Murphy, D.L., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, C.J.; Wiberg, A.; Oreland, L.; Marcusson, J.; Winblad, B. The Effect of Age on the Activity and Molecular Properties of Human Brain Monoamine Oxidase. J. Neural Transm. 1980, 49, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kang, P.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel coumarin-N-benzyl pyridinium hybrids as multi-target agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.; Chen, K. MAO-A and-B gene knock-out mice exhibit distinctly different behavior. Neurobiology 1999, 7, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woods, S.; Clarke, N.; Layfield, R.; Fone, K. 5-HT6 receptor agonists and antagonists enhance learning and memory in a conditioned emotion response paradigm by modulation of cholinergic and glutamatergic mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, K.; Engdahl, C.; Henning, P.; Lerner, U.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Lagerquist, M.K.; Bäckhed, F.; Ohlsson, C. The gut microbiota regulates bone mass in mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Anfora, A.T.; Liu, J.; Schultz, P.G.; Lesley, S.A.; Peters, E.C.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Bdnf | TAATGCAGCATGATGGGAAA | ACACTGAGGCCACAATCATGC |
| Tph2 | GAGCAGGGTTACTTTCGTCCATC | AAGCAGGTCGTCTTTGGGTCA |
| Maoa | GAGGCTCCAATTTCAATCACTCTG | ATGTAGTTTAGCAAGTCGTTCAGC |
| Maob | AAGCGATGTGATCGTGGTGG | CAATGAGCCAAGTGAGCGAGA |
| Actb | AGTGTGACGTTGACATCCGT | TGCTAGGAGCCAGAGCAGTA |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corpuz, H.M.; Ichikawa, S.; Arimura, M.; Mihara, T.; Kumagai, T.; Mitani, T.; Nakamura, S.; Katayama, S. Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8. Nutrients 2018, 10, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060762
Corpuz HM, Ichikawa S, Arimura M, Mihara T, Kumagai T, Mitani T, Nakamura S, Katayama S. Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8. Nutrients. 2018; 10(6):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060762
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorpuz, Henry M., Saki Ichikawa, Misa Arimura, Toshihiro Mihara, Takehisa Kumagai, Takakazu Mitani, Soichiro Nakamura, and Shigeru Katayama. 2018. "Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8" Nutrients 10, no. 6: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060762
APA StyleCorpuz, H. M., Ichikawa, S., Arimura, M., Mihara, T., Kumagai, T., Mitani, T., Nakamura, S., & Katayama, S. (2018). Long-Term Diet Supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei K71 Prevents Age-Related Cognitive Decline in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8. Nutrients, 10(6), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060762