Dietary Nutrients and Bioactive Substances Modulate Heat Shock Protein (HSP) Expression: A Review
Abstract
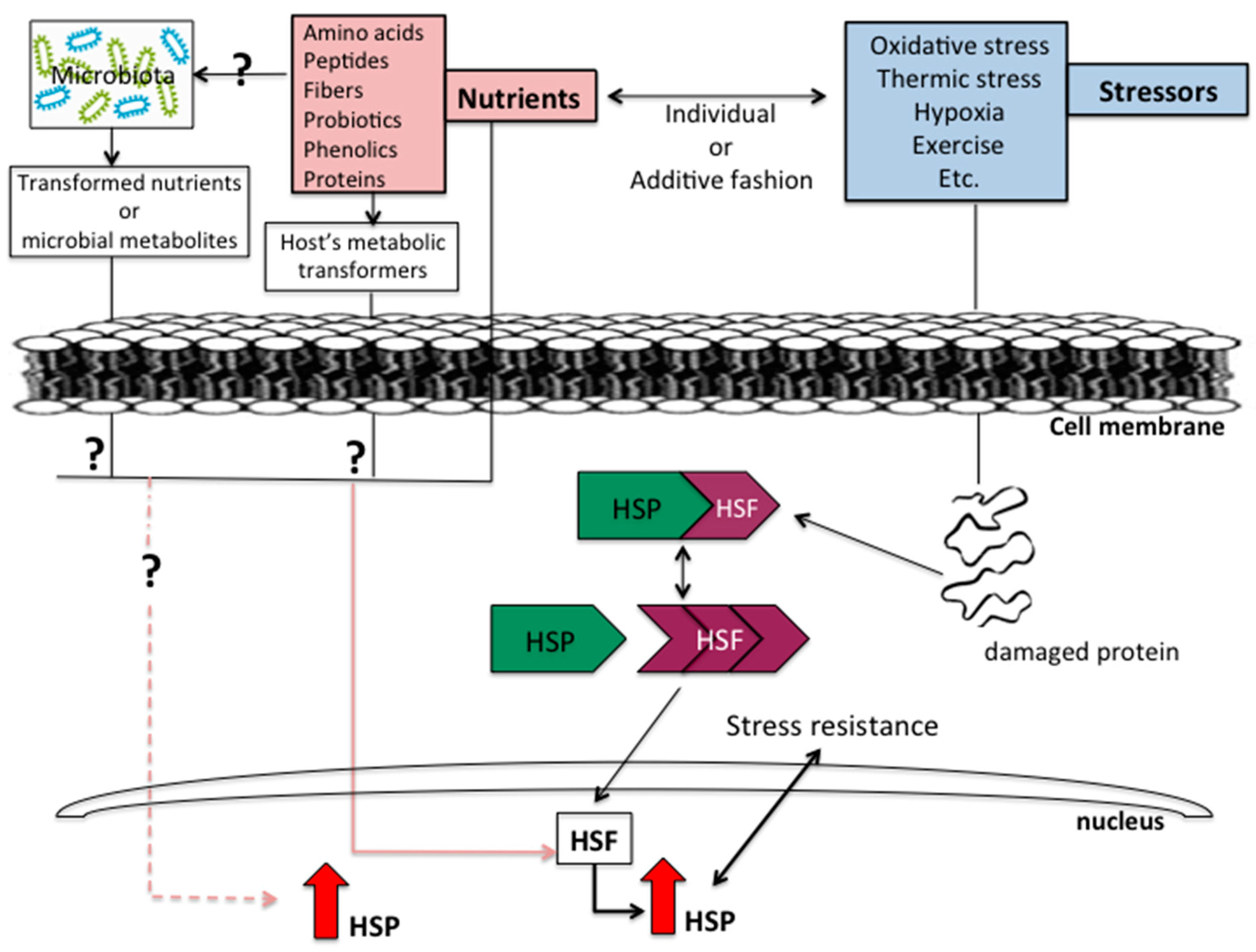
:1. Introduction
2. Heat Shock Proteins
3. Effects of Amino Acids on HSPs
4. Proteins and Bioactive Peptides
5. Dietary Fiber
6. Probiotics
7. Phenolic Compounds
8. High-Fat Diet and HSPs
9. Other Foods and Nutrients
9.1. Chia
9.2. Copper
9.3. Garlic
9.4. Dietary Restriction
10. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Risso, E.M.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Bioactivity of food peptides: Biological response of rats to bovine milk whey peptides following acute exercise. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1290740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Risso, E.M.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Modulatory effects of arginine, glutamine and branched-chain amino acids on heat shock proteins, immunity and antioxidant response in exercised rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Risso, E.M.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Functional effects of milk bioactive peptides on skeletal muscle of rats. Food Res. Int. 2016, 84, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Nisishima, L.H.; Carneiro, E.M.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Whey protein hydrolysate enhances HSP90 but does not alter HSP60 and HSP25 in skeletal muscle of rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N. Whey protein hydrolysate enhances the exercise-induced heat shock protein (HSP70) response in rats. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, A.A.; Bomhoff, G.L.; Morris, J.K.; Gorres, B.K.; Geiger, P.C. Lipoic acid increases heat shock protein expression and inhibits stress kinase activation to improve insulin signaling in skeletal muscle from high-fat-fed rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritossa, F. A new puffing pattern induced by temperature shock and DNP in Drosophila. Experientia 1962, 18, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, A.; Santoro, M.G.; Tanguay, R.M.; Hightower, L.E. Ferruccio Ritossa’s scientific legacy 50 years after his discovery of the heat shock response: A new view of biology, a new society, and a new jornal. Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, A.; Vazquez, D. Extracellular heat shock proteins: A new location, a new function. Shock 2013, 40, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampinga, H.H.; Bergink, S. Heat shock proteins as potential targets for protective strategies in neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampinga, H.H.; Craig, E.A. The HSP70 chaperone machinery: J proteins as drivers of functional specificity. Nature 2010, 11, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, K.R. Stress protein expression kinetics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeyer, P.E. Glutamine and Heat Shock Protein Expression. Nutrition 2002, 18, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.G. Heat Shock Factors and the control of the stress response. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, I.J.; McMillan, D.R. Stress (Heat Shock) Proteins: Molecular Chaperones in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 1998, 83, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiang, J.G.; Tsokos, G.C. Heat Shock Protein 70 kDa: Molecular Biology, Biochemistry, and Physiology. Pharmacol Ther. 1998, 80, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anckar, J.; Sistonen, L. Regulation of HSF1 function in the heat stress response: Implications in aging and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 1089–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.S.L.; Westwood, J.T. Transcriptional regulation of the mammalian heat shock genes. In Exercise and the Stress Response: The Role of Stress Proteins; Noble, E.G., Locke, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 13–41. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido, C. The small heat shock proteins family: The long forgotten chaperones. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukau, B.; Weissman, J.; Horwich, A. Molecular chaperones and protein quality control. Cell 2006, 125, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiqi, G. Pre-treatment with glutamine attenuates lung injury in rats subjected to intestinal ischaemia–Reperfusion injury. Int. J. Care Inj. 2011, 42, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, K.D.; Wischmeyer, P.E. Glutamine protection against sepsis and lung injury is dependent on heat shock protein 70 expression. Am. J. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; Kahana, M.; Wolfson, R.; Ren, H.; Musch, M.M.; Chang, E.B. Glutamine induces heat shock protein and protects against endotoxin shock in the rat. J Appl Physiol. 2001, 90, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenfried, J.A. Glutamine-mediated regulation of heat shock protein expression in intestinal cells. Surgery 1995, 118, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhl, M.; Dokladny, K.; Mermier, C.; Schneider, S.; Salgado, R.; Moseley, P. The effects of acute oral glutamine supplementation on exercise-induced gastrointestinal permeability and heat shock protein expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Sawyer, M.B.; Field, C.J.; Dieleman, L.A.; Murray, D.; Baracos, V.E. Bolus oral glutamine protects rats against CPT-11-induced diarrhea and differentially activates cytoprotective mechanisms in host intestine but not tumor. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phanvijhitsiri, K.; Musch, M.W.; Ropeleski, M.J.; Chang, E.B. Heat induction of heat shock protein 25 requires cellular glutamine in intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 291, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamiel, C.R.; Pinto, S.; Hau, A. Glutamine enhances heat shock protein 70 expression via increased hexosamine biosynthetic pathway activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, C.H.; Niederlechner, S.; Beck, R. l-Threonine induces heat shock protein expression and decreases apoptosis in heat-stressed intestinal epithelial cells. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.Y.; Mu, T.; Yang, Z. Methionine protects against hyperthermia-induced cell injury in cultured bovine mammary epithelial cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ruan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Geng, M.; Hou, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary supplementation with l-arginine or N-carbamylglutamate enhances intestinal growth and heat shock protein-70 expression in weanling pigs fed a corn- and soybean meal-based diet. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonosova, Y.N.; Shenkman, B.S.; Kalamkarov, G.R.; Kostrominova, T.Y.; Nemirovskaya, T.L. l-arginine supplementation protects exercise performance and structural integrity of muscle fibers after a single bout of eccentric exercise in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensen, S.M.M.; Heldens, L.; Van Enckevort, C.M.W. Heat shock factor 1 is inactivated by amino acid deprivation. Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitts, D.D.; Weiler, K. Bioactive proteins and peptides from food sources. Applications of bioprocesses used in isolation and recovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedel, J.L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shiou, S.R.; Chen, S.; Petrof, E.O.; Hu, S.; Musch, M.W.; Claud, E.C. Mother’s Milk-Induced Hsp70 Expression Preserves Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function in an Immature Rat Pup Model. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 61, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Farfan, J.; Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N. Dietary whey proteins and type 2 diabetes. Molecular aspects. In Molecular Nutrition and Diabetes; Mauricio, D., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, J.S.; Raizel, R.; Hypólito, T.M.; Rosa, T.D.; Cruzat, V.F.; Tirapegui, J. l-glutamine and l-alanine supplementation increase glutamine-glutathione axis and muscle HSP-27 in rats trained using a progressive high-intensity resistance exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Hunga, T.V.; Tarib, H.; Arakawa, T.; Suzuki, T. Dietary psyllium fiber increases intestinal heat shock protein 25 expression in mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 39, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, S.; Koya, T.; Ohno, Y.; Goto, A.; Ikuita, A.; Suzuki, M.; Ohira, T.; Egawa, T.; Nakai, A.; Sugiura, T.; et al. Regeneration of injured skeletal muscle in heat shock transcription factor 1-null mice. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Lundh, T.; Dicksved, J.; Lindberg, J.E. Expression of heat shock protein 27 in gut tissue of growing pigs fed diets without and with inclusion of chicory fiber. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrof, E.O.; Kojima, K.; Ropeleski, M.J.; Musch, M.W.; Tao, Y.; De Simone, C.; Chang, E.B. Probiotics inhibit nuclear factor-kb and induce heat shock proteins in colonic epithelial cells through proteasome inhibition. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Esmerino, E.A.; Margalho, L.P.; Santos-Junior, V.A.; Coimbra, P.T.; Cappato, L.P.; Silva, M.C.; Garcia-Gomes, A.S.; et al. Assessment of antioxidant activity, lipid profile, general biochemical and immune system responses of Wistar rats fed with dairy dessert containing Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Drabik, K.A.; Waypa, T.S.; Musch, M.W.; Alverdy, J.C.; Schneewind, O.; Chang, E.B.; Petrof, E.O. Soluble factors from Lactobacillus GG activate MAPKs and induce cytoprotective heat shock proteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C1018–C1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, M.E.; Zhang, J.; Messori, S.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Lalles, J.P. Early Changes in Microbial Colonization Selectively Modulate Intestinal Enzymes, but Not Inducible Heat Shock Proteins in Young Adult Swine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; He, J.H.; Xie, H.B.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, J.C.; Zou, Y. Resveratrol induces antioxidant and heat shock protein mRNA expression in response to heat stress in black-boned chickens. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ahn, Y.H.; Benjamin, I.J.; Honda, T.; Hicks, R.J.; Calabrese, V.; Cole, P.A.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. HSF1-Dependent Upregulation of Hsp70 by Sulfhydryl-Reactive Inducers of the KEAP1/NRF2/ARE Pathway. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussou, I.; Lambropoulos, I.; Pagoulatos, G.N.; Fotsis, T.; Roussis, I.G. Decrease of Heat Shock Protein Levels and Cell Populations by Wine Phenolic Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönmez, M.F.; Çilenk, K.T.; Karabulut, D.; Ünalmış, S.; Deligönül, E.; Öztürk, İ.; Kaymak, E. Protective effects of propolis on methotrexate-induced testis injury in rat. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 79, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Heikkila, J.J. Curcumin-induced inhibition of proteasomal activity, enhanced HSP accumulation and the acquisition of thermotolerance in Xenopus laevis A6 cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 158, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chander, K.; Vaibhav, K.; Ahmed, M.E. Quercetin mitigates lead acetate-induced behavioral and histological alterations via suppression of oxidative stress, Hsp-70, Bak and upregulation of Bcl-2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henstridge, D.C.; Whltham, M.; Febbralo, M.A. Chaperoning to the metabolic party: The emerging therapeutic role of heat-shock proteins in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Ludwig, M.S.; Heck, T.G.; Takahashi, H.K. Heat shock proteins and heat therapy for type 2 diabetes: Pros and cons. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Nguyen, A.K.; Henstridge, D.C. HSP72 protects against obesity-induced insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, C.R.; Carey, A.L.; Hawley, J.A. Intramuscular heat shock protein 72 and heme oxygenase-1 mRNA are reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurucz, I.; Morva, A.; Vaag, A.; Eriksson, K.F.; Huang, X.; Groop, L.; Koranyi, L. Decreased expression of heat shock protein 72 in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetescorrelates with insulin resistance. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, K.; Zhang, L.; Wagner, J.D. Tissue-specific regulation and expression of heat shock proteins in type 2 diabetic monkeys. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, A.A.; Bomhoff, G.L.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Geiger, P.C. Heat Treatment Improves Glucose Tolerance and Prevents Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. Diabetes 2009, 58, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.C.B.C.; Moura, C.S.; Roquetto, A.R.; Barrera-Arellano, D.; Yamada, A.T.; Santos, A.D.; Saad, M.J.A.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Impact of trans-fats on heat-shock protein expression and the gut microbiota profile of mice. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, A.M.; Midwood, K.S. DAMPening Inflammation by Modulating TLR Signalling. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 672395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Burkart, V.; Flohé, S.; Kolb, H. Cutting Edge: Heat Shock Protein 60 Is a Putative Endogenous Ligand of the Toll-Like Receptor-4 Complex. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jialal, I.; Kaur, H.; Devaraj, S. Toll-like Receptor Status in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: A Translational Perspective. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Märker, T.; Sell, H.; Zilleßen, P.; Glöde, A.; Kriebel, J.; Ouwens, D.M.; Pattyn, P.; Ruige, J.; Famulla, S.; Roden, M.; et al. Heat Shock Protein 60 as a Mediator of Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2012, 61, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasu, M.R.; Devaraj, S.; Park, S.; Jialal, I. Increased Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Activation and TLR Ligands in Recently Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, H.; Poitou, C.; Habich, C.; Bouillot, J.L.; Eckel, J.; Clément, K. Heat Shock Protein 60 in Obesity: Effect of Bariatric Surgery and its Relation to Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk. Obesity 2017, 25, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Hait, S.H.; Andrews-Shigaki, B.; Carus, S.; Deuster, P.A. Plasma HSP70 levels correlate with health risk factors and insulin resistance in african american subjects. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2014, 122, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Krause, J.; Krause, M.; O’Hagan, C.; De Vito, G.; Boreham, C.; Murphy, C.; Newsholme, P.; Colleran, G. Divergence of intracellular and extracellular HSP72 in type 2 diabetes: Does fat matter? Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marineli, R.S.; Moura, C.S.; Moraes, E.A.; Lenquiste, S.A.; Lollo, P.C.; Morato, P.N.; Amaya-Farfan, J.; Maróstica, M.R., Jr. Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) enhances HSP, PGC-1a expressions and improves glucose tolerance in diet-induced obese rats. Nutrition 2015, 31, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, J.M.; Blake, M.J.; Saari, J.T.; Bode, A.M. Dietary copper deficiency reduces heat shock protein expression in cardiovascular tissues. FASEB J. 1993, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, D. Allicin protects traumatic spinal cord injury through regulating the HSP70/Akt/iNOS pathway in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.A.; Lopez, A.; Richardson, A.; Pahlavani, M.A. Effect of age and dietary restriction on expression of heat shock protein 70 in rat alveolar macrophages. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1998, 104, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynes, R.; Leckey, B.D.; Nguyen, K., Jr.; Westerheide, S.D. Heat shock and caloric restriction have a synergistic effect on the heat shock response in a sir2.1-dependent manner in caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29045–29053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancsó, B.; Spiró, Z.; Arslan, M.A. The Heat Shock Connection of Metabolic Stress and Dietary Restriction. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, A.B.; Takahashi, R.; Strong, R.; Richardson, A. Expression of heat shock protein 70 is altered by age and diet at the level of transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dietary Nutrients | Effect on HSP | Tissue/Cell | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamine | Increase HSP70, HSP25, HSP90 | Lung, intestine, intestinal cell, blood mononuclear cells | [21,22,24,25,26] |
| l-threonine | Increase HSP70, HSP25 | Intestinal epithelial cells | [29] |
| l-methionine | Increase HSP70 | Mammary epithelial cells | [30] |
| l-arginine | Increase HSP70 | Intestine | [31] |
| l-arginine | None change HSP70, HSP90 | Muscle | [32] |
| l-arginine | Increase HSP70, HSP90; none change HSP25 | Muscle | [2] |
| Leu-Val dipeptide | Increase HSP70, HSP90, HSP25 | Muscle | [1,3] |
| lle-Leu dipeptide | Increase HSP70, HSP60, extracellular HSP70 | Muscle/plasma | [1,3] |
| Whey protein hydrolysate | Increase HSP70, HSP90; none change HSP60, HSP25 | Lung and muscle | [4,5] |
| Formula for premature pups | Reduce HSP70 | Intestine | [35] |
| l-glutamine, l-alanine or alanyl-glutamine dipeptide | Increase HSP27 | Muscle | [37] |
| Psyllium fiber | Increase HSP25; none change HSP70 | Intestine | [38] |
| Chicory fiber | Increase HSP27 | Intestine | [40] |
| Probiotic formulation | Increase HSP70, HSP25 | Colon | [41] |
| Probiotic (L. acidophilus) | None change HSP60, HSP90, HSP70 | Muscle | [42] |
| Probiotic (Lactobacillus GG) | Increase HSP70, HSP25 | Colon cell | [43] |
| Phenolic (Syrah red wine) | Inhibit HSP70, HSP27 | Tumor cells | [47] |
| White wine | None change HSP70, HSP27 | Tumor cells | [47] |
| Própolis | Increase HSP70 | Testis | [48] |
| Curcumin | Increase HSP30, HSP70 | A6 kidney cells | [49] |
| Quercetin | Reduce HSP70 | Cerebellum, cortex and hippocampus | [50] |
| High-fat diet (lard) | Reduce HSP70 | Muscle | [52,53,54,55] |
| Hyperlipidic oil diet | Reduce HSP25 | Muscle | [58] |
| Hyperlipidic high trans-fats content diet | None change HSP25, HSP60, HSP90, HSP70 | Muscle | [58] |
| High-fat diet | Increase extracellular HSP60 | Plasma | [62] |
| Chia oil with high-fat-high-fructose | Increase HSP70, HSP25 | Muscle | [67] |
| Copper deficiency | Reduce HSP70, HSP60; none change HSP90 | Myocardial | [68] |
| Allicin | Increase HSP70 | Spinal cord | [69] |
| Dietary restriction | Increase HSP70 | Alveolar macrophages | [70] |
| Caloric restriction | Increase HSP70 | Caenorhabditis elegans | [71] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Dietary Nutrients and Bioactive Substances Modulate Heat Shock Protein (HSP) Expression: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060683
Moura CS, Lollo PCB, Morato PN, Amaya-Farfan J. Dietary Nutrients and Bioactive Substances Modulate Heat Shock Protein (HSP) Expression: A Review. Nutrients. 2018; 10(6):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060683
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoura, Carolina Soares, Pablo Christiano Barboza Lollo, Priscila Neder Morato, and Jaime Amaya-Farfan. 2018. "Dietary Nutrients and Bioactive Substances Modulate Heat Shock Protein (HSP) Expression: A Review" Nutrients 10, no. 6: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060683
APA StyleMoura, C. S., Lollo, P. C. B., Morato, P. N., & Amaya-Farfan, J. (2018). Dietary Nutrients and Bioactive Substances Modulate Heat Shock Protein (HSP) Expression: A Review. Nutrients, 10(6), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060683





