Comparison of Human Milk Immunoglobulin Survival during Gastric Digestion between Preterm and Term Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Reparation and ELISAs
2.3. Peptidomic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Infant Demographics
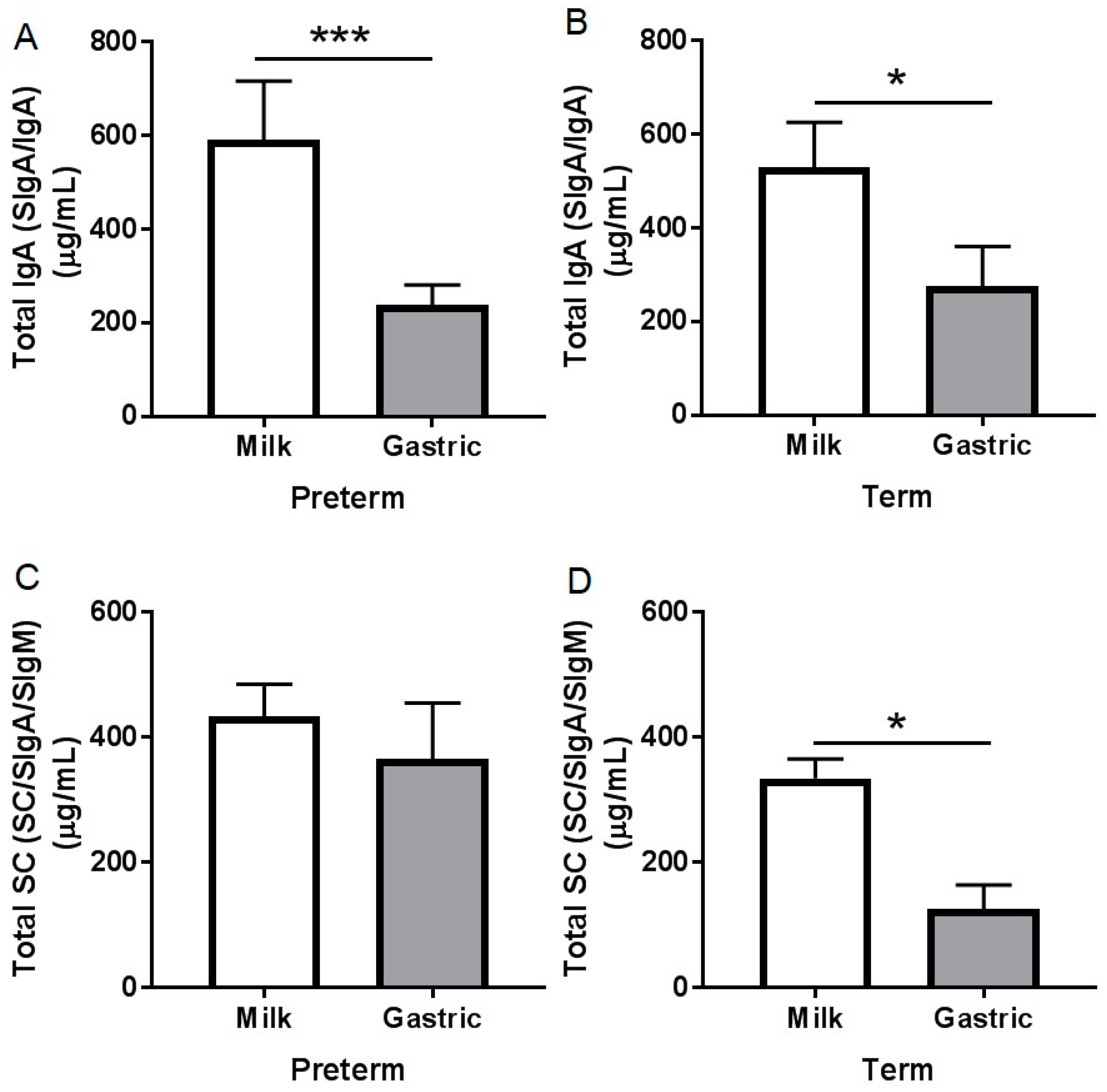
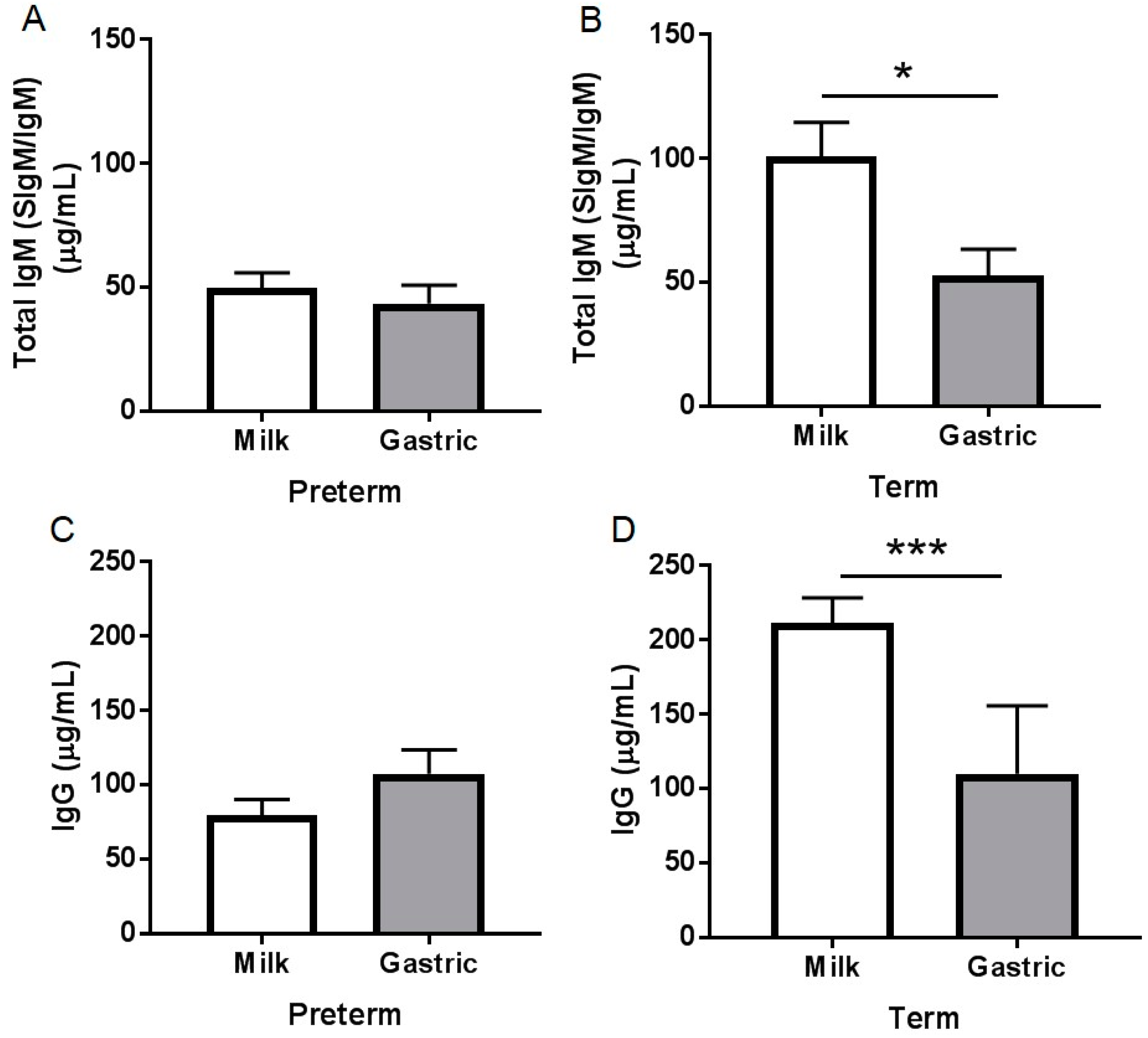
3.2. Ig Concentrations
3.2.1. Total IgA Concentration
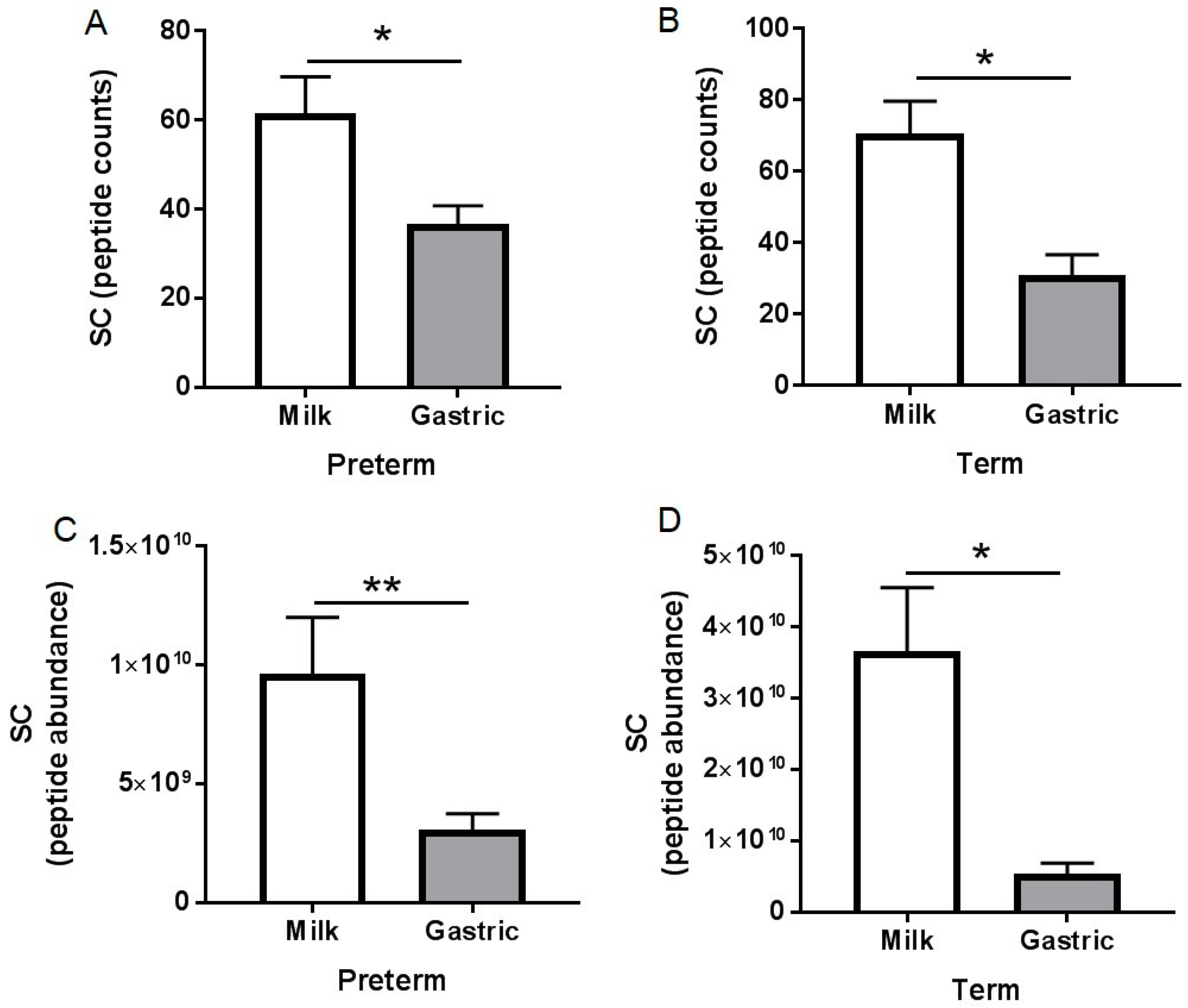
3.2.2. Total SC Concentration
3.2.3. Total IgM Concentration
3.2.4. IgG Concentration
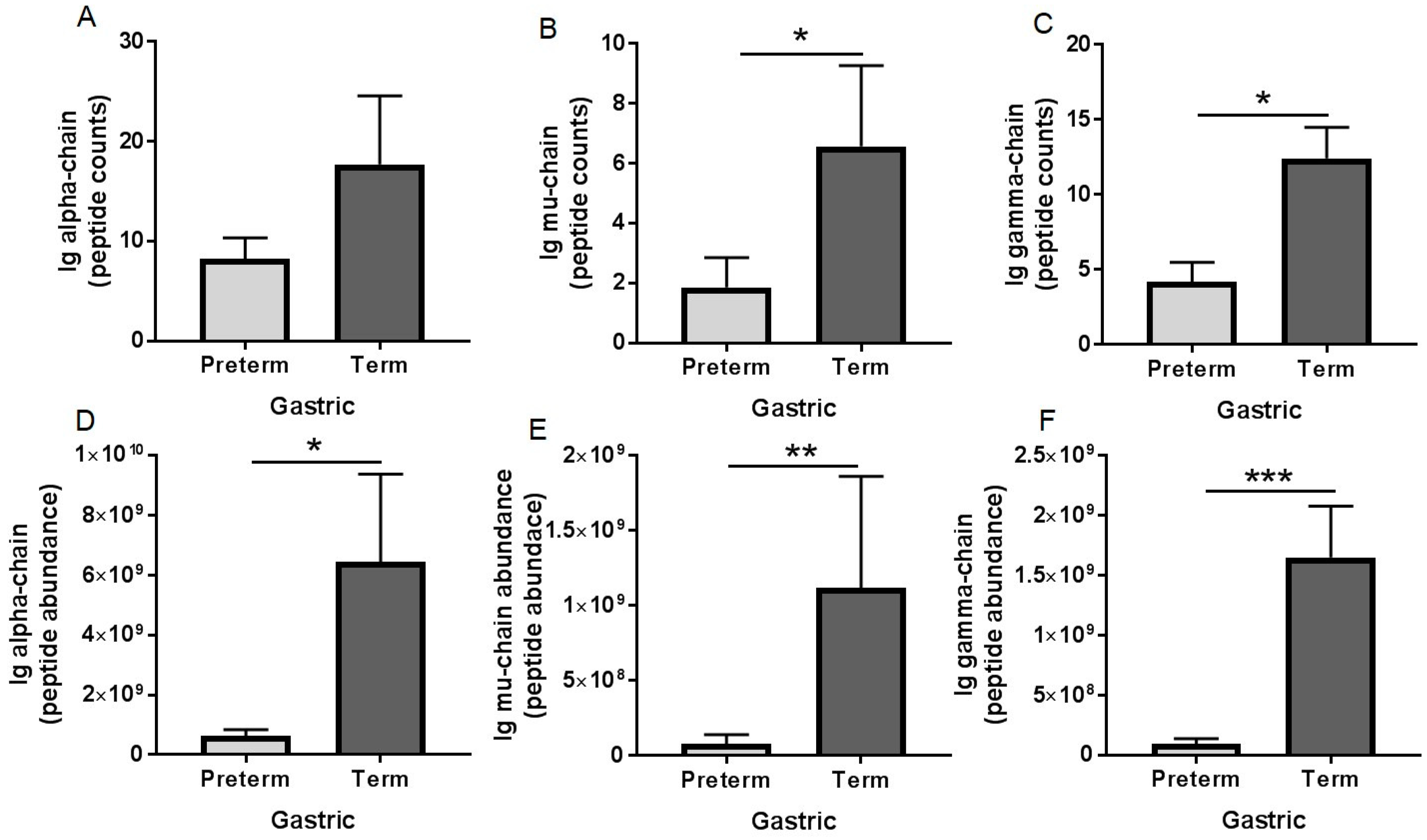
3.3. Peptidomic Results
3.4. pH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tha-In, T.; Bayry, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; Kaveri, S.V.; Kwekkeboom, J. Modulation of the cellular immune system by intravenous immunoglobulin. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeira, P.; Quinello, C.; Silveira-Lessa, A.L.; Zago, C.A.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M. IgG placental transfer in healthy and pathological pregnancies. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 2012, 985646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R. Immunoglobulin and protein levels in breast milk produced by mothers of preterm infants. Nutr. Res. 1982, 2, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.S.; Garza, C.; Nichols, B.L.; Goldblum, R.M. Immunologic factors in human milk during the first year of lactation. J. Pediatr. 1982, 100, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijts, L.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Moll, H.A. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. The distribution and functions of immunoglobulin isotypes. In Immunobiology, the Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, J.P.; Strumane, K.; Ruuls, S.R.; Beurskens, F.J.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P.W. Complement in therapy and Disease: Regulating the complement system with antibody-based therapeutics. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker-Zierikzee, A.; Tol, E.; Kroes, H.; Alles, M.; Kok, F.; Bindels, J. Faecal SIgA secretion in infants fed on pre-or probiotic infant formula. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 17, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantis, N.J.; Rol, N.; Corthésy, B. Secretory IgA’s complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Hunziker, L.; McCoy, K.; Lamarre, A. IgA responses in the intestinal mucosa against pathogenic and non-pathogenic microorganisms. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Claypool, S.M.; Wagner, J.S.; Mizoguchi, E.; Mizoguchi, A.; Roopenian, D.C.; Lencer, W.I.; Blumberg, R.S. Human neonatal Fc receptor mediates transport of IgG into luminal secretions for delivery of antigens to mucosal dendritic cells. Immunity 2004, 20, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkkiö, M.; Savilahti, E. Time of appearance of immunoglobulin-containing cells in the mucosa of the neonatal intestine. Pediatr. Res. 1980, 14, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Guroff, M. IgG surfaces as an important component in mucosal protection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, G.H.; Niels-Christiansen, L.-L.; Immerdal, L.; Danielsen, E.M. Antibodies in the small Intestine: Mucosal synthesis and deposition of anti-glycosyl IgA, IgM, and IgG in the enterocyte brush border. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G82–G90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hansen, G.H.; Pedersen, E.D.; Immerdal, L.; Niels-Christiansen, L.-L.; Danielsen, E.M. Anti-glycosyl antibodies in lipid rafts of the enterocyte brush Border: A possible host defense against pathogens. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G1100–G1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, N.; Mahe, S.; Benamouzig, R.; Sick, H.; Rautureau, J.; Tome, D. 15N-labeled immunoglobulins from bovine colostrum are partially resistant to digestion in human intestine. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eibl, M.M.; Wolf, H.M.; Fürnkranz, H.; Rosenkranz, A. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in low-birth-weight infants by IgA–IgG feeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanler, R.J.; Goldblum, R.M.; Garza, C.; Goldman, A.S. Enhanced fecal excretion of selected immune factors in very low birth weight infants fed fortified human milk. Pediatr. Res. 1986, 20, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblum, R.M.; Schanler, R.J.; Garza, C.; Goldman, A.S. Human milk feeding enhances the urinary excretion of immunologic factors in low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 1989, 25, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers-Mathieu, V.; Qu, Y.; Underwood, M.; Borghese, R.; Dallas, D. Premature infants have lower gastric digestion capacity for human milk proteins than term infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers-Mathieu, V.; Nielsen, S.D.; Underwood, M.A.; Borghese, R.; Dallas, D.C. Changes in proteases, antiproteases and bioactive proteins from mother’s breast milk to the premature infant stomach. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 66, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers-Mathieu, V.; Underwood, M.A.; Beverly, R.L.; David, D.C. Survival of immunoglobulins from human milk to preterm infant gastric samples at 1, 2, and 3 hours postprandial. Neonatology 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, A.; Sager, R.; Kuhn, P.; Nicolaides, K.H.; Schneider, H. Evolution of maternofetal transport of immunoglobulins during human pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1996, 36, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemlin, M.; Hoersch, G.; Zemlin, C.; Pohl-Schickinger, A.; Hummel, M.; Berek, C.; Maier, R.F.; Bauer, K. The postnatal maturation of the immunoglobulin heavy chain IgG repertoire in human preterm neonates is slower than in term neonates. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langkamp, D.L.; Davis, J.P. Increased risk of reported pertussis and hospitalization associated with pertussis in low birth weight children. J. Pediatr. 1996, 128, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothuis, J.R.; Simoes, E.A.; Hemming, V.G. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in preterm infants and the protective effects of RSV immune globulin (RSVIG). J. Pediatr. 1995, 95, 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Victor, Y. Effect of body position on gastric emptying in the neonate. Arch. Dis. Child. 1975, 50, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, F.; Romeo, C.; Baldari, S.; Arena, S.; Antonuccio, P.; Campennì, A.; Zuccarello, B.; Romeo, G. Gastrointestinal sequelae in survivors of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr. Int. 2008, 50, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faingold, R.; Cassia, G.; Prempunpong, C.; Morneault, L.; Sant’Anna, G.M. Intestinal ultrasonography in infants with moderate or severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy receiving hypothermia. Pediatr. Radiol. 2016, 46, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers-Mathieu, V.; Nielsen, S.D.; Underwood, M.A.; Borghese, R.; Dallas, D.C. Analysis of milk from mothers who delivered prematurely reveals few changes in proteases and protease inhibitors across gestational age at birth and infant postnatal age. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, M.; Lebenthal, E.; Topper, W.; Krantz, B.; Li, P.K. Gastric emptying in prematures of isocaloric feedings with differing osmolalities. Pediatr. Res. 1982, 16, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Dallas, D.C. Peptides released from foremilk and hindmilk proteins by breastmilk proteases are highly similar. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Dallas, D.C. Milk proteins are human mammary gland. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2017, 22, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, C.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A.; Fabris, C.; Fuggetta, D.; Molfino, S.; Testa, T.; Sgarrella, M.; Sabatino, G.; Restani, P. Immunoglobulin-A profile in breast milk from mothers delivering full term and preterm infants. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2007, 20, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, P.; Cuillière, M.L.; Molé, C.; Béné, M.C.; Faure, G. Immunological and nutritional composition of human milk in relation to prematurity and mothers’ parity during the first 2 weeks of lactation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 29, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, S.J.; Buckley, R.H.; Wakil, S.S.; McAllister, D.C.; David, R.J.; Faix, R.G. Elevated IgA concentration in milk produced by mothers delivered of preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 1981, 99, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellote, C.; Casillas, R.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Castell, M.; Moretones, M.G.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Franch, À. Premature delivery influences the immunological composition of colostrum and transitional and mature human milk. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, P.M.; Phelps, D.L.; Ank, B.J.; Krantman, H.J.; Stiehm, E.R. Survival of oral human immune serum globulin in the gastrointestinal tract of low birth weight infants. Pediatr. Res. 1981, 15, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Sanctuary, M.R.; Qu, Y.; Khajavi, S.H.; Van Zandt, A.E.; Dyandra, M.; Frese, S.A.; Barile, D.; German, J.B. Personalizing protein nourishment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3313–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.; Ryley, H.; Neale, L.; Dodge, J.; Lewarne, V. Effect of storage and heat on antimicrobial proteins in human milk. Arch. Dis. Child. 1978, 53, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, Á.; Diniz, E.M.d.A.; Barbosa, S.F.C.; Vaz, F.A.C. Immunologic factors in human Milk: The effects of gestational age and pasteurization. J. Hum. Lact. 2005, 21, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, E.D.; Gonçalves, A.K.; Cornetta, M.d.C.; Cunha, H.; Cardoso, M.L.; Morais, S.S.; Giraldo, P.C. Evaluation of the secretory immunoglobulin A levels in the colostrum and milk of mothers of term and pre-trerm newborns. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 9, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Guerrero, A.; Khaldi, N.; Borghese, R.; Bhandari, A.; Underwood, M.A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J.B.; Barile, D. A peptidomic analysis of human milk digestion in the infant stomach reveals protein-specific degradation patterns. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographics | Preterm-Delivering Mother Infant Pairs 1–2 | Term-Delivering Mother-Infant Pairs 1–2 |
|---|---|---|
| GA, weeks | 27 ± 3 (23−32) | 38.9 ± 0.5 (38−40) |
| Postnatal age, day | 39 ± 28 (7−98) | 23 ± 11 (16−42) |
| Postmenstrual age, day | 32 ± 2 (30−37) | 42 ± 2 (41−45) |
| Birth weight, kg | 1.0 ± 0.4 (0.5−1.6) | 3.5 ± 0.3 (3.0−3.8) |
| Infant sex | 13 females; 2 males | 6 females; 2 males |
| Mother’s age, year | 35 ± 3 (32−39) | 24 ± 10 (17−42) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demers-Mathieu, V.; Underwood, M.A.; Beverly, R.L.; Nielsen, S.D.; Dallas, D.C. Comparison of Human Milk Immunoglobulin Survival during Gastric Digestion between Preterm and Term Infants. Nutrients 2018, 10, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050631
Demers-Mathieu V, Underwood MA, Beverly RL, Nielsen SD, Dallas DC. Comparison of Human Milk Immunoglobulin Survival during Gastric Digestion between Preterm and Term Infants. Nutrients. 2018; 10(5):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050631
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemers-Mathieu, Veronique, Mark A. Underwood, Robert L. Beverly, Søren D. Nielsen, and David C. Dallas. 2018. "Comparison of Human Milk Immunoglobulin Survival during Gastric Digestion between Preterm and Term Infants" Nutrients 10, no. 5: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050631
APA StyleDemers-Mathieu, V., Underwood, M. A., Beverly, R. L., Nielsen, S. D., & Dallas, D. C. (2018). Comparison of Human Milk Immunoglobulin Survival during Gastric Digestion between Preterm and Term Infants. Nutrients, 10(5), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10050631






