Milk Fat Globule Membrane Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Increasing Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression in White Adipose Tissue of Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Treatments
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Total RNA Isolation and Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
2.5. Measurement of Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MFGM Suppresses HFD-Induced Increases in Body Weight of Mice
3.2. MFGM Prevents Alterations in Adipose Tissue Mediated by HFD of Mice
3.3. MFGM Prevents Alterations in Adipose Tissue Mediated by HFD of Mice
3.4. MFGM Regulates the Expression of Adipogenesis-Related Genes and Proteins in Epididymal WAT of HFD-Fed Mice
3.5. MFGM Activates AMPK Pathway in Epididymal WAT of HFD-Fed Mice
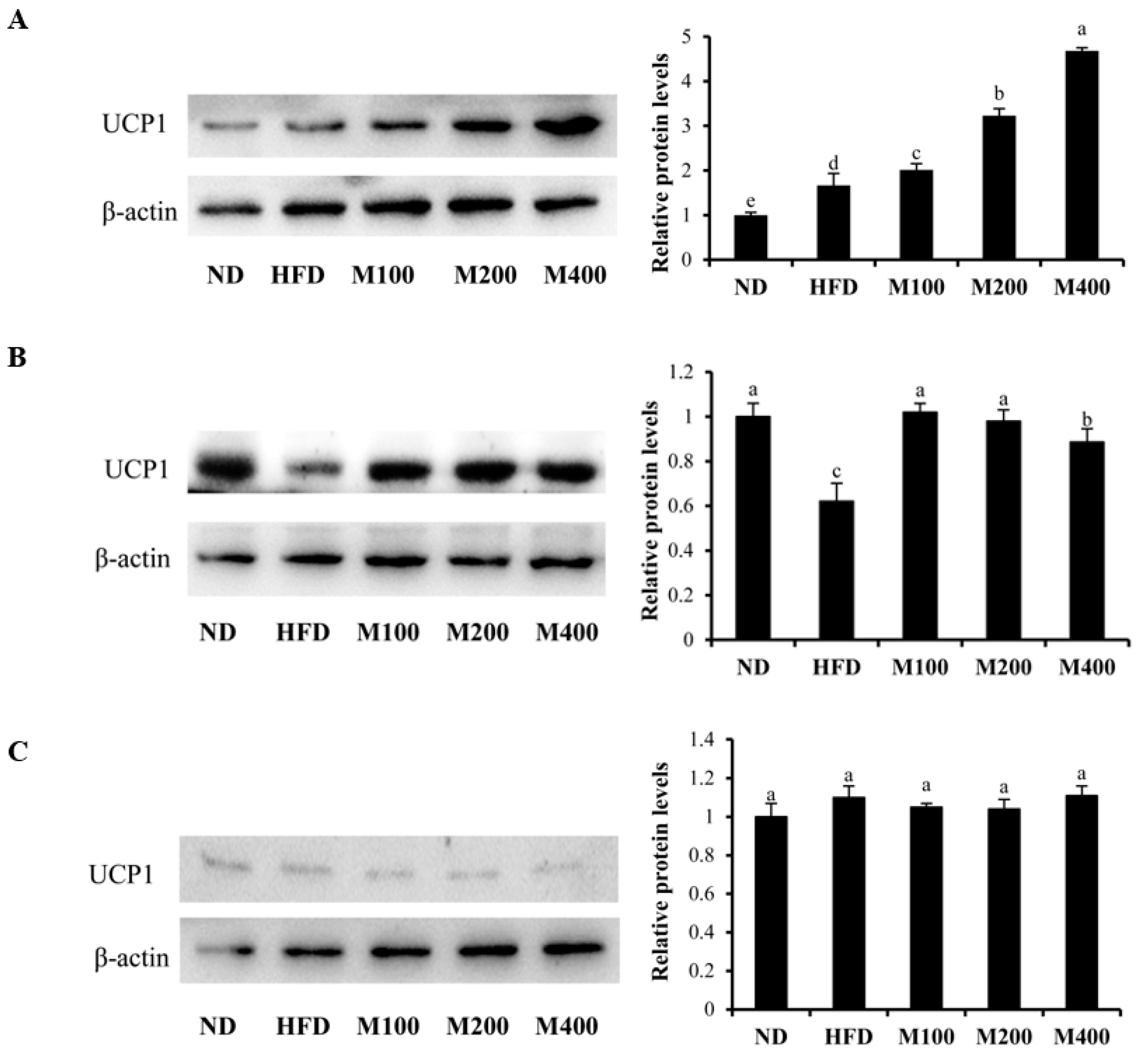
3.6. MFGM Upregulates UCP1 Protein Expression in Inguinal WAT and BAT of HFD-Fed Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavie, C.; Milani, R.; Ventura, H. Obesity and cardiovascular disease risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ferranti, S.; Mozaffarian, D. The perfect storm: Obesity, adipocyte dysfunction, and metabolic consequences. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, X. Molecular pathways regulating the formation of brown-like adipocytes in white adipose tissue. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langin, D. Recruitment of brown fat and conversion of white into brown adipocytes: Strategies to fight the metabolic complications of obesity? BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2010, 1801, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, L.; Anunciado-Koza, R. UCP1: Its involvement and utility in obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S7–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Ma, Q.; Jin, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlin, J.; Evans, B.; Dehvari, N.; Sato, M.; Bengtsson, T.; Hutchinson, D. Could burning fat start with a brite spark? Pharmacological and nutritional ways to promote thermogenesis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.A.; Caroline, T.; Gupta, R.K.; Scherer, P.E. Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chan, K.; Lee, Y.; Chang, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, C. Sechium edule shoot extracts and active components improve obesity and a fatty liver that involved reducing hepatic lipogenesis and adipogenesis in high-fat-diet-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4587–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, K.; Yu, J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, Y.; Hong, J.T.; Yun, Y.; et al. Sulforaphane attenuates obesity by inhibiting adipogenesis and activating the AMPK pathway in obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, D.; Boisvert, P. AMP-activated protein kinase in obesity: Metabolic node and beyond-introduction. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, B.; Norris, C.; MacGibbon, A. Protein and lipid composition of bovine milk-fat-globule membrane. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, D.R.; Ward, R.E.; Olsen, A.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Hintze, K.J. Membrane-rich milk fat diet provides protection against gastrointestinal leakiness in mice treated with lipopolysaccharide. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, I.; Uemura, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Iwashima-Suzuki, A.; Shiota, M.; Miyashita, K. The dietary effect of milk sphingomyelin on the lipid metabolism of obese/diabetic KK-Ay mice and wild-type C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3854–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, G.H.; Jiang, C.; Ryan, J.; Porter, C.M.; Blesso, C.N. Milk sphingomyelin improves lipid metabolism and alters gut microbiota in high fat diet-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 30, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmer, E.; Van Loan, M.D.; Rivera, N.; Rogers, T.S.; Gertz, E.R.; German, J.B.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Zivkovic, A.M. Addition of a dairy fraction rich in milk fat globule membrane to a high-saturated fat meal reduces the postprandial insulinaemic and inflammatory response in overweight and obese adults. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baars, A.; Oosting, A.; Engels, E.; Kegler, D.; Kodde, A.; Schipper, L.; Verkade, H.J.; van der Beek, E.M. Milk fat globule membrane coating of large lipid droplets in the diet of young mice prevents body fat accumulation in adulthood. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Ai, W.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Gao, P.; Shu, G.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Phytol increases adipocyte number and glucose tolerance through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in mice fed high-fat and high-fructose diet. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conforti, F.; Pan, M. Natural products in anti-obesity therapy. Molecules 2016, 21, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, J.; Fierce, Y.; Drivdahl, R.; Treuting, P.M.; Seamons, A.; Brabb, T.; Maggio-Price, L. Effects of murine norovirus infection on a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Comp. Med. 2010, 60, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Yang, G.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Tsai, M.; Wu, J.; Badmaev, V.; Ho, C.; Lai, C. Combination of citrus polymethoxyflavones, green tea polyphenols, and lychee extracts suppresses obesity and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Stern, J.H.; Scherer, P.E. The cell biology of fat expansion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducharme, N.A.; Bickel, P.E. Minireview: Lipid droplets in lipogenesis and lipolysis. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.; Fuentes, F.; Vilahur, G.; Badimon, L.; Palomo, I. Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristancho, A.G.; Lazar, M.A. Forming functional fat: A growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; MacDougald, O.A. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.M.; Barish, G.D.; Wang, Y.X. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Barrick, C.; Kim, K.A.; Lindner, J.; Blondeau, B.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shiota, M.; Kesterson, R.A.; Kahn, B.B.; Magnuson, M.A. Deletion of PPARgamma in adipose tissues of mice protects against high fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Hsu, C.; Wang, X.; Sakai, S.; Freeman, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Spiegelman, B. C/EBP alpha induces adipogenesis through PPAR gamma: A unified pathway. Gene Dev. 2002, 16, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolehmainen, M.; Vidal, H.; Alhava, E.; Uusitupa, M.I. Sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) expression in human obesity. Obesity 2001, 9, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhu, M.; Rodgers, B.D.; Jiang, Q.; Dodson, M.V.; Du, M. Resveratrol enhances brown adipocyte formation and function by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α1 in mice fed high-fat diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ha, J.H.; Okla, M.; Chung, S. 4-Hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol from Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) suppress differentiation of preadiopocytes to adipocytes via AMPK and MAPK pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Corton, J.; Ching, Y.P.; Davies, S.P.; Hawley, S. Regulation of lipid metabolism by the AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1997, 25, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Tse, I.; Li, E.; Wang, M. Oxyresveratrol supplementation to C57bl/6 mice fed with a high-fat diet ameliorates obesity-associated symptoms. Nutrients 2017, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Lee, Y.; Shin, D.; Lee, S.; Yoo, K.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Hong, J.; et al. Green tomato extract attenuates high-fat-diet-induced obesity through activation of the AMPK pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Yun, J.W. Curcumin induces brown fat-like phenotype in 3T3-L1 and primary white adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
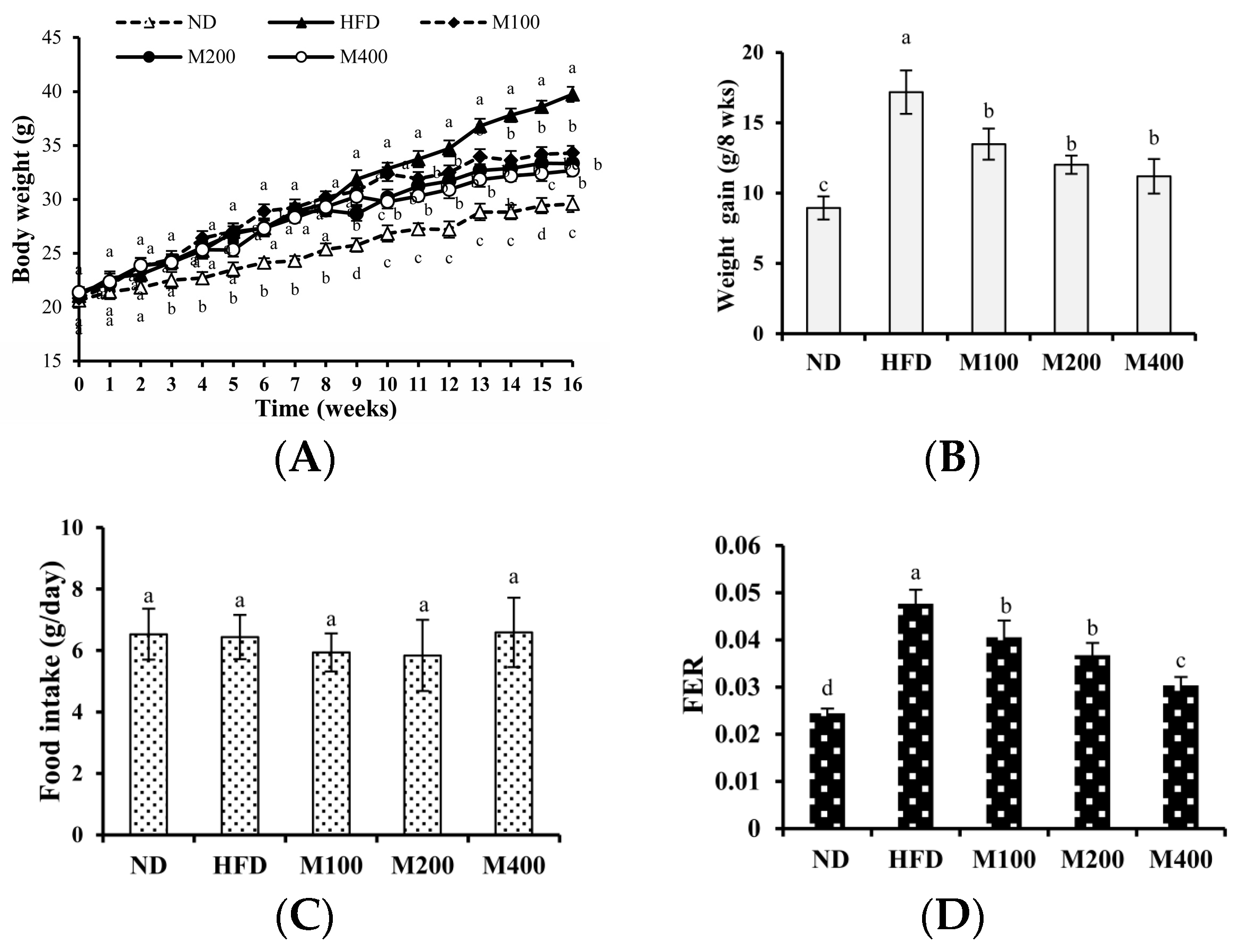
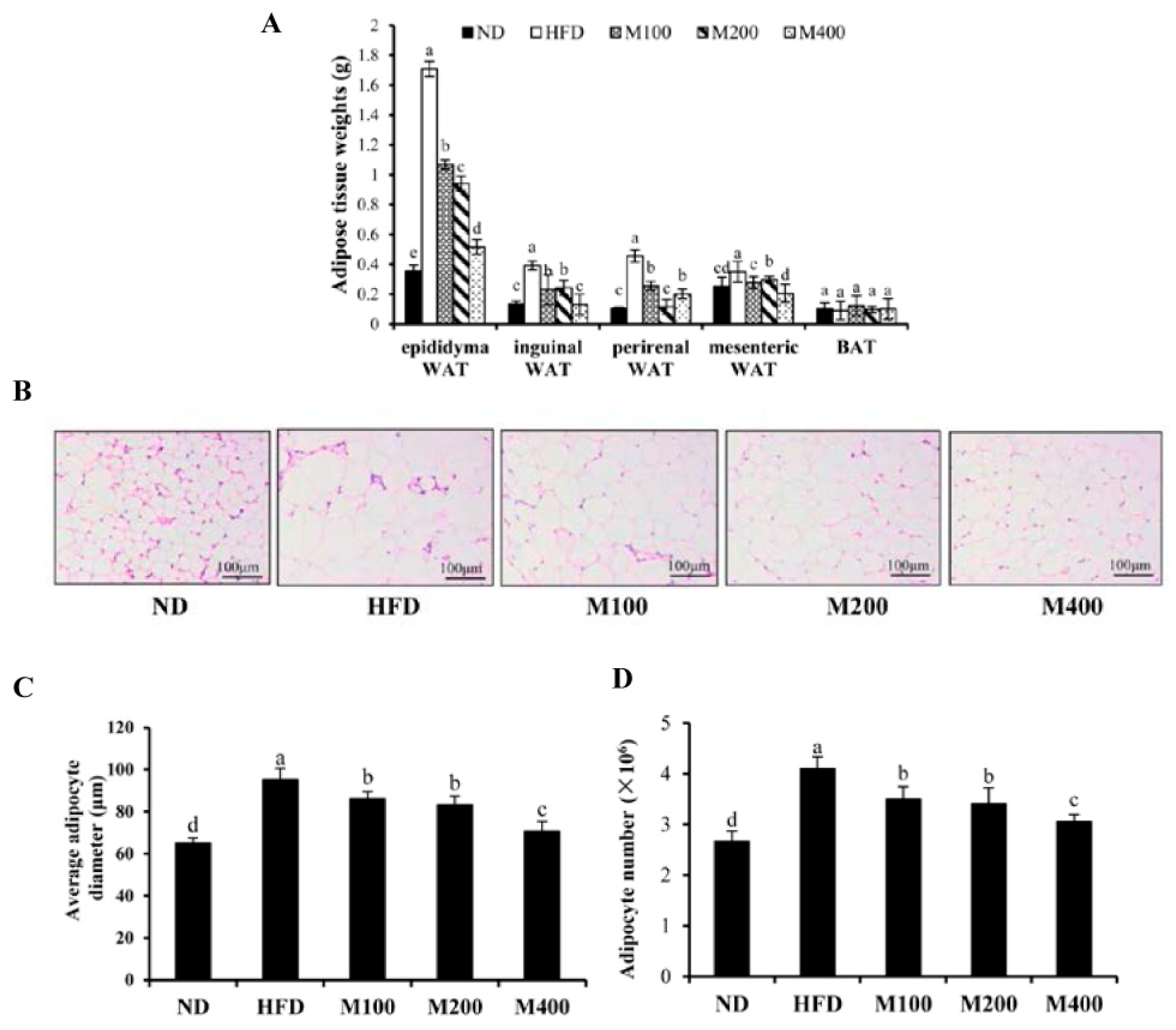
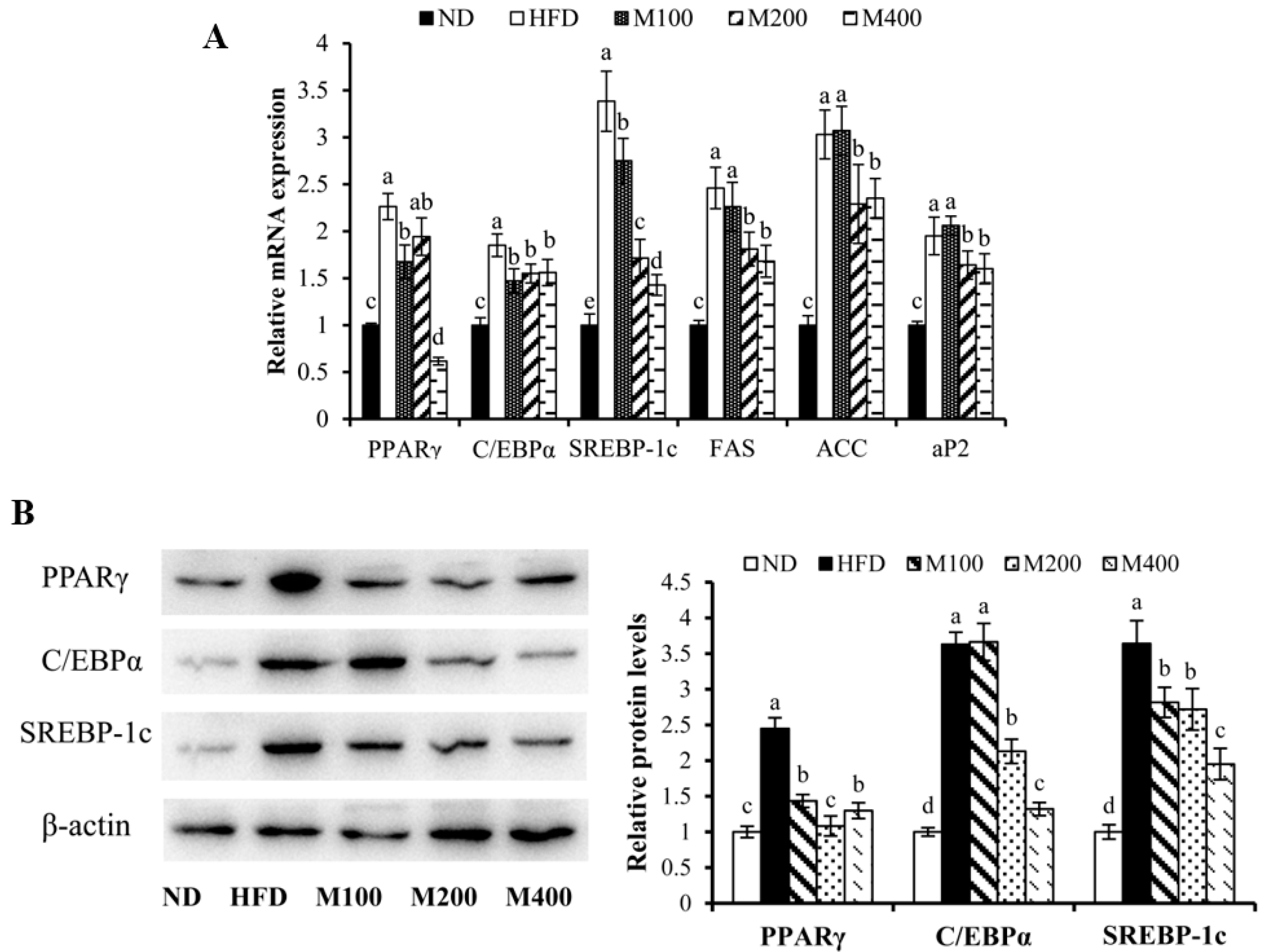
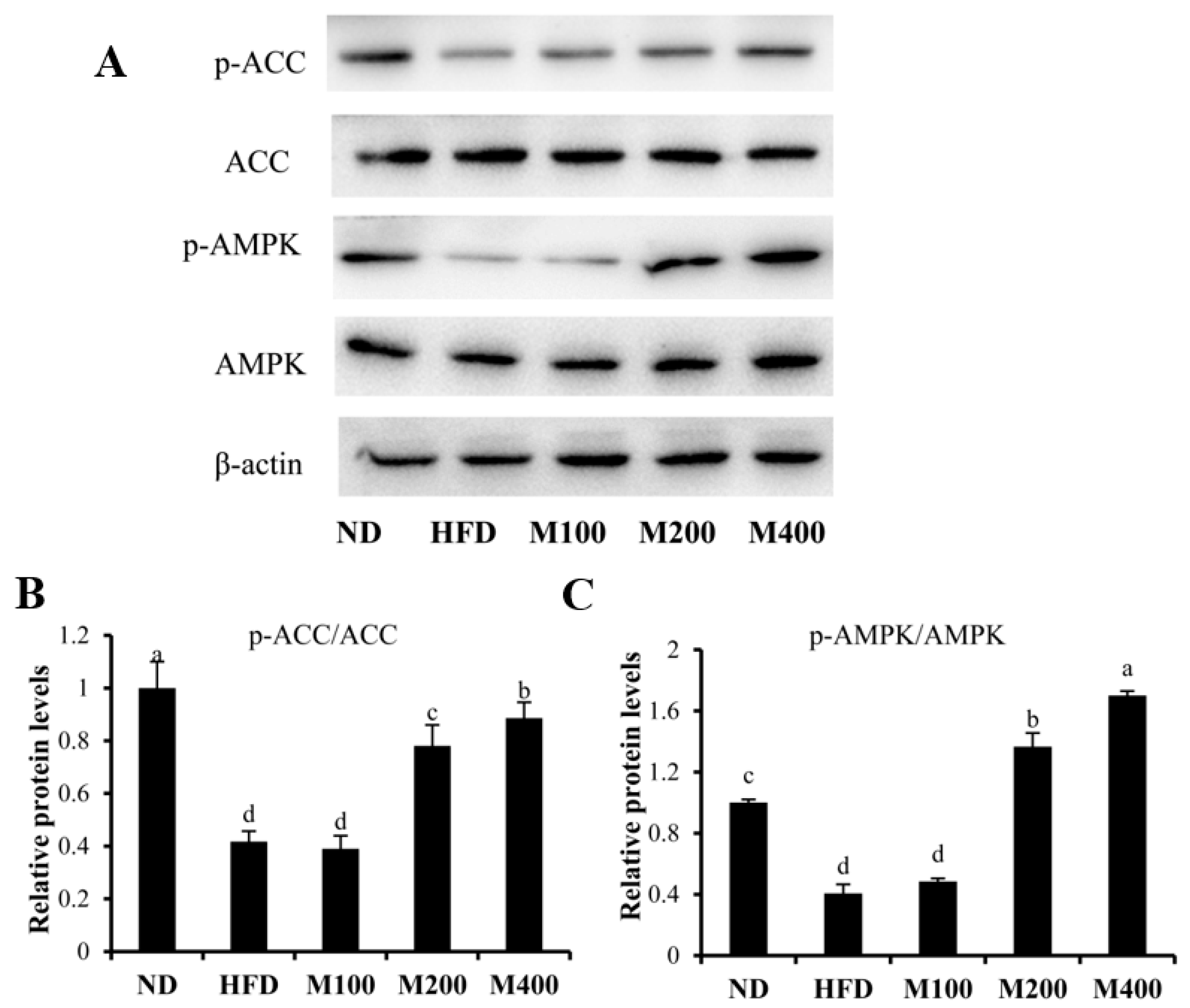
| Gene | Gene Bank No. | Forward Sequence (5′–3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPARγ | NM_011146.3 | AGCTCCAAGAATACCAAAGTGCGAT | AGGTTCTTCATGAGGCCTGTTGTAGA |
| C/EBPα | NM_007678.3 | AAACAACGCAACGTGGAGA | GCGGTCATTGTCACTGGTC |
| SREBP-1c | NM_011480.4 | CCCTGTGTGTACTGGCCTTT | TTGCGATGTCTCCAGAAGTG |
| FAS | NM_007988.3 | AGAGATCCCGAGACGCTTCT | GCCTGGTAGGCATTCTGTAGT |
| ACC | NM_133360.2 | GAATCTCCTGGTGACAATGCTTATT | GGTCTTGCTGAGTTGGGTTAGCT |
| aP2 | NM_024406.2 | CATGGCCAAGCCCAACAT | CGCCCAGTTTGAAGGAAATC |
| Parameters | Dietary Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND | HFD | M100 | M200 | M400 | |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.17 ± 0.04 c | 0.42 ± 0.03 a | 0.37 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ± 0.03 b | 0.25 ± 0.04 b |
| TC (mmol/L) | 2.58 ± 0.42 c | 5.58 ± 0.61 a | 4.28 ± 0.24 b | 3.97 ± 0.33 b | 3.71 ± 0.41 b |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.35 ± 0.20 c | 2.25 ± 0.34 a | 1.93 ± 0.11 a,b | 1.69 ± 0.07 b,c | 1.61 ± 0.13 b,c |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 0.14 ± 0.04 e | 0.41 ± 0.02 a | 0.33 ± 0.02 b | 0.26 ± 0.03 c | 0.21 ± 0.01 d |
| FFA (mmol/L) | 1.37 ± 0.12 d | 2.74 ± 0.33 a | 2.23 ± 0.19 b | 1.79 ± 0.15 c | 1.74 ± 0.21 c |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Gao, J.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Mao, X. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Increasing Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030331
Li T, Gao J, Du M, Song J, Mao X. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Increasing Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tiange, Jing Gao, Min Du, Jiajia Song, and Xueying Mao. 2018. "Milk Fat Globule Membrane Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Increasing Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression in White Adipose Tissue of Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030331
APA StyleLi, T., Gao, J., Du, M., Song, J., & Mao, X. (2018). Milk Fat Globule Membrane Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Increasing Uncoupling Protein 1 Expression in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. Nutrients, 10(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030331





