Preventive Potential of Resveratrol in Carcinogen-Induced Rat Thyroid Tumorigenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental Design
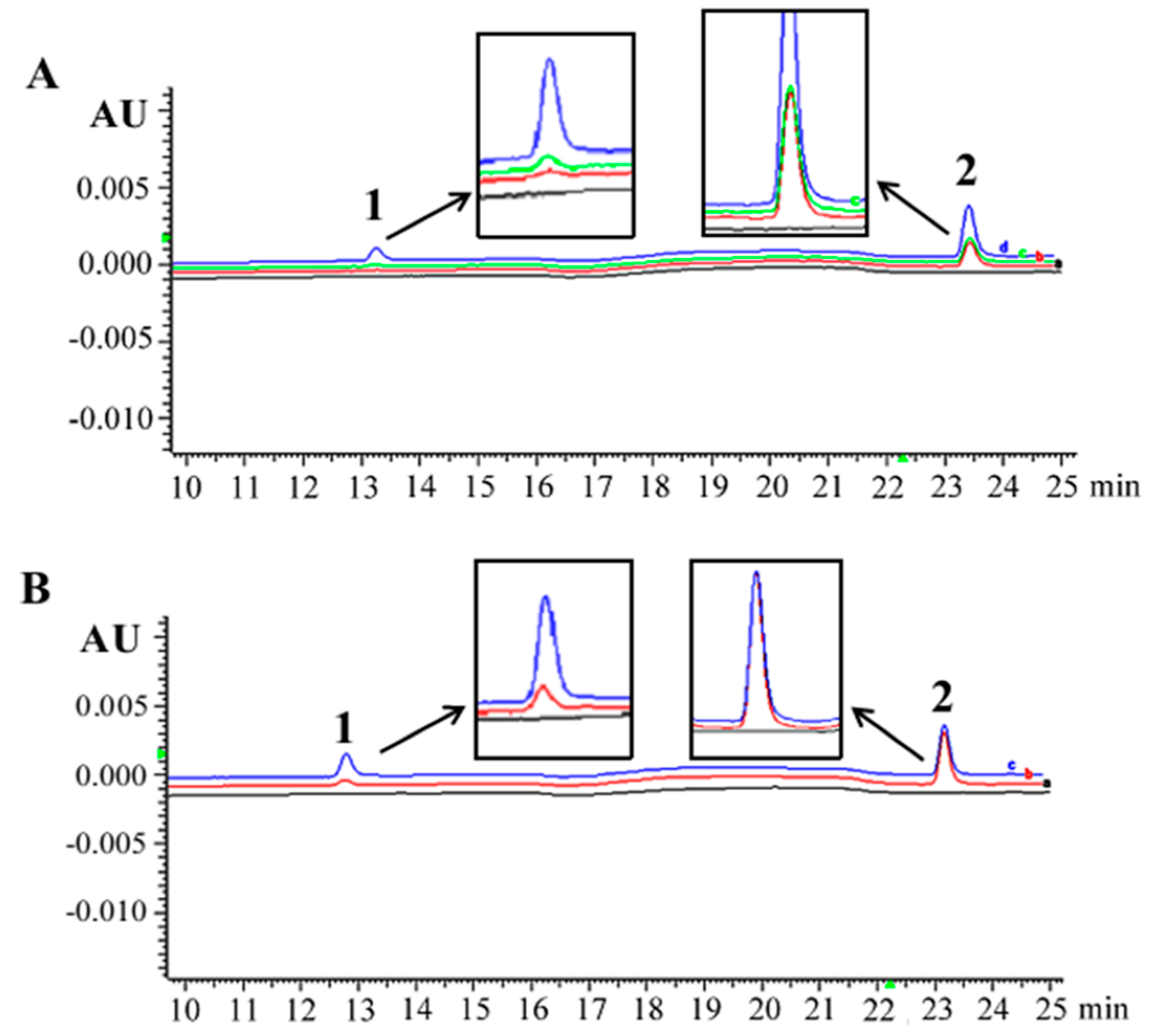
2.4. Elucidation of Resveratrol Availability in Thyroid Tissues and ATC Cells
2.4.1. Sample Collection and Treatments
2.4.2. Sample Preparation and HPLC Analyses
2.5. ELISA Assay for Thyroid Cancer-Related Markers
2.6. Histological Staining and Examination
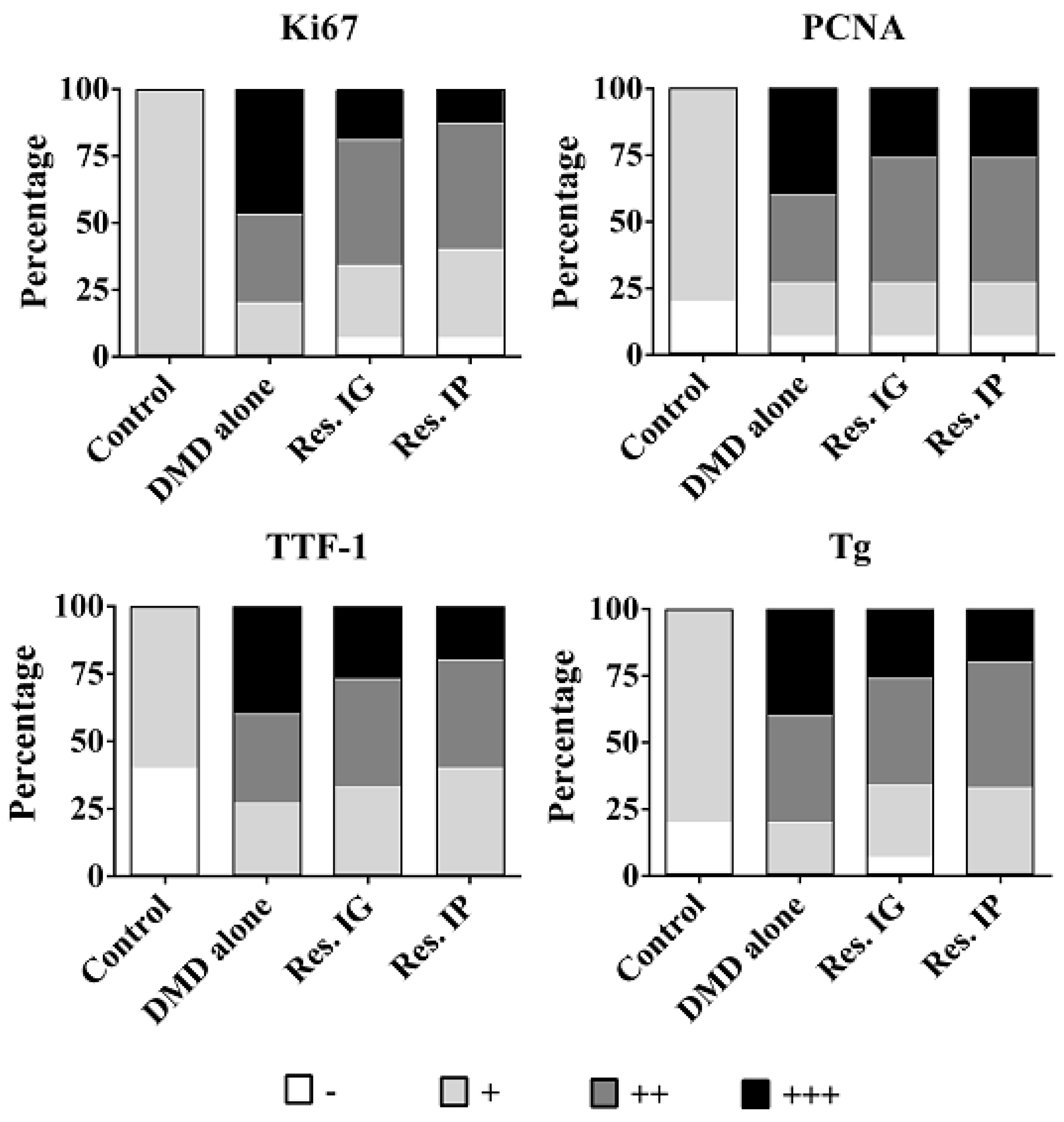
2.7. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sufficient Resveratrol Availability in Thyroids
3.2. Safety of Long-Term Resveratrol Treatment
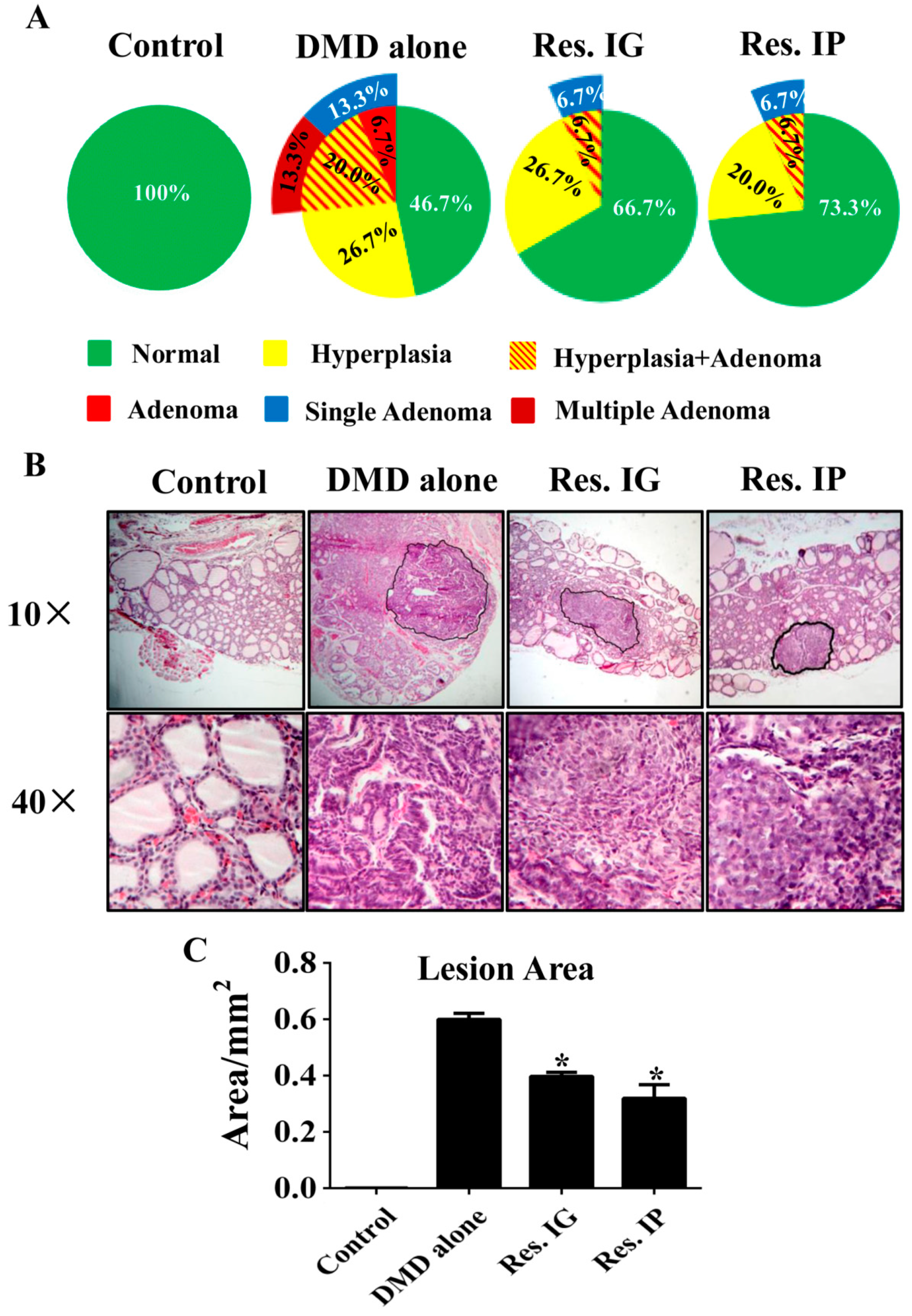
3.3. Resveratrol Alleviated Thyroid Tissue Lesions
3.4. Pathological Abnormalities in Other Organs
3.5. Lower Serum Tg and CEA Levels in Resveratrol-Treated Rats
3.6. Variable Levels of Growth-Related Factors in the Experimental Groups
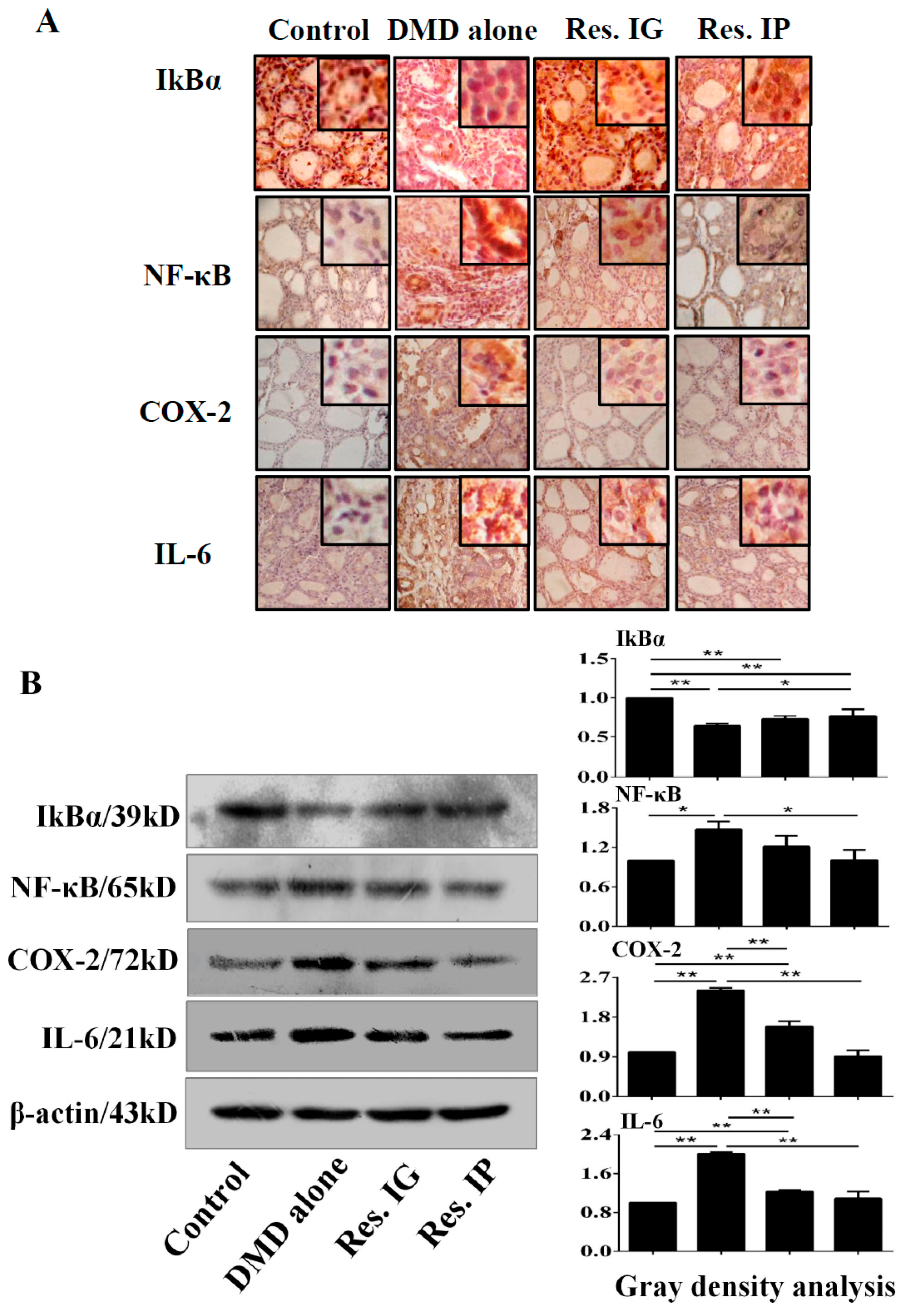
3.7. Resveratrol Inhibited NF-κB/p65 Signaling and IL-6 and COX-2 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vigneri, R.; Malandrino, P.; Vigneri, P. The changing epidemiology of thyroid cancer: Why is incidence increasing? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, W.; Shan, Z.; Teng, X.; Guan, H.; Li, Y.; Teng, D.; Jin, Y.; Yu, X.; Fan, C.; Chong, W.; et al. Effect of iodine intake on thyroid diseases in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2783–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lence-Anta, J.J.; Xhaard, C.; Ortiz, R.M.; Kassim, H.; Pereda, C.M.; Turcios, S.; Velasco, M.; Chappe, M.; Infante, I.; Bustillo, M.; et al. Environmental, lifestyle, and anthropometric risk factors for differentiated thyroid cancer in Cuba: A case-control study. Eur. Thyroid J. 2014, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kitahara, C.M.; Sosa, J.A. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K.; Preston, D.; Funamoto, S.; Yonehara, S.; Ito, M.; Tokuoka, S.; Sugiyama, H.; Soda, M.; Ozasa, K.; Mabuchi, K. Long-term trend of thyroid cancer risk among Japanese atomic-bomb survivors: 60 years after exposure. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagzag, J.; Malone, M.K.; Lopresti, M.A.; Ogilvie, J.B.; Patel, K.N.; Heller, K.S. Method of detection of well-differentiated thyroid cancers in obese and non-obese patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valerio, L.; Pieruzzi, L.; Giani, C.; Agate, L.; Bottici, V.; Lorusso, L.; Cappagli, V.; Puleo, L.; Matrone, A.; Viola, D.; et al. Targeted therapy in thyroid cancer: State of the art. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2017, 29, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D.; Valcavi, R.; Thompson, G.B.; Pedroni, C.; Renna, L.; Gradoni, P.; Barbieri, V. Complications of central neck dissection in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: Results of a study on 1087 patients and review of the literature. Thyroid 2012, 22, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Applewhite, M.K.; James, B.C.; Kaplan, S.P.; Angelos, P.; Kaplan, E.L.; Grogan, R.H.; Aschebrook-Kilfoy, B. Quality of life in thyroid cancer is similar to that of other cancers with worse survival. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastin, J.; Djouadi, F. Resveratrol and myopathy. Nutrients 2016, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Bhardwaj, A.; Aggarwal, R.S.; Seeram, N.P.; Shishodia, S.; Takada, Y. Role of resveratrol in prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 2783–2840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juan, M.E.; Vinardell, M.P.; Planas, J.M. The daily oral administration of high doses of trans-resveratrol to rats for 28 days is not harmful. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.T.; Tian, X.T.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.X.; Zhu, G.W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Resveratrol suppressed growth and reversed retinoic acid resistance of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia, G.J.; Azuine, M.A.; Takayasu, J.; Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Nishino, H.; Tokuda, H. Inhibition of epstein-barr virus early antigen activation promoted by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate by the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cancer Lett. 2000, 161, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Wanibuchi, H.; Salim, E.I.; Shen, J.; Wei, M.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Kudoh, S.; Hirata, K.; Fukushima, S. Revised rat multi-organ carcinogenesis bioassay for whole-body detection of chemopreventive agents: Modifying potential of S-methylcysteine. Cancer Lett. 2004, 206, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Yoshii, J.; Ikenaka, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Tsujinoue, H.; Nakatani, T.; Imazu, H.; Yanase, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Fukui, H. Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system attenuates liver enzyme-altered preneoplastic lesions and fibrosis development in rats. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Yokohira, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Yamakawa, K.; Kishi, S.; Ninomiya, F.; Kanie, S.; Saoo, K.; Imaida, K. Rat strain differences in levels and effects of chronic inflammation due to intratracheal instillation of quartz on lung tumorigenesis induced by DHPN. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 66, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, Y.; Kondo, H.; Ikeda, T.; Kawabata, A.; Shoji, Y.; Denda, A. Effect of dose on the carcinogenic activity of orally administered N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)nitrosamine in rats. Gan 1978, 69, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pula, B.; Malicka, I.; Pawlowska, K.; Paslawska, U.; Cegielski, M.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P.; Wozniewski, M. Immunohistochemical characterization of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary tumours of Sprague-Dawley rats. In Vivo 2013, 27, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohyama, W.; Okada, E.; Fujiishi, Y.; Narumi, K.; Yasutake, N. In vivo rat glandular stomach and colon micronucleus tests: Kinetics of micronucleated cells, apoptosis, and cell proliferation in the target tissues after a single oral administration of stomach- or colon-carcinogens. Mutat. Res. 2013, 755, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Han, B.S.; Ahn, B.; Hasegawa, R.; Shirai, T.; Ito, N.; Tsuda, H. Enhancement by indole-3-carbinol of liver and thyroid gland neoplastic development in a rat medium-term multiorgan carcinogenesis model. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlow, L.A.; D’Innocenzi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Rohl, S.D.; Cooper, S.J.; Sebo, T.; Grant, C.; McIver, B.; Kasperbauer, J.L.; Wadsworth, J.T.; et al. Detailed molecular fingerprinting of four new anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell lines and their use for verification of RhoB as a molecular therapeutic target. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5338–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Li, H.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, C.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Metabolic patterns and biotransformation activities of resveratrol in human glioblastoma cells: Relevance with therapeutic efficacies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, X.H.; Wang, L.L.; Li, H.; Song, X.; Shi, S.; Gu, J.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Liu, J. Diffusion Efficiency and Bioavailability of Resveratrol Administered to Rat Brain by Different Routes: Therapeutic Implications. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boorman, G.A.; Haseman, J.K.; Waters, M.D.; Hardisty, J.F.; Sills, R.C. Quality review procedures necessary for rodent pathology databases and toxicogenomic studies: The National Toxicology Program experience. Toxicol. Pathol. 2002, 30, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.L.; Wu, M.L.; Li, H.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, N.N.; Chen, X.Y.; Kong, Q.Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J. CRABP-II- and FABP5-independent responsiveness of human glioblastoma cells to all-trans retinoic acid. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5889–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Shu, X.-H.; Sha, L.; Bian, J.; Wang, L.-L.; Gu, J.-Y.; Shi, S.; Li, P.-N.; Wu, M.-L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Lumbar puncture-administered resveratrol inhibits STAT3 activation, enhancing autophagy and apoptosis in orthotopic rat glioblastomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75790–75799. [Google Scholar]
- Petric, R.; Perhavec, A.; Gazic, B.; Besic, N. Preoperative serum thyroglobulin concentration is an independent predictive factor of malignancy in follicular neoplasms of the thyroid gland. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinski, K.; Kaznowski, J.; Klimowicz, A.; Maciejewski, A.; Łapińska-Cwojdzińska, D.; Gurgul, E.; Car, A.D.; Fichna, M.; Gut, P.; Gryczyńska, M.; et al. Diagnostic value of selected biochemical markers in the detection of recurrence of medullary thyroid cancer-comparison of calcitonin, procalcitonin, chromogranin A, and carcinoembryonic antigen. Endokrynol. Pol. 2017, 68, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupain, C.; Ali, H.M.; Mouhoub, T.A.; Urbinati, G.; Massaad-Massade, L. Induction of TTF-1 or PAX-8 expression on proliferation and tumorigenicity in thyroid carcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.G.; Lu, N.; Lu, B.H.; Chen, Z.H. Expression of Ki67 in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma and its clinical significance. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2015, 16, 1605–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurikova, M.; Danihel, L.; Polak, S.; Varga, I. Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Brown, R.E. Morphoproteomic confirmation of an activated nuclear factor-small Ka, CyrillicBp65 pathway in follicular thyroid carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasumura, M.; Imai, T.; Takizawa, T.; Ueda, M. Promotion of thyroid carcinogenesis by para-aminobenzoic acid in rats initiated with N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)nitrosamine. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Borkhuu, O.; Bao, W.; Yang, Y.T. Signaling pathways in thyroid cancer and their therapeutic implications. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureldine, S.I.; Tufano, R.P. Association of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and thyroid cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, F.; Castagna, M.G.; Brilli, L.; Pentheroudakis, G. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 7), vii110–vii119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual Corrales, E.; Príncipe, R.M.; Laguna Muro, S.; Martínez Regueira, F.; Alcalde Navarrete, J.M.; Guillén Grima, F.; Galofré, J.C. Incidental differentiated thyroid carcinoma is less prevalent in Graves’ disease than in multinodular goiter. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2012, 59, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, G. Parvovirus B19 infection associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in adults. J. Infect. 2010, 60, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Mondal, D.; Kandil, E. The nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathway as a therapeutic target against thyroid cancers. Thyroid 2013, 23, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Jain, S.; Khurana, N.; Kakar, A.K. Expression of p63 and Bcl-2 in malignant thyroid tumors and their correlation with other diagnostic immunocytochemical markers. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, EC04–EC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.F.S.; Silva, G.D.B.; Pavan, A.R.; Chiba, D.E.; Chin, C.M.; Dos Santos, J.L. Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms Induced by Resveratrol. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, M.; Back, J.H.; Kopelovich, L.; Bickers, D.R.; Kim, A.L. Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol: Anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 486, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinimehr, S.J.; Hosseini, S.A. Resveratrol sensitizes selectively thyroid cancer cell to 131-iodine toxicity. J. Toxicol. 2014, 2014, 839597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambini, J.; Inglés, M.; Olaso, G.; Lopez-Grueso, R.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Abdelaziz, K.M.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Vina, J.; et al. Properties of resveratrol: In vitro and in vivo studies about metabolism, bioavailability, and biological effects in animal models and humans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 837042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Hao, L.; Fan, S.; Jiang, F.; Xie, Y.; et al. Low dose of Bisphenol A enhance the susceptibility of thyroid carcinoma stimulated by DHPN and iodine excess in F344 rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69874–69887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, A.M.; Provatopoulou, X.; Kalogera, E.; Zografos, G.N.; Gounaris, A. Circulating thyroid cancer biomarkers: Current limitations and future prospects. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2017, 87, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, A.; Barczynski, M.; Nowak, W.; Richter, P. Prognostic factors in differentiated thyroid cancer—A 20-year surgical outcome study. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2012, 397, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, S.; Dave, Y.; Rakhit, A.; Sarkar, D.K. Hypothalamic beta-endorphin neurons suppress preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions development in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine induced rat colon cancer model. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigaray, P.; Belpomme, D. Basic properties and molecular mechanisms of exogenous chemical carcinogens. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Vijayalekshmi, R.V.; Sung, B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: Short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, F.; Leonardi, A. Role of NF-κB in thyroid cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 321, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Treatment | No. of Rats | Body Weight | Relative Organ Weights | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 w | 30 w | 0 w | 30 w | Thyroid | Liver | Lung | Kidneys | Spleen | |
| Control | 5 | 5 | 162.8 ± 5.4 | 610.1 ± 24.8 | 0.011 ± 0.000 | 2.49 ± 0.21 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.59 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| DMD alone | 15 | 15 | 162.6 ± 7.0 | 549.1 ± 42.1 | 0.013 ± 0.002 | 2.92 ± 0.65 | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| Res. IG | 15 | 15 | 163.1 ± 7.7 | 580.5 ± 37.7 * | 0.012 ± 0.002 | 2.73 ± 0.34 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Res. IP | 15 | 15 | 163.9 ± 7.2 | 591.3 ± 38.4 * | 0.012 ± 0.001 | 2.69 ± 0.39 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.61 ± 0.07 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| Organs | Control | DMD Alone | Res. IG | Res. IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 5) a | (n = 15) a | (n = 15) a | (n = 15) a | |
| Liver carcinoma | 0 | 4 (26.7) b | 1 (6.7) b | 1 (6.7) b |
| Colon lymphadenosis | 0 | 7 (46.7) b | 4 (26.7) b | 4 (26.7) b |
| Lung fibrous hyperplasia | 0 | 3 (20.0) b | 2 (13.3) b | 1 (6.7) b |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Jia, B.; Song, X.; Kong, Q.-Y.; Wu, M.-L.; Qiu, Z.-W.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Preventive Potential of Resveratrol in Carcinogen-Induced Rat Thyroid Tumorigenesis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030279
Zheng X, Jia B, Song X, Kong Q-Y, Wu M-L, Qiu Z-W, Li H, Liu J. Preventive Potential of Resveratrol in Carcinogen-Induced Rat Thyroid Tumorigenesis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(3):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030279
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xu, Bin Jia, Xue Song, Qing-You Kong, Mo-Li Wu, Ze-Wen Qiu, Hong Li, and Jia Liu. 2018. "Preventive Potential of Resveratrol in Carcinogen-Induced Rat Thyroid Tumorigenesis" Nutrients 10, no. 3: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030279
APA StyleZheng, X., Jia, B., Song, X., Kong, Q.-Y., Wu, M.-L., Qiu, Z.-W., Li, H., & Liu, J. (2018). Preventive Potential of Resveratrol in Carcinogen-Induced Rat Thyroid Tumorigenesis. Nutrients, 10(3), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030279





