Physiological Translocation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Pregnancy Contributes to the Composition of the Milk Microbiota in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Media
2.2. Construction of pMG36e::luxAB and pMG36e::luxABCDE
2.3. Transformation of L. lactis MG1614 and L. salivarius PS2
2.4. Bioluminescence Assays
2.5. In Vivo Translocation Model
2.6. Statistics Analysis: Sample Size Calculation
3. Results
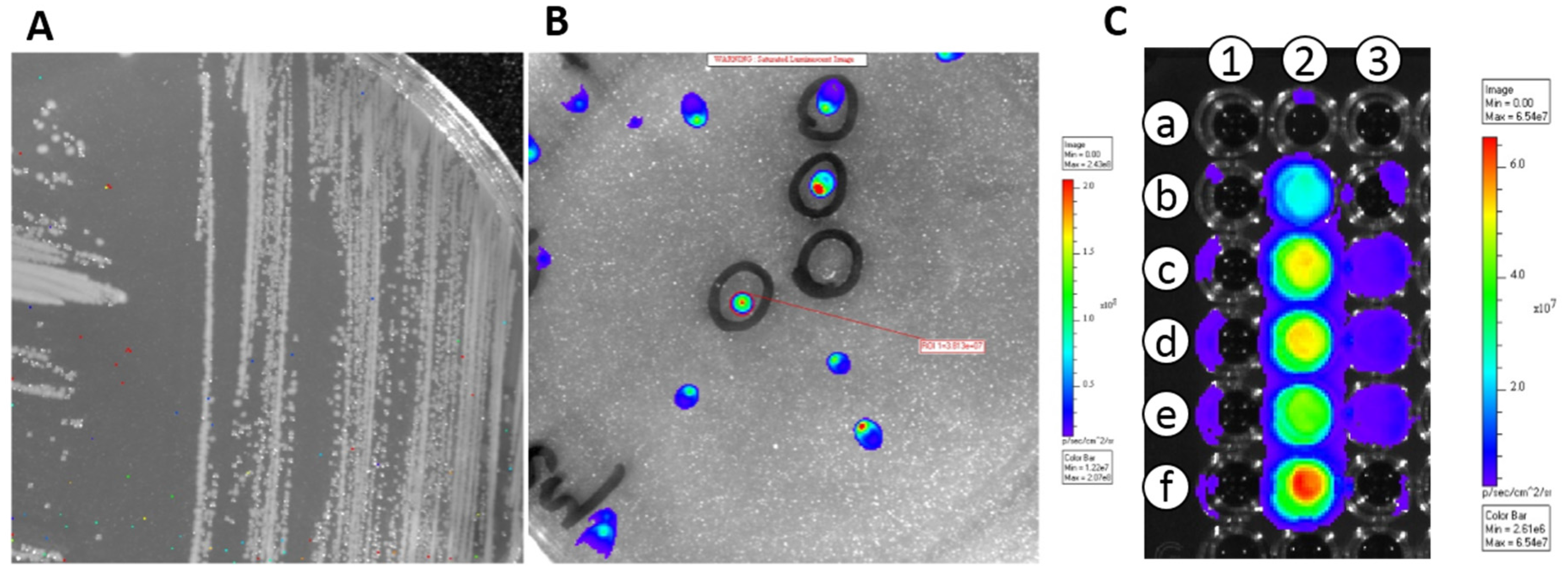
3.1. Transformation of E. coli and LAB Strains with pMG36e::luxAB and pMG36e::luxABCDE
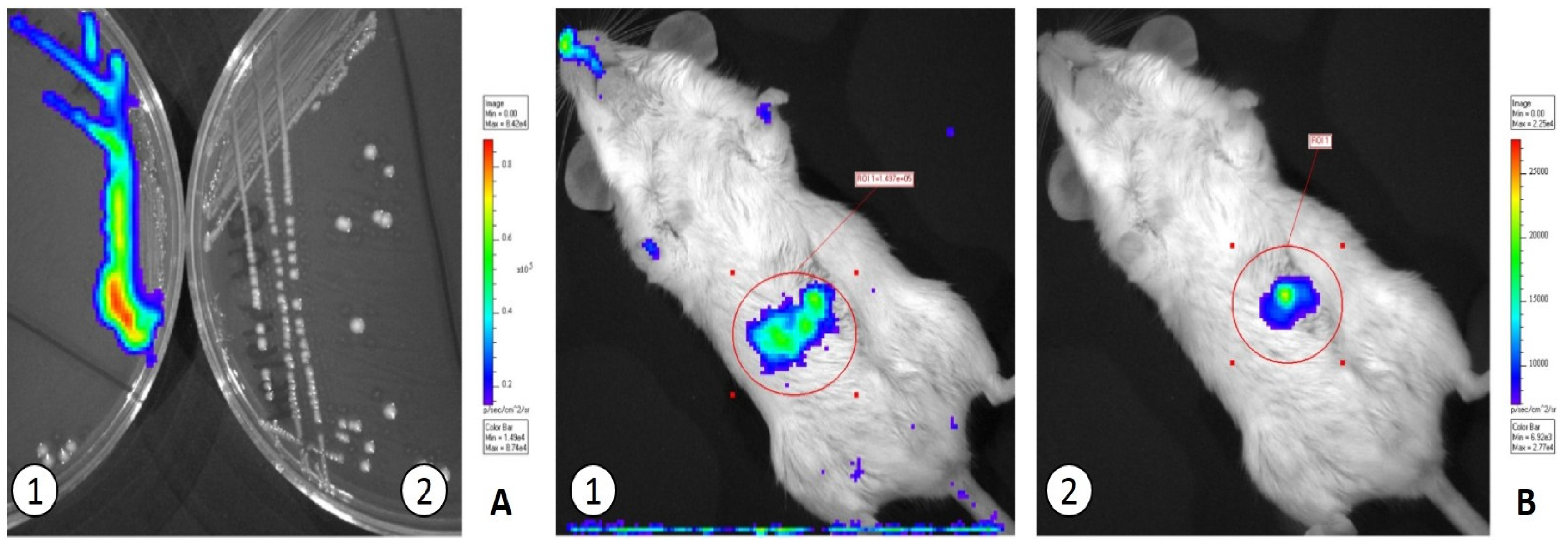
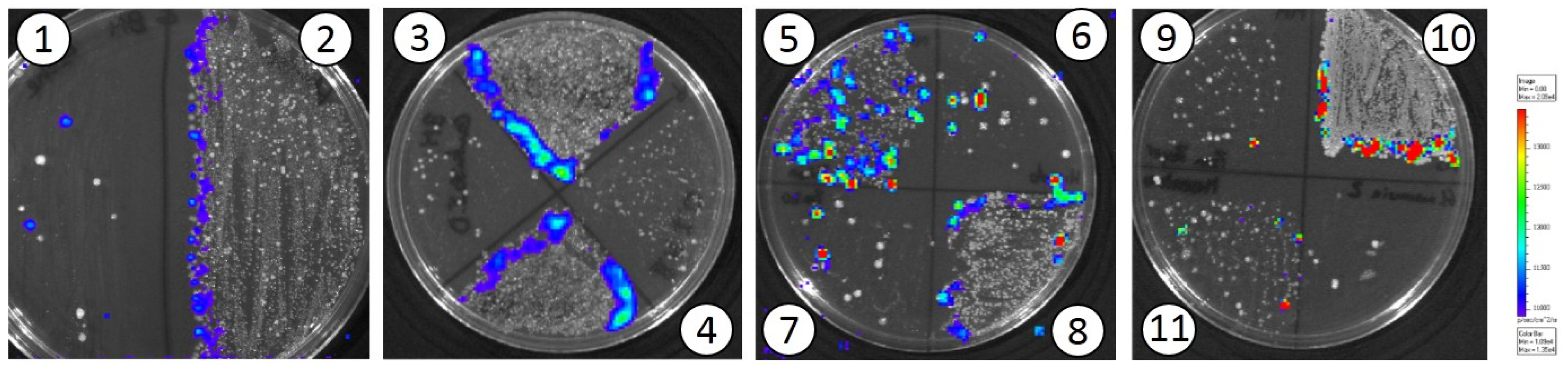
3.2. In Vivo Translocation Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez, L.; Langa, S.; Martin, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jimenez, E.; Martin, R.; Rodriguez, J.M. The Human Milk Microbiota: Origin and Potential Roles in Health and Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeurink, P.V.; van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Jimenez, E.; Knippels, L.M.; Fernandez, L.; Garssen, J.; Knol, J.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Martin, R. Human Milk: A Source of More Life than We Imagine. Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martı́n, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiménez, E.; Marı́n, M.L.; Olivares, M.; Boza, J.; Jiménez, J.; Fernández, L.; Xaus, J.; et al. The commensal microflora of human milk: New perspectives for food bacteriotherapy and probiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.F.; Dore, J.; Leclerc, M.; Levenez, F.; Benyacoub, J.; Serrant, P.; Segura-Roggero, I.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Donnet-Hughes, A. Bacterial imprinting of the neonatal immune system: Lessons from maternal cells? Pediatrics 2007, 119, e724–e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; Fernandez, L.; Maldonado, A.; Martin, R.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Rodriguez, J.M. Oral administration of Lactobacillus strains isolated from breast milk as an alternative for the treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4650–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, R.; Martin, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jimenez, E.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation: Antibiotics versus oral administration of lactobacilli isolated from breast milk. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, P. Biochemistry and genetics of bacterial bioluminescence. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 144, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rocchetta, H.L.; Boylan, C.J.; Foley, J.W.; Iversen, P.W.; LeTourneau, D.L.; McMillian, C.L.; Contag, P.R.; Jenkins, D.E.; Parr, T.R., Jr. Validation of a Noninvasive, Real-Time Imaging Technology using Bioluminescent Escherichia coli in the Neutropenic Mouse Thigh Model of Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, S.; Clare, S.; Harker, J.; Huett, A.; Young, D.; Dougan, G.; Frankel, G. Organ specificity, colonization and clearance dynamics in vivo following oral challenges with the murine pathogen citrobacter rodentium. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, A.K.; Rader, B.A.; Stabb, E.V.; Mandel, M.J. Regulation of bioluminescence in photobacterium leiognathi strain KNH6. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 3676–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, G.E.; Longman, R.S.; Zhang, J.X.; Breart, B.; Galan, C.; Cuesta, A.; Schwab, S.R.; Littman, D.R. Microbiota restricts trafficking of bacteria to mesenteric lymph nodes by CX3CR1Hi cells. Nature 2013, 494, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, M.; Morrissey, D.; Rajendran, S.; El Mashad, S.M.; van Sinderen, D.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Tangney, M. Orally administered bifidobacteria as vehicles for delivery of agents to systemic tumors. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasson, M.J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 154, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Llorach, R.; Marinic, J.; Tulipani, S.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Jimenez, E.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Urinary metabolomic fingerprinting after consumption of a probiotic strain in women with mastitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 87, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Martos, I.; Jimenez, E.; de Andres, J.; Rodriguez-Alcala, L.M.; Tavarez, S.; Manzano, S.; Fernandez, L.; Alonso, E.; Fontecha, J.; Rodriguez, J.M. Milk and blood biomarkers associated to the clinical efficacy of a probiotic for the treatment of infectious mastitis. Benef. Microbes 2016, 7, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, L.; Cardenas, N.; Arroyo, R.; Manzano, S.; Jimenez, E.; Martin, V.; Rodriguez, J.M. Prevention of Infectious Mastitis by Oral Administration of Lactobacillus salivarius PS2 during Late Pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, K.P.; Joh, D.; Bellinger-Kawahara, C.; Hawkinson, M.J.; Purchio, T.F.; Contag, P.R. Monitoring Bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Living Mice using a Novel luxABCDE Construct. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3594–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Guchte, M.; van der Vossen, J.M.; Kok, J.; Venema, G. Construction of a lactococcal expression vector: Expression of hen egg white lysozyme in Lactococcus. lactis subsp. Lactis Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holo, H.; Nes, I.F. High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus. lactis Subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mason, C.K.; Collins, M.A.; Thompson, K. Modified electroporation protocol for lactobacilli isolated from the chicken crop facilitates transformation and the use of a genetic tool. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 60, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Martin, P.; O’Connell-Motherway, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Mayo, B. Functional analysis of the pBC1 replicon from Bifidobacterium catenulatum L48. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, E.; Arroyo, R.; Cárdenas, N.; Marín, M.; Serrano, P.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Mammary candidiasis: A medical condition without scientific evidence? PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; Marin, M.L.; Martin, R.; Odriozola, J.M.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Is meconium from healthy newborns actually sterile? Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, L.F., ІІІ; Szalay, A.A. Imaging of light emission from the expression of luciferases in living cells and organisms: A review. Luminescence 2002, 17, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahan, C.G. The bacterial lux reporter system: Applications in bacterial localisation studies. Curr. Gene Ther. 2012, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediano, P.; Fernandez, L.; Jimenez, E.; Arroyo, R.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Marin, M. Microbial diversity in milk of women with mastitis: Potential role of coagulase-negative staphylococci, viridans group streptococci, and corynebacteria. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Heilig, H.G.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Jimenez, E.; Fernandez, L.; Smidt, H.; Rodriguez, J.M. Cultivation-independent assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk among healthy women. Res. Microbiol. 2007, 158, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, K.M.; Foster, J.A.; Forney, L.J.; Schutte, U.M.; Beck, D.L.; Abdo, Z.; Fox, L.K.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Collado, M.C.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Mira, A. The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Rochat, F.; Chassard, C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.; Chassard, C. Assessment of bacterial diversity in breast milk using culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; de Andres, J.; Manrique, M.; Pareja-Tobes, P.; Tobes, R.; Martinez-Blanch, J.F.; Codoner, F.M.; Ramon, D.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Metagenomic analysis of milk of healthy and mastitis-suffering women. J. Hum. Lact. 2015, 31, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albesharat, R.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Korakli, M.; Yazaji, S.; Vogel, R.F. Phenotypic and genotypic analyses of lactic acid bacteria in local fermented food, breast milk and faeces of mothers and their babies. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Maldonado-Barragan, A.; Moles, L.; Rodriguez-Banos, M.; Campo, R.D.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Jimenez, E. Sharing of Bacterial Strains between Breast Milk and Infant Feces. J. Hum. Lact. 2012, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Ferrario, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Viappiani, A.; Ferretti, P.; Gorfer, V.; et al. Exploring vertical transmission of bifidobacteria from mother to child. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7078–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.M. The origin of human milk bacteria: Is there a bacterial entero-mammary pathway during late pregnancy and lactation? Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salter, S.J.; Cox, M.J.; Turek, E.M.; Calus, S.T.; Cookson, W.O.; Moffatt, M.F.; Turner, P.; Parkhill, J.; Loman, N.J.; Walker, A.W. Reagent and laboratory contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses. BMC Biol. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, H.; Kushiro, A.; Ishikawa, E.; Muylaert, D.; Kubota, H.; Sakai, T.; Oishi, K.; Martin, R.; Ben Amor, K.; Oozeer, R.; et al. Transmission of intestinal bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum strains from mother to infant, determined by multilocus sequencing typing and amplified fragment length polymorphism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6788–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Mikami, K.; Nishino, R.; Matsuoka, T.; Kimura, M.; Koga, Y. Comparative analysis of the properties of bifidobacterial isolates from fecal samples of mother-infant Pairs. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulagina, E.V.; Shkoporov, A.N.; Kafarskaia, L.I.; Khokhlova, E.V.; Volodin, N.N.; Donskikh, E.E.; Korshunova, O.V.; Efimov, B.A. Molecular genetic study of species and strain variability in bifidobacteria population in intestinal microflora of breastfed infants and their mothers. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 150, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, T.R.; Sinkiewicz, G.; Jakobsson, T.; Fredrikson, M.; Bjorksten, B. Probiotic lactobacilli in breast milk and infant stool in relation to oral intake during the first year of life. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Jimenez, E.; Olivares, M.; Marin, M.L.; Fernandez, L.; Xaus, J.; Rodriguez, J.M. Lactobacillus salivarius cect 5713, a potential probiotic strain isolated from infant feces and breast milk of a mother-child Pair. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiminez, E.; Marin, M.L.; Xaus, J.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Human Milk is a Source of Lactic Acid Bacteria for the Infant Gut. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira, A.; Rodríguez, J.M. The origin of human milk bacteria. In Prebiotics and Probiotics in Human Milk; McGuire, M., McGuire, M., Bode, L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Begier, E.M.; Barrett, N.L.; Mshar, P.A.; Johnson, D.G.; Hadler, J.L. Connecticut bioterrorism field epidemiology response team. Gram-positive rod surveillance for early anthrax detection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; Fernandez, L.; Marin, M.L.; Martin, R.; Odriozola, J.M.; Nueno-Palop, C.; Narbad, A.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Rodriguez, J.M. Isolation of commensal bacteria from umbilical cord blood of healthy neonates born by cesarean section. Curr. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankerckhoven, V.; Van Autgaerden, T.; Huys, G.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Goossens, H. Establishment of the PROSAFE collection of probiotic and human lactic acid bacteria. Microb. Ecol. Health. Dis. 2004, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Isolauri, E.; He, F.; Hashimoto, H.; Benno, Y.; Salminen, S. Differences in Bifidobacterium Flora Composition in Allergic and Healthy Infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasanayake, A.P.; Li, Y.; Wiener, H.; Ruby, J.D.; Lee, M.J. Salivary actinomyces naeslundii genospecies 2 and lactobacillus casei levels predict pregnancy outcomes. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Torres, A.; Jones-Carson, J.; Baumler, A.J.; Falkow, S.; Valdivia, R.; Brown, W.; Le, M.; Berggren, R.; Parks, W.T.; Fang, F.C. Extraintestinal dissemination of salmonella by cd18-expressing phagocytes. Nature 1999, 401, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M.; Urbano, M.; Valzasina, B.; Francolini, M.; Rotta, G.; Bonasio, R.; Granucci, F.; Kraehenbuhl, J.P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Uhr, T. Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roitt, I.M.; Delves, P.J. Essential Immunology, 10th ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bertotto, A.; Gerli, R.; Castellucci, G.; Scalise, F.; Vaccaro, R. Human milk lymphocytes bearing the gamma/delta T-cell receptor are mostly delta TCS1-positive cells. Immunology 1991, 74, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newburg, D.S. Innate Immunity and Human Milk. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, R.D.; Garlington, A.W. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect. Immun. 1979, 23, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, R.D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 473, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balzan, S.; de Almeida Quadros, C.; de Cleva, R.; Zilberstein, B.; Cecconello, I. Bacterial Translocation: Overview of mechanisms and clinical impact. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtman, S.M. Bacterial [Correction of Baterial] Translocation in Humans. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2001, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedman, P.C.; Macfie, J.; Sagar, P.; Mitchell, C.J.; May, J.; Mancey-Jones, B.; Johnstone, D. The Prevalence of Gut Translocation in Humans. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.D. Bacterial Translocation from the Gastrointestinal Tract. Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F.A.; Moore, E.E.; Poggetti, R.S.; Read, R.A. Postinjury shock and early bacteremia. A lethal combination. Arch. Surg. 1992, 127, 897–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.V.; Baigori, M.D.; Alvarez, S.; Castro, G.R.; Oliver, G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in lactobacillus rhamnosus with capacity to translocate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 204, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, M.T. Safety of probiotics: Translocation and infection. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, S.; Machii, K.; Tsuyuki, S.; Momose, H.; Kawashima, T.; Ueda, K. Immunological responses to monoassociated Bifidobacterium longum and their relation to prevention of bacterial invasion. Immunology 1985, 56, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bengmark, S.; Jeppsson, B. Gastrointestinal surface protection and mucosa reconditioning. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFie, J. Current status of bacterial translocation as a cause of surgical sepsis. Br. Med. Bull. 2004, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danino, T.; Prindle, A.; Kwong, G.A.; Skalak, M.; Li, H.; Allen, K.; Hasty, J.; Bhatia, S.N. Programmable probiotics for detection of cancer in urine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, M. Pregnancy and Periodontal Tissues. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2011, 32, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammond, K.A. Adaptation of the maternal intestine during lactation. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1997, 2, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beischer, N.A.; Mackay, E.V.; Colditz, P.B. Obstetrics and the Newborn; WB Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fu, G.F.; Fan, Y.R.; Liu, W.H.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, J.J.; Xu, G.X. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a delivery system of endostatin for cancer gene therapy: Selective inhibitor of angiogenesis and hypoxic tumor growth. Cancer Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.A.; Shabahang, S.; Timiryasova, T.M.; Zhang, Q.; Beltz, R.; Gentschev, I.; Goebel, W.; Szalay, A.A. Visualization of tumors and metastases in live animals with bacteria and vaccinia virus encoding light-emitting proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, D.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Tangney, M. Tumour targeting with systemically administered bacteria. Curr. Gene Ther. 2010, 10, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Li, X.M.; Jiang, P.; Baranov, E.; Li, S.; Xu, M.; Penman, S.; Hoffman, R.M. Tumor-targeting bacterial therapy with amino acid auxotrophs of GFP-expressing Salmonella Typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Tan, X.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Hoffman, R.M. Targeted therapy with a Salmonella Typhimurium leucine-arginine auxotroph cures orthotopic human breast tumors in nude mice. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7647–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagakura, C.; Hayashi, K.; Zhao, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Tsuchiya, H.; Tomita, K.; Bouvet, M.; Hoffman, R.M. Efficacy of a genetically-modified Salmonella Typhimurium in an orthotopic human pancreatic cancer in nude mice. Anticancer. Res. 2009, 29, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Reference or Source |
|---|---|---|
| XAF1 | CCC CGA GCT CAT GAA GCA AGA GGA GGA CTC TCT ATG | Modified from [17] |
| XBR1 | GGC CCC GGG TTA GGT ATA TTC CAT GTG GTA C | Modified from [17] |
| XAF1 | CCC CGA GCT CAT GAA GCA AGA GGA GGA CTC TCT ATG | Modified from [17] |
| XER2 | GGC GGC GTC GAC TTA ACT ATC AAA CGC TTC GGT TA | Modified from [17] |
| lux1280 | ACG CCG CAG GAA TGT ATT GA | This study |
| lux1732 | TAT GGC GAC AGG ATG ATG AG | This study |
| lux4807 | GTC AAT GAA CGC CGA ATG AG | This study |
| lux5068 | GTC ACT ACT GTC AGG CAC AC | This study |
| Sample | Mice | Growth Medium | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRS | MRS-Ema | ||
| Feces | 1 | na | 5.92 |
| 2 | 7.96 | 4.72 | |
| 3 | 7.54 | 4.26 | |
| 4 | 7.96 | 3.48 | |
| Small intestine | 1 | 4.80 | 3.00 |
| 2 | 4.64 | nd | |
| 3 | 4.96 | nd | |
| 4 | na | na | |
| Large intestine | 1 | 6.65 | 5.54 |
| 2 | na | na | |
| 3 | 6.48 | 2.70 | |
| 4 | 6.23 | 4.56 | |
| Spleen | 1 | nd | nd |
| 2 | nd | nd | |
| 3 | nd | nd | |
| 4 | 3.65 | 3.90 | |
| Mammary gland tissue | 1 | nd | nd |
| 2 | nd | nd | |
| 3 | 4.98 | 3.30 | |
| 4 | 4.98 | 3.00 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Andrés, J.; Jiménez, E.; Chico-Calero, I.; Fresno, M.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Physiological Translocation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Pregnancy Contributes to the Composition of the Milk Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010014
De Andrés J, Jiménez E, Chico-Calero I, Fresno M, Fernández L, Rodríguez JM. Physiological Translocation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Pregnancy Contributes to the Composition of the Milk Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Andrés, Javier, Esther Jiménez, Isabel Chico-Calero, Manuel Fresno, Leónides Fernández, and Juan Miguel Rodríguez. 2018. "Physiological Translocation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Pregnancy Contributes to the Composition of the Milk Microbiota in Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010014
APA StyleDe Andrés, J., Jiménez, E., Chico-Calero, I., Fresno, M., Fernández, L., & Rodríguez, J. M. (2018). Physiological Translocation of Lactic Acid Bacteria during Pregnancy Contributes to the Composition of the Milk Microbiota in Mice. Nutrients, 10(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010014





