Abstract
Sub-Saharan Africa currently has the world’s highest urban population growth rate of any continent at roughly 4.2% annually. A better understanding of the spatiotemporal dynamics of urbanization across the continent is important to a range of fields including public health, economics, and environmental sciences. Nighttime lights imagery (NTL), maintained by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, offers a unique vantage point for studying trends in urbanization. A well-documented deficiency of this dataset is the lack of intra- and inter-annual calibration between satellites, which makes the imagery unsuitable for temporal analysis in their raw format. Here we have generated an ‘intercalibrated’ time series of annual NTL images for Africa (2000–2013) by building on the widely used invariant region and quadratic regression method (IRQR). Gaussian process methods (GP) were used to identify NTL latent functions independent from the temporal noise signals in the annual datasets. The corrected time series was used to explore the positive association of NTL with Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and urban population (UP). Additionally, the proportion of change in ‘lit area’ occurring in urban areas was measured by defining urban agglomerations as contiguously lit pixels of >250 km2, with all other pixels being rural. For validation, the IRQR and GP time series were compared as predictors of the invariant region dataset. Root mean square error values for the GP smoothed dataset were substantially lower. Correlation of NTL with GDP and UP using GP smoothing showed significant increases in R2 over the IRQR method on both continental and national scales. Urban growth results suggested that the majority of growth in lit pixels between 2000 and 2013 occurred in rural areas. With this study, we demonstrated the effectiveness of GP to improve conventional intercalibration, used NTL to describe temporal patterns of urbanization in Africa, and detected NTL responses to environmental and humanitarian crises. The smoothed datasets are freely available for further use.
1. Introduction
Urbanization can be broadly defined as the transition of settlements from rural to urban environments and the growth of existing metropolitan areas. The proportion of the world’s population living in urban areas is projected to be 66% by 2050 [1] and sub-Saharan Africa currently has the world’s highest annual urban growth rate of any continent at 4.2% [2]. Urbanization is known to impact a range of socio-economic issues including public health, education, environmental quality, and economic development [3]. The public health effects of urbanization are complex with both negative and positive outcomes. For example, numerous studies have indicated that urban environments may have a mitigating effect on malaria transmission [4], while at the same time increasing the incidence of dengue fever [5]. Thus, innovative and reliable methods and datasets for monitoring spatiotemporal changes in urban areas are paramount.
Nighttime lights imagery (NTL) [6], maintained by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), offer a unique viewpoint for studying urban trends. These data, available as annual composite images from 1992 to 2013 provide a means for spatiotemporal analysis on a global scale. Although noise removal and other corrective processing are applied to the NTL imagery by NOAA to make them usable for analyses, inherent shortcomings remain. Foremost among these is the lack of inter- and intra-annual calibration between satellites. The satellite sensors that collected these data lacked on-board calibration capabilities and a system for recording in-flight gain changes [7]. When observing raw imagery, this causes annual fluctuations in recorded brightness rather than the gradual increase expected with typical growth in urban populations. Elvidge et al. [7] developed an empirical procedure to allow ‘intercalibration’ of the NTL data. Often referred to as the invariant region and quadratic regression method (IRQR), this method has been applied across a number of settings [8,9,10,11,12,13]. It is a regression based method that relies on a high gain reference image and a reference area where illumination has changed little over time.
An alternative intercalibration method was developed by Liu et al. [11]. These authors built on the IRQR method by applying intra- and inter-annual corrective algorithms and make use of a thresholding technique [12] that relies on land use/land cover data to extract urban information. Wu et al. [13] presented an alternative strategy for applying the IRQR method that included pixel saturation correction and the use of the power-law function for regression analysis. Li et al. [14] used an automatic algorithm to extract reference area pixels and entered them into a linear regression model where outliers were iteratively discarded to refine the intercalibration equation. Finally, Zhang et al. [15] employed a novel sampling strategy along the ‘ridgeline’, i.e., the densest part of plots generated between the reference and target images, to derive calibration models. Regardless of the approach, the intercalibration methods reviewed here all showed improved performance as indicated by their respective evaluation procedures. In general, method evaluation was based on the use of GDP, which has demonstrated a positive linear relationship to NTL in various studies [14,15,16,17]. However, the shortcomings of these alternative intercalibration methods is that they were conducted within a limited geographic scope, required multiple reference datasets such as land use/land cover or population, and were not sufficiently validated.
Precisely intercalibrated NTL data is ideal for mapping urban extents as Li and Zhou [18] describe in their recent systematic methodology review of this subject. Others, such as Ju et al. [19] have focused on the characterization of urban dynamics in China using pixel-based time series trajectories to identify five distinct patterns of urban growth. Similarly, Zhang and Seto [20] identified urbanization typologies on a worldwide basis and validated the accuracy of their results with multispectral imagery. Ma et al. [21] both analyzed and predicted urban development at the municipal level using three different regression models to measure the relationships between NTL and population, GDP, built-up area, and electric power. Finally, Cauwels et al. [22] applied NTL to the concept of urban agglomerations by using a threshold method combined with a segmentation function that identifies clusters of contiguously lighted pixels.
The primary objective of this study was to generate an intercalibrated time series of annual NTL images at the continental scale for Africa from 2000 to 2013 for use in measuring changes in urbanization over time. This particular period was chosen to align with significant reductions in the incidence of malaria in Africa, which occurred primarily as a result of scale-up of large-scale interventions, but also due to environmental changes and economic development, including urbanization [23]. Since substantial inter-annual noise remained even after IRQR intercalibration, we evaluated the use of Gaussian process methods (GP) to generate a smoothed series of NTL images free of temporal noise signals. We then demonstrated the utility of the smoothed dataset for describing patterns of urbanization in Africa and studying relationships between NTL and economic and population indices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
The Nighttime lights imagery used for this study was produced by the U.S. Air Force as part of their Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP). The Operational Linescan System (OLS) sensors on DMSP satellites have specialized low light detection capabilities across visible and near infrared wavelengths. During the 22 years spanning 1992 through 2013, six satellites were active and their sun-synchronous near-polar orbits provided global coverage twice per day. The NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (formerly National Geophysical Data Center) has been the custodian of the DMSP-OLS data archives since 1992. More recently in 2010, NOAA produced a complete time series consisting of cloud-free composites made using the archived data for each calendar year by satellite. This product is known as the version 4 DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series and is freely available on the NOAA website [6]. The composites are provided on 30 arc second image grids spanning from −180 to 180 degrees longitude and from −65 to 75 degrees latitude. The digital numbers (DN) have a 6-bit dynamic range with values from 0 to 63. They also contain four bands representing distinct levels of data processing: raw average of the DN values, a cloud-free coverage tally, average DN of cloud-free light detections multiplied by the percent frequency of light detection, and stable lights. We utilized the stable lights band which consists of the average of the visible band DN values and represents areas with persistent lighting. It includes gas flares from petroleum operations, but ephemeral events such as fires have been discarded and background noise from other sources has been removed.
For this study, the NTL stable lights composites from satellite-years 2000–2013 were used (Table 1). Google Earth Engine [24] provided easy access to Version 4 annual composites of the DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series and the image processing tools required to perform the bulk of the analysis.

Table 1.
Stable lights composites for DMSP-OLS satellite-years 2000–2013.
2.2. Image Processing
Not all the variation observed in the stable lights composites of NTL can be attributed to actual changes in urbanization [7]. For instance, variation across time and space in the DN values recorded can also be explained by human activities other than urbanization, by physical phenomena like the refraction of light or by measurement error due to the use of different satellites. Here we explain the steps taken to address the different sources of variation.
2.2.1. Intercalibration
Since the NTL satellites had no standard for calibration of their sensors, the data were pre-processed for temporal analysis. Elvidge et al. [7] developed an empirical procedure for intercalibration of NTL annual composites from different satellite-years. Also known as the IRQR method, it is a regression based method that relies on a reference area where illumination has changed little over time and an accurate baseline image dataset. Sicily is the standard reference area for intercalibration since it has an even spread of data across the full dynamic range and its population is relatively stable with only a 0.17% growth rate from 2001 to 010 [10]. Likewise, satellite year F12-1999 has relatively high brightness values and is used as the baseline with images from all other satellite years adjusted to match its data range.
To implement the adjustment, the region of Sicily was resampled on each NTL image to a standard 0.825 km grid. This grid cell size was chosen based on the area of a 30 arc second pixel at Sicily’s latitude. The relationship between each satellite-year image and the baseline image F12-1999 was fit using the following quadratic regression model:
where Xi,0 is the DN of the ith grid cell in the baseline image, Xi,j is the DN of the ith grid cell in satellite-year image j, and the parameters C0, C1 and C2 are the intercept, linear, and quadratic coefficients, respectively. For all images, DNs values less than 2 were excluded in keeping with the author’s method [7]. Figure 1 shows an example regression scattergram for satellite-year F18-2013 versus F12-1999 for Sicily. Regression coefficients generated by the model were then used to adjust the DN values observed for Africa. For each year, a set of calibrated values were computed using Equation (2):
where is the calibrated digital number of the ith pixel cell in satellite-year image j of Africa. To ensure calibrated DN values were within the 0–63 range, calibrated values that exceeded 63 were set to 63 and where the minimum value was greater than zero, the original zeroes were restored to preserve the background ‘darkness’ matrix.
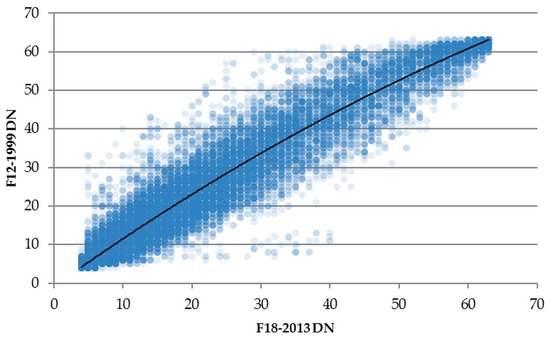
Figure 1.
Scatterplot F18-2013 vs. F12-1999 with the fitted quadratic relationship.
2.2.2. Gaussian Process Smoothing
Once the satellites have been intercalibrated, there are still discrepancies between DN values at the same location-year recorded by different satellites. The occurrence of such discrepancies suggests that the observed data are in fact a noisy realization of an actual but unobserved NTL signal. This relationship can be expressed as
where is the observed NTL signal, and is the actual and unobserved NTL signal of the ith pixel at satellite-year and the associated observation error. The intercalibration step does not eliminate the error term, rather, it results in the error being rescaled to the same magnitude across the different satellite-years.
Gaussian process methods [25] are commonly used with models similar to that in Equation (3) for solving inference problems in time series [26,27,28] where the aim is to distinguish an unobserved signal or latent function from noisy data. The main assumptions of such models are that the noise terms are independent and identically distributed, while the realizations of the latent function are not independent and follow a multivariate normal distribution. In our case, the second assumption guarantees that the observations and latent function are correlated across time.
Here we estimated by fitting a Gaussian process with a covariance kernel [29] composed of a linear and an exponentiated quadratic term to each of 22 satellite-years (Table 1). While the first kernel implements the estimation of the NTL trend across time, the second allows identification of non-constant increments/decrements of the DN values. Additional details on our use of Gaussian process modeling and kernel function types can be found in Appendix A.
2.2.3. Annual Averaging
From 2000 to 2007, there were multiple satellites operating in any given year (Table 1). For the uncalibrated (UC) and intercalibrated (IC) test cases used throughout this study, DN values for each satellite during this time period were intra-annually averaged to produce a single annual image.
2.2.4. Gas Flare Removal
Gas flares are present in the stable lights band of the Version 4 NTL dataset and, given they are not generally associated with human settlements, they were removed. In a previous study, Elvidge et al. [30] estimated flare volume and evolution and mapped their locations and extent. As part of this study, flare locations as polygonal masks have been made available on NOAA’s website as shapefiles, a common spatial data format [6]. These were downloaded, merged, and used to mask all known flares. While these have not been updated since 2009, this dataset represents the best estimate of the locations of gas flares available. Since most gas flares in African occur in marine environments or the remote Sahara Desert, newer flares should not result in significant inaccuracies.
2.2.5. Blooming Correction
Probably the most serious non-temporal errors in the NTL images are caused by ‘overglow’ and ‘blooming’, which is the diffusion of urban light into rural areas and the magnification of light by reflective surfaces such as water and sand, respectively. In either case, the errors are not entirely due to reflected light. Additional sources of this error are the composite building process and image registration errors [31]. It was noted that overglow occurring on a single image dataset can be compounded in composite images. Also, numerous small errors in geo-registration may cause brightly lit urban cores to grow slightly at their peripheries. In both cases, the result is overestimation of urban extents and settlements on land and their deceptive extension into uninhabitable aqueous environments.
Pixel blooming caused by water reflectance from inland water bodies and coastal waters was accounted for by masking via the World Water Bodies and World Countries datasets [32], respectively. Mediating urban overestimation due to overglow is considerably more problematic. Typical solutions to this problem involve use of low light thresholding which is intended to filter out a portion of the lowest predicted DNs. The goal of these somewhat empirical approaches are to remove ‘noise’ associated with overglow from the urban boundaries without fragmenting the urban core or excluding genuine smaller settlements [33]. We have chosen to forgo the use of thresholding due to its uncertain efficacy.
2.2.6. Re-Projection
NTL composites are produced on a 30 arc second grid, so the land surface area of the pixels naturally differs according to their geographic latitude. For example, in Kampala, Uganda which is essentially on the Equator, a pixel represents approximately 0.86 square kilometers, whereas in Cape Town, South Africa (34°S latitude) pixels represent 0.71 square kilometers. This becomes problematic with spatial analysis requiring surface area measurements. When investigating temporal changes in urbanization, this is quite often the case. Thus, the processed NTL composites were projected to the Mollweide equal-area map projection for analytical purposes. This is a pseudo cylindrical map projection where the accuracy of area representation takes precedence over the accuracy of angle and shape. The composites were projected to a 1 km cell size using the nearest neighbor re-sampling technique. This step was only applied to the imagery used for the urban growth analysis described below.
2.3. Method Validation and Urban Growth Analysis
To determine relative success of the intercalibration method, the ‘sum-of-lights’ index (SOL) [7] was calculated for each satellite year. The SOL is simply the sum of the predicted DNs for an NTL image within a region of interest. Once calculated by region, it is plotted as a time series. Success is indicated by a relative convergence of SOL values in years where two satellite products are available, and a relatively continuous growth trend across the time series (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
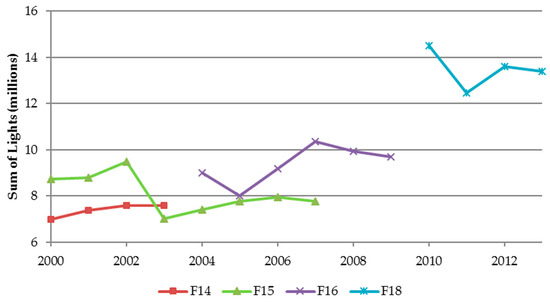
Figure 2.
Uncalibrated sum-of-lights by satellite-year for Africa.
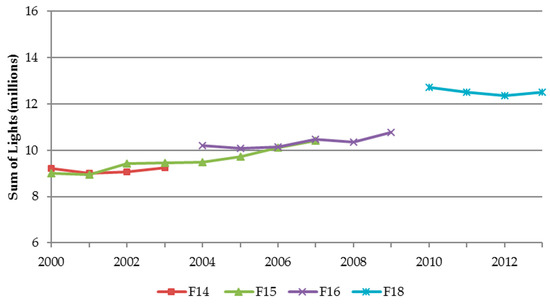
Figure 3.
IRQR calibrated sum-of-lights by satellite-year for Africa.
For procedural validation, the IRQR and Gaussian process time series were compared as predictors of the satellite F12-1999 annual composite image of Sicily. Given the assumption that NTL values have not changed in Sicily 2000–2013, the F12-1999 image can be considered the gold-standard ‘observed’ values for 2000–2013 in our study. When the IRQR and GP time series are similarly considered ‘predicted’ values, the mean squared error (MSE) measurement can be used to validate and compare methods. Given that the Gaussian process calculations were based on the entire time series, MSEs were calculated using data from all years.
This enhanced intercalibration method was also used to evaluate the positive association of the intercalibrated and processed NTL time series to GDP and urban population on a continental and country-wise basis. These relationships have been demonstrated in earlier studies [34,35] and therefore are used as an indication of the efficacy of our own methods. Statistics for GDP per country were sourced from the World Bank [36] using the US dollar price in July 2016 as the benchmark. Corresponding urban population data were also obtained from the World Bank [37]. The correlation of SOL to these factors was compared both before and after intercalibration. The relationship between uncalibrated and annually averaged (UC), intercalibrated and annually averaged (IC), and intercalibrated and Gaussian process smoothed (GP) NTL with GDP and UP was estimated using linear regression. Models were fit at continental scale and for sub-Saharan African countries. Since GDP and UP data were not available for Somalia and Western Sahara, they were not included in the continental analysis.
The amount of growth in urban and rural settlements was also calculated both in absolute and proportional terms. Total urban and rural statistics are based on the area represented by all ‘lit’ pixels (DN > 0), whereas urban agglomerations were defined as contiguously lit pixels with an area >250 km2 (~97 mi2).
Figure 4 provides a flow chart outlining the work flow for NTL intercalibration, image processing procedures, and validation and analysis. Figure 5 provides an enhanced view of the intercalibrated 2013 nighttime lights image for continental Africa.
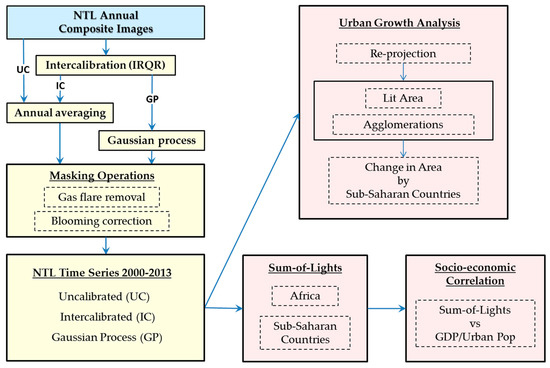
Figure 4.
Work flow for NTL image processing procedures (yellow) and validation/analysis products (red).
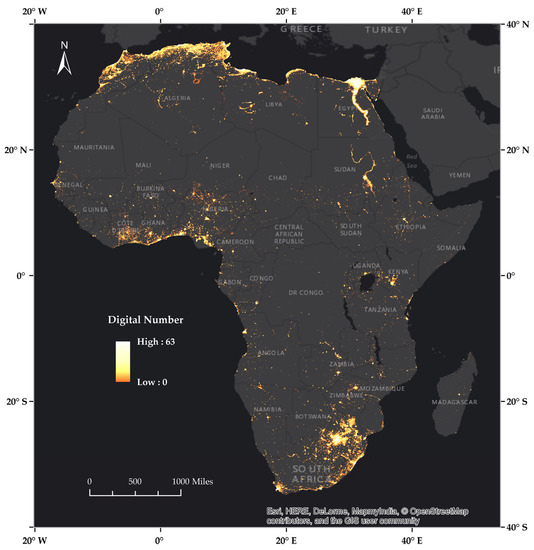
Figure 5.
Intercalibrated 2013 nighttime lights imagery for Africa.
3. Results
As described above in Materials and Methods, the regression based IRQR intercalibration method relies on a reference area where illumination has changed little over time and an accurate baseline image dataset. Using Sicily as the reference area and satellite year F12-1999, regression models were generated for all satellite-years (Table 2). Following gas flare removal and blooming correction, these regression coefficients were used to adjust the raw DN values for NTL images of Africa. These steps were followed by Gaussian Process smoothing to produce the final intercalibrated time series.

Table 2.
Regression coefficients for intercalibration.
3.1. Method Evaluation
3.1.1. Sum-of-Lights Index
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show SOL plotted for uncalibrated and IRQR (only) NTL series, respectively. Successful intercalibration is indicated by a relative convergence of SOL values in years where two satellite products are available. Another indication of successful intercalibration is a clear continuous growth trend in light values across the time series. Figure 3 illustrates how IRQR calibrated datasets for Africa visually comply with these criteria, despite noticeable discontinuity introduced by satellite F18.
When annual averaging was applied in addition to IRQR intercalibration, it resulted in a smoother SOL growth trend between most years, with exceptions occurring in the transition years between satellite F16 and F18 (2008–2010). However, when Gaussian process smoothing was applied using all intercalibrated satellite-year images, it yielded a smooth trajectory of continuous SOL growth (Figure 6).
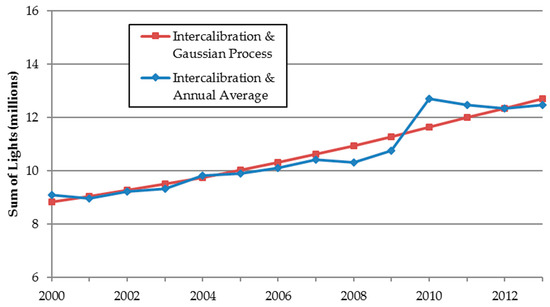
Figure 6.
Sum-of-Lights after annual averaging and Gaussian process smoothing (Africa).
3.1.2. Validation Using the Invariant Region
For procedural validation, the uncalibrated (UC), IRQR intercalibrated (IC), and GP smoothed time series were compared as predictors of the invariant region dataset: satellite-year F12-1999. The mean squared error was calculated for each of these test cases using DN values for Sicily (Table 3).

Table 3.
MSE for intercalibration test cases vs. F12-1999.
Whereas conventional intercalibration exhibited considerably lower MSE than the uncalibrated, the Gaussian process approach was clearly the best predictor of the reference dataset with an MSE half that of the UC test case. While these results are not evidence of improved accuracy, they do substantiate the use of Gaussian process smoothing to produce refined NTL time series while observing the principles of the IRQR method.
3.2. Correlation of SOL with GDP and Urban Population
In terms of the relationships between the NTL layers (UC, IC and GP) and GDP and urban population, the UC layer showed the least correlation, while IC and GP case adjustments each incrementally increased the strength of the relationship. The regression results and root-mean-squared error (RMSE) values for continental Africa are listed in Table 4. The coefficients of determination indicate that the SOLs in the GP case have a stronger linear relationship with GDP than those from the IC case. Thus, when Gaussian process smoothing was applied, R2 increased from 0.92 to 0.98 and from 0.90 to 0.9997 for GDP and urban population, respectively. Corresponding RMSE values also decreased dramatically. The high R2 and relatively low RMSE value for the Gaussian process SOL vs. urban population clearly indicates the advantage of this enhanced intercalibration method. Figure 7 and Figure 8 graphically illustrate these improvements.

Table 4.
Coefficient of determination and RMSE for SOL vs. GDP and urban population.
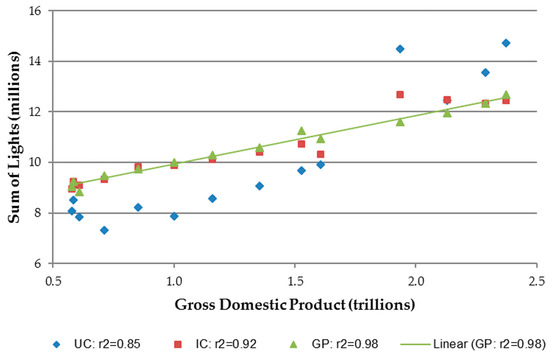
Figure 7.
Linear regression results for Africa SOL vs. GDP. (UC) Uncalibrated and annually averaged. (IC) Intercalibrated and annually averaged. (GP) Intercalibrated and Gaussian process smoothed.
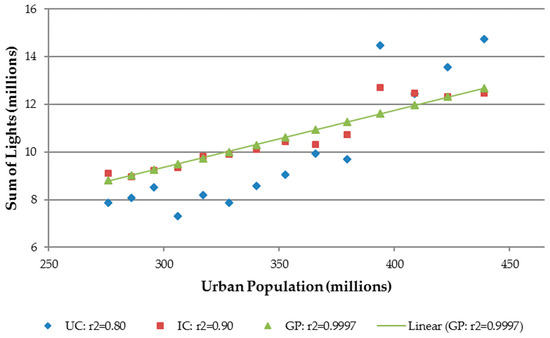
Figure 8.
Linear regression results for Africa SOL vs. Urban Population. (UC) Uncalibrated and annually averaged. (IC) Intercalibrated and annually averaged. (GP) Intercalibrated and Gaussian process smoothed.
Regression analyses performed at the country level yielded similar results. Figure 9 and Figure 10 display regression results for these analyses. The GP test case is shown to perform notably better than the IC case in nearly all cases with positive with correlation coefficients ranging from 0.72 to 0.997 for GDP and 0.76 to 0.9996 for urban population. The Gambia and Eritrea were two exceptions where the correlation coefficient for the IC method exceeded that of our GP method in the case of GDP.
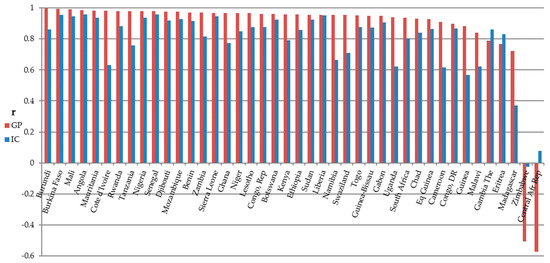
Figure 9.
Correlation coefficient by sub-Saharan country SOL vs. GDP. Columns are sorted by correlation coefficient values for GP test case in decreasing order.
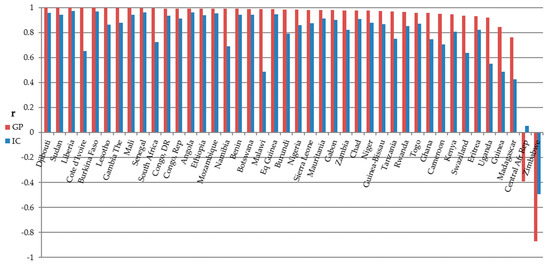
Figure 10.
Correlation coefficient by sub-Saharan country SOL vs. urban population. Columns are sorted by correlation coefficient values for GP test case in decreasing order.
Other exceptions were the notably poor and negative correlations of SOL to both GDP and UP for Zimbabwe and the Central African Republic. Figure 11 and Figure 12 illustrate these atypical temporal patterns of SOL in relation to GDP and UP.
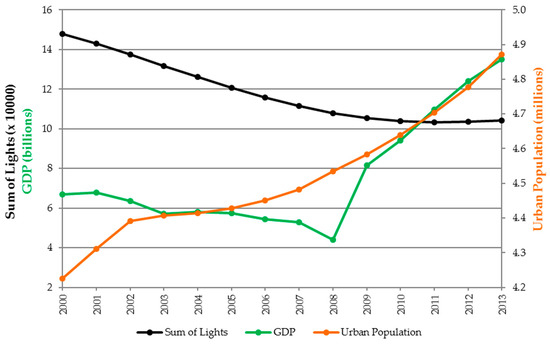
Figure 11.
Temporal patterns of SOL, GDP, and UP for Zimbabwe, where SOL is inversely correlated with GDP (R = −0.50) and UP (R = −0.87).
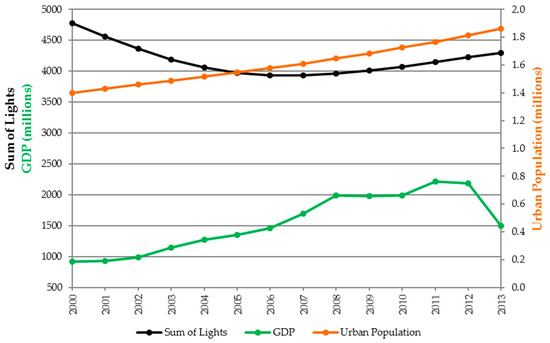
Figure 12.
Temporal patterns of SOL, GDP, and UP for the Central African Republic, where SOL is inversely correlated with GDP (R = −0.57) and UP (R = −0.39).
3.3. Urban Growth Analysis
The absolute and percent changes in lit and agglomerated area for the 2000–2013 time period have been calculated to model total settlement (urban and rural) and urban growth, respectively. These are shown in Table 5 and illustrated as bar graphs in Figure 13 and Figure 14. The red bars represent absolute change in lit area and the blue bars indicate change in agglomerated area. In general, the growth in total lit area per country exceeds that of agglomerations, though it is possible for growth in urban agglomerations to be greater than growth in total lit area. Although this seems counterintuitive, given that agglomerations have been filtered by size, merging of small urban clusters over time can produce such results. This can be illustrated with an example of growth analysis in Kenya’s Nairobi metropolitan area (Figure 15). Note that in Figure 15a the lit area in the year 2000 is derived from all cluster sizes, whereas in Figure 15b agglomerations in 2000 only include two clusters that exceed the 250 km2 filtering threshold. In both cases, the yellow areas outside the dashed lines of the year 2000 polygons represent the area of absolute change. In this case, the urban/peri-urban communities surrounding Mount Kenya merged with greater Nairobi by 2013. Consequently, agglomerations increased by 3936 km2, while lit area increased by only 2919 km2. Countries displaying greater growth in agglomerated than lit area include Cote d’Ivoire, Swaziland, Lesotho, and Djibouti (Figure 13 and Figure 14).

Table 5.
Absolute and percent change in lit and agglomerated area, 2000–2013.
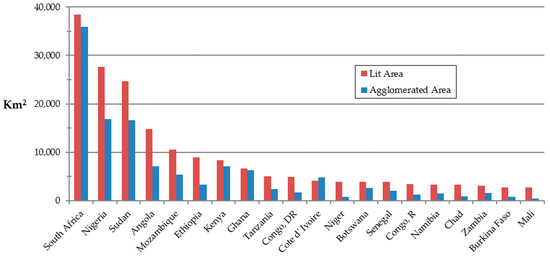
Figure 13.
Sub-Saharan countries with significant growth in lit and agglomerated area (>2500 km2 lit), 2000–2013. Columns are sorted by lit area growth in descending order.
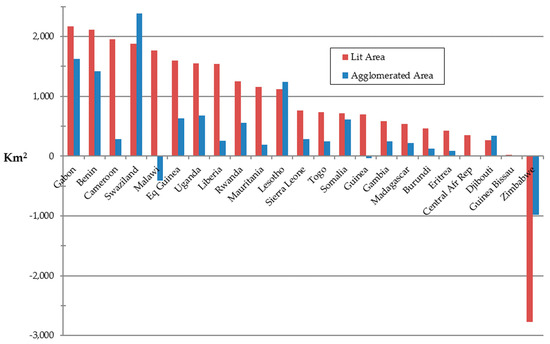
Figure 14.
Sub-Saharan countries with minimal growth in lit and agglomerated area (<2500 km2 lit), 2000–2013. Columns are sorted by lit area growth in descending order.
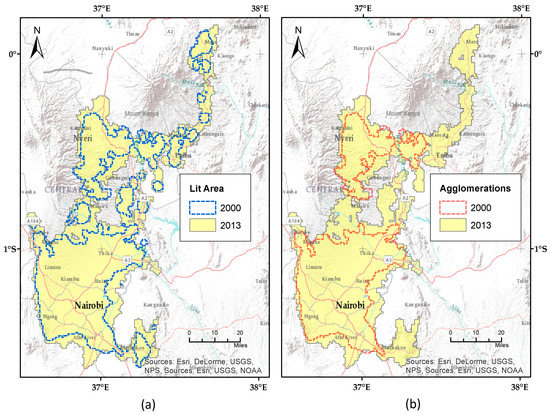
Figure 15.
Example of lit area growth (a) versus agglomerated area growth (b) in the Nairobi metropolitan area.
4. Discussion
For the first time, we report here on the production of an intercalibrated open access NTL dataset spanning continental Africa 2000–2013 using a GP statistical approach. This improved dataset can be applied to a broad range of disciplines including public health, economic development, and environmental monitoring. While NTL data offer an opportunity to measure and map the human footprint, in its raw format, these data are difficult to interpret and can lead to spurious conclusions.
Gaussian process smoothing, the key enhancement of our intercalibration method, yielded a more intuitively smooth increase in SOL over Africa and was less noisy than that produced by using IRQR and annual averaging alone. While there is no gold standard short of calibration with known light sources as ground truth [38] against which to validate this approach, the SOL plots indicate a relatively effective intercalibration. However, what is achieved through IRQR intercalibration is not the elimination of errors, but their re-scaling such that they have the same magnitude across satellite-years. Through the use Gaussian process methods, independent temporal noise signals have been separated from latent functions in the annual NTL datasets. We have attempted to validate the GP method results against the premises of the conventional IRQR method. That is, the assumption that the reference dataset for the invariant region represents the NTL brightness across the time series. While invariably information is lost in the process, the overall result is an NTL time series for Africa that is standardized and comparable across both time and space.
The success of intercalibration with GP smoothing was also evaluated by comparing the resultant time series to known indicators of urbanization: GDP and UP. Improvements in the correlations found between the SOL and these indices when using the GP method provide further support for its use. When the same relationships are explored on a national basis, it provides sub-regional insights into urban and economic growth patterns, as well as the consequences of political and humanitarian events. While we have not compared GDP/UP figures to NTL values in countries outside Africa, we would expect similar relationships in these countries. The country based regression analysis for sub-Saharan Africa yielded generally positive results with only a few exceptions. The GP method performed notably better than the IC method in nearly all cases with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.9 for 80% and 90% of the countries for GDP and urban population, respectively. The exceptions were The Gambia and Eritrea, where positive correlation coefficients for the IC method exceeded that of our GP method for the GDP regression. For Eritrea, a partial explanation for this anomaly is the fact that GDP data for 2012–2013 are unavailable. However, also at the root of this data omission are a series of military disputes and border disputes with Ethiopia and Djibouti during our study period. In the case of The Gambia their economy, and therefore GDP, struggled between 2000 and 2004 and the unsmoothed IC dataset reflected this short term trend more accurately than the globally smoothed GP case.
Among the national statistics there were two countries with notably poor negative correlations to both GDP and UP: Zimbabwe and the Central African Republic. Notable is Zimbabwe’s unusual patterns with the SOL decreasing from 2000 through 2011 when it begins to recover. This pattern coincides with a disputed presidential and parliamentary election in 2008 preceded by periods of political unrest. The GDP trended slightly downward during the lead up to the election and then rose sharply thereafter. However, UP rose steadily from 2000 to 2013, even while SOL was decreasing. The Central African Republic also displays an unusual pattern, with relatively low SOL values, an urban population that rises steadily, and GDP that rises but drops abruptly in 2013 in response to a coup d’état. In general, anomalies such as these can be traced to the effects of insurgent warfare, political unrest, and humanitarian crises on nighttime lighting. Bennett and Smith [39] studied socioeconomic changes that caused reductions in NTL in post-Soviet Russia and war-torn Syria, while Li et al. [40] observed similar reductions as a result of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) insurgency in Northern Iraq. Humanitarian crises often come in the form of drought, famine, earthquakes, and tropical storms. Gillespie et al. [41] examined the effects of tsunami damage in Sumatra (2004–2008) using NTL imagery. Several authors have suggested NTL based metrics for monitoring at risk populations. For instance, Coscieme et al. [42] propose an NTL based index of regional disparity and Li et al. [43] similarly suggest a nighttime light variation index (NLVI) to predict the risk of armed conflicts. All these insights underscore the potential for well calibrated NTL data as a tool for monitoring the regional effects and outcomes of such events.
Urban growth analysis using the improved NTL time series data indicate that the extent of urban growth appears to vary widely across African countries, with an overall trend of increasing areas of the continent being lit, particularly around urban agglomerations. We have described basic patterns of urban growth in Africa by computing changes in the area of lit NTL pixels and agglomerated pixels (>250 km2) on a national basis. The lit area serves as an indicator of overall growth of human settlements, whereas the agglomerations are meant to be a measure of large metropolitan areas, a proxy for urbanization.
Most sub-Saharan countries exhibited substantially greater growth in lit area than agglomerated lit area. Exceptions included Cote d’Ivoire, Swaziland, Lesotho, and Djibouti which all showed greater growth in agglomerated area. In Cote d’Ivoire, this may be due the effects of civil wars occurring in 2002 and 2011, with increased agglomerated area resulting from migration away from centers of conflict to urban areas. In the case of Swaziland and Lesotho, this is likely related to their proximity to South Africa which has the highest growth rates. In both cases, lit area growth was concentrated along borders with South Africa and internal major roadways. Thus, merging of smaller, patchy urban areas caused a relatively high increase in agglomerated area. In the case of Djibouti, most growth in lit area occurred in the city of Djibouti causing it to surpass the 250 km2 threshold.
A variety of other anomalous patterns are expressed by countries with minimal growth in lit area many of which likely reflect human events, as previously discussed. Zimbabwe uniquely showed decreases in both lit and agglomerated area which were likely the effects of persistent political unrest during the study period. Malawi increased in lit area while decreasing its agglomerated area, apparently due to disaggregation of the city of Zomba metropolitan area. Finally, other notable anomalies are the Central African Republic and Guinea Bissau. The Central African Republic had no change in agglomerated area, while Guinea Bissau had no agglomerated area as of 2013 despite a modest 19% increase in lit area. In both of these situations, annual growth patterns may be attributed to their relatively sparse populations and the margin of error associated with the processed NTL data.
While we have demonstrated the utility of our enhanced approach to intercalibration of NTL imagery, for the purpose of this study we focused on imagery up to 2013. Continued growth in NTL applications hinge on new NTL data sources such as the Visible Infrared Imager Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) of the National Polar-Orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System launched in 2011 [44,45,46]. Although nighttime lights imagery from VIIRS are superior to DMSP-OLS data in both spatial resolution (0.5 km) and dynamic range (14-bit), it is currently only available as monthly composites and only since 2014. Furthermore, VIIRS data processing methods are relatively unexplored, with relatively few publications to date that make use of the imagery. Thus, DMSP-OLS will likely remain the de facto standard for nighttime lights based investigations for a number of years. As part of this study, integration of VIIRS data with DMSP-OLS data was briefly explored as way to extend the time series to 2015. However, the relative complexity of data processing necessary to interface the two datasets was prohibitive and deemed beyond the scope of this study. Future research on data processing of VIIRS imagery and their integration with DMSP-OLS data is vital if NTL based research and application development is to continue. Toward this end, release of a VIIRS NTL time series of processed annual composites similar to DMSP Version 4 would be of great benefit to the scientific community.
5. Conclusions
The NTL dataset has been widely used during the past two decades with the number of related publications increasing dramatically as reported in the systematic literature review by Huang et al. [47]. With the release of the Version 4 DMSP/OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series dataset by NOAA in 2010, the publication rate increased further with 25 papers published in 2013 alone. Clearly, these numbers speak to both the unique worth of the dataset and the benefits of open access to high quality annual NTL composites. Numerous publications have proposed methods to correct well-documented calibration deficiencies in the version 4 composites, and here we add our own refined technique.
Here we report on the use of Gaussian process methods to estimate NTL latent functions free from noise signals prevalent in IRQR intercalibrated datasets. The method was validated by comparing uncalibrated, intercalibrated, and GP smoothed time series as predictors of the invariant region dataset. We have also demonstrated the value of the improved time series by investigating the established relationship of NTLs to GDP and urban populations, by describing basic patterns of urban growth in Africa, and considering its potential to detect and monitor environmental and humanitarian crises. Finally, the intercalibrated NTL time series (2000–2013) has been made available to global health researchers as well as the broader scientific community in the hopes of spawning continued growth in NTL based research (see Supplementary Materials).
Supplementary Materials
The intercalibrated nighttime lights imagery series (2000–2013) produced as part of this study are available online at http://geodata.globalhealthapp.net/.
Acknowledgments
D.J.S., R.A., A.M., A.B. and H.J.W.S. and are funded by grants from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Numbers OPP1132900, OPP1089413, and OPP1116450), the Novartis Foundation for Sustainable Development, and a gift from the Parker Foundation. P.W.G. is a Career Development Fellow (No. K00669X) jointly funded by the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the UK Department for International Development (DFID) under the MRC/DFID Concordat agreement, also part of the EDCTP2 program supported by the European Union, and receives support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (No. OPP1068048, No. OPP1106023).
Author Contributions
D.J.S., A.B., H.J.W.S. and P.W.G. conceived and designed the experiments; D.J.S. and R.A. performed the image processing, and geo-spatial and statistical analysis of the data; A.M. contributed technical and analytical support; D.J.S. wrote the paper and all other authors reviewed the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The Gaussian process smoothing of NTL imagery in this study was implemented at the pixel level. That is, for each pixel location in Africa, the dependent variable was the DN values across time and the image year is the only covariate. Since the input images were previously intercalibrated using the IQRQ method, we did not incorporate the type of satellite as a source of variation into the model.
In Figure A1, we present samples smoothed DN values obtained using this method. It should be noted that the IQRQ intercalibrated data points present non-consistent trends and as well as discrepancies between observations in the same year. The smoothed curve captures the long term trend of the DN values and is free from the inter-annual variation, which we hypothesize is mainly noise. Note that although our results are presented from 2000, the smoothing process uses data from 1998 which helps to provide better estimates on the left tail of the data distribution.
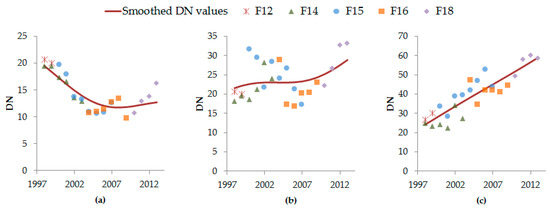
Figure A1.
Gaussian process regression on pixel at coordinates using all satellite-year images: (a) Coordinates (8.592, 35.668); (b) Coordinates (14.270, 29.981); (c) Coordinates (−13.183, 27.125).
Appendix A.1. Gaussian Process Regression
Let be a collection of random variables such that any finite number of them has a joint Gaussian distribution, then is known as a Gaussian process. A typical setting of a Gaussian process regression tries to estimate an unobserved from a set of observations corrupted by additive noise according to equation
where is a vector with independent entries and is a Gaussian process with some mean function and covariance kernel . For simplicity, it can be assumed a prior mean function of zero, so that the process if fully specified by its covariance kernel. Then the predictive distribution of the process at a new set of inputs has the moments
and
where is the identity matrix.
Appendix A.2. Examples of Covariance Kernels
Autocorrelated data across time or space is characterized for presenting similar values depending on the closeness of the observations. In Gaussian process models, it is the covariance kernel that defines the closeness or similarity between observations. It is through the covariance kernels that a Gaussian process encodes the behavior of . Next, we present three examples of kernels that summarize different functional forms.
Appendix A.2.1. Linear Kernel
A covariance kernel that encodes a linear relation between inputs and output , equivalent to a linear regression model, is defined as
where is a scale parameter (Figure A2).
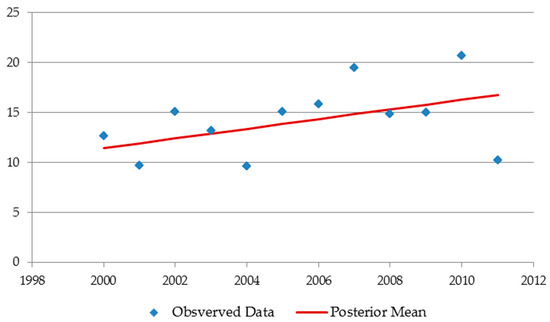
Figure A2.
Linear kernel: encodes a linear regression model. It delineates the trend, but cannot represent non-constant changes across time.
Appendix A.2.2. Exponentiated Quadratic Kernel
An exponentiated quadratic covariance kernel defines an exponential decay in the correlation of observations depending on their inputs distance. It is defined as
where is a scale parameter and is the characteristic length-scale of the covariance kernel and defines the maximum length at which data can be extrapolated (Figure A3).
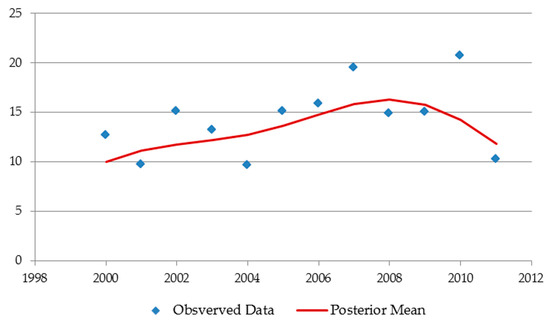
Figure A3.
Exponentiated quadratic kernel: encodes an exponential decay in the autocorrelation. It produces a smooth function across time, but cannot represent a constant trend.
Appendix A.2.3. Composed Linear—Exponentiated Quadratic Kernel
A composed covariance kernel that combines features from the linear and exponentiated quadratic kernels can be obtained by simply adding the kernels as defined by Equations (A4) and (A5).
Below we present examples of the posterior mean produced by the three types of kernels reviewed above using a ‘toy’ data set (Figure A4).
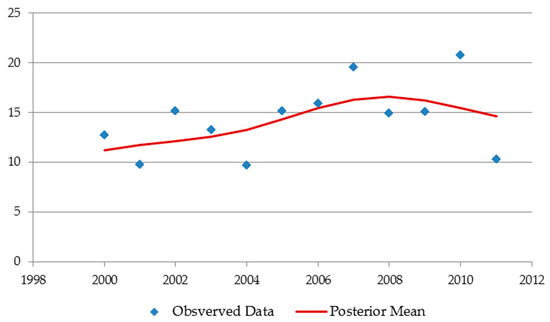
Figure A4.
Composed kernel: delineates a trend line like a linear model, while allowing smooth changes across time.
References
- Nations, United. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision, Highlights. Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- The World Bank. World Development Indicators. Urban and Rural Population (% Annual Growth). Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?Report_Name=Urban-and-rural-growth&Id=eee35bac (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Dociu, M.; Dunarintu, A. The socio-economic impact of urbanization. Int. J. Acad. Res. Account. Financ. Manag. Sci. 2012, 2, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gething, P.W.; Smith, D.L.; Patil, A.P.; Tatem, A.J.; Snow, R.W.; Hay, S.I. Climate change and the global malaria recession. Nature 2010, 465, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubler, D.J. Dengue, urbanization and globalization: The unholy trinity of the 21st century. Trop. Med. Health 2011, 39, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP). Available online: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp.html (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T. National trends in satellite-observed lighting. Glob. Urban Monit. Assess. Earth Obs. 2014, 23, 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Ghosh, T.; Samson, E.L. Mapping spatio-temporal changes of Chinese electric power consumption using night-time imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 6304–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestalozzi, N.; Niederhuber, M. Nighttime Lights as Proxy for the Spatial Growth of Dense Urbanized Areas. Master’s Thesis, Department of Management, Technology and Economics (D-MTEC) Chair of Entrepreneurial Risks, Chair of Land Use Engineering ETH Zürich 94, Zurich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS night-time light data by the invariant region method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Li, H. Automatic intercalibration of night-time light imagery using robust regression. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. A Robust Method to Generate a Consistent Time Series from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Rayner, P.J.; Paget, M. Regional variations in spatial structure of nightlights, population density and fossil-fuel CO2 emissions. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4756–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.-P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. AMBIO 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Dronova, I.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X. Analysis of urbanization dynamics in mainland China using pixel-based night-time light trajectories from 1992 to 2013. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Can night-time light data identify typologies of urbanization? A global assessment of successes and failures. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3476–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwels, P.; Pestalozzi, N.; Sornette, D. Dynamics and spatial distribution of global nighttime lights. EPJ Data Sci. 2014, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Weiss, D.J.; Cameron, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Mappin, B.; Dalrymplem, U.; Battle, K.; Moyes, C.; Henry, A.; Eckhoff, P.A.; et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature 2015, 526, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Earth Engine Team. Google Earth Engine: A Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis Platform. 2015. Available online: https://earthengine.google.com (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; MIT Press (Massachusetts Institute of Technology): Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Parzen, E. Statistical Inference on Time Series by Hilbert Space Methods; Technical Report 23; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Parzen, E. An approach to time series analysis. Ann. Math. Stat. 1961, 32, 951–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. Statistical Inference on Time Series by RKHS Methods; Technical Report-14; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1970; pp. 1–37.
- Shawe-Taylor, J.; Cristianini, N. Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS “city lights” satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESRI Incorporated; DeLorme Publishing Company; CIA World Factbook. World Water Bodies 2016. World Countries. Available online: http://www.arcgis.com (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Balk, D.; Montgomery, M. Spatial scaling of stable night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Currit, N.; Samson, E. Net primary production and gross domestic product in China derived from satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. World Development Indicators. GDP (Current US$). 2015. Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?Code=NY.GDP.MKTP.CD&id=af3ce82b&report_name=Popular_indicators&populartype=series&ispopular=y# (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- The World Bank. World Development Indicators. Urban Population (% of Total). 2015. Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?source=2&series=SP.URB.TOTL.IN.ZS&country=# (accessed on 1 July 2016).
- Tuttle, B.; Anderson, S.; Elvidge, C.; Ghosh, T.; Baugh, K.; Sutton, P. Aladdin’s magic lamp: Active target calibration of the DMSP-OLS. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12708–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, C.; Li, D. Detecting 2014 Northern Iraq Insurgency using night-time light imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, T.W.; Frankenberg, E.; Chum, K.F.; Thomas, D. Night-time lights time series of tsunami damage, recovery, and economic metrics in Sumatra, Indonesia. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscieme, L.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S.; Liu, Q.; Elvidge, C.D. Dark Times: Nighttime satellite imagery as a detector of regional disparity and the geography of conflict. GISci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, X. Satellite-observed nighttime light variation as evidence for global armed conflicts. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, W. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data for mapping global fossil fuel combustion CO2 emissions: A comparison with DMSP-OLS nighttime light data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Zhang, Q. A global analysis of factors controlling VIIRS nighttime light levels from densely populated areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS nighttime light images: A meta-analysis and a systematic literature review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).