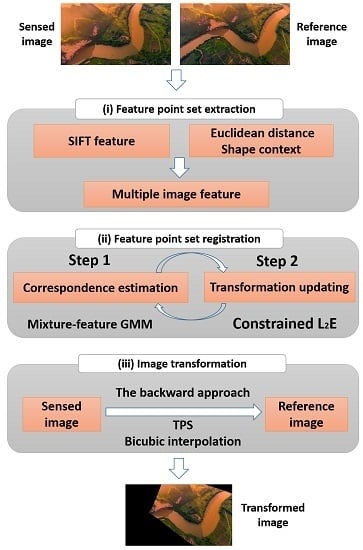
Remote Sensing Image Registration Using Multiple Image Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
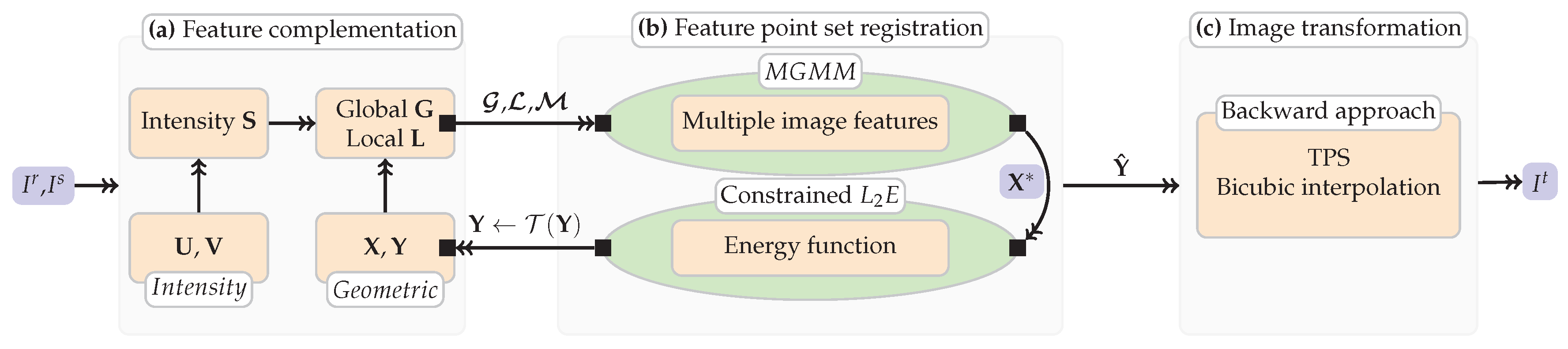
2. Methodology
2.1. Mixture-Feature Gaussian Mixture Model (MGMM)
2.2. Combination and Complementation of Multiple Image Features
2.2.1. Euclidean Distance
2.2.2. Shape Context (SC)
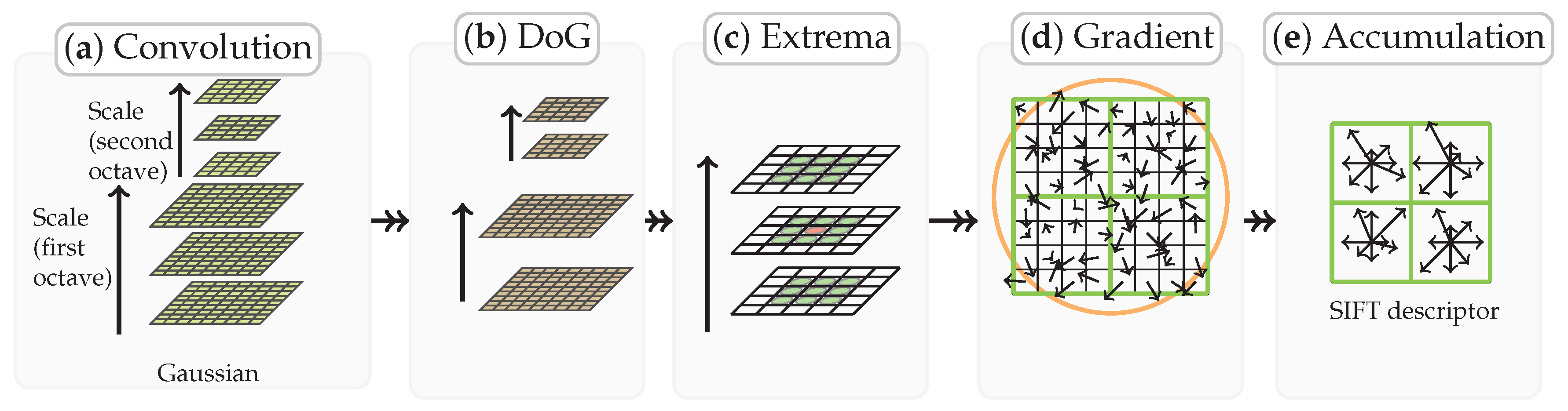
2.2.3. SIFT Distance
2.2.4. Multiple Image Feature Based Correspondence Estimation
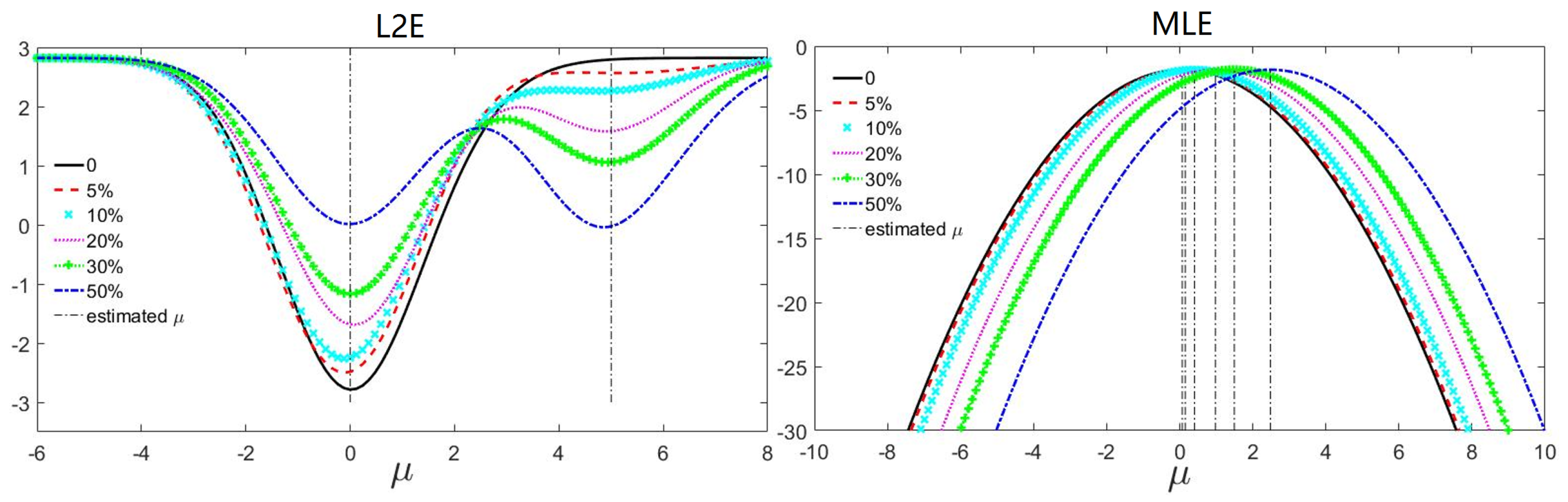
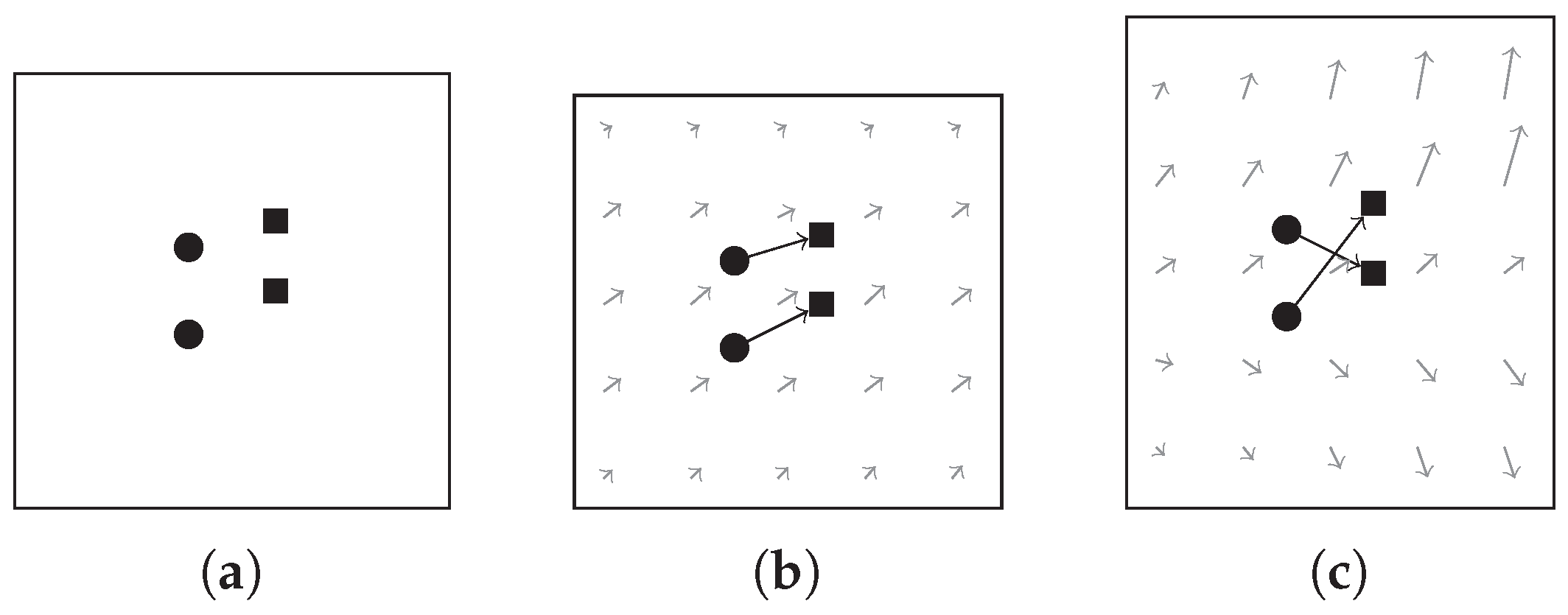
2.3. Geometric Constraint for L2E Based Energy Optimization
2.3.1.
2.3.2. Motion Coherent Based Geometric Constraint
2.4. Main Process
2.4.1. Extraction of the Feature Point Sets
2.4.2. Feature Point Set Registration
| Algorithm 1: Feature matching using multiple features for remote sensing registration |
 |
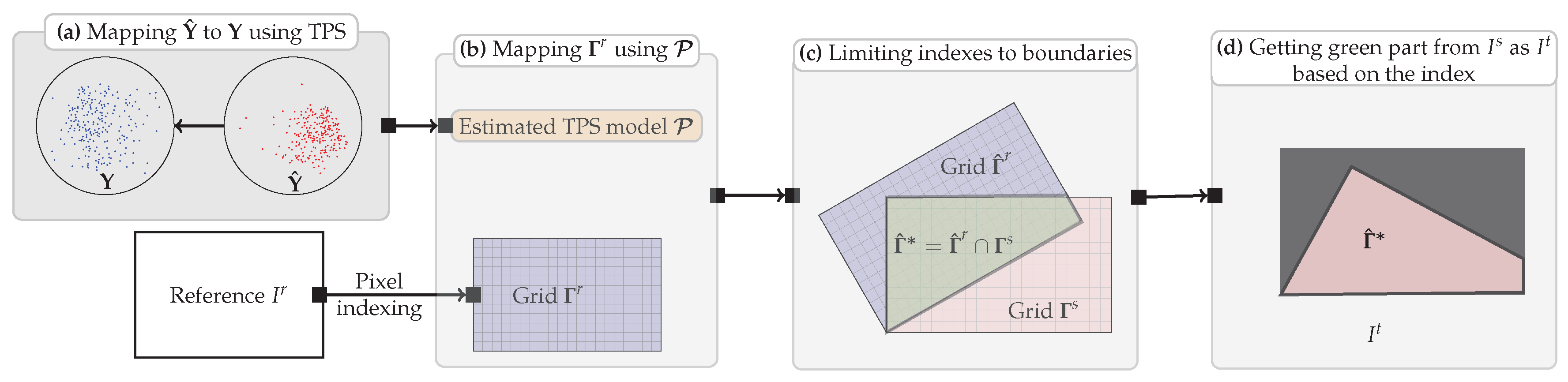
2.5. Image Transformation and Resampling
2.6. Method Analysis
2.6.1. Computational Complexity
2.6.2. Parametric Setting
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Evaluation Criterion
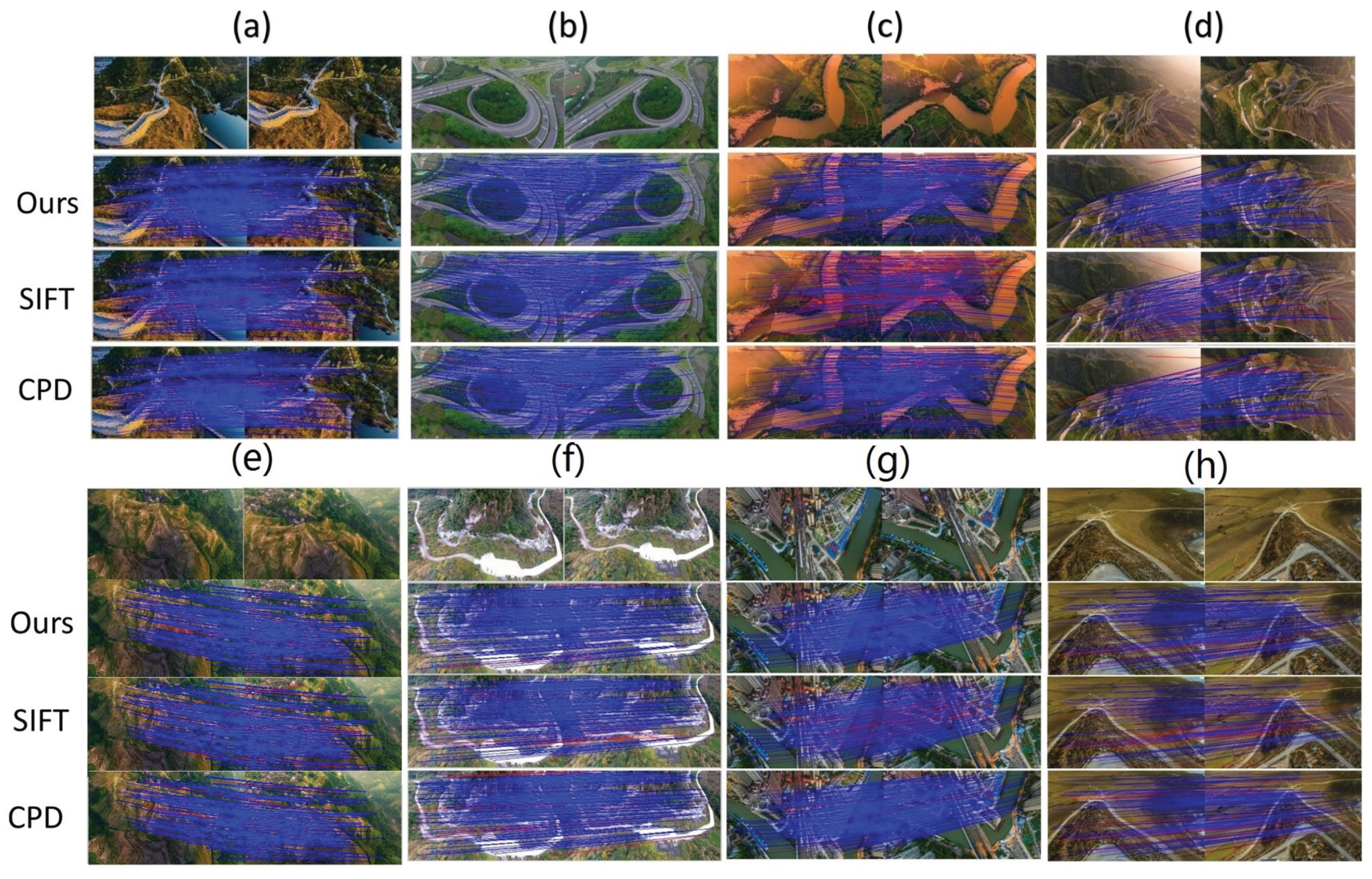
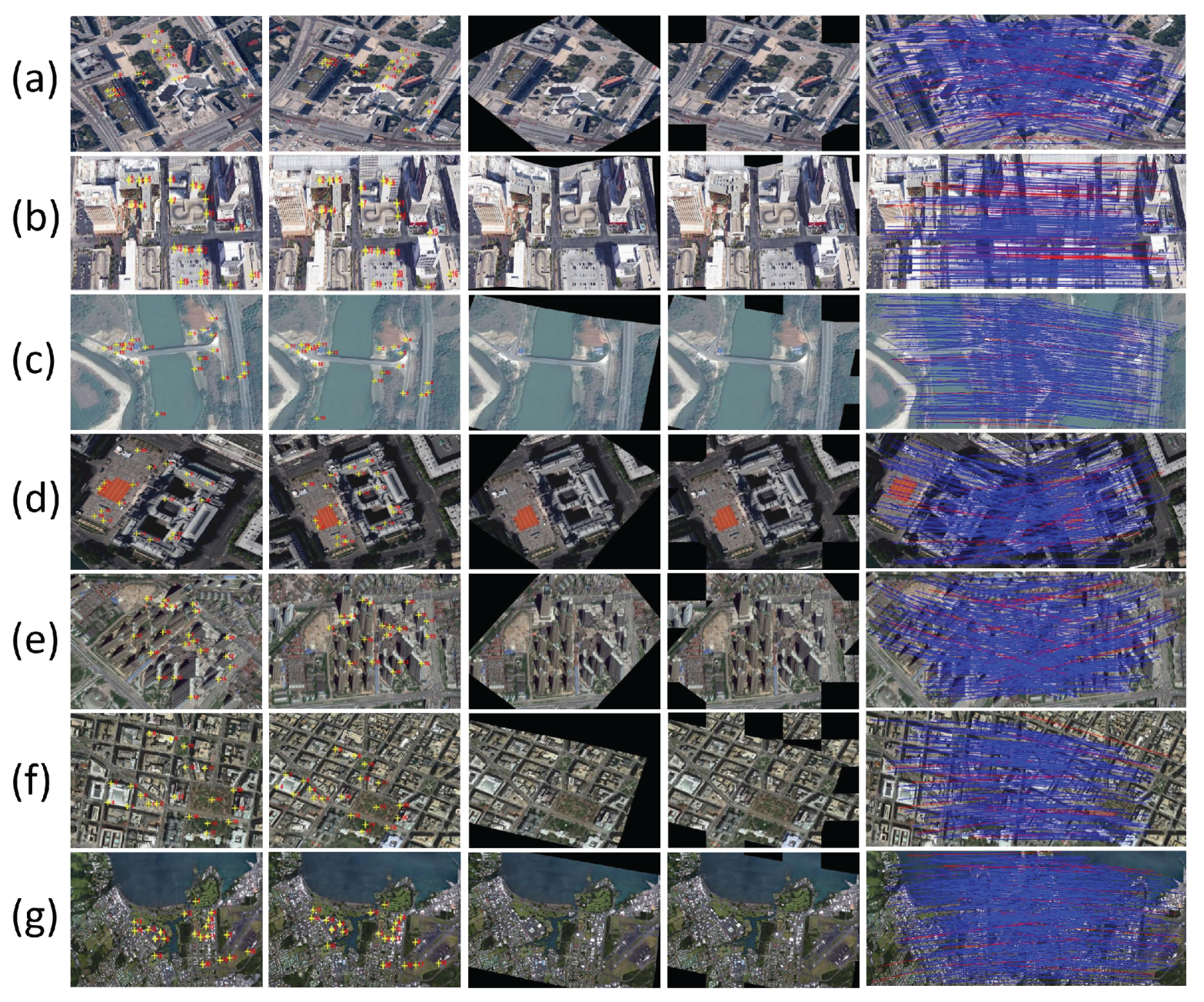
3.2. Results on Feature Matching
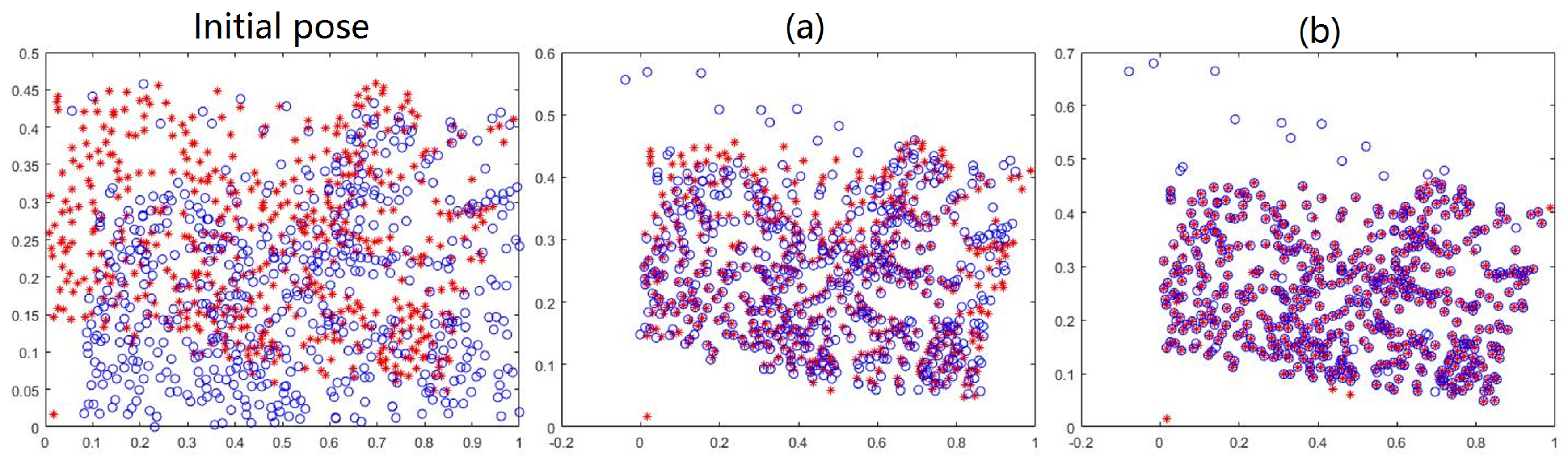
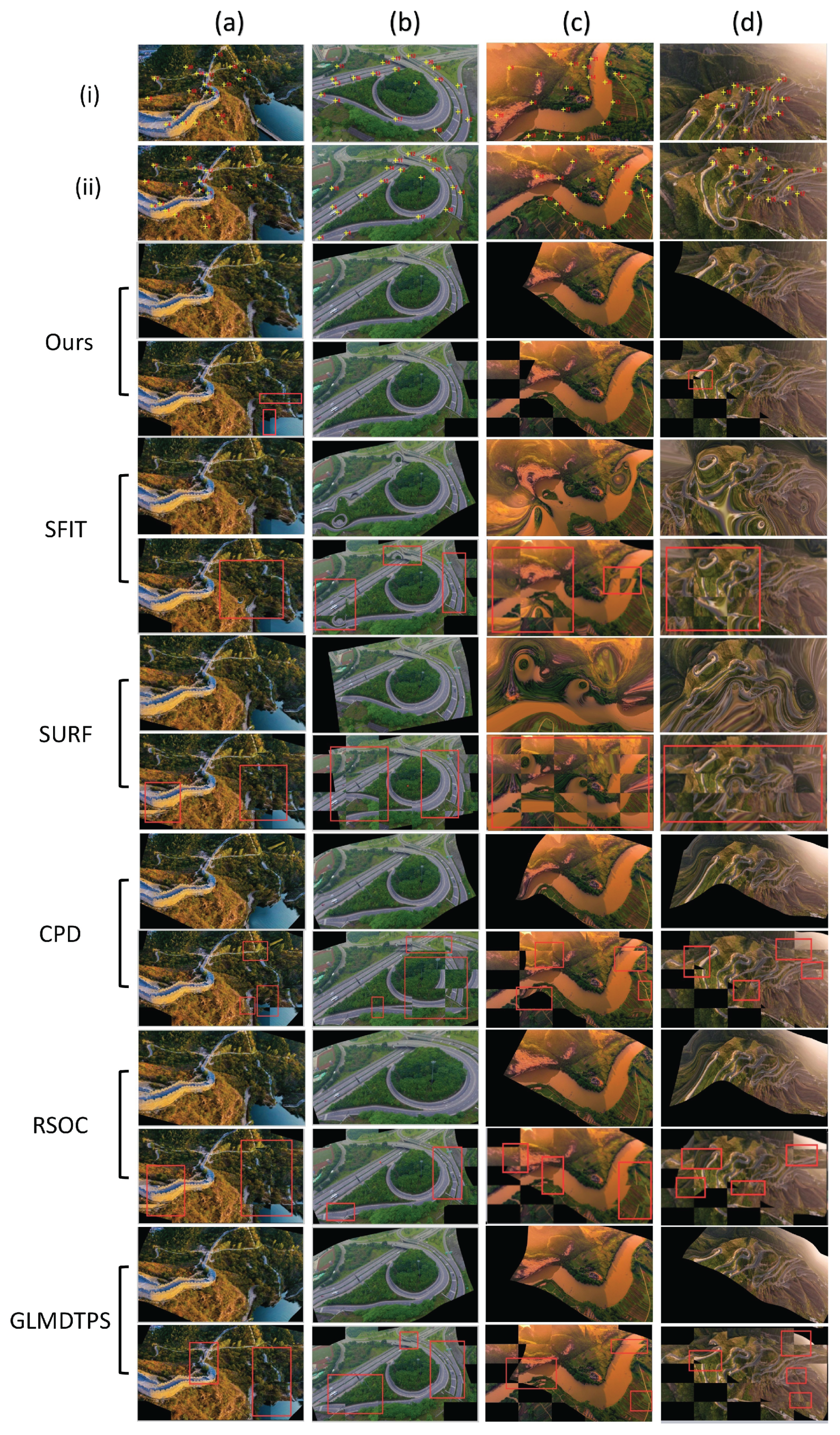
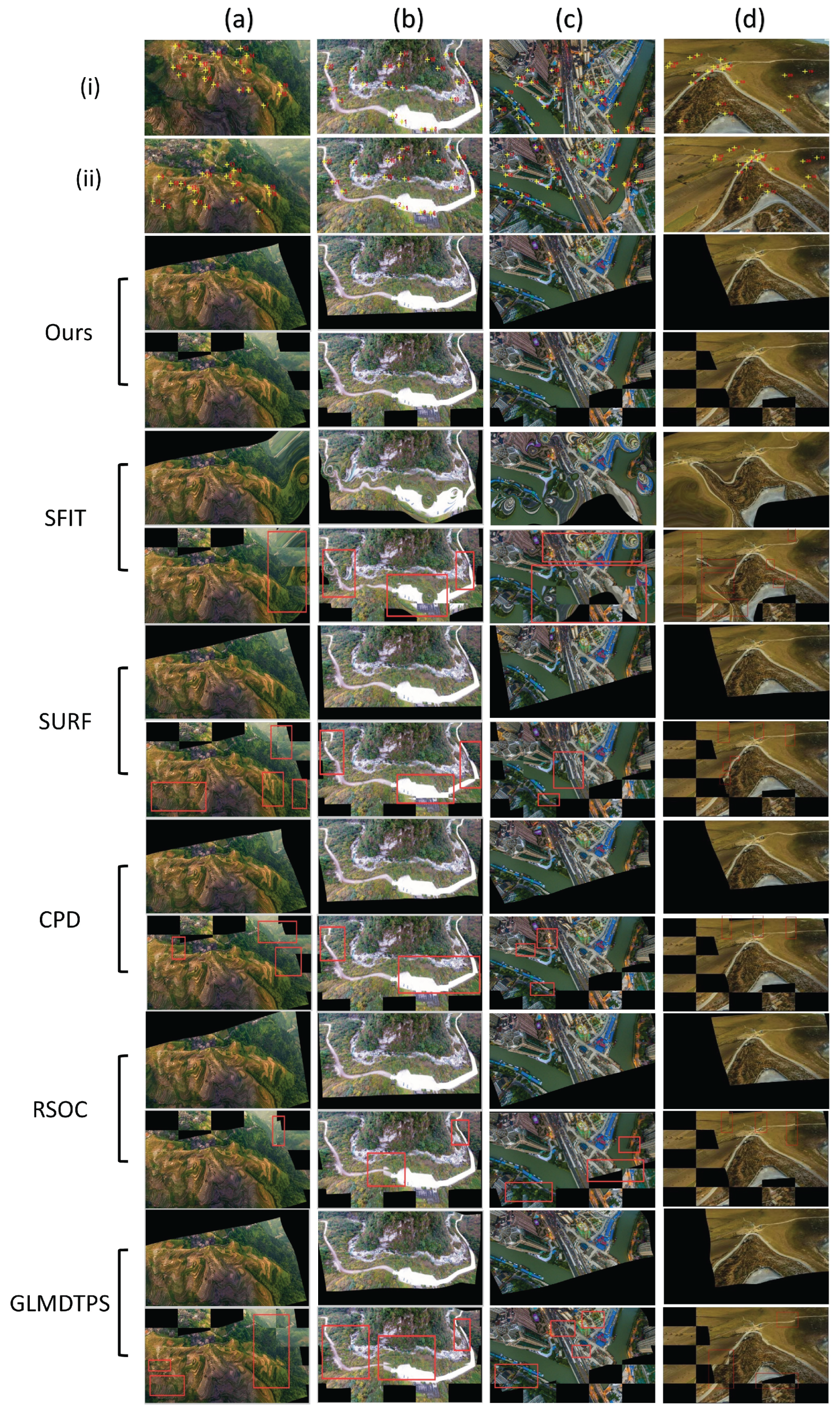
3.3. Results on Image Registration
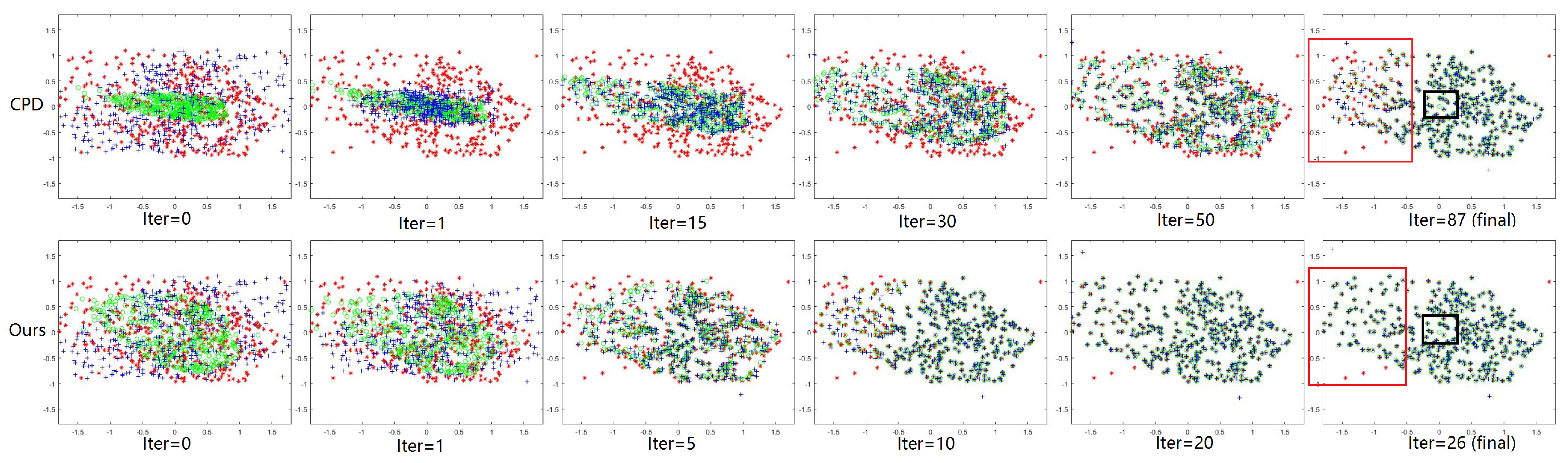
3.4. Reliability and Availability Examination of Our Method
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zitov, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L. A survey of image registration techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. 1992, 41, 325–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maintz, J.; Viergever, M. A survey of medical image registration. Med. Image Anal. 1998, 2, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Liu, F. An asift-based local registration method for satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7044–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tong, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, W.; Xie, H.; Chen, P.; Jin, Y.; Ye, Z. A Linear Feature-Based Approach for the Registration of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remotely-Sensed Images and Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Mokhtarzade, M.; Ebadi, H. Uniform Robust Scale-Invariant Feature Matching for Optical Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4516–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J. Introductory Digital Image Processing; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Chmid, C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Wu, F.; Hu, Z. Rotationally Invariant Descriptors Using Intensity Order Pooling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C. A combined corner and edge detector. In Proceedings of the 4th Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988; Volume 1988, pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, p. 1150. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 21, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Robust Scale-Invariant Feature Matching for Remote Sensing Image Registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Sukthankar, R. PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004; Volume 2, pp. 506–513. [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger, F.; Delon, J.; Gousseau, Y.; Michel, J. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-Like Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Ebadi, H. Remote Sensing Image Matching Based on Adaptive Binning SIFT Descriptor. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Bi, F.; Chen, L.; Shi, H. Feature-Area Optimization: A Novel SAR Image Registration Method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, H.; Corte-Real, L.; Goncalves, J. Automatic Image Registration Through Image Segmentation and SIFT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, L.; Tian, D. A Novel Coarse-to-Fine Scheme for Automatic Image Registration Based on SIFT and Mutual Information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, J.; Jing, Y. A simple and robust feature point matching algorithm based on restricted spatial or derconstraints for aerial image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Tian, J.; Bai, X.; Tu, Z. Regularized vector field learning with sparse approximation for mismatch removal. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 3519–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Tian, J.; Yuille, A.; Tu, Z. Robust point matching via vector field consensus. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 2014, 23, 1706–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.; Bolles, R. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1980, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronenko, A.; Song, X. Point set registration: coherent point drift. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 2262–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yan, S. Common visual pattern discovery via spatially coherent correspondences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognit, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 1609–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, X. Simultaneous remote sensing image classification and annotation based on the spatial coherent topic model. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2014—2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1698–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y. Robust L2E Estimation of Transformation for Non-Rigid Registration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Tian, J. Robust Feature Matching for Remote Sensing Image Registration via Locally Linear Transforming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6469–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ong, S.; Foong, K. A robust global and local mixture distance based non-rigid point set registration. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belongie, S.; Malik, J.; Puzicha, J. Shape Matching and Object Recognition Using Shape Contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2002, 24, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortgen, M.; Park, G.; Novotni, M.; Klein, R. 3D shape matching with shape context. In Proceedings of the 7th Central European Seminar on Computer Graphics, Budmerice, Slovakia, 22–24 April 2003; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, A.N.; Arsenin, V.Y. Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems; Winston & Sons Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D. Parametric statistical modeling by minimum integrated sqaure error. Technometrics 2001, 43, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuille, A.; Grzywacz, N. A Mathematical Analysis of the Motion Coherence Theory. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1989, 3, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, B.; Vemuri, B. Robust Point Set Registration Using Gaussian Mixture Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
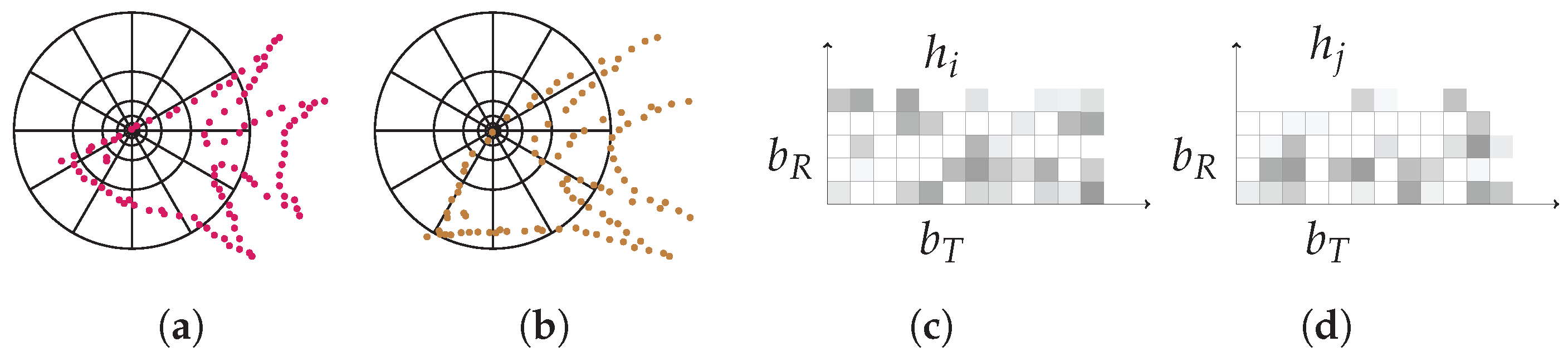
| Series | Criteria | Compared Methods | Datasets Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | PR | SIFT, CPD, Ours | (i), (ii) |
| II | All | All | (i), (ii) |
| III | All | Ours | (iii) |
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 |
|---|---|---|
| 87 to 505 | 30 | 35 to 165 |
| Dataset | SIFT | CPD | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | 78.30 | 90.81 | 98.25 |
| (ii) | 72.78 | 90.17 | 97.15 |
| Dataset | SIFT | SURF | CPD | GLMDTPS | RSOC | OURS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | (i) | 13.5287 | 7.9837 | 3.2386 | 3.0152 | 2.2737 | 1.0171 |
| (ii) | 11.4466 | 7.0627 | 7.2645 | 5.5991 | 4.1743 | 1.4331 | |
| MAE | (i) | 16.0080 | 12.2803 | 7.5404 | 7.1459 | 6.4448 | 4.0271 |
| (ii) | 14.2989 | 9.8411 | 10.3778 | 9.1102 | 7.3585 | 3.9188 | |
| SD | (i) | 14.1826 | 10.2241 | 5.8594 | 5.4353 | 4.8013 | 3.1957 |
| (ii) | 11.9613 | 8.2523 | 4.3619 | 7.6531 | 5.7844 | 3.0021 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 96.88 | 96.77 | 95.97 | 95.77 | 95.09 | 98.19 | 95.57 | 96.54 | |
| 0.8358 | 1.3963 | 1.9556 | 1.4272 | 0.7743 | 1.4342 | 0.3171 | 1.1628 | |
| 2.1458 | 4.0208 | 2.9097 | 1.9317 | 2.5778 | 2.3542 | 2.2958 | 2.6051 | |
| 1.8562 | 2.5498 | 2.5171 | 1.8061 | 2.1429 | 2.0098 | 2.0717 | 2.1362 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Pan, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ong, S.H.; Tang, H. Remote Sensing Image Registration Using Multiple Image Features. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060581
Yang K, Pan A, Yang Y, Zhang S, Ong SH, Tang H. Remote Sensing Image Registration Using Multiple Image Features. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(6):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060581
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kun, Anning Pan, Yang Yang, Su Zhang, Sim Heng Ong, and Haolin Tang. 2017. "Remote Sensing Image Registration Using Multiple Image Features" Remote Sensing 9, no. 6: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060581
APA StyleYang, K., Pan, A., Yang, Y., Zhang, S., Ong, S. H., & Tang, H. (2017). Remote Sensing Image Registration Using Multiple Image Features. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060581