Validation of Sentinel-1A SAR Coastal Wind Speeds Against Scanning LiDAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sentinel-1A SAR
Wind Direction Input for SAR Wind Retrieval
2.2. LiDAR Measurements
2.2.1. Scanning LiDARs
2.2.2. Profiling LiDAR
2.3. Meteorological Mast
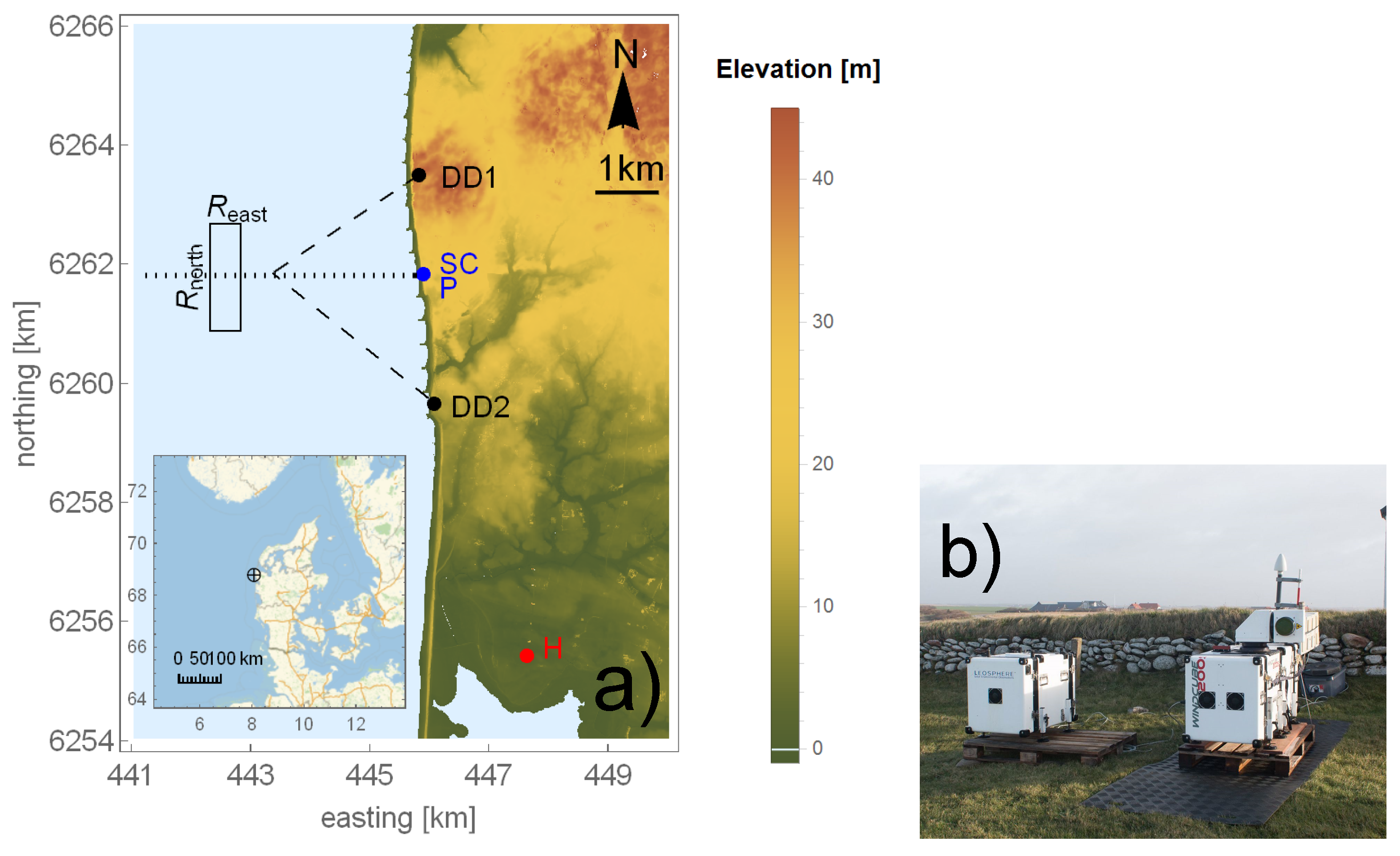
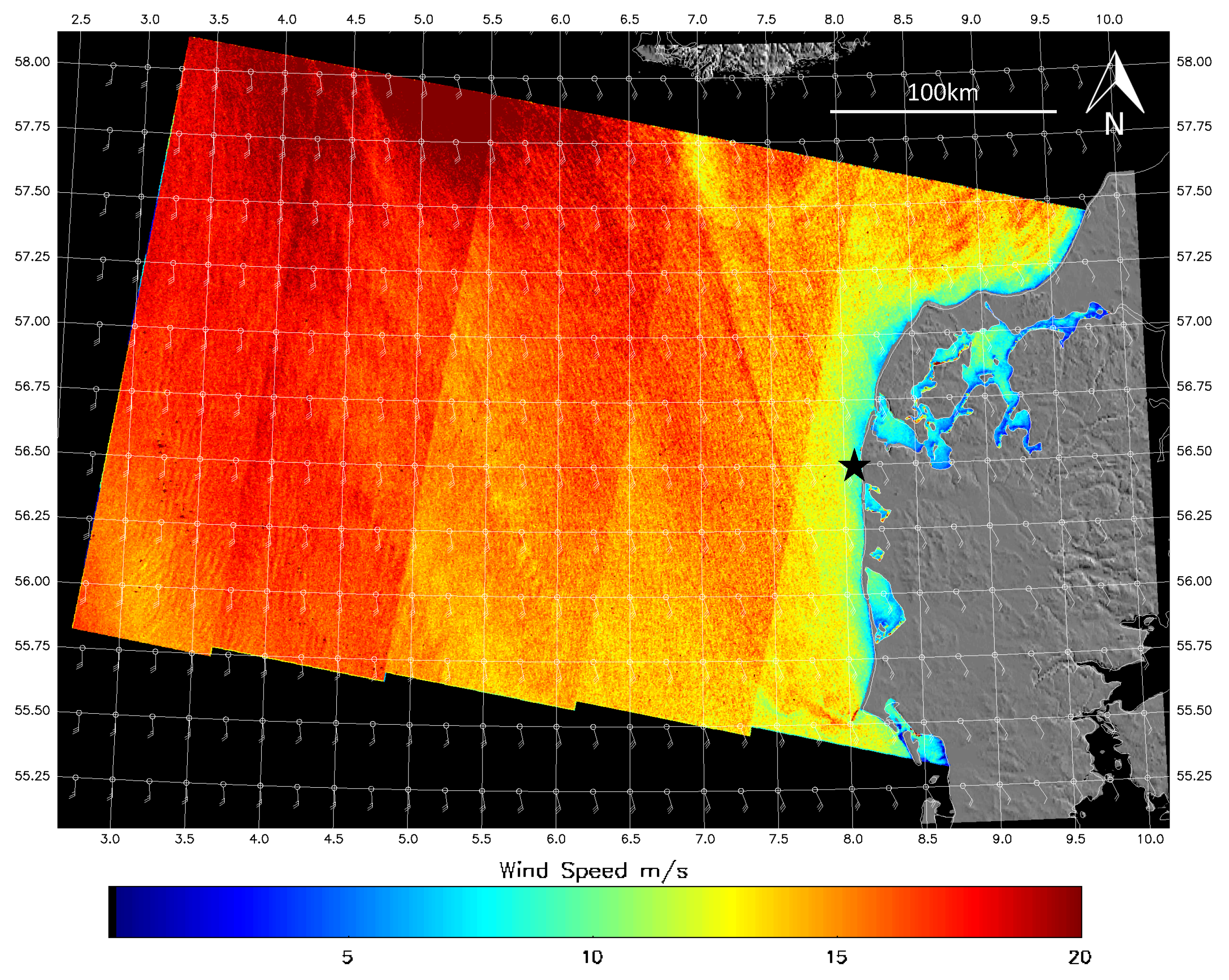
2.4. Available Cases
2.5. Method for Comparing SAR and LiDAR Data
2.5.1. Vertical Displacement
2.5.2. Temporal and Horizontal Displacement
3. Results
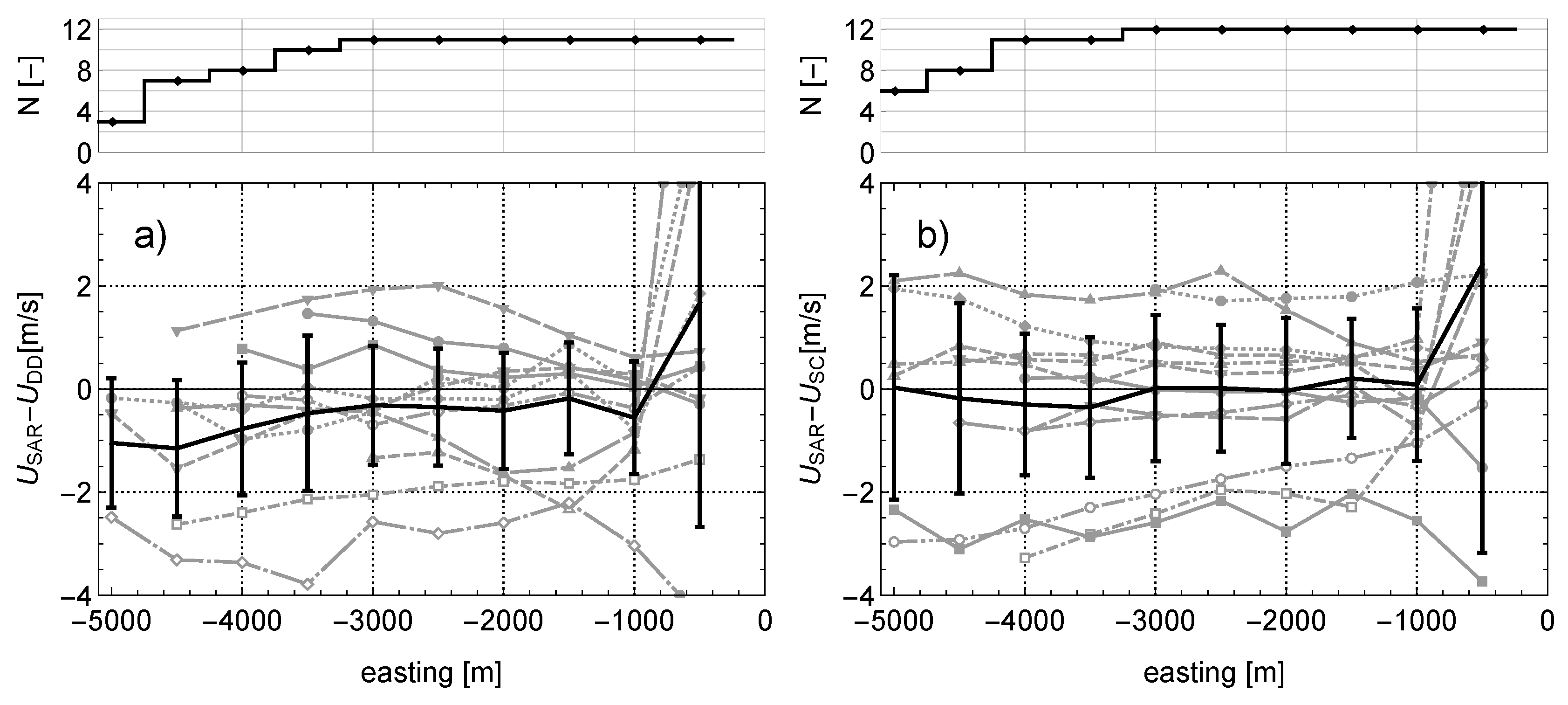
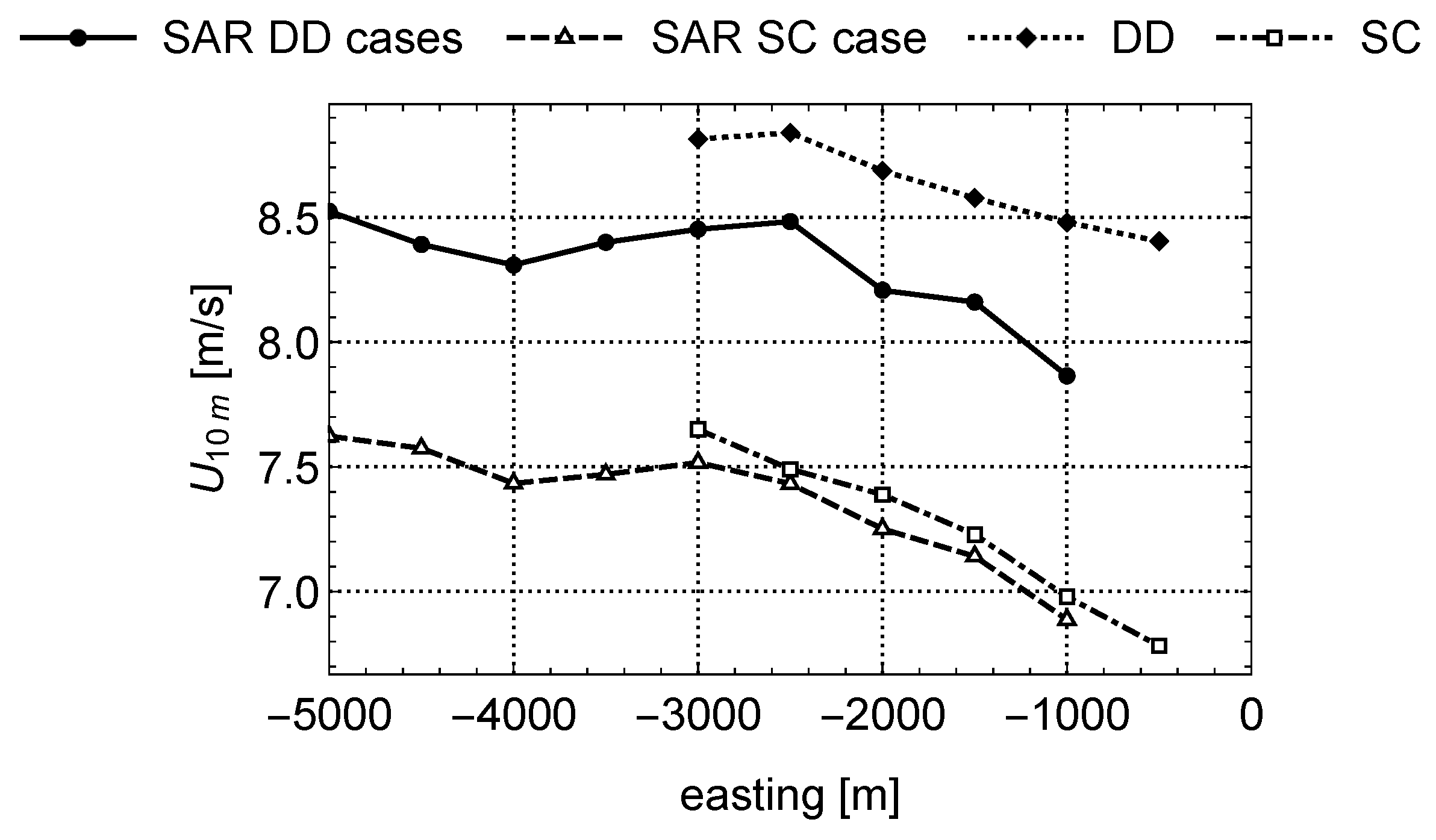
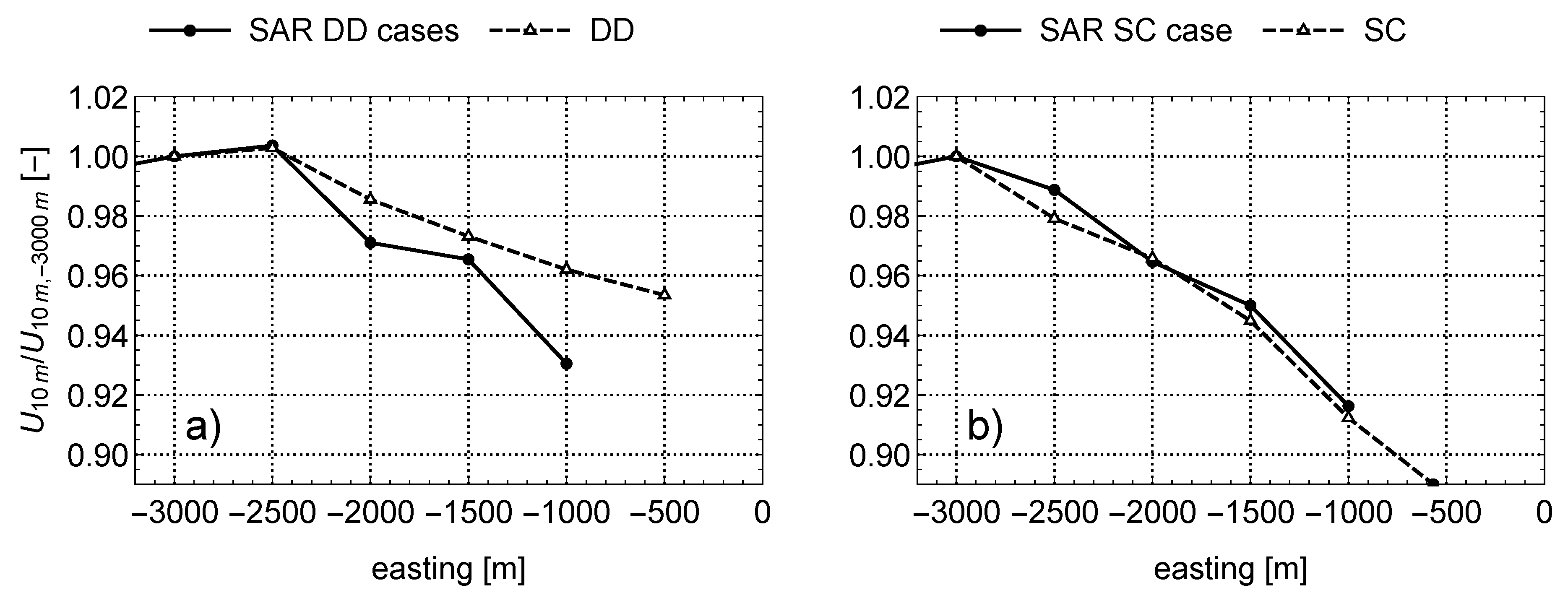
3.1. Differences over the Transect
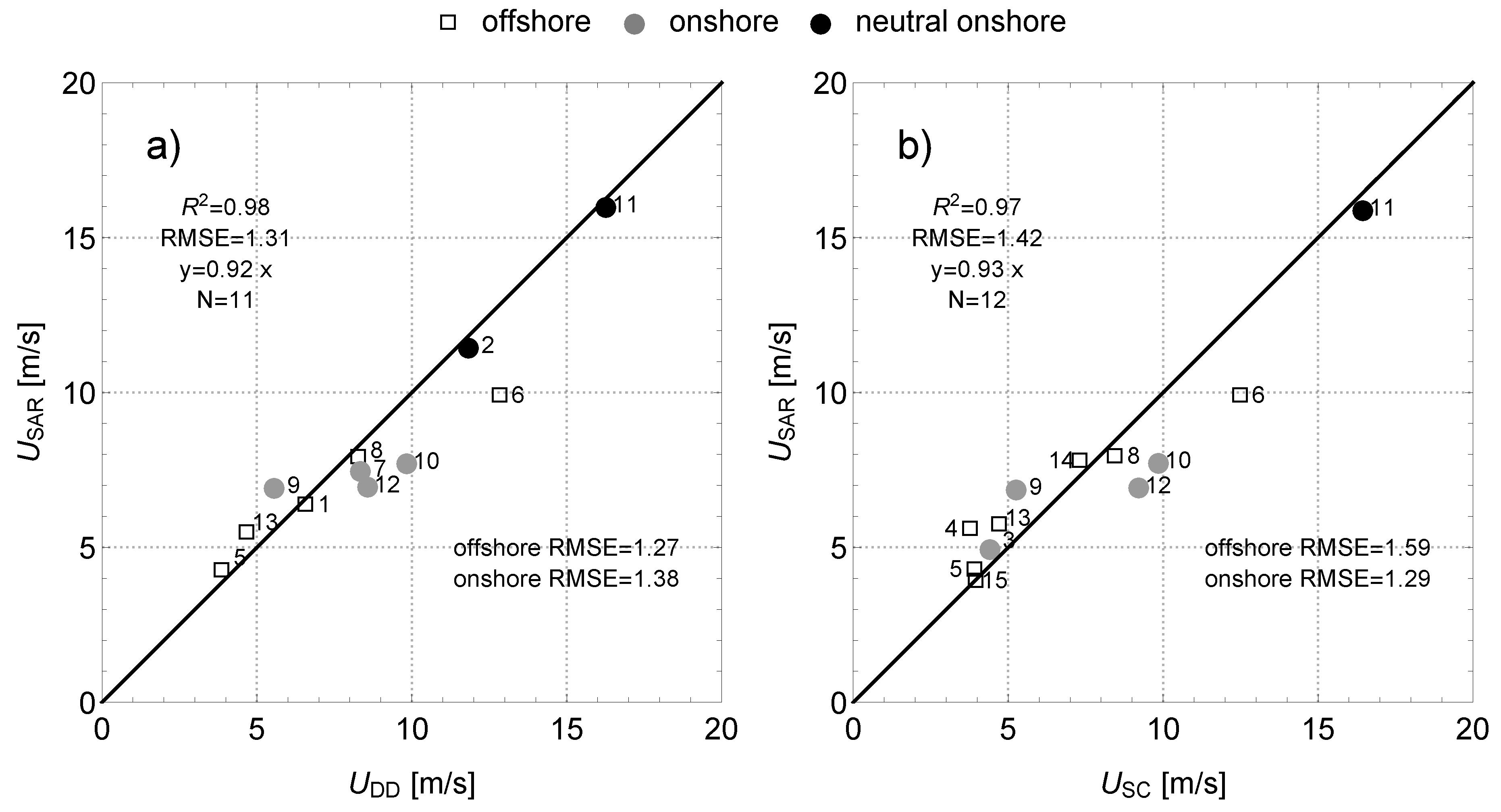
3.2. Spatially Averaged Wind Speed
3.3. Ensemble Averaged Wind Speed
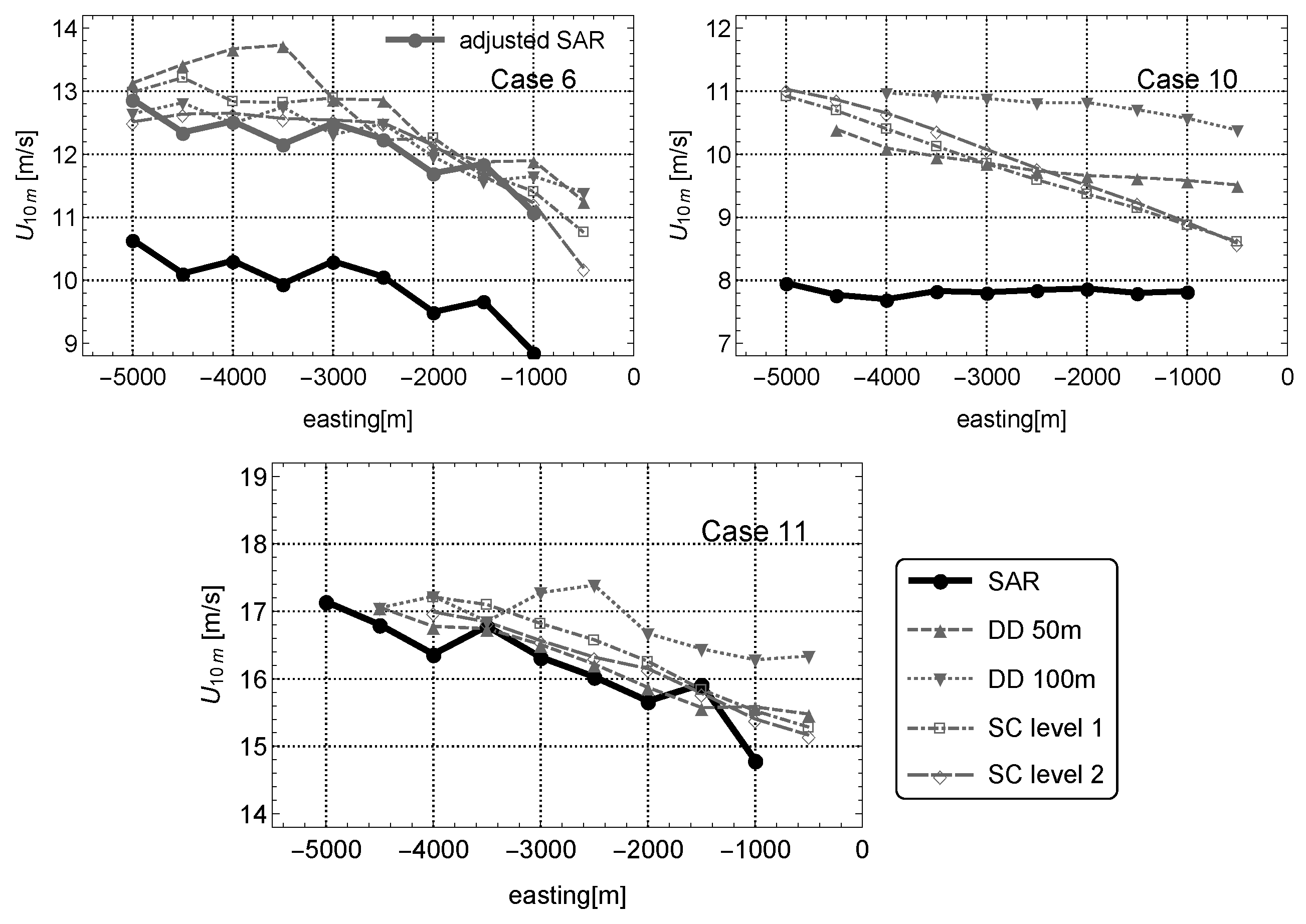
3.4. Example Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| GMF | Geophysical Model Function |
| CMOD | C-band model |
| CMOD5.N | C-band model 5.N |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RUNE | Reducing uncertainty of near-shore wind resource estimates using onshore LiDAR |
| SAROPS | SAR Ocean Products System |
| DD | Dual Doppler |
| SC | Sector Scan |
| STD | Standard deviation |
| DTU | Technical University of Denmark |
References
- Dagestad, K.F.; Horstmann, J.; Mouche, A.; Perrie, W.; Shen, H. Wind Retrieval From Synthetic Aperture Radar—An Overview; SeaSar 2012 Oceanography Workshop: Tromsø, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Karagali, I.; Larsen, X.G.; Badger, M.; Peña, A.; Hasager, C.B. Spectral Properties of ENVISAT ASAR and QuikSCAT Surface Winds in the North Sea. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6096–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A.; Anderson, D. Scatterometer data interpretation: Estimation and validation of the transfer function CMOD4. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilfen, Y.; Chapron, B.; Elfouhaily, T.; Katsaros, K.; Tournadre, J. Observation of tropical cyclones by high-resolution scatterometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. Comparison of C-Band Scatterometer CMOD5.N Equivalent Neutral Winds with ECMWF. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W. Using ERS-2 SAR images for routine observation of marine pollution in European coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 237–238, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Romeiser, R.; Alpers, W. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 2. Model response to surface roughness variations and the radar imaging of underwater bottom topography. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1997, 102, 25251–25267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, M.B.; Hasager, C.B.; Thompson, D.R.; Monaldo, F.M. Ocean winds from synthetic aperture radar. In Ocean Remote Sensing: Recent Techiniques and Applications; Chapter Ocean Wind; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2008; pp. 31–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hasager, C.B.; Mouche, A.; Badger, M.; Bingöl, F.; Karagali, I.; Driesenaar, T.; Stoffelen, A.; Peña, A.; Longépé, N. Offshore wind climatology based on synergetic use of Envisat ASAR, ASCAT and QuikSCAT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.B.; Xing, X.; Jiang, Y. Offshore wind resources assessment from multiple satellite data and WRF modeling over South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, Y.; Ohsawa, T.; Kozai, K.; Hasager, C.B.; Badger, M. Effectiveness of WRF wind direction for retrieving coastal sea surface wind from synthetic aperture radar. Wind Energy 2014, 16, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.B.; Zhou, R.; Ye, D.; Zhang, X. Applicability of synthetic aperture radar wind retrievals on offshore wind resources assessment in Hangzhou Bay, China. Energies 2014, 7, 3339–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, Y.; Ohsawa, T.; Kozai, K.; Hasager, C.B.; Badger, M. Comparison of geophysical model functions for SAR wind speed retrieval in japanese coastal waters. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1956–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasager, C.B.; Badger, M.; Peña, A.; Larsén, X.G.; Bingöl, F. SAR-based wind resource statistics in the Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, M.B.; Koch, W.; Horstmann, J.; Hasager, C.B.; Nielsen, M. Wind resource assessment from C-band SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasager, C.B.; Dellwik, E.; Nielsen, M.; Furevik, B.R. Validation of ERS-2 SAR offshore wind-speed maps in the North Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3817–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F.M.; Thompson, D.R.; Beal, R.C.; Pichel, W.G.; Clemente-Colón, P. Comparison of SAR-derived wind speed with model predictions and ocean buoy measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F.M.; Thompson, D.R.; Pichel, W.G.; Clemente-Colon, P. A systematic comparison of QuikSCAT and SAR ocean surface wind speeds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F.; Jackson, C.; Li, X.; Member, S.; Pichel, W.G. Preliminary Evaluation of Sentinel-1A Wind Speed Retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Hasager, C.B.; Gryning, S.E.; Courtney, M.; Antoniou, I.; Mikkelsen, T. Offshore wind profiling using light detection and ranging measurements. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, N. A Time-Space Synchronization of Coherent Doppler Scanning LiDARs for 3D Measurements of Wind Fields. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschall, J.; Courtney, M.; Wagner, R.; Jørgensen, H.; Antoniou, I. LiDAR profilers in the context of wind energy—A verification procedure for traceable measurements. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, M. Calibrating Nacelle LiDARs; DTU Wind Energy: Roskilde, Denmark, 2013; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiljević, N.; Lea, G.; Courtney, M.; Cariou, J.p.; Mann, J. Long-Range WindScanner System. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Vasiljevíc, N.; Kelly, M.; Lea, G.; Courtney, M. Addressing Spatial Variability of Surface-Layer Wind with Long-Range WindScanners. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 32, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmie, R.; Badger, J.; Pryor, S.; Hasager, C.B.; Christiansen, M.; Jørgensen, B. Offshore Coastal Wind Speed Gradients: Issues for the design and development of large offshore windfarms. Wind Eng. 2007, 31, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubrawa, P.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Pryor, S.C.; Hasager, C.B.; Badger, M. Satellite winds as a tool for offshore wind resource assessment: The Great Lakes Wind Atlas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagali, I.; Badger, M.; Hahmann, A.N.; Peña, A.; Hasager, C.B.; Sempreviva, A.M. Spatial and temporal variability of winds in the Northern European Seas. Renew. Energy 2013, 57, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floors, R.; Peña, A. The RUNE experiment—A database of remote-sensing observations of near-shore winds. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Lehner, S.; Hieronimus, J.; Schneemann, J.; Kühn, M. Joint Offshore Wind Field Monitoring With Spaceborne Sar and Platform-Based Doppler LiDAR Measurements. In Proceedings of the 36th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Berlin, Germany, 1–15 May 2015; Volume XL-7/W3. [Google Scholar]
- De Zan, F.; Guarnieri, A.M. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Stoffelen, A.; De Haan, S. The Improved C-Band Geophysical Model Function CMOD5; European Space Agency (Special Publication): Paris, France, 2005; Volume 112, pp. 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Mouche, A.A.; Hauser, D.; Daloze, J.F.; Guérin, C. Dual-polarization measurements at C-band over the ocean: Results from airborne radar observations and comparison with ENVISAT ASAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, F.M.; Jackson, C.; Pichel, W.; Li, X. A Weather Eye on Coastal Winds. Eos 2015, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, W. Directional analysis of SAR images aiming at wind direction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floors, R.; Lea, G.; Peña, A.; Karagali, I.; Ahsbahs, T. Report on RUNE ’s Coastal Experiment and First Inter-Comparisons between Measurements Systems; E-Report DTU Wind Energy: Roskilde, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, A.; Floors, R.; Sathe, A.; Gryning, S.E.; Wagner, R.; Courtney, M.S.; Larsen, X.G.; Hahmann, A.N.; Hasager, C.B. Ten Years of Boundary-Layer and Wind-Power Meteorology at Hovsore, Denmark. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 158, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyngaard, J.C. Turbulence in the Atmosphere; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; p. 392. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, E.; Courtney, M. A Comparison of Sector-Scan and Dual Doppler Wind Measurements at Høvsøre Test Station—One LiDAR or Two? Technical Report; DTU Wind Energy: Roskilde, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grachev, A.A.; Fairall, C.W. Dependence of the Monin-Obukhov Stability Parameter on the Bulk Richardson Number over the Ocean. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 36, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasager, C.B.; Badger, M.; Nawri, N.; Furevik, B.R.; Petersen, G.N.; Björnsson, H.; Clausen, N.E. Mapping offshore winds around Iceland using satellite synthetic aperture radar and mesoscale model simulations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5541–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.F. A micrometeorological study of velocity profiles and surface drag in the region modified by a change in surface roughness. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1968, 94, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Wyngaard, J.C.; Cote, O. The Structure of the Two-Dimensional Internal Boundary Layer over a Sudden Change of Surface Roughness. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troen, I.; Petersen, E.L. European Wind Atlas; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1989; p. 656.
- Kara, A.B.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Bourassa, M.A. Air-sea stability effects on the 10 m winds over the global ocean: Evaluations of air-sea flux algorithms. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagali, I.; Peña, A.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.B. Wind characteristics in the North and Baltic Seas from the QuikSCAT satellite. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Samples | Location | RMSE () | Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hasager et al. [9] | 149 to 197 | Denmark/The Netherlands | 1.27 to 1.65 | Envisat |
| Chang et al. [10] | 552 | South Chinese Sea | 2.09 | Envisat |
| Takeyama et al. [11] | 42 | Japan | 0.75 to 2.24 | Envisat |
| Chang et al. [12] | 522 | East Chinese Sea | 1.99 | Envisat |
| Takeyama et al. [13] | 33 to 73 | Japan | 0.64 to 2.34 | Envisat |
| Hasager et al. [14] | 875 | Baltic Sea | 1.17 | Envisat |
| Christiansen et al. [15] | 91 | Denmark | 1.1 to 1.8 | ERS2 |
| Hasager et al. [16] | 61 | Denmark | 0.9 to 1.14 | ERS2 |
| Case | Date | Time | Pol. | Mode | Orbit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 December 2015 | 17:09 | HH | EW | D | 37 |
| 2 | 9 December 2015 | 05:40 | VV | EW | A | 43 |
| 3 | 12 December 2015 | 17:17 | VV | IW | D | 44 |
| 4 | 14 December 2015 | 05:48 | HH | EW | A | 36 |
| 5 | 26 December 2015 | 05:48 | HH | IW | A | 36 |
| 6 | 31 December 2015 | 05:56 | HH | IW | D | 27 |
| 7 | 31 December 2015 | 17:09 | HH | IW | D | 37 |
| 8 | 12 January 2016 | 17:09 | HH | EW | A | 37 |
| 9 | 19 January 2016 | 05:48 | VV | EW | A | 36 |
| 10 | 26 January 2016 | 05:40 | VV | EW | D | 43 |
| 11 | 29 January 2016 | 17:17 | HH | EW | D | 44 |
| 12 | 5 February 2016 | 17:09 | HH | EW | D | 37 |
| 13 | 12 February 2016 | 05:48 | VV | IW | A | 36 |
| 14 | 17 February 2016 | 17:09 | HH | IW | D | 37 |
| 15 | 29 February 2016 | 05:57 | HH | EW | A | 27 |
| Case | DD | SC | m | (40 m) (m) | Stab Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x | 7.5 | 148.5 | 40 | very stable | |
| 2 | x | 13.6 | 277 | 1320 | neutral | |
| 3 | x | 5.2 | 234 | 123 | stable | |
| 4 | x | 4.7 | H:167 | 50 | very stable | |
| 5 | x | x | 5.0 | 80 | 31 | very stable |
| 6 | x | x | 13.0 | 149 | −1480 | neutral |
| 7 | x | 10.0 | 205 | 46 | very stable | |
| 8 | x | x | 10.5 | 56 | 596.5 | neutral |
| 9 | x | x | 7.3 | 347 | - | - |
| 10 | x | x | 11.5 | 264 | 175 | stable |
| 11 | x | x | 19.0 | 250 | 1001 | neutral |
| 12 | x | x | 10.0 | 213 | 53 | very stable |
| 13 | x | x | 6.4 | 40 | 39 | very stable |
| 14 | x | 8.3 | 141 | 41 | very stable | |
| 15 | x | 4 | 133 | 43 | very stable |
| - | 1 km | 1.5 km | 2 km | 3 km | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cells (-) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| (ms) | - | −0.01 | −0.02 | −0.03 | −0.04 |
| (ms) | - | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.28 |
| RMSE () | 1.53 | 1.45 | 1.41 | 1.42 | 1.43 |
| Mean Bias (ms) | Median STD (ms) | Min STD (ms) | Max STD () | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | −0.57 | 1.30 | 1.07 | 1.62 |
| SC | −0.17 | 1.47 | 1.17 | 1.98 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahsbahs, T.; Badger, M.; Karagali, I.; Larsén, X.G. Validation of Sentinel-1A SAR Coastal Wind Speeds Against Scanning LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060552
Ahsbahs T, Badger M, Karagali I, Larsén XG. Validation of Sentinel-1A SAR Coastal Wind Speeds Against Scanning LiDAR. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(6):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060552
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhsbahs, Tobias, Merete Badger, Ioanna Karagali, and Xiaoli Guo Larsén. 2017. "Validation of Sentinel-1A SAR Coastal Wind Speeds Against Scanning LiDAR" Remote Sensing 9, no. 6: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060552
APA StyleAhsbahs, T., Badger, M., Karagali, I., & Larsén, X. G. (2017). Validation of Sentinel-1A SAR Coastal Wind Speeds Against Scanning LiDAR. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060552







