Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States
Abstract
1. Background and Rationale
2. Goals and Objectives
3. Approach and Methods
3.1. Comparison and Combination of Approaches
3.2. AmeriFlux Data Processing and Comparisons
4. Results
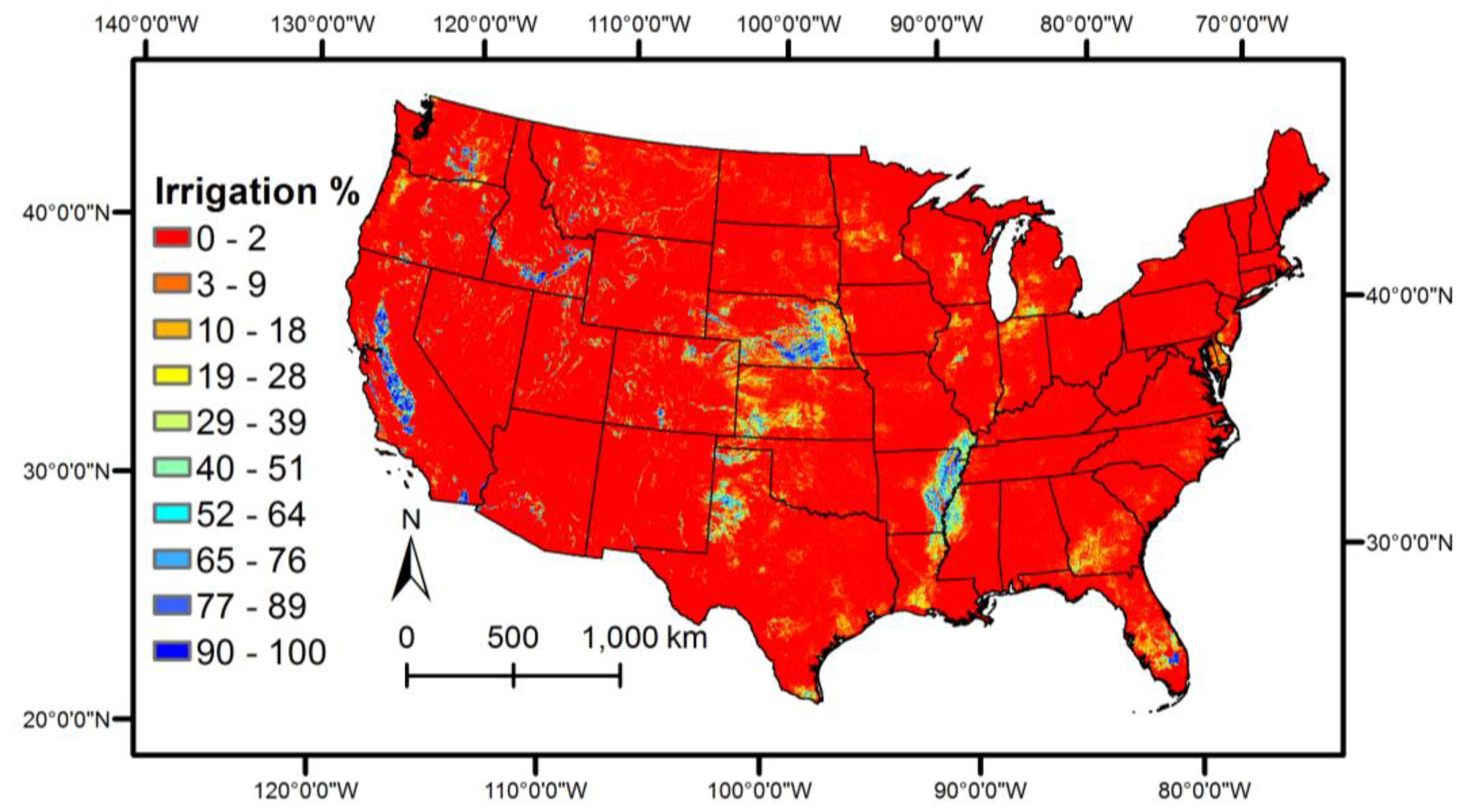
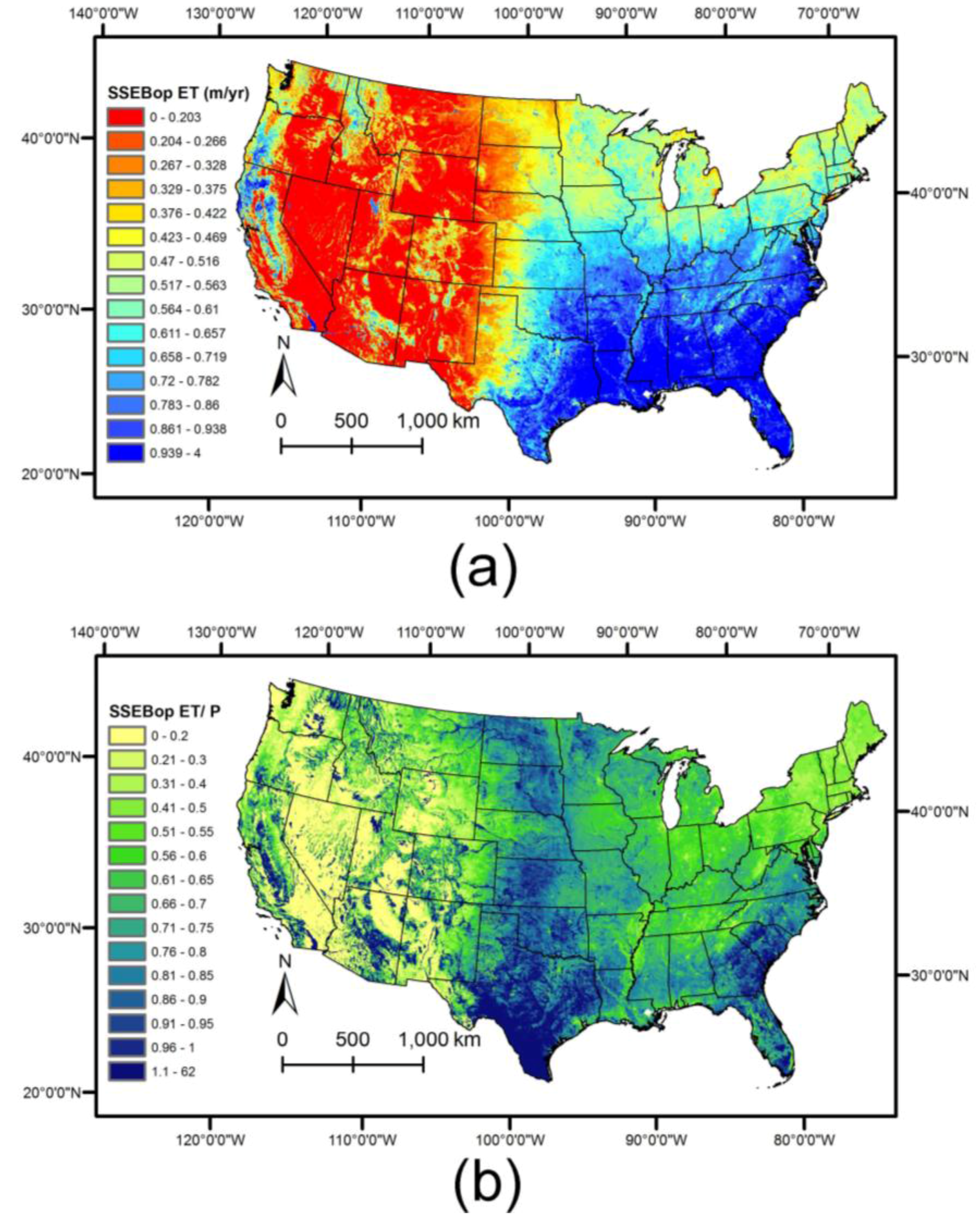
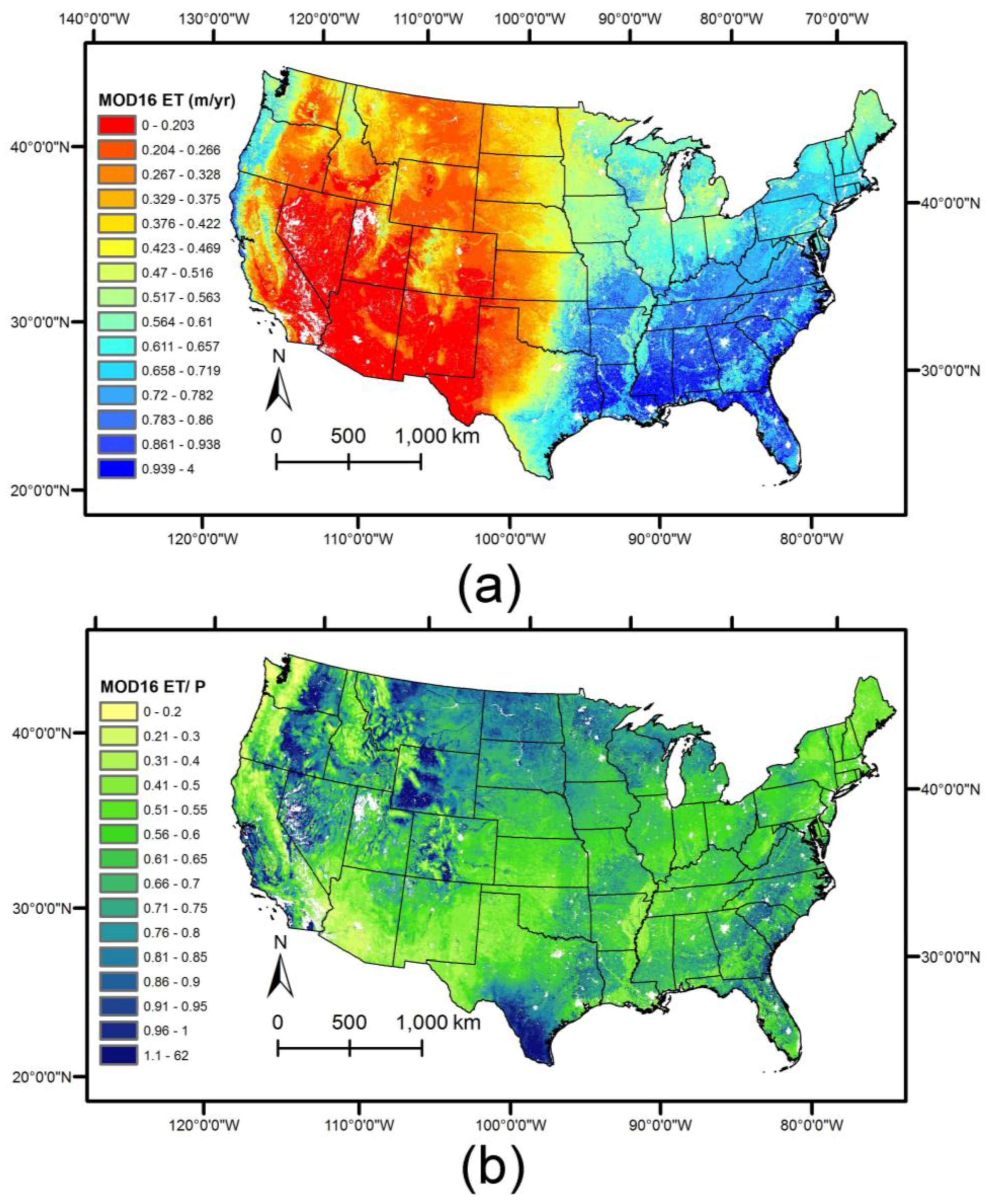
4.1. Annual Average ET Maps
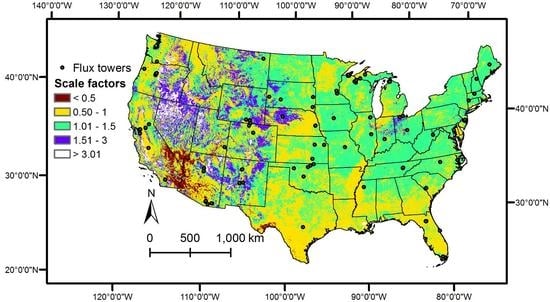
4.2. Comparisons with AmeriFlux Data
4.3. Combined Product and Monthly, Seasonal Comparisons
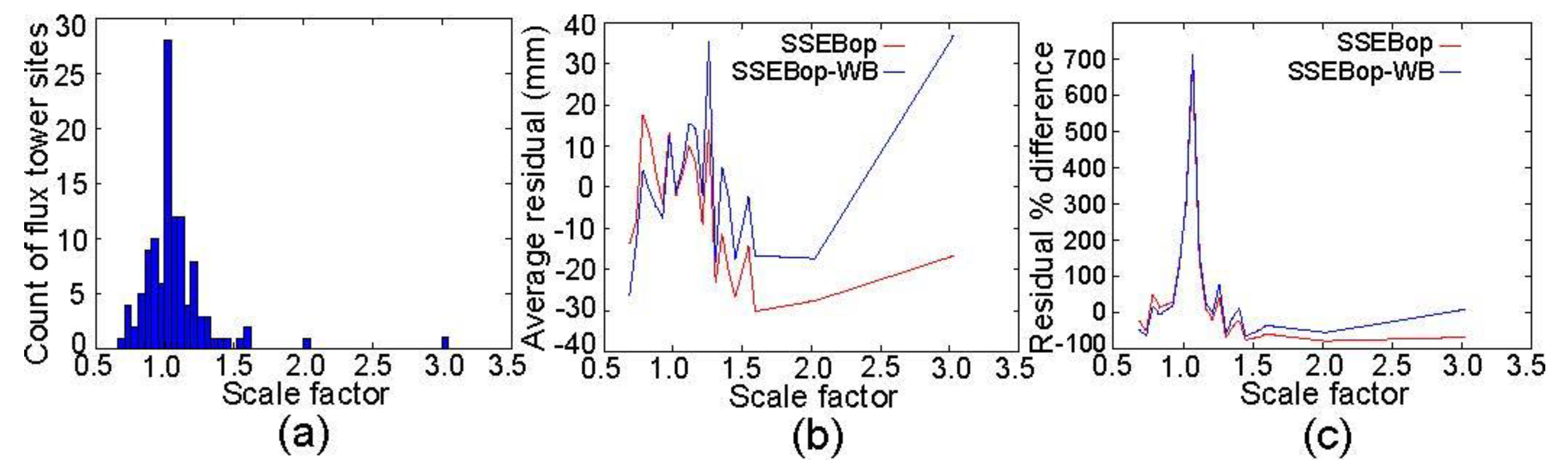
4.4. Analysis of Residuals
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reitz, M.; Sanford, W.E.; Senay, G.B.; Cazenas, J. Annual estimates of ET, recharge and quick-flow runoff for the contiguous US using empirical regression equations. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B. Partitioning Evapotranspiration into Green and Blue Water Sources in the Conterminous United States. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, Y.A.; Kar, S.K. Evapotranspiration estimation with remote sensing and various surface energy balance algorithms—A review. Energies 2014, 7, 2821–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Chambouleyron, J.; Menenti, M. Relating crop water consumption to irrigation water supply by remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 1997, 11, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.M.; Maxwell, R.M. Examining regional groundwater-surface water dynamics using an integrated hydrologic model of the San Joaquin River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 923–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olioso, A.; Chauki, H.; Courault, D.; Wigneron, J.P. Estimation of evapotranspiration and photosynthesis by assimilation of remote sensing data into SVAT models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational evapotranspiration mapping using remote sensing and weather data sets: A new parameterization for the SSEB approach. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera-Guerra, L.; Mattar, C.; Merlin, O.; Durán-Alarcón, C.; Santamaría-Artigas, A.; Fuster, R. An operational method for the disaggregation of land surface temperature to estimate actual evapotranspiration in the arid region of Chile. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, D.; Jiménez, C.; Miralles, D.G.; Jung, M.; Hirschi, M.; Ershadi, A.; Martens, B.; McCabe, M.F.; Fisher, J.B.; Mu, Q.; et al. The WACMOS-ET project—Part 1: Tower-scale evaluation of four remote sensing-based evapotranspiration algorithms. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Jiménez, C.; Jung, M.; Michel, D.; Ershadi, A.; McCabe, M.F.; Hirschi, M.; Martens, B.; Dolman, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; et al. The WACMOS-ET project—Part 2: Evaluation of global terrestrial evaporation data sets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, C.; Franch, B.; Sobrino, J.A.; Corbari, C.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Skokovic, D.; Sória, G.; Oltra-Carriò, R.; Julien, Y.; et al. Impacts of the broadband albedo on actual evapotranspiration estimated by S-SEBI model over an agricultural area. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “AmeriFlux: Measuring carbon, water and energy flux across the Americas.” Hosted by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy. Available online: http://ameriflux.lbl.gov (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C.; et al. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, W.E.; Selnick, D.L. Estimation of Evapotranspiration across the Conterminous United States Using a Regression with Climate and Land-Cover Data. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031. Available online: prism.oregonstate.edu (accessed on 19 October 2017). [CrossRef]
- Hutson, S.S.; Barber, N.L.; Kenny, J.F.; Linsey, K.S.; Lumia, D.S.; Maupin, M.A. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2000; U.S. Geological Survey Circular; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004.
- Kenny, J.F.; Barber, N.L.; Hutson, S.S.; Linsey, K.S.; Lovelace, J.K.; Maupin, M.A. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2005; U.S. Geological Survey Circular; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009.
- Maupin, M.A.; Kenny, J.F.; Hutson, S.S.; Lovelace, J.K.; Barber, N.L.; Linsey, K.S. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2010; U.S. Geological Survey Circular; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- Reitz, M.; Sanford, W.E.; Senay, G.B.; Cazenas, J. Annual estimates of recharge, quick-flow runoff, and ET for the contiguous US using empirical regression equations. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 961–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Walt, S.; Colbert, S.C.; Varoquaux, G. The NumPy Array: A Structure for Efficient Numerical Computation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, T.E. Python for scientific computing. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.S.; Maxwell, S. Mapping irrigated lands across the United States using MODIS satellite imagery. In Remote Sensing of Global Croplands for Food Security; Thenkabail, P.S., Biradar, C.M., Turral, H., Lyon, J.G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, J.; Xian, G.; Jin, S.; Dewitz, J.; Homer, C.; Yang, L.; Barnes, C.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J. Completion of the 2006 National Land Cover Database for the Conterminous United States. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 858–864. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Web Soil Survey. Available online: http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 19 October 2017).
- Velpuri, N.M.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Bohms, S.; Verdin, J.P. A comprehensive evaluation of two MODIS evapotranspiration products over the conterminous United States: Using point and gridded FLUXNET and water balance ET. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, M.; Senay, G.B.; Sanford, W.E. Combined Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates (SSEBop-WB) for the Conterminous United States. U.S. Geological Survey Data Release. 2017. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5066/F7QC02FK (accessed on 19 October 2017).

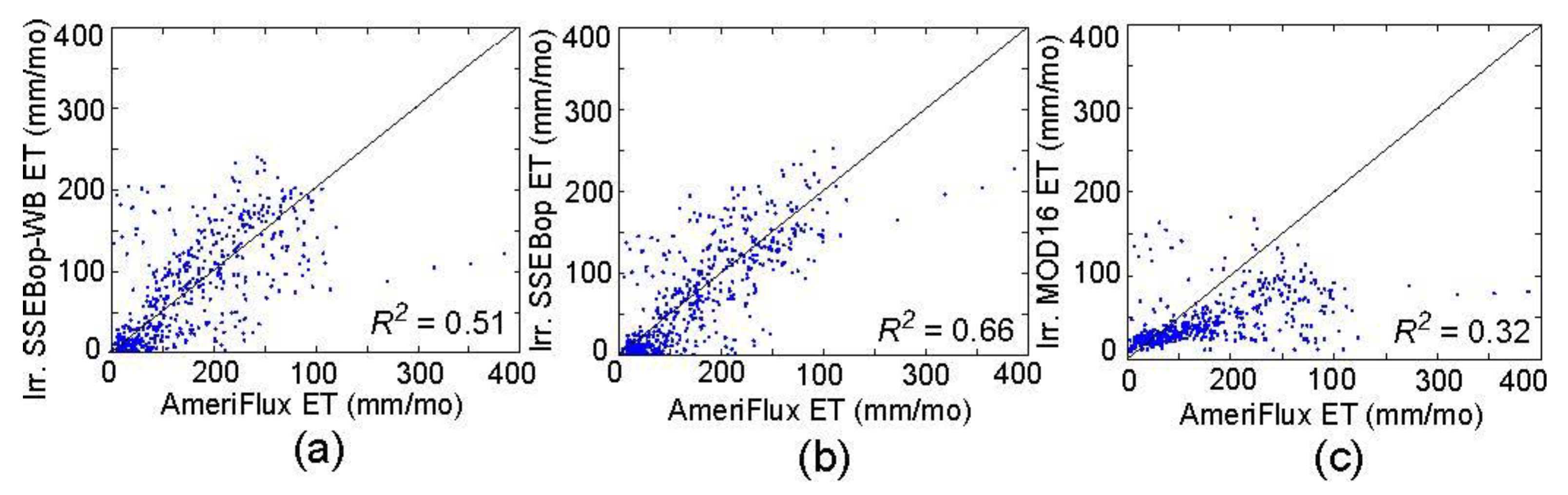

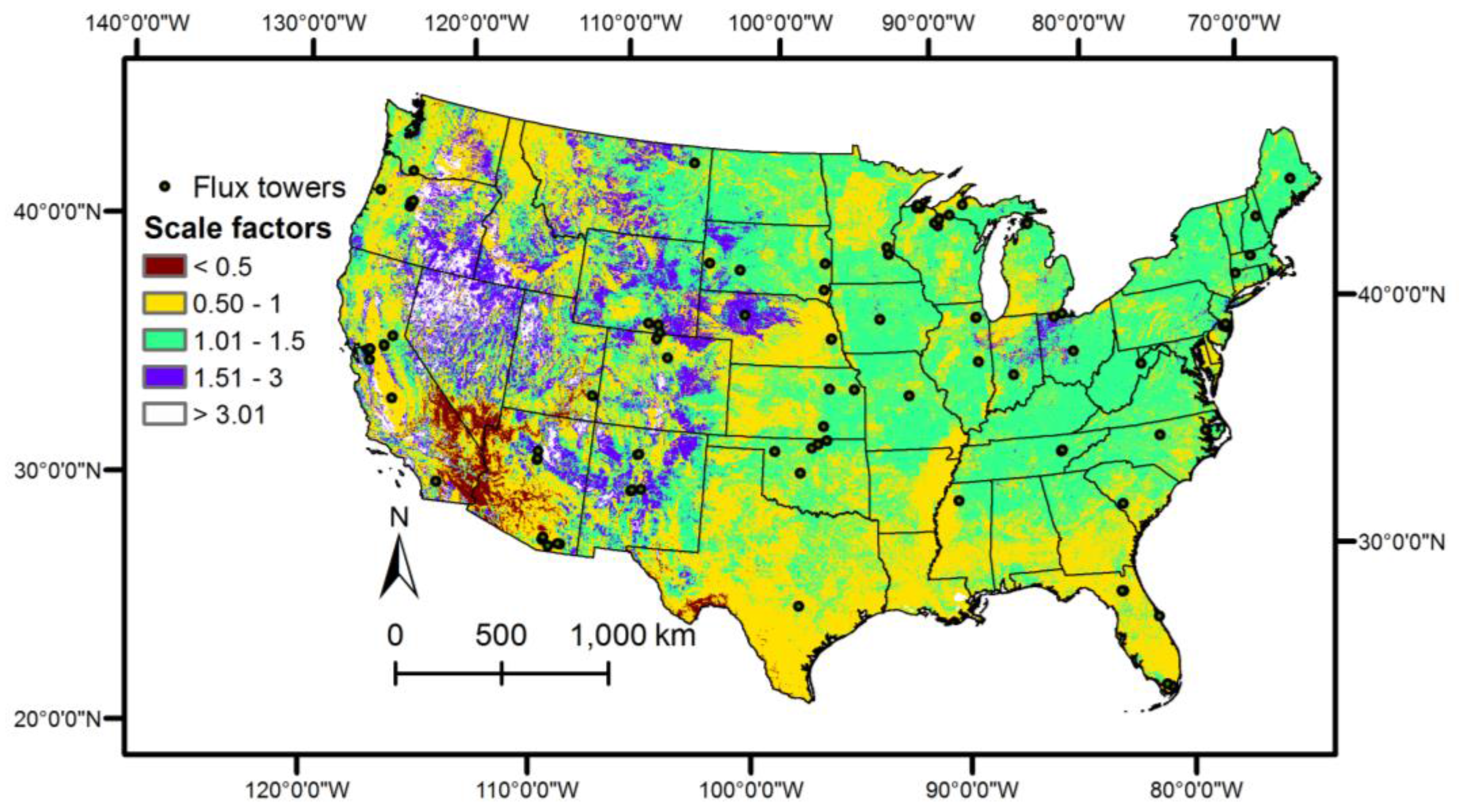
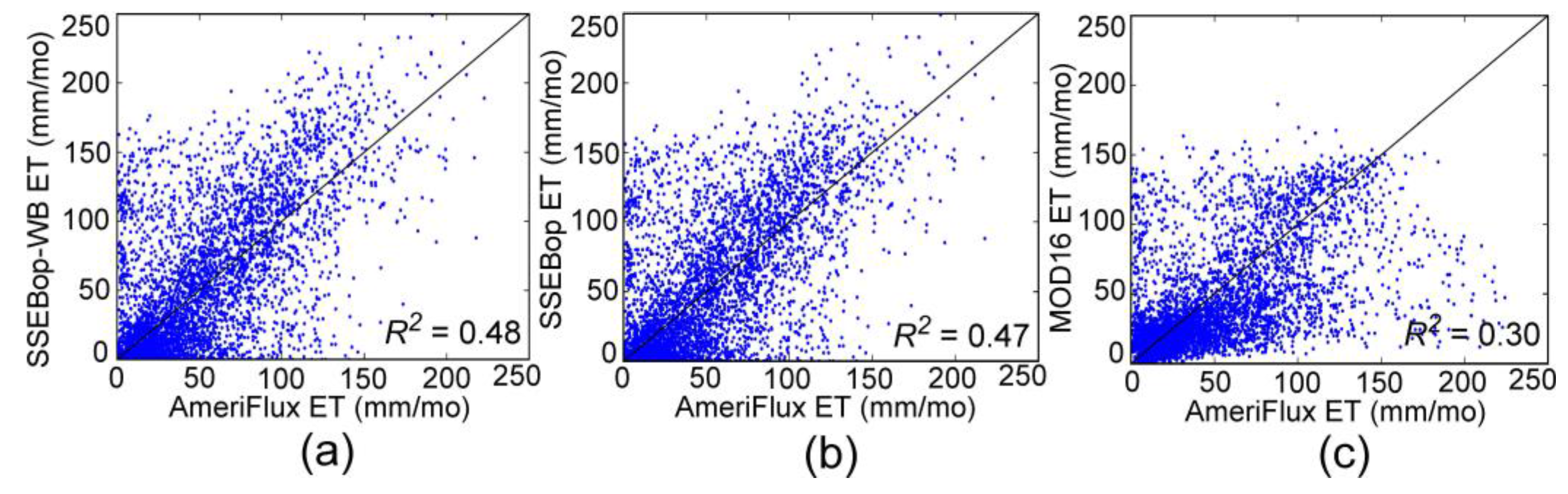

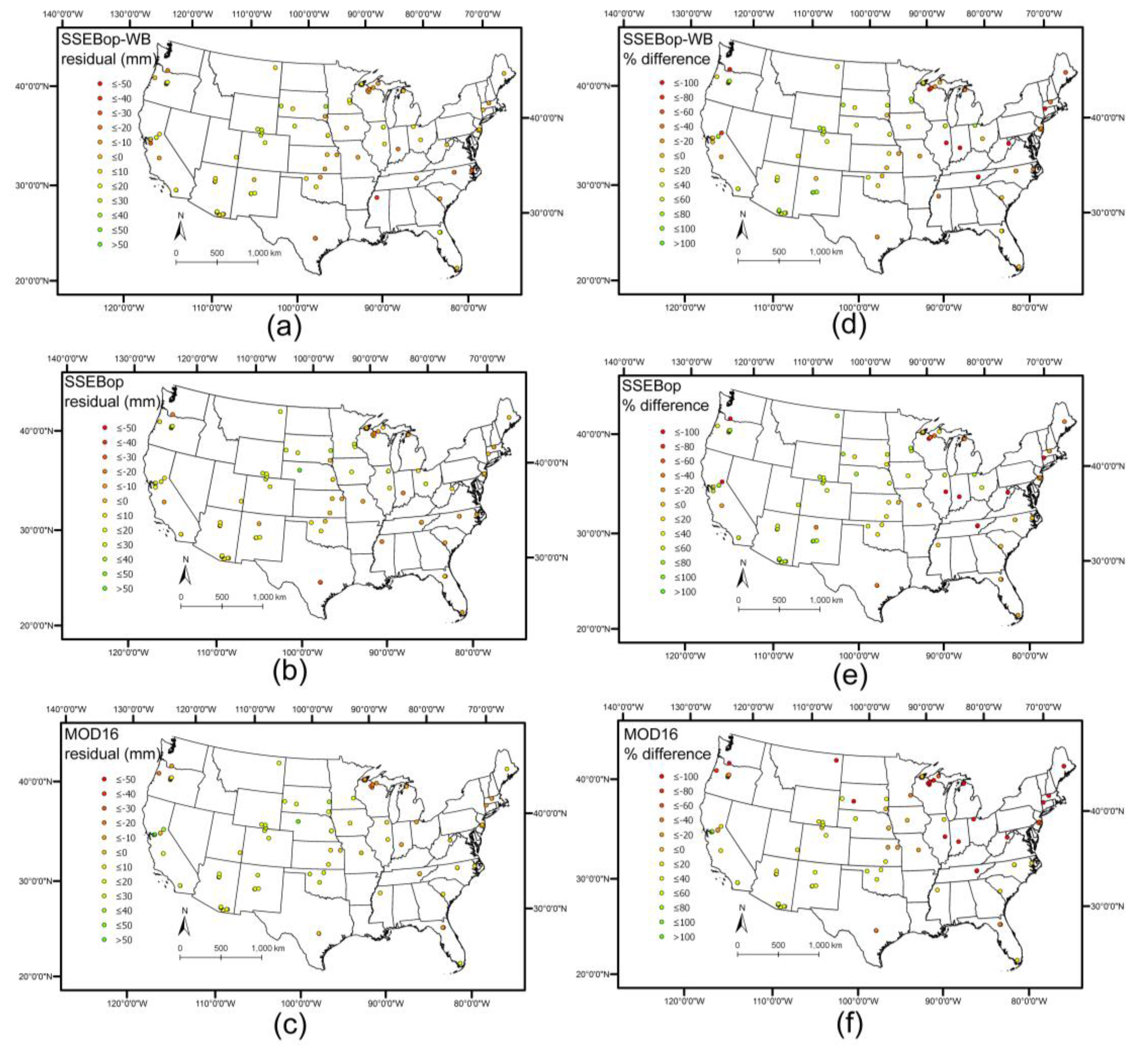
| Time Period | R2, SSEBop-WB | R2, SSEBop | R2, MOD16 | Number of Sites | Months of Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 85 | 395 |
| February | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 77 | 357 |
| March | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 89 | 433 |
| April | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 90 | 424 |
| May | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 89 | 437 |
| June | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 97 | 444 |
| July | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 94 | 448 |
| August | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 91 | 449 |
| September | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 90 | 443 |
| October | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 89 | 459 |
| November | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 84 | 419 |
| December | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 85 | 381 |
| Winter (DJF) | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 92 | 1133 |
| Spring (MAM) | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 99 | 1294 |
| Summer (JJA) | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 100 | 1341 |
| Fall (SON) | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 100 | 1321 |
| All | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 119 | 5089 |
| Product | Metric | Agriculture | Urban | Barren | Forest | Shrubs | Grass | Marsh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSEBop-WB | R2 | 0.513 | 0.834 | 0.426 | 0.322 | 0.55 | 0.584 | 0.505 |
| RMSE (m/mo) | 0.042 | 0.016 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.023 | 0.033 | 0.047 | |
| bias (m/mo) | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.005 | −0.012 | 0.003 | 0.01 | |
| SSEBop | R2 | 0.513 | 0.834 | 0.423 | 0.324 | 0.572 | 0.575 | 0.496 |
| RMSE (m/mo) | 0.039 | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.043 | 0.023 | 0.031 | 0.043 | |
| bias (m/mo) | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.003 | 0.006 | −0.011 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| MOD16 | R2 | 0.155 | 0.81 | 0.51 | 0.328 | 0.398 | 0.62 | 0.235 |
| RMSE (m/mo) | 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.035 | 0.026 | 0.024 | 0.053 | |
| bias (m/mo) | −0.014 | 0.021 | −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.013 | −0.004 | −0.014 |
| Variable | R2, SSEBop-WB | R2, SSEBop | R2, MOD16 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (mm/mo) | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.004 |
| Temp max (°C) | 0.168 | 0.17 | 0.003 |
| Temp min (°C) | 0.163 | 0.172 | 0.002 |
| Temp mean (°C) | 0.169 | 0.174 | 0.002 |
| Temp range (°C) | 0.019 | 0.011 | 0.001 |
| Soil saturated hydraulic conductivity | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.035 |
| Soil available water capacity | 0 | 0 | 0.01 |
| Soil field capacity | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.049 |
| Soil porosity | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.01 |
| Soil thickness | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| Percent impervious | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Site ID | State | Latitude | Longitude | SSEBop-WB Residual (mm/mo) | SSEBop Residual (mm/mo) | MOD16 Residual (mm/mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US-Tw4 | CA | 38.103 | −121.641 | 25 | 25 | 118 |
| US-Myb | CA | 38.0498 | −121.765 | 23 | 23 | 114 |
| US-Tw1 | CA | 38.1074 | −121.647 | −3 | −3 | 154 |
| US-SdH | NE | 42.0693 | −101.407 | 29 | 51 | 61 |
| US-SP1 | FL | 29.7381 | −82.2188 | −29 | −40 | −44 |
| US-Bkg | SD | 44.3453 | −96.8362 | 32 | 32 | 36 |
| US-Wi7 | WI | 46.6491 | −91.0693 | −17 | −37 | −32 |
| US-Wi8 | WI | 46.7223 | −91.2524 | −12 | −27 | −37 |
| US-Los | WI | 46.0827 | −89.9792 | −28 | −21 | −26 |
| US-CPk | WY | 41.068 | −106.119 | 25 | 11 | 35 |
| Site ID | State | Latitude | Longitude | SSEBop-WB Residual Percent Diff. | SSEBop Residual Percent Diff. | MOD16 Residual Percent Diff. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US-Oho | OH | 41.5545 | −83.8438 | 71 | 74 | −164 |
| US-Ses | NM | 34.3349 | −106.744 | 93 | 92 | 70 |
| US-Los | WI | 46.0827 | −89.9792 | −89 | −66 | −80 |
| US-Seg | NM | 34.3623 | −106.702 | 73 | 77 | 58 |
| US-PFa | WI | 45.9459 | −90.2723 | −65 | −59 | −76 |
| US-Wrc | WA | 45.8205 | −121.952 | −83 | −75 | −38 |
| US-SP1 | FL | 29.7381 | −82.2188 | −48 | −66 | −73 |
| US-SRC | AZ | 31.9083 | −110.84 | 67 | 54 | 65 |
| US-Sta | WY | 41.3966 | −106.802 | 69 | 76 | 37 |
| US-LPH | MA | 42.5419 | −72.185 | −58 | −45 | −68 |
© 2017 by the U.S. Geological Survey (the work is in the public domain). Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reitz, M.; Senay, G.B.; Sanford, W.E. Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121181
Reitz M, Senay GB, Sanford WE. Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(12):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121181
Chicago/Turabian StyleReitz, Meredith, Gabriel B. Senay, and Ward E. Sanford. 2017. "Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States" Remote Sensing 9, no. 12: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121181
APA StyleReitz, M., Senay, G. B., & Sanford, W. E. (2017). Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sensing, 9(12), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121181