Abstract
In recent years, very high-rate (10–50 Hz) Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has gained a rapid development and has been widely applied in seismology, natural hazard early warning system and structural monitoring. However, existing studies on stochastic models of GNSS observations are limited to sampling rates not higher than 1 Hz. To support very high-rate GNSS applications, we assess the precisions, cross correlations and time correlations of very high-rate (50 Hz) Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou code and phase observations. The method of least-squares variance component estimation is applied with the geometry-based functional model using the GNSS single-differenced observations. The real-data experimental results show that the precisions are elevation-dependent at satellite elevation angles below 40° and nearly constant at satellite elevation angles above 40°. The precisions of undifferenced observations are presented, exhibiting different patterns for different observation types and satellites, especially for BeiDou because different types of satellites are involved. GPS and BeiDou have comparable precisions at high satellite elevation angles, reaching 0.91–1.26 mm and 0.13–0.17 m for phase and code, respectively, while, at low satellite elevation angles, GPS precisions are generally lower than BeiDou ones. The cross correlation between dual-frequency phase is very significant, with the coefficients of 0.773 and 0.927 for GPS and BeiDou, respectively. The cross correlation between dual-frequency code is much less significant, and no correlation can be found between phase and code. Time correlations exist for GPS/BeiDou phase and code at time lags within 1 s. At very small time lags of 0.02–0.12 s, time correlations of 0.041–0.293 and 0.858–0.945 can be observed for phase and code observations, respectively, indicating that the correlations in time should be taken into account in very high-rate applications.
1. Introduction
The adjustment of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) observations, e.g., in GNSS relative positioning or precise point positioning, is based on functional and stochastic models [1]. The functional model describes the relations between observations and unknown parameters, which is sufficiently known and well-documented in the literature. The stochastic model, represented by the (co)variance matrix, reflects the precisions, cross correlations between observation types and time correlations. Only with a realistic stochastic model can one obtain minimum variance estimators of the parameters in a linear model and arrive at a proper description of the estimator’s quality [2]. Therefore, various studies have been conducted to improve our knowledge of the GNSS stochastic model by estimating unknown components of the (co)variance matrix, which is generally known as variance component estimation (VCE).
Earlier studies of Eueler and Goad [3], Gerdan [4] and Jin and de Jong [5] investigated the elevation dependence of observation variances. Jonkman [6] and Wang et al. [7] stepped further and took cross correlations and time correlations of observations into consideration. Bona [8] examined the precisions, cross correlations and time correlations of Global Positioning System (GPS) phase and code observations using seven types of GPS receivers. Tiberius and Kenselaar [9] presented reasonably simple VCE formulas and analyzed stochastic models of GPS observables on a zero baseline. The elevation dependence of precisions, cross correlations between observation types and time correlations are found to be significant, while the correlation between different channels/satellites turns out to be quite small, indicating that a tracking loop is dedicated to one satellite and operates autonomously. Li et al. [10] assessed the stochastic models of GPS measurements collected by different types of receivers on ultra-short baselines, and identified the existence of elevation dependence of precisions, time correlations and cross correlations between observation types. They pointed out that the stochastic model should be specified for the receiver and observation types. Amiri-Simkooei et al. [11] assessed the stochastics of GPS observables on zero baselines and found significant cross correlations between C1 and P2 code observations and between L1 and L2 phase observations. Li [12] presented a comprehensive study on stochastic modeling of triple-frequency signals of the Chinese BeiDou navigation satellite system with four types of BeiDou receivers. For more studies on GNSS stochastic models, the readers can refer to Teunissen and Amiri-Simkooei [13].
Although GNSS stochastic models have been extensively studied, only GNSS data with low sampling rates, i.e., 1 Hz or lower, have been analyzed up to present. With the recent development of receiver technology, very high-rate (10–50 Hz, or even up to 100 Hz) GNSS data have become readily available, leading to numerous very high-rate GNSS applications, such as very high-rate GNSS seismology [14,15,16,17], earthquake/tsunami early warning [18,19], and structural monitoring [20,21,22]. Very high-rate data may have a different sampling mechanism from low sampling-rate data, e.g., with different parameters of signal processing in receivers (such as phase-locked loop bandwidth) adapted to fast sampling [23], leading to different stochastic models. Therefore, precisions and cross correlations estimated from low sampling-rate data may not hold true for high-rate data, and time correlations within very short intervals (less than 1 s) need to be specially investigated. The lack of realistic stochastic models for very high-rate data may have us misunderstand high-rate solutions and decrease the data value. To fully exploit the benefits brought by very high-rate GNSS data, detailed studies of stochastic models for very high-rate data have become an urgent issue.
Over the past decades, the GPS has made remarkable contributions to scientific applications and engineering services as a standalone global navigation satellite system. In recent years, new constellations have emerged and been put into operation, resulting in significant improvement in terms of satellite visibility, spatial geometry and dilution of precision. The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, independently established and operated by China, began to offer positioning and navigation services in the Asia-Pacific region at the end of 2012. It is expected to provide global services by about 2020 [24]. The rapid development of multi-constellation GNSS can bring about wider and more precise applications, e.g., for positioning, timing and remote sensing [25].
This paper aims to study the stochastic models of very high-rate data from two GNSS constellations, namely GPS and BeiDou. It is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the method of least-squares variance component estimation, describes the functional model used in this study, which is a geometry-based model using GNSS single-differenced observations, and describes the stochastic model, namely the precisions, cross correlations and time correlations of GNSS observations. Section 3 describes the very high-rate (50 Hz) data used in this study along with the VCE procedure, and presents the results of GPS/BeiDou stochastic models. Section 4 gives the conclusions.
2. Methods
2.1. Least-Squares Variance Component Estimation
There exist many methods for VCE, such as the minimum norm quadratic unbiased estimator (MINQUE), the best invariant quadratic unbiased estimator (BIQUE), the least-squares variance component estimator (LS-VCE), the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) and VCE by the Bayesian approach [13,26,27,28,29,30,31]. These methods mainly differ in the estimation principle and distributional assumptions. The LS-VCE method is based on the least-squares and automatically inherits all the well-known properties of least-squares principle. LS-VCE has been widely applied to study the stochastic models of GNSS observations, e.g., by Tiberius and Kenselaar [1], Bona [8], Amiri-Simkooei [2] and Li [12], which has been proven to be a very simple, flexible and attractive VCE method. Therefore, the LS-VCE method is applied in this study.
A linear observation model with unknown (co)variance components can be expressed as
where Equations (1) and (2) are the functional and stochastic model, respectively; is the observation vector; is the unknown parameter vector; is the design matrix relating and ; is the (co)variance matrix of with its known part; is the known cofactor matrix; and is the vector of unknown (co)variance components. The operators and denote the mathematical expectation and dispersion, respectively.
The goal of VCE is to estimate the unknown (co)variance components, namely . The normal equation of LS-VCE is [2]
where is the estimate of . The entries of normal matrix and vector are
where is the projection matrix orthogonal to , is an identity matrix of proper size, is the LS residual vector, and is the trace operator. Then, the least-squares variance component estimator reads
with its (co)variance matrix
The redundancy of the stochastic model is [2]
with the redundancy of the functional model Equation (1). Both Xu et al. [32] and Amiri-Simkooei [2] proved that at most independent (co)variance components are estimable, leading to here.
The entries of normal matrix and vector used to estimate (co)variance components contain the unknown (co)variance matrix , which is dependent on . Therefore, to obtain estimates of co(variance) components, an iteration procedure has to be performed starting from given initial values. Amiri-Simkooei [2] showed that only 2–4 iterations are needed to obtain converged (co)variance components by LS-VCE.
Variance components obtained from VCE may turn out to be negative in practice, which is an undesired result. It may be caused by improperly designed stochastic model, a low redundancy of functional model or badly chosen initial (co)variance components for the iteration [2]. Several techniques have been presented to avoid non-negative variance components, e.g., by incorporating inequality constraints [33] and reparameterizing the model [34] which leads to a nonlinear VCE problem. Besides, we may apply the almost unbiased estimator for the variance component [35], which always results in non-negative variance components. It can be formulated as [2]
where the variables are already defined in above equations. Again, an iterative procedure should be performed to obtain convergent variance components.
2.2. Geometry-Based Functional Model Using GNSS Single-Differenced Observations
The GNSS functional models for VCE can be categorized into two, namely the geometry-free and geometry-based models [11,36,37,38,39]. The geometry-free model parameterizes GNSS observations in terms of satellite-receiver ranges and ambiguities. It is applied by some researchers, e.g., Amiri-Simkooei [2] and Li [12]. It offers some advantages, e.g., easy estimation of ambiguities and independence of satellite orbit information and tropospheric delay. However, it has the drawback that each tracked satellite introduces one unknown satellite-receiver range, resulting in a large number of unknown parameters and a low redundancy, which decreases the number and degrades the precision of estimable (co)variance components. The geometry-based model is the usual mathematical model for geodetic applications, which is parameterized by coordinates and ambiguities with satellite orbit information involved. It is used for VCE by some researchers, e.g., Bona [8] and Li et al. [10], constrained by pre-determined coordinates and double-differenced ambiguities. It has a larger redundancy, or equivalently, stronger model strength than the geometry-free model. Therefore, the geometry-based model is more suitable for VCE than the geometry-free model and is used in our study.
To eliminate external errors of GNSS observations, single-differenced (SD) or double-differenced (DD) observations on a short or zero baseline are usually used in the functional model. Differencing observations on a short baseline cancels atmospheric delay and receiver/satellite clock errors, while differencing observations on a zero baseline can further eliminate antenna phase center and multipath errors, leaving only pure random receiver noises. We choose the SD model in our study because it allows estimation of stochastic properties for individual satellites. The SD geometry-based functional model on a short or zero baseline for code and phase observations can be expressed as [10]
where denotes the between-receiver SD operator; and are the code and phase observations of the satellite on the frequency, respectively; is the SD receiver to satellite range; , , and are the receiver clock errors and hardware delays for code and phase observations respectively; is the SD ambiguity with the corresponding wavelength; and and are noises of code and phase observations, respectively.
With known baseline and satellite coordinates, the SD receiver to satellite range can be accurately determined. To exploit pre-determined DD ambiguities, we rewrite with the SD ambiguity of the satellite and the DD ambiguity referred to the satellite. Meanwhile, we parameterize the equivalent SD receiver clock errors as
for the code and phase observations, respectively. Therefore, by bringing known terms to the left side, we can rewrite Equation (9) as
where and .
Assuming satellites are tracked and frequencies are considered, by stacking the observations of one epoch together we will get the vector/matrix form of the observation equations as
where is the observation vector, , , , ; is the parameter vector, , ; and is the design matrix which can be written as
with the vector whose elements are all equal to 1; and the noise vector is structured analogously to . The single-epoch functional model of Equation (12) can be readily expanded to the multi-epoch one as the following:
with the subscripts indicating the epoch number.
2.3. Stochastic Model of GNSS Code and Phase Observations
To allow estimating more stochastic properties, one may expect to construct a stochastic model with as many unknown components as possible, with the extreme case of a fully unknown stochastic model. Unfortunately, this results in excessive complication and may be faced with the problem of poor estimability or precision. Therefore, we need to simplify the stochastic model with some reasonable assumptions. In the present study, the following three assumptions are made: (1) there is no correlation between different channels/satellites or between different constellations; (2) the correlation between each observation-type pair is the same for all satellites; and (3) the time correlation of each observation type is the same for all satellites. With these assumptions, the following three stochastic properties are to be investigated: (1) precisions of individual satellites for each observation type; (2) cross correlations between different observation types within one constellation; and (3) time correlations for each observation type. The precision is assumed to be constant during a short time interval, say, tens of seconds, since the variations of satellite elevation angles and physical environment surrounding the receivers within this time interval are negligible. In the long run, however, the precision is assumed to change over time. Both cross and time correlations are assumed to be time-invariant.
In the following, the above three stochastic properties will be sequentially introduced. When introducing the stochastic models, the compact form of the (co)variance matrix is firstly given, which is clearly structured and easy to understand. We then present the (co)variance matrix rewritten as Equation (2) in terms of a known part , the co(variance) components and the known cofactor matrices , . This prepares for the implementation of VCE and allows us to obtain co(variance) components directly through Equation (5) or (8). The observation types within one constellation can be listed as the following:
where and represent the types of code and phase observations, respectively, the subscript represents the frequency, and totally frequencies are considered. The number of considered observation types is .
2.3.1. Precisions
The single-epoch stochastic model only considering precisions can be expressed in a compact form as
where represents the variance matrix of ; is the observation vector of the th epoch; the superscript indicates that only the variance components are captured; , with the operator of diagonal or block diagonal matrix; and is the variance of the satellite for the observation type , the observation type in the list of Equation (15). There are totally (or equivalently, ) variance components in .
The compact form of in Equation (16) can be rewritten in the form of Equation (2) as
where is the variance of the element in the observation vector , is the corresponding cofactor matrix with all zero elements except its diagonal element with the value of one.
2.3.2. Cross Correlations
The single-epoch structure of the stochastic model considering precisions as well as cross correlations between observation types can be expressed as
where the superscript indicates that both precisions and cross correlations are captured, is the same as in Equation (16), , is the square root of , and is the cross correlation coefficient between observation types and . Note that is assumed to be time-invariant and therefore not tagged with the epoch. Note that is a symmetric matrix and only the upper-triangle elements are listed in Equation (18), similarly for the following (co)variance and cofactor matrices.
Assuming totally observation types are considered, the number of cross correlation coefficients to be estimated is , which can be listed as
Rewriting Equation (18) in the form of Equation (2), we will obtain
where captures the variance components as defined in Equation (16); is the cross correlation coefficient between the observation-type pair - in the list of Equation (19), with and the and observation types in the list of Equation (15), respectively; and is the corresponding cofactor matrix which has the following form
where is described in Equation (18) and occupies the th to th rows and the th to th columns.
2.3.3. Time Correlations
To introduce the time correlations, we should consider the stochastic model in a multi-epoch case, which can be expressed as
where the superscript indicates that variances, cross correlations and time correlations are considered, is the single-epoch (co)variance matrix of the epoch structured as Equation (18) which captures the precisions and cross correlations, and captures the time correlations between the and epoch, which can be written as
where is the time correlation of time lag for the observation type , and . There are totally time correlation coefficients to be estimated for observations and epochs, which can be listed as
Expressing Equation (22) in the form of Equation (2), we will obtain
where is the term in the list of Equation (24), denoting the time correlation coefficient for the observation type and time lag , and is the corresponding cofactor matrix which can be expressed as
where captures the time correlations between the and epochs, which is described in Equation (23) and occupies the to rows and to columns.
If SD observations are used in the functional model, the estimated stochastic properties are related to the SD observations. With the assumption that observations from two receivers of the same brand and firmware are independent and identically distributed, the stochastic properties of undifferenced observations are obtained using the following relationship:
where , , and , , are the precisions, cross correlations and time correlations for SD and undifferenced observations, respectively.
3. Very-High (50 Hz) Data, VCE Procedure and Results
3.1. Data Description
To study the stochastic model of very high-rate GNSS, 50 Hz static GPS/BeiDou data on a zero baseline was collected on the roof of a 16-story building of Wuhan University. Two Trimble NetR9 receivers of the same firmware were connected to a Trimble 57971.00 antenna (located at 30.5°N, 114.4°E) using a signal splitter. The collected data span 24 h from 14:00 31 October 2017 to 14:00 1 November 2017 (GPS time), with the satellite skyplots shown in Figure 1. Tracked observation types and satellite types are listed in Table 1. Dual-frequency GPS/BeiDou code and phase observations were recorded. For each constellation, four observation types were recorded, namely L1/L2 code and phase observations for GPS and B1/B2 code and phase observations for BeiDou. The L1/L2 code observations for GPS in this paper refer in particular to C1 and P2 observations. All GPS satellites are MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) ones, while BeiDou has three types of satellites, namely GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit), IGSO (Inclined Geosynchronous Satellite Orbit) and MEO satellites. Our collected 24-h data cover all available GPS/BeiDou MEO satellites (except G04), BeiDou GEO satellites and BeiDou IGSO satellites with full revolution periods.
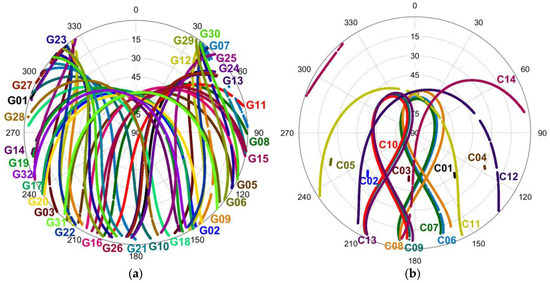
Figure 1.
Satellite skyplots from 14:00 31 October 2017 to 14:00 1 November 2017 (GPS time): (a) GPS; and (b) BeiDou.

Table 1.
Tracked dual-frequency GPS/BeiDou observation types and satellite types.
3.2. VCE Procedure
The raw GPS/BeiDou code and phase observations were preprocessed to generate SD observations as in Equation (11) with a satellite elevation cut-off angle of 10°. The SD receiver-to-satellite ranges and DD ambiguities needed to generate SD observations were obtained through a conventional relative positioning process. The generated SD observations were then used to construct the function model of Equation (12) or (14) and estimate the (co)variance components.
The stochastic models of the two constellations, GPS and BeiDou, are estimated independently. For each constellation, the stochastic model is estimated in a group-wise way for computation efficiency. For time-invariant (co)variance components, namely the cross and time correlations, the final estimates are obtained by averaging the groupwise estimates [2].
Simultaneous estimation of all (co)variance components is time consuming and often leads to unreliable estimates because of a large number of unknowns and high-dimensional matrices involved. This is particularly the case when dealing with very high-rate GNSS data. Therefore, we adopt the three-step estimation procedure proposed by Li [12]. In this procedure, the precisions are estimated in the first step, and the cross correlations and time correlations are estimated in the second and third steps, respectively, with estimates from the previous step held fixed.
With the 50 Hz GPS/BeiDou data at hand, precisions, and cross and time correlations are estimated group by group, using Equations (5) and (8), following the three-step procedure described above. Since we use SD observations on a zero baseline, which can eliminate the satellite clock/orbit errors, the atmospheric errors, the phase center offsets/variations and the multipath errors, what we analyze are pure random receiver noises. The stochastic properties of SD observations are obtained, and then transformed to those of undifferenced observations. The precisions and cross/time correlations of undifferenced observations are presented in the following.
3.3. Results and Analysis
3.3.1. Precisions of GNSS Observations
When estimating the precisions, the 50 Hz data are divided into 30-s groups, each group containing 1500 epochs. After excluding those groups with insufficient data due to obstacles in the signal path, there are totally 2735 groups in our study. Within each group, the precisions are assumed to be constant.
The precisions of GPS/BeiDou are estimated using Equation (8) in an iterative way. To see the convergence performance, the GPS precision estimates with respect to the iteration number within one group is shown in Figure 2. Totally 10 iterations were performed, and the precisions are vertically shifted by their estimates at the 10th iteration for clarity. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the convergence is very fast, and the precision estimates are almost invariant after the 4th iteration. The phase precisions converge to ~1 mm, and the code precisions converge to 0.12–0.20 m, dependent on the observation types and satellites. It is noticeable that even estimates of the 1st iteration are very close to the convergent values. The differences of the 1st and 10th iterations are less than 0.04 mm and 0.007 m for phase and code precisions, respectively. In this study, the precisions are estimated by performing four iterations.

Figure 2.
GPS precision estimates with respect to the iteration number within one group. The horizontal axis represents the iteration number, and the vertical axis represents the precision estimates for GPS L1/L2 phase and code observations, which are shifted vertically by the convergent values at the 10th iteration for clarity. The convergent values are shown in the legend for each satellite.
The GPS/BeiDou phase and code precisions of all groups are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. They are shown with respect to the satellite elevation angles to demonstrate their elevation-dependent patterns. They are also differently colored to demonstrate the satellite-dependent behavior.
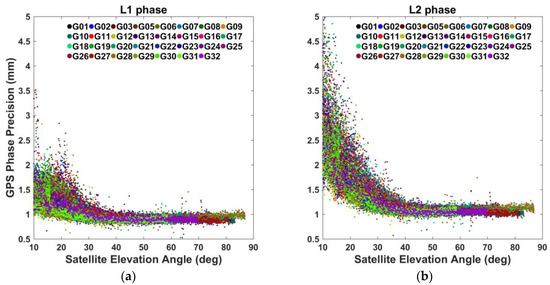
Figure 3.
The precisions of: (a) GPS L1 phase observations; and (b) GPS L2 phase observations.
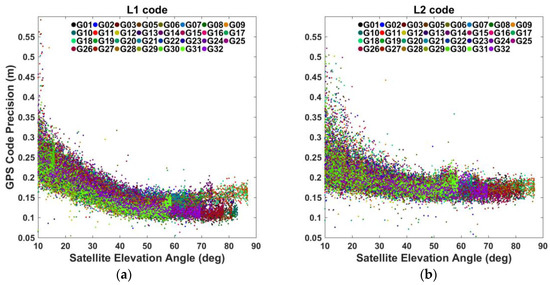
Figure 4.
The precisions of: (a) GPS L1 code observations; and (b) GPS L2 code observations.
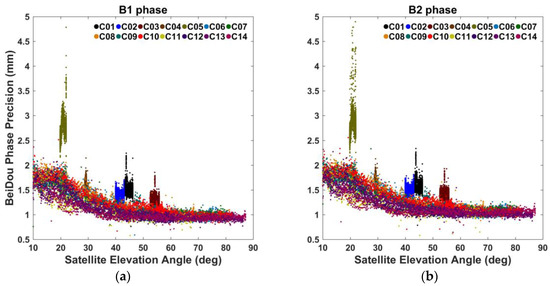
Figure 5.
The precisions of: (a) BeiDou B1 phase observations; and (b) BeiDou B2 phase observations.

Figure 6.
The precisions of: (a) BeiDou B1 code observations; and (b) BeiDou B2 code observations.
As shown in Figure 3, at satellite elevation angles lower than 40°, the GPS phase precisions exhibit a significant downward variability as the satellite elevation angle increases. At satellite elevation angles above 40°, however, they are flat and have an almost constant value of ~1 mm (see the mean precision at satellite elevation angles above 40° in Table 2). These results suggest modeling the phase precisions with a two-piece function. The first piece describes the low-elevation precisions with an elevation-dependent function, e.g., the ones proposed by Eueler and Goad [3] or Bradford et al. [40] or the one used by PANDA software developed by Wuhan University [15]. The second piece represents high-elevation precisions with a constant value. The corner satellite elevation angle of the two-piece function is empirically chosen, e.g., 40° in our case. The mean precisions for all GPS satellites at satellite elevation angles above 40° are 0.91 and 1.07 mm for L1 and L2 phase, respectively (see Table 2). When comparing the L1 and L2 phase precisions, we find that L2 precisions are generally lower than L1 precisions. At satellite elevation angles above 30°, the L2 precisions are only slightly lower than L1 precisions, while, at satellite elevation angles below 30°, the L2 precisions are significantly lower than L1 precisions. The difference between L1 and L2 phase precisions is reasonable because of different wavelengths of L1 and L2 phase, which are about 0.19 m and 0.24 m, respectively. When we look into the precisions of individual satellites, we find that at satellite elevation angles above 40°, the precisions of different satellites are almost the same, while at satellite elevation angles below 40°, they exhibit very different patterns. These results indicate that, when modeling the precisions, the parameters should be individually considered for each frequency and each satellite. This has also been identified and further investigated by Li [12].

Table 2.
GPS/BeiDou mean precisions (mm) at satellite elevation angles above 40°.
The GPS code precisions are shown in Figure 4. Just as the GPS phase precisions, they exhibit elevation dependence at low (<40°) satellite elevation angles, dropping from ~0.6 m to less than 0.2 m as the satellite elevation angle increases. The high-elevation (>40°) precisions are almost a constant around 0.13–0.17 m (see Table 2). When comparing L1 and L2 code precisions, we find that L2 code precisions are generally lower than L1 ones. The phenomenon that GPS C1 code is more precise than P1 code is possibly because of phase smoothing of C1 code. If we look into individual satellites, we find that GPS code precisions have similar variabilities with respect to the satellite elevation angles, but with a bit different absolute values.
The BeiDou phase precisions are shown in Figure 5 for three different satellite types, namely GEO (C01–C05), IGSO (C06–C10) and MEO (C11–C14) satellites. The elevation angles of GEO satellites vary less than 3° in Figure 5. Among the 5 GEO satellites, C03 and C01 have the highest satellite elevation angles, about 54° and 45° for C03 and C01, respectively. Their phase precisions are relatively stable, around 1.3 mm for C03 and 1.5 mm for C01. C02 and C04 have lower satellite elevation angles (about 41° and 29°), with precisions around 1.4 and 1.6 mm, respectively. C05 has the lowest satellite elevation angles (about 21°), whose precisions are the lowest and most dispersive with the values of 2–5 mm. The IGSO and MEO satellites have elevation-dependent phase precisions, which are higher than GEO at overlapping satellite elevation angles. If the satellite elevation angles are above 40°, the phase precisions of IGSO and MEO satellites are well within 0.8–1.3 mm. The mean precisions for all BeiDou satellites at satellite elevation angles above 40° are 1.16 and 1.26 mm for B1 and B2 phase, respectively (see Table 2). When comparing B1 and B2 phase precisions, we find that B2 phase precisions are slightly lower than B1 ones, which is possibly caused by their difference of wavelengths. Compared with GPS phase precisions, we find that, at satellite elevation angles above 40°, BeiDou has comparable precisions with GPS, while at satellite elevation angles below 40°, BeiDou has much higher precisions than GPS.
The BeiDou code precisions are shown in Figure 6. The precisions of GEO satellites overlap very well with those of IGSO and MEO satellites. At satellite elevation angles below 40°, they exhibit a slow drop as the satellite elevation angle increases, while at satellite elevation angles above 40°, they become rather stable around 0.14 m for both B1 and B2 frequencies (see Table 2). The B1 code precisions are slightly lower than B2 ones at satellite elevation angles lower than 40°. Compared with GPS, BeiDou has comparable code precisions at satellite elevation angles above 40°, and slightly higher code precisions at satellite elevation angles below 40°.
3.3.2. Cross Correlations
Just as the precisions, the cross correlations are estimated in every 30-s group using 50 Hz data. After excluding those groups with insufficient data or bad estimates, there are totally 2652 and 2481 groups of cross correlation estimates for GPS and BeiDou, respectively. Figure 7 shows the GPS cross correlations of one group within 10 iterations. For clarity, they are vertically shifted by the estimates of the 10th iteration shown in the legend. The convergence is so fast that after only two iterations the estimates have become very stable already. Even after only one iteration the estimates are already very close to the final convergent values, with differences less than 0.0006. In this study, the cross correlations are estimated by performing only one iteration. We have calculated the precisions of our cross-correlation estimates, which are generally higher than 0.007 within a single group. When averaged over groups, the precisions can be further improved by with the number of groups.

Figure 7.
GPS cross correlation coefficients between observation types with respect to the iteration number within one group, which contains 30-s 50 Hz data. The horizontal axis represents the iteration number, and the vertical axis represents the cross-correlation coefficients, which are shifted vertically by the convergent values at the 10th iteration for clarity. The convergent values are shown in the legend for each observation type pair.
The GPS/BeiDou cross correlations of all groups are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. For each observation type pair, the cross correlations are relatively stable among all groups, indicating that the cross correlations are stable over time. Therefore, we calculate the mean values for each observation type pair, regard them as the final estimates and list them in Table 3.

Figure 8.
GPS groupwise cross correlations between observation types for 2652 groups, each containing 30-s 50 Hz data.

Figure 9.
BeiDou groupwise cross correlations between observation types for 2481 groups, each containing 30-s 50 Hz data.

Table 3.
Mean cross correlations of GPS and BeiDou.
In Table 3, we find that the cross correlation between GPS L1 and L2 phase observations is very significant with the coefficient to be 0.773. This is consistent with the results of Amiri-Simkooei et al. [11], who observed significant correlations (0.72 and 0.83 for two datasets) between GPS L1 and L2 phase observations from the Trimble R7 receivers. The L1 and L2 code observations are also correlated but less significant, with the coefficient of 0.141. The other four observation type pairs for GPS, namely L1 phase/L1 code, L1 phase/L2 code, L2 phase/L1 code and L2 phase/L2 code, have much smaller cross correlation coefficients (less than 0.01), indicating that code and phase observations are essentially not correlated. The BeiDou cross correlation between B1 and B2 phase observations is 0.927, which is very close to 1, indicating that B1 and B2 phase observations have a nearly linear relationship. The B1 and B2 code observations are much less correlated with the coefficient of 0.111. The BeiDou code and phase observations can be regarded as not correlated at all, since the coefficients are less than 0.03.
3.3.3. Time Correlations
The number of time-correlation coefficients to be estimated depends largely on the epoch numbers. For example, if we want to estimate time correlations at time lags of 0.02–30 s using 50 Hz data, at least 30-s 50 Hz data are needed, and then there are totally epochs. With observation types, the number of time-correlation coefficients to be estimated will be . Such a large number of unknowns will make the estimation process too time-consuming to be acceptable. In order improve the efficiency to some extent, we present the following double sampling-rate procedure to estimate the time correlations: (1) using 50 Hz data to calculate time correlations of the time lags of 0.02–5 s in every 5-s group; and (2) decimating 50 Hz data into 1 Hz ones, and using the 1 Hz data to calculate the time correlations of the time lags of 1–180 s in every 3-min group. In this way we can obtain the time correlations covering a broad range of time lags (0.02–180 s), and meanwhile improve the efficiency within each group since the epoch number is only 250 and 180 for 5-s 50 Hz data and 3-min 1 Hz data, respectively. To further reduce the computation burden, we only use the first 5-s 50 Hz data in every 3 min to calculate the time correlations at time lags 0.02–5 s. Besides, only the first 4-h data of our collected 24-h data are used to estimate the time correlations. Excluding those groups with insufficient data or bad estimates, there are totally 65 groups for both 50 Hz and 1 Hz data in this study. The two sets of results from this procedure have overlapping time lags, i.e., 1–5 s, which can be used to cross check each other.
When estimating the time correlations, our experience indicates that the second iteration is far more consuming than the first iteration and usually produces undesirable estimates. We infer that the divergence may be caused by the ill-posedness of the model. Therefore, only one iteration is performed to produce the time correlation estimates, which is also the practice of Li [12]. To justify the reliability of group-wise time correlations with only one iteration, we have shown in Figure 10 the single-group precisions of time-correlation estimates at time lags of 0.02–5 s derived from 50 Hz GPS data. As the time lag gets larger, the precision gets poorer because fewer data are involved in estimating them. The code time correlations are less precise than the phase ones because the code observations are less precise than the phase ones. At time lags within 1 s, the precisions of phase are higher than 0.008, and the precisions of code are higher than 0.02. When averaged over groups, the precisions can be further improved by with the number of groups. The reliability of time-correlation estimates can also be validated by the consistence of estimates calculated from different groups presented in the following.
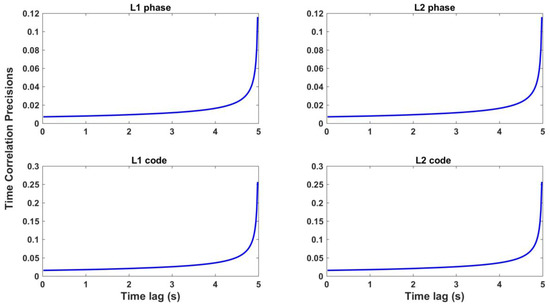
Figure 10.
Precisions of GPS time correlations of time lags 0.02–5 s within one group and one iteration.
Following the above procedure, we obtain 65-group estimates of time correlations, at time lags 0.02–5 s derived from 50 Hz data and time lags of 1–180 s derived from 1 Hz data. All-group GPS time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s derived from 50 Hz data are shown in Figure 11. Time correlations of different groups are well consistent with one another. As the time lag gets larger, the time correlations of different groups get more dispersive. The code time correlations from different groups are more dispersive than the phase ones. These are consistent with the precision results of time-correlation estimates presented in Figure 10.
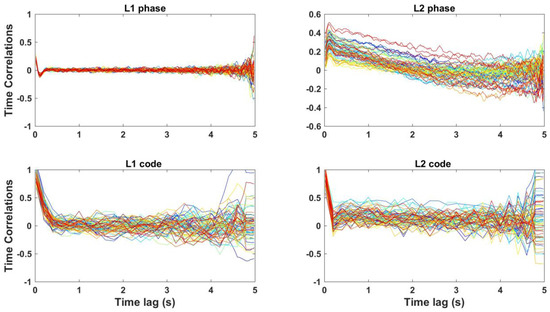
Figure 11.
GPS group-wise time correlations of time lags 0.02–5 s calculating from 50 Hz data. Totally, 65 groups are considered, with each group containing 5-s 50 Hz data. These groups are colored differently to be distinguished.
The average GPS time correlations over all groups are regarded as the final estimates, which are shown in Figure 12. The main panels show the time correlations at time lags of 0.02–180 s, while the insets show the time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s in order to get a close look at the time correlations at very small time lags. Time correlations calculating using 50 Hz and 1 Hz data cover the time lags of 0.02–5 s and 1–180 s and are represented by red and blue lines, respectively. In the insets of Figure 12, we find that these two sets of time correlations agree very well with each other at the common time lags of 1–5 s. At very small time lags of 0.02–0.2 s, the time correlations are significant for all observation types, especially for the code observations. The maximum time correlations for L1 and L2 phase are 0.175 at the time lag of 0.02 s, 0.293 at the time lag of 0.12 s, respectively, and the maximum time correlations for L1 and L2 code are 0.882 and 0.858, respectively, at the time lag of 0.02 s. At the time lag of 1 s, time correlations decrease a lot, reaching 0.000–0.141 and 0.014–0.177 for phase and code, respectively. The maximum values along with the corresponding time lags, values at the time lag of 1 s, and the stable values at large time lags (mean values over time lags 50–150 s) are listed in Table 4. The variabilities of time correlations as the time lag increases for the four observations types differ significantly, which is probably caused by different filtering strategies for different observation types in the receivers. For L1 phase, the time correlation drops sharply from 0.175 at the time lag of 0.02 s to a negative value −0.089 at the time lag of 0.12 s. Then it rapidly rises and reaches nearly zero at the time lag of 0.26 s. After that, it keeps close to zero, indicating no time correlations at time lags larger than 0.26 s. For L2 phase, the time correlation undergoes a transient rise first, to 0.293 at the time lag of 0.12 s, then decreases slowly, reaching zero at the time lag of 2.5 s, then continues to decrease until the time lag of 4 s, reaching −0.057, and then it begins to rise and reaches zero at the time lag of 8 s. After that, it is stable around zero, indicating that no time correlation can be found at time lags larger than 8 s. Note that the time correlations of both L1 and L2 phase have a turning point at the time lag of 0.12 s. The time correlations of L1/L2 code are very significant at the first a few time lags, and decrease as the time lag gets larger, although a transient increase can be found at time lags of 0.2–0.4 s for L2 code. They reach 0.014 at the time lag of 1 s for L1 code, and 0.007 at the time lag of 50 s for L2 code. After that, they are stable around zero values, indicating that time correlations do not remain at time lags larger than 1 and 50 s for L1 and L2 code, respectively.

Figure 12.
GPS time correlations at time lags 0.02–180 s, averaged over all groups. The 50 Hz data generate time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s, which are represented with the red lines. Decimated 1 Hz data generate time correlations at time lags of 1–180 s, which are represented with the blue lines. Time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s are also shown in the insets.

Table 4.
Maximum time correlations over all time lags, time correlations at the time lag of 1 s, and mean time correlations over time lags 50–150 s.
The BeiDou time correlations are shown in Figure 13 and partly listed in Table 4. Time correlations can be found for BeiDou phase at time lags smaller than 1 s, especially at 0.02–0.3 s, with the maximum coefficients of 0.051 at the time lag of 0.02 s and 0.041 at the time lag of 0.12 s, for B1 and B2 phase, respectively. They are much less significant than those of GPS. Again, the turning point at the time lag of 0.12 s can be observed, for both B1 and B2 phase. At time lags larger than 1 s, time correlations are stable around zero, indicating no time correlations after that. Time correlations of BeiDou code are more significant than those of GPS at the first a few time lags, with the maximum coefficients of 0.945 and 0.904 for B1 and B2 code, respectively, at the time lag of 0.02 s. As the time lag increases, they slowly decrease and reach nearly zero values at the time lags of 1 and 8 s for B1 and B2 code, respectively, indicating that BeiDou code observations are essentially not time correlated at time lags larger than 1 and 8 s for B1 and B2 frequencies, respectively.

Figure 13.
BeiDou time correlations at time lags 0.02–180 s, averaged over all groups. The 50 Hz data generate time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s, which are represented with the red lines. Decimated 1 Hz data generate time correlations at time lags of 1–180 s, which are represented with the blue lines. Time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s are also shown in the insets.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we assess the stochastic models of very high-rate (50 Hz) GPS/BeiDou phase and code observations. Since previous studies on stochastic models of GNSS code and phase observations are limited to sampling rates not higher than 1 Hz, this study provides significant results of very high-rate (50 Hz) data, especially the time correlations at very small time lags 0.02–1 s. This helps to enrich our knowledge about very high-rate GNSS data and support very high-rate GNSS applications.
The geometry-based functional model is adopted, which has a larger redundancy and is more suitable for VCE than the geometry-free model. We use the between-receiver SD observations rather than DD observations in the functional model because in this way we can estimate the stochastic properties of individual satellites. Three stochastic properties are considered: the precisions of individual satellites, cross correlations between observation types and time correlations of each observation type. The (co)variance matrices considering these properties are elaborately constructed following the three assumptions (1) there is no correlation between different channels/satellites or between different constellations; (2) the correlation between each observation-type pair is the same for all satellites; and (3) the time correlation of each observation type is the same for all satellites. The method of least-squares variance component estimation is applied to estimate the precisions, cross and time correlations in a step-wise way. Estimating the time correlations is time-consuming because of too many unknowns involved. To improve the efficiency, we present the double sampling-rate procedure to estimate the time correlations, namely using 50 Hz data to calculate time correlations at time lags of 0.02–5 s, and using decimated 1 Hz data to calculate time correlations at time lags of 1–180 s. The 50 Hz GPS/BeiDou phase and code observations spanning 24 h collected on a zero baseline are analyzed in this study.
When estimating precisions and cross correlations iteratively, the convergence is so fast that estimates after 2–4 iterations are almost invariant. Even the estimates of the first iteration are already very close to the final convergent values. In our study, precisions and cross correlations are estimated by performing four iterations and one iteration, respectively. However, the time correlations hardly achieve convergence through iterations, which may be caused by the ill-posedness of the model. Therefore, the time correlations are obtained by performing only one iteration.
We have presented the precisions of cross and time correlation estimates. Within one group, the precisions of cross correlation estimates are generally higher than 0.007. The precisions of time correlation estimates depend on the time lags, getting lower as the time lag increases. At the time lag of 1 s, the precisions of phase time correlations are generally higher than 0.008, and the precisions of code time correlations are generally higher than 0.02 within one group. When the estimates are averaged over all groups, the precisions can be improved by with the number of groups. This precision level, together with the consistence of estimates from different groups, has validated the reliability of our cross and time correlation estimates.
The precisions of undifferenced GNSS observations are shown to be elevation-dependent at satellite elevation angles below 40°. Above 40°, they are relatively stable and can be assumed as constants. Therefore, the precisions can be modeled using a two-piece function. The first piece describes the low-elevation precisions with an elevation-dependent function, while the second piece represents high-elevation precisions with a constant value. Note, however, the precision patterns differ for different observation types and satellites, especially for BeiDou because different types of satellites are involved. Therefore, when modeling the precisions the parameters should be individually considered for each observation type and each satellite. GPS and BeiDou have comparable precisions at high satellite elevation angles, reaching 0.91–1.26 mm and 0.13–0.17 m for phase and code, respectively, while at low satellite elevation angles, GPS precisions are generally lower than BeiDou ones. At satellite elevation angles above 30°, the GPS L2 phase precisions are only slightly lower than L1 phase precisions, while at satellite elevation angles below 30°, the GPS L2 phase precisions are significantly lower than L1 phase precisions. For BeiDou, the B2 phase precisions are slightly lower than B1 ones over all satellite elevation angles. The B1 code precisions are slightly lower than B2 ones at satellite elevation angles lower than 40°.
Cross correlations are very significant between GPS L1 and L2 phase and between BeiDou B1 and B2 phase, reaching 0.773 and 0.927, respectively. Cross correlations between GPS L1 and L2 code and between BeiDou B1 and B2 code are less significant, reaching 0.141 and 0.111, respectively. Cross correlations of other observation type pairs, mixed with phase and code, are less than 0.03, indicating that phase and code observations are essentially not correlated.
Time correlations are significant at very small time lags of 0.02–0.12 s, especially for code observations. The maximum time correlations reach 0.175–0.293 and 0.858–0.882 for GPS phase and code, respectively, and reach 0.041–0.051 and 0.904–0.945 for BeiDou phase and code, respectively. The turning point of time correlations at the time lag of 0.12 s has been observed for both GPS and BeiDou phase observations. At the time lag of 1 s, the time correlations decrease a lot and reach 0.000–0.141 and 0.014–0.177 for phase and code, respectively. All of them reach zero values and show no time correlations at all starting from some larger time lags, which are dependent on the constellations and observation types.
In high-precision GNSS positioning applications, the satellite elevation angle-dependent and satellite-specific precisions should be applied to weight the observations. Cross correlations between phase observations on different frequencies and between code observations on different frequencies are significant and must be taken into account. In traditional applications with data sampling rate equal to or less than 1 Hz, time correlations of phase can be safely neglected. However, in very high-rate applications, time correlations of phase at very small time lags must be taken into account in order to achieve the most precise positioning.
More comprehensive researches are needed by including more receiver types, more observation types, e.g., triple-frequency observations, and more constellations, e.g., Russia’s GLONASS and Europe’s Galileo. Data collected on a short baseline will be analyzed in the future to investigate the stochastic models of external errors such as multipath. We also need to study how to further increase the computation efficiency of variance component estimation when large amounts of data and large numbers of unknown (co)variance components are involved. Besides, the impact analysis of an improved stochastic model of very high-rate GNSS observations on estimating coordinates and zenith tropospheric delays also needs to be conducted in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41231174).
Author Contributions
Yuanming Shu conceived and performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. Jingnan Liu and Rongxin Fang reviewed the paper and helped with the writing of the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tiberius, C.C.J.M.; Kenselaar, F. Estimation of the stochastic model for GPS code and phase observables. Surv. Rev. 2000, 35, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A. Least-Squares Variance Component Estimation: Theory and GPS Applications; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eueler, H.-J.; Goad, C.C. On optimal filtering of GPS dual frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull. Geod. 1991, 65, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdan, G.P. A comparison of four methods of weighting double difference pseudorange measurements. Aust. Surv. 1995, 40, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.X.; de Jong, C.D. Relationship between satellite elevation and precision of GPS code observations. J. Navig. 1996, 49, 253–265. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman, N. Integer GPS-Ambiguity Estimation without the Receiver-Satellite Geometry; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Stewart, M.P.; Tsakiri, M. Stochastic modeling for static GPS baseline data processing. J. Surv. Eng. 1998, 124, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, P. Precision, cross correlation, and time correlation of GPS phase and code observations. GPS Solut. 2000, 4, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberius, C.; Kenselaar, F. Variance component estimation and precise GPS positioning: Case study. J. Surv. Eng. 2003, 129, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Xu, P. Assessment of stochastic models for GPS measurements with different types of receivers. Chi. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Simkooei, A.; Teunissen, P.; Tiberius, C. Application of least-squares variance component estimation to GPS observables. J. Surv. Eng. 2009, 135, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Stochastic modeling of triple-frequency BeiDou signals: Estimation, assessment and impact analysis. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.R. Least-squares variance component estimation. J. Geod. 2007, 82, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, A.; Marzario, M.; Cirella, A.; Piatanesi, A.; Rovelli, A.; Di Alessandro, C.; D′Anastasio, E.; D′Agostino, N.; Giuliani, R.; Mattone, M. Very high rate (10 Hz) GPS seismology for moderate-magnitude earthquakes: The case of the Mw 6.3 L′Aquila (central Italy) event. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B02305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shi, C.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yanagidani, T. High-rate precise point positioning (PPP) to measure seismic wave motions: An experimental comparison of GPS PPP with inertial measurement units. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. High-rate (1-Hz and 50-Hz) GPS seismology: Application to the 2013 Mw 6.6 Lushan earthquake. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xu, P.; Niu, X.; Liu, J. Error analysis of high-rate GNSS precise point positioning for seismic wave measurement. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2691–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, G.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A. Real-time GPS seismology with a stand-alone receiver: A preliminary feasibility demonstration. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Xie, X.; Fang, R.; Su, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Real-time capture of seismic waves using high-rate multi-GNSS observations: Application to the 2015 Mw 7.8 Nepal earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Dodson, A.H.; Roberts, G.W. Detecting bridge dynamics with GPS and triaxial accelerometers. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.-H.; Li, H.-N.; Gu, M. Experimental assessment of high-rate GPS receivers for deformation monitoring of bridge. Mearsurement 2013, 46, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. Dynamic deflections of a stiff footbridge using 100-Hz GNSS and accelerometer data. J. Surv. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschas, F.; Stiros, S. PLL bandwidth and noise in 100 Hz GPS measurements. GPS Solut. 2014, 19, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, L.Z.; Zhao, Q.L.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Li, X.T. Precise point positioning with the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2014, 14, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Ren, X.D.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Precise positioning with current multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.R. Estimation of variance and covariance components—MINQUE theory. J. Multivar. Anal. 1971, 1, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K. Bayesian inference for variance components. Manuscr. Geod. 1987, 12, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z. A generalization theory of estimation of variance-covariance components. Manuscr. Geod. 1992, 17, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z. A universal formula of maximum likelihood estimation of variance-covariance components. J. Geod. 1996, 70, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shen, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Liu, Y. Variance component estimation in linear inverse ill-posed models. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satirapod, C.; Wang, J.; Rizos, C. A simplified MINQUE procedure for the estimation of variance-covariance components of GPS observables. Surv. Rev. 2013, 36, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Fukuda, Y. Estimability analysis of variance and covariance components. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.L.; Hanson, R.J. Solving Least Squares Problems; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P. Towards a Least-Squares Framework for Adjusting and Testing of Both Functional and Stochastic Models; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, W. Ein verfahren zur schätzung von varianz-und kovarianzkomponenten. Allgemeine Vermessungsnachrichten 1979, 86, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part I: The baseline precision. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part II: The ambiguity precision and correlation. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part III: The geometry of the ambiguity search space. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part IV: Precision versus reliability. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, P.W.; Spilker, J.; Enge, P. Global Positioning System: Theory and Applications; American Institute of Astronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 163–164. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).