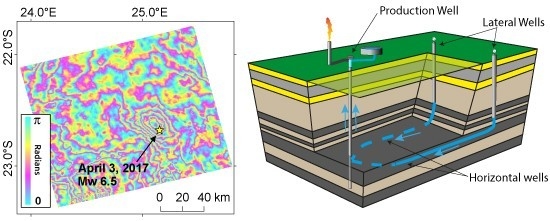
Did Anthropogenic Activities Trigger the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Botswana Earthquake?
Abstract
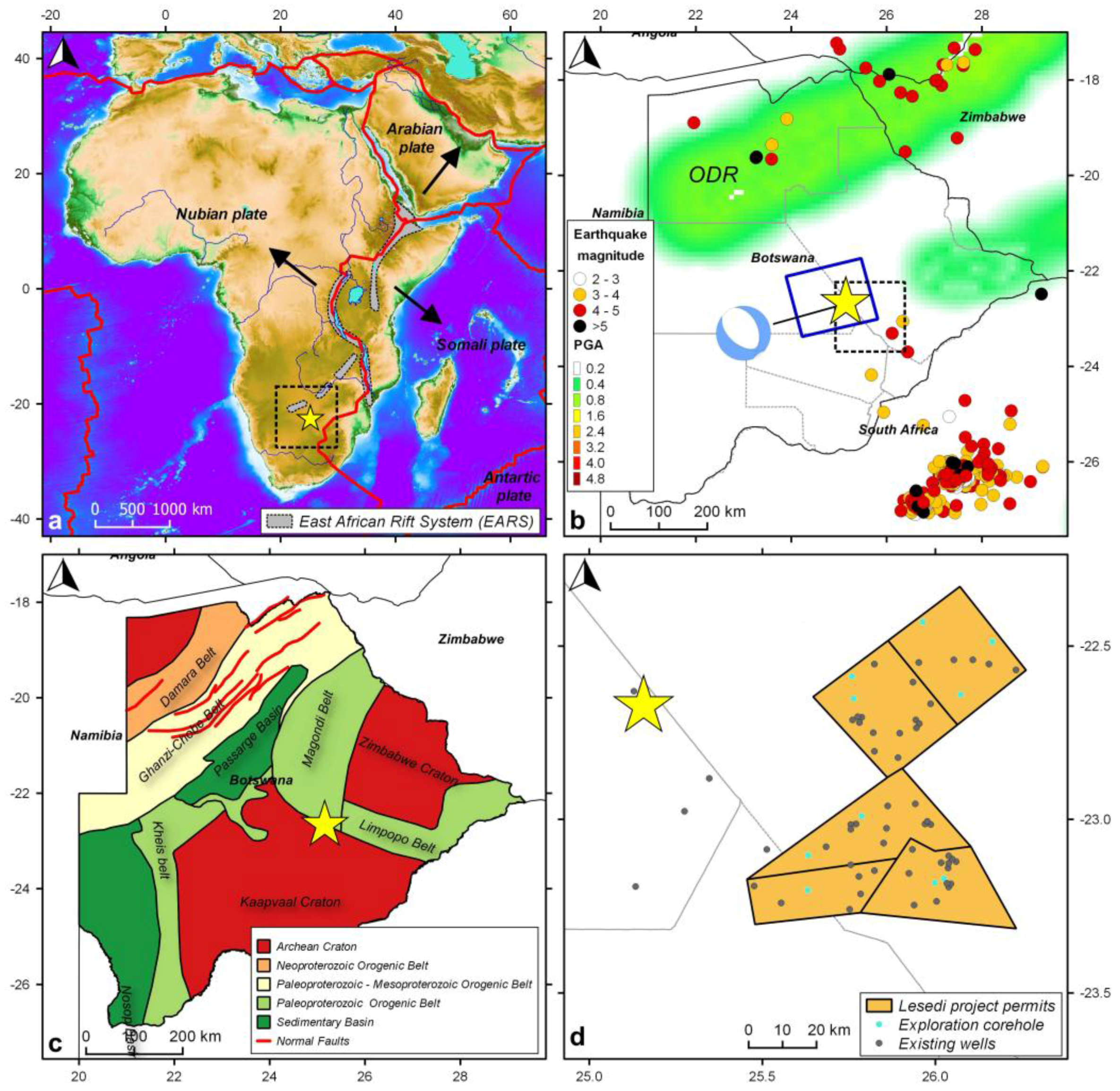
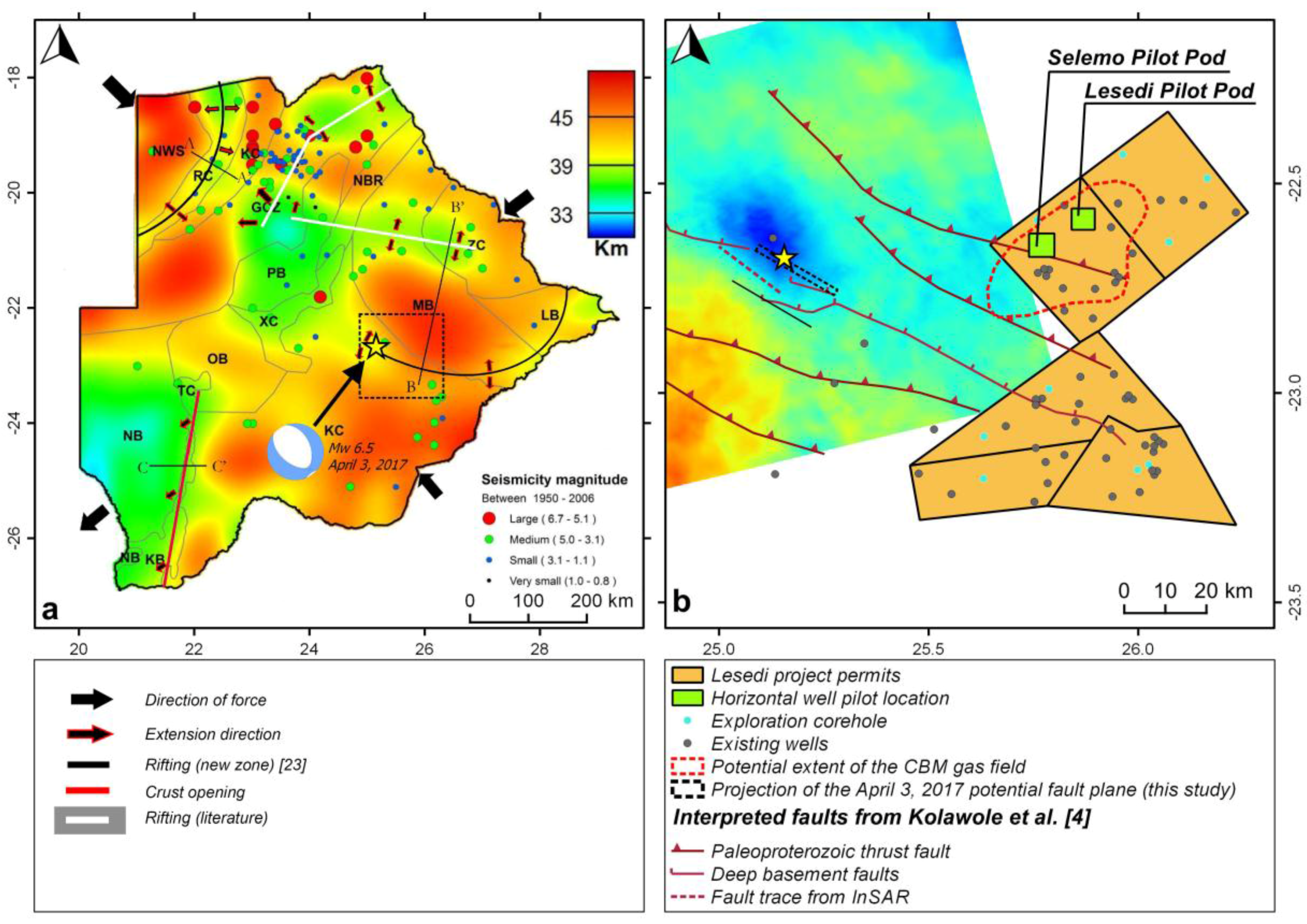
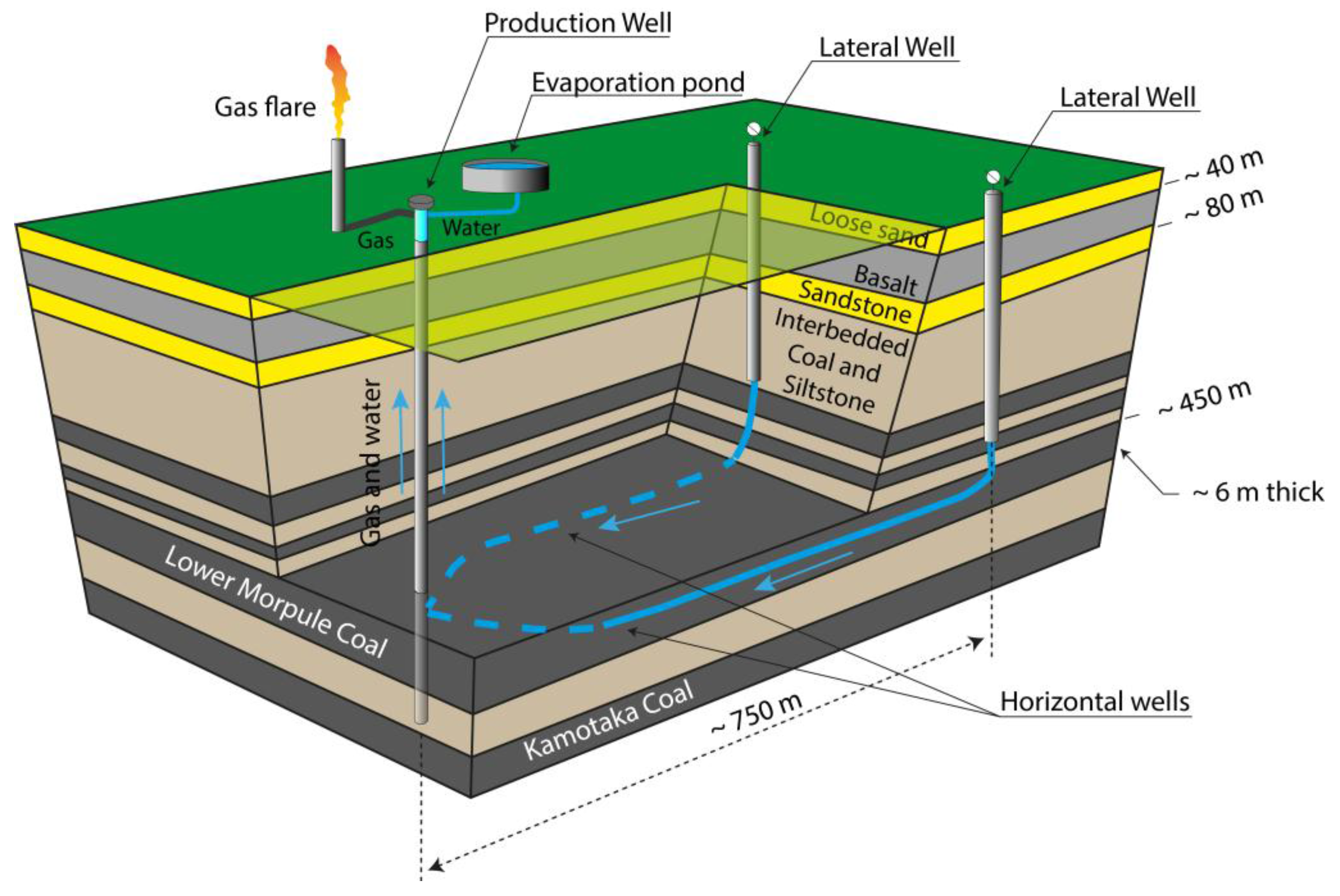
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
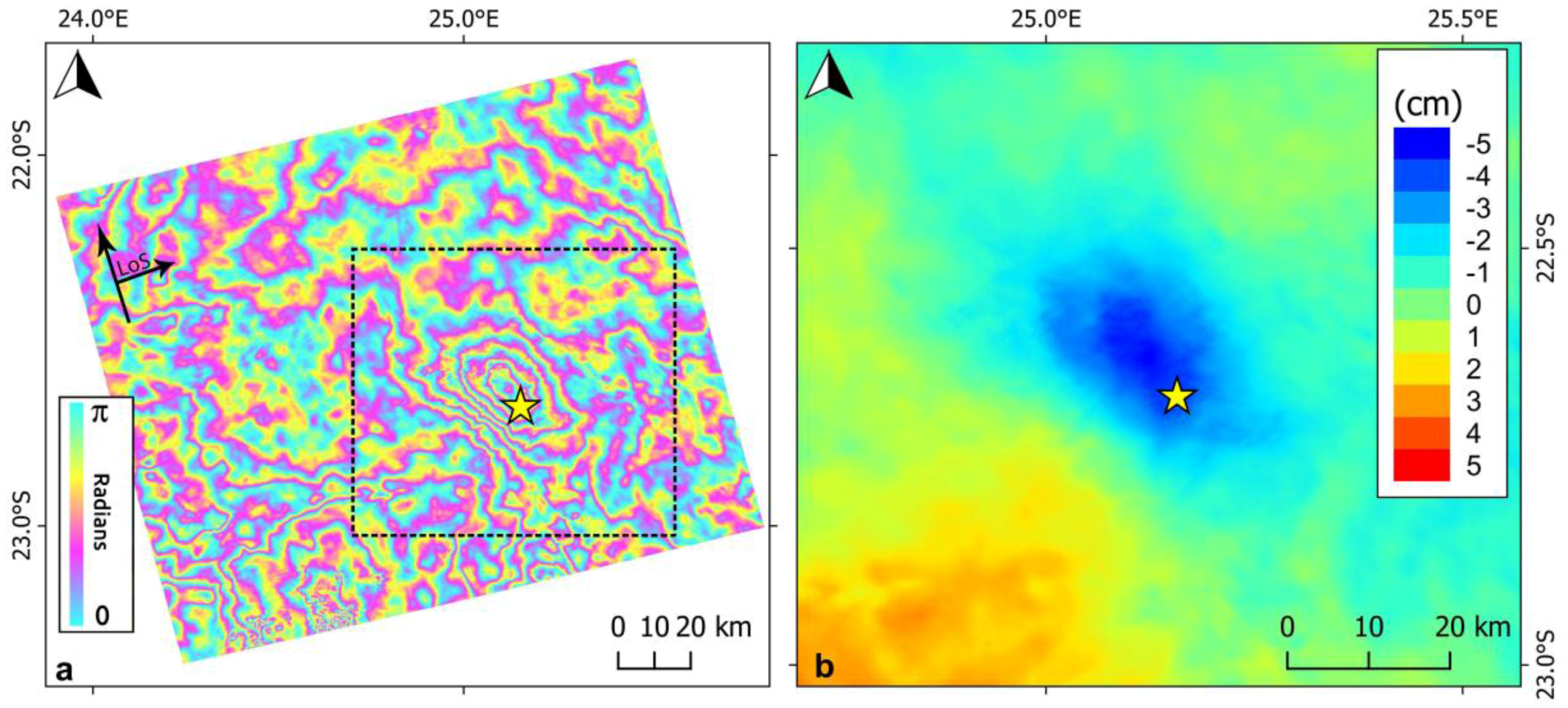
2.1. SAR Data
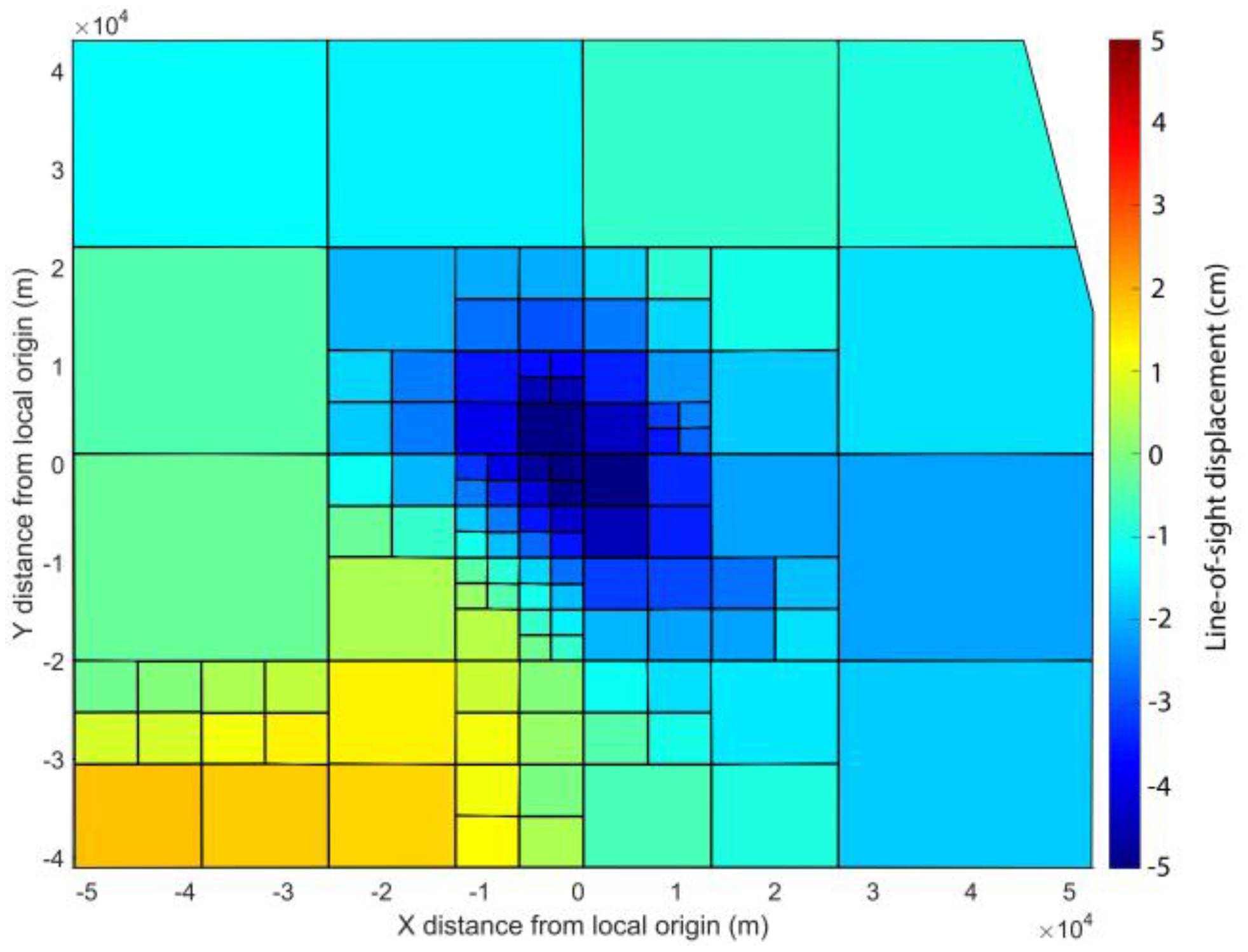
2.2. Data Modelling
3. Results
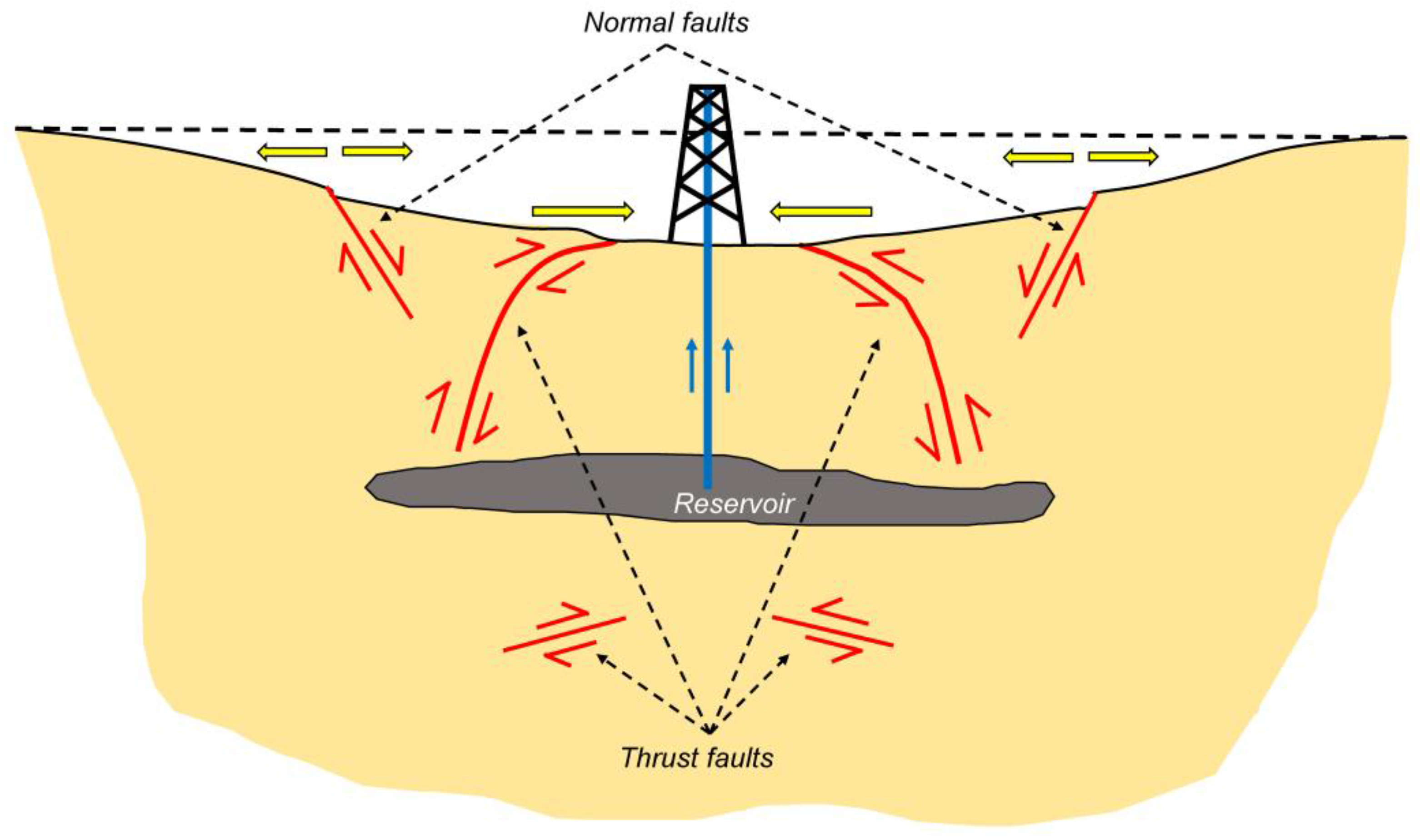
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, R.; Kwadiba, M.; King, J.; Moidaki, M. A history of Botswana’s seismic network. Botsw. Notes Rec. 2012, 44, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koothupile, B. Botswana Quake: At Least 36 Students “Affected”, Structural “Defects” Reported. Available online: http://www.news24.com/Africa/News/botswana-quake-at-least-36-students-injured-structural-defects-reported-20170404 (accessed on 3 May 2017).
- Vallée, M.; Charléty, J.; Ferreira, A.M.G.; Delouis, B.; Vergoz, J. SCARDEC: A new technique for the rapid determination of seismic moment magnitude, focal mechanism and source time functions for large earthquakes using body-wave deconvolution. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 184, 338–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, F.; Atekwana, E.A.; Malloy, S.; Stamps, D.S.; Grandin, R.; Abdelsalam, M.G.; Leseane, K.; Shemang, E.M. Aeromagnetic, gravity, and Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (DInSAR) analyses reveal the causative fault of the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Moiyabana, Botswana Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8837–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardini, D.; Grünthal, G.; Shedlock, K.M.; Zhang, P. The GSHAP Global Seismic Hazard Map. In International Handbook of Earthquake & Engineering Seismology; Lee, W., Kanamori, H., Jennings, P., Kisslinger, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1233–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, C.V. Rifting in the Kalahari? Nature 1972, 237, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.P. The earthquake potential of the New Madrid seismic zone. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakun, W.H.; Hopper, M.G. Magnitudes and locations of the 1811–1812 New Madrid, Missouri, and the 1886 Charleston, South Carolina, earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2004, 94, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Spence, R.J.S.; Going, C.; Markus, M. Using high-resolution satellite images for post-earthquake building damage assessment: A study following the 26 January 2001 Gujarat earthquake. Earthq. Spectra 2004, 20, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.K.; Kundu, B.; Gahalaut, K.; Catherine, J.; Gahalaut, V.K.; Ambikapthy, A.; Naidu, M.S. Coseismic offsets due to the 11 April 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes (Mw 8.6 and 8.2) derived from GPS measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3389–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, P. An updated digital model of plate boundaries. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leseane, K.; Atekwana, E.A.; Mickus, K.L.; Abdelsalam, M.G.; Shemang, E.M.; Atekwana, E.A. Thermal perturbations beneath the incipient Okavango Rift Zone, northwest Botswana. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keranen, K.M.; Savage, H.M.; Abers, G.A.; Cochran, E.S.; Humphreys, E.; Karlstrom, K.; Ekström, G.; Carlson, C.; Dixon, T.; Gurnis, M.; et al. Potentially induced earthquakes in Oklahoma, USA: Links between wastewater injection and the 2011 Mw 5.7 earthquake sequence. Geology 2013, 41, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, W.L. Injection-induced earthquakes. Science 2013, 341, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbee, J. Did Fracking in Botswana Cause Johannesburg to Tremble? Available online: https://www.dailymaverick.co.za/article/2017-04-04-did-fracking-in-botswana-cause-johannesburg-to-tremble/#.WSWA-2jyi72 (accessed on 5 May 2017).
- Tlou Energy Ltd. Tlou Energy Limited Annual Report (2010–2016). Available online: http://tlouenergy.com/reports (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Stramondo, S.; Trasatti, E.; Albano, M.; Moro, M.; Chini, M.; Bignami, C.; Polcari, M.; Saroli, M. Uncovering deformation processes from surface displacements. J. Geodyn. 2016, 102, 58–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.C.; Tateishi, R.; Hara, K.; Nguyen, H.T.; Gharechelou, S.; Nguyen, L.V. Earthquake Damage Visualization (EDV) technique for the rapid detection of earthquake-induced damages using SAR data. Sensors 2017, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Q. Investigating the ground deformation and source model of the Yangbajing geothermal field in Tibet, China with the WLS InSAR technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C. Gamma SAR processor and interferometry software. In ERS Symposium on Space at the Service of Our Environment; ESA Publications Division: Florence, Italy, 1997; pp. 1687–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of real-time mode high-resolution water vapor fields from GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnardi, M.; Hooper, A. Bayesian inversion of surface deformation data for rapid estimate of source parameters: A proposed approach. 2017; (in prep.). [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, W.K. Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 1970, 57, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosegaard, K.; Tarantola, A. Monte Carlo sampling of solutions to inverse problems. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1995, 100, 12431–12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, A.; Pietrzak, J.; Simons, W.; Cui, H.; Riva, R.; Naeije, M.; Terwisscha van Scheltinga, A.; Schrama, E.; Stelling, G.; Socquet, A. Importance of horizontal seafloor motion on tsunami height for the 2011 Mw = 9.0 Tohoku-Oki earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 361, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-02858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Atzori, S.; Antonioli, A. Optimal fault resolution in geodetic inversion of coseismic data. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 185, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisenga, C. Understanding the Earth Structure Underneath Botswana: The Tectonic Model and Its Relationship to the Basement and Crustal Thickness. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Albano, M.; Barba, S.; Tarabusi, G.; Saroli, M.; Stramondo, S. Discriminating between natural and anthropogenic earthquakes: Insights from the Emilia Romagna (Italy) 2012 seismic sequence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.; Foulger, G.; Bindley, A.; Styles, P. Induced seismicity and hydraulic fracturing for the recovery of hydrocarbons. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 45, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarr, A.; Simpson, D.; Seeber, L. Case histories of induced and triggered seismicity. Int. Geophys. 2002, 81, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckale, J. Moderate-to-large seismicity induced by hydrocarbon production. Lead. Edge 2010, 29, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarr, A.; Bekins, B.; Burkardt, N.; Dewey, J.; Earle, P.; Ellsworth, W.; Ge, S.; Hickman, S.; Holland, A.; Majer, E.; et al. Coping with earthquakes induced by fluid injection. Science 2015, 347, 830–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulargia, F.; Bizzarri, A. Anthropogenic Triggering of Large Earthquakes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Talwani, P. Reservoir-induced seismicity in the Danjiangkou Reservoir: A quantitative analysis. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 185, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P. Earthquakes triggered by fluid extraction. Geology 1989, 17, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, V.; Mustaqeem, A.; Bell, S. A model for induced seismicity caused by hydrocarbon production in the Western Canada sedimentary basin. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1999, 36, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P. Stress and subsidence resulting from subsurface fluid withdrawal in the epicentral region of the 1983 Coalinga Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 6801–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odonne, F.; Ménard, I.; Massonnat, G.J.; Rolando, J.P. Abnormal reverse faulting above a depleting reservoir. Geology 1999, 27, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
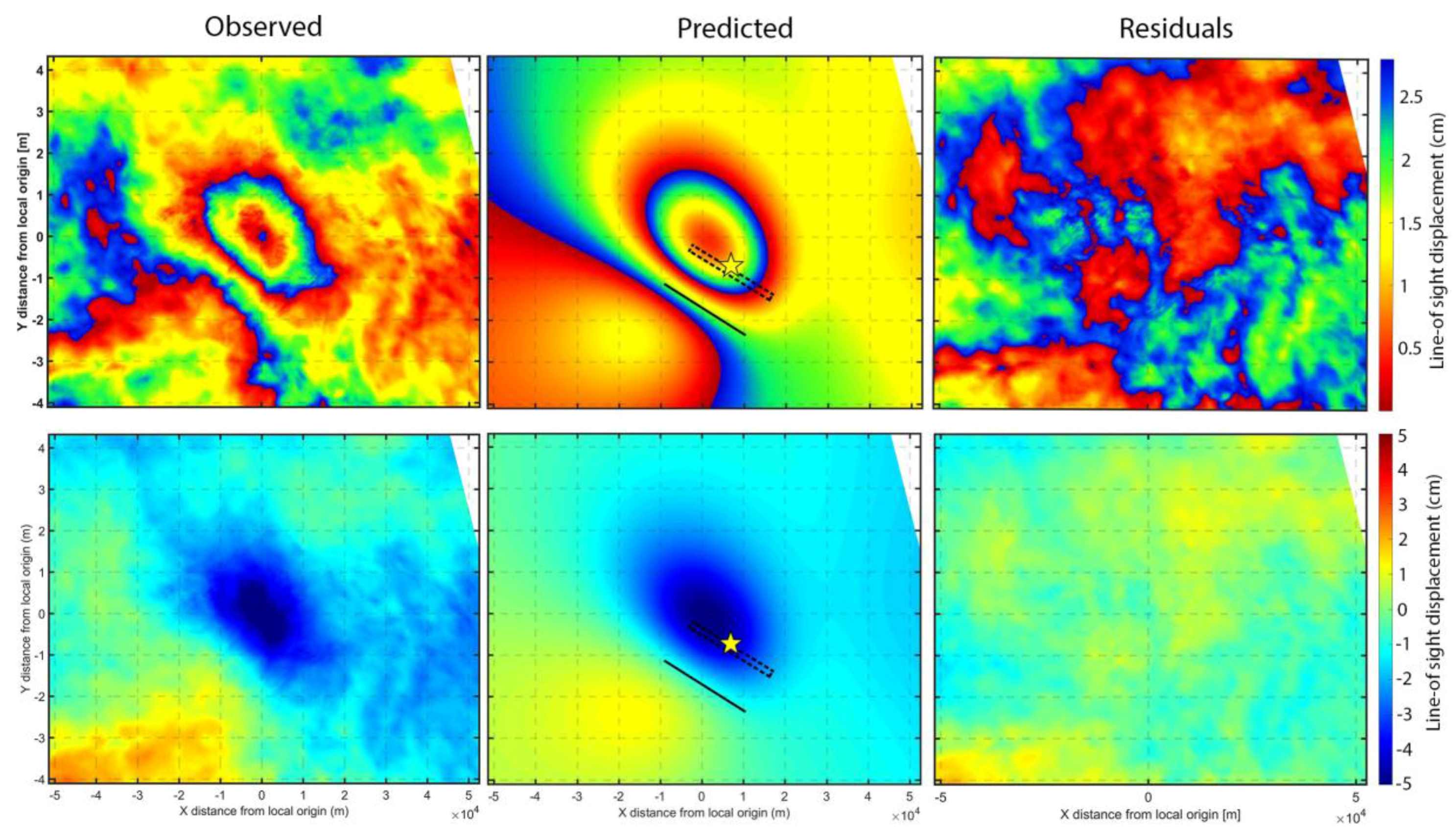
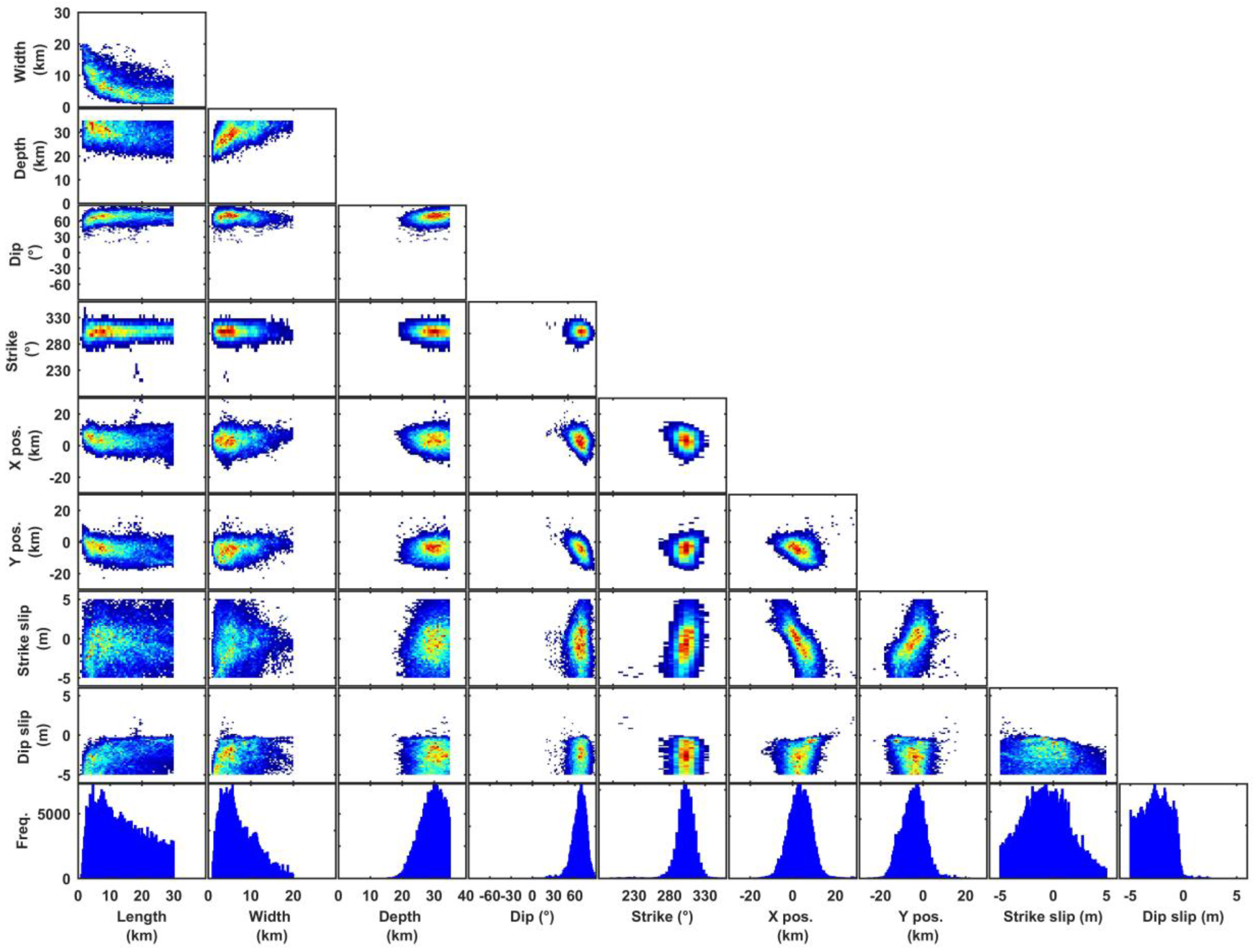
| Parameter | Length (km) | Width (km) | Depth (km) | Dip (°) | Strike (°) | X-pos. 1 (km) | Y-pos. 1 (km) | Strike slip (m) | Dip slip (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | 26 | 12 | 20 | 53 | 320 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Lower bound | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | −90 | 180 | −30 | −30 | −5 | −5 |
| Upper bound | 30 | 20 | 35 | 90 | 360 | 30 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
| Optimal | 21 | 3.6 | 25 | 65 | 304 | 6.4 | −8.1 | −1.97 | −1.85 |
| Parameter | Optimal | Mean | Median | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (km) | 21.1 | 13.6 | 12.5 | 2.3 | - | 28.9 |
| Width (km) | 3.6 | 7.2 | 6.2 | 1.6 | - | 17.1 |
| Depth (km) | 25.2 | 29.1 | 29.5 | 21.4 | - | 34.6 |
| Dip (°) | 65.5 | 66.4 | 67.4 | 44.6 | - | 82.2 |
| Strike (°) | 304.4 | 302.4 | 303 | 277.5 | - | 324.5 |
| X-pos. (km) | 6.4 | 3.3 | 3.4 | −7 | - | 12.9 |
| Y-pos. (km) | −8.1 | −4.7 | −4.6 | −14.7 | - | 5.5 |
| Strike slip (m) | −1.97 | −0.65 | −0.71 | −4.6 | - | 3.9 |
| Dip slip (m) | −1.85 | −2.62 | −2.6 | −4.87 | - | −0.45 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albano, M.; Polcari, M.; Bignami, C.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M.; Stramondo, S. Did Anthropogenic Activities Trigger the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Botswana Earthquake? Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101028
Albano M, Polcari M, Bignami C, Moro M, Saroli M, Stramondo S. Did Anthropogenic Activities Trigger the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Botswana Earthquake? Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101028
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbano, Matteo, Marco Polcari, Christian Bignami, Marco Moro, Michele Saroli, and Salvatore Stramondo. 2017. "Did Anthropogenic Activities Trigger the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Botswana Earthquake?" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101028
APA StyleAlbano, M., Polcari, M., Bignami, C., Moro, M., Saroli, M., & Stramondo, S. (2017). Did Anthropogenic Activities Trigger the 3 April 2017 Mw 6.5 Botswana Earthquake? Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101028