Application of Remote Sensing Data to Constrain Operational Rainfall-Driven Flood Forecasting: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
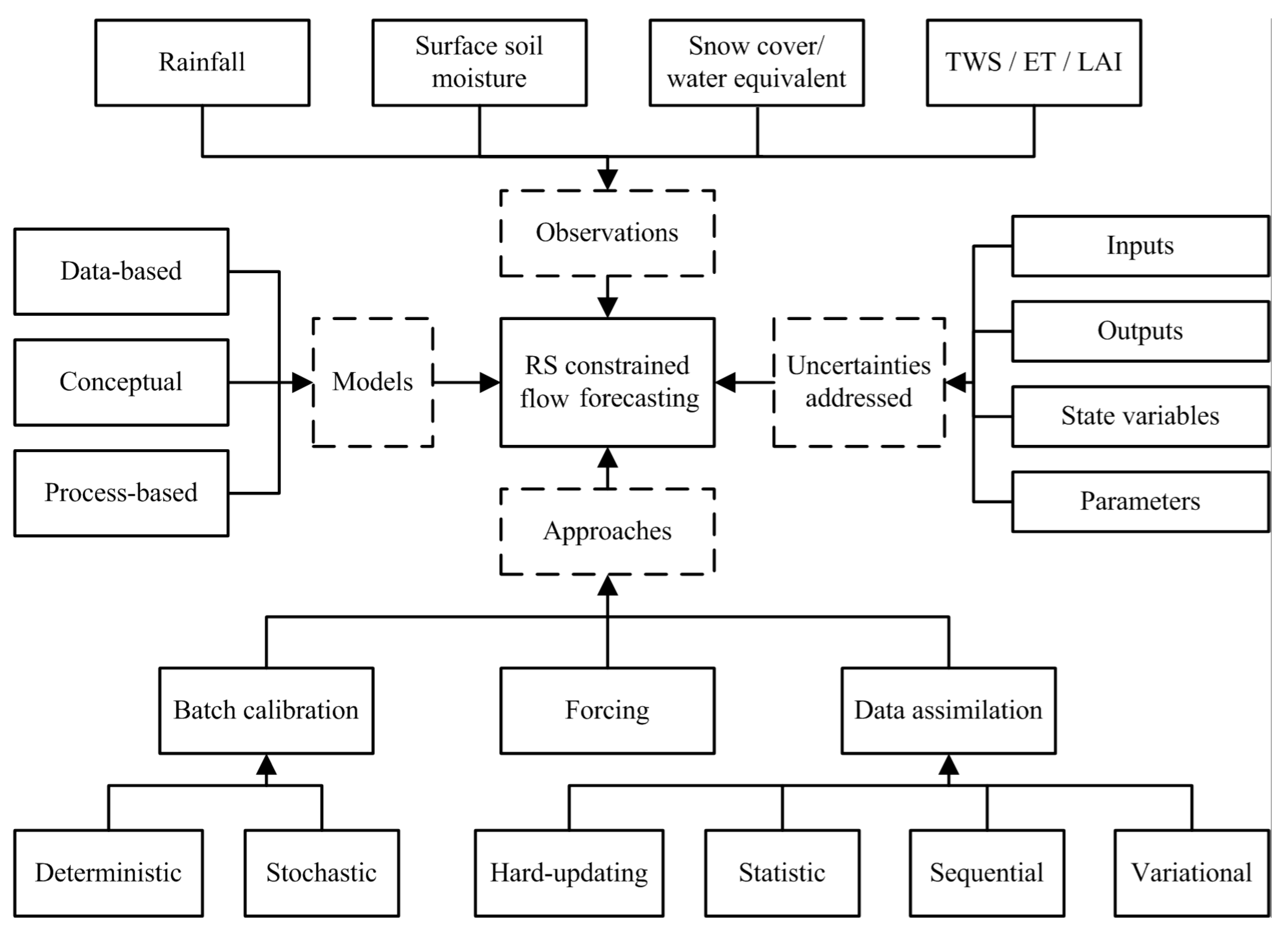
2. Background on Remote Sensing Constrained Flood Forecasting
3. Remotely Sensed Precipitation
3.1. Overview of Products
- the Precipitation Estimation from Remote Sensing Information using Artificial Neural Networks (PERSIANN) [50];
- the PERSIANN-Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) [51];
- the Self-Calibrating Multivariate Precipitation Retrieval (SCaMPR) [52];
- the combined Passive Microwave-Infrared (PMIR) algorithm [53];
- the Climate Prediction Center morphing approach (CMORPH) [46];
- the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL)-Blend Precipitation [54];
- the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) [55];
- the TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) [48]; and
- the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission [56].
3.2. Implementation of Weather Radar Precipitation
3.3. Implementation of Satellite Precipitation
3.4. Challenges and Opportunities
- large uncertainties in satellite-based and ground-radar precipitation estimates;
- developing a systematic guideline of choosing rainfall products and operational use of multiple source of information, e.g., gauged, satellite-based, and ground radar precipitations; and
- the use of remotely sensed precipitation for rainfall nowcast/forecast so as to drive flood forecasting.
3.4.1. Uncertainties in QPEs
3.4.2. Operational Use of Multiple Products
3.4.3. Remotely Sensed Precipitation for Rainfall Forecast
4. Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture
4.1. Overview of Products
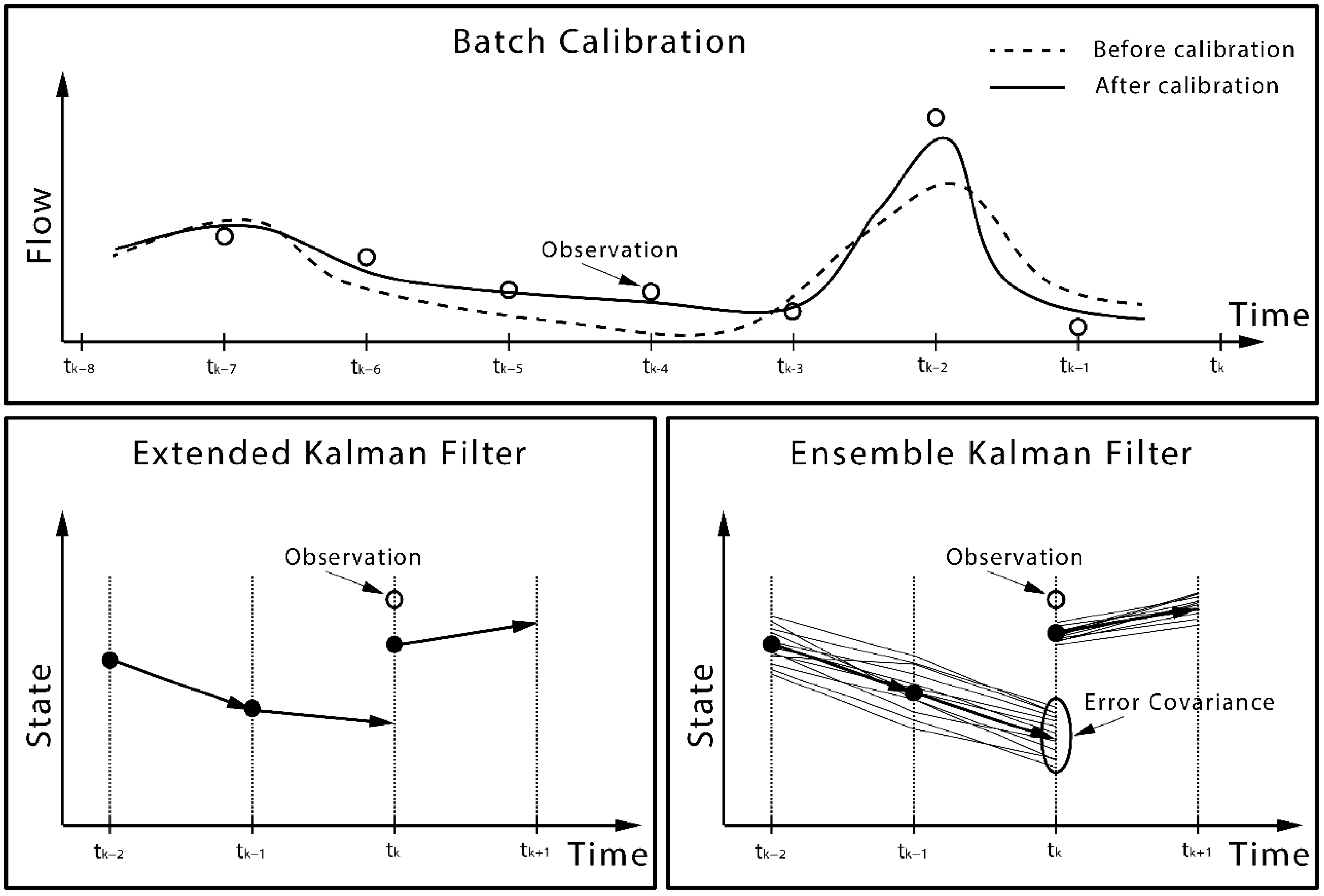
4.2. Batch Calibration
4.3. Data Assimilation
4.3.1. The Development of Flood-Orientated RS-SM Assimilation Studies
4.3.2. Model Types for RS-SM Assimilation
4.3.3. Uncertainties Addressed in RS-SM Assimilation
4.3.4. Capability to Improve Flood Forecasting
4.4. Challenges and Opportunities
- the spatial mismatch between the model and the remote sensing products;
- the different representativeness of the soil layers in the model; and
- remote sensing techniques, and limited data availability.
- bias between remotely sensed and modelled soil moistures;
- error quantification for data assimilation; and
- the best strategy to optimally use multiple data sources to constrain the flood forecasting models.
4.4.1. Representativeness of the Soil Layers
4.4.2. Bias between Remotely Sensed and Modelled Soil Moistures
4.4.3. Error Quantification
4.4.4. Strategy to Optimally Use Multiple Products
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sene, K. Flood Warning, Forecasting and Emergency Response; Springer: Berlin, Germany; London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pagano, T.C.; Wood, A.W.; Ramos, M.-H.; Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F.; Clark, M.P.; Cranston, M.; Kavetski, D.; Mathevet, T.; Sorooshian, S.; et al. Challenges of operational river forecasting. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1692–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerton, R.E.; Stephens, E.M.; Pappenberger, F.; Pagano, T.C.; Weerts, A.H.; Wood, A.W.; Salamon, P.; Brown, J.D.; Hjerdt, N.; Donnelly, C.; et al. Continental and global scale flood forecasting systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Dijk, M.V. Developing flood forecasting systems: Examples from the UK, Europe, and Pakistan. In Proceedings of the ACTIF International Conference on Innovation Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005.
- Elliott, J.; Catchlove, R.; Sooriyakumaran, S.; Thompson, R. Recent advances in the development of flood forecasting and warning services in Australia. In Proceedings of the ACTIF International Conference on Innovation, Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005.
- Vehviläinen, B.; Huttunen, M.; Huttunen, I. Hydrological forecasting and real time monitoring in Finland: The watershed simulation and forecasting system (WSFS). In Proceedings of the ACTIF International Conference on Innovation Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005.
- Guan, H. Flood forecasting and management in China. In Proceedings of the ACTIF International Conference on Innovation Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005.
- Mcenery, J.; Ingram, J.; Duan, Q.; Adams, T.; Anderson, L. NOAA’s advanced hydrologic prediction service: Building pathways for better science in water forecasting. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Burek, P.; Dutra, E.; Krzeminski, B.; Muraro, D.; Thielen, J.; Pappenberger, F. GloFAS—Global ensemble streamflow forecasting and flood early warning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewelde, J.; Verbeke, S.; Quintelier, E.; Cabus, P.; Vermeulen, A.; Vansteenkiste, T.; Jongh, I.D.; Cauwenberghs, K. Real-time flood forecasting system in Flanders. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, New York, NY, USA, 17–21 August 2014.
- Wang, Q.J.; Robertson, D.E.; Chiew, F.H.S. A Bayesian joint probability modeling approach for seasonal forecasting of streamflows at multiple sites. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W05407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietroniro, A.; Fortin, V.; Kouwen, N.; Neal, C.; Turcotte, R.; Davison, B.; Verseghy, D.; Soulis, E.D.; Caldwell, R.; Evora, N.; et al. Development of the MESH modelling system for hydrological ensemble forecasting of the Laurentian Great Lakes at the regional scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loumagne, C.; Weisse, A.; Normand, M.; Riffard, M. Integration of remote sensing data into hydrological models for flood forecasting. In Remote Sensing and Hydrology 2000; IAHS Publication: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2001; pp. 592–594. [Google Scholar]
- Lettenmaier, D.P.; Alsdorf, D.; Dozier, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Inroads of remote sensing into hydrologic science during the WRR era. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 7309–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weerts, A.H.; Clark, M.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Kumar, S.V.; Moradkhani, H.; Seo, D.J.; Schwanenberg, D.; Smith, P.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; et al. Advancing data assimilation in operational hydrologic forecasting: Progresses, challenges, and emerging opportunities. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3863–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montzka, C.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Franssen, H.-J.; Han, X.; Vereecken, H. Multivariate and multiscale data assimilation in terrestrial systems: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 16291–16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, J.; Tolson, B.A. Progress in integrating remote sensing data and hydrologic modeling. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 38, 464–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhu, M. A review on evapotranspiration data assimilation based on hydrological models. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Seidou, O.; Nistor, I.; Liu, K. Review of the Kalman type hydrological data assimilation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Solomatine, D.P.; Schumann, G.J.P. A review of low-cost space-borne data for flood modelling: Topography, flood extent and water level. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3368–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, Z.N.; Popescu, I.; Mynett, A. A review of applications of satellite SAR, optical, altimetry and DEM data for surface water modelling, mapping and parameter estimation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3755–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, M.; Hossain, F. Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tangdamrongsub, N.; Steele-Dunne, S.C.; Gunter, B.C.; Ditmar, P.G.; Weerts, A.H. Data assimilation of GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates into a regional hydrological model of the Rhine River basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2079–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J. The genetic algorithm and its application to calibrating conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, J.D.; Sorooshian, S.; Brazil, L.E. Comparison of Newton-type and direct search algorithms for calibration of conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Bayesian analysis of input uncertainty in hydrological modeling: 1. Theory. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W03407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Clark, M.P.; Hyman, J.M.; Robinson, B.A. Treatment of input uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: Doing hydrology backward with Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00B09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Binley, A. The future of distributed models: Model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol. Process. 1992, 6, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H. Hydrologic remote sensing and land surface data assimilation. Sensors 2008, 8, 2986–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, P.R.; Reichle, R.H.; Walker, J.P. New technologies require advances in hydrologic data assimilation. EOS Trans. AGU 2003, 84, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, J.P.; Houser, P.R. Hydrologic Data Assimilation. In Advances in Water Science Methodologies; Aswathanarayana, A., Ed.; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S. General review of rainfall-runoff modeling: Model calibration, data assimilation, and uncertainty analysis. In Hydrological Modelling and the Water Cycle: Coupling the Atmosheric and Hydrological Models; Sorooshian, S., Hsu, K.L., Coppola, E., Tomassetti, B., Verdecchia, M., Visconti, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 63, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelides, S.C. Precipitation: Advances in Measurement, Estimation and Prediction; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Vasiloff, S.; Kaney, B.; Arthur, A.; Van Cooten, S.; Kelleher, K.; Kitzmiller, D.; Ding, F.; et al. National Mosaic and Multi-Sensor QPE (NMQ) system: Description, results, and future plans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1321–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.F. Cokriging radar-rainfall and rain gage data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertino, A.; Allamano, P.; Claps, P.; Cremonini, R.; Laio, F. Radar estimation of intense rainfall rates through adaptive calibration of the Z-R relation. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1559–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Howard, K.; Zhang, J. An automated radar technique for the identification of tropical precipitation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, H.Y.; Man, C.; Chan, S.T.; Seed, A. Development of an operational rainfall data quality-control scheme based on radar-raingauge co-kriging analysis. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Cocchi, D.; Greco, F.; Scardovi, E. Spatial reconstruction of rainfall fields from rain gauge and radar data. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pintado, J.; Barberá, G.G.; Erena, M.; Castillo, V.M. Rainfall estimation by rain gauge-radar combination: A concurrent multiplicative-additive approach. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W01415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenhoofdt, E.; Delobbe, L. Evaluation of radar-gauge merging methods for quantitative precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Forero, C.A.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Cassiraga, E.F.; Jaime Gómez-Hernández, J. A non-parametric automatic blending methodology to estimate rainfall fields from rain gauge and radar data. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrieu, G.; Bonnifait, L.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Boudevillain, B. Dependence of radar quantitative precipitation estimation error on the rain intensity in the Cévennes region, France. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Janowiak, J.E.; Kidd, C. Comparison of near-real-time precipitation estimates from satellite observations and numerical models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Kummerow, C.D. The remote sensing of clouds and precipitation from space: A review. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3742–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite–based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed Imagery using an artificial neural network cloud classification system. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, R.J. A self-calibrating real-time GOES rainfall algorithm for short-term rainfall estimates. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 112–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, C.; Kniveton, D.R.; Todd, M.C.; Bellerby, T.J. Satellite rainfall estimation using combined passive microwave and infrared algorithms. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1088–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, F.J.; Miller, S.D. Toward improved characterization of remotely sensed precipitation regimes with MODIS/AMSR-E blended data techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Iwanami, K.; et al. Global precipitation map using satellite-borne microwave radiometers by the GSMaP project: Production and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, F. Improvement of multi-satellite real-time precipitation products for ensemble streamflow simulation in a middle latitude basin in south China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2259–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Koike, T.; Tanizawa, H. Application of a distributed hydrological model and weather radar observations for flood management in the upper Tone River of Japan. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 3119–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, M.; Overgaard, J.; Viaene, P.; Dubicki, A.; Stronska, K.; Szalinska, W.; Lewandowski, A.; Olszewski, T.; Kolerski, T. Flexible process-based hydrological modeling framework for flood forecasting-MIKE SHE. In Proceedings of the International Conference Innovation, Advances and Implementation of Flood Forecasting Technology, Tromsø, Norway, 17–19 October 2005.
- Kalinga, O.A.; Gan, T.Y. Semi-distributed modelling of basin hydrology with radar and gauged precipitation. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3725–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.J.; Moore, R.J. Distributed hydrological modelling using weather radar in gauged and ungauged basins. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Gan, T. Hydrologic modeling of the Blue River Basin using NEXRAD precipitation data with a semidistributed and a fully distributed model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 04015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, B.E.; Bedient, P.B. Estimation of rainfall for flood prediction from WSR-88D reflectivity: A case study, 17–18 October 1994. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, J.J.; Flamig, Z.L.; Hong, Y.; Howard, K.W. Evaluation of past, present and future tools for radar-based flash-flood prediction in the USA. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javelle, P.; Demargne, J.; Defrance, D.; Pansu, J.; Arnaud, P. Evaluating flash-flood warnings at ungauged locations using post-event surveys: A case study with the AIGA warning system. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, E.; Yakir, H. Hydrological impact and potential flooding of convective rain cells in a semi-arid environment. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Mein, R.G.; Keenan, T.D.; Elliott, J.F. Flood estimation using radar and raingauge data. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.J.; Moore, R.J. Hydrological modelling using raingauge- and radar-based estimators of areal rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, E.M.; Atkinson, P.M. A comparison of gauge and radar precipitation data for simulating an extreme hydrological event in the Severn Uplands, UK. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Flamig, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Vergara, H.; Anagnostou, E.N. Hydrologic evaluation of rainfall estimates from radar, satellite, gauge, and combinations on Ft. Cobb Basin, Oklahoma. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, T.-J.; Lai, J.-S.; Tan, Y.-C. Sensitivity analysis of the hydrological response of the Gaping River basin to radar-raingauge quantitative precipitation estimates. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1335–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzmiller, D.; Van Cooten, S.; Ding, F.; Howard, K.; Langston, C.; Zhang, J.; Moser, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Kim, D.; et al. Evolving multisensor precipitation estimation methods: Their impacts on flow prediction using a distributed hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1414–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Vejen, F.; Stisen, S.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Jensen, K.H. An operational weather radar–based quantitative precipitation estimation and its application in catchment water resources modeling. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Dybkjaer, G.; Jensen, K.H.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Rasmussen, K. Use of remotely sensed precipitation and leaf area index in a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2002, 264, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Jensen, K.H.; Sandholt, I.; Grimes, D.I.F. A remote sensing driven distributed hydrological model of the Senegal River basin. J. Hydrol. 2008, 354, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.I.F.; Diop, M. Satellite-based rainfall estimation for river flow forecasting in Africa. I: Rainfall estimates and hydrological forecasts. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Willems, P.; Feng, X.W.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Bao, A.M.; Chen, X.; Veroustraete, F.; Dong, Q.H. On the usefulness of remote sensing input data for spatially distributed hydrological modelling: Case of the Tarim River basin in China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Anagnostou, E.N. Assessment of current passive-microwave- and infrared-based satellite rainfall remote sensing for flood prediction. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D07102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinga, O.A.; Gan, T.Y. Estimation of rainfall from infrared-microwave satellite data for basin-scale hydrologic modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2068–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Hong, Y.; Ren, L.-L.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, S.I. Assessment of evolving TRMM-based multisatellite real-time precipitation estimation methods and their impacts on hydrologic prediction in a high latitude basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D09108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, K.O.; Arlan, G.A.; Pervez, S.; Rowland, J. A linear geospatial streamflow modeling system for data sparse environments. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2008, 6, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Adhikari, P.; Hong, Y.; Vergara, H.; F Adler, R.; Policelli, F.; Irwin, D.; Korme, T.; Okello, L. Hydroclimatology of Lake Victoria region using hydrologic model and satellite remote sensing data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Kunstmann, H.; Bárdossy, A.; Conrad, C.; Colditz, R.R. Water balance estimation of a poorly gauged catchment in West Africa using dynamically downscaled meteorological fields and remote sensing information. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, V.; Alcayaga, H.; Alvarez, E. Assimilation of TRMM Precipitation into a Hydrological Model of a Southern Andes Watershed, Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 468–476. [Google Scholar]
- Zulkafli, Z.; Buytaert, W.; Onof, C.; Manz, B.; Tarnavsky, E.; Lavado, W.; Guyot, J.L. A comparative performance analysis of TRMM 3B42 (TMPA) versions 6 and 7 for hydrological applications over Andean-Amazon River Basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, R.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Impact of TRMM data on a low-latency, high-resolution precipitation algorithm for flash-flood forecasting. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zhang, Y.; Seo, D.-J.; Kuligowski, R.J.; Kitzmiller, D.; Corby, R. Utility of SCaMPR satellite versus ground-based quantitative precipitation estimates in operational flood forecasting: The effects of TRMM data Ingest. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zhang, Y.; Seo, D.-J.; Xie, P. Utilizing satellite precipitation estimates for streamflow forecasting via adjustment of mean field bias in precipitation data and assimilation of streamflow observations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, J.; Kniveton, D.; Andersson, L.; Layberry, R.; Todd, M.C.; Hughes, D.; Ringrose, S.; Vanderpost, C. Estimating rainfall and water balance over the Okavango River Basin for hydrological applications. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Tumbo, M. Interpolation of daily raingauge data for hydrological modelling in data sparse regions using pattern information from satellite data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Hsu, K.; Hong, Y.; Sorooshian, S. Investigating the impact of remotely sensed precipitation and hydrologic model uncertainties on the ensemble streamflow forecasting. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M. Accuracy of radar rainfall estimates for streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Aduvala, A.V.; Meselhe, E.A. Analysis of radar-rainfall error characteristics and implications for streamflow simulation uncertainty. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 568–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Malakpet, C.; Tokay, A.; Kucera, P. Sensitivity of streamflow simulations to temporal variability and estimation of Z–R relationships. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.G. On the propagation of uncertainty in weather radar estimates of rainfall through hydrological models. Meteorol. Appl. 2009, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Yong, B.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F.; Ma, M. Comprehensive evaluation of multi-satellite precipitation products with a dense rain gauge network and optimally merging their simulated hydrological flows using the Bayesian model averaging method. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Crow, W.T.; Ryu, D. Dual forcing and state correction via soil moisture assimilation for improved rainfall–runoff modeling. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1832–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Garreton, C.; Ryu, D.; Western, A.W.; Su, C.H.; Crow, W.T.; Robertson, D.E.; Leahy, C. Improving operational flood ensemble prediction by the assimilation of satellite soil moisture: Comparison between lumped and semi-distributed schemes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Ryu, D. A new data assimilation approach for improving runoff prediction using remotely-sensed soil moisture retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; van den Berg, M.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Pellarin, T. Correcting rainfall using satellite-based surface soil moisture retrievals: The Soil Moisture Analysis Rainfall Tool (SMART). Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W. A new method for rainfall estimation through soil moisture observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabatta, L.; Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Puca, S.; Rinollo, A.; Gabellani, S.; Wagner, W. Integration of satellite soil moisture and rainfall observations over the Italian territory. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Panziera, L.; Beven, K.J. Forecasting flash floods using data-based mechanistic models and NORA radar rainfall forecasts. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.A.; Gallus, W.A.; Mantilla, R. An initial assessment of radar data assimilation on warm season rainfall forecasts for use in hydrologic models. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 1491–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrban, M.; Walker, J.P.; Wang, Q.J.; Seed, A.; Steinle, P. An evaluation of numerical weather prediction based rainfall forecasts. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; Mahmood, R.; Levia, D.F.; DeLiberty, T.L.; Quiring, S.M.; Houser, C.; Nelson, F.E. Soil moisture: A central and unifying theme in physical geography. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R. Exploits and endeavors in soil water management and conservation using nuclear techniques. In Proceedings of the an International Symposium, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria, 29 October–1 November 2001.
- Gardner, W.; Kirkham, D. Determination of soil moisture by neutron scattering. Soil Sci. 1952, 73, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, T.E.; Cosh, M.H.; Cuenca, R.H.; Dorigo, W.A.; Draper, C.S.; Hagimoto, Y.; Kerr, Y.H.; Njoku, E.G.; Small, E.E.; Zreda, M. State of the art in large-scale soil moisture monitoring. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1888–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Berg, A.A.; Cosh, M.H.; Loew, A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Panciera, R.; de Rosnay, P.; Ryu, D.; Walker, J.P. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barre, H.M.J.; Duesmann, B.; Kerr, Y.H. SMOS: The mission and the system. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Fujii, H.; Murakami, H.; Hori, M.; Ono, A.; Igarashi, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T.; Honda, Y.; et al. Global Change Observation Mission (GCOM) for monitoring carbon, water cycles, and climate change. IEEE Proc. 2010, 98, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouki, A.; McNairn, H.; Pacheco, A. Mapping soil moisture using RADARSAT-2 data and local autocorrelation statistics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalis, Z.; Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Hasenauer, S.; Scipal, K.; Bonekamp, H.; Figa, J.; Anderson, C. Initial soil moisture retrievals from the METOP-A Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission. IEEE Proc. 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loumagne, C.; Chkir, N.; Normand, M.; OttlÉ, C.; Vidal-Madjar, D. Introduction of the soil/vegetation/atmosphere continuum in a conceptual rainfall/runoff model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N. Soil moisture at local scale: Measurements and simulations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Campbell, C.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: A review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J. Satellite remote sensing applications for surface soil moisture monitoring: A review. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Du, Y.; Du, J.; Jiang, L.; Chai, L.; Mao, K.; Xu, P.; Ni, W.; Xiong, C.; Liu, Q.; et al. Progresses on microwave remote sensing of land surface parameters. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1052–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V. Remote sensing of soil moisture. ISRN Soil Sci. 2013, 2013, 424178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Johnson, F.M.; Parinussa, R.M.; Sharma, A. A global comparison of alternate AMSR2 soil moisture products: Why do they differ? Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, D.J.; Kerr, Y.H.; Al Bitar, A.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Berthelot, B.; Portet, G. Comparison between SMOS, VUA, ASCAT, and ECMWF soil moisture products over four watersheds in U.S. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.M.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.R.; de Jeu, R.A.M. An intercomparison of remotely sensed soil moisture products at various spatial scales over the Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4865–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, C.; Calvet, J.-C.; Gruhier, C.; Holmes, T.R.H.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Wagner, W. An intercomparison of ERS-Scat and AMSR-E soil moisture observations with model simulations over France. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schalie, R.; Parinussa, R.M.; Renzullo, L.J.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Su, C.H.; de Jeu, R.A.M. SMOS soil moisture retrievals using the land parameter retrieval model: Evaluation over the Murrumbidgee Catchment, southeast Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Ryu, D.; Young, R.I.; Western, A.W.; Wagner, W. Inter-comparison of microwave satellite soil moisture retrievals over the Murrumbidgee Basin, southeast Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; de Jong, S.M.; de Roo, A.; Karssenberg, D. The benefits of using remotely sensed soil moisture in parameter identification of large-scale hydrological models. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6874–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, D.; Loumagne, C.; Oudin, L. Sequential assimilation of soil moisture and streamflow data in a conceptual rainfall-runoff model. J. Hydrol. 2003, 280, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montzka, C.; Moradkhani, H.; Weihermüller, L.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Canty, M.; Vereecken, H. Hydraulic parameter estimation by remotely-sensed top soil moisture observations with the particle filter. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, R.; Walker, J.P.; Rudiger, C. Towards soil property retrieval from space: Proof of concept using in situ observations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Drake, S.; Hao, Z.; Sudicky, E.A. Dual state-parameter estimation of root zone soil moisture by optimal parameter estimation and extended Kalman filter data assimilation. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanello, J.A., Jr.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Garcia, M.E.; Mocko, D.M.; Tischler, M.A.; Moran, M.S.; Thoma, D.P. Using remotely-sensed estimates of soil moisture to infer soil texture and hydraulic properties across a semi-arid watershed. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, V.; Moreda, F.; Smith, M. Use of soil moisture observations to improve parameter consistency in watershed calibration. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 33, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvucci, G.D.; Entekhabi, D. An alternate and robust approach to calibration for the estimation of land surface model parameters based on remotely sensed observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; de Jong, S.M.; van Geer, F.C.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Calibrating a large-extent high-resolution coupled groundwater-land surface model using soil moisture and discharge data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Naeimi, V.; Blöschl, G.; Komma, J. Matching ERS scatterometer based soil moisture patterns with simulations of a conceptual dual layer hydrologic model over Austria. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Naeimi, V.; Blöschl, G.; Wagner, W.; Merz, R.; Scipal, K. Assimilating scatterometer soil moisture data into conceptual hydrologic models at the regional scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, F.; Gabellani, S.; Rudari, R.; Delogu, F.; Laiolo, P.; Boni, G. Uncertainty reduction and parameter estimation of a distributed hydrological model with ground and remote-sensing data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1727–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Hain, C.R.; Fang, L. Impact of quality control of satellite soil moisture data on their assimilation into land surface model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, GL060659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.M.; Forman, B.; Draper, C.S.; Liu, Q. Connecting satellite observations with water cycle variables through land data assimilation: Examples using the NASA GEOS-5 LDAS. Surv. Geophys. 2014, 35, 577–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; van den Berg, M.J. An improved approach for estimating observation and model error parameters in soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Reichle, R.H.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Liu, Q. Assimilation of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L04401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.N.; Bras, R.L.; Entekhabi, D. Hydrologic data assimilation with a hillslope-scale-resolving model and L band radar observations: Synthetic experiments with the ensemble Kalman filter. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, D.A.; De Keyser, R.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P.; Pauwels, V.R.N. The importance of parameter resampling for soil moisture data assimilation into hydrologic models using the particle filter. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, G.B.; Medina, H.; Romano, N. Kalman filters for assimilating near-surface observations into the Richards equation—Part 1: Retrieving state profiles with linear and nonlinear numerical schemes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2503–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Yilmaz, M.T. The Auto-Tuned Land Data Assimilation System (ATLAS). Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Harrison, K.W.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Santanello, J.A.; Kirschbaum, D. Assessing the impact of L-band observations on drought and flood risk estimation: A decision-theoretic approach in an OSSE environment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.R.H.; Crow, W.T.; De Jeu, R.A.M. Leveraging microwave polarization information for the calibration of a land data assimilation system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2014GL061991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumedah, G.; Walker, J.P. Intercomparison of the JULES and CABLE land surface models through assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture in southeast Australia. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 74, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D.; Crow, W.T.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. Role of subsurface physics in the assimilation of surface soil moisture observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Sekhar, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Assimilation of remote sensing and hydrological data using adaptive filtering techniques for watershed modelling. Curr. Sci. 2009, 97, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, C.S.; Mahfouf, J.F.; Walker, J.P. An EKF assimilation of AMSR-E soil moisture into the ISBA land surface scheme. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D20104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cai, X.M. Robust data assimilation in hydrological modeling—A comparison of Kalman and H-infinity filters. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Crow, W.T.; Keppenne, C.L. An adaptive ensemble Kalman filter for soil moisture data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W03423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H. Monitoring root-zone soil moisture through the assimilation of a thermal remote sensing-based soil moisture proxy into a water balance model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Chehbouni, A.; Boulet, G.; Kerr, Y. Assimilation of disaggregated microwave soil moisture into a hydrologic model using coarse-scale meteorological data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Wood, E.F.; Gao, H. Observation operators for the direct assimilation of TRMM microwave imager retrieved soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Walker, J.P.; Koster, R.; Houser, P.R. Extended versus ensemble Kalman filtering for land data assimilation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Mclaughlin, D.B.; Entekhabi, D. Hydrologic data assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2002, 130, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; McLaughlin, D.B.; Entekhabi, D. Variational data assimilation of microwave radiobrightness observations for land surface hydrology applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaldo, N.; Albertson, J.D.; Mancini, M.; Kiely, G. Robust simulation of root zone soil moisture with assimilation of surface soil moisture data. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, P.R.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Gupta, H.V.; Syed, K.H.; Goodrich, D.C. Integration of soil moisture remote sensing and hydrologic modeling using data assimilation. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 3405–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Entekhabi, D.; McLaughlin, D.B. Downscaling of radio brightness measurements for soil moisture estimation: A four-dimensional variational data assimilation approach. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipal, K.; Drusch, M.; Wagner, W. Assimilation of a ERS scatterometer derived soil moisture index in the ECMWF numerical weather prediction system. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Crow, W.T.; Mo, X.; Liu, S. Impact of temporal autocorrelation mismatch on the assimilation of satellite-derived surface soil moisture retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3534–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Mahfouf, J.F.; Walker, J.P. Root zone soil moisture from the assimilation of screen-level variables and remotely sensed soil moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D02127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumedah, G.; Walker, J.P.; Merlin, O. Root-zone soil moisture estimation from assimilation of downscaled Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity data. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 84, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.P.; Willgoose, G.R.; Kalma, J.D. One-dimensional soil moisture profile retrieval by assimilation of near-surface observations: A comparison of retrieval algorithms. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.P.; Willgoose, G.R.; Kalma, J.D. One-dimensional soil moisture profile retrieval by assimilation of near-surface measurements: A simplified soil moisture model and field application. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, V.R.N.; Hoeben, R.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Troch, F.P. The importance of the spatial patterns of remotely sensed soil moisture in the improvement of discharge predictions for small-scale basins through data assimilation. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Garreton, C.; Ryu, D.; Western, A.W.; Crow, W.T.; Robertson, D.E. The impacts of assimilating satellite soil moisture into a rainfall–runoff model in a semi-arid catchment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, C.; Quesney, A.; Ottlé, C. Sequential assimilation of ERS-1 SAR data into a coupled land surface-hydrological model using an extended Kalman filter. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Karssenberg, D.; de Roo, A.; de Jong, S.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. The suitability of remotely sensed soil moisture for improving operational flood forecasting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridler, M.-E.; Madsen, H.; Stisen, S.; Bircher, S.; Fensholt, R. Assimilation of SMOS-derived soil moisture in a fully integrated hydrological and soil-vegetation-atmosphere transfer model in Western Denmark. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8962–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Fenicia, F.; Heitz, S.; Plaza, D.; de Keyser, R.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Wagner, W.; Savenije, H. Can ASCAT-derived soil wetness indices reduce predictive uncertainty in well-gauged areas? A comparison with in situ observed soil moisture in an assimilation application. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 44, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Merwade, V.; Heathman, G.C. Implementation of surface soil moisture data assimilation with watershed scale distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Bartalis, Z.; Hasenauer, S. Improving runoff prediction through the assimilation of the ASCAT soil moisture product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, D.; Loumagne, C.; Oudin, L.; Le Hegarat-Mascle, S. Assimilation of soil moisture into hydrological models: The sequential method. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, V.R.N.; Hoeben, R.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Troch, F.P.; Troch, P.A. Improvement of TOPLATS-based discharge predictions through assimilation of ERS-based remotely sensed soil moisture values. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesney, A.; Francois, C.; Ottlé, C.; Le Hegarat, S.; Loumagne, C.; Normand, M. Sequential assimilation of SAR/ERS data in a lumped rainfall-runoff model with an extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Hydrology 2000, Santa Fe, NM, USA, April 2001; Owe, M., Braubaker, K., Ritchie, J., Rango, A., Eds.; pp. 495–497.
- Ottlé, C.; Vidal-Madjar, D. Assimilation of soil moisture inferred from infrared remote sensing in a hydrological model over the HAPEX-MOBILHY region. J. Hydrol. 1994, 158, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W.; Hasenauer, S.; Hahn, S. Assimilation of surface- and root-zone ASCAT soil moisture products into rainfall-runoff modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2542–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Brocca, L.; Barbetta, S.; Papathanasiou, C.; Mimikou, M.; Moramarco, T. Using globally available soil moisture indicators for flood modelling in Mediterranean catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, D.C.; Schmugge, T.J.; Jackson, T.J.; Unkrich, C.L.; Keefer, T.O.; Parry, R.; Bach, L.B.; Amer, S.A. Runoff simulation sensitivity to remotely sensed initial soil water content. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loumagne, C.; Normand, M.; Riffard, M.; Weisse, A.; Quesney, A.; HÉGarat-Mascle, S.L.; Alem, F. Integration of remote sensing data into hydrological models for reservoir management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2001, 46, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Myers, D.A.; Whitfield, B.M. Improved rainfall/runoff estimates using remotely sensed soil moisture. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Crow, W.T.; Starks, P.J.; Moriasi, D.N. Improving hydrologic predictions of a catchment model via assimilation of surface soil moisture. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.S.; Mahfouf, J.F.; Calvet, J.C.; Martin, E.; Wagner, W. Assimilation of ASCAT near-surface soil moisture into the SIM hydrological model over France. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3829–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Tomer, S.K.; Al Bitar, A.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Drusch, M.; Dumedah, G.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Kerr, Y.H.; Martens, B.; Pan, M.; et al. SMOS soil moisture assimilation for improved hydrologic simulation in the Murray Darling Basin, Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Davis, K.J.; Zhang, F.; Duffy, C.J.; Yu, X. Parameter estimation of a physically-based land surface hydrologic model using an ensemble Kalman filter: A multivariate real-data experiment. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 83, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Singh, V.P. Assimilation of observed soil moisture data in storm rainfall-runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J.; Koren, V. Assimilation of streamflow and in situ soil moisture data into operational distributed hydrologic models: Effects of uncertainties in the data and initial model soil moisture states. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J.; Coulibaly, P.; Dumedah, G.; Moradkhani, H. Assessing model state and forecasts variation in hydrologic data assimilation. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, E.E.; Troch, P.A. Tikhonov regularization as a tool for assimilating soil moisture data in distributed hydrological models. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 531–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Weisse, A.; Loumagne, C.; Le Hegarat-Mascle, S. Assimilation of soil moisture into hydrological models for flood forecasting: A variational approach. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 29, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Antecedent wetness conditions based on ERS scatterometer data. J. Hydrol. 2009, 364, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ryu, D.; Western, A.W.; Wang, Q.J.; Robertson, D.E.; Crow, W.T. An integrated error parameter estimation and lag-aware data assimilation scheme for real-time flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2722–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Meng, S.; Liang, S.; Yao, Y. Improving streamflow predictions at ungauged locations with real-time updating: Application of an EnKF-based state-parameter estimation strategy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3923–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ryu, D.; Western, A.W.; Wang, Q.J. Assimilation of stream discharge for flood forecasting: Updating a semidistributed model with an integrated data assimilation scheme. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3238–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Houser, P.R.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Verhoest, N.E.C. State and bias estimation for soil moisture profiles by an ensemble Kalman filter: Effect of assimilation depth and frequency. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W06401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Reichle, R.H.; Houser, P.R.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Correcting for forecast bias in soil moisture assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W09410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, V.R.N.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. Error covariance calculation for forecast bias estimation in hydrologic data assimilation. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 86, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, V.R.N.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Vereecken, H. Simultaneous estimation of model state variables and observation and forecast biases using a two-stage hybrid Kalman filter. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3499–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, B.; Kavetski, D.; Leblois, E.; Thyer, M.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Toward a reliable decomposition of predictive uncertainty in hydrological modeling: Characterizing rainfall errors using conditional simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, N.K.; Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S. An integrated hydrologic Bayesian multimodel combination framework: Confronting input, parameter, and model structural uncertainty in hydrologic prediction. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W01403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Ryu, D.; Crow, W.T.; Western, A.W. Stand-alone error characterisation of microwave satellite soil moisture using a Fourier method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensor Type | Platform Examples | Horizontal Resolution | Revisit | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Radar | Ground stations | 10 m–1 km | <10 min (local) | High |
| TIR | TRMM, GOES, METEOSAT, MTSAT, Himawari, Fengyun | 1–5 km | 30 min–3 h | Low |
| Passive microwave | GPM, TRMM, DMSP, Aqua, NOAA, MetOp | 5–70 km | 3 h–1 d | High |
| Satellite radar | GPM, TRMM | ~5 km | 12 h–3 d | High |
| Passive | Active | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor (Satellite) | Band | Period | Product Resolution | Revisit | Sensor (Satellite) | Band | Period | Product Resolution | Revisit |
| SMMR (Nimbus-7) | C, X, K | 1978–1987 | ~50 km | 1–2 days | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | C | 1991–1999/1995–2011 | 30/25 m | 35 days |
| SSM/I (DMSP) | K | 1987– | 25~50 km | 1–3 days | SCAT (ERS-1/-2) | C | 1991–1999/1995–2011 | 25/50 km | 2–7 days |
| TMI (TRMM) | X, K | 1997– | 25~50 km | 1–3 days | ASAR (Envisat) | C | 2002–2012 | 30–1000 m | 35 days |
| AMSR-E (Aqua) | C, X, K | 2002–2011 | 25~50 km | 1–3 days | SAR (TerraSAR-X) | X | 2007– | 1–18 m | 11 days |
| AMSR-2 (GCOM-W1) | C, X, K | 2012– | 25~50 km | 1–3 days | SAR (RADARSAT-1/-2) | C | 1995–2013/2007– | 3–100 m | 24 days |
| MIRAS (SMOS) | L | 2010– | 43 km | 1–3 days | SAR (JERS-1) | L | 1992–1998 | 18 m | 44 days |
| PALSAR (ALOS-1/-2) | L | 2006–2011/2014– | 7–100 m | 46/14 days | |||||
| ASCAT (Metop) | C | 2006– | 25/50 km | 1–2 days | |||||
| Passive (SMAP) | L | 2015– | 36 km | 1–3 days | Active (SMAP) | L | January–July 2015 | 9 km | 1–3 days |
| Authors | Year | Remote Sensing Data | Data Period | Models | Time Scales | Algorithms | Study Basins |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parajka et al. [146] | 2006 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1992–2000 | HBV (Semi-distributed) | daily | SCE-UA | 320 Austrian catchments |
| Parajka et al. [145] | 2009 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1992–2000 | HBV (Semi-distributed) | daily | SCE-UA | 148 Austrian catchments |
| Wanders et al. [136] | 2014 | AMSR-E, ASCAT and SMOS | 2010–2011 | LISFLOOD (distributed) | daily | Dual EnKF | Upper Danube catchment, Europe |
| Sutanudjaja et al. [144] | 2014 | SCAT (ERS-1/-2) | 1995–2000 | PCR-GLOBWB-MOD (distributed) | daily | Stepwise | Rhine-Meuse basin, Europe |
| Silvestro et al. [147] | 2015 | EUMETSAT | 2006–2011 | Continuum (distributed) | hourly | Brute-force | Orba basin and Casentino basin, Italy |
| Authors | Year | Remote Sensing Data | Data Period | Models | Time Scales | Assimilation Algorithms | Study Basins |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goodrich et al. [193] | 1994 | Aircraft microwave SM | 07–08/1990 | KINEROS (Semi-distributed) | daily | Direct insertion | Lucky-Hills-104 watershed, USA |
| Ottlé and Vidal-Madjar [193] | 1994 | Infrared (NOAA-AVHRR) | 1985–1986 | Hydrological-SVA (Lumped) | daily | Direct insertion | Adour river catchment, France |
| Loumagne et al. [13] | 2001 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | Not provided | GRHUM (Lumped) | daily | KF | Seine catchment upstream of Paris, France; Arade catchment in southern Portugal |
| Loumagne et al. [194] | 2001 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1995–1997 | GRHUM (Lumped) | daily | Variational and EKF | Seine catchment upstream of Paris, France |
| Quesney et al. [189] | 2001 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1995–1997 | GRHUM (Lumped) | daily | EKF | The Orgeval river basin, France |
| Pauwels et al. [179] | 2001 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1995–1998 | TOPLATS (Lumped and semi-d) | hourly | Nudging and statistic correction | The Zwalm catchment, Belgium |
| Pauwels et al. [188] | 2002 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1995–2000 | TOPLATS (Lumped) | hourly | Statistic correction | The Zwalm catchment, Belgium |
| Jacobs et al. [195] | 2003 | Aircraft microwave | 01–07/1997 | SCS (Empirical) | daily | Statistic correction | The Little Washita Watershed, USA |
| Aubert et al. [187] | 2003 | SAR (ERS-1/-2) | 1999–2000 | GR4J (Lumped) | daily | EKF | Seine River basin, France; Arade basin, Portugal |
| Francois et al. [181] | 2003 | SAR (ERS-1) | 1995–1997 | GRKAL (Lumped) | daily | EKF | The Orgeval river basin, France |
| Crow and Ryu [104] | 2009 | Synthetic SM | 1949–2003 | SAC-SMA (Lumped) | subdaily | EnKF, EnKS and KF | MOPEX basins, USA |
| Brocca et al. [186] | 2010 | ASCAT | 2007–2009 | MISDc (Lumped) | hourly | Nudging | Upper Tiber river basin, Italy |
| Draper et al. [197] | 2011 | ASCAT | 2007–2010 | SIM (Distributed) | sub-daily | EKF | France |
| Chen et al. [196] | 2011 | Synthetic and ground SM | 2005–2008 | SWAT (semi-distributed) | daily | EnKF | Cobb Creek Watershed, USA |
| Brocca et al. [191] | 2012 | ASCAT | 2007–2010 | MISDc-2L two layer model (Lumped) | hourly | EnKF | Upper Tiber river basin, Italy |
| Han et al. [185] | 2012 | Synthetic SM | 2008–2009 | SWAT (Semi-distributed) | daily | EnKF | Upper Cedar Creek Watershed, USA |
| Matgen et al. [184] | 2012 | ASCAT | 2007–2008 | BibModel (Lumped) | hourly | Particle filter | Bibeschbach experimental catchment, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg |
| Alvarez-Garreton et al. [180] | 2014 | AMSR-E | 2002–2011 | PDM (Lumped) | daily | EnKF | Warrego River catchment, Australia |
| Chen et al. [102] | 2014 | ASCAT and SMOS | 2010–2012 | SAC-SMA (Lumped) | subdaily | EnKF, EnKS and KF | 13 basins, central USA |
| Ridler et al. [183] | 2014 | SMOS | 04–11/2010 | SW-ET-MIKE (Lumped and semi-distributed) | daily | Bias-aware ETKF | Ahlergaarde river basin, Western Denmark |
| Wanders et al. [182] | 2014 | AMSR-E, ASCAT and SMOS | 12–11/2011 | LISFLOOD (Distributed) | daily | EnKF | Upper Danube catchment upstream of Bratislava, Europe |
| Massari et al. [192] | 2014 | ASCAT, AMSR-E and ECMWF | 2009–2013 | SCRRM (Lumped) | hourly | Direct insertion | Rafina river basin upstream from the Rafina, Greece |
| Alvarez-Garreton et al. [103] | 2015 | AMSR-E, ASCAT and SMOS | 2007–2014 | PDM (Lumped and semi-distributed) | daily | EnKF | Warrego River catchment, Australia |
| Lievens et al. [198] | 2015 | SMOS | 2010–2011 | VIC (Distributed) | daily | EnKF | Murray-Darlin Basin, Australia |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Grimaldi, S.; Walker, J.P.; Pauwels, V.R.N. Application of Remote Sensing Data to Constrain Operational Rainfall-Driven Flood Forecasting: A Review. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060456
Li Y, Grimaldi S, Walker JP, Pauwels VRN. Application of Remote Sensing Data to Constrain Operational Rainfall-Driven Flood Forecasting: A Review. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(6):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060456
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuan, Stefania Grimaldi, Jeffrey P. Walker, and Valentijn R. N. Pauwels. 2016. "Application of Remote Sensing Data to Constrain Operational Rainfall-Driven Flood Forecasting: A Review" Remote Sensing 8, no. 6: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060456
APA StyleLi, Y., Grimaldi, S., Walker, J. P., & Pauwels, V. R. N. (2016). Application of Remote Sensing Data to Constrain Operational Rainfall-Driven Flood Forecasting: A Review. Remote Sensing, 8(6), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060456






