Telecouplings in the East–West Economic Corridor within Borders and Across
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Land Change, Teleconnections and Telecouplings
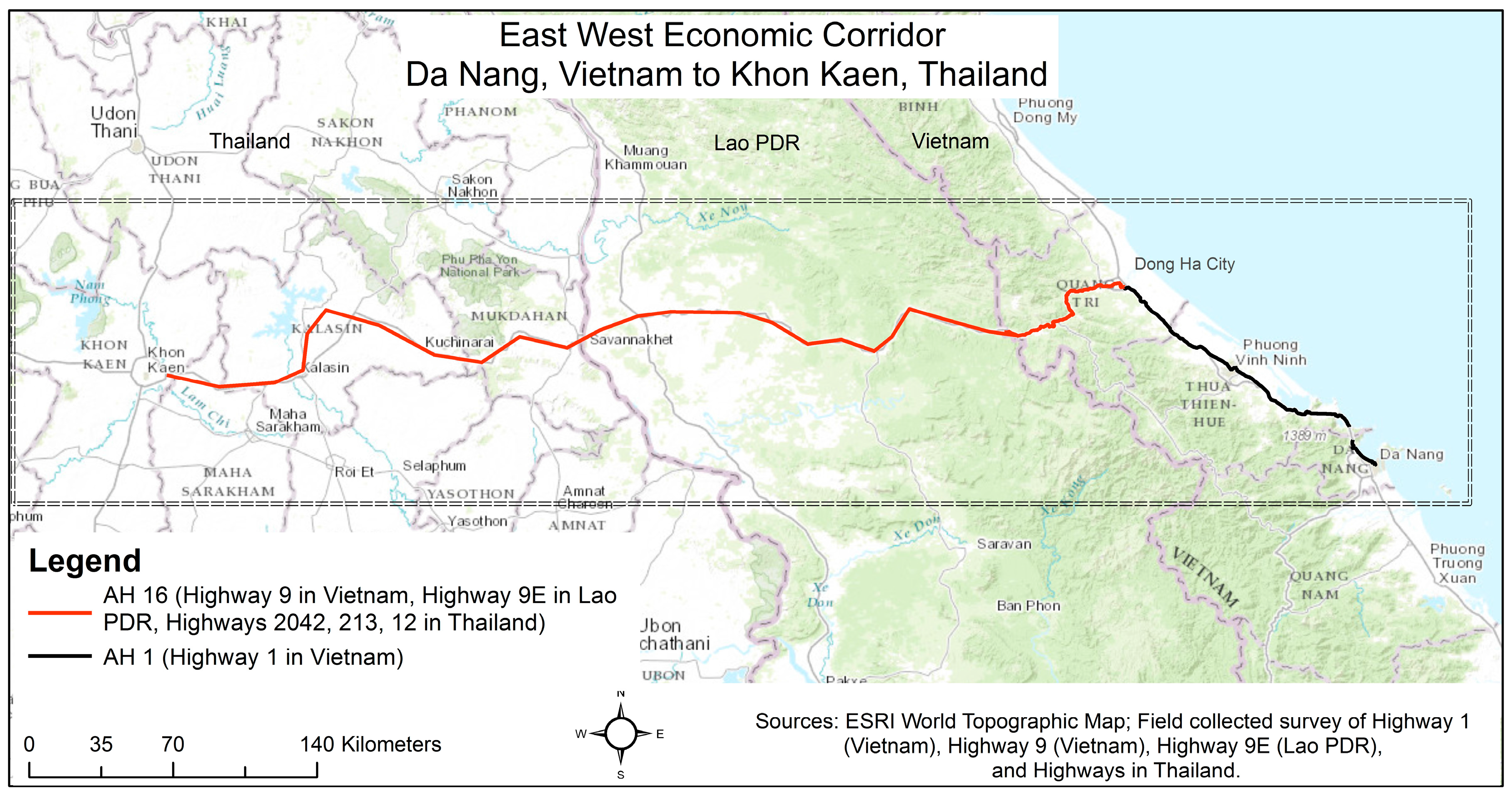
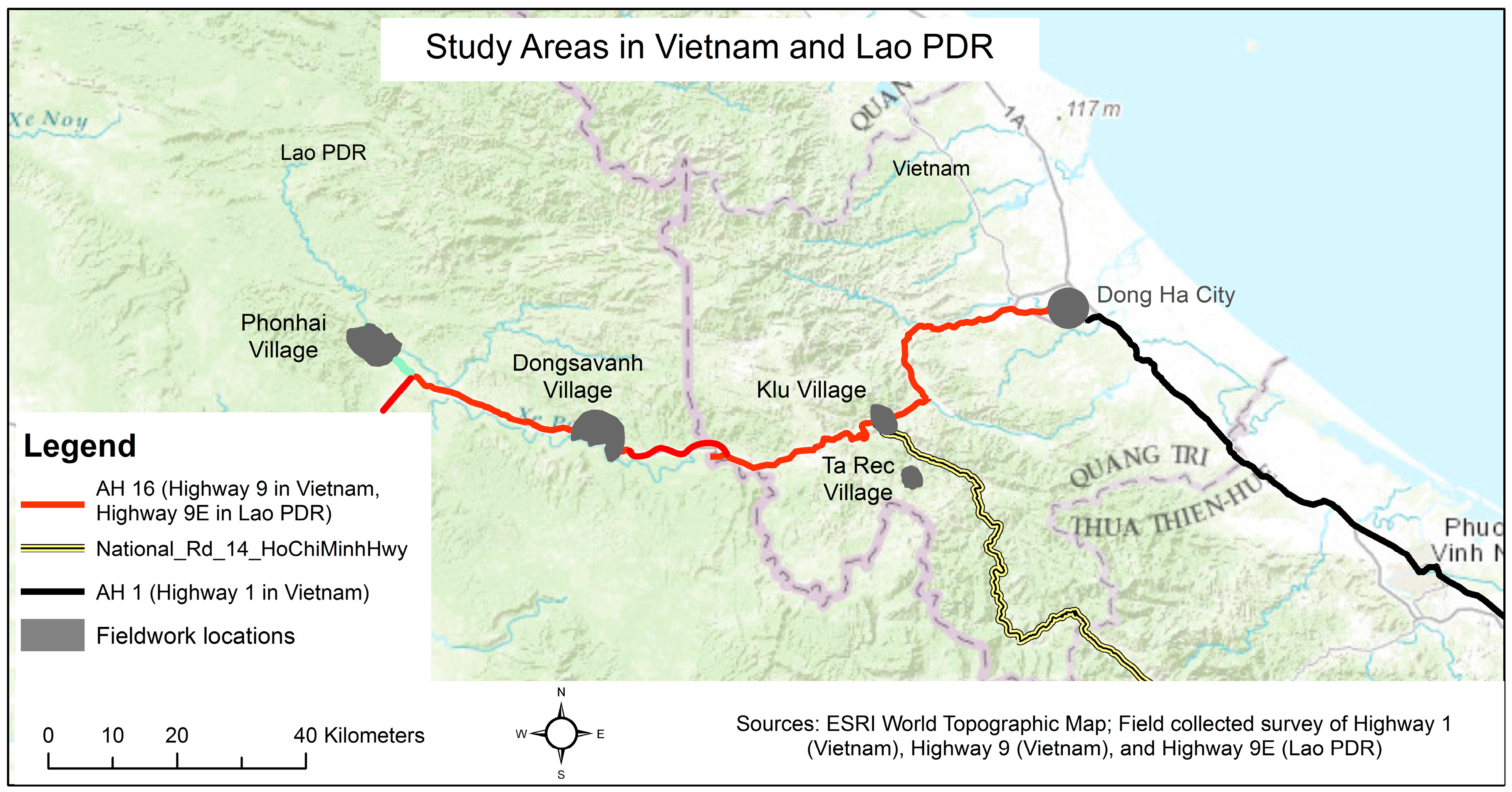
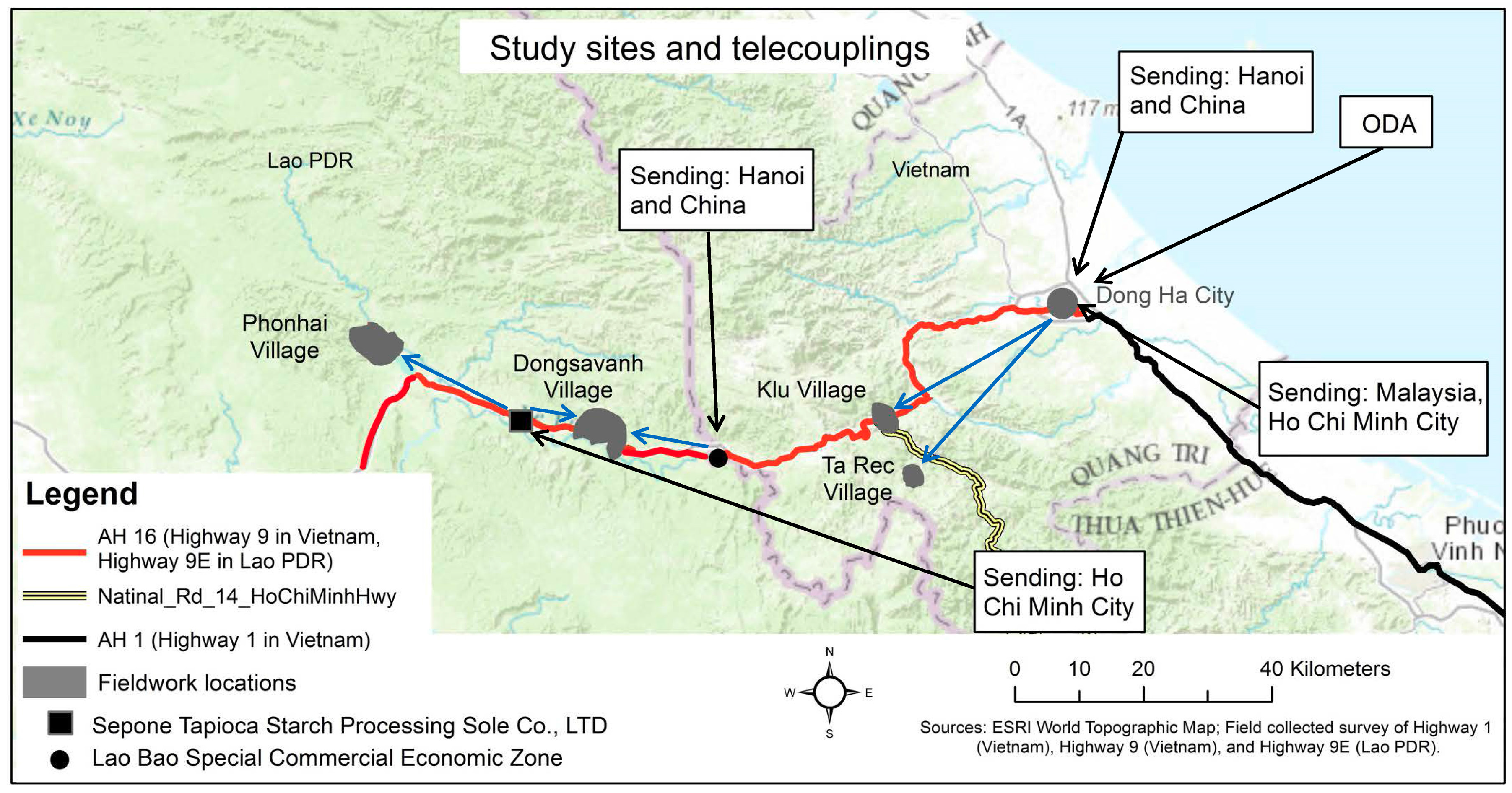
1.3. Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
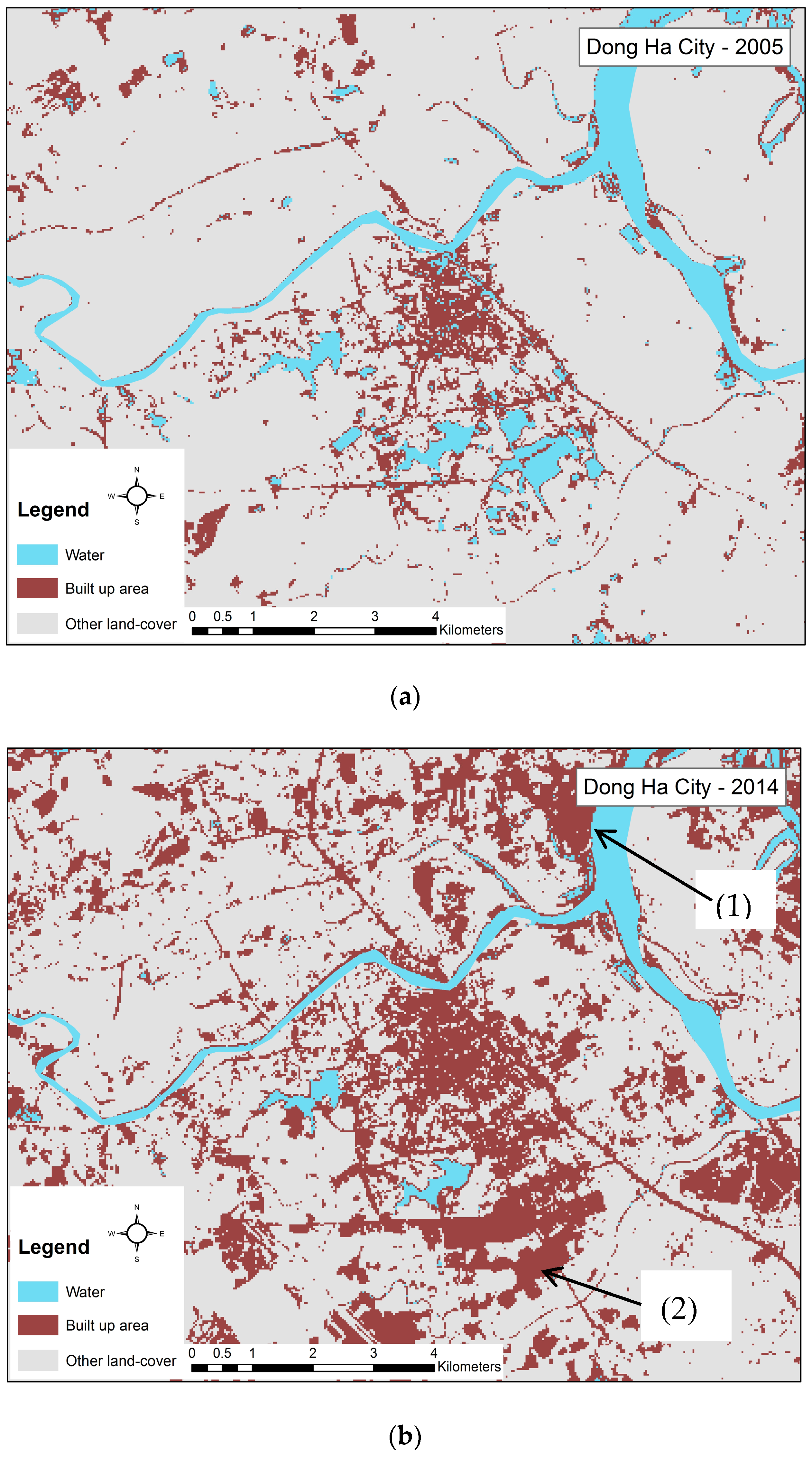
2.1. Urban Change Data Collection in Dong Ha City
2.2. Village Livelihood System and Land-Use/Cover Data Collection
2.3. Satellite Image Interpretation
2.4. Analysis of Upland Agricultural Field Placement
3. Results
3.1. Growth of Dong Ha City
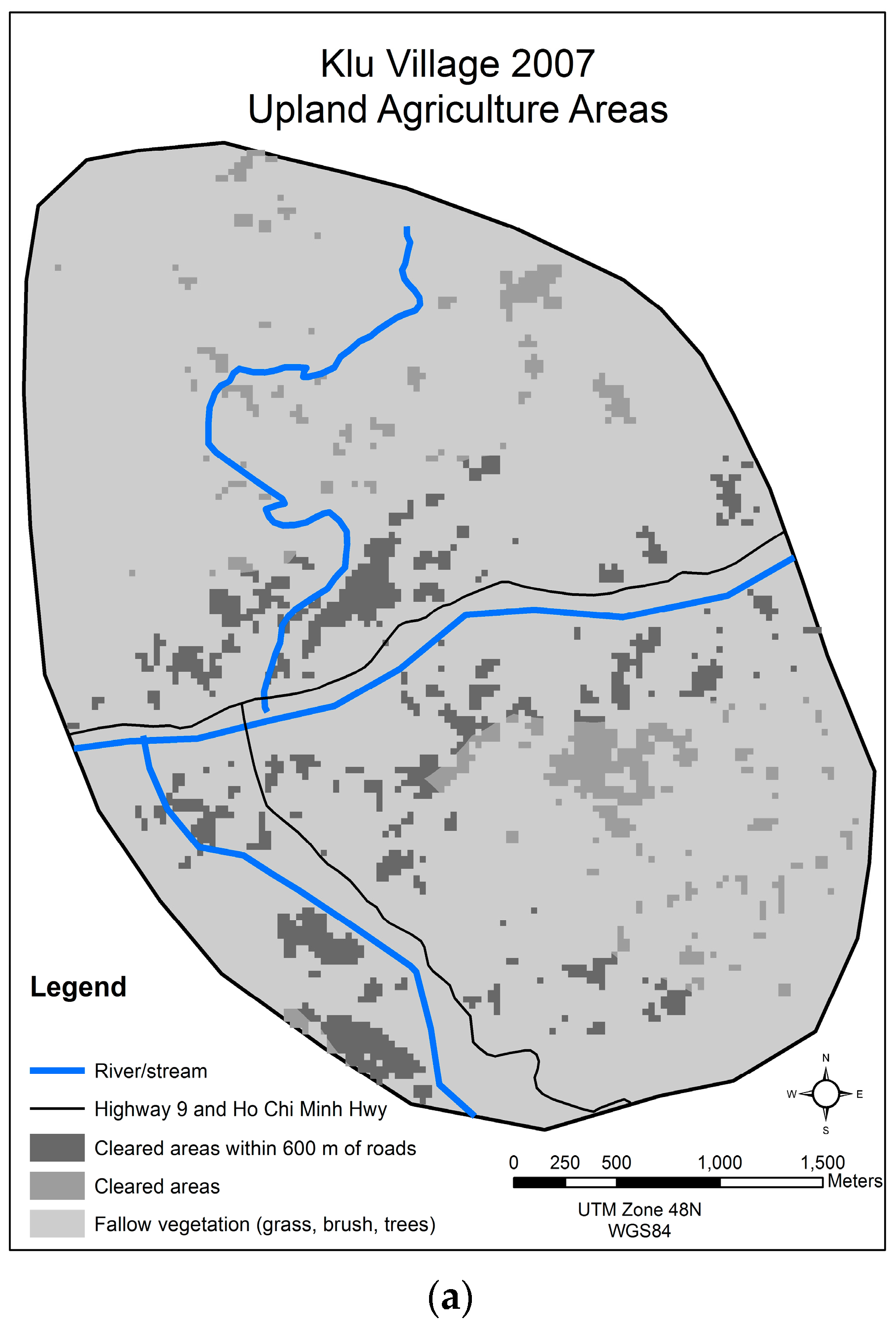
3.2. Klu, Da Krong District, Quang Tri Province
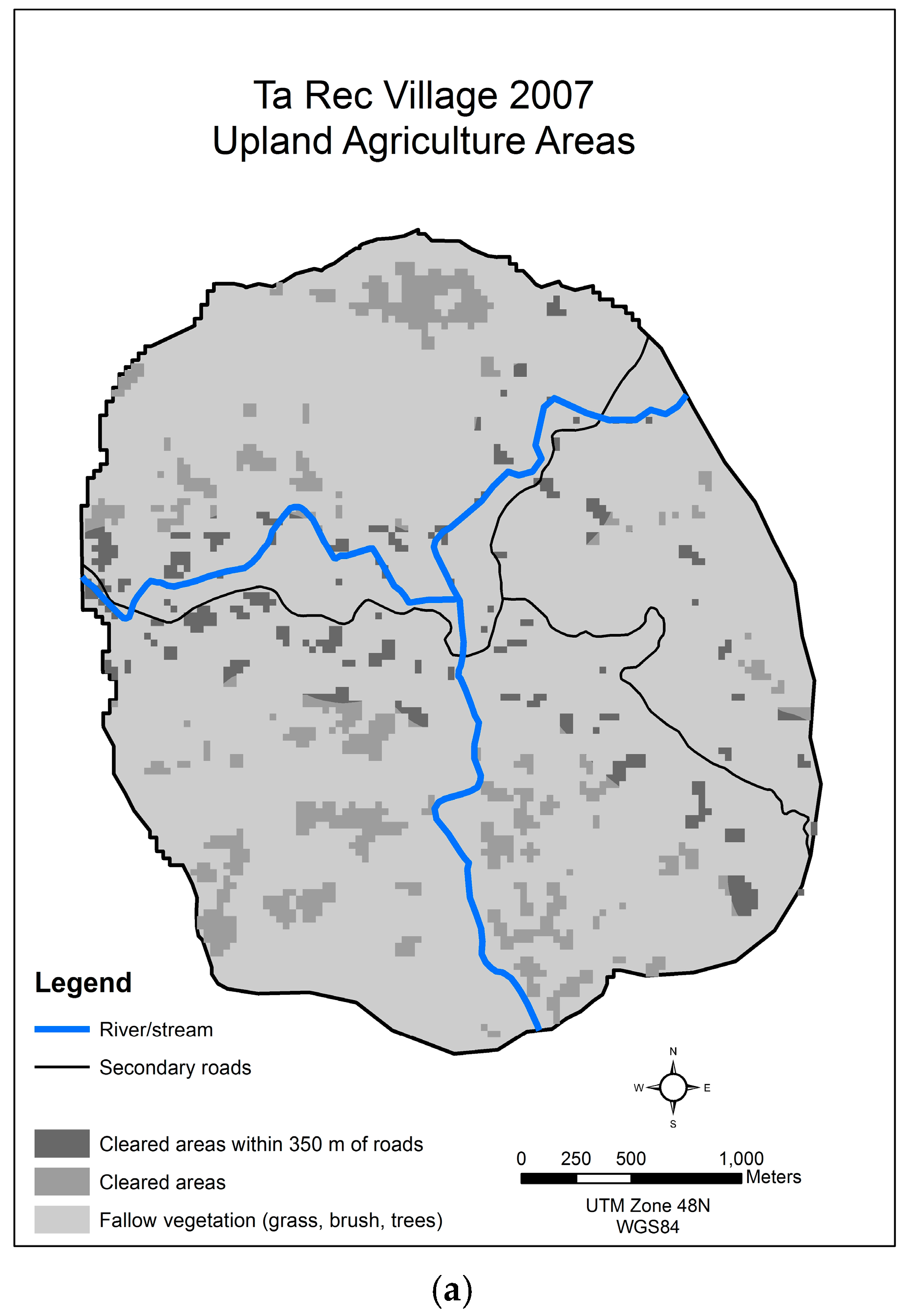
3.3. Ta Rec, Da Krong District, Quang Tri Province
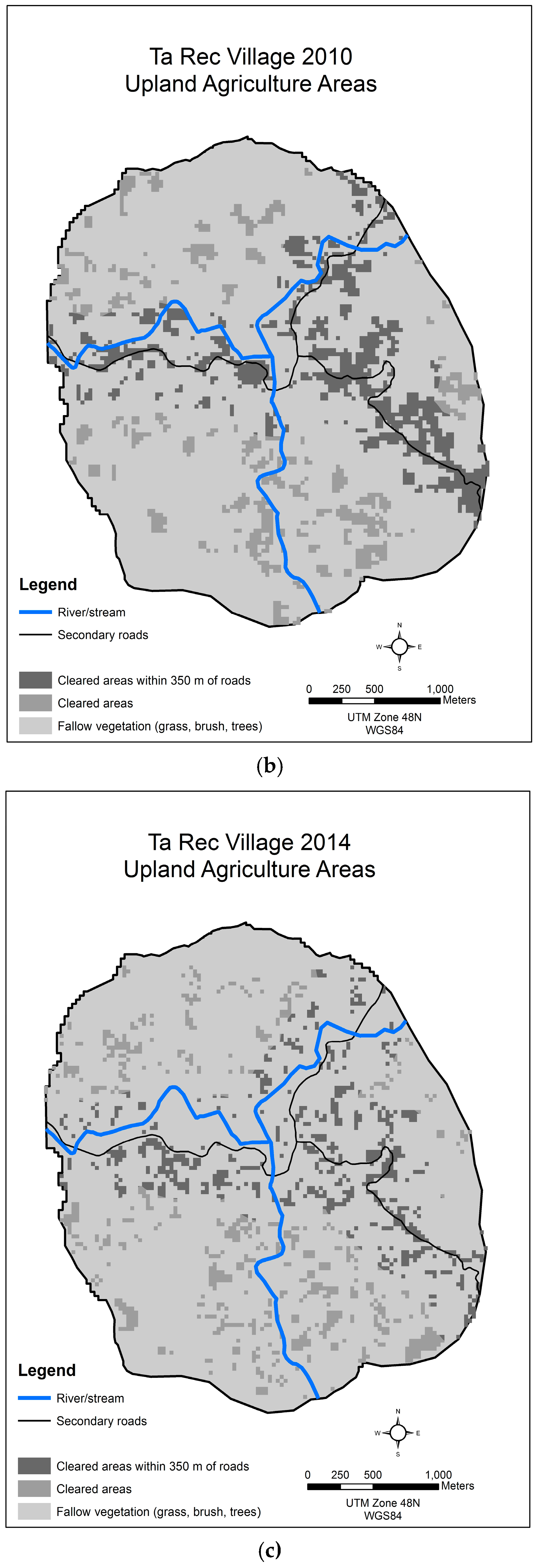
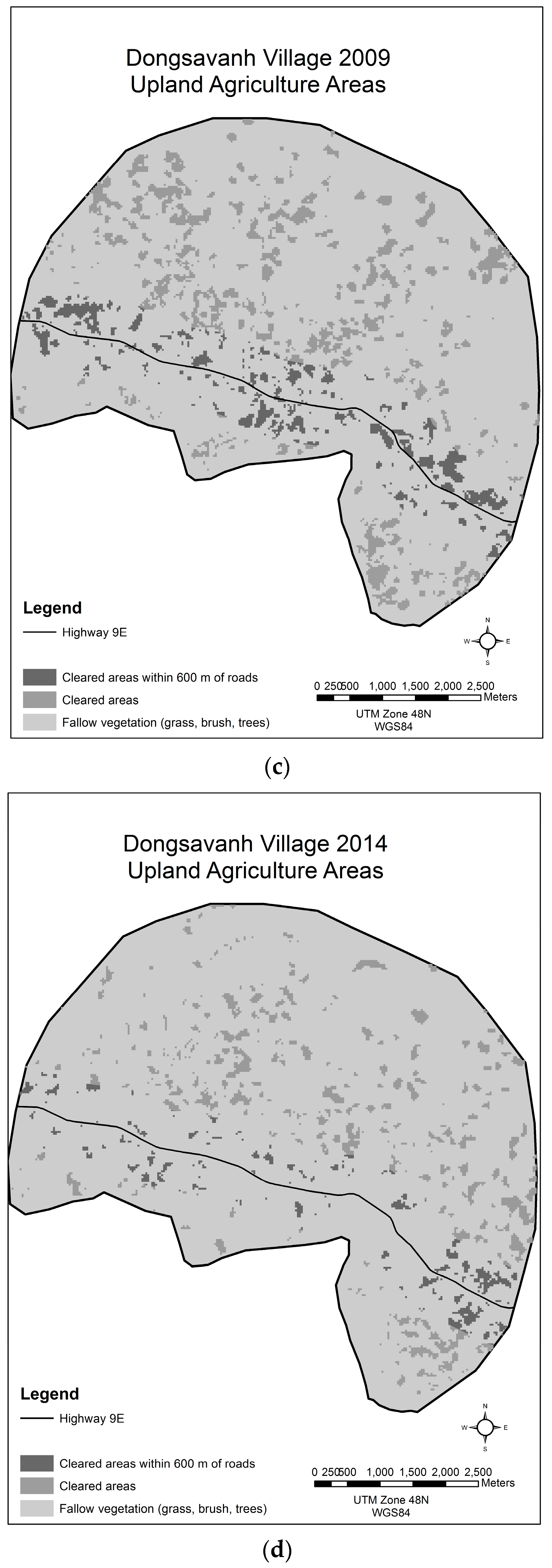
3.4. Dongsavanh, Sepon District, Savannakhet Province
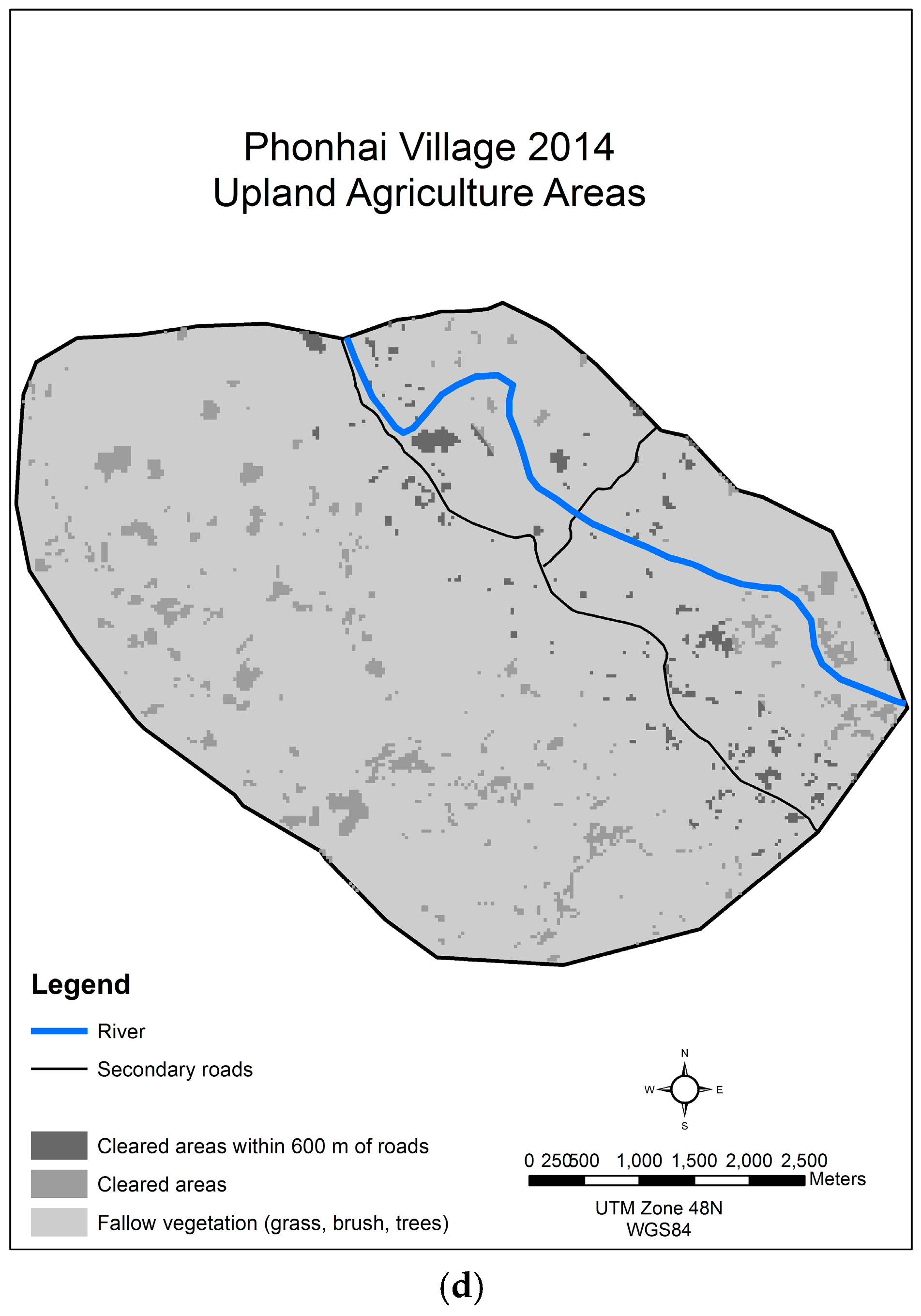
3.5. Phonhai, Sepon District, Savannakhet Province
3.6. Validation
4. Discussion: The Multiple Telecoupled Systems within the EWEC in Quang Tri Province, Vietnam, and Sepon District, Savannakhet Province, Lao PDR
4.1. Dong Ha City
4.2. Lao Bao Special Commercial Economic Zone System
4.3. Sepone Tapioca Starch Processing Sole Co., LTD
4.4. Rural Village Spillover Systems
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asian Development Bank. Strategy and Action Plan for the Greater Mekong Subregion East-West Economic Corridor; Asian Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Taillard, C. The continental grid of economic corridors in the Greater Mekong Subregion towards transnational ntegration. In Transnational Dynamics in Southeast Asia: The Greater Mekong Subregion and Malacca Straits Economic Corridors; Nathalie, F., Sirivanh, K., Christian, T., Eds.; ISEAS Publishing: Singapore, 2014; pp. 23–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pholsena, V. There is more to road: Modernity, memory and economic corridors in Huong Hoa-Sepon Lao-Veitnamese border area. In Transnational Dynamics in Southeast Asia: The Greater Mekong Subregion and Malacca Straits Economic Corridors; Nathalie, F., Sirivanh, K., Christian, T., Eds.; ISEAS Publishing: Singapore, 2014; pp. 379–398. [Google Scholar]
- Binswanger, H.P.; Khandker, S.R. How infrastructure and financial institutions affect agricultural output and investment in India. J. Dev. Econ. 1993, 41, 337–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, H.G. Access to markets and the benefits of rural roads. Econ. J. 2000, 110, 713–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, D.V.D. Choosing rural road investments to help reduce poverty. World Dev. 2002, 30, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, J.; Cramb, R.A. Remoteness and rural development: Economic impacts of rural roads on upland farmers in Sarawak, Malaysia. Asia Pac. Viewp. 1997, 38, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarasuk, R.; Binford, M.W. Longitudinal analysis of the road network development and land-cover change in Lop Buri province, Thailand, 1989–2006. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, P. How road improvement reduces poverty: The case of Laos. Agric. Econ. 2008, 39, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, P. Roads and poverty in rural Laos: An econometric analysis. Pac. Econ. Rev. 2010, 14, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizaki, Y. Suphanburi in the fast lane: Roads, prestige, and domination in provincial Thailand. J. Asian Stud. 2008, 67, 433–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerman, R.; Spiekermann, K.; Wegener, M. Accessibility and economic development in Europe. Reg. Stud. 1999, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, H.J.; Lambin, E.F. Proximate causes and underlying driving forces of tropical deforestation. Bioscience 2002, 52, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Alexander, L.E. Roads and their major ecological effects. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.S.; Pereira, J.L.G.; de Sousa, C.L.; Soares, J.V.; Yamaguchi, F. Characterizing landscape changes in central Rondonia using Landsat TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Filho, B.; Alencar, A.; Nepstad, D.; Cerqueira, G.; del Carmen, M.; Diaz, V.; Rivero, S.; Solarzano, L.; Voll, E. Simulating the response of land-cover changes to road paving and governance along a major Amazon highway: The Santarem-Cuiaba corridor. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.A.; Brown, I.F.; Woodwell, G.M. Estimation, by remote sensing, of deforestation in central Rondonia, Brazil. For. Ecol. Manag. 1991, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropper, M.; Puri, J.; Griffiths, C. Predicting the location of deforestation: The role of roads and protected areas in North Thailand. Land Econ. 2001, 77, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomitz, K.M.; Gray, D.A. Roads, land use, and deforestation: A spatial model applied to Belize. World Bank Econ. Rev. 1996, 10, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, H.; McConnell, W.; Lambin, E.E.; Moran, E.; Digenese, A.; Rudel, T. Causes and trajectories of land-use/cover change. In Land-Use and Land-Cover Change, Local Processes and Global Impacts; Global Change—the IGBP Series; Eric, F., Lambin, H.J.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 41–70. [Google Scholar]
- Adger, W.N.; Eakin, H.; Winkels, A. Nested and teleconnected vulnerabilities to environmental change. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Erb, K.; Krausmann, F.; Berecz, S.; Ludwiczek, N.; Martinez-Alier, J.; Musel, A.; Schaffartzik, A. Using embodied HANPP to analyze teleconnections in the global land system: Conceptual considerations. Geogr. Tidsskr. Dan. J. Geogr. 2013, 109, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Feng, K.; Hubacek, K. Tele-connecting local consumption to global land use. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Gutzler, D.S. Teleconnections in the geopotential height field during the northern hemisphere winter. Mon. Weather Rev. 1981, 109, 784–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W. The arctic in an earth system context: From brake to accelerator of change. AMBIO 2006, 35, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneralp, B.; Seto, K.C.; Ramachandran, M. Evidence of urban land teleconnections and impacts on hinterlands. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepstad, D.C.; Stickler, C.M.; Almeida, O.T. Globalization of the Amazon soy and beef industries: Opportunities for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friis, C.; Nielsen, J.O. Exploring the Potential of the Telecoupling Framework for Understanding Land Change; THESys Discussion Paper No.1; Integrative Research Institute: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Friis, C.; Nielson, J.O.; Otero, I.; Haberl, H.; Niewohner, J.; Hostert, P. From teleconnection to telecoupling: Taking stock of an emerging framework in land system science. J. Land Use 2016, 11, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eakin, H.; DeFries, R.; Kerr, S.; Lambin, E.F.; Liu, J.; Marcotullio, P.J.; Messerl, P.; Rueda, X.; Swaffield, S.R.; Wicke, B.; et al. Significance of telecoupling for exploration of land-use change. In Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era; Karen, C.S., Anette, R., Eds.; MIT Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hull, V.; Moran, E.; Nagendra, H.; Swaffield, S.R.; Turner, B.L. Applications of the telecoupling framework to land-change science. In Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era; Karen, C.S., Anette, R., Eds.; MIT Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Eakin, H.; Winkels, A.; Jan, S. Nested vulnerability: Exploring cross-scale linkages and vulnerability teleconnections in Mexican and Vietnamese coffee systems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hull, V.; Batistella, M.; DeFries, R.; Dietz, T.; Fu, F.; Hertel, T.W.; Izaurralde, C.R.; Lambin, E.F.; Li, S.; et al. Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hull, V.; Luo, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Vina, A.; Vogt, C.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Multiple telecouplings and their complex interrelationships. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, I.; Fox, J. How land concessions affect places elsewhere: Telecoupling, political ecology, and large-scale plantations in Southern Laos and Northeastern Cambodia. Land 2015, 4, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R. Rapid rural appraisal: Rationale and repertoire. Public Adm. Dev. 1981, 1, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonmaker-Freudenberger, K. Rapid Rural Appraisal (RRA) and Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA): A Manual for CRS Field Workers and Partners; Catholic Relief Services: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.S.; Fernandez-Gimenez, M.E. Engaging communities through participatory research. In Forest Community Connections: Implications for Research, Management, Governance; Donaghue, E.M., Sturtevant, V.S., Eds.; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 66–87. [Google Scholar]
- Leisz, S.J. Reinterpreting the Uplands of Vietnam: Towards Understanding and Correcting a Misreading of Its Land Cover, Land Use, and Resource Management Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geography, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Product Guide: Landsat 4–7 Climate Data Record (CDR) Surface Reflectance; Version 6.8.; Department of Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- U.S. Geological Survey. Product Guide: Provisional Landsat 8 Surface Reflectance Code (LaSRC) Product; Version 3.2.; Department of Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat Surface Reflectance High Level Data Products. Available online: http://landsat.usgs.gov/CDR_LSR.php (accessed on 18 September 2016).
- Li, P.; Genf, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liao, C.; Zhang, J. A review of swidden agriculture in Southeast Asia. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1654–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byomkesh, T.; Nakagoshi, N.; Dewan, A.M. Urbanization and green space dynamics in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 8, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B. Analysis of urban growth pattern using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of Kolkata, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Rahman, M.Z. Dynamics of land use/cover changes and the analysis of landscape fragmentation in Dhaka Metropolitan, Bangladesh. GeoJ. 2012, 77, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyfroidt, P.; Lambin, E.F.; Erb, K.; Hertel, T.W. Globalization of land use: Distant drivers of land change and geographic displacement of land use. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.D.; Fox, J.M.; Xu, J. The rubber juggernaut. Science 2009, 324, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friis, C.; Reenberg, A.; Heinimann, A.; Schonweger, O. Changing local land systems: Implications of a Chinese rubber plantation in Nambak District, Lao PDR. Singap. J. Trop. Geogr. 2016, 37, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis, C.; Nielsen, J.O. Small-scale land acquisition, large scale implications: Exploring the case of Chinese banana investments in Northern Laos. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Casella, J. Expansion of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) in Mainland Southeast Asia: What are the prospects for smallholders? J. Peasant Stud. 2013, 40, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisz, S.J.; Rasmussen, M.S. Mapping fallow lands in Vietnam’s north central mountains using yearly Landsat imagery and a land-cover succession model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 6281–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, S.A.; Bertran, M.; Wilson, E.H. Satellite change detection of forest harvest patterns on an industrial forest landscape. For. Sci. 2003, 49, 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.H.; Sader, S.A. Detection of forest harvest type using multiple dates of Landsat TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Fiorella, M.; Gray, J.; Helmer, E.; Anderson, K. An efficient and accurate method for mapping forest clearcuts in the Pacific Northwest using Landsat imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1998, 64, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, V.; Phan, A. Managers and Management in Vietnam: 25 Years of Economic Renovation (Doi Moi); Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Fortier, F.; Trang, T.T.T. Agricultural modernization and climate change in Vietnam’s post-socialist transition. Dev. Chang. 2013, 44, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiep, L. Performance-based legitimacy: The case of the Communist Party of Vietnam and Doi Moi. Contemp. Southeast Asia 2012, 34, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietnam Trade and Promotion Agency. Economic Zones and Industrial Parks in Quang Tri Province—Part 1. Available online: http://www.vietrade.gov.vn/en/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2020:economic-zones-and-industrial-parks-in-quang-tri-province-part-1&catid=272:investment-opportunities&Itemid=250 (accessed on 21 August 2016).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency; ALMEC Corporation. The Research on the Cross-border Transportation Infrastructure: Phase 2 Final Report; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2007.
- Ishida, M. Special economic zones and economic corridors. In Research on Development Strategies for CLMV Countries; ERIA Research Project Report 2008-5; Kuchiki, A., Uchikawa, S., Eds.; ERIA: Chiba, Japan, 2009; pp. 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Viet Nam News. Switch to Banana Farming Bears Fruit for Commune. 27 October 2013. Available online: http://vietnamnews.vn/sunday/features/246822/switch-to-banana-farming-bears-fruit-for-commune.html (accessed on 28 September 2015).
- Thang, N.M.; Popkin, B.M. Patterns of food consumption in Vietnam: Effects on socioeconomic groups during an era of economic growth. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 58, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hop, L.; Mai, L.; Khan, N.C. Trends in food production and food consumption in Vietnam during the period 1980-2000. Malays. J. Nutr. 2003, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dung, D.V.; Ba, N.X.; Van, N.H.; Phung, L.; Ngoan, L.; Cuong, V.C.; Yao, W. Practice on improving fattening local cattle production in Vietnam by increasing crude protein level in concentrate and concentrate level. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2013, 45, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
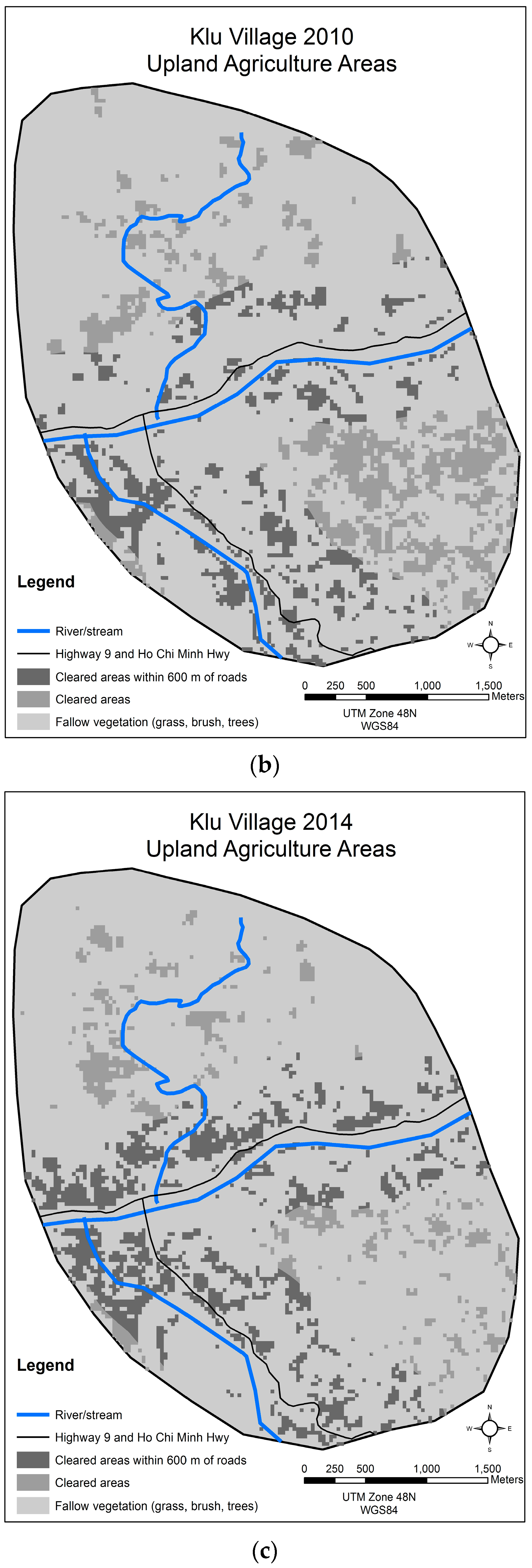


| Year | All Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture within 600 m of Highway | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture >600 m from Highway |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 85.77 | 24.03 | 61.74 |
| 2002 | 122.58 | 19.53 | 103.05 |
| 2004 | 169.56 | 22.14 | 147.42 |
| 2006 | 139.86 | 52.29 | 87.57 |
| 2007 | 139.86 | 51.21 | 88.65 |
| 2010 | 263.52 | 50.40 | 213.12 |
| 2014 | 229.05 | 92.07 | 136.98 |
| Year | All Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture within 350 m of Secondary Roads | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture >350 m from Secondary Roads |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 27.90 | 0 | 27.90 |
| 2002 | 44.28 | 0 | 44.28 |
| 2004 | 60.93 | 0 | 60.93 |
| 2006 | 62.46 | 26.46 | 36.00 |
| 2007 | 52.11 | 10.26 | 41.85 |
| 2010 | 105.48 | 57.69 | 47.79 |
| 2014 | 89.28 | 42.75 | 46.53 |
| Year | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture within 600 m of Highway | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture >600 m from Highway |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | 214.56 | 58.86 | 155.70 |
| 1998 | 475.92 | 105.03 | 370.89 |
| 2003 | 411.21 | 110.61 | 300.60 |
| 2008 | 557.28 | 94.23 | 463.05 |
| 2009 | 538.02 | 150.84 | 387.18 |
| 2014 | 324.27 | 66.87 | 257.40 |
| Year | All Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture within 600 m of Roads | Cleared Land for Upland Agriculture >600 m from Roads |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | 213.57 | 4.48 | 189.09 |
| 1998 | 351.63 | 60.03 | 291.60 |
| 2003 | 114.30 | 21.69 | 92.61 |
| 2008 | 151.20 | 49.68 | 101.52 |
| 2009 | 242.73 | 64.26 | 178.47 |
| 2014 | 218.34 | 50.40 | 167.94 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leisz, S.J.; Rounds, E.; The An, N.; Thi Bich Yen, N.; Nguyen Bang, T.; Douangphachanh, S.; Ninchaleune, B. Telecouplings in the East–West Economic Corridor within Borders and Across. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8121012
Leisz SJ, Rounds E, The An N, Thi Bich Yen N, Nguyen Bang T, Douangphachanh S, Ninchaleune B. Telecouplings in the East–West Economic Corridor within Borders and Across. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(12):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8121012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeisz, Stephen J., Eric Rounds, Ngo The An, Nguyen Thi Bich Yen, Tran Nguyen Bang, Souvanthone Douangphachanh, and Bounheuang Ninchaleune. 2016. "Telecouplings in the East–West Economic Corridor within Borders and Across" Remote Sensing 8, no. 12: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8121012
APA StyleLeisz, S. J., Rounds, E., The An, N., Thi Bich Yen, N., Nguyen Bang, T., Douangphachanh, S., & Ninchaleune, B. (2016). Telecouplings in the East–West Economic Corridor within Borders and Across. Remote Sensing, 8(12), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8121012






