Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data: An Analysis of the State of the Art
Abstract
:1. Introduction
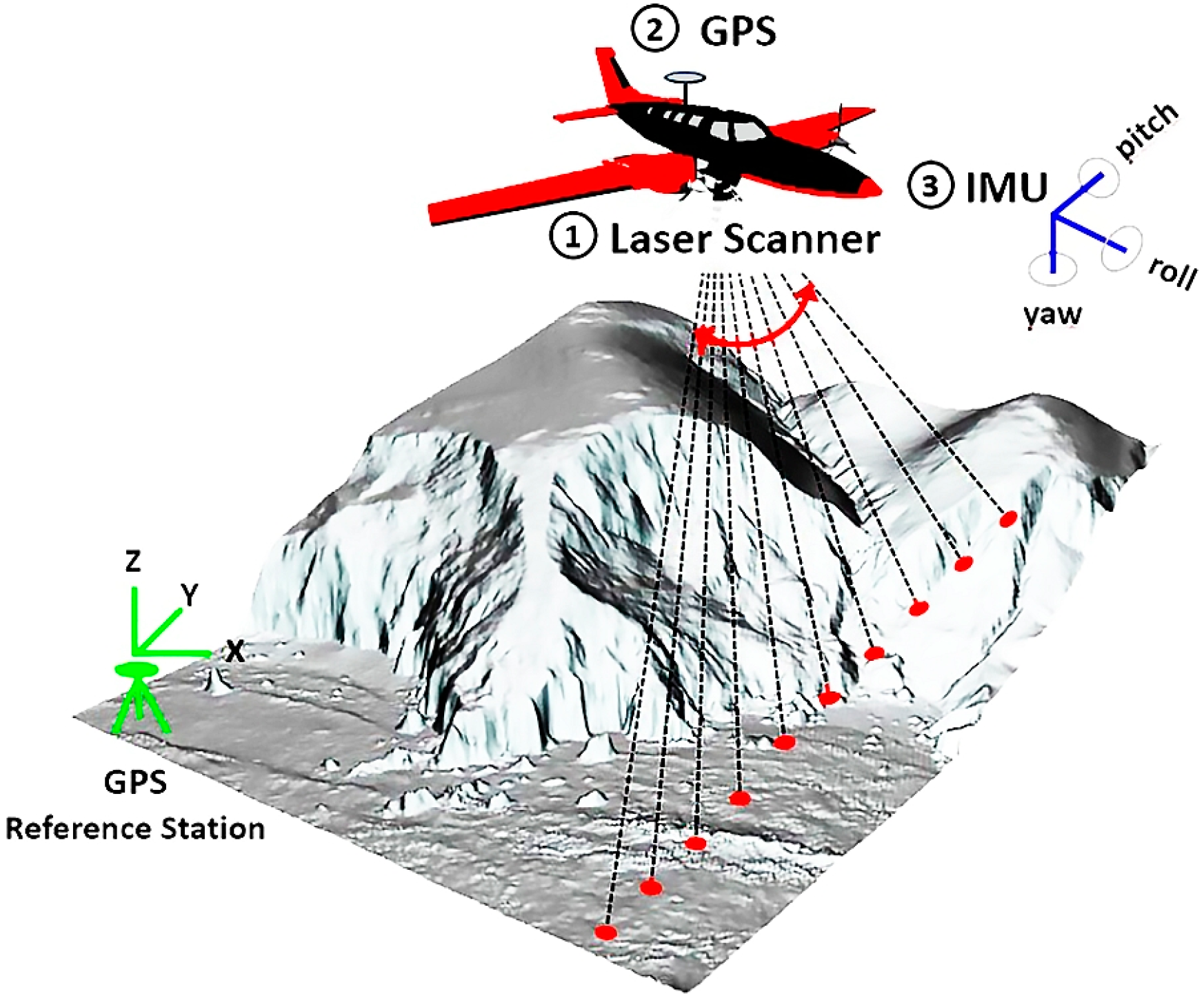
1.1. Short Overview of Airborne Laser Scanning
1.2. Problem Definition and Added Value of This Review Paper
- (a)
- 2D building polygon extraction describing the outlines of the building (roof outlines) from ALS based point cloud or fusion of ALS data with other data sources
- (b)
- 3D model reconstruction which represent generalized, abstracted and scaled virtual representation of the real building [8] based on the ALS data only or fusion of ALS data and other data sources, or
- (c)
- extracted roof contours in 3D (classified point cloud, generated 3D model or delineated roof as a set of planes in 3D space) from ALS data or fusion of ALS data and other sources.
2. Paper Selection Process and Overview of Search Results
2.1. Analysis of Peer-Reviewed Literature
- (a)
- Papers were selected based on citation count with a lower limit set at three citations
- (b)
- In case of more recent publications (published between 2013 and 2014) we opted for those with lower citation level than previous limit (three citations) and from higher ranked journals since they perform—in theory—a more strict review processes, and
- (c)
- We tried to avoid conference proceedings that are not peer reviewed and can be considered as grey literature (for publications published between 2013 and 2014).
| Operator | Search Term | Search location WoS/Scopus |
|---|---|---|
| Building* extraction* (LiDAR OR ALS) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords | |
| OR | Building* extraction* Airborne Laser Scanning | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* detection* (LiDAR OR ALS) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* (LiDAR OR Airborne Laser Scanning) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* delineation* from (LiDAR* OR Airborne Laser Scanning*) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* LiDAR* | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* Airborne* Laser* Scanning* | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* reconstruction* from (LiDAR* OR Airborne laser scanning) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Building* reconstruction* from point* cloud* | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Roof* Delineation* from (LiDAR OR Airborne Laser Scanning) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Roof* Extraction* from (LiDAR OR Airborne Laser Scanning) | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| OR | Roof* Delineation* from Point* Cloud* | Title/Title, Abstract, Keywords |
| Timespan: 1998–2014/Last time query was used: July 2014 |
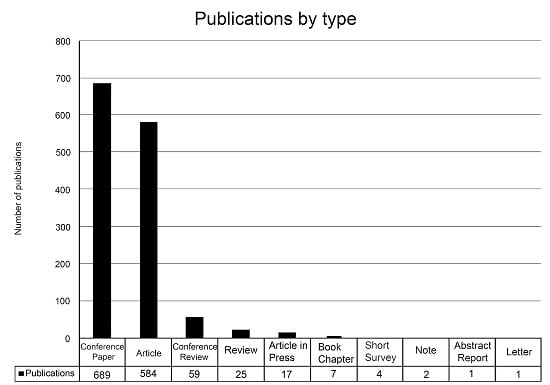
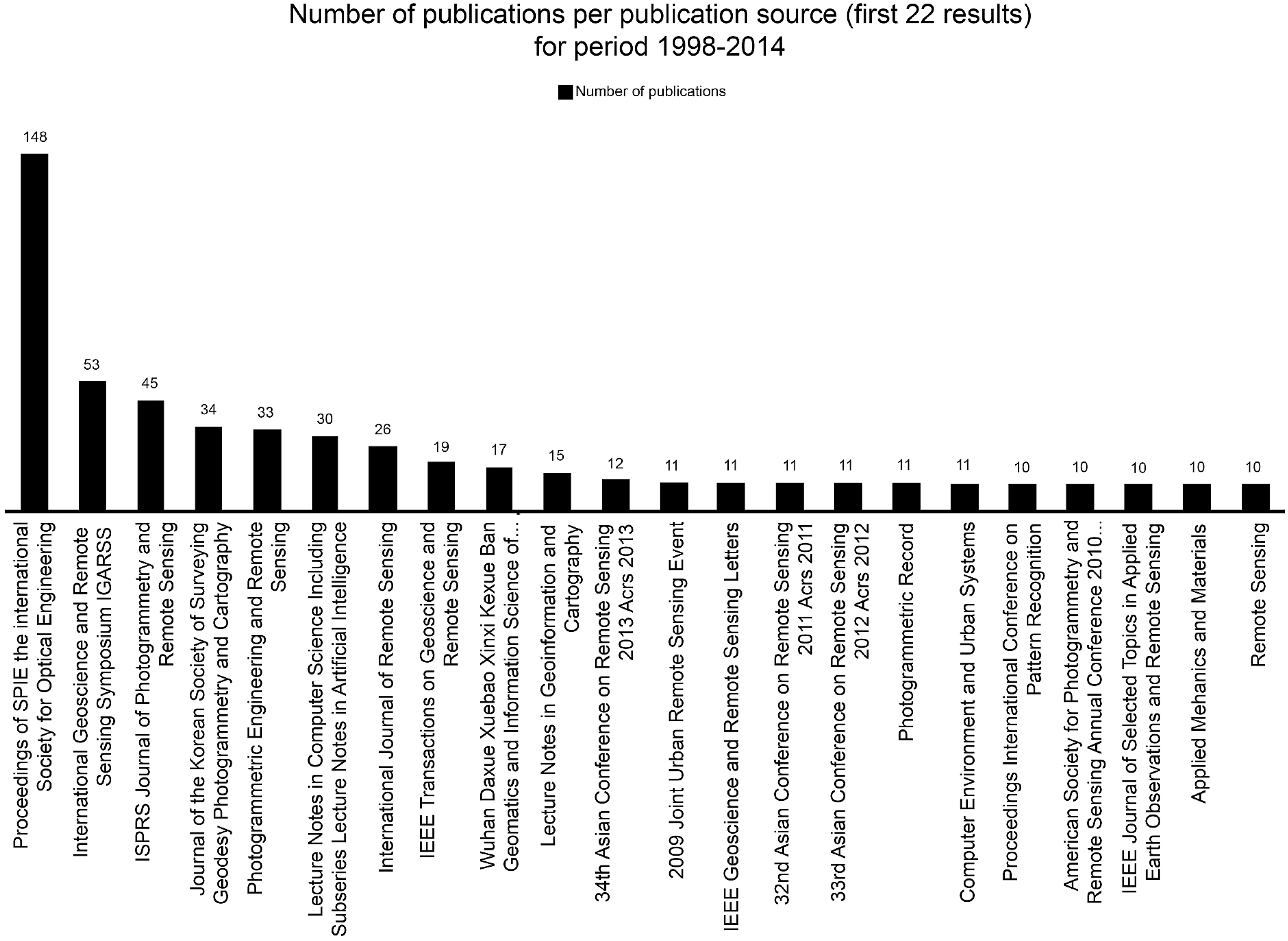
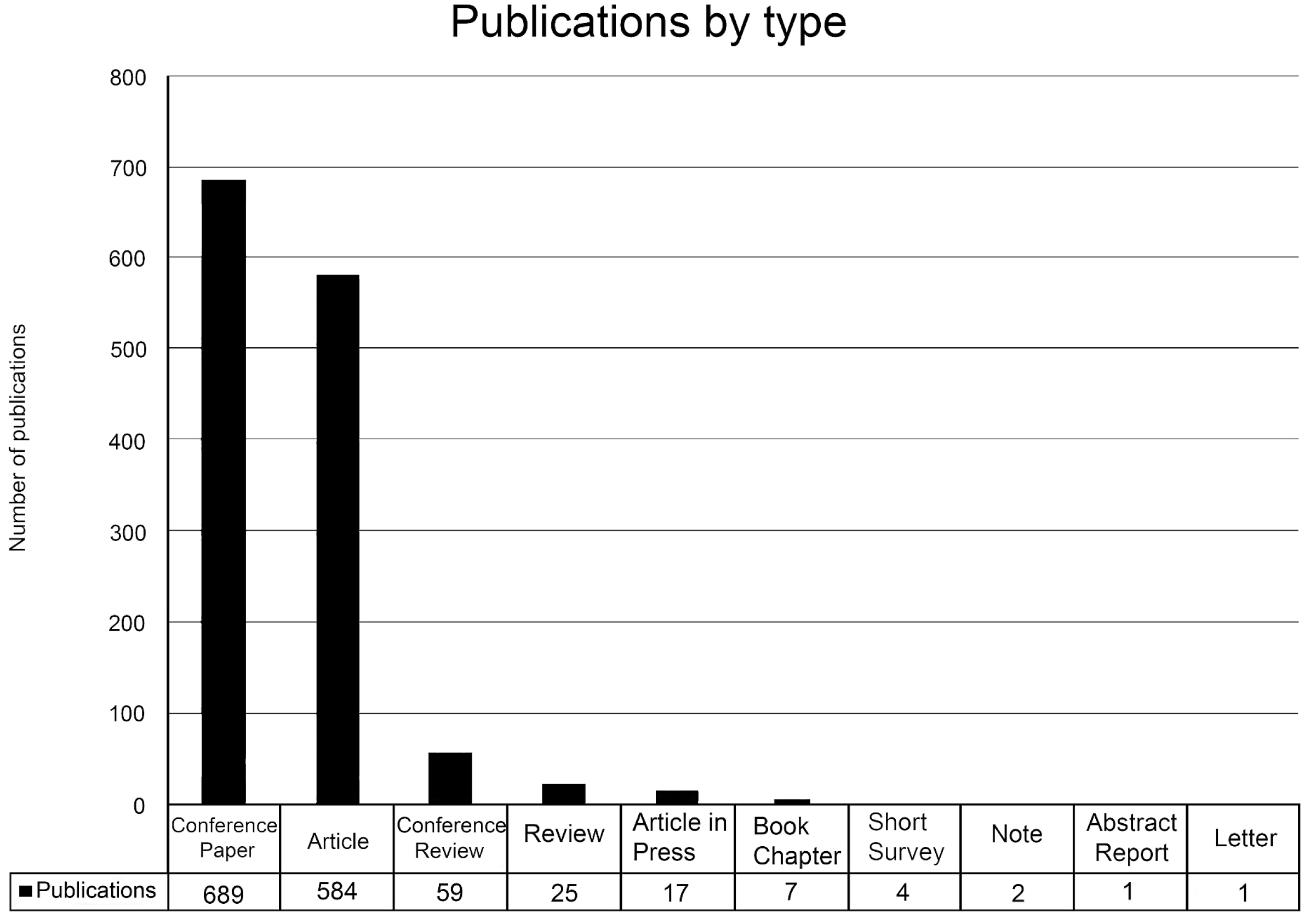
- Proceedings of SPIE the International Society for Optical Engineering (n = 148, h = 96)
- International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGRASS (n = 53, h = 31)
- ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (n = 45, h = 62)
- Journal of the Korean Society of Surveying Geodesy Photogrammetry and Cartography (n = 34, h = 3).
- Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing (n = 33, h = 78).
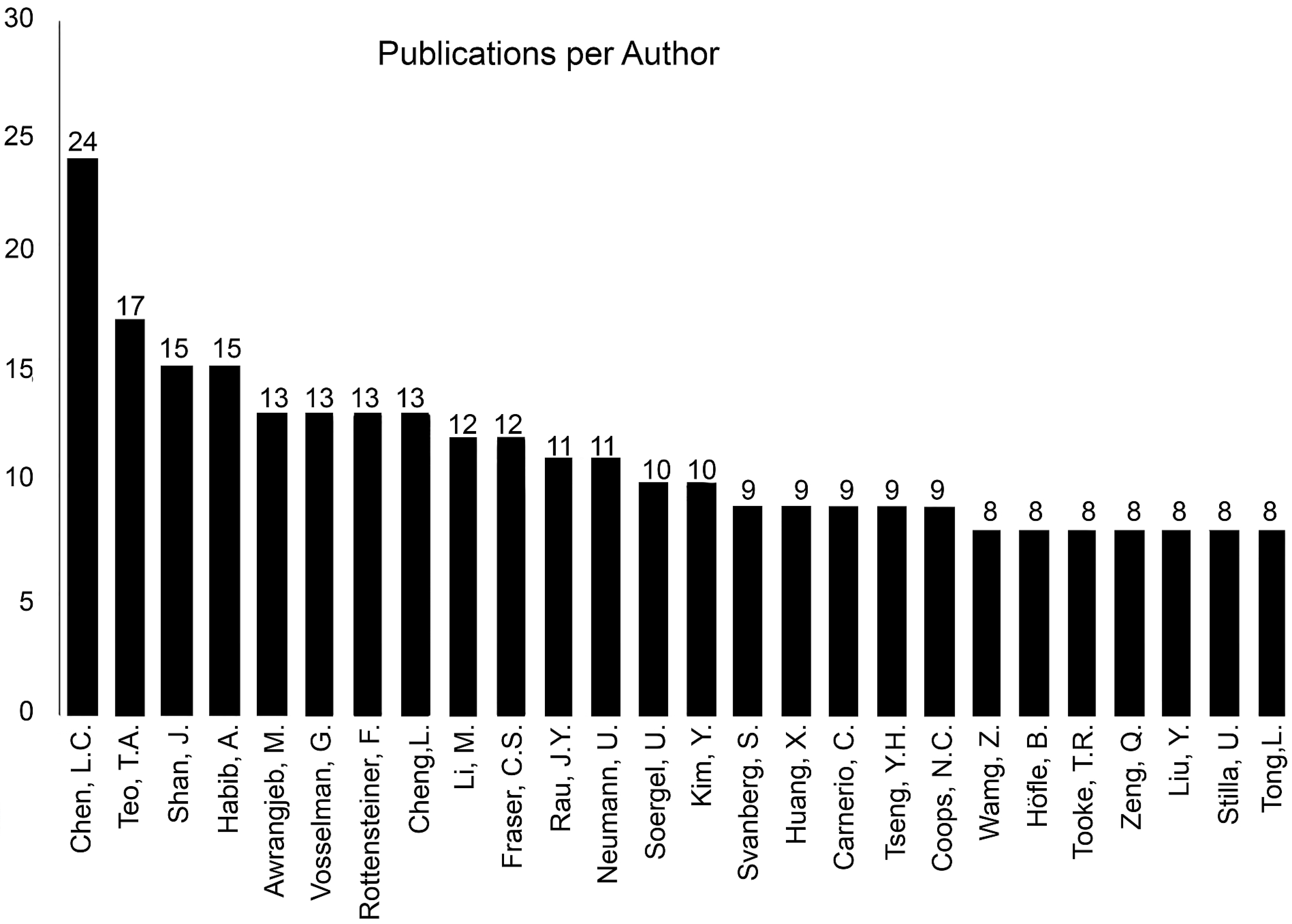
- Liang-Chien Chen (n = 24, h = 10)
- Tee-Ann Teo (n = 17, h = 7)
- Jie Shan (n = 15, h = 11) and Ayman Habib (n = 15, h = 16)
- Mohammad Awrangjeb (n = 13, h = 8), George Vosselman (n = 13, h = 16), Franz Rottensteiner (n = 13, h = 8) and Liang Cheng (n = 13, h = 5).
- Manchun Li (n = 12, h = 7) and Clive S. Fraser (n = 12, h = 20)
2.2. Additional Analysis of Non-Indexed Literature through Google Scholar
3. In-Depth Analysis of Gathered Literature
| Publication | Classes Extracted | Number of Publications |
|---|---|---|
| Conference proceedings | Buildings | 8 |
| Ground/Vegetation/Man-Made | 1 | |
| Tree, Grass land, Bare soil, Buildings | 1 | |
| Journal articles | Buildings | 34 |
| Ground, Tree, Roof edge, Rood ridge | 1 | |
| Ground/Buildings | 1 | |
| Roof | 6 | |
| Vegetation, Buildings, Art. Ground, Nat. Ground | 1 | |
| Buildings, Trees, Grass-covered areas | 1 |
3.1. Existing Methods for Building Extraction
| Year | Authors | Publication Type | Point Cloud Density | Type of Extracted Information | ALS System Used | Type of Additional Data Used | Data Set Origin | Data Set Size (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Kim and Habib | JA | 1.3 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 3100 | Aerial images | - | - |
| 2009 | Salah et al. | JA | 16 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 1225 | Multi-Spectral | University of New South Wales campus (Sydney, Australia) | <1 |
| 2010 | Sampath and Shan | JA | - | Roof | - | - | Purdue University campus, Indianapolis | - |
| 2010 | Awranjeb et al. | JA | - | Buildings | Optech | Multi-Spectral | Fairfield, Australia | <1 |
| 2010 | Matikainen et al. | JA | 3 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 3100 | Aerial images | Espoonlahti, Finland | 5 |
| 2010 | Kabolizade et al. | JA | - | Buildings | - | Aerial images | Taft, Iran | - |
| 2010 | Yu et al. | JA | 0.44 | Buildings | Terra-Point LLC | - | Houston, USA | 1 |
| 2011 | Guo et al. | JA | 2.5 | Vegetation, Building, Art. Ground, Nat. Ground | RIEGL LMS Q560 | Multi-Spectral | Biberach, Germany | 1 |
| 2011 | Elberink and Vosselman | JA | 20 | Buildings | - | - | Netherlands | - |
| 2011 | Kim and Shan | JA | 1 | Roof | Optech ALTM 1210 | - | Purdue University campus, Indianapolis | - |
| 2011 | Hermosilla et al. | JA | 2 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 3025 | Aerial images | Valencia (Spain) | - |
| 2011 | Cheng et al. | JA | 1 | Buildings | - | Aerial images | - | <1 |
| 2012 | Awranjeb et al. | JA | 1 | Buildings | - | Aerial images | Australia: Fairfield, Moonee Ponds, Knox and Hobart | <1 |
| 2012 | Aparecida dos Santos Galvanin and Dal Poz | JA | 2 | Roof | LACTEC | - | Curitiba/Brazil | 10 |
| 2012 | Jochem et al. | JA | 17 | Roof | Leica ALS50 | - | Feldkirch, Austria | 49 |
| 2013 | Sun and Salvaggio | JA | 4 | Buildings | - | - | Greater Rochester, NY, USA | <1 |
| 2013 | Liu et al | JA | 6.7 | Buildings | Leica ALS50 | - | Vaihingen, Germany | - |
| 2013 | Yu et al. | JA | 6.7 | Buildings | Leica ALS50 | - | “Downtown Toronto” and “Vaihingen” | 1.45 |
| 2013 | Susaki | JA | 0.7 | Buildings | - | Aerial images | Higashiyama ward of Kyoto, Japan | <1 |
| 2013 | Cheng et al. | JA | 1 | Buildings | - | - | - | 4 |
| 2013 | Awranjeb et al. | JA | 35 | Ground, Tree, Roof edge, Roof ridge | - | Multi-Spectral | Aitkevale, Queensland, Australia | <1 |
| 2014 | Suyoung et al. | JA | 1.02 | Buildings | - | - | Kyungpook National University campus in Daegu, South Korea | <1 |
| 2014 | Kong et al. | JA | - | Roof | - | Aerial images | - | <1 |
| 2014 | Niemeyer et al. | JA | 6.7 | Buildings | Leica ALS50 | - | Vaihingen, Germany | - |
| 2014 | Mongus et al. | JA | 6.7 | Ground/Buildings | - | - | Vaihingen, Germany/Toronto Canada | 10 |
| NON ISI-INDEXED ARTICLES | ||||||||
| 1998 | Wang and Schenk | CP | 0.5 | Buildings | - | - | Airport/Place unknown | - |
| 2000 | Morgan and Tempfli | CP | 2-3 | Buildings | TopoSys | - | Haren/Netherlands | - |
| 2000 | Wang and Schenk | CP | 0.2 | Buildings | - | Aerial images | - | 0.4 |
| 2002 | Rottensteiner and Briese | CP | 0.1 | Buildings | - | - | Vienna/Austria | 0.1 |
| 2002 | Morgan and Habib | CP | 1.5 | Buildings | - | - | - | <1 |
| 2002 | Elaksher and Bethel | CP | - | Buildings | - | - | - | <1 |
| 2003 | Sohn and Dowman | CP | 0.3 | Buildings | - | IKONOS imagery | Greenwich/London | <1 |
| 2004 | Cho et al. | CP | 0.2 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 1020 | - | Chungjoo/Korea | <1 |
| 2008 | Zhou and Neumann | CP | 6-17 | Buildings | - | - | Denvor & Oakland / USA | - |
| 2008 | Wei | CP | 6 | Buildings | Optech | - | Malaysia | - |
| 2008 | Ekhtari et al. | CP | 9 | Buildings | - | - | - | - |
| 2008 | Sampath and Shan | CP | - | - | - | - | - | <1 |
| 2009 | Kada and McKinely | CP | Buildings | - | - | East Berlin & Cologne | >400 | |
| 2009 | Höfle et al. | CP | 3 | Buildings | Optech ALTM 2050 | ‘ | Hohenems/Austria | 0.35 |
3.1.1. Building Extraction Methods Dealing with 3D Object Extraction
3.1.2. Building Extraction Methods Dealing with 2D Object Extraction
3.1.3. Methodologies Identified in Non-ISI Indexed Articles
3.2. Analysis of Gathered Building Extraction Accuracies
| Year | Author | Addition Data | Reference Data for Accuracy Assessment | Accuracy | Method for Accuracy Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | Haithcoat et al. | N/A | Manually digitized air photography | 100% | Completeness |
| 2002 | Krishnamoorthy et al. | N/A | Manually segmented and labeled DSM | >82% | Classification rate (%) |
| 2003 | Rottensteiner | Aerial images | Aerial images | <0.40 | Distribution of RSME of the planar fit |
| 2005 | Chen et al. | Aerial images | Aerial images | >81% | Correctness |
| 2006 | Zhang et al. | N/A | Aerial images and building footprint map | 12% | Omission/Commission |
| 2007 | Sohn and Dowman | IKONOS | Ordnance Survey MasterMap | 90.01% | Correctness |
| 2007 | Rottensteiner et al. | Multi-Spectral | Rasterized reference polygons from imagery | 87% | Pixel detection level |
| 2007 | Miliaresis and Kokkas | N/A | Digitized building outlines | 0.097 | Mean square error |
| 2008 | Dorninger and Pfeifer | N/A | Point acquired by tacheometer | 75% | Properly modeled buildings |
| 2008 | Lee et al. | Aerial images | Digital ground truth map | 89.9% | Overlapped pixel number |
| 2009 | Vu et al. | Orthoimage | Manually digitized building footprints | 82.98% | Correctness |
| 2009 | Alexander et al. | N/A | Manually created building model from stereo images | 86.2% | Overall users accuracy |
| 2009 | Kim and Habib | Aerial images | Manually derived ground truth data | 95% | Correctness |
| 2009 | Salah et al. | Multi-Spectral | Manually digitized buildings | 89.5% | Correctness |
| 2010 | Awrangjeb et al. | Multi-Spectral | Manual building tracing from orthoimagery | 99.25% | Correctness |
| 2010 | Matikainen et al. | Aerial images | Digital map | 85% | Correctness |
| 2010 | Kabolizade et al. | Aerial images | Aerial imagery | 96% | Shape accuracy |
| 2010 | Yu et al. | N/A | Digital cadastral map | 96% | Random sampling |
| 2011 | Guo et al. | Multi-Spectral | Digital ground truth data | 3.20% | Omission error |
| 2011 | Kim and Shan | N/A | Original LiDAR data | 90% | Correctness |
| 2011 | Hermosilla et al. | Aerial images | Manually delineated buildings from imagery | 92.2% | Correctness |
| 2011 | Cheng et al. | Aerial images | True orthophoto and manually made 3D models | 95% | Correctness |
| 2012 | Awrangjeb et al. | Aerial images | Building polygons | 96% | Correctness |
| 2012 | Aparecida dos Santos Galvanin and Dal Poz | N/A | Manually extracted roof outlines from intensity | 91% | Completeness |
| 2012 | Jochem et al. | DSM/DTM | Digital Cadastral Map | >88.4% | Correctness |
| 2013 | Liu et al | N/A | ISPRS Benchmark data (2014) | >96% | Correctness |
| 2013 | Yu et al. | N/A | ISPRS Benchmark data (2014) | >96% | Correctness |
| 2013 | Susaki | Aerial images | Manual interpretation of aerial imagery | 76% | Correctness |
| 2013 | Cheng et al. | N/A | True orthophoto | 5.7%/8.7% | Commission/Omission |
| 2013 | Awrangjeb et al. | Multi-Spectral | Monoscopic image measurement with Barista software | >98% | Correctness |
| 2014 | Suyoung et al. | N/A | DSM in colour shaded mode | 0.65 | RMSE (m) X, Y and radial direction |
| 2014 | Niemeyer et al. | N/A | ISPRS Benchmark data (2014) | >96% | Correctness |
| 2014 | Mongus et al. | N/A | ISPRS Benchmark data (2014) | >96% | Correctness |
3.3. Analysis of the Dataset Size in Respect to the Area of the Used Dataset
| Year | Author | Test Area | Area Size sq km | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | Maas and Vosselman | Netherlands | 1.25 | |||
| 1999 | Haala and Brenner | Karlsruhe, Germany | - | |||
| 2000 | Priestnall et al. | Trent floodplain at Newark-on-Trent, Nottinghamshire, UK | - | |||
| 2000 | Gamba and Houshmand | Los Angeles | 2 | |||
| 2001 | Stilla et al. | Frankfurt airport | <1 | |||
| 2001 | Nardinocchi an Scaioni | Pavia/Italy | - | |||
| 2002 | Krishnamoorthy et al. | Stockholm, Belgium, Ravensburg and Baltimore | <1 | |||
| 2002 | Weed et al. | Austin campus area / University of Texas | <1 | |||
| 2003 | Rottensteiner | Vienna/Austria | <1 | |||
| 2003 | You et al. | USC Campus/Los Angeles | <1 | |||
| 2004 | Vu et al. | Roppongi, Tokyo, Japan | - | |||
| 2004 | Rottensteiner et al. | Memmingen / Germany | 4 | |||
| 2005 | Chen et al. | Science-based Industrial Park, Taiwan | - | |||
| 2006 | Zhang et al. | Campus, Florida International University | 6 | |||
| 2007 | Sohn and Dowman | Greenwich, London, UK | 1.4 | |||
| 2007 | Rottensteiner et al. | Fairfield, Australia and Memmingen, Germany | 4 | |||
| 2007 | Sampath and Shan | Baltimore, Maryland Toronto, Canada Purdue Uni Campus, Indiana | <1 | |||
| 2007 | Miliaresis and Kokkas | Bloomsbury area, London | 1 | |||
| 2008 | Lee et al. | Daejeon, Republic of Korea | 4 | |||
| 2009 | Vu et al. | Roppongi, Tokyo, Japan | <1 | |||
| 2009 | Alexander et al. | Portbury, Bristol, UK | <1 | |||
| 2009 | Salah et al. | University of New South Wales campus (Sydney, Australia) | <1 | |||
| 2010 | Sampath and Shan | Purdue University campus, Indianapolis | - | |||
| 2010 | Awranjeb et al. | Fairfield, Australia | <1 | |||
| 2010 | Matikainen et al. | Espoonlahti, Finland | 5 | |||
| 2010 | Kabolizade et al. | Taft, Iran | - | |||
| 2010 | Yu et al. | Houston, USA | 1 | |||
| 2011 | Guo et al. | Biberach, Germany | 1 | |||
| 2011 | Elberink and Vosselman | Netherlands | - | |||
| 2011 | Kim and Shan | Purdue University campus, Indianapolis | - | |||
| 2011 | Hermosilla et al. | Valencia (Spain) | - | |||
| 2012 | Awranjeb et al. | Australia: Fairfield, Moonee Ponds, Knox and Hobart | <1 | |||
| 2012 | Aparecida dos Santos Galvanin and Dal Poz | Curitiba/Brazil | 10 | |||
| 2012 | Jochem et al. | Feldkirch, Austria | 49 | |||
| 2013 | Sun and Salvaggio | Greater Rochester, New York, USA | <1 | |||
| 2013 | Liu et al | Vaihingen, Germany | - | |||
| 2013 | Yu et al. | “Downtown Toronto” and “Vaihingen” | 1.45 | |||
| 2013 | Susaki | Higashiyama ward of Kyoto, Japan | <1 | |||
| 2013 | Awranjeb et al. | Aitkevale, Queensland, Australia | <1 | |||
| 2014 | Suyoung et al. | Kyungpook National University campus in Daegu, South Korea | <1 | |||
| 2014 | Niemeyer et al. | Vaihingen, Germany | - | |||
| 2014 | Mongus et al. | Vaihingen, Germany/Toronto Canada | 10 | |||
| NON-ISI Indexed Literature | ||||||
| 1998 | Wang and Schenk | Airport/Place unknown | - | |||
| 2000 | Morgan and Tempfli | Haren/Netherlands | - | |||
| 2000 | Wang and Schenk | - | 0.4 | |||
| 2002 | Rottensteiner and Briese | Vienna/Austria | 0.1 | |||
| 2002 | Morgan and Habib | - | <1 | |||
| 2002 | Elaksher and Bethel | - | <1 | |||
| 2003 | Sohn and Dowman | Greenwich/London | <1 | |||
| 2004 | Cho et al. | Chungjoo/Korea | <1 | |||
| 2008 | Zhou and Neumann | Denver & Oakland/USA | - | |||
| 2008 | Wei | Malaysia | - | |||
| 2008 | Sampath and Shan | - | <1 | |||
| 2009 | Kada and McKinely | East Berlin and Cologne | >400 | |||
| 2009 | Höfle et al. | Hohenems/Austria | 0.35 | |||
3.4. Use of Auxiliary Data for Building Object Extraction
4. Discussion
4.1. Observed Trends and Remaining Challenges

4.2. Prediction of Future Trends
- Generation of automated approaches for building delineation from ALS data sources in 2D (polygon representation) and 3D models.
- Full transition from 2D to 3D approaches and thus preserving all the valuable data within the 3D data source.
- Generation of methods, which are applicable to datasets which incorporate large areas. (emergency response, derivation of change detection within hours not days).
- Formation of transferable methods, which will be exempt from parameter modification – the generation of a “One-Click” solution for object extraction.
- Deeper integration of ALS data with other sensors (imagery, terrestrial + airborne + mobile laser scanning, point clouds from dense image matching) in order to improve the temporal, spectral and spatial resolution of the data.
- Formation of standards regarding processing and deliverables of ALS systems.
- Formation of standards for quality assessment of derived outputs from ALS data source. Increase in interdisciplinary development and research (e.g., between photogrammetry/LiDAR community, satellite image remote sensing, group GEOBIA, GIScience, computer vision, etc.)
- Developed system solution for building inventory updating from different ALS data sets over time.
5. Conclusions
- Fully automated extraction of either building models (3D) or building outlines (2D).
- Transferable methods which are applicable to any point cloud data obtained from ALS systems
- A set of well-defined accuracy metrics which is needed to establish a cross comparable measure of accuracy.
- High quality reference data sets for accuracy assessment should make manually (self-)digitized reference data sets redundant.
- Use of large area data sets in order to fully proof solutions to real world problems in many applications.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altmaier, A.; Kolbe, T. Applications and solutions for interoperable 3D geo-visualization. In Proceedings of the Photogrammetric Week, Stuttgart, Germany, 1–5 September 2003; pp. 1–15.
- Höfle, B.; Rutzinger, M. Topographic airborne LiDAR in geomorphology: A technological perspective. Zeitschrift für Geomorphol. 2011, 55, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G.; Maas, H.G. Airborne and Terrestrial Laser Scanning; Whittles Publishing: Dunbeath, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Höfle, B.; Pfeifer, N. Correction of laser scanning intensity data: Data and model-driven approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W. Radiometric calibration of small-footprint full-waveform airborne laser scanner measurements: Basic physical concepts. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Krzystek, P.; Heurich, M. Tree species classification and estimation of stem volume and DBH based on single tree extraction by exploiting airborne full-waveform LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitberger, J.; Krzystek, P.; Stilla, U. Analysis of full waveform LIDAR data for the classification of deciduous and coniferous trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, C.; Wang, Y.; Iercan, O. Airborne laser scanning: Methods for processing and automatic feature extraction for natural artificial objects. In Laser Scanning for the Environmental Sciences; Heritage, G., Large, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 115–133. [Google Scholar]
- Raber, G.T.; Jensen, J.R.; Schill, S.R.; Schuckman, K. Creation of digital terrain models using an adaptive lidar vegetation point removal process. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2002, 68, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Sithole, G.; Vosselman, G. ISPRS test on extracting DEMs from point clouds: A comparison of existing automatic filters. Available online: http://www.itc.nl/isprswgiii-3/filtertest/report.html (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Kraus, K.; Pfeifer, N. Advanced DTM generation from LIDAR data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2001, XXXIV-3/W4, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, K.; Pfeifer, N. Determination of terrain models in wooded areas with airborne laser scanner data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1998, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, P.; Székely, B. Automated detection and interpretation of geomorphic features in LiDAR point clouds. Vermessung Geoinf. 2011, 99, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; Anders, N.S.; Bouten, W. Geomorphological change detection using object-based feature extraction from multi-temporal lidar data. In Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 7–9 May 2012; pp. 484–489.
- Laycock, R.; Day, A. Automatically generating large urban environments based on the footprint data of buildings. In Proceedings of the Symposium on solid modeling and applications, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–20 June 2003; pp. 346–351.
- Vu, T.T.; Yamazaki, F.; Matsuoka, M. Multi-scale solution for building extraction from LiDAR and image data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliaresis, G.; Kokkas, N. Segmentation and object-based classification for the extraction of the building class from LIDAR DEMs. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, G.; Dowman, I. Data fusion of high-resolution satellite imagery and LiDAR data for automatic building extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Habib, A. Object-based integration of photogrammetric and LiDAR data for automated generation of complex polyhedral building models. Sensors 2009, 9, 5679–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, T.; Ruiz, L.A.; Recio, J.A.; Estornell, J. Evaluation of automatic building detection approaches combining high resolution images and LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1188–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Salvaggio, C. Aerial 3D building detection and modeling from airborne LiDAR point clouds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Guan, H.; Wang, C. A marked point process for automated building detection from lidar point-clouds. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, J.; Rottensteiner, F.; Soergel, U. Contextual classification of lidar data and building object detection in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, S.; Huang, J. Rapid extraction and updating of road network from airborne LiDAR data. In Proceedings of IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR), Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 October 2011; pp. 1–7.
- Han, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, M.; Sunwoo, M. Enhanced road boundary and obstacle detection using a downward-looking LIDAR sensor. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technol. 2012, 61, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clode, S.; Kootsookos, P.; Rottensteiner, F. The automatic extraction of roads from lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2004, 35, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Tao, C.V. Automatic road extraction from dense urban area by integrated processing of high resolution imagery and lidar data. Int. Arc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2004, 35, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Livny, Y.; Yan, F.; Olson, M.; Chen, B. Automatic reconstruction of tree skeletal structures from point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2007, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Russeltsfnswgovau, R.T. 3D modelling of individual trees using full-waveform lidar. Available online: http://www.sage.unsw.edu.au/snap/publications/park_etal2009a.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Swatantran, A.; Dubayah, R.; Roberts, D.; Hofton, M.; Blair, J.B. Mapping biomass and stress in the Sierra Nevada using lidar and hyperspectral data fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2917–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.; Nichol, C.; Woodhouse, I. Recovery of forest canopy parameters by inversion of multispectral LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, P.; Boyer, K.L.; Flynn, P.J. Robust detection of buildings in digital surface models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2002; pp. 159–163.
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, W.; Han, P.; Zhang, W.; Shan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Building region derivation from LiDAR data using a reversed iterative mathematic morphological algorithm. Opt. Commun. 2013, 286, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilla, U.; Soergel, U.; Thoennessen, U.; Michaelsen, E. Segmentation of LIDAR and InSAR elevation data for building reconstruction. In Automatic Extraction of Man-Made Objects from Aerial and Space Images (iii); Lisse, Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Haala, N.; Brenner, C. Extraction of buildings and trees in urban environments. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Sui, L. Building contours extraction from light detect and ranging data. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Photonics and Optoelectronics (SOPO), Wuhan, China, 16–18 May 2011; pp. 1–3.
- Reuters, T. Web of Science. Available online: http://scientific.thomson.com/isi/ (accessed on 26 March 2015).
- Elsevier Scopus. Available online: http://www.scopus.com/ (accessed on 26 March 2015).
- Google Google Scholar. Available online: http://scholar.google.at/ (accessed on 26 March 2015).
- Harzing, A.W. Publish or Perish. Available online: http://www.harzing.com/pop.htm (accessed on 26 March 2015).
- Maas, H.-G.; Vosselman, G. Two algorithms for extracting building models from raw laser altimetry data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, B.; Yang, X.; Li, N.; Wu, H. Automatic buildings extraction from LiDAR data in urban area by neural oscillator network of visual cortex. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yan, J.; Chen, S. Automatic construction of building footprints from airborne LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F. Automatic generation of high-quality building models from lidar data. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2003, 23, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, P.; Pfeifer, N. A comprehensive automated 3D approach for building extraction, reconstruction, and regularization from airborne laser scanning point clouds. Sensors 2008, 8, 7323–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Kumar, R.; Hsu, S. 3D building detection and modeling from aerial lidar data. Comput. Vis. Pattern 2006, 2, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath, A.; Shan, J. Segmentation and reconstruction of polyhedral building roofs from aerial lidar point clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Houshmand, B. Digital surface models and building extraction: A comparison of IFSAR and LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Shan, J. Building roof modeling from airborne laser scanning data based on level set approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Teo, T.; Rau, J. Building reconstruction from LIDAR data and aerial imagery. In Proceedings 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; Volume 4, pp. 2846–2849.
- Cheng, L.; Gong, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. 3D building model reconstruction from multi-view aerial imagery and lidar data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, P.; Nothegger, C. 3D segmentation of unstructured point clouds for building modelling. Photogramm. Image Anal. Proc. 2007, 36, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Awrangjeb, M.; Zhang, C.; Fraser, C. S. Automatic extraction of building roofs using LIDAR data and multispectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestnall, G.; Jaafar, J.; Duncan, a. Extracting urban features from LiDAR digital surface models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2000, 24, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Trinder, J.; Clode, S.; Kubik, K. Building detection by fusion of airborne laser scanner data and multi-spectral images: Performance evaluation and sensitivity analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, A.; Shan, J. Building boundary tracing and regularization from airborne LiDAR point clouds. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awrangjeb, M.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Fraser, C.S. Automatic detection of residential buildings using LIDAR data and multispectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chehata, N.; Mallet, C.; Boukir, S. Relevance of airborne lidar and multispectral image data for urban scene classification using Random Forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Automated derivation of urban building density information using airborne LiDAR data and object-based method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 98, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awrangjeb, M.; Zhang, C.; Fraser, C.S. Building detection in complex scenes thorough effective separation of buildings from trees. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabolizade, M.; Ebadi, H.; Ahmadi, S. An improved snake model for automatic extraction of buildings from urban aerial images and LiDAR data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2010, 34, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, L.; Hyyppä, J.; Ahokas, E.; Markelin, L.; Kaartinen, H. Automatic detection of buildings and changes in buildings for updating of maps. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1217–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.; Trinder, J.; Shaker, A. Evaluation of the self-organizing map classifier for building detection from lidar data and multispectral aerial images. J. Spat. Sci. 2009, 54, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Trinder, J.; Clode, S.; Kubik, K.; Lovell, B.C. Building detection by Dempster-Shafer fusion of LIDAR data and multispectral aerial imagery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 24–26 August 2004; pp. 339–342.
- Mongus, D.; Lukač, N.; Žalik, B. Ground and building extraction from LiDAR data based on differential morphological profiles and locally fitted surfaces. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Sohn, G.; Gerke, M.; Wegner, J.D.; Breitkopf, U.; Jung, J. Results of the ISPRS benchmark on urban object detection and 3D building reconstruction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.; Tempfli, K. Automatic building extraction from airborne laser scanning data. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 616–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Schenk, T. Building extraction and reconstruction from LiDAR data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2000, XXXIII, 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Briese, C. A new method for building extraction in urban areas from high-resolution LIDAR data. Int. Arc. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2002, 34, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, M.; Habib, A. Interpolation of lidar data and automatic building extraction. Available online: http://twiki.cis.rit.edu/twiki/pub/Main/FengAndSteveSIMG786/interpolationoflidardataandautomaticbuildingextraction.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Elaksher, A.F.; Bethel, J.S. Building extraction using LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the ASPRS-ACSM Annual Conference and FIG XXII Congress, Washington, DC, USA, 22–26 April 2002.
- Sohn, G.; Dowman, I. Building extraction using Lidar DEMs and Ikonos images. Available online: http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXIV/3-W13/papers/Sohn_ALSDD2003.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Cho, W.; Jwa, Y.; Chang, H.; Lee, S. Pseudo-Grid based building extraction using airborne LIDAR data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress Istanbul 2004, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; pp. 3–6.
- Zhou, Q.-Y.; Neumann, U. Fast and extensible building modeling from airborne LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems—GIS ’08, Irvine, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2008.
- Sampath, A.; Shan, J. Building roof segmentation and reconstruction from LiDAR point clouds using clustering techniques. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kada, M.; McKinley, L. 3D building reconstruction from LiDAR based on a cell decomposition approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2009, 38, W4. [Google Scholar]
- Höfle, B.; Mücke, W.; Dutter, M.; Rutzinger, M.; Dorninger, P. Detection of building regions using airborne LiDAR—A new combination of raster and point cloud based GIS methods. Available online: http://www.agit.at/php_files/myagit/papers/2009/7504.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Höfle, B.; Vetter, M. Water surface mapping from airborne laser scanning using signal intensity and elevation data. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2009, 34, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schenk, T. Extracting building information from lidar data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission III Symposium on Object Recognition and Scene Classification from Multispectral and Multisensor Pixels, Columbus, OH, USA, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 279–284.
- Wei, S. Building boundary extraction based on lidar point clouds data. Available online: http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXVII/congress/3b_pdf/37.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Ekhtari, N.; Sahebi, M. Automatic building detection from LIDAR point cloud data. Available online: http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXVII/congress/4_pdf/84.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Nardinocchi, C.; Scaioni, M. Building extraction from LIDAR data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ISPRS Joint Workshop on Remote Sensing and Data Fusion over Urban Areas, Rome, Italy, 8–9 November 2001; pp. 79–83.
- Weed, C.; Crawford, M.; Neuenschwander, A.; Gutierrez, R. Classification of LIDAR data using a lower envelope follower and gradient-based operator. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 1384–1386.
- Peternell, M.; Steiner, T. Reconstruction of piecewise planar objects from point clouds. Comput. Des. 2004, 36, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, V.; Wang, C.-J.; Banerjee, S. Lidar detection of underwater objects using a neuro-SVM-based architecture. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2006, 17, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongjian, Y.; Shiqiang, Z. 3D building reconstruction from aerial CCD image and sparse laser sample data. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Elberink, S.; Vosselman, G. Quality analysis on 3D building models reconstructed from airborne laser scanning data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Nguyen, T.; He, Q.; Hong, S. Global remote sensing research trends during 1991–2010: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2012, 96, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutzinger, M.; Rottensteiner, F.; Pfeifer, N. Extraction from airborne laser scanning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Sohn, G.; Jung, J. The ISPRS benchmark on urban object classification and 3D building reconstruction. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, I-3, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochem, A.; Höfle, B.; Wichmann, V.; Rutzinger, M.; Zipf, A. Area-wide roof plane segmentation in airborne LiDAR point clouds. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil-Dunne, J.P.M.; MacFaden, S.W.; Royar, A.R.; Pelletier, K.C. An object-based system for LiDAR data fusion and feature extraction. Geocarto Int. 2012, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Vosselman, G. Fusion of laser scanning data, maps, and aerial photographs for building reconstruction. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 85–88.
- Susaki, J. Knowledge-Based modeling of buildings in dense urban areas by combining airborne LiDAR data and aerial images. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5944–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Li, S. K-plane-based classification of airborne LiDAR data for accurate building roof measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinecke, N.; Lueken, T.; Korn, B.R. Lidar simulation using graphics hardware acceleration. In Proceedings of the AIAA/IEEE Digital Avionics Systems Conference, St. Paul, MN, USA, 26–30 October 2008; pp. 4D41–4D48.
- Evans, J.S.; Hudak, A.T.; Faux, R.; Smith, A.M.S. Discrete return lidar in natural resources: Recommendations for project planning, data processing, and deliverables. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 776–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, H.; Hinz, S.; Bacher, U.; Baltsavias, E. A test of automatic road extraction approaches. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2006, 36, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.; Smith-Voysey, S.; Jarvis, C.; Tansey, K. Integrating building footprints and LiDAR elevation data to classify roof structures and visualise buildings. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomljenovic, I.; Rousell, A. Influence of point cloud density on the results of automated Object-Based building extraction from ALS data. In Proceedings of the AGILE 2014 International Conference on Geographic Information Science, Castellon, Spain, 3–6 June 2014.
- Cheng, L.; Tong, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Integration of LiDAR data and optical multi-view images for 3D reconstruction of building roofs. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, G.S.; Smith, G.J.; Crane, M.P.; Demas, C.R.; Robbins, L.L.; Lavoie, D.L. Science and the storms : The USGS response to the hurricanes of 2005. U.S. Geol. Surv. Circ. 2007, 1306, 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Klonner, C.; Barron, C.; Neis, P.; Höfle, B. Updating digital elevation models via change detection and fusion of human and remote sensor data in urban environments. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomljenovic, I.; Höfle, B.; Tiede, D.; Blaschke, T. Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data: An Analysis of the State of the Art. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3826-3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70403826
Tomljenovic I, Höfle B, Tiede D, Blaschke T. Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data: An Analysis of the State of the Art. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(4):3826-3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70403826
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomljenovic, Ivan, Bernhard Höfle, Dirk Tiede, and Thomas Blaschke. 2015. "Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data: An Analysis of the State of the Art" Remote Sensing 7, no. 4: 3826-3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70403826
APA StyleTomljenovic, I., Höfle, B., Tiede, D., & Blaschke, T. (2015). Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data: An Analysis of the State of the Art. Remote Sensing, 7(4), 3826-3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70403826