Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Soil Samples
| pH | ECe | CaCO3 | OM | Clay | Silt | Sand | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dSm−1 | % | ||||||
| Min | 7.10 | 3.30 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 16.00 |
| Max | 8.50 | 166.80 | 21.90 | 2.30 | 54.30 | 34.60 | 100.00 |
| Mean | 7.86 | 33.03 | 2.97 | 0.83 | 27.22 | 20.81 | 50.68 |
| St.dev | 0.29 | 31.33 | 3.07 | 0.52 | 16.77 | 10.21 | 26.63 |
| CV(100) * | 3.7 | 94.85 | 103.26 | 63.03 | 61.62 | 49.04 | 52.55 |
2.3. Soil Spectrometry and Spectral Characteristics of the Soils
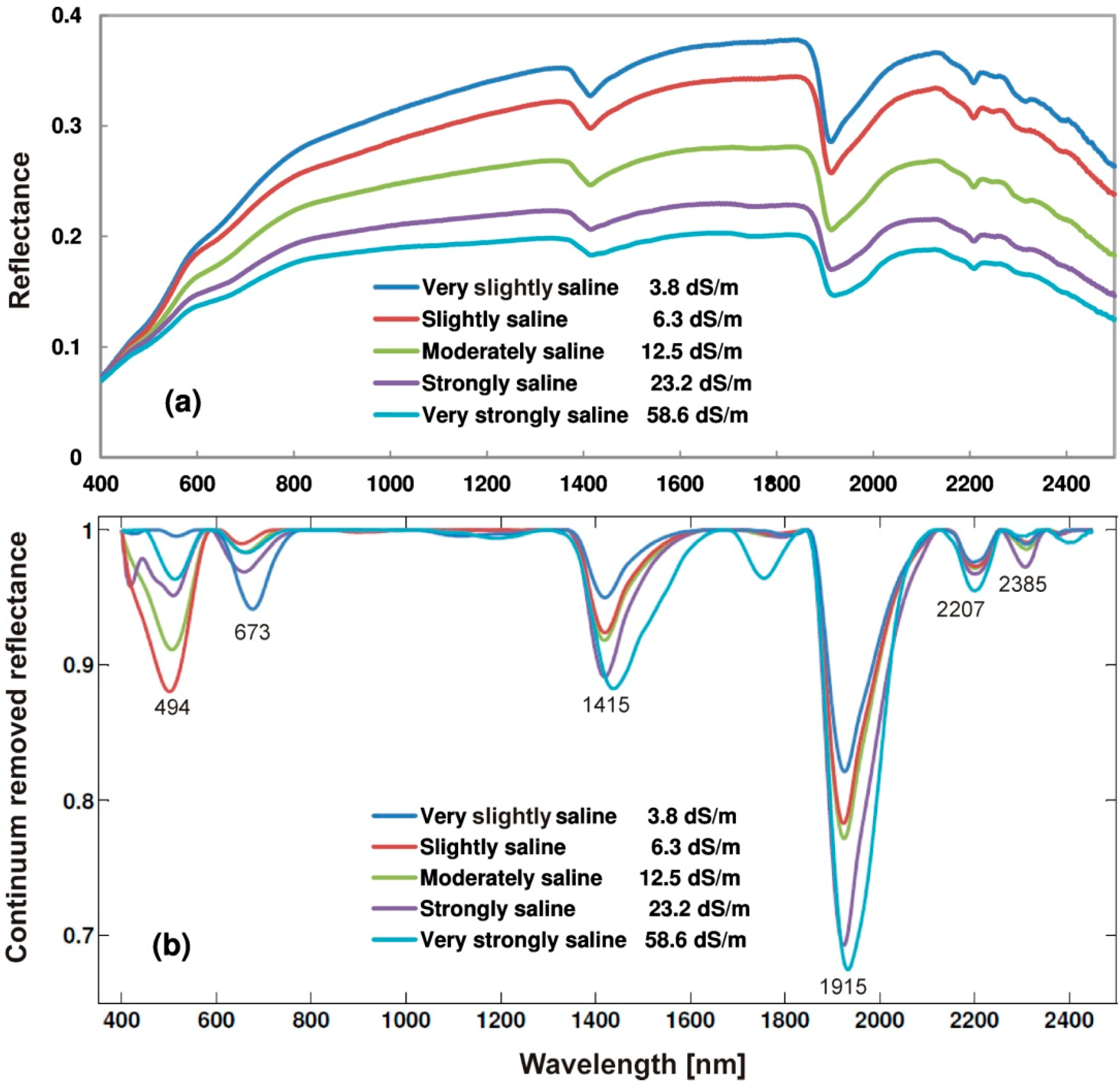
2.4. Soil Salinity Modeling
2.5. Estimation of Soil Salinity Based on Landsat Data
2.5.1. Landsat Data Pre-Processing
2.5.2. Application of the PLSR and MARS Models to Landsat Data
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of ETM+ Data

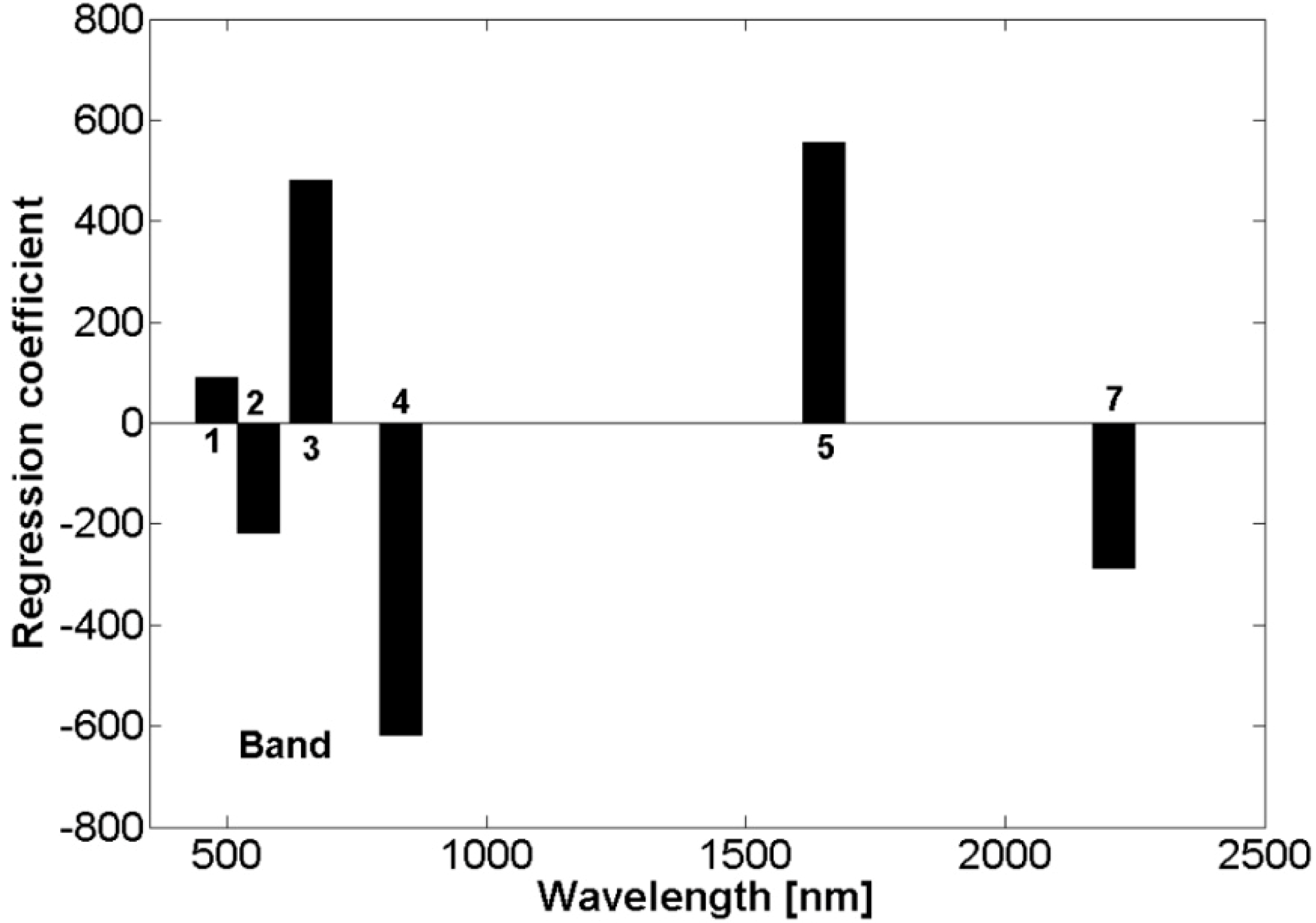
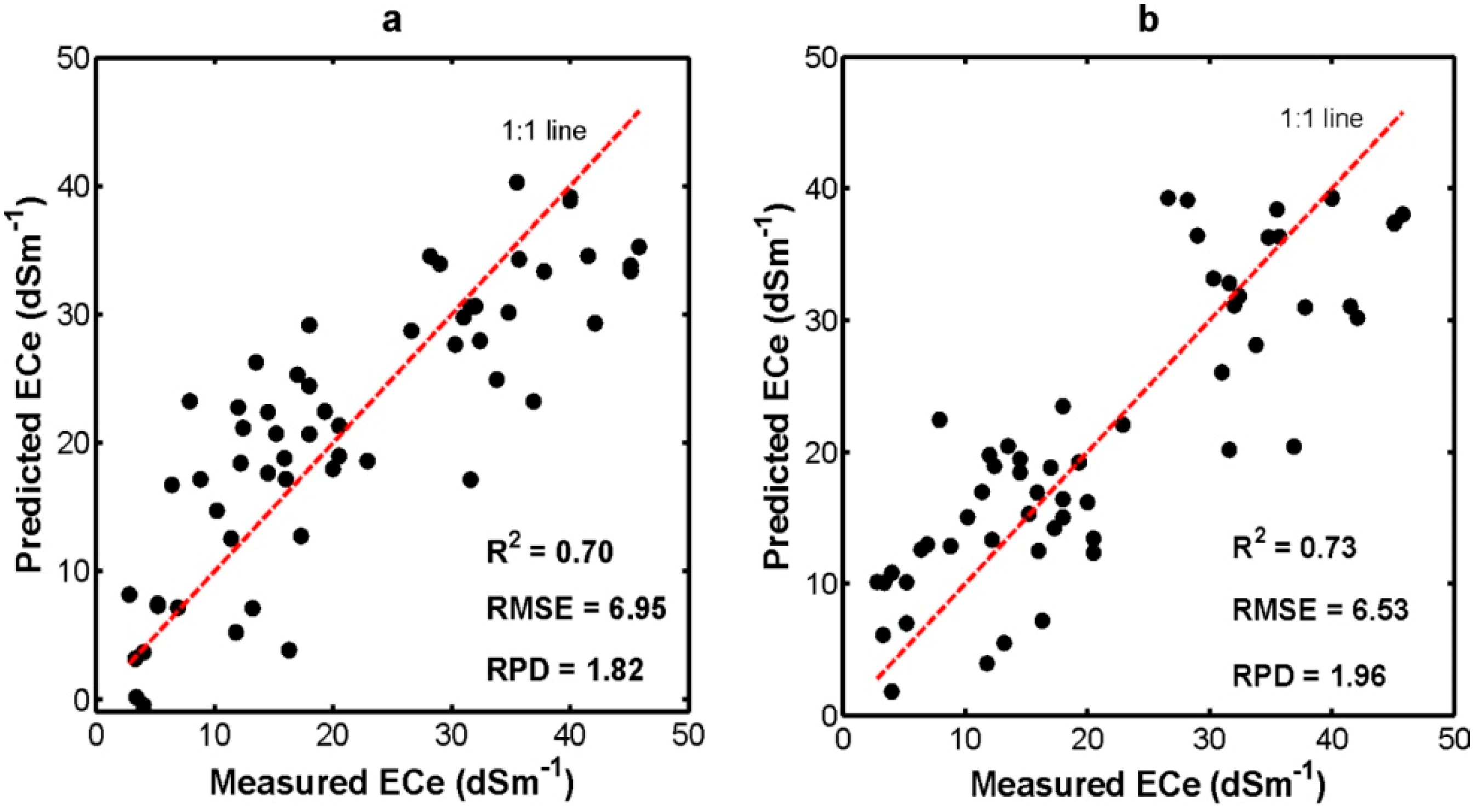
3.2. Soil Salinity Estimation Using the PLSR and MARS Models
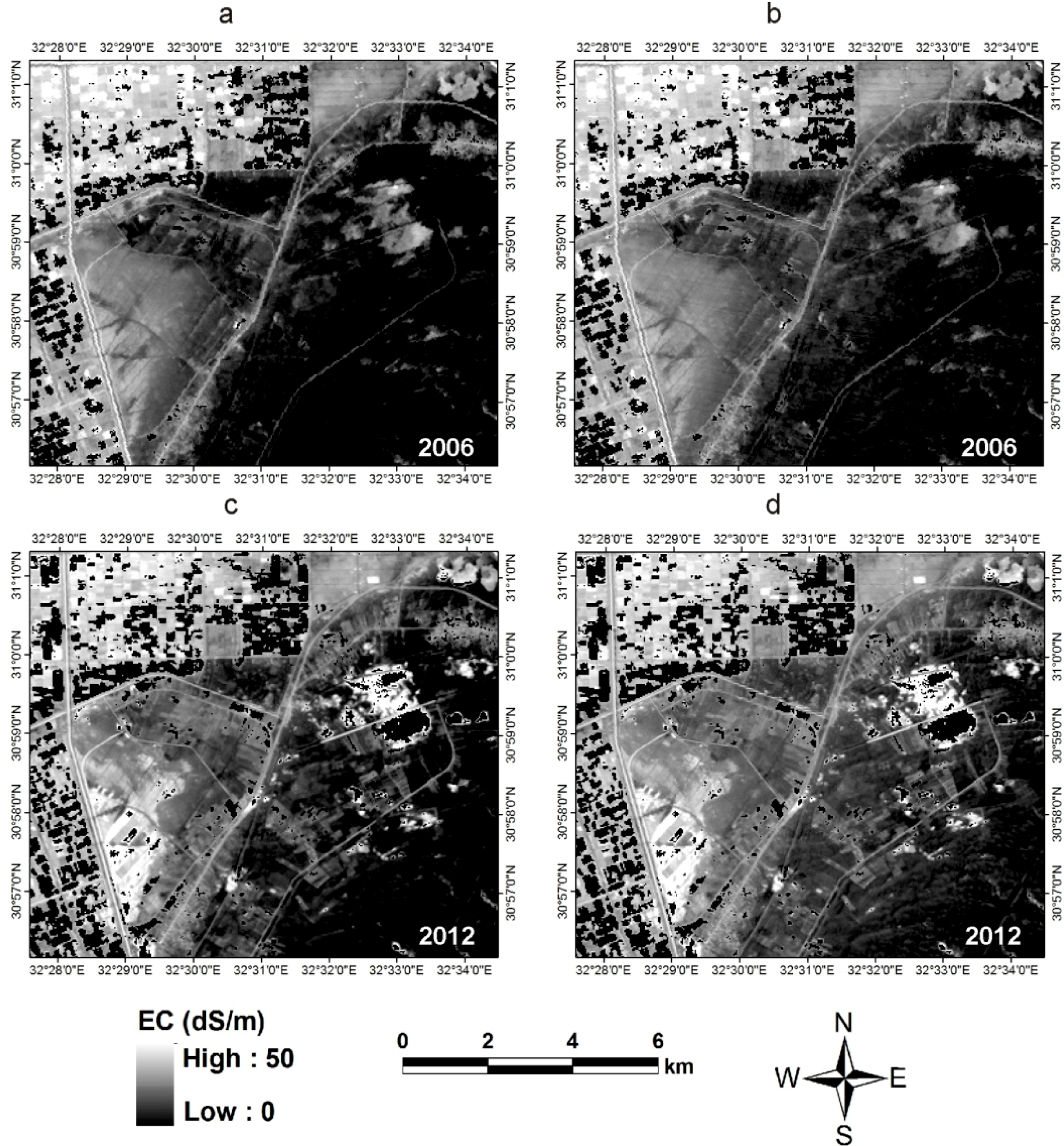
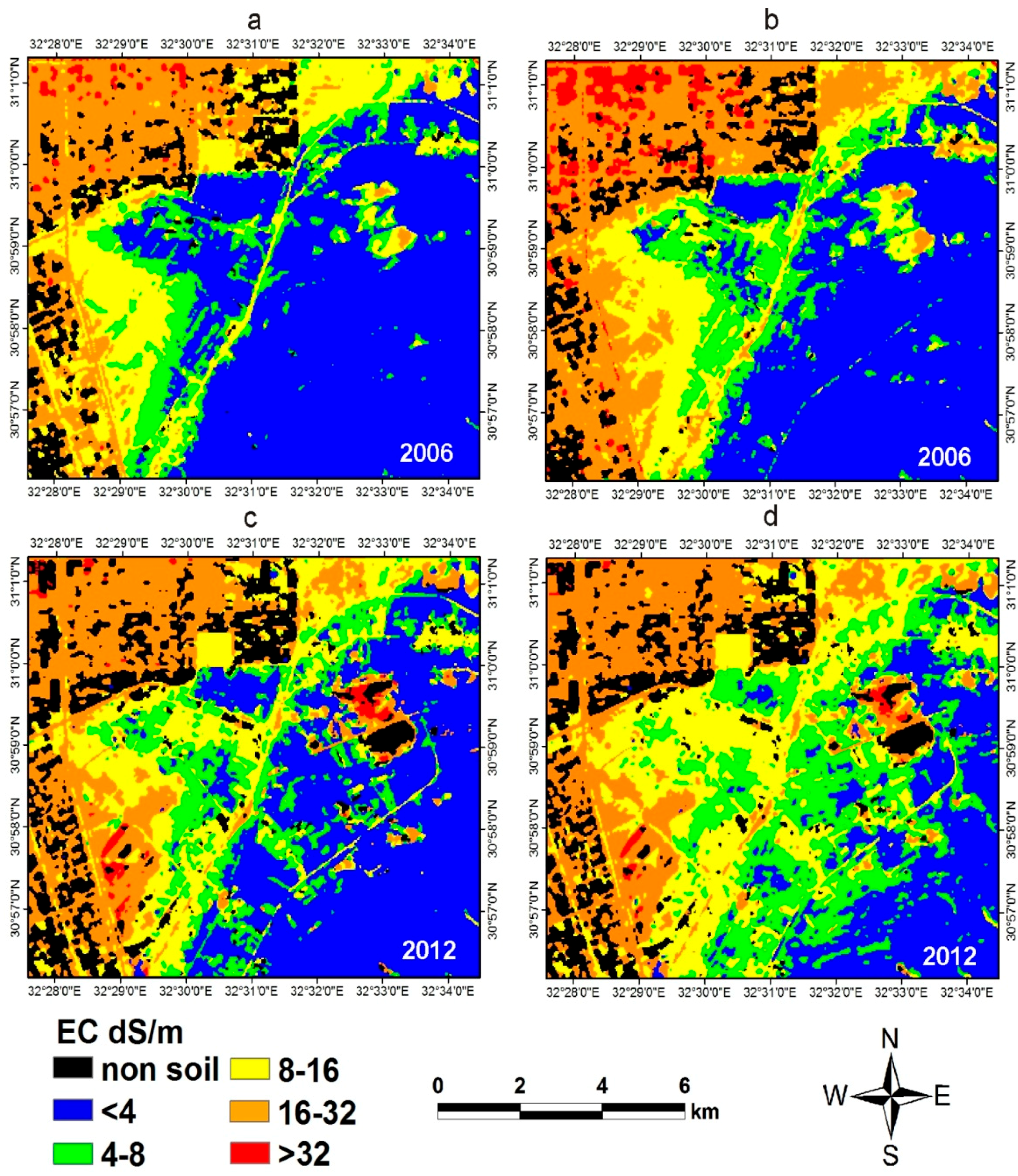

4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Salinity Estimation Using the PLSR and MARS Models
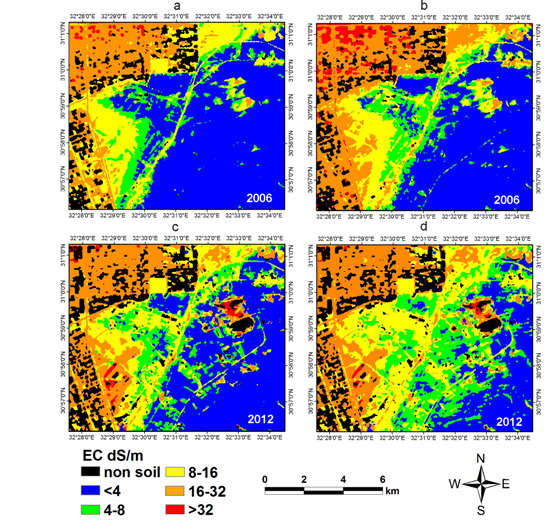
4.2. Soil Salinity: Mapping and Assessment
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Field-derived spectra of salinized soils and vegetation as indicators of irrigation-induced soil salinization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockle, C.O. Environmental impact of irrigation: A review. Available online: http://www.swwrc.wsu.edu/newsletter/fall2001/IrrImpact2.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2013).
- Eynard, A.; Lal, R.; Wiebe, K. Salt-affected soils. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science, 2nd ed.; Lal, R., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1538–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ma, F.; Chai, X.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, S. Spatiotemporal changes in soil salinity in a drip-irrigated field. Geoderma 2009, 149, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, S.; Buyuktas, D.; Okturen, F.; Citak, S. Assessment of different soil to water ratios (1:1, 1:2.5, 1:5) in soil salinity studies. Geoderma 2008, 144, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A. Remote sensing of soils and soil processes. In Remote Sensing for Natural Resource Management and Environmental Monitoring; Ustin, S.L., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinization: Impact on Land Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Howari, F.M.; Goodell, P.C. Characterization of salt-crust buildup and soil salinization in the United Arab Emirates by means of field and remote sensing techniques. In Remote Sensing of Soil Salinization: Impact on Land Management; Metternicht, G.I., Zinck, J.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Elnaggar, A.A.; Noller, J.S. Application of remote-sensing data and decision-tree analysis to mapping salt-affected soils over large areas. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.S.; Rao, B.R.M. The selection of the best possible Landsat TM band combination for delineating salt-affected soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Sato, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Assessment of hydrosaline land degradation by using a simple approach of remote sensing indicators. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Buces, N.; Siebe, C.; Cram, S.; Palacio, J.L. Mapping soil salinity using a combined spectral response index for bare soil and vegetation: A case study in the former lake Texcoco, Mexico. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 65, 644–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, S.J; Boettinger, J.L.; Ramsey, R.D. Digitally mapping gypsic and natric soil areas using Landsat ETM data. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeiry, A.A.; Garcia, L.A. Detecting soil salinity in alfalfa fields using spatial modeling and remote sensing. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Pat kin, K.; Banin, A.; Karnieli, A. Mapping of several soil properties using DAIS-7915 hyperspectral scanner data—A case study over clayey coils in Israel. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Image-derived spectral end members as indicators of salinisation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Forrester, S.T.; Rawson, A. The prediction of soil chemical and physical properties from mid-infrared spectroscopy and combined partial least-squares regression and neural networks (PLS-NN) analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2009, 97, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A spectral index for estimating soil salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China using EO-1 Hyperion data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shao, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, L.; Wang, L. Salt content distribution and paleoclimatic significance of the lop nur “Ear” feature: Results from analysis of EO-1 hyperion imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7783–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K. Hyperspectral satellite data in mapping salt-affected soils using linear spectral unmixing analysis. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judkins, G.; Myint, S. Spatial variation of soil salinity in the Mexicali valley, Mexico: Application of a practical method for agricultural monitoring. Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. Soil salt content estimation in the Yellow River delta with satellite hyperspectral data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 34, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Multivariate adaptive regressions splines. Ann. Stat. 1991, 19, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, M.; Hjort, J. Evaluation of current statistical approaches for predictive geomorphological mapping. Geomorphology 2005, 67, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, A.V.; van Es, H.M.; Akbas, F.; Durak, A.; Hively, W.D. Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for assessment of soil properties in a semi-arid area of Turkey. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicísimo, Á.M.; Cuartero, A.; Remondo, J.; Quirós, E. Mapping landslide susceptibility with logistic regression, multiple adaptive regression splines, classification and regression trees, and maximum entropy methods: A comparative study. Landslides 2012, 10, 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Samui, P. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline (MARS) for prediction of elastic modulus of jointed rock mass. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2012, 31, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, P.; Kurup, P. Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline (MARS) and Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) for OCR prediction. Soft Comput. 2012, 16, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, A.V.; Cullu, M.A.; van Es, H.; Aydemir, A.; Aydemir, S. The use of hyperspectral visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for the characterization of salt-affected soils in the Harran Plain, Turkey. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2011, 25, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J. Estimation of soil salinity using three quantitative methods based on visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy: A case study from Egypt. Arab J. Geosci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A. Predicting salt abundance in slightly saline soils from Landsat ETM+ imagery using spectral mixture analysis and soil spectrometry. Geoderma 2014, 217–218, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidike, A.; Zhao, S.; Wen, Y. Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo county of China using QuickBird data and soil reflectance spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L. Soil salinity mapping and monitoring in arid and semi-arid regions using remote sensing technology: A review. Advanc. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, V.L.; de Bruin, S.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mayr, T.R. The use of remote sensing in soil and terrain mapping—A review. Geoderma 2011, 162, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nawar, S.; Reda, M.; Farag, F.; El-Nahry, A. Mapping soil salinity in El-Tina plain in Egypt using geostatistical approach. In Proceedings of the Geoinformatics Forum Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria, 5–8 July 2011.
- Aly, E.H.M. Pedological Studies on Some Soils Along El-Salam Canal, North East of Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nawar, S.; Reda, M.; Farag, F.; El-Nahry, A. Sustainability assessment using geostatistical analysis and spatial modeling in El-Tina plain in Egypt. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference EnviroInfo, Ispera, Italy, 5–7 October 2011.
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice-Hall of India private limited: New Delhi, India, 1973; p. 498. [Google Scholar]
- Mouazen, A.M.; Maleki, M.R.; de Baerdemaeker, J.; Ramon, H. On-line measurement of some selected soil properties using a VIS–NIR sensor. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 93, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Kowalski, B.R. Partial least-squares regression: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddenbaum, H.; Stern, O.; Stellmes, M.; Stoffels, J.; Pueschel, P.; Hill, J.; Werner, W. Field imaging spectroscopy of beech seedlings under dryness stress. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3721–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, A.; Lau, I.; Hewson, R.; Carter, D.; Wheaton, B.; Ong, C.; Cudahy, T.J.; Chabrillat, S.; Kaufmann, H. Applicability of the thermal infrared spectral region for the prediction of soil properties across semi-arid agricultural landscapes. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3265–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Shi, T.; Song, A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Estimating soil organic carbon using Vis/NIR spectroscopy with SVMR and SPA methods. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2699–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, M.; Buddenbaum, H. Laboratory imaging spectroscopy of a stagnic Luvisol profile—High resolution soil characterisation, classification and mapping of elemental concentrations. Geoderma 2013, 195–196, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Prasher, S.O.; Lacroix, R.; Kim, S.H. A multivariate adaptive regression splines model for simulation of pesticide transport in soils. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 86, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 763. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—principal components regression analysis of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. MATLAB 8.0; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2012. Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab/whatsnew.html (accessed on 6 November 2014).
- Exelis Visual Information Solutions. ENVI Tutorials; Boulder, Colorado, USA, 2012. Available online: http://www.exelisvis.com/docs/Tutorials.html (accessed on 26 May 2013).
- Frazier, B. Satellite mapping. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science, 2nd ed.; Lal, R., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 2; pp. 1542–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Micijevic, E.; Chander, G. SLC gap-filled products phase one methodology. 2004. Available online: http://landsat.usgs.gov/documents/SLC_Gap_Fill_Methodology.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2014). [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, S.; Phinn, S.; Gill, T. Preparing Landsat Image Time Series (LITS) for monitoring changes in vegetation phenology in Queensland, Australia. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1856–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Chabrillat, S.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Taylor, G.R.; Hill, J.; Whiting, M.L.; Sommer, S. Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S38–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.; Schläpfer, D. Atmospheric/Topographic Correction for Satellite Imagery, ATCOR-2/3 User Guide, Version 8.2.1; DLR, Germany’s Aerospace Research Center and Space Agency: Wessling, Germany, 2013; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, J.B.; Zolfonoun, E. Application of principal component analysis-multivariate adaptive regression splines for the simultaneous spectrofluorimetric determination of dialkyltins in micellar media. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. Reflectance spectroscopy for the assessment of soil salt content in soils of the Yellow River Delta of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5511–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshayand, M.R.; Abdollahi, H.; Shariatpanahi, M.; Saadatfard, A; Mohammadi, A. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of paracetamol, ibuprofen and caffeine in pharmaceuticals by chemometric methods. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 70, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, F.R.S.; Sanaz, Z.; Abtahi, A.S. Soil salinity characteristics using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) images and statistical analysis. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Sinha, P. Mapping and modelling spatial variation in soil salinity in the Al Hassa Oasis based on remote sensing indicators and regression techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1137–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, M.; Matschullat, J.; Gloaguen, R. Improved remote sensing detection of soil salinity from a semi-arid climate in Northeast Brazil. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2011, 343, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Tong, Q. Simulation of EO-1 hyperion data from ALI multispectral data based on the spectral reconstruction approach. Sensors 2009, 9, 3090–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.; dos Santos Teixeira, A.; Galvão, L. Laboratory salinization of Brazilian alluvial soils and the spectral effects of Gypsum. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2647–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, M.F.; Silva, L.; Biehl1, L.L.; Stoner, E.R. Reflectance properties of soils. Adv. Agron. 1985, 38, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, F.M. Mineral-Chemical Characteristics of the Canal Area. Master’s Thesis, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Reda, M. Soil resources and their Potentiality in Sinai. In Proceedings of the Regional Symposium on Agro-technologies Based on Biological Nitrogen Fixation for Desert Agriculture, El-Arish, North Sinai, Egypt, 14–16 April 1998.
- Arasteh, P.D. Soil salinity change detection in irrigated area under Gazvin Plain irrigation network using satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the 9th International Drainage Symposium, Québec, QC, Canada, 13–16 June 2010; pp. 1–9.
- El Hajj, M.; Bégué, A.; Lafrance, B.; Hagolle, O.; Dedieu, G.; Rumeau, M. Relative radiometric normalization and atmospheric correction of a SPOT 5 time series. Sensors 2008, 8, 2774–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, T.; Koch, M.; Gumuzzio, J. Applications of hyper-spectral imagery to soil salinity mapping. In Remote Sensing of Soil Salinization: Impact on Land Management; Metternicht, G., Zinck, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 113–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jardine, A.; Speldewinde, P.; Carver, S.; Weinstein, P. Dryland salinity and ecosystem distress syndrome: Human health implications. EcoHealth 2007, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Martius, C.; Park, S.J.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Environmental factors of spatial distribution of soil salinity on flat irrigated terrain. Geoderma 2011, 163, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, A.V. Spatial assessment of soil salinity in the Harran Plain using multiple Kriging techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 777–795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.; Öztürk, M.A.; Athar, H.R. Salinity and Water Stress: Improving Crop Efficiency; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; p. 260. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J.; Kozak, J. Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10813-10834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61110813
Nawar S, Buddenbaum H, Hill J, Kozak J. Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS). Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(11):10813-10834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61110813
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawar, Said, Henning Buddenbaum, Joachim Hill, and Jacek Kozak. 2014. "Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS)" Remote Sensing 6, no. 11: 10813-10834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61110813
APA StyleNawar, S., Buddenbaum, H., Hill, J., & Kozak, J. (2014). Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS). Remote Sensing, 6(11), 10813-10834. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs61110813