Water Balance Modeling in a Semi-Arid Environment with Limited in situ Data Using Remote Sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
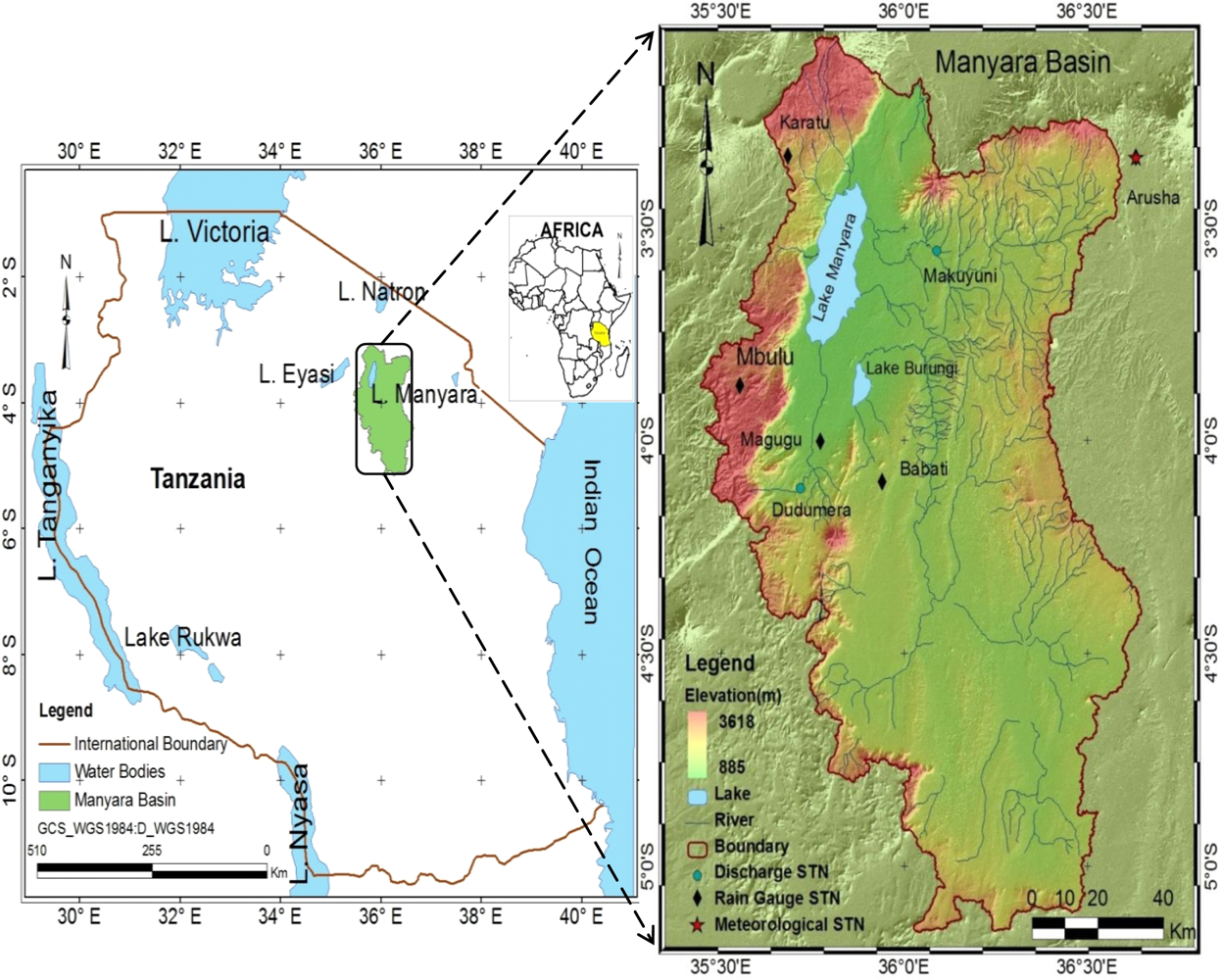
2. Description of the Study Area
2.1. Setting
2.2. Climate
3. Data and Parameters
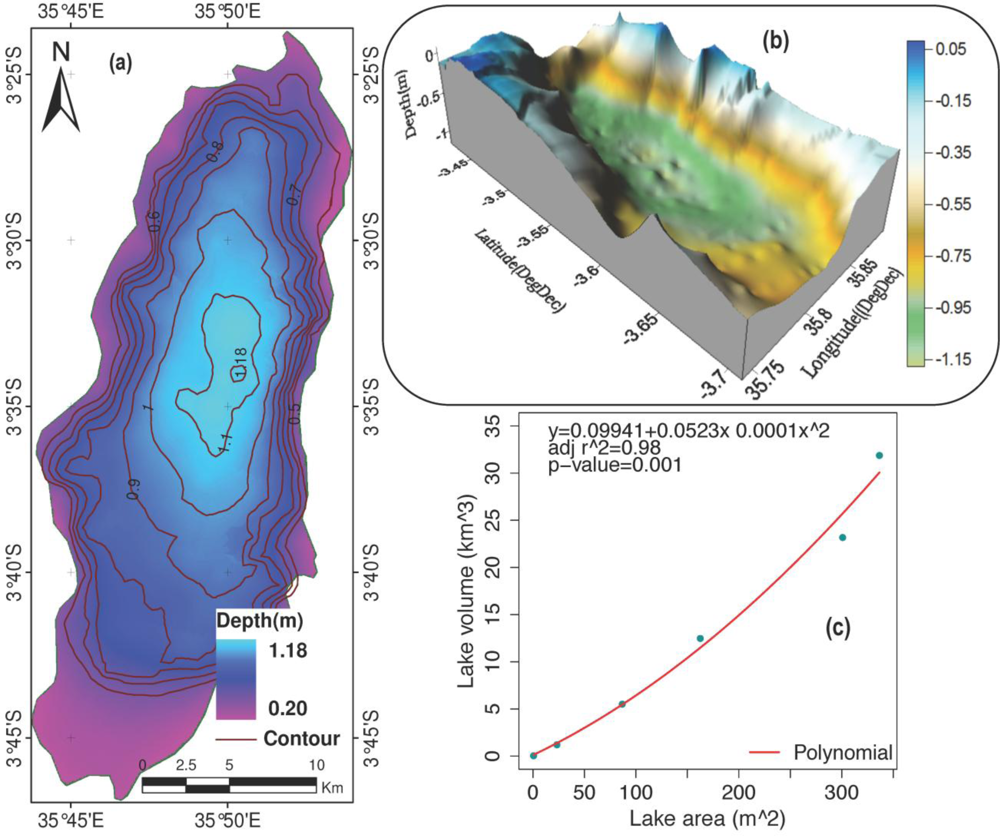
3.1. Data Sets
3.1.1. Remote Sensing Observation
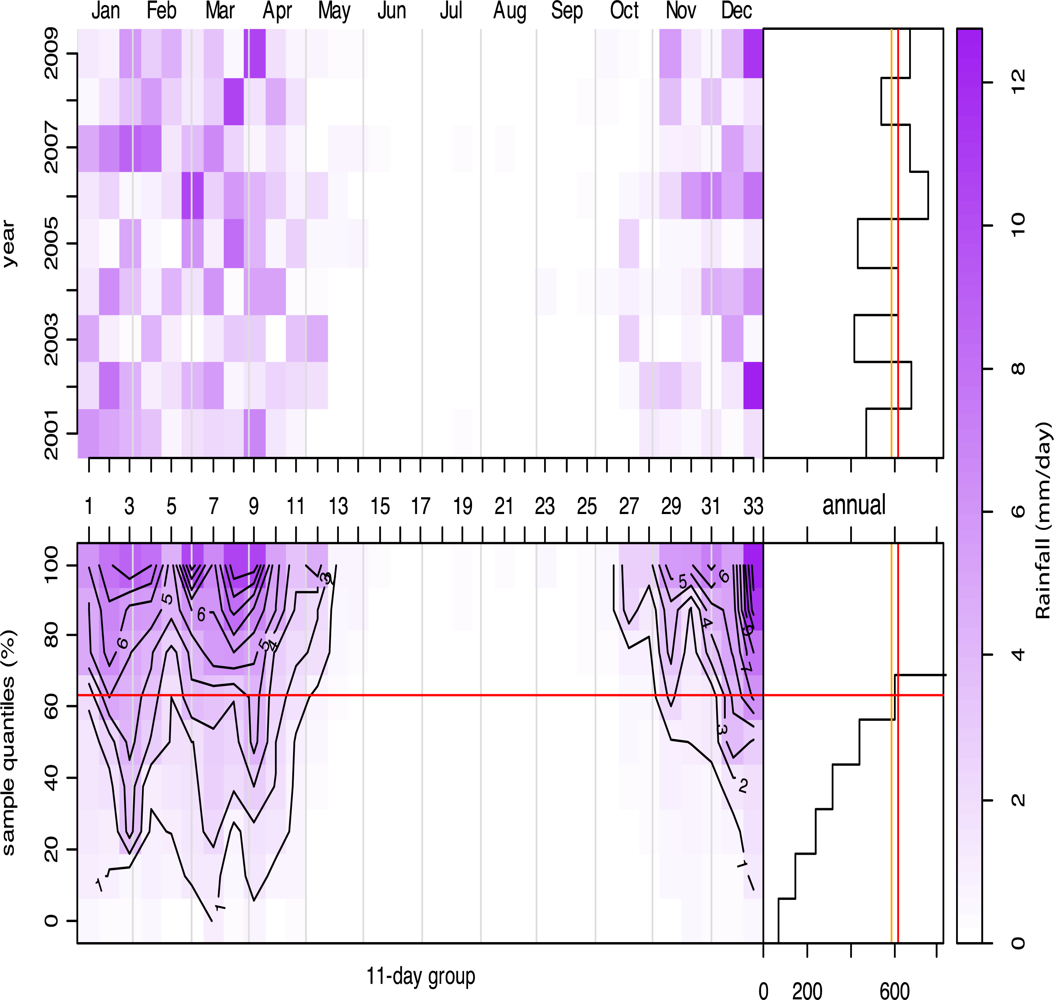
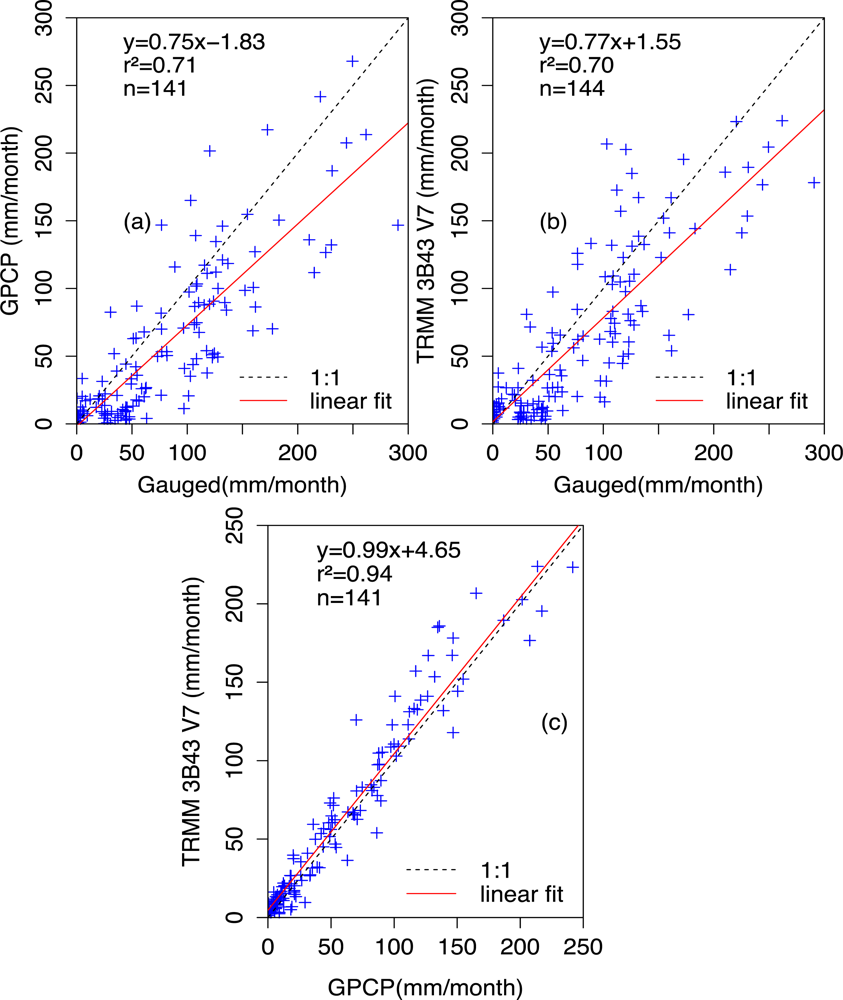
Rainfall
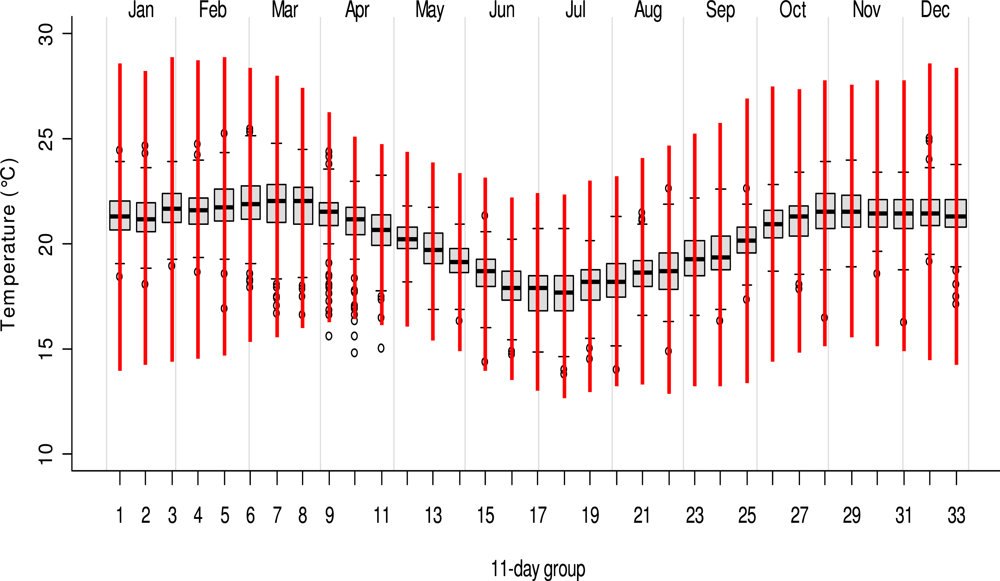
Temperature
GRACE Equivalent Water Thickness
Altimetric Lake Height
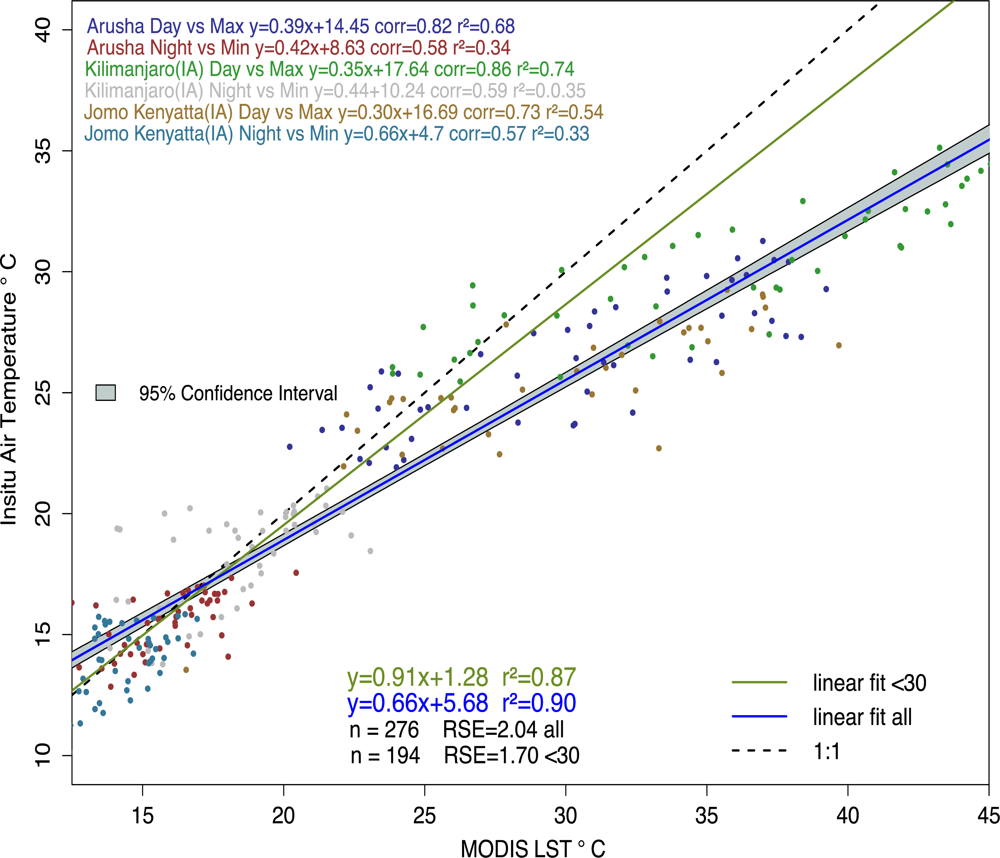
3.1.2. In situ Datasets
3.2. Model Input Parameters
4. Methodology
4.1. Water Balance
- Qin = Qdirect + Qbaseflow
4.2. Evapotranspiration
4.3. Model Setup, Calibration and Validation
4.3.1. Model Setup and Parameterization
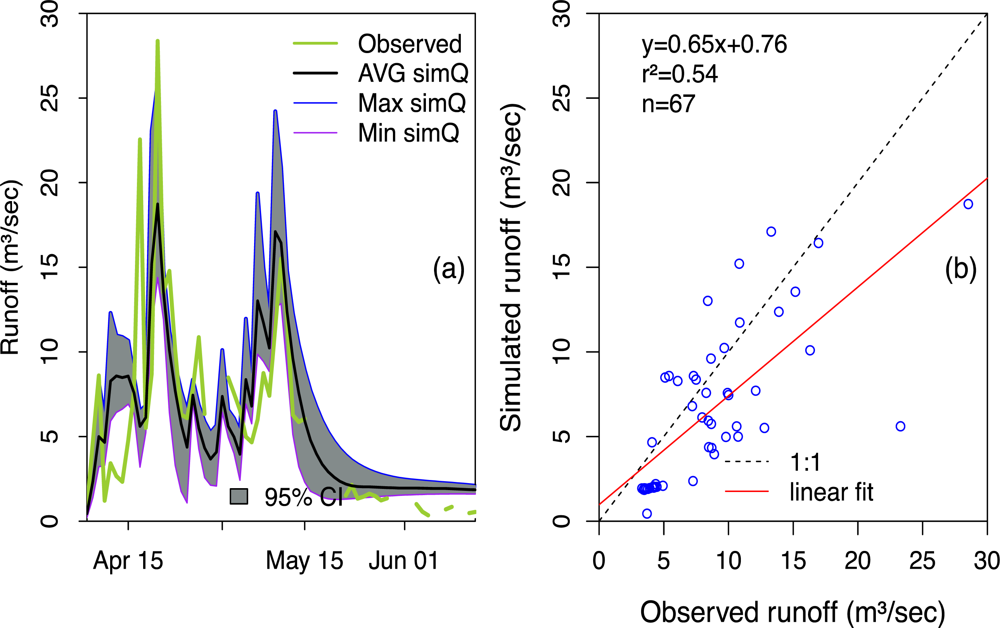
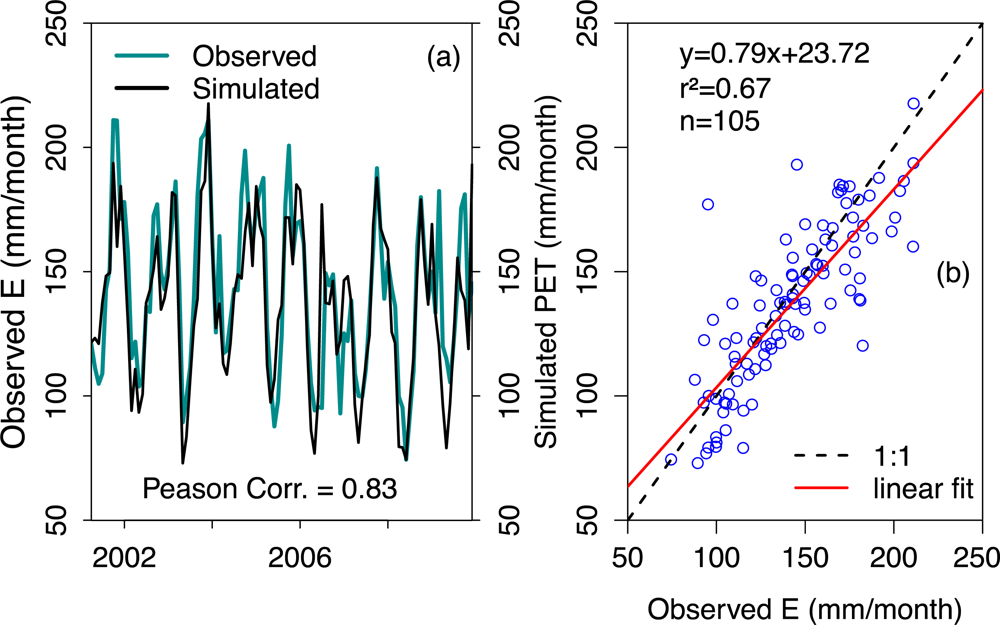
4.3.2. Model Calibration and Validation
5. Modeling Results and Discussion
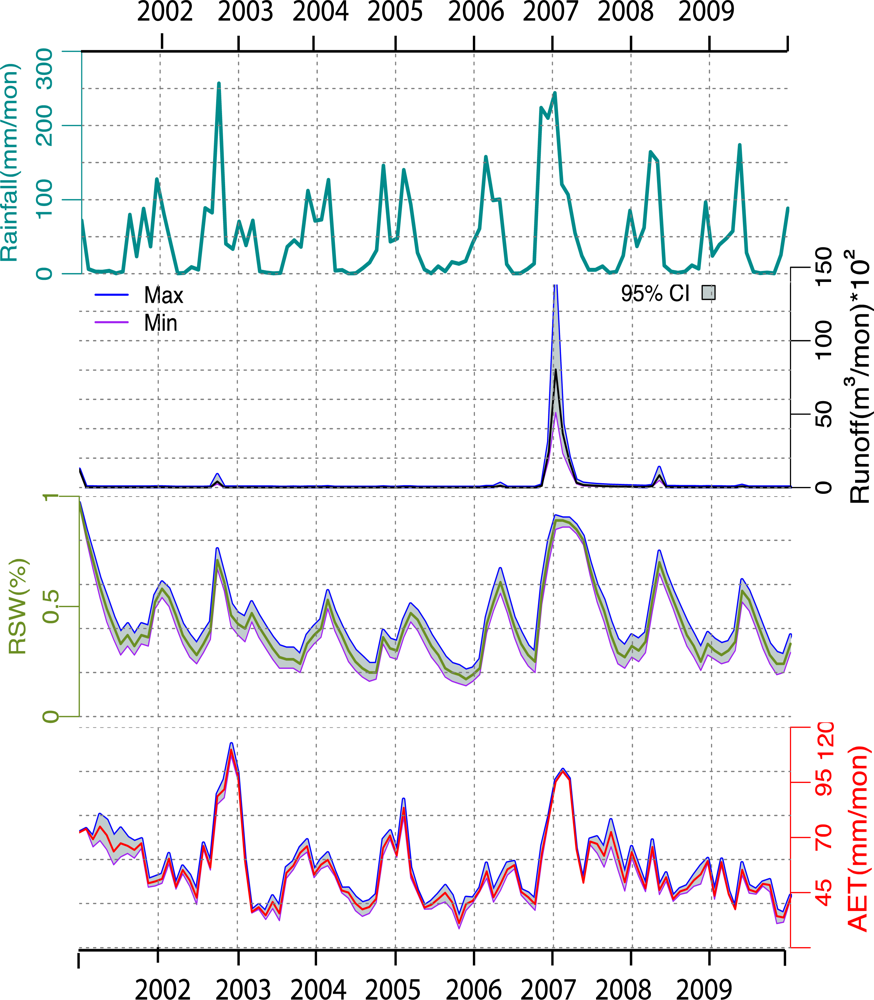
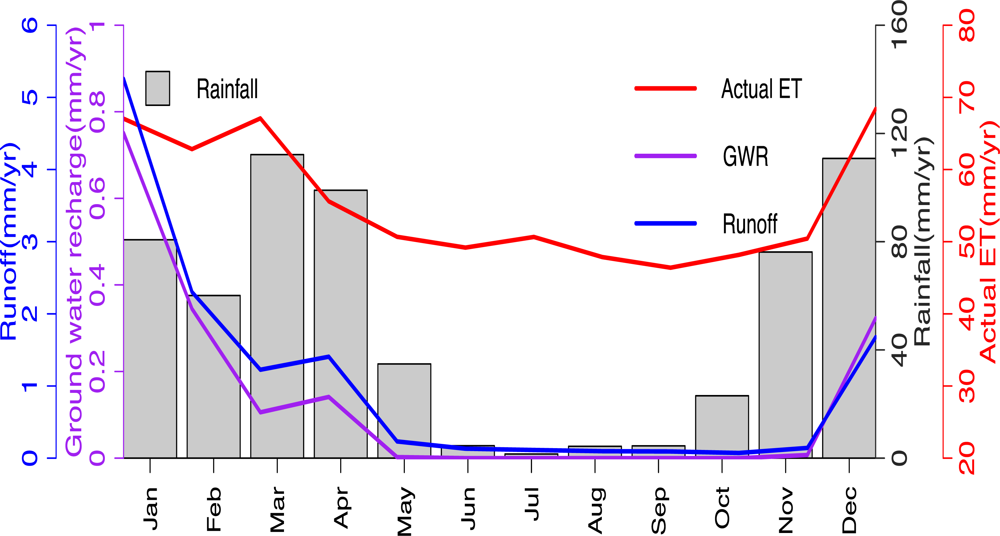
5.1. Monthly Basin Water Budget Components
Precipitation
Evapotranspiration (ET)
Runoff
Ground Water Recharge and Storage
5.2. Annual Water Balance Components
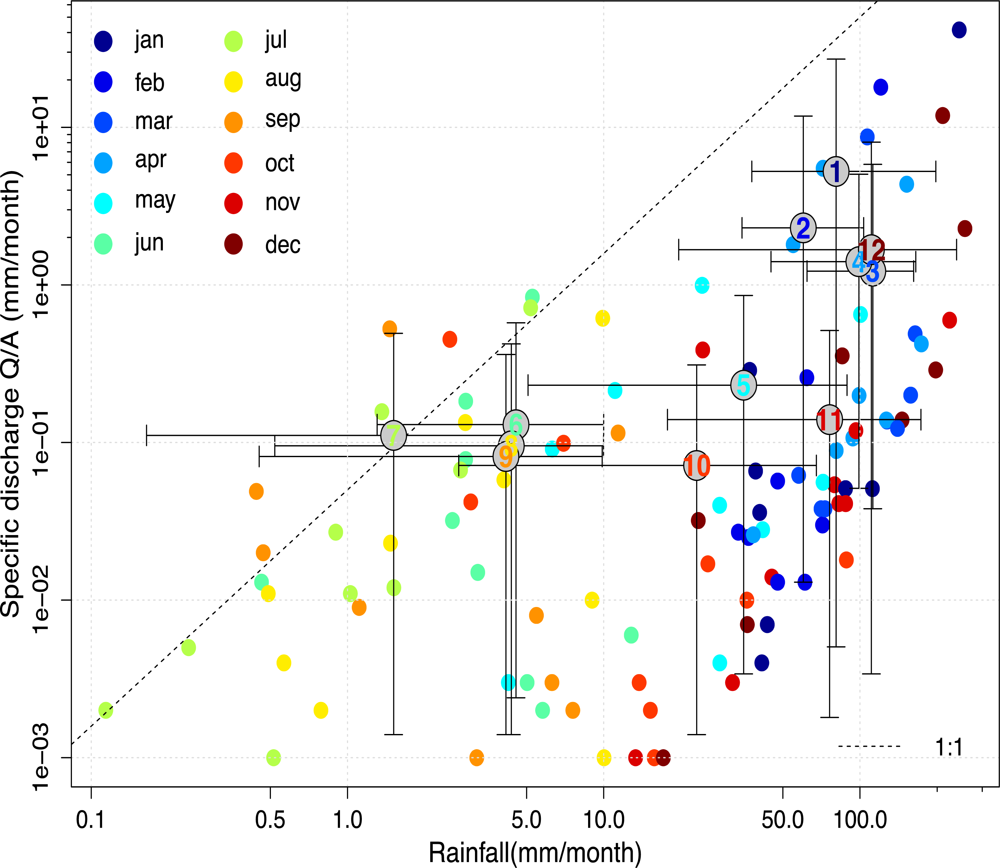
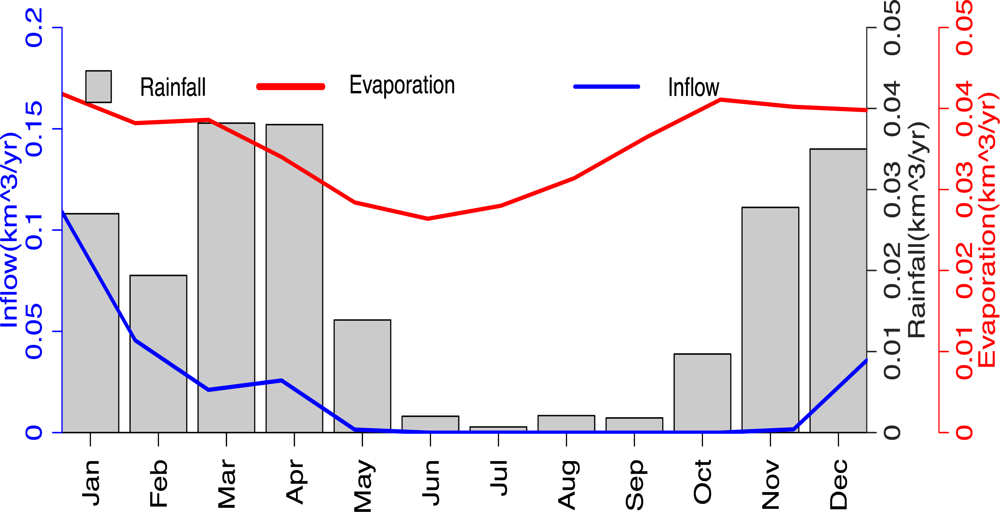
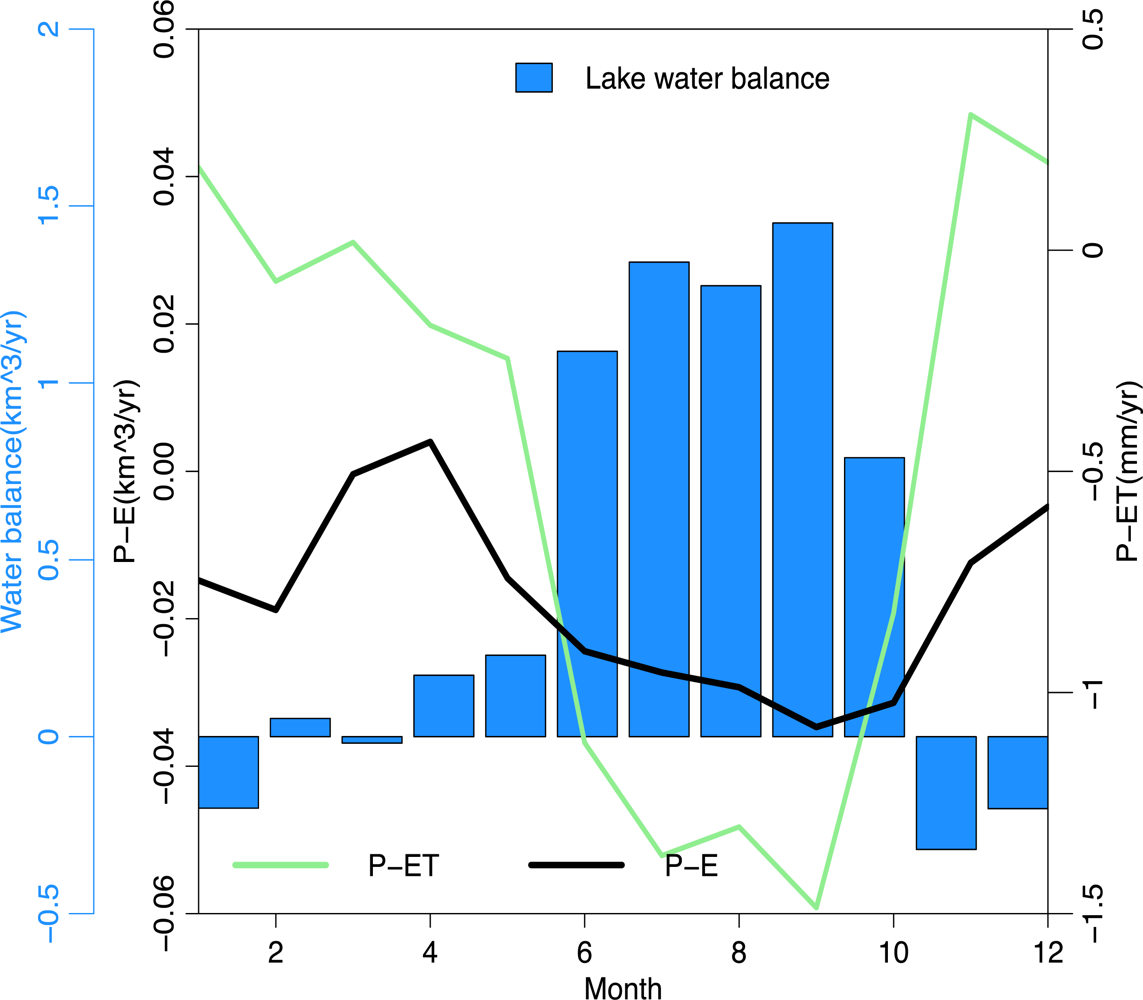
5.3. Lake Water Balance and Comparison
Lake Water Balance and GRACE Equivalent Water Thickness Comparison
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Troch, P.A. Data Assimilation for Regional Water Balance Studies in Arid and Semi-arid Areas (Case Study: The Volta Basin Upstream the Akosombo Dam in Ghana). In Proceedings of the First MSG RAO Workshop, European Space Agency ESASP-452, Bologna, Italy, 17–19 May 2000; 2000CNR; Harris, R.A., Ed.; ESA: Bologna, Italy, 2000; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Güntner, A.; Krol, M.S.; de Araújo, J.C.; Bronstert, A. Simple water balance modelling of surface reservoir systems in a large data-scarce semi-arid region. Hydrol. Sci 2004, 49, 901–918. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, F.H. Hydrological Modeling in a Semi-arid Area Using Remote Sensing Data; University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Güntner, A.; Bronstert, A. Representation of landscape variability and lateral redistribution processes for large-scale hydrological modelling in semi-arid areas. J. Hydrol 2004, 267, 136–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yanda, P.Z.; Madulu, N.F. Water resource management and biodiversity conservation in the Eastern Rift Valley Lakes, Northern Tanzania. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 717–725. [Google Scholar]
- Böhme, B.; Steinbruch, F.; Gloaguen, R.; Heilmeier, H.; Merkel, B. Geomorphology, hydrology, and ecology of Lake Urema, central Mozambique, with focus on lake extent changes. Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Goerner, A.; Jolie, E.; Gloaguen, R. Non-climatic growth of the saline Lake Beseka, Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Arid Environ 2008, 73, 287–295, ISSN 0140-1963.. [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson, L. Applied Landscape Assessment in a Holistic Perspective, A Case Study from Babati District, North-central Tanzania; Department of Earth Science, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.; Hanisch, S. Simulation and analysis of the impact of projected climate change on the spatially distributed waterbalance in Thuringia, Germany. Adv. Geosci 2009, 21, 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Milzow, C.; Krogh, P.E.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Combining satellite radar altimetry, SAR surface soil moisture and GRACE total storage changes for hydrological model calibration in a large poorly gauged catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci 2011, 15, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.I.; Adhikari, P.; Hong, Y.; Vergara, H.; Adler, R.F.; Policelli, F.; Irwin, D.; Korme, T.; Okello, L. Hydroclimatology of Lake Victoria region using hydrologic model and satellite remote sensing data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci 2011, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; LLovel, W.; Cazenave, A.; Güntner, A.; Cretaux, J. Recent hydrological behavior of the East African great lakes region inferred from GRACE, satellite altimetry and rainfall observations. Comptes Rendus Geosci 2010, 342, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.; Kao, Y.; Tangdamrongsub, N. A preliminary analysis of lake level and water storage changes over lakes Baikal and Balkhash from satellite altimetry and gravimetry. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci 2011, 22, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Swenson, S.C.; Wahr, J. Monitoring the water balance of Lake Victoria, East Africa, from space. J. Hydrol 2009, 370, 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Santillan, J.; Makinano, M.; Paringit, E. Integrated landsat image analysis and hydrologic modeling to detect impacts of 25-year land-cover change on surface runoff in a philippine watershed. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 1067–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Awange, J.L.; Sharifi, M.; Ogonda, G.; Wickert, J.; Grafarend, E.W.; Omulo, M. The falling Lake Victoria water levels: GRACE, TRIMM and CHAMP satellite analysis of the lake basin. Water Resour. Manag 2008, 22, 775–796. [Google Scholar]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res 2012, 48, W04531. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, M.; Ebinger, C.; Keir, D.; Gloaguen, R.; Mohamed, F. Strain accommodation in transitional rifts: Extension by magma intrusion and faulting in Ethiopian Rift magmatic segments. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ 2006, 259, 143–163. [Google Scholar]
- Keranen, K.; Klemperer, S.L.; Gloaguen, R. Three-dimensional seismic imaging of a protoridge axis in the Main Ethiopian rift. Geology 2004, 32, 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, T.; Gloaguen, R.; Ebinger, C.; Casey, M.; Abebe, B. Deformation distribution and type in the Main Ethiopian Rift (MER): A remote sensing study. J. Afr. Earth Sci 2007, 48, 100–114. [Google Scholar]
- Somi, E.J. Palaeoenvironmental Change in Central and Coastal Tanzania during the Upper Cenozoic. 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar, F.; Cubasch, U.; Offenbach, G. Simulation of East African precipitation patterns with the regional climate model CLM. Meteorol. Z 2008, 17, 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Reason, C.J.C. Sensitivity of the southern African circulation to dipole sea-surface temperature patterns in the South Indian Ocean. Int. J. Climatol 2002, 22, 377–393. [Google Scholar]
- Birkett, C.; Murtugudde, R.; Allan, T. Indian Ocean climate event brings floods to East Africa’s lakes and the Sudd Marsh. Geophys. Resour. Lett 1999, 26, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Wheater, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Sharma, K.D. Hydrological Modelling in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim, D.H.; Chapman, T.G.; Doran, D.G. Problems of rainfallrunoff modelling in arid and semiarid regions. Hydrol. Sci 1988, 33, 379–400. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, S.R. Potential hominin plant foods in northern Tanzania: Semi-arid savannas versus savanna chimpanzee sites. J. Hum. Evol 2009, 57, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Prins, H.T.; Loth, P.E. Rainfall patterns as background to plant phenology in northern Tanzania. J. Biogeogr 1988, 15, 451–463. [Google Scholar]
- Loveland, T.R.; Belward, A.S. The IGBP-DIS global 1 km land cover data set, DISCover first results. Int. J. Remote Sens 1997, 18, 3289–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Rabus, B.; Eineder, M.; Roth, A.; Baler, R. The shuttle radar topography mission—A new class of digital elevation models acquired by spaceborne radar. ISPRS J. Photogramm 2003, 57, 241–262. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4. available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 5 June 2010).
- Sorooshian, S.; Lawford, R.; Try, P.; Rossow, W.; Roads, J.; Polcher, J.; Sommeria, G.; Schiffer, R. Water and energy cycles: Investigating the links. World Meteorol. Org. Bull 2005, 54, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremichael, M.; Over, T.M.; Krajewski, W.F. Comparison of the scaling characteristics of rainfall derived from spacebased and ground-based radar observations. J. Hydrometeorol 2006, 7, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar]
- Andermann, C.; Bonnet, S.; Gloaguen, R. Evaluation of precipitation data sets along the Himalayan front. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Keehn, P.R. Global precipitation estimates based on a technique for combining satellite-based estimates, rain-gauge analysis, and NWP model precipitation. J. Clim 1995, 8, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; Gruber, A.; Susskind, J.; Arkin, P.; Nelkin, E. The version 2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-Present). J. Hydrometeorol 2003, 4, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Prigent, C. Precipitation retrieval from space: An overview. Comptes Rendus Geosci 2010, 342, 380–389. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the MODIS Land-Surface Temperature/Emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhoff, A.L.; Paz, A.R.; Collischonn; Aragao, L.E.O.C.; Rocha, H.R.; Malhi, Y.S. A MODIS-based energy balance to estimate evapotranspiration for clear-sky days in Brazilian tropical Savannas. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 703–725. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.-L. Quality assessment and validation of the MODIS land surface temperature. Int. J. Remote Sens 2004, 25, 261–274. [Google Scholar]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C.H. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J. Geophys. Res 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar]
- Wahr, J.; Swenson, S.; Zlotnicki, V.; Velicogna, I. Time-variable gravity from GRACE: First results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.; Birkett, C. Lake studies from satellite radar altimetry. Comptes Rendus Geosci 2006, 338, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar]
- FAO.; IIASA.; ISRIC.; ISSCAS.; JRC. Harmonized World Soil Database (version 1.1); FAO: Rome, Italy, IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M. An Introduction to Solar Radiation; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell, N.C.; Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C. A global albedo data set derived from AVHRR data for use in climate simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett 2001, 28, 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.M.; Liu, J.; Cihlar, J.; Goulden, M.L. Daily canopy photosynthesis model through temporal and spatial scaling for remote sensing applications. Ecol. Model 1999, 124, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F. Monitoring forest degradation in tropical regions by remote sensing: Some methodological issues. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr 1999, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yucel, I. Effects of implementing MODIS land cover and albedo in MM5 at two contrasting US regions. J. Hydrometeorol 2006, 7, 1043–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, L.; Eckhardt, K.; Frede, H.G. Plant parameter values for models in temperate climates. Ecol. Model 2003, 169, 237–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Qi, J.; Lofgren, B.M.; Moore, N.; Torbick, N.; Olson, J.M. Impacts of land use/cover classification accuracy on regional climate simulations. J. Geophys. Res 2007, 112, D05107, doi:05110.01029/02006JD007404. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X. Global vegetation root distribution for land modeling, notes and correspondence. J. Hydrometeorol 2001, 2, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kralisch, S.; Krause, P. JAMS: A Framework for Natural Resource Model Development and Application. Proceedings of the iEMSs Third Biennial Meeting of International Environmental Modelling and Software Society, Burlington, VM, USA, 9–13 July 2006.
- Dingman, S.L. Physical Hydrology; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thornthwaite, C. An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J.; Rowe, C.M.; Mintz, Y. Climatology of the terrestrial seasonal water cycle. Int. J. Clim 1985, 5, 589–606. [Google Scholar]
- Cardille, J.; Coe, M.T.; Vano, J. Impacts of climate variation and catchment area on water balance and lake hydrologic type in groundwater-dominated systems: A generic lake model. Earth Interact 2004, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Awulachew, S.B. Modelling natural conditions and impacts of consumptive water use and sedimentation of Lake Abaya and Lake Chamo, Ethiopia. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag 2006, 11, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, B.; Seyfried, M.; Breshears, D. The Water Balance on Rangelands. In Encyclopedia of Water Science; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 791–794. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, S.; Travia, Y.; Alemayehub, T.; Marca, V. Water balance of Lake Tana and its sensitivity to fluctuations in rainfall, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol 2006, 316, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Penman, H.L. Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass. Proc. R. Soc. Lond 1948, 193, 120–145. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.E.; Burman, R.D.; Allen, R.G.E. (Eds.) Evaporation and Irrigation Water Requirements; ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practices No. 70; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 360.
- Liu, Y.B.; Batelaan, O.; de Smedt, F.; Poórová, J.; Velcická, L. Automated Calibration Applied to a GIS-based Flood Simulation Model Using PEST. In Floods, from Defence to Management; van Alphen, J., van Beek, E., Taal, M., Eds.; Taylor-Francis Group: London, UK, 2005; pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Abram, N.J.; Gagan, M.K.; Liu, Z.; Hantoro, W.S.; McCulloch, M.T.; Suwargadi, B. Seasonal characteristics of the Indian Ocean Dipole during the Holocene epoch. Nature 2007, 445, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Paeth, H.; Hense, A. On the linear response of tropical African climate to SST changes deduced from regional climate model simulations. Theor. Appl. Clim 2006, 83, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, C.; Davies, T.D. Causes of concentration/discharge hysteresis and its potential as a tool for the analysis of episode hydrochemistry. Water Resour. Res 1998, 34, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Chanat, J.G.; Rice, K.C.; Hornberger, G.M. Consistency of patterns in concentration-discharge plots. Water Resour. Res 2002, 38, 1147. [Google Scholar]
- Andermann, C.; Longuevergne, L.; Bonnet, S.; Crave, A.; Philippe Davy, P.; Gloaguen, R. Impact of transient groundwater storage on the discharge of Himalayan rivers. Nat. Geosci 2012, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, H. Estimating and Enhancing Groundwater Recharge. In Groundwater Recharge; Sharma, M.L., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.; Biskop, S.; Helmschrot, J.; Flugel, W.A.; Kang, S.; Gao, T. Hydrological system analysis and modelling of the Nam Co basin in Tibet. Adv. Geosci 2010, 27, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bormann, H. Evaluation of hydrological models for scenario analyses: Signal-to-noise-ratio between scenario effects and model uncertainty. Adv. Geosci 2005, 5, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Frappart, F.; Papa, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Seyler, F. Interannual variations of river water storage from a multiple satellite approach: A case study for the Rio Negro River basin, Atmospheres. J. Geophys. Res 2008, 113, D21104, doi:21110.21029/22007JD009438. [Google Scholar]
- Calmant, S.; Seyler, F.; Cretaux, J. Monitoring continental surface waters by Satellite Altimetry. Surv. Geophys 2008, 29, 247–269, doi: 210.1007/s10712-10008-19051-10711. [Google Scholar]
- Mercier, F.; Cazenave, A.; Maheu, C. Interannual lake level fluctuations (1993–1999) in Africa from Topex/Poseidon: Connections with ocean-atmosphere interactions over the Indian Ocean. Glob. Planet. Chang 2002, 32, 141–163. [Google Scholar]


| Land Cover Type | Albedo (%) | RSC0 (s/m) | LAI | Hmax (m) | RDmax (dm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0.08 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Evergreen broadleaf forest | 0.14 | 100 | 6 | 3 | 22 |
| Deciduous broadleaf forest | 0.16 | 100 | 6 | 3 | 20 |
| Mixed forests | 0.16 | 125 | 2 | 10 | 22 |
| Closed shrub land | 0.22 | 100 | 5 | 3 | 22 |
| Open shrub lands | 0.22 | 100 | 1 | 3 | 22 |
| Woody savannahs | 0.15 | 100 | 6 | 2 | 17 |
| Savannahs | 0.18 | 100 | 4 | 2 | 22 |
| Grasslands | 0.22 | 50 | 2 | 1 | 15 |
| Permanent wetlands | 0.16 | 150 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Urban and built-up | 0.18 | 200 | 3 | 2 | 15 |
| Cropland-natural vegetation | 0.17 | 50 | 4 | 1 | 15 |
| Barren or sparsely vegetated | 0.27 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 22 |
| Parameter | Cal. Value | Upper Boundary | Lower Boundary |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCA | 2.65 | 2.385 | 2.915 |
| LVD | 2.84 | 2.556 | 3.124 |
| ETR | 0.8 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| MPA | 100 | 90 | 110 |
| DK | 4 | 3.6 | 4.4 |
| BK | 21 | 18.9 | 23.1 |
| Component | Catchment Basin | Lake Manyara | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflow | Loss | Inflow | Loss | |
| Precipitation | 611.587 (99.73%) | - | 0.216 (47%) | - |
| ET/E | - | 664.234 (98.13%) | - | 0.424 (100%) |
| Runoff | - | 12.731 (2.07%) | - | - |
| Inflow | - | - | 0.240 (53%) | - |
| Ground water | 1.675 (0.27%) | - | - | - |
| Total | 613.261 | 676.964 | 0.456 | 0.424 |
| Water balance | −63.703 | 0.032 | ||
Share and Cite
Deus, D.; Gloaguen, R.; Krause, P. Water Balance Modeling in a Semi-Arid Environment with Limited in situ Data Using Remote Sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1651-1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5041651
Deus D, Gloaguen R, Krause P. Water Balance Modeling in a Semi-Arid Environment with Limited in situ Data Using Remote Sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania. Remote Sensing. 2013; 5(4):1651-1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5041651
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeus, Dorothea, Richard Gloaguen, and Peter Krause. 2013. "Water Balance Modeling in a Semi-Arid Environment with Limited in situ Data Using Remote Sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania" Remote Sensing 5, no. 4: 1651-1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5041651
APA StyleDeus, D., Gloaguen, R., & Krause, P. (2013). Water Balance Modeling in a Semi-Arid Environment with Limited in situ Data Using Remote Sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania. Remote Sensing, 5(4), 1651-1680. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5041651






