Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps Associated with Climate Change in the Hoh Xil Region, in the Hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
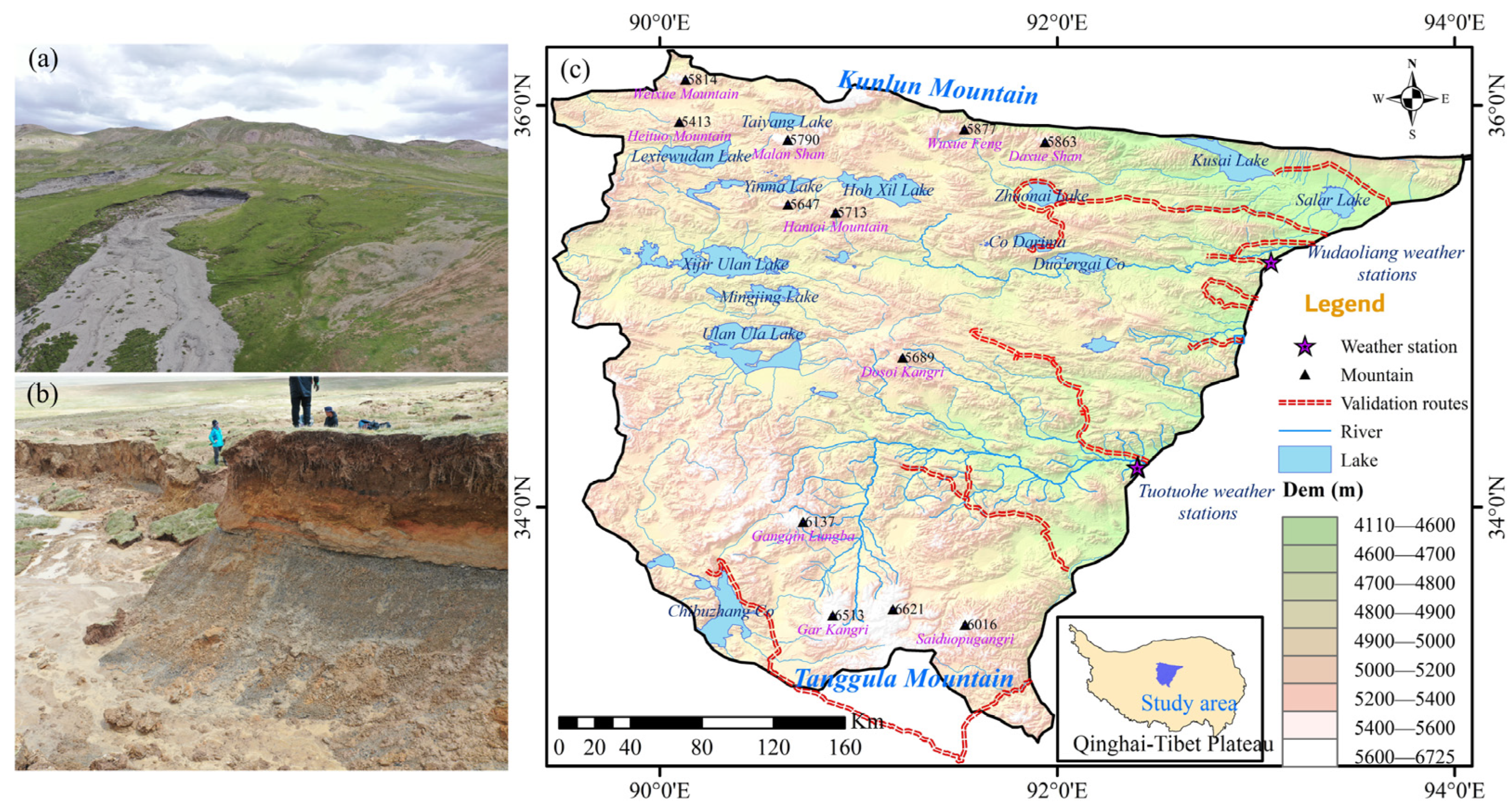
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Image Data Acquisition and Processes
2.3. Visual Interpretation and Validity Verification
2.4. The Informativeness Method and the Random Forest Principle
3. Results
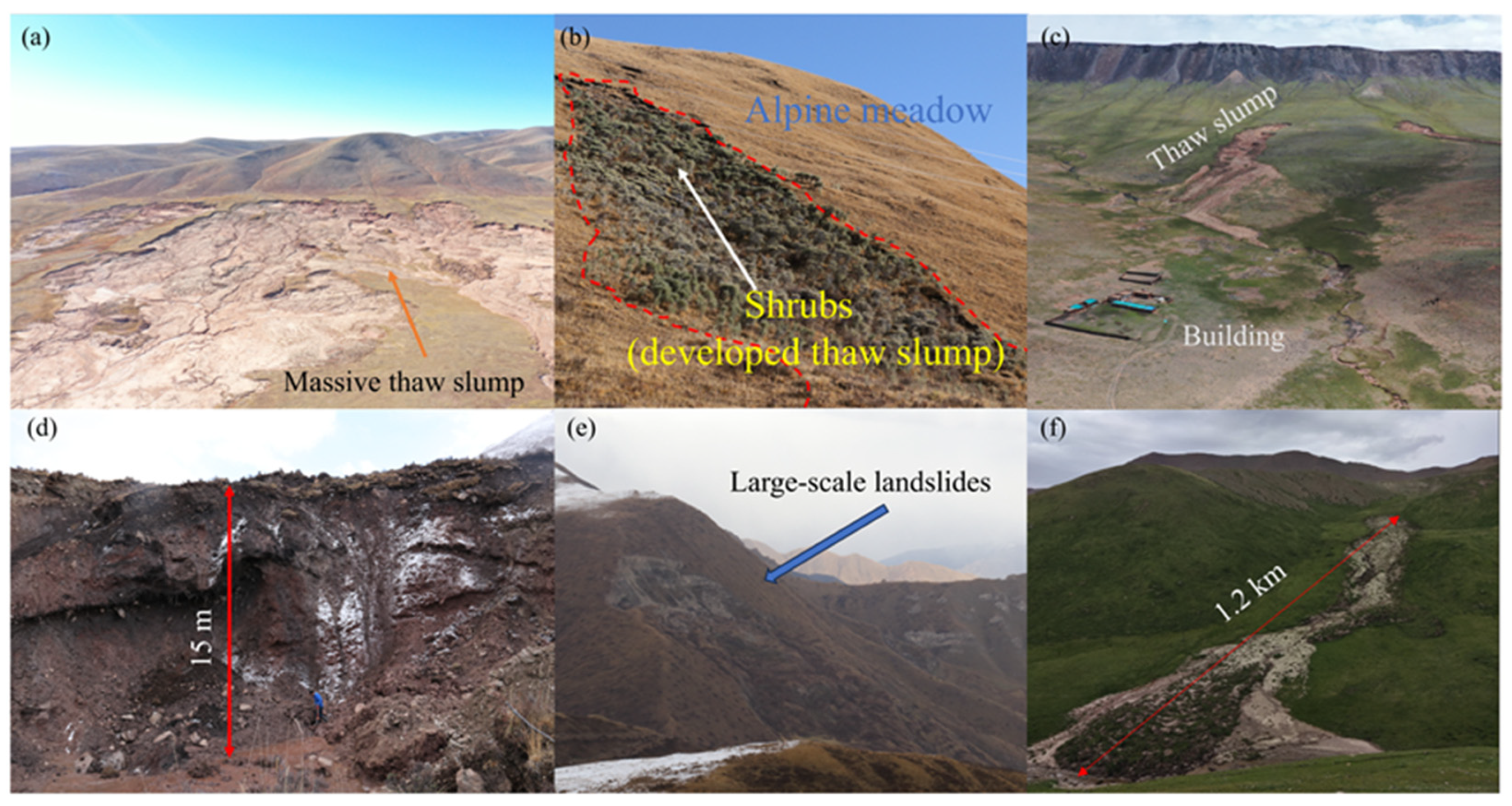
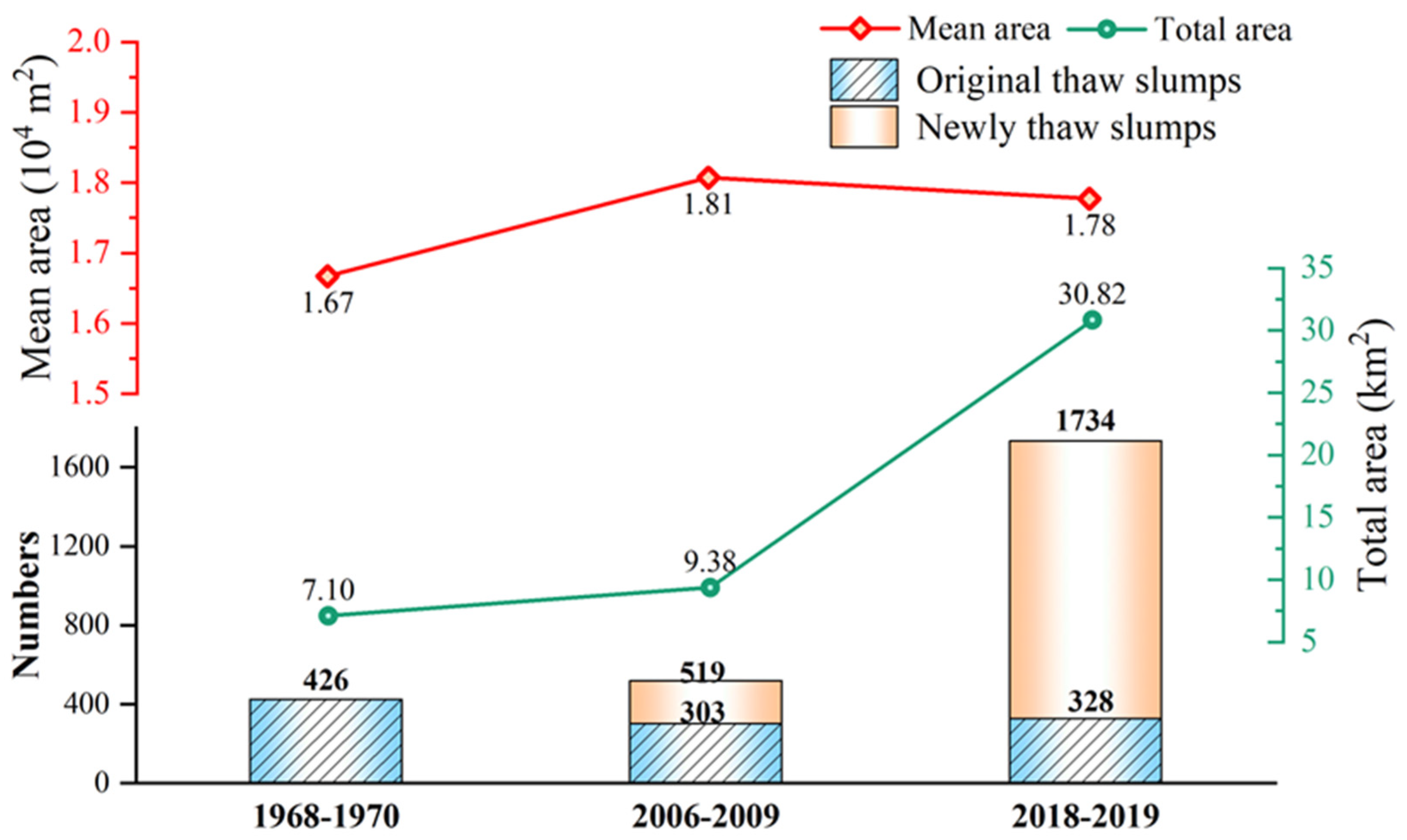
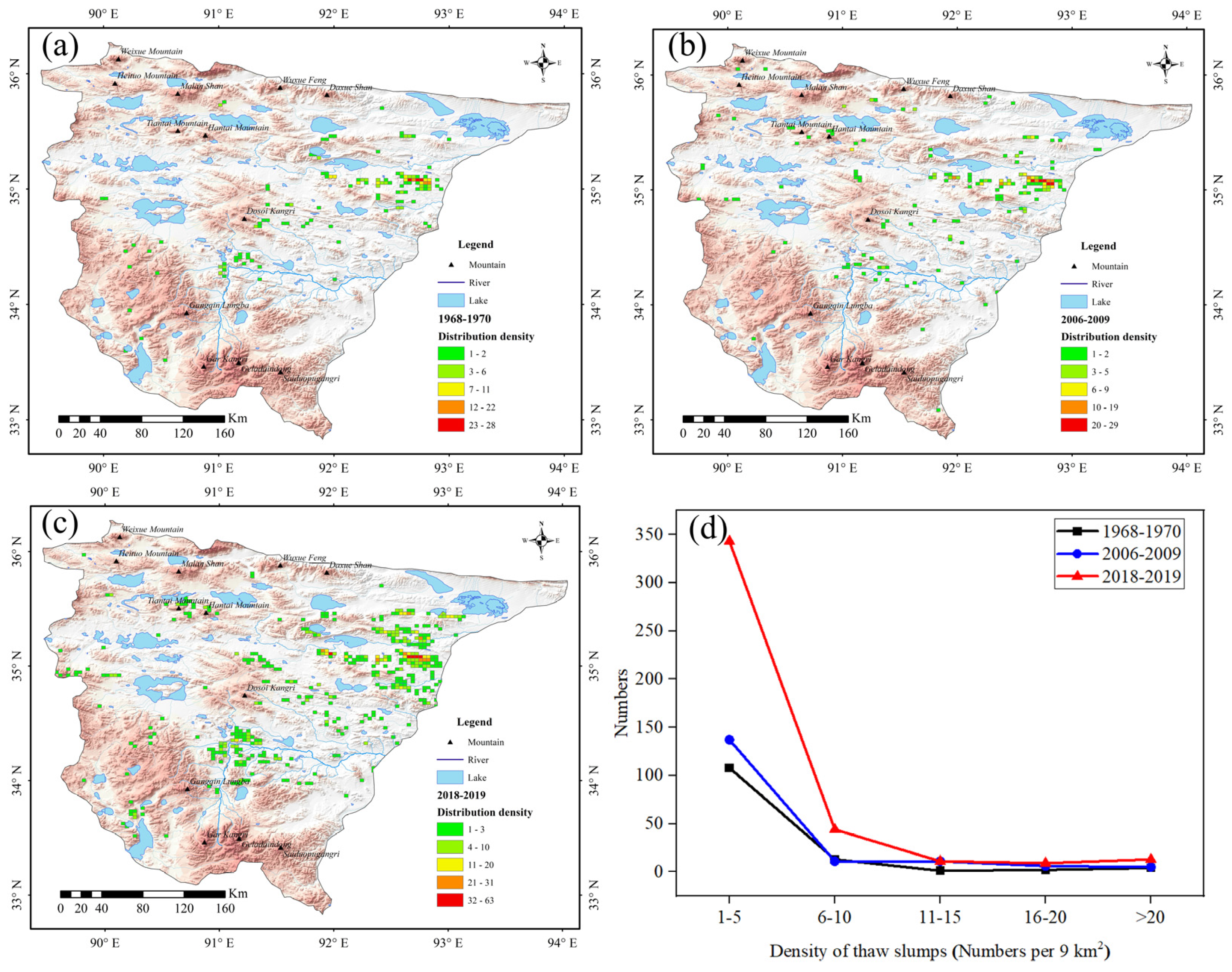
3.1. Changes in Thaw Slump Activity in Past 60 Years
3.2. Spatial Distribution of the Thaw Slumps
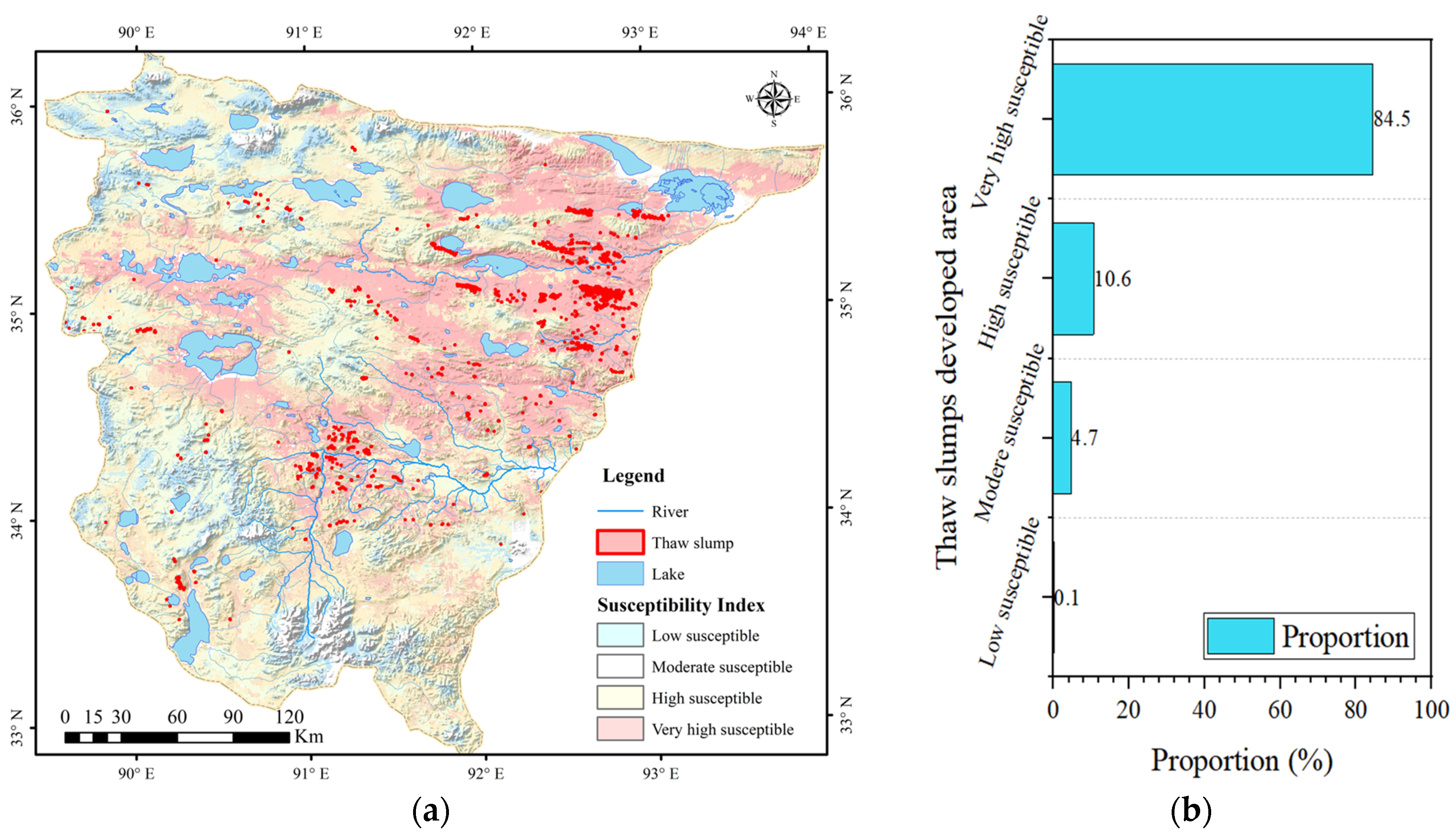
3.3. Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps
4. Discussion
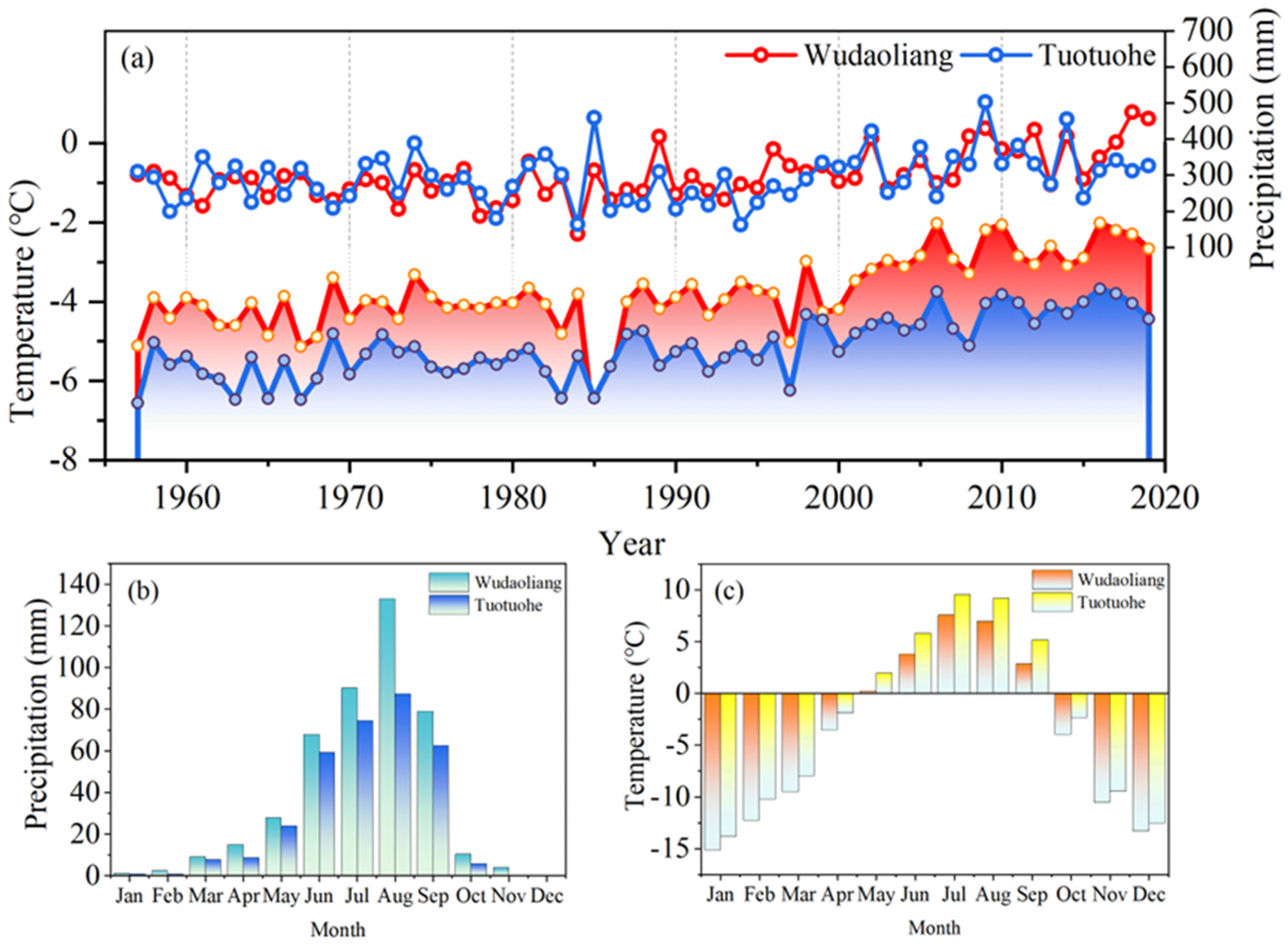
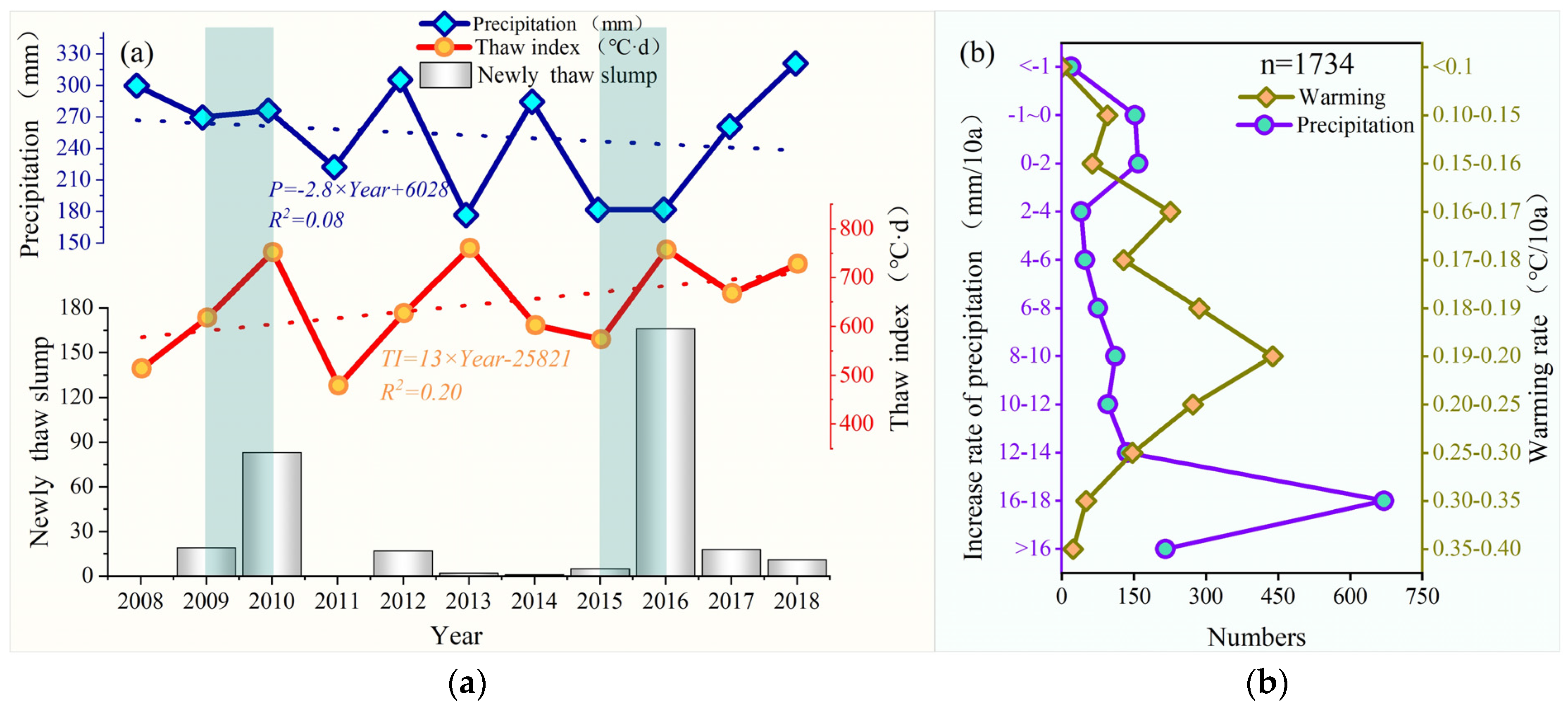
4.1. Relationship Between Thaw Slump and Warming Climate and Precipitation
4.2. Driving Mechanism of Thaw Slump
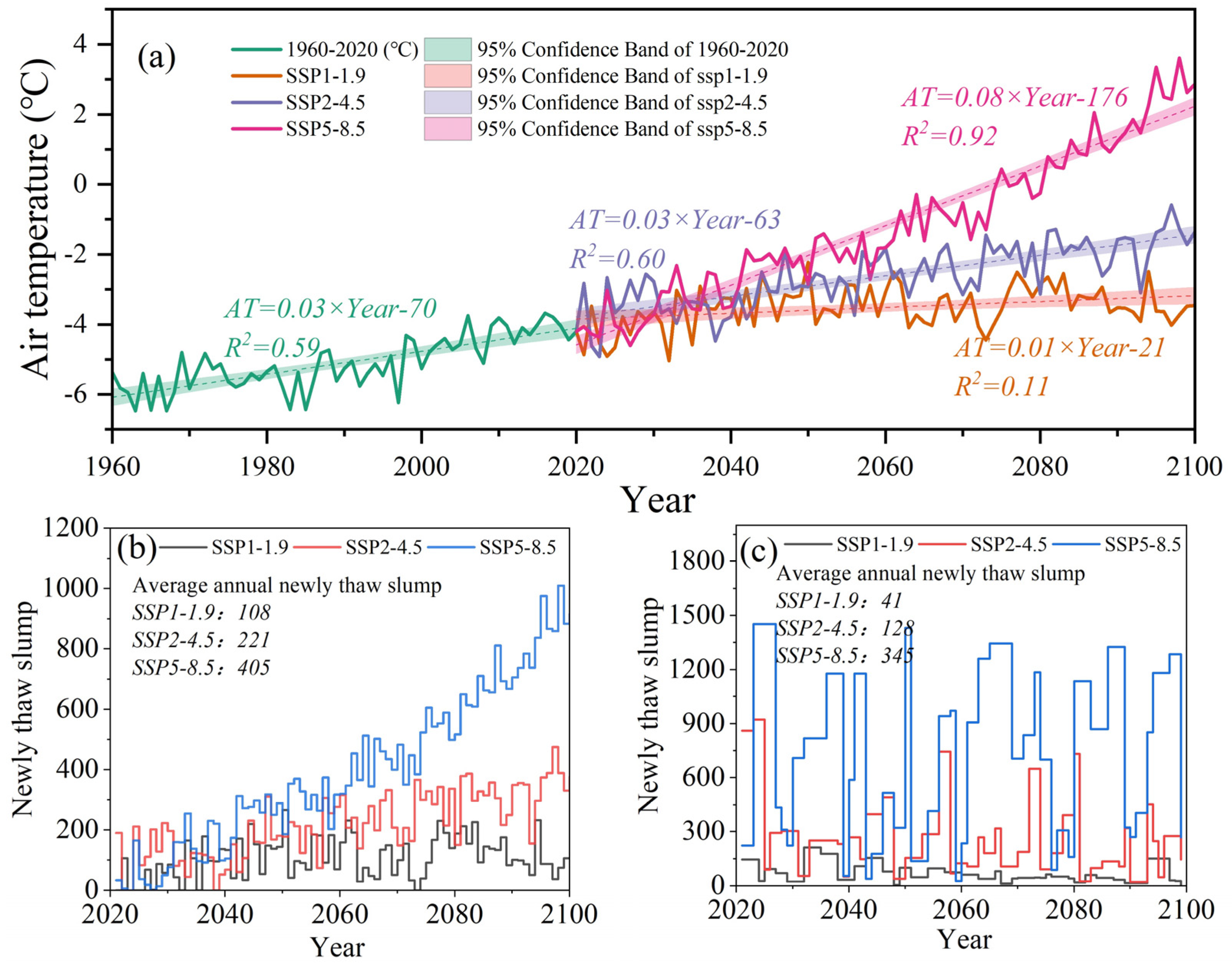
4.3. Future Trends in Thaw Slump Development
4.4. Disaster Effect Caused by Thaw Slump
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QTP | Qinghai–Tibet Plateau |
| GF | Gaofen |
References
- Salzmann, N.; Frei, C.; Vidale, P.L.; Hoelzle, M. The application of Regional Climate Model output for the simulation of high-mountain permafrost scenarios. Glob. Planet. Change 2007, 56, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Slater, A.G.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Nicolsky, D.J. Sensitivity of a model projection of near-surface permafrost degradation to soil column depth and representation of soil organic matter. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, F02011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaphoff, S.; Heyder, U.; Ostberg, S.; Gerten, D.; Heinke, J.; Lucht, W. Contribution of permafrost soils to the global carbon budget. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmy, A.; Salzmann, N.; Scherler, M.; Hauck, C. Permafrost model sensitivity to seasonal climate changes and extreme events in mountainous regions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 035048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fan, X.; Wang, M. Recent warming amplification over high elevation regions across the globe. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskaborn, B.K.; Smith, S.L.; Noetzli, J.; Matthes, H.; Vieira, G.; Streletskiy, D.A.; Schoeneich, P.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Lewkowicz, A.G.; Abramov, A.; et al. Permafrost is warming at a global scale. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; O’Neill, H.B.; Isaksen, K.; Noetzli, J.; Romanovsky, V.E. The changing thermal state of permafrost. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.D.; Wu, T.H. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.J.; Luo, D.L.; Wang, S.L.; Lü, L.Z.; Wu, J.C. Spatiotemporal variability of permafrost degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2011, 3, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Jin, H.; Bensead, V.F.; Jin, X.; Li, X. Hydrothermal processes of near-surface warm permafrost in response to strong precipitation events in the Headwater Area of the Yellow River, Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Guo, D.X.; Qiu, G.Q.; Cheng, G.D.; Li, S.D. Geocryology in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, M.M. Geological and Geomorphological Description of Bol’shoi Lyakhovskii Island; Trudy SOPS AN SSSR, Ser. 7; Publishing House of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR: Yakutsk, Russia, 1932. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Soloviev, P.A. Thermokarst phenomena and landforms due to frost heaving in Central Yakutia. Biul. Peryglac. 1973, 23, 135–155. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kokelj, S.V.; Lantz, T.C.; Tunnicliffe, J.; Segal, R.; Lacelle, D. Climate-driven thaw of permafrost preserved glacial landscapes, northwestern Canada. Geology 2017, 45, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, P. Thermal regime of a thermokarst lake and its influence on permafrost, Beiluhe Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Ma, W.; Lu, J. Development and thermal regime of a thaw slump in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2012, 83–84, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, C.R.; Lewkowicz, A.G. Canadian Landform Examples—17: Retrogressive thaw slumps. Can. Geogr. 1990, 34, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, N. Solifluction and mudflow on a limestone periglacial slope in the Swiss Alps: 14 years of monitoring. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljedahl, A.K.; Boike, J.; Daanen, R.P.; Fedorov, A.N.; Frost, G.V.; Grosse, G.; Hinzman, L.D.; Iijma, Y.; Jorgen-son, J.C.; Matveyeva, N.; et al. Pan-Arctic ice-wedge degradation in warming permafrost and its influence on tundra hydrology. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.H.; Kokelj, S.V.; Lantz, T.C.; McFarlane-Winchester, M.; Olthof, I.; Lacelle, D. Climate sensitivity of high Arctic permafrost terrain demonstrated by widespread ice-wedge thermokarst on Banks Island. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yin, G.; Ding, Z.; Shang, Y.; Luo, J. Extreme degradation of alpine wet meadow decelerates soil heat transfer by preserving soil organic matter on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2025, 653, 132748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowicz, A.G.; Way, R.G. Extremes of summer climate trigger thousands of thermokarst landslides in a High Arctic environment. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowicz, A.G. Dynamics of active-layer detachment failures, Fosheim Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2007, 18, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudy, A.C.A.; Lamoureux, S.F.; Treitz, P.; Van Ewiijk, K.; Bonnaventure, P.P. Terrain controls and landscape-scale susceptibility modelling of active-layer detachments, Sabine Peninsula, Melville Island, Nunavut. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2016, 28, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borge, A.F.; Westermann, S.; Solheim, I.; Etzelmüller, B. Strong degradation of palsas and peat plateaus in northern Norway during the last 60 years. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamet, S.D.; Chun, K.P.; Kershaw, G.G.L.; Loranty, M.M.; Kershaw, G.P. Recent increases in permafrost thaw rates and areal loss of palsas in the western Northwest Territories, Canada. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2017, 28, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; McGuire, A.D.; Schädel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J.W.; Hayes, D.J.; Hugelius, G.; Koven, C.D.; Kuhry, P.; Lawrence, D.M.; et al. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature 2015, 520, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Schuster, P.F.; Abbott, B.W.; Kang, S.; Guo, J.; Sun, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, T. Permafrost degradation enhances the risk of mercury release on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 708, 135127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Niu, F.; Lin, Z.; Liu, M.; Yin, G. Recent acceleration of thaw slumping in permafrost terrain of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An example from the Beiluhe Region. Geomorphology 2019, 341, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Fang, J.; Liu, M. Thaw-induced slope failures and stability analyses in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Landslides 2016, 13, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balser, A.W.; Jones, J.B.; Gens, R. Timing of retrogressive thaw slump initiation in the Noatak Basin, northwest Alaska, USA. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Liu, L. Using deep learning to map retrogressive thaw slumps in the Beiluhe region (Tibetan Plateau) from CubeSat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 237, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Niu, F.; Lin, Z.; Liu, M.; Yin, G.; Gao, Z. Inventory and frequency of retrogressive thaw slumps in permafrost region of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Niu, F.J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Ding, Z.; Pang, W.; Lin, Z. Environmental Characteristics of High Ice-Content Permafrost on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Cheng, G.; Ni, W.; Jin, D. Engineering-related slope failure in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2005, 42, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Lewkowicz, A.G.; Rouse, W.R. Response of the Canadian permafrost environment to climatic change—Physical geography. Phys. Geogr. 1992, 13, 287–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraysse, F.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Meunier, J.D. Experimental study of terrestrial plant litter interaction with aqueous solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, M.A.; Striegl, R.G. Complex vulnerabilities of the water and aquatic carbon cycles to permafrost thaw. Front. Clim. 2021, 3, 730402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Huang, Y.; Bense, V.F.; Ma, Q.; Marchenko, S.S. Permafrost Degradation and Its Hydrogeological Impacts. Water 2022, 14, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yang, G.; Frauenfeld, O.W.; Tian, W.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Wei, G.; Luo, J.; Mu, C.; Niu, F. The first hillslope thermokarst inventory for the permafrost region of the Qilian Mountains. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 2023–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Nan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, G. Qinghai-Tibet Plateau wetting reduces permafrost thermal responses to climate warming. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 562, 116858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yao, M.; Fan, X.; Yin, G.; Meng, X.; Lin, Z. Evidence of warming from long-term records of climate and permafrost in the hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 836085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Gu, G.A.; Li, S.D. Natural Environment on the Hoh Xil Hill Region of Qinghai; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Fan, X.; Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Yin, G.; Liu, M. Factors controlling near surface ground-ice characteristics in a region of warm permafrost, Beiluhe Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.A.; Niu, F.J.; Lin, Z.J.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.H. Data-driven Spatiotemporal Projections of Shallow Permafrost Based on CMIP6 across the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau at 1 km2 Scale. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Geo-Science Analysis of Remote Sensing; China Surveying and Mapping Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Liu, X. The present research condition and development trend of remotely sensed imagery interpretation. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2004, 16, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Thaw slumping in Fenghuo Mountain area along Qinghai-Xizang highway. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1990, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ling, S.; Li, X.; Sun, C.W.; Xu, J.X.; Huang, T. Comparative study on rapid assessment models of landslide susceptibility in Jiuzhaigou County. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2020, 39, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wolfe, S.A.; Morse, P.D.; Olthof, I.; Fraser, R.H. Spatiotemporal impacts of wildfire and climate warming on permafrost across a subarctic region, Canada. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 120, 2338–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantanen, M.; Karpechko, A.Y.; Lipponen, A.; Nordling, K.; Hyvärinen, O.; Ruosteenoja, K.; Vihma, T.; Laaksonen, A. The Arctic has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Cai, Z.; Pepin, N.; Chen, D.; Ahrens, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, F.; Kang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, T.; et al. Warming amplification over the Arctic Pole and Third Pole: Trends, mechanisms and consequences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 103625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacelle, D.; Bjornson, J.; Lauriol, B. Climatic and geomorphic factors affecting contemporary (1950–2004) activity of retrogressive thaw slumps on the Aklavik Plateau, Richardson Mountains, NWT, Canada. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.B.; Zhang, T.J. Changes in active layer thickness over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1995–2007. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D09107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.J.; Wu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Du, E.; Liu, G.; Qiao, Y. Temporal and spatial variations of the active layer along the Qinghai-Tibet highway in a permafrost region. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 4609–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Study on the Evolution of Lakes and Ecological Environmental Effects on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Lin, Z.; Fan, X.; Lan, A.; Li, W. Development characteristics and disaster effects of thermokarst slumps in Hoh Xil, central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2023, 45, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar]
- French, H.M. The Periglacial Environment; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Gao, S.; Lewkowicz, A.G.; Zhao, H.; Pang, S.; Wu, Q. Development of a rapid active layer detachment slide in the Fenghuoshan Mountains, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2022, 33, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y. Impacts of permafrost changes on alpine ecosystem in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, T.C.; Kokelj, S.V.; Gergel, S.E.; Henry, G.H.R. Relative impacts of disturbance and temperature: Persistent changes in microenvironment and vegetation in retrogressive thaw slumps. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokelj, S.V.; Jorgenson, M.T. Advances in Thermokarst Research. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2013, 24, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; Mack, M.C. Ecological response to permafrost thaw and consequences for local and global ecosystem services. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, J.; Qin, S.; Liu, L.; Fang, K.; Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y. Determinants of carbon release from the active layer and permafrost deposits on the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

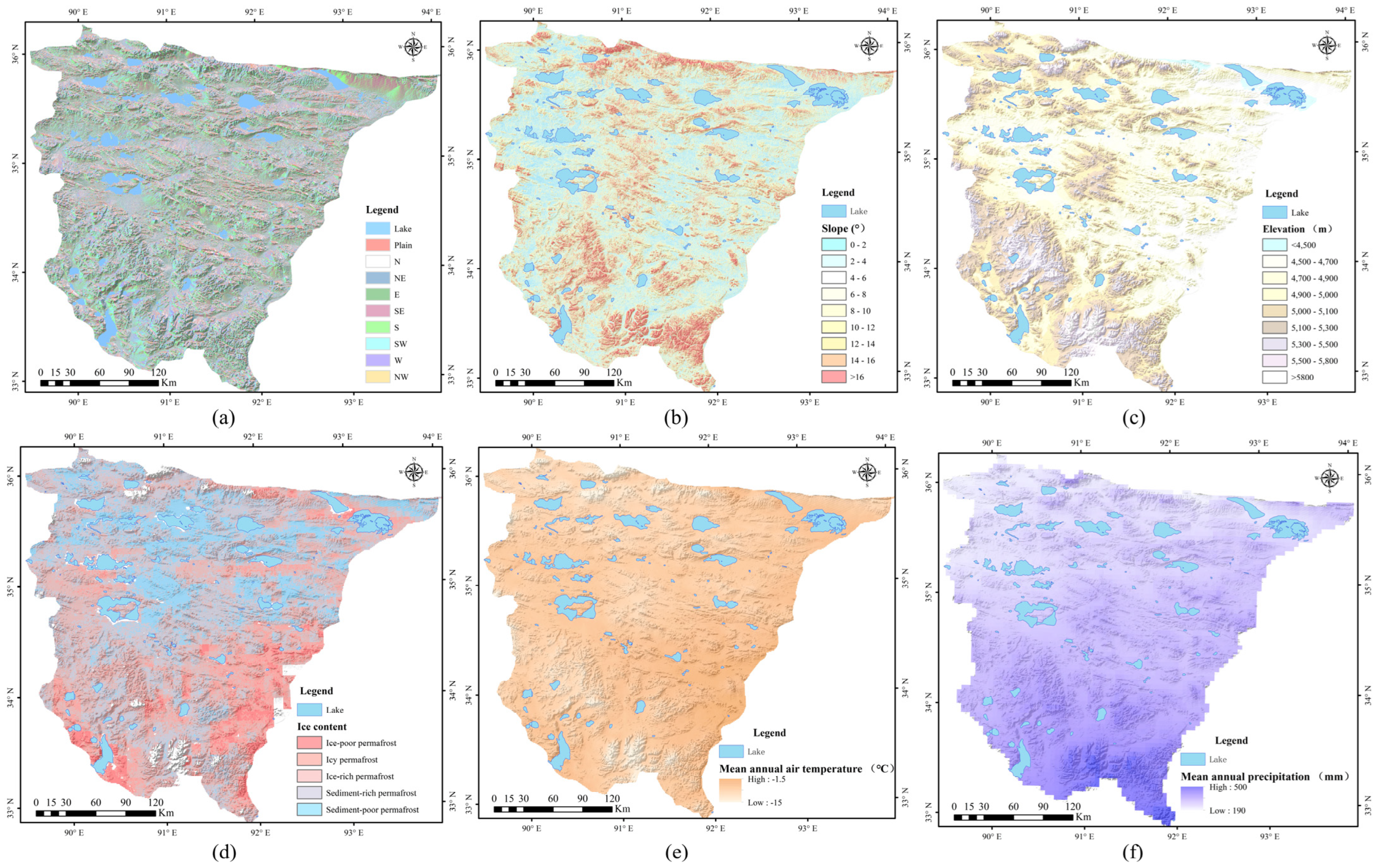


| Factors | Classification | Information Value | Factors | Classification | Information Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation (m) | <4500 | - | Slope (°) | 0–2 | −0.616333 |
| 4500–4600 | 0.041871 | 2–4 | −0.180810 | ||
| 4600–4700 | 0.359353 | 4–6 | 0.262187 | ||
| 4700–4800 | 1.168563 | 6–8 | 0.348616 | ||
| 4800–4900 | 0.476836 | 8–10 | 0.451103 | ||
| 4900–5000 | −0.747066 | 10–12 | 0.118902 | ||
| 5000–5100 | −1.105579 | 12–14 | −0.309901 | ||
| 5100–5200 | −1.605407 | 14–16 | −0.332266 | ||
| 5300–5400 | −2.429923 | >16 | −1.041154 | ||
| 5400–5500 | −2.077762 | Slope aspect | N | 0.540414 | |
| Mean annual air temperature (°C) | <−8 | −3.754438 | NE | 0.538344 | |
| −7~−8 | −1.718537 | E | 0.026313 | ||
| −6~−7 | −1.182438 | SE | −0.506935 | ||
| −5~−6 | 0.325547 | S | −0.680544 | ||
| −4~−5 | 0.673817 | SW | −0.693052 | ||
| −3~−4 | −0.508229 | W | −0.215437 | ||
| −1.7~−3 | −1.989411 | Ice content | Ice-poor | −1.152652 | |
| Mean annual precipitation (mm) | 200–300 | −1.788738 | Icy | −0.206302 | |
| 300–400 | 0.224823 | Ice-rich | −0.074456 | ||
| 400–500 | 0.020186 | Sediment-rich | 0.146778 | ||
| 500–600 | −3.262990 | Sediment-poor | 0.225083 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Lin, Z.; Yao, M.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; Gao, Z. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps Associated with Climate Change in the Hoh Xil Region, in the Hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091614
Fan X, Lin Z, Yao M, Wang Y, Gu Q, Luo J, Wu X, Gao Z. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps Associated with Climate Change in the Hoh Xil Region, in the Hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091614
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xingwen, Zhanju Lin, Miaomiao Yao, Yanhe Wang, Qiang Gu, Jing Luo, Xuyang Wu, and Zeyong Gao. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps Associated with Climate Change in the Hoh Xil Region, in the Hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091614
APA StyleFan, X., Lin, Z., Yao, M., Wang, Y., Gu, Q., Luo, J., Wu, X., & Gao, Z. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Susceptibility Assessment of Thaw Slumps Associated with Climate Change in the Hoh Xil Region, in the Hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091614







