An Enhanced Algorithm Based on Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet for Synthetic Aperture Radar Operating Mode Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Simulation of Intercepted SAR Signals Under Different Operating Modes
2.1. Modeling of the Intercepted SAR Signals
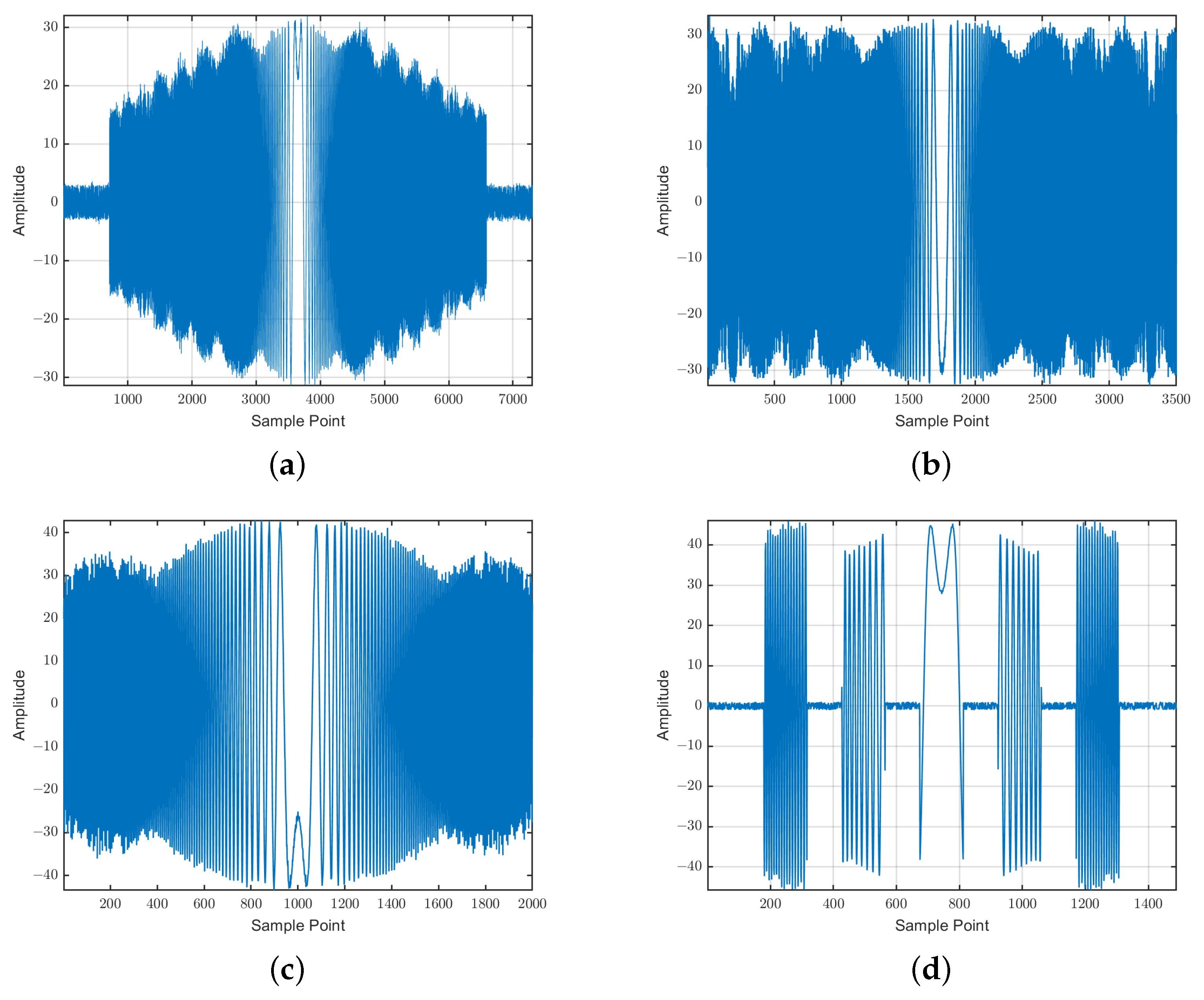
2.2. Simulation of the Intercepted Signals
3. The Proposed Algorithm
3.1. RPC and Azimuth Time–Frequency Analysis
3.1.1. The RPC Processing
3.1.2. Azimuth Time–Frequency Analysis
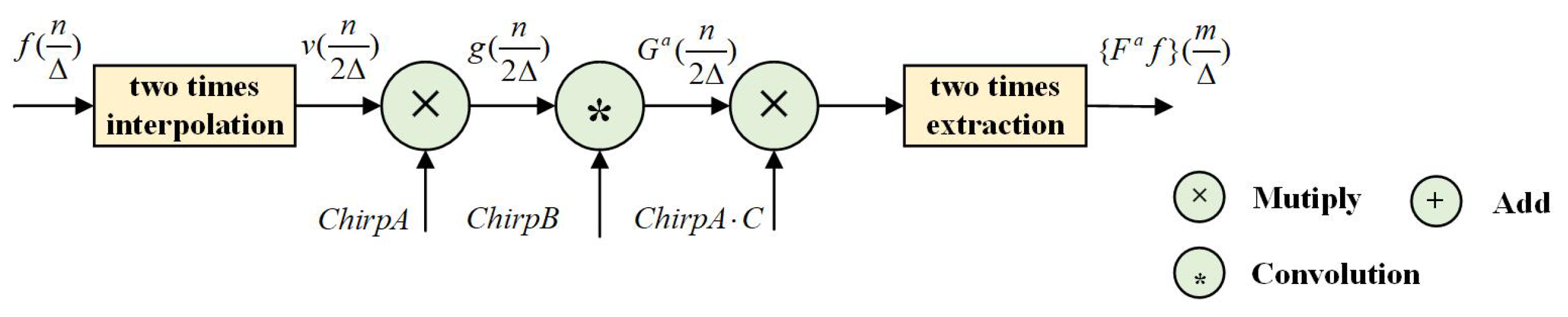
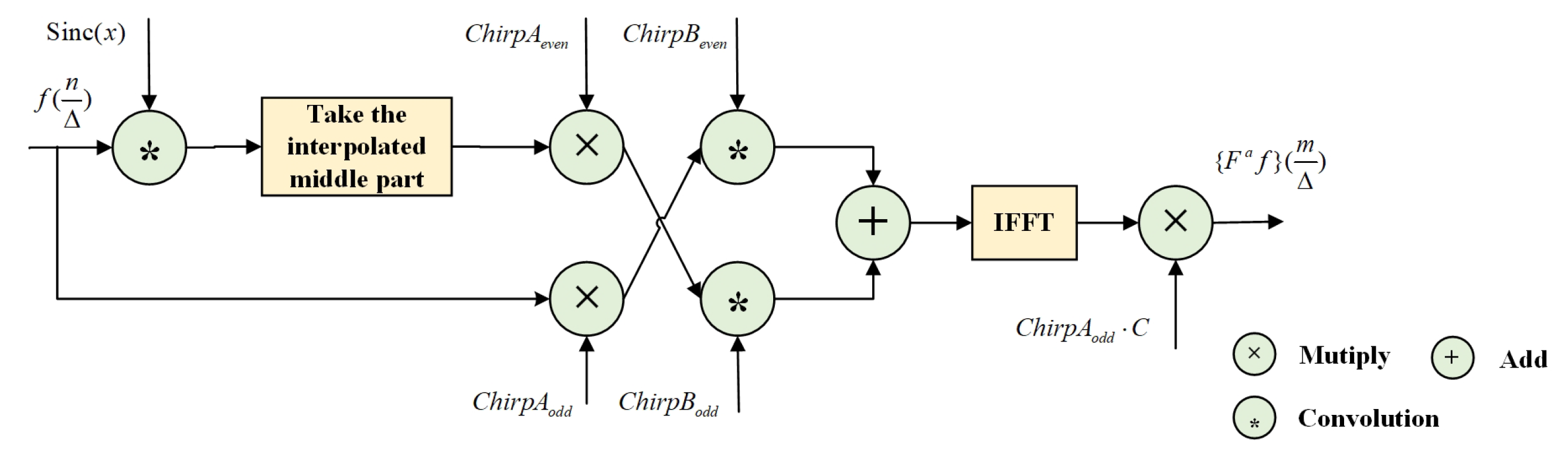
3.2. The Improved CFS-FRFT Algorithm
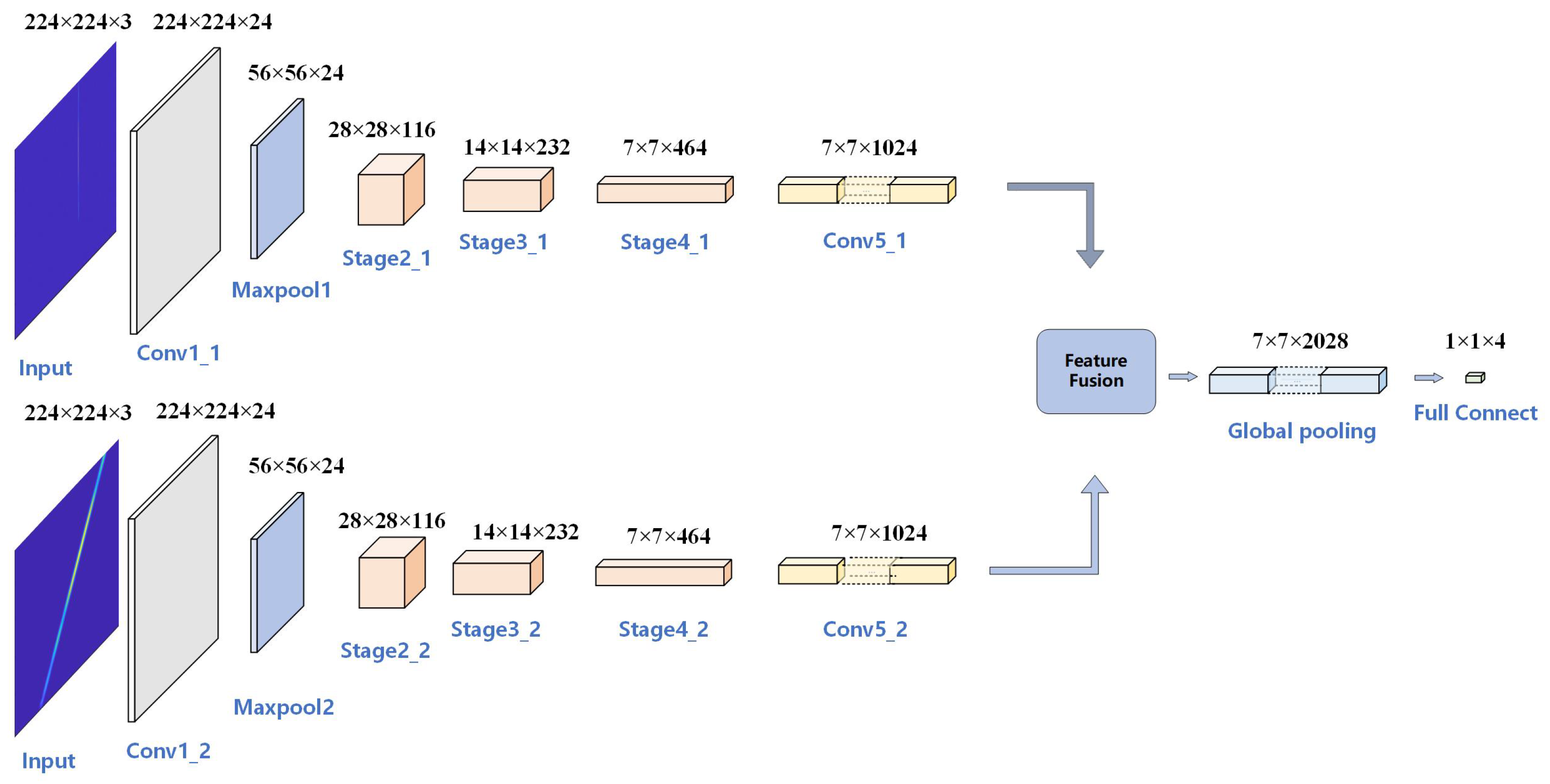
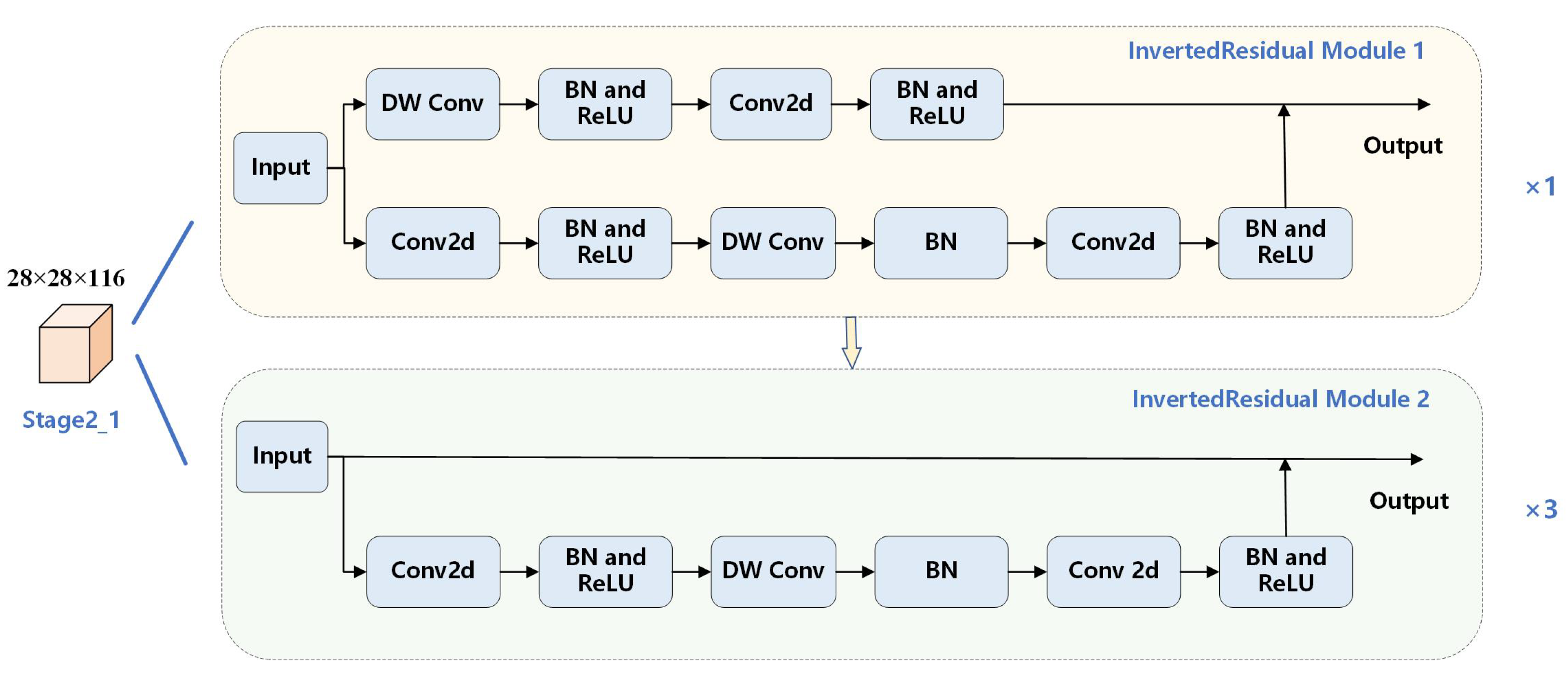
3.3. The Proposed DIFF-ShuffleNet
4. Results
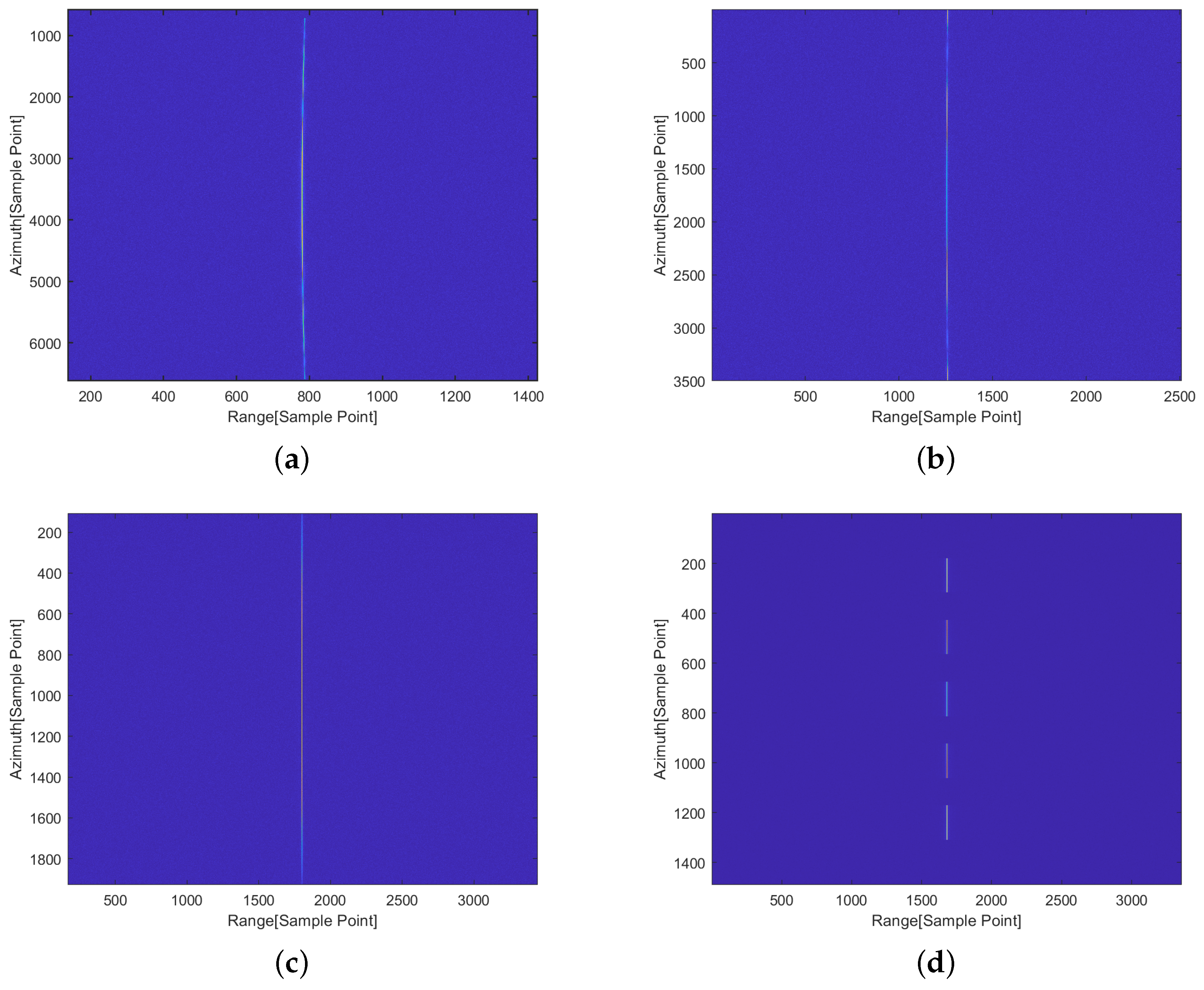
4.1. Performance Comparison of Parameter Estimation Algorithms
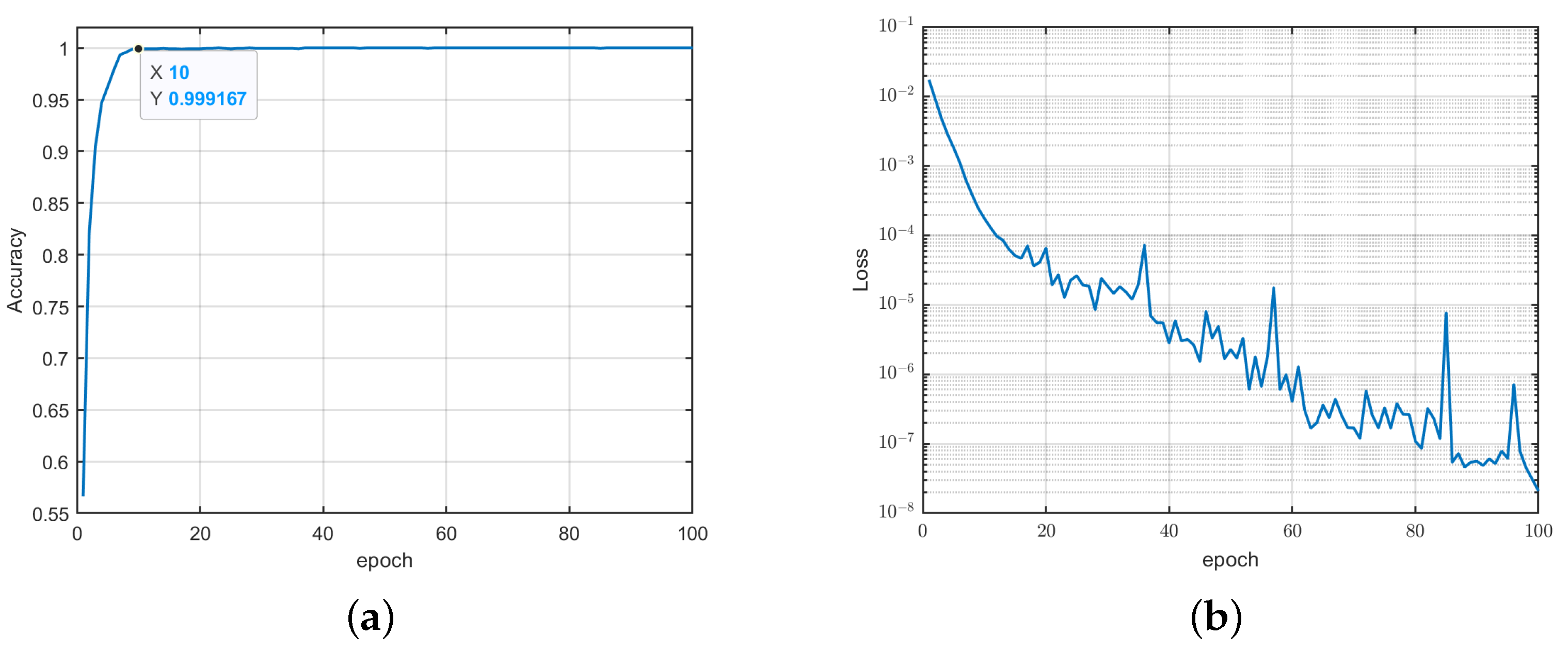
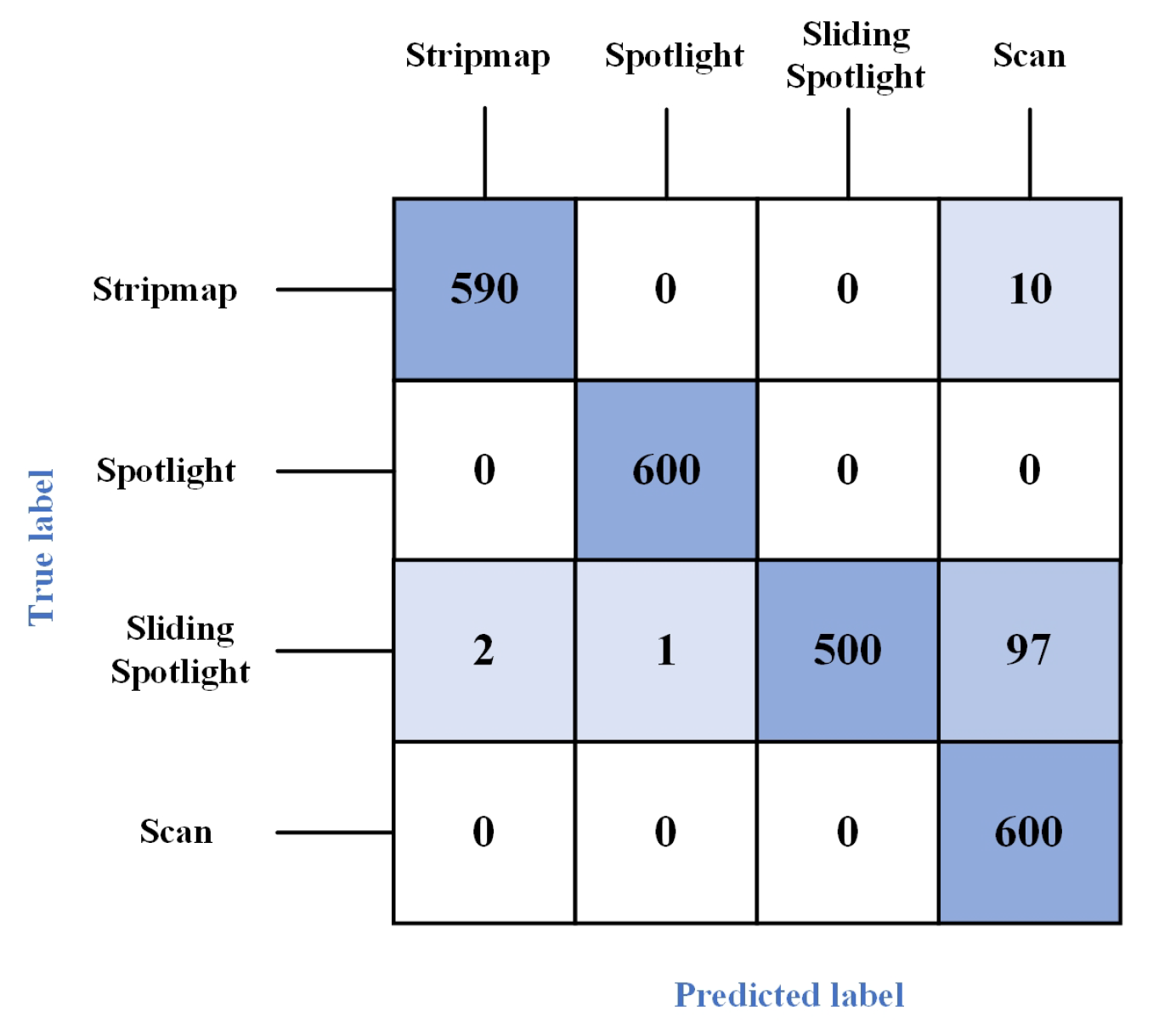
4.2. Analysis of DIFF-ShuffleNet Recognition Performance
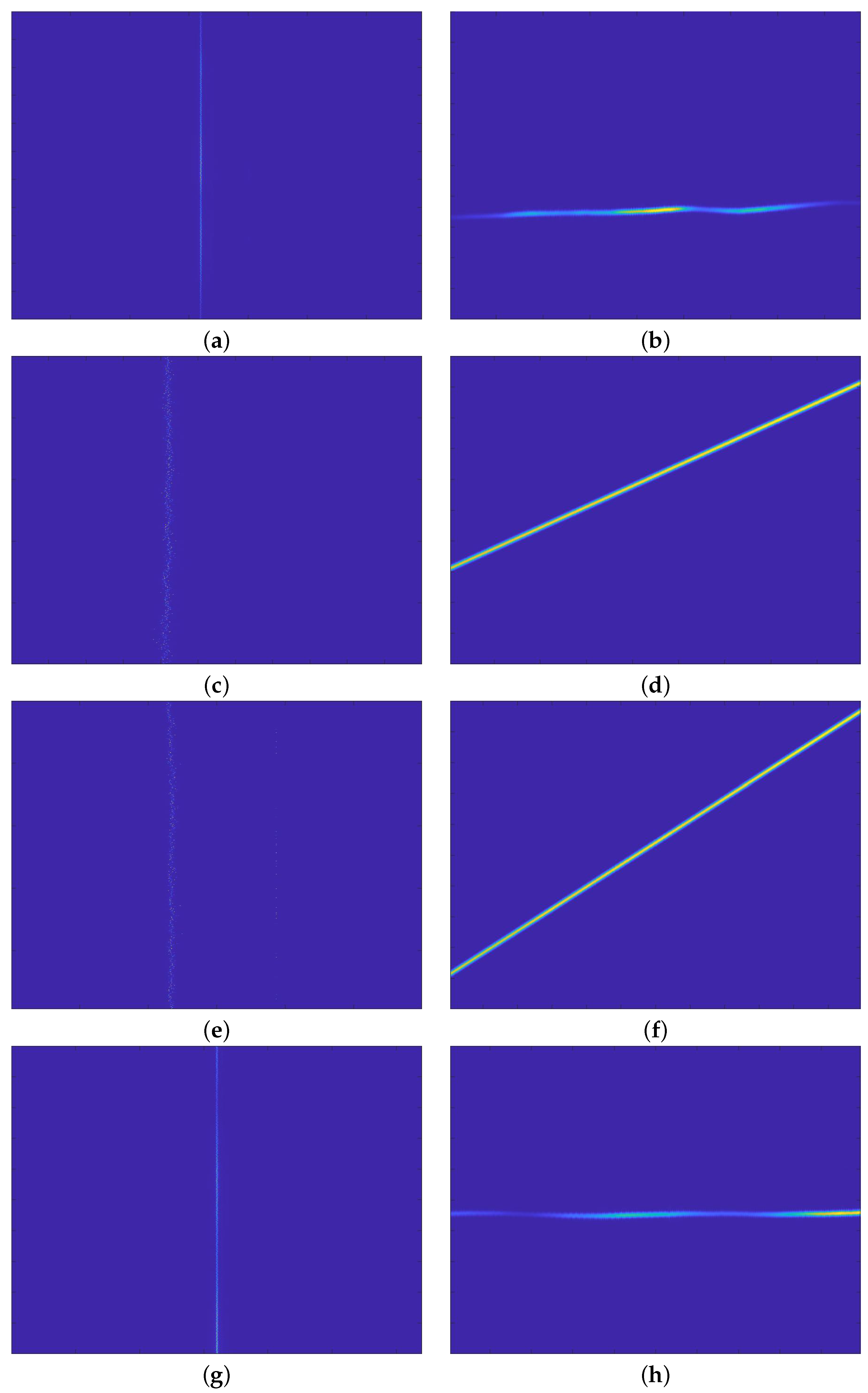
4.3. Actual SAR Data Processing
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SAR | synthetic aperture radar |
| RPC | range pulse compression |
| DIFF-ShuffleNet | Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet |
| NRMSE | normalized root mean square error |
| CFS-FRFT | coarse-to-fine search fractional Fourier transform |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| PRF | pulse repetition frequency |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| BP | back propagation |
| LFM | linear frequency modulation |
| FRFT | fractional Fourier transform |
| STFT | short-time Fourier transform |
References
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, C.; Shi, S.; Fang, G. An Efficient Algorithm Based on CSA for THz Stepped-Frequency SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Shi, S.; Li, C.; Cheng, W.; Fang, G. An Efficient Algorithm Based on Frequency Scaling for THz Stepped-Frequency SAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5225815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. An Efficient Digital Channelized Receiver for low SNR and Wideband Chirp Signals Detection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, W.; Cheng, W.; Liu, X. Hybrid Domain Efficient Modulation-Based Deceptive Jamming Algorithm for Nonlinear-Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, G. Influence of Estimate Error of Radar Kinematic Parameter on Deceptive Jamming Against SAR. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Shu, T.; Yu, K.B.; Yu, W. Efficient Deceptive Jamming Method of Static and Moving Targets Against SAR. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, H.; Cheng, H. Comparative Study on Stripmap Mode, Spotlight Mode, and Sliding Spotlight Mode. J. Grad. Sch. CAS 2011, 28, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y. The Sidelobe Surveillance Study of Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar in Spotlight and Sliding Spotlight Mode. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2012, 12, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, Y. Optimal Selection of PRF for Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar in Different Working Mode. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2012, 35, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jia, X. Surveillance Study of Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar in Different Working Modes. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2013, 49, 223–227+241. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Li, C.; Gao, J.; Sun, B. Research on Operation Inversion Method of Spaceborne SAR. Radio Eng. 2012, 42, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Li, C.; Sun, B. An Operation Inversion Method of Spaceborne SAR Based on Genetic Algorithm. Space Electron. Technol. 2013, 10, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Da, R.; Xin, J.; Yin, C.; Lao, G.; Yang, G. In Synthetic Aperture Radar Operation Mode Recognition Based on Time-Frequency Analysis. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference, Hangzhou, China, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Zhong, H.; Chen, W. Identification of the Spaceborne SAR Operating Modes under Reconnaissance Mode. J. Hangzhou Dianzi Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 37, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, C. Operating Modes Identification of Spaceborne SAR Based on Deep Learning. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Sci. 2022, 56, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, C.; Fang, Y. Operating Modes of Spaceborne SAR Recognition Based on CGRU-SVM. Command Control Simul. 2022, 44, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Jin, G.; Song, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D. A Novel Method to Identify the Spaceborne SAR Operating Mode based on Sidelobe Reconnaissance and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, W.; Liu, W. Accurate Reconstruction and Suppression for Azimuth Ambiguities in Spaceborne Stripmap SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ye, S.; Zhu, Z. Polar Format Agorithm Using Chirp Scaling for Spotlight SAR Image Formation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 1433–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, D.; Baker, C. High Resolution Processing of Hybrid Strip-map/Spotlight Mode SAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, London, UK, 1 December 1996; pp. 366–374. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Eineder, M. Scansar Processing Using Standard High Precision SAR Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzner, J.; Bamler, R. Burst-mode and Scansar Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1917–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, F. Improved Full-Aperture ScanSAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Aperture Interpolation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, C. Time-Frequency Analysis: Theory and Applications; Pnentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Serbes, A. On the Estimation of LFM Signal Parameters: Analytical Formulation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldimashki, O.; Serbes, A. Performance of Chirp Parameter Estimation in the Fractional Fourier Domains and an Algorithm for Fast Chirp-rate Estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 3685–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Y. A Fast Algorithm of LFM Signal Detection and Parameter Estimation Based on Efficient FrFT. J. Electron. Inform. Technol. 2017, 39, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Capus, C.; Brown, K. Fractional Fourier Transform of the Gaussian and Fractional Domain Signal Support. In Proceedings of the IEEE Proceedings-Vision Image and Signal Processing, London, UK, 1 April 2003; pp. 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Capus, C.; Rzhanov, Y.; Linnett, L. The Analysis of Multiple Linear Chirp Signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Time-Scale and Time-Frequency Analysis and Applications, London, UK, 29 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Tao, R.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y. Detection and Parameter Estimation of Multicomponent LFM Signal Based on the Fractional Fourier Transform. Sci. China Ser. F Inform. Sci. 2004, 47, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J. The parameter estimation of wideband LFM signal based on down-chirp and compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 14–16 December 2018; pp. 1436–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Ozaktas, H.M.; Barshan, B.; Mendlovic, D.; Onural, L. Convolution, Filtering, and Multiplexing in Fractional Fourier Domains and Their Relation to Chirp and Wavelet Transforms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1994, 11, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Liang, G.; Zhao, X.-H. An Efficient FPGA-Based Implementation of Fractional Fourier Transform Algorithm. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2010, 60, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z. Research on UWB Radar Signal Detection Based on Compressed Sensing. Master’s Thesis, Xidian University, Xi’an China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. In Shufflenet v2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.A. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Determination Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
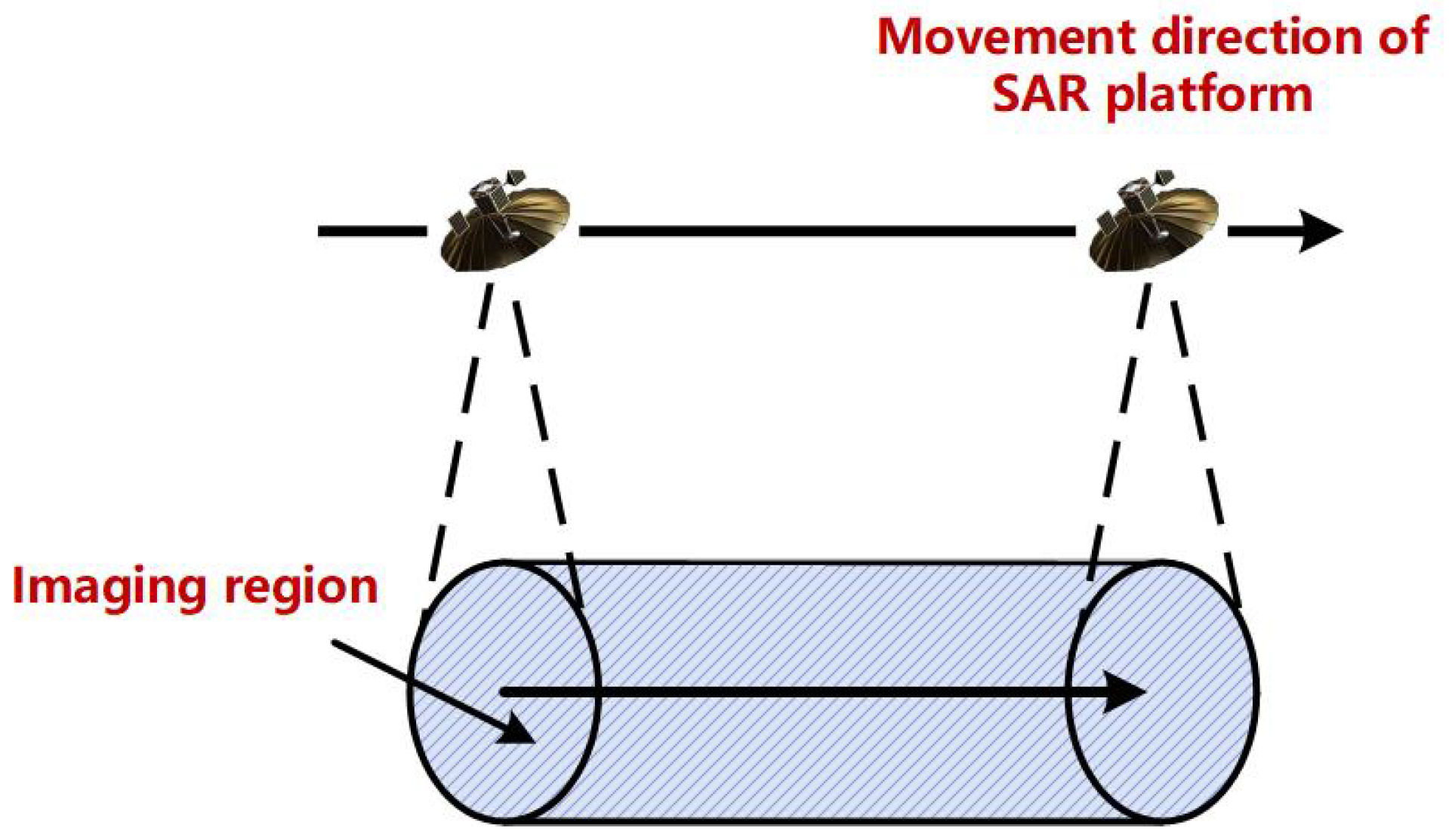

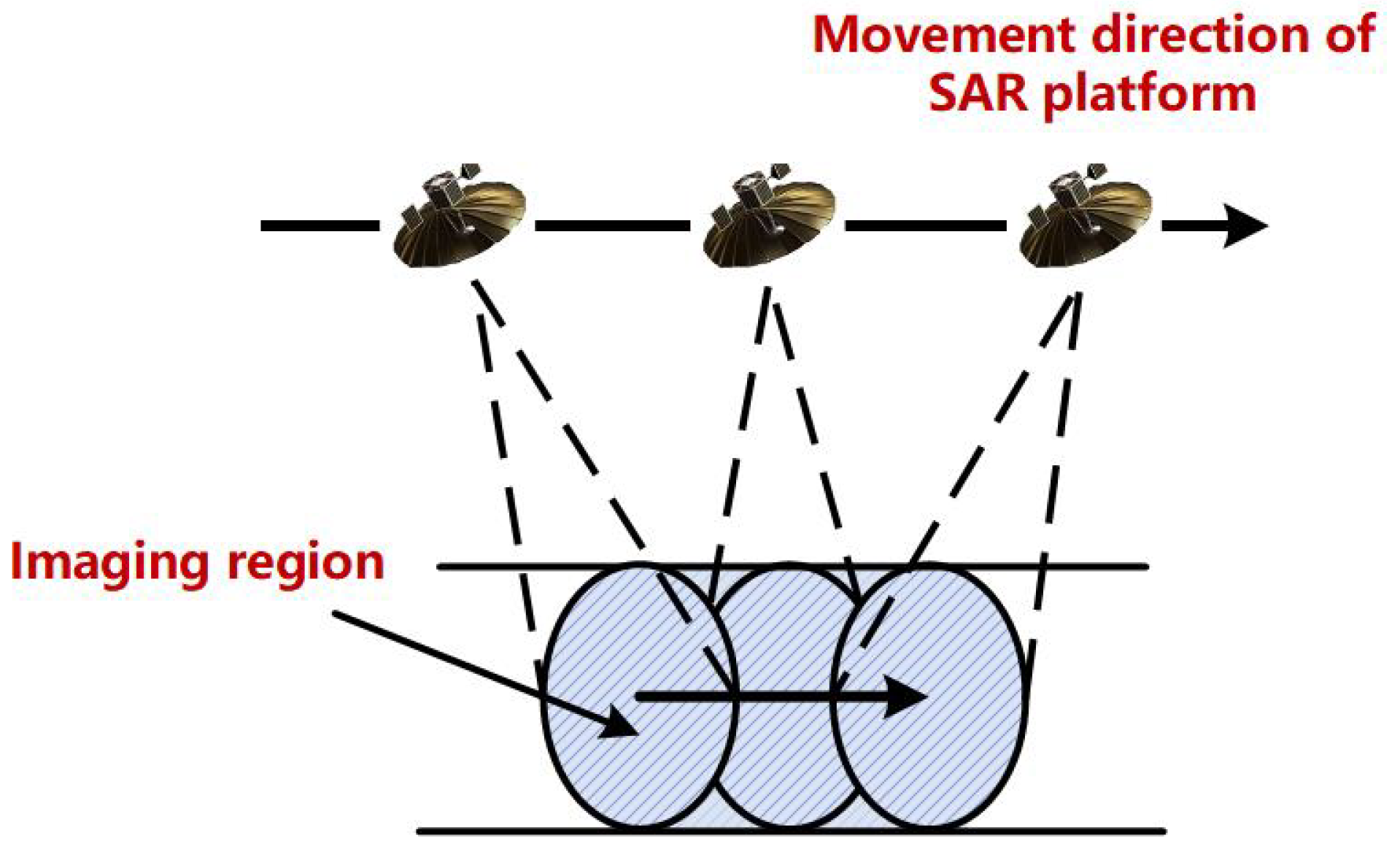






| Stripmap SAR | |||
| Carrier frequency | 9.6 GHz | Slant range of scene center | 600 km |
| Velocity of SAR platform in motion | 7000 m/s | Azimuth resolution | 1.14 |
| Range signal pulse width | 10 s | Range signal bandwidth | 100 MHz |
| Range sampling frequency | 150 MHz | PRF | 5000.00 Hz |
| Spotlight SAR | |||
| Carrier frequency | 9.6 GHz | Slant range of scene center | 600 km |
| Velocity of SAR platform in motion | 7000 m/s | Antenna length | 6.0 m |
| Range signal pulse width | 10 s | Range signal bandwidth | 100 MHz |
| Range sampling frequency | 150 MHz | PRF | 3500 Hz |
| Sliding Spotlight SAR | |||
| Carrier frequency | 9.6 GHz | Height of SAR platform | 600 km |
| Velocity of SAR platform in motion | 7500 m/s | Antenna length | 4.8 m |
| Range signal pulse width | 20 s | Range signal bandwidth | 90 MHz |
| Range sampling frequency | 120 MHz | PRF | 3500 Hz |
| Scan SAR | |||
| Carrier frequency | 5.3 GHz | Height of SAR platform | 800 km |
| Velocity of SAR platform in motion | 7500 m/s | Azimuth resolution | 1.14 |
| Range signal pulse width | 20 s | Range signal bandwidth | 100 MHz |
| Range sampling frequency | 150 MHz | PRF | 2100 Hz |
| Revisit time (the number of sub-bands is 5) | 120 ms | Dwell time | 66.75 ms |
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Normalized Amplitude | 1 |
| Pulse Width | 10 s |
| Bandwidth | 800 MHz |
| Center Frequency | 600 MHz |
| Sampling Frequency | 2.4 GHz |
| Algorithm | The Minimum SNR for Effective Estimation | Average Running Time |
|---|---|---|
| FRFT (0.001) | −11 dB | 84.108 s |
| CFS-FRFT | −10 dB | 8.088 s |
| CFS-FRFT2 | −5 dB | 4.424 s |
| Ours | −10 dB | 4.645 s |
| Algorithm | Computational Complexity |
|---|---|
| FRFT (0.001) | O(72,000Nlog2N + 168,000N) |
| CFS-FRFT | O(7920Nlog2N + 18,480N) |
| CFS-FRFT2 | O(5280Nlog2N + 7700N) |
| Ours | O(5520Nlog2N + 8680N) |
| SNR | −8 dB | −4 dB | 0 dB | 4 dB | 8 dB | 12 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy [15] | 77.16% | 82.10% | 84.57% | 80.73% | 87.35% | 88.58% |
| Accuracy [17] | 89.81% | 91.67% | 91.67% | 90.74% | 90.43% | 91.35% |
| RPC maps with ShuffleNet | 88.13% | 90.00% | 97.50% | 99.38% | 99.38% | 99.38% |
| Ours | 95.00% | 96.25% | 96.25% | 95.63% | 97.50% | 99.38% |
| Pulse Number | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm [17] | Ours | |
| 200 | 78.09% | 82.50% |
| 400 | 87.65% | 95.63% |
| 600 | 90.12% | 98.13% |
| 800 | 88.89% | 94.38% |
| 1000 | 91.36% | 95.00% |
| Data Name | SAR Platform | Wave Band | Actual Operating Mode | Recognition Results | Correctness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data1.dat | Airborne | Ku | Stripmap | Stripmap | Correct |
| Data2.dat | Spaceborne | C | Spotlight | Spotlight | Correct |
| Data3.dat | Spaceborne | C | Spotlight | Spotlight | Correct |
| Data4.dat | Airborne | Ku | Stripmap | Stripmap | Correct |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Fang, G. An Enhanced Algorithm Based on Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet for Synthetic Aperture Radar Operating Mode Recognition. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091523
Wang H, Lu W, Wu Y, Zhang Q, Liu X, Fang G. An Enhanced Algorithm Based on Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet for Synthetic Aperture Radar Operating Mode Recognition. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091523
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haiying, Wei Lu, Yingying Wu, Qunying Zhang, Xiaojun Liu, and Guangyou Fang. 2025. "An Enhanced Algorithm Based on Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet for Synthetic Aperture Radar Operating Mode Recognition" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091523
APA StyleWang, H., Lu, W., Wu, Y., Zhang, Q., Liu, X., & Fang, G. (2025). An Enhanced Algorithm Based on Dual-Input Feature Fusion ShuffleNet for Synthetic Aperture Radar Operating Mode Recognition. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091523







