Improving the Accuracy of Soil Classification by Using Vis–NIR, MIR, and Their Spectra Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Spectral Pre-Processing
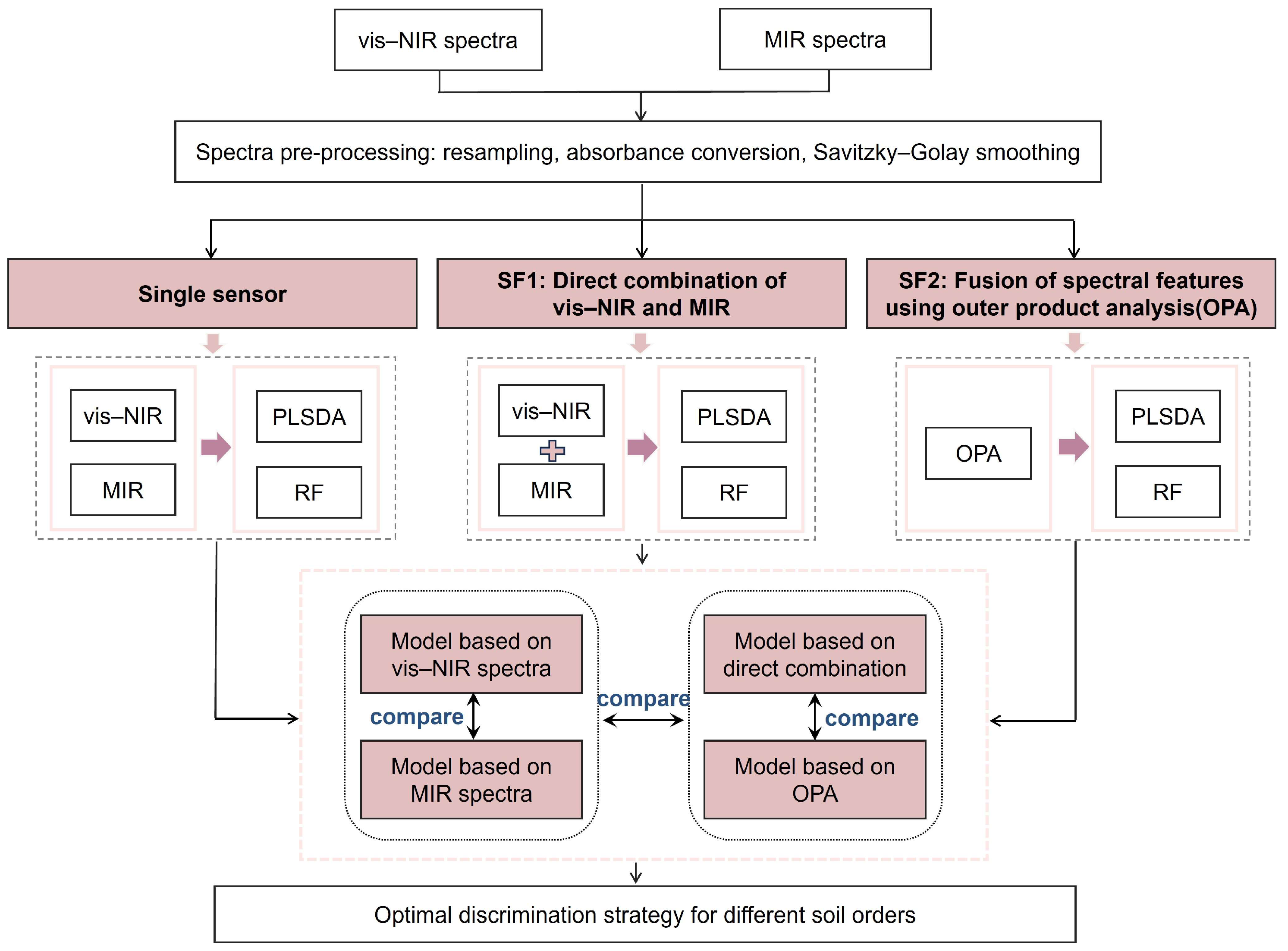
2.3. Spectra Fusion
2.3.1. Low-Level Fusion (SF1)
2.3.2. Middle-Level Fusion (SF2)
2.4. Model Construction and Assessment
2.4.1. Partial Least–Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLSDA)
2.4.2. Random Forest (RF)
2.4.3. Model Performance Evaluation
3. Results
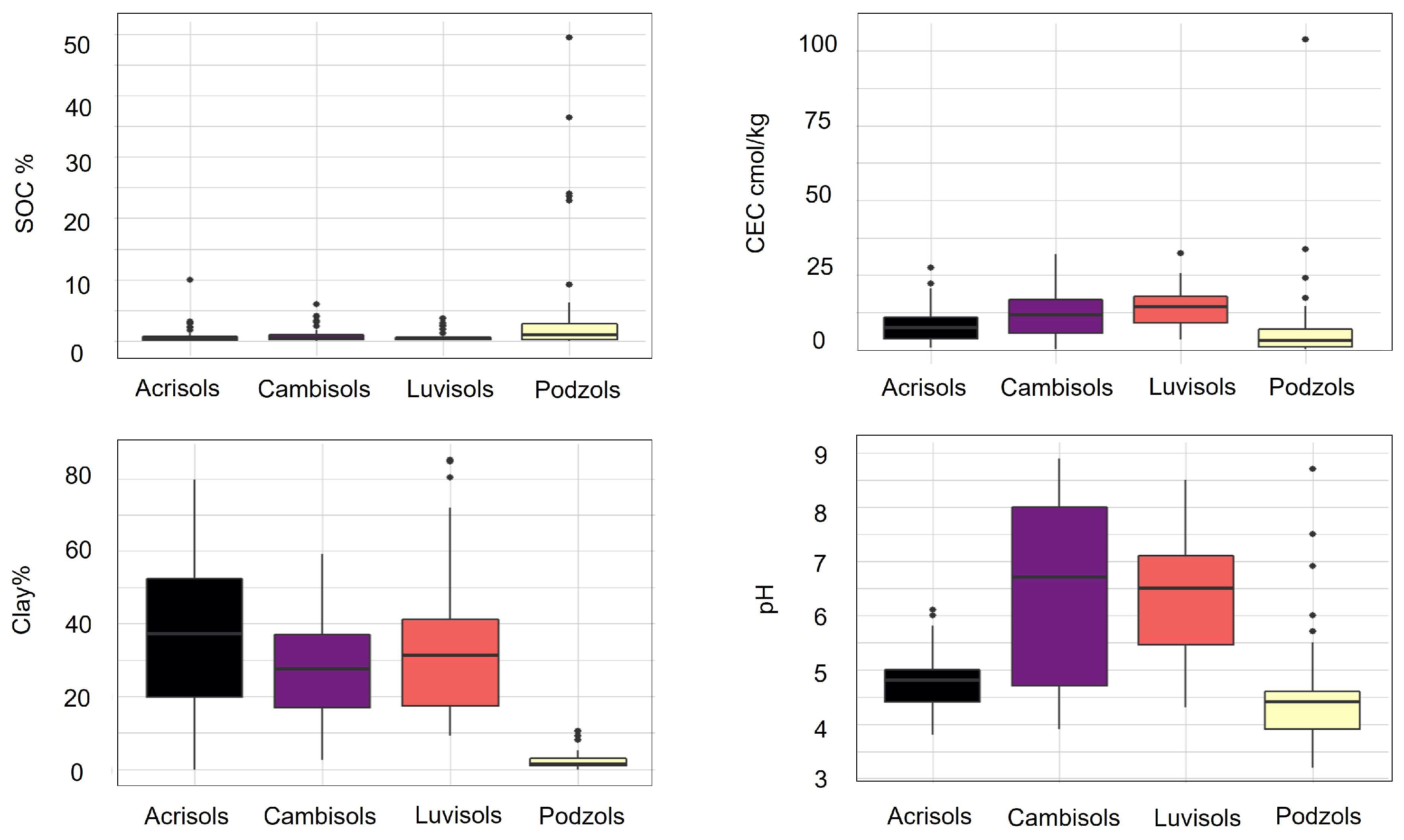
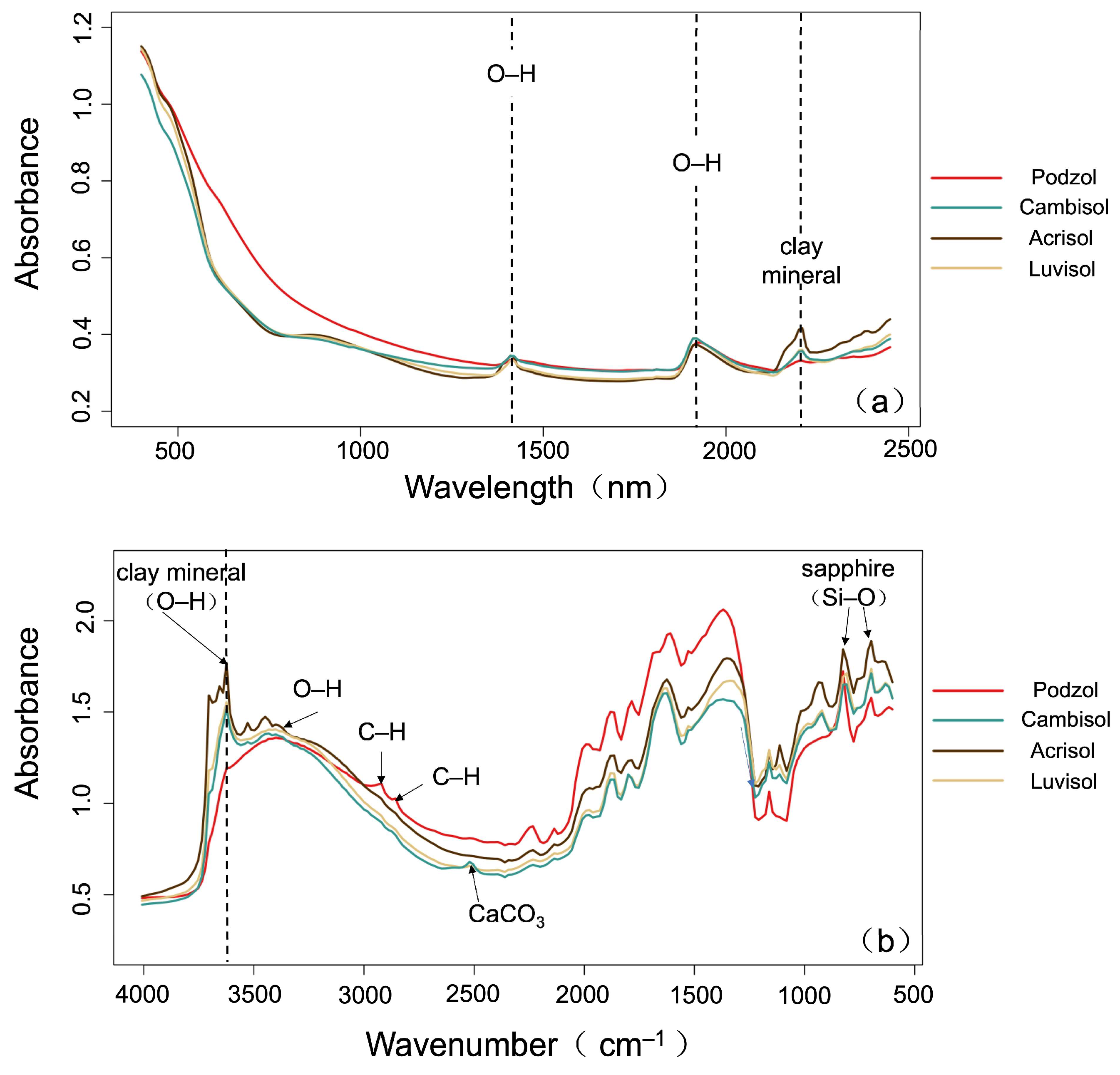
3.1. Soil Properties and Spectral Characteristic
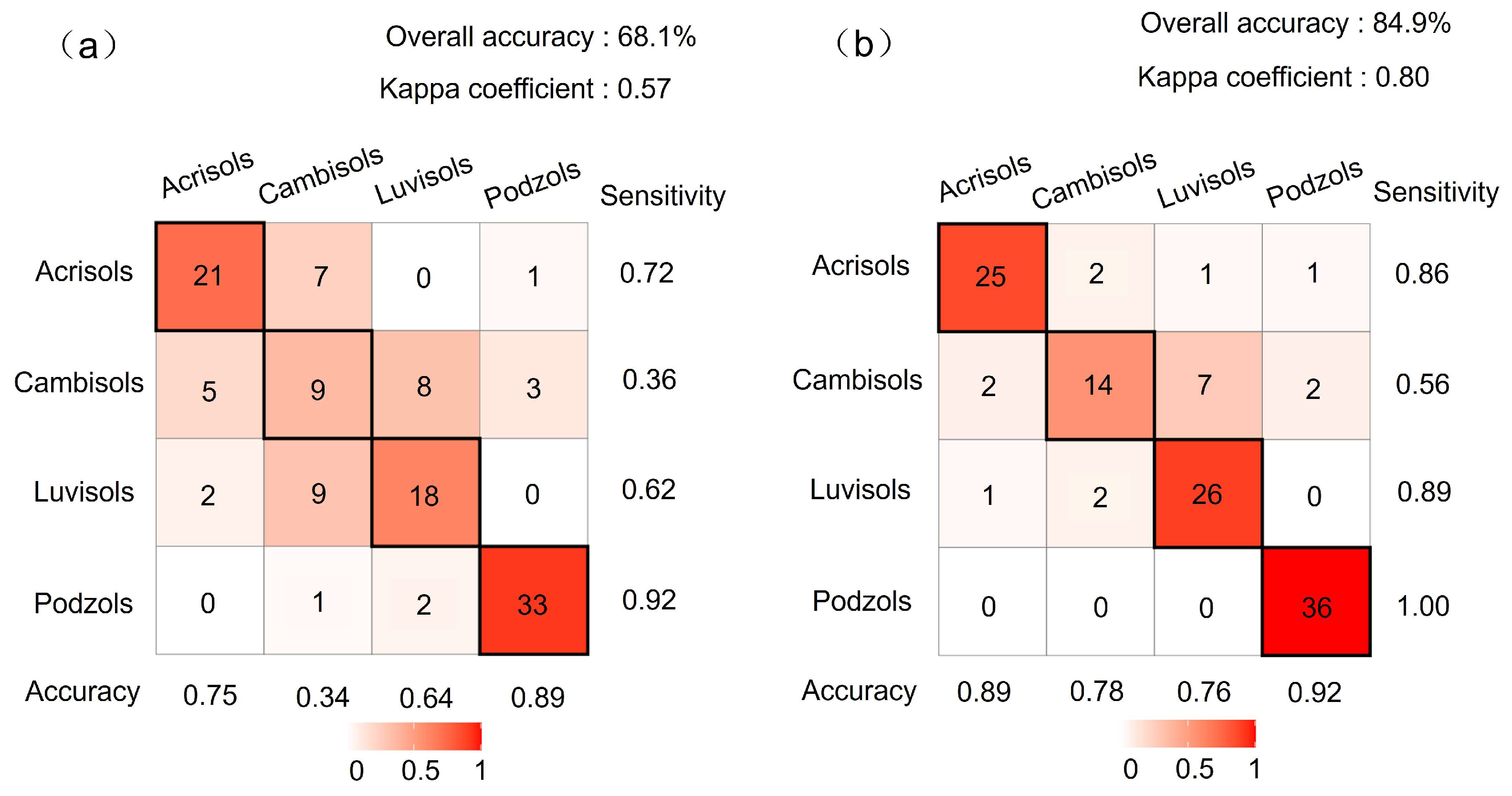
3.2. Classification Model Analyses Using Single Sensor
3.3. Classification Model Analyses Using Sensor Fusion
3.3.1. Low-Level Fusion Predictions (SF1)
3.3.2. Middle-Level Fusion Predictions (SF2)
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Comparison: Single Sensor vs. Sensor Fusion
4.2. Optimal Strategy for Four Soil Classes Determination
4.3. Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- RF outperforms PLSDA: The RF model outperforms the PLSDA model in soil classification. By integrating multiple decision trees, RF captures more detailed soil information and achieves better classification accuracy than the linear PLSDA model.
- (2)
- MIR-RF achieves optimal accuracy: The MIR-RF model reaches the highest classification accuracy of 89.1%, demonstrating the superior information content of MIR spectra for soil discrimination. While fused spectra offers slight accuracy gains over vis–NIR spectra in the RF model, the fusion methods do not surpass the performance of the single MIR spectrum, suggesting that MIR spectroscopy captures the most essential soil classification information.
- (3)
- Soil-specific performance patterns: The MIR spectrum performs well for classifying Podzols and Acrisols due to their distinctive organic matter and clay mineral features. However, neither single sensors nor fusion models effectively classify Luvisols and Cambisols with the same accuracy, highlighting the need for specialized approaches when dealing with spectrally similar soil classes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monger, C.; Michéli, E.; Aburto, F.; Itkin, D. Soil classification as a tool for contributing to sustainability at the landscape scale and forecasting impacts of management practices in agriculture and forestry. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Webster, R. The cost-effectiveness of reflectance spectroscopy for estimating soil organic carbon. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Sanderman, J.; Hengl, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Peng, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Potential of globally distributed topsoil mid-infrared spectral library for organic carbon estimation. Catena 2024, 235, 107628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Abdul Munnaf, M.; Mouazen, A.M. Machine learning based on-line prediction of soil organic carbon after removal of soil moisture effect. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Emami, M.; Daccache, A.; He, L. Soil properties prediction for precision agriculture using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Agronomy 2021, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, F.; Miao, T.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Ji, W. Prediction of soil properties in a field in typical black soil areas using in situ MIR spectra and its comparison with vis–NIR spectra. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Ji, W.; Xu, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, G. Rapid determination of soil classes in soil profiles using vis–NIR spectroscopy and multiple objectives mixed support vector classification. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, G.M.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Ramírez-López, L.; Terra, F.S. Soil classification using visible/near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra from multiple depths. Geoderma 2014, 223, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Li, A.B. Identification of soil profile classes using depth-weighted visible–near-infrared spectral reflectance. Geoderma 2018, 325, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afriyie, E.; Verdoodt, A.; Mouazen, A.M. Data fusion of visible near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopy for rapid estimation of soil aggregate stability indices. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yin, J.; Li, B.; Sun, F.; Miao, T.; Cao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Hu, B.; Ji, W.; et al. Comparison of depth-specific prediction of soil properties: MIR vs. vis–NIR spectroscopy. Sensors 2023, 23, 5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Ji, W.; Zhou, L.; Yu, W.; Webster, R. In situ measurements of organic carbon in soil profiles using vis–NIR spectroscopy on the Qinghai–Tibet plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4980–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Seidel, M.; Oertel, F.; Ludwig, B.; Vohland, M. In situ and laboratory soil spectroscopy with portable visible-to-near-infrared and mid-infrared instruments for the assessment of organic carbon in soils. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, R. Soil classification via mid-infrared spectroscopy. Comput. Comput. Technol. Agric. 2008, 259, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hartemink, A.E.; Huang, J. Spectral signatures of soil horizons and soil orders–An exploratory study of 270 soil profiles. Geoderma 2021, 389, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Caon, L.; Crowther, T.W.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Montanarella, L.; Navarro, L.M.; Orgiazzi, A.; Singh, B.K.; Tedersoo, L. Tracking, targeting, and conserving soil biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; Montazerolghaem, M.; Padarian, J.; Ferguson, R.; Bailey, S.; McBratney, A.B. Convolutional neural network for simultaneous prediction of several soil properties using visible/near-infrared, mid-infrared, and their combined spectra. Geoderma 2019, 352, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, S.; Vasques, G.M.; Rivero, R.G. Fusion of soil and remote sensing data to model soil properties. Adv. Agron. 2015, 131, 1–109. [Google Scholar]
- Veum, K.S.; Sudduth, K.A.; Kremer, R.J.; Kitchen, N.R. Sensor data fusion for soil health assessment. Geoderma 2017, 305, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.L.; Llinas, J. An introduction to multisensor data fusion. Proc. IEEE 1997, 85, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.S.; Safar, M.; Devaux, M.F.; Robert, P.; Bertrand, D.; Rutledge, D.N. Relations between mid-infrared and near-infrared spectra detected by analysis of variance of an intervariable data matrix. Appl. Spectrosc. 1997, 51, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, F.S.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Demattê, J.A.M. Spectral fusion by Outer Product Analysis (OPA) to improve predictions of soil organic C. Geoderma 2019, 335, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillais, B.; Ottenhof, M.A.; Farhat, I.A.; Rutledge, D.N. Outer-product analysis (OPA) using PLS regression to study the retrogradation of starch. Vib. Spectrosc. 2006, 40, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, M. Improving the estimation accuracy of soil organic matter based on the fusion of near-infrared and Raman spectroscopy using the outer-product analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Spectral fusion modeling for soil organic carbon by a parallel input-convolutional neural network. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, W.; Li, D.; Gao, W.; Zeng, R.; Zheng, G.; Cai, K.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, C. Can fusion of vis–NIR and MIR spectra at three levels improve the prediction accuracy of soil nutrients? Geoderma 2024, 441, 116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Adamchuk, V.I.; Chen, S.; Su, A.S.M.; Ismail, A.; Gan, Q.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A. Simultaneous measurement of multiple soil properties through proximal sensor data fusion: A case study. Geoderma 2019, 341, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hartemink, A.E. Data fusion of vis–NIR and PXRF spectra to predict soil physical and chemical properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Ma, W.; Shi, Z. Rapid determination of soil class based on visible-near infrared, mid-infrared spectroscopy and data fusion. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Biswas, A.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z. X-ray fluorescence and visible near infrared sensor fusion for predicting soil chromium content. Geoderma 2019, 352, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.R.; Molin, J.P.; Javadi, S.H.; de Carvalho, H.W.P.; Mouazen, A.M. Combined use of vis-NIR and XRF sensors for tropical soil fertility analysis: Assessing different data fusion approaches. Sensors 2020, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T.; Ben-Dor, E.; Brown, D.J.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Shepherd, K.D.; Shi, Z.; Stenberg, B.; Stevens, A.; Adamchuk, V.; et al. A global spectral library to characterize the world’s soil. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhoeven-Urselmans, T.; Vagen, T.G.; Spaargaren, O.; Shepherd, K.D. Prediction of soil fertility properties from a globally distributed soil mid-infrared spectral library. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial least squares for discrimination. J. Chemom. 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Support vector machines for classification and regression. Analyst 2010, 135, 230–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.; Liong, C.Y.; Jemain, A.A. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) for classification of high-dimensional (HD) data: A review of contemporary practice strategies and knowledge gaps. Analyst 2018, 143, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forest. Mar. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, H.C. Extension of the kappa coefficient. Biometrics 1980, 36, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscarra, R.A.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S. Predicting organic carbon using data fusion of visible near-infrared and middle infrared spectra by proximal soil sensing. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 53, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coblinski, J.A.; Giasson, É.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Dotto, A.C.; Costa, J.J.F.; Vašát, R. Prediction of Soil Texture Classes through Different Wavelength Regions of Reflectance Spectroscopy at Various Soil Depths. Catena 2020, 189, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Janik, L.J.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Macdonald, L.M.; McLaughlin, M.J. The performance of visible, near-, and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 139–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon-Maurel, V.; McBratney, A. Near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopic techniques for assessing the amount of carbon stock in soils—Critical review and research perspectives. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.H.; Mouazen, A.M. Data fusion of XRF and vis–NIR using outer product analysis, granger–ramanathan, and least squares for prediction of key soil attributes. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocita, M.; Stevens, A.; van Wesemael, B.; Aitkenhead, M.; Bachmann, M.; Barthes, B.; Gholizadeh, A.; Lobsey, C. Soil spectroscopy: An alternative to wet chemistry for soil monitoring. Adv. Agron. 2015, 132, 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Afriyie, E.; Verdoodt, A.; Mouazen, A.M. Estimation of aggregate stability of some soils in the loam belt of belgium using mid-infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Mouazen, A.M.; Wetterlind, J. Visible and near infrared spectroscopy in soil science. Adv. Agron. 2010, 107, 163–215. [Google Scholar]
- Vohland, M.; Ludwig, M.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Hutengs, C. Determination of soil properties with visible to near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of spectral variable selection. Geoderma 2014, 223, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, N.M.; Grunwald, S.; McDowell, M.L.; Bruland, G.L.; Myers, D.B.; Harris, W.G. Modelling soil carbon fractions with visible near-infrared (VNIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy. Geoderma 2015, 239, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, I.; Seidel, M.; Vohland, M.; Ludwig, B. Performance of field-scale lab vs in situ visible/near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy for estimation of soil properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, X. A Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms for Mapping Soil Iron Parameters Indicative of Pedogenic Processes by Hyperspectral Imaging of Intact Soil Profiles. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santana, F.B.; Daly, K. A comparative study of MIR and NIR spectral models using ball-milled and sieved soil for the prediction of a range of soil physical and chemical parameters. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 279, 121441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z. Multi-sensor fusion for the determination of several soil properties in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Munnaf, M.A.; Guerrero, A.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Mouazen, A.M. Fusion of visible-to-near-infrared and mid-infrared spectroscopy to estimate soil organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Lu, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, N.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. The validity domain of sensor fusion in sensing soil quality indicators. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, F.S.; Dematte, J.A.M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Proximal spectral sensing in pedological assessments: Vis–NIR spectra for soil classification based on weathering and pedogenesis. Geoderma 2018, 318, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, W.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Q.; He, K.; Shi, Z. Assessment of important soil properties related to Chinese Soil Taxonomy based on vis–NIR reflectance spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, M.; Buddenbaum, H. Laboratory imaging spectroscopy of a stagnic luvisol profile—High resolution soil characterisation, classification and mapping of elemental concentrations. Geoderma 2013, 195, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Biswas, A.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Enhancing soil profile analysis with soil spectral libraries and laboratory hyperspectral imaging. Geoderma 2024, 450, 117036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Applications in Soil Science. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 76, e70093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
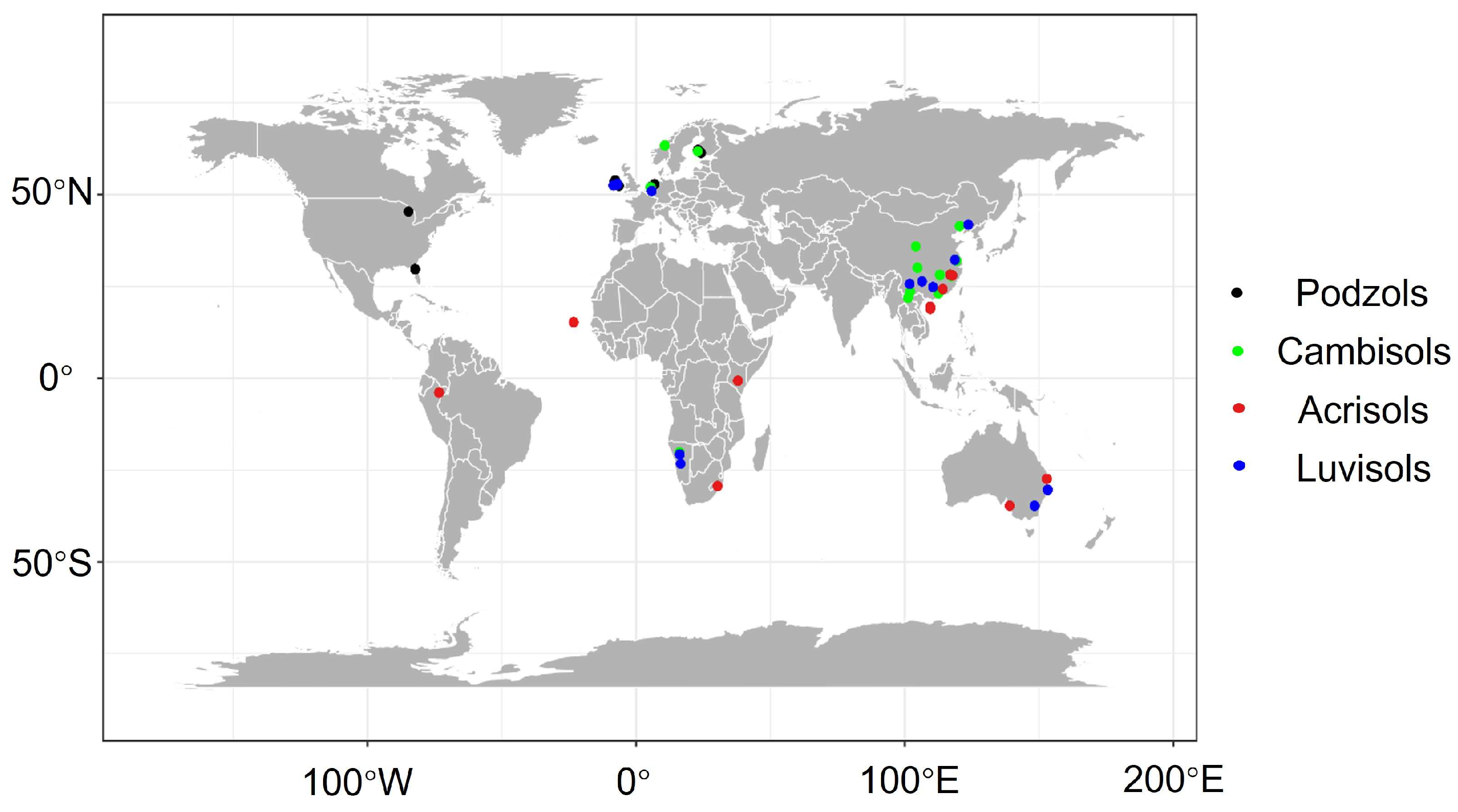




| Soil Class | Numbers of Profiles/Samples | Soil Class | Numbers of Profiles/Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cambisols | 17/84 | Fluvisols | 4/27 |
| Luvisols | 16/85 | Alisols | 3/21 |
| Podzols | 14/99 | Albeluvisols | 3/19 |
| Acrisols | 13/89 | Planosols | 3/24 |
| Arenosols | 9/51 | Plinthosols | 3/20 |
| Phaeozems | 9/42 | Umbrisols | 3/16 |
| Anthrosols | 7/28 | Chernozems | 2/12 |
| Ferralsols | 7/40 | Gypsisols | 2/14 |
| Vertisols | 7/47 | Gleysols | 2/9 |
| Andosols | 6/28 | Regosols | 2/11 |
| Solonetzs | 6/47 | Cryosols | 1/6 |
| Nitisols | 5/36 | Durisols | 1/6 |
| Lixisols | 5/22 | Kastanozems | 1/8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Shen, X.; Shen, X.; Cheng, J.; Xu, D.; Makar, R.S.; Guo, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; et al. Improving the Accuracy of Soil Classification by Using Vis–NIR, MIR, and Their Spectra Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091524
Li S, Shen X, Shen X, Cheng J, Xu D, Makar RS, Guo Y, Hu B, Chen S, Hong Y, et al. Improving the Accuracy of Soil Classification by Using Vis–NIR, MIR, and Their Spectra Fusion. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091524
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuo, Xinru Shen, Xue Shen, Jun Cheng, Dongyun Xu, Randa S. Makar, Yan Guo, Bifeng Hu, Songchao Chen, Yongsheng Hong, and et al. 2025. "Improving the Accuracy of Soil Classification by Using Vis–NIR, MIR, and Their Spectra Fusion" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091524
APA StyleLi, S., Shen, X., Shen, X., Cheng, J., Xu, D., Makar, R. S., Guo, Y., Hu, B., Chen, S., Hong, Y., Peng, J., & Shi, Z. (2025). Improving the Accuracy of Soil Classification by Using Vis–NIR, MIR, and Their Spectra Fusion. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091524













