Analysis and Experiments of an Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism for Repeated Docking and Separation of the CubeSats
Abstract
1. Introduction
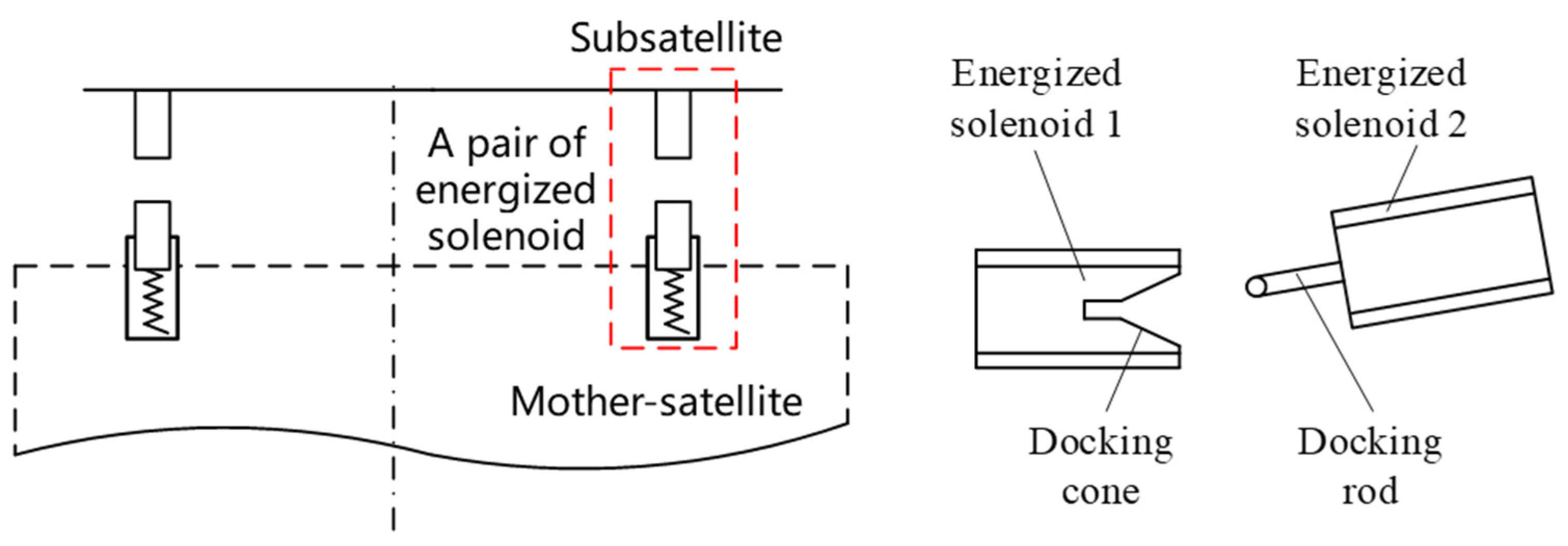
2. Structure and Working Principle
3. Mathematical Model
3.1. Electromagnetic Force/Torque Model
- The electromagnetic force/torque between the subsatellite and the mother-satellite is an internal force between spacecraft. The motion of the system’s center of mass will not be altered by the electromagnetic force/torque, and the angular momentum and mechanical energy are conserved.
- The electromagnetic force/torque is inversely proportional to the nth power of the relative distance between the mother and subsatellites (where n = 3 or 4). The electromagnetic force/torque is also nonlinearly coupled with the product of the magnetic moments generated by the magnetization of the energized solenoid and the orientation angle of the magnetic moment vector.
3.2. Attitude Model
4. Optimization Design
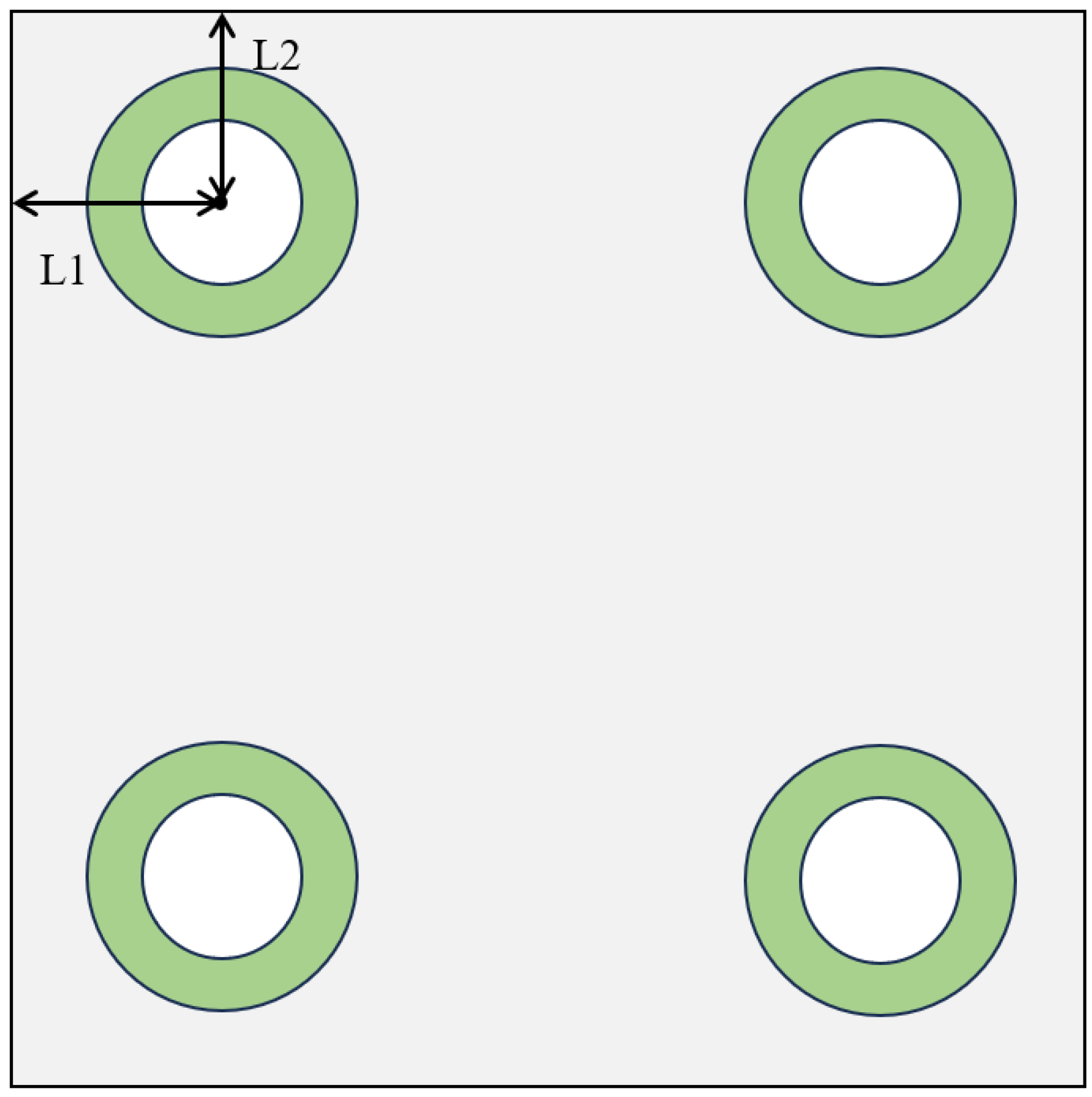
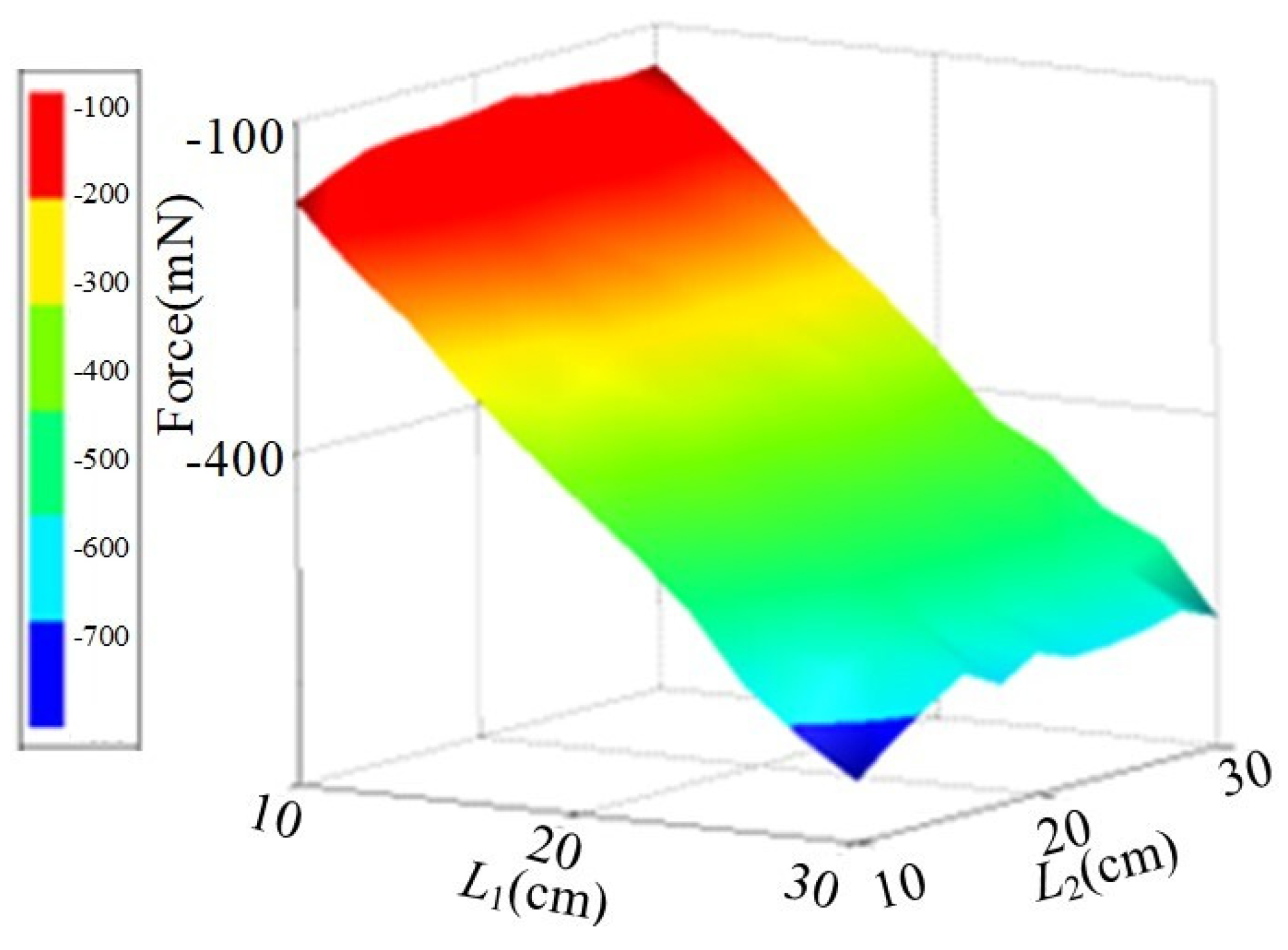
4.1. Layout Arrangement
4.2. The Direction of Current
5. Simulation and Experimental Research
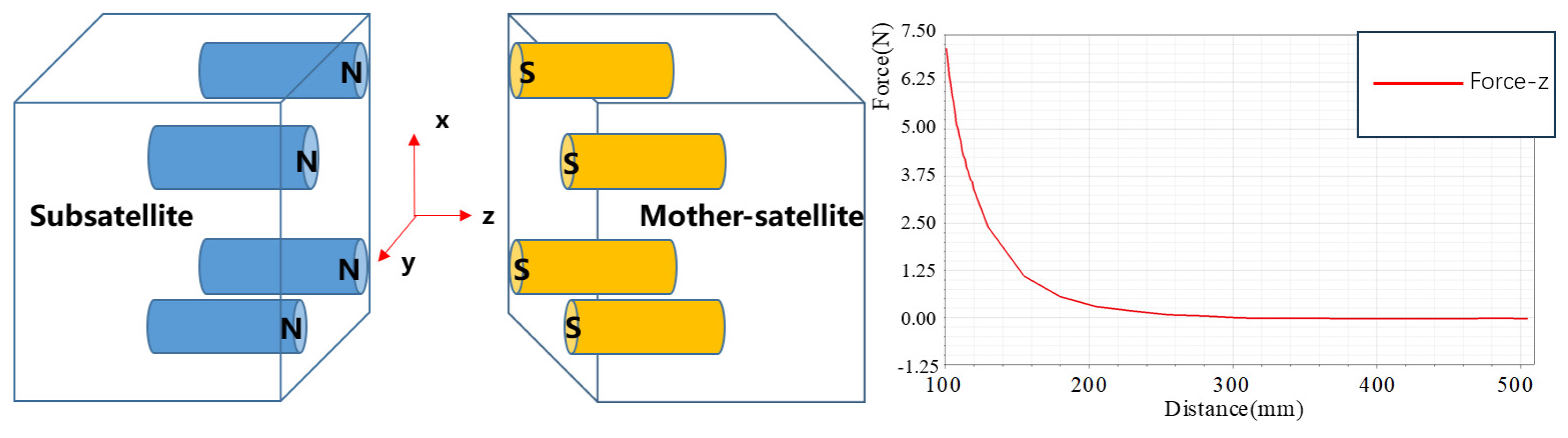
5.1. Simulation Analysis of Electromagnetic Attraction Separation Unit
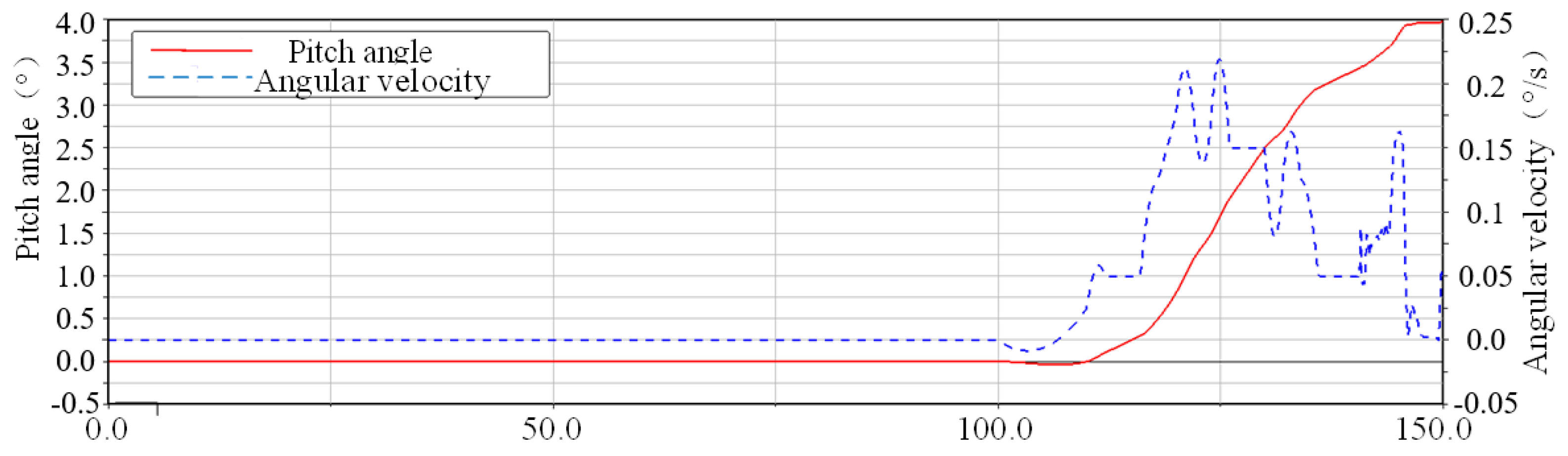
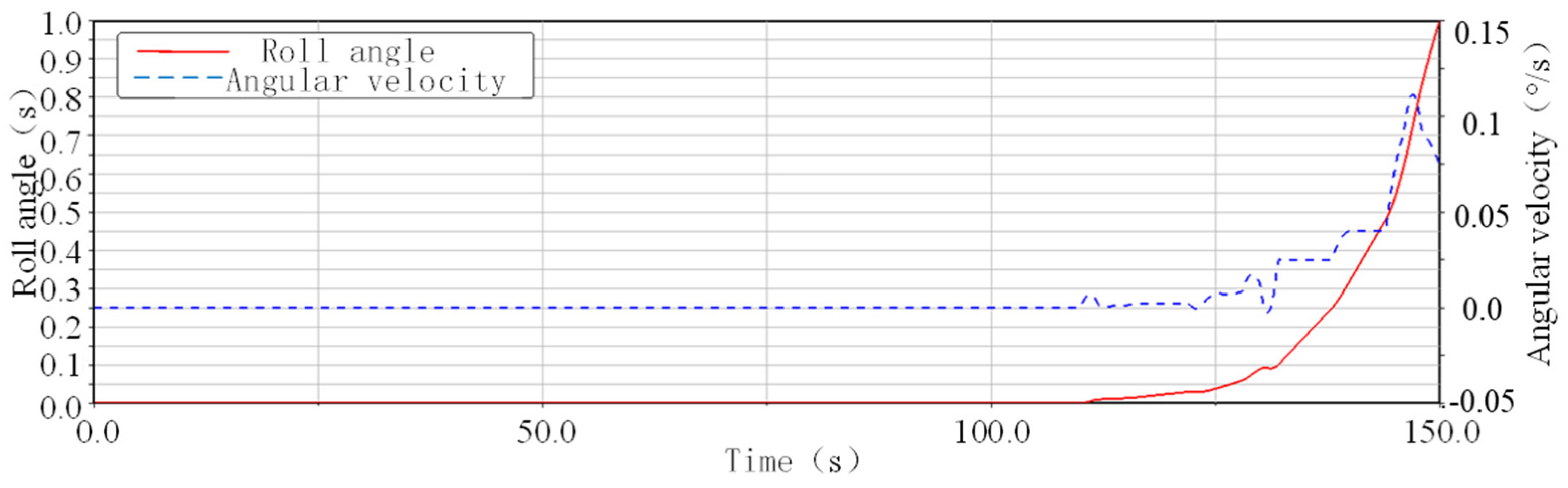
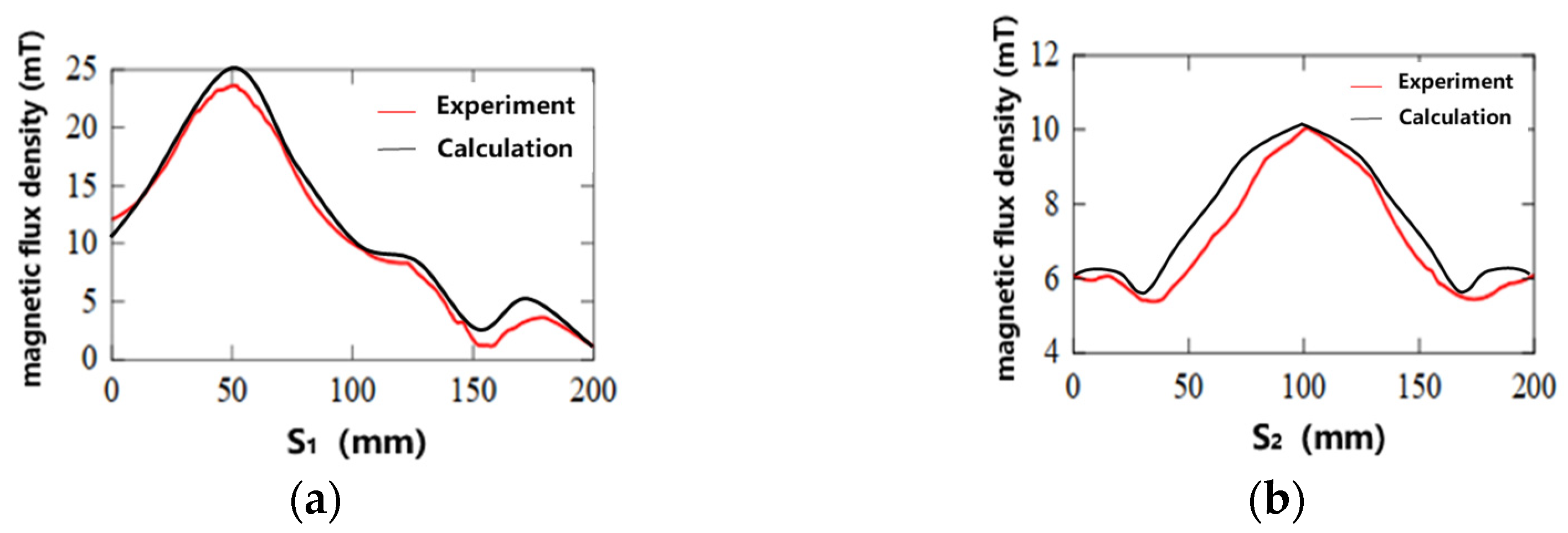
5.2. Analysis of the Impact of Electromagnetic Fields
5.3. Electromagnetic Attraction Separation Unit Captive Separation Test
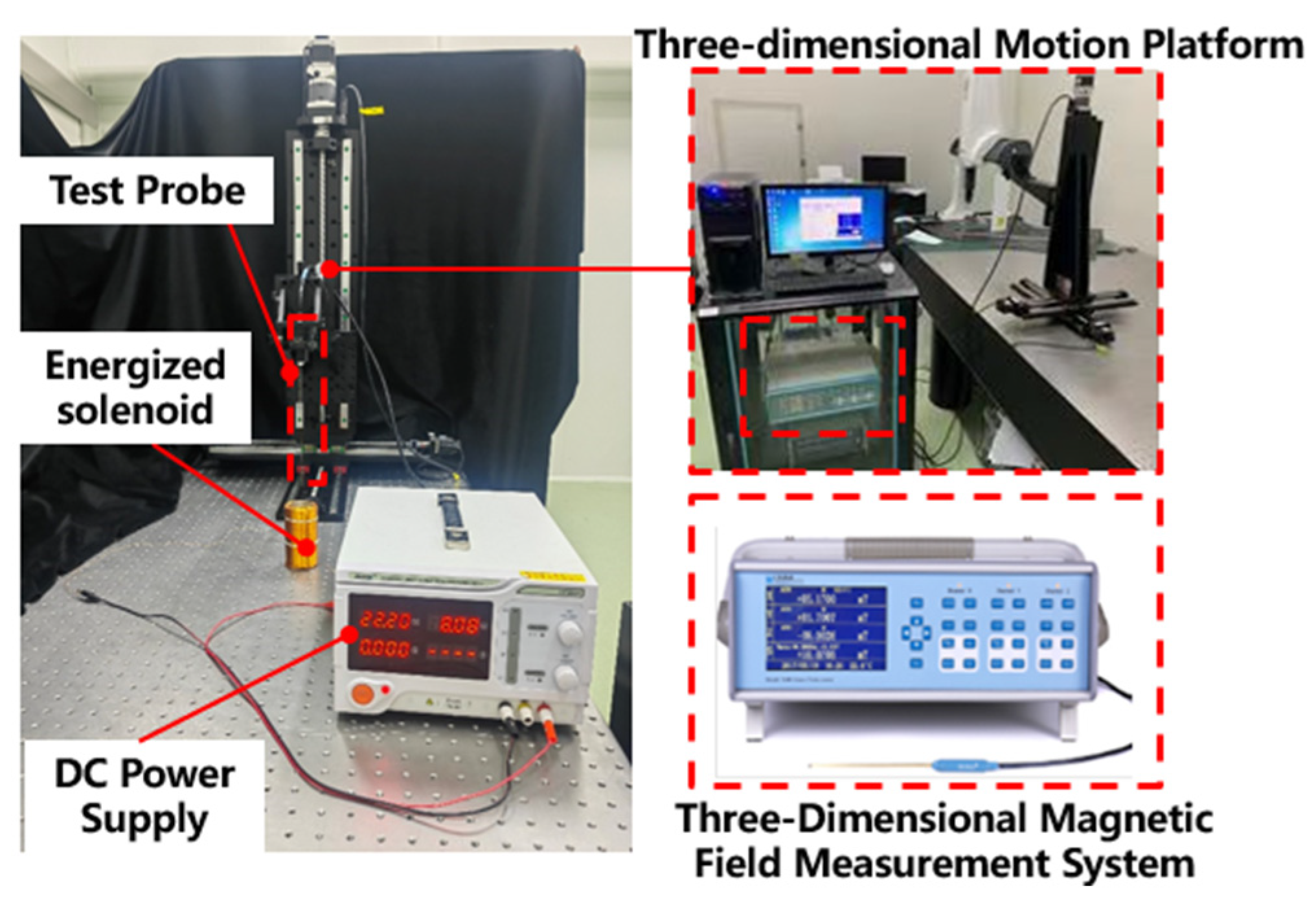
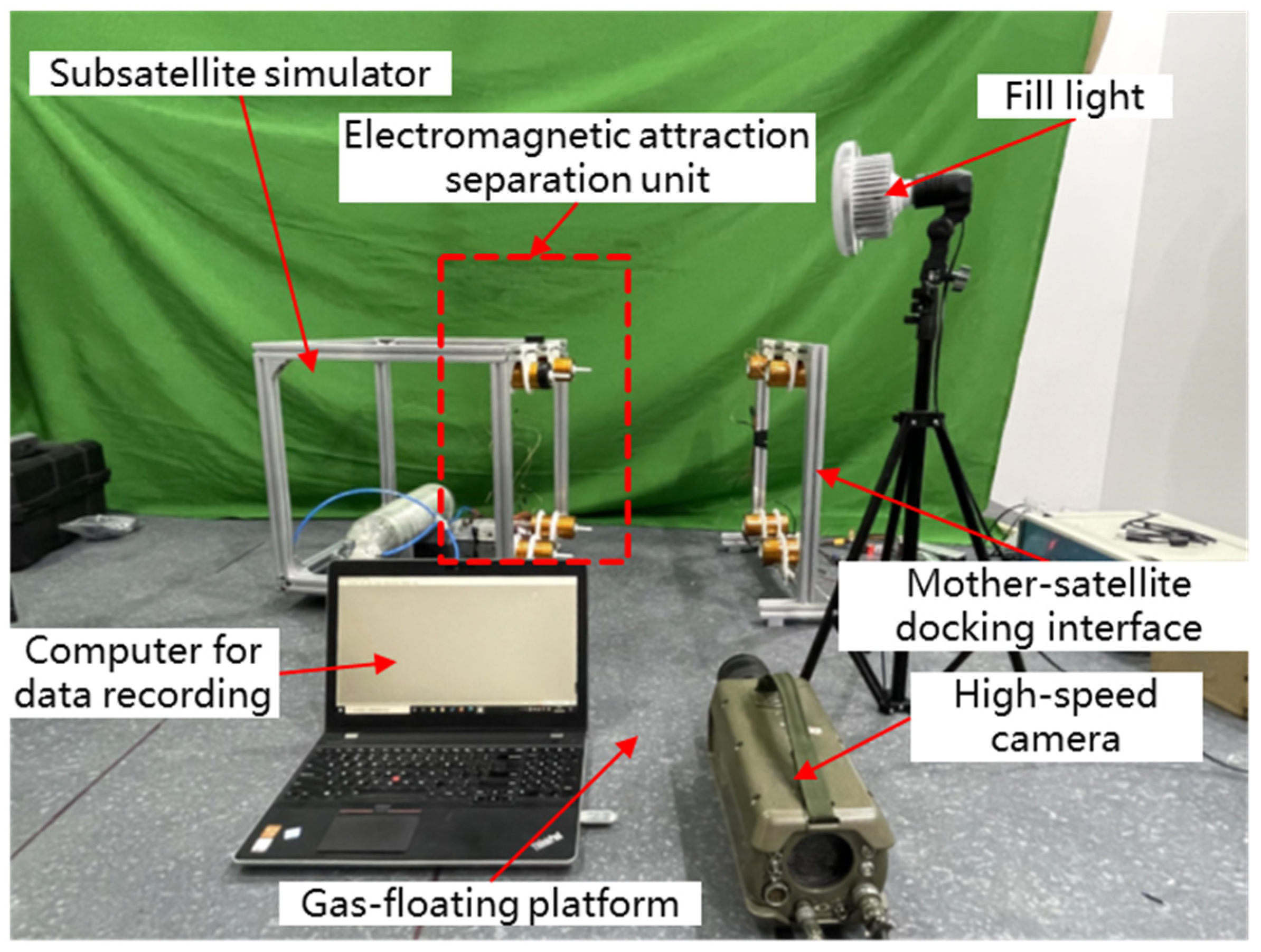
5.3.1. Composition of the Testing System
5.3.2. Testing Procedure
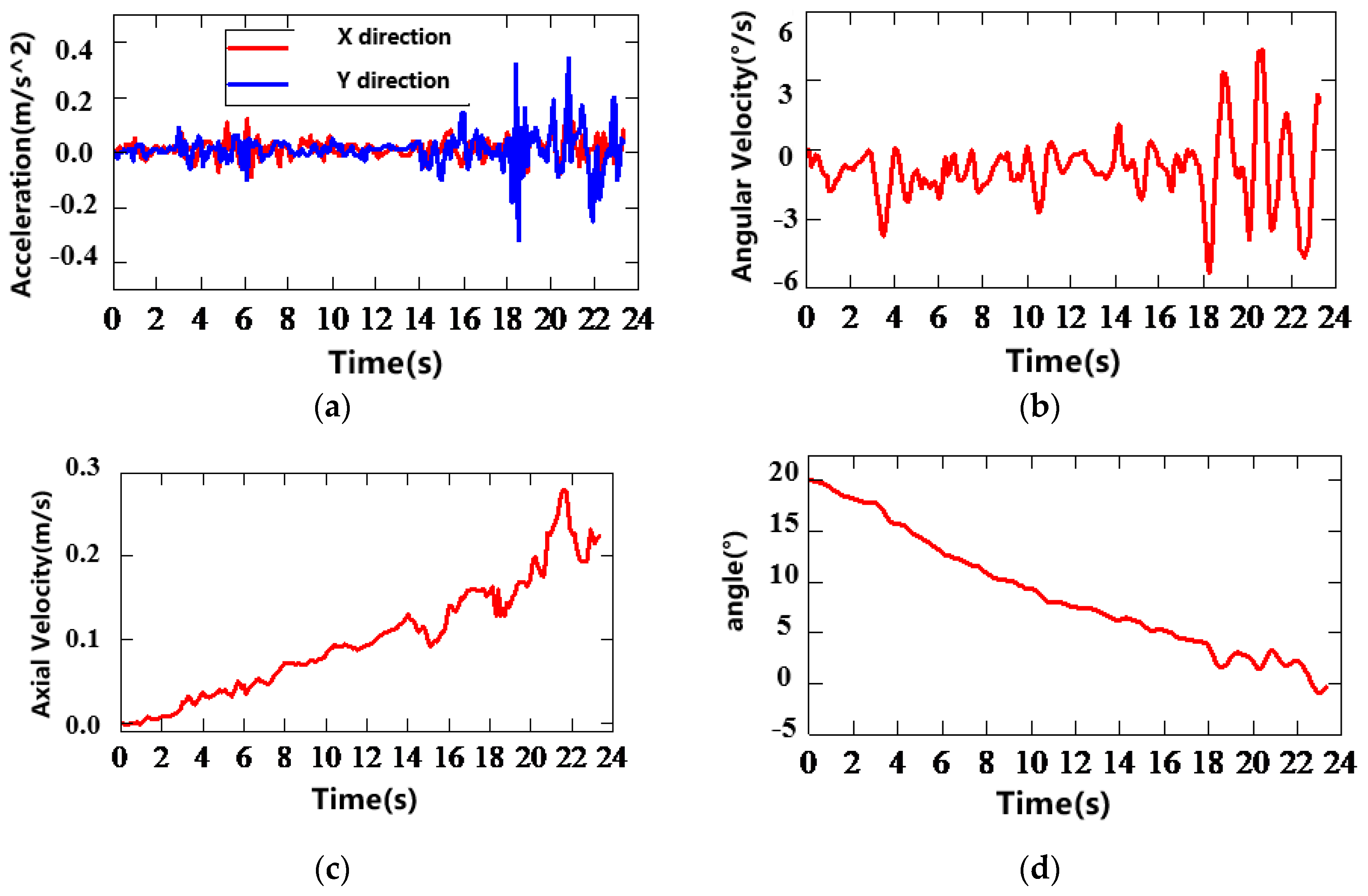
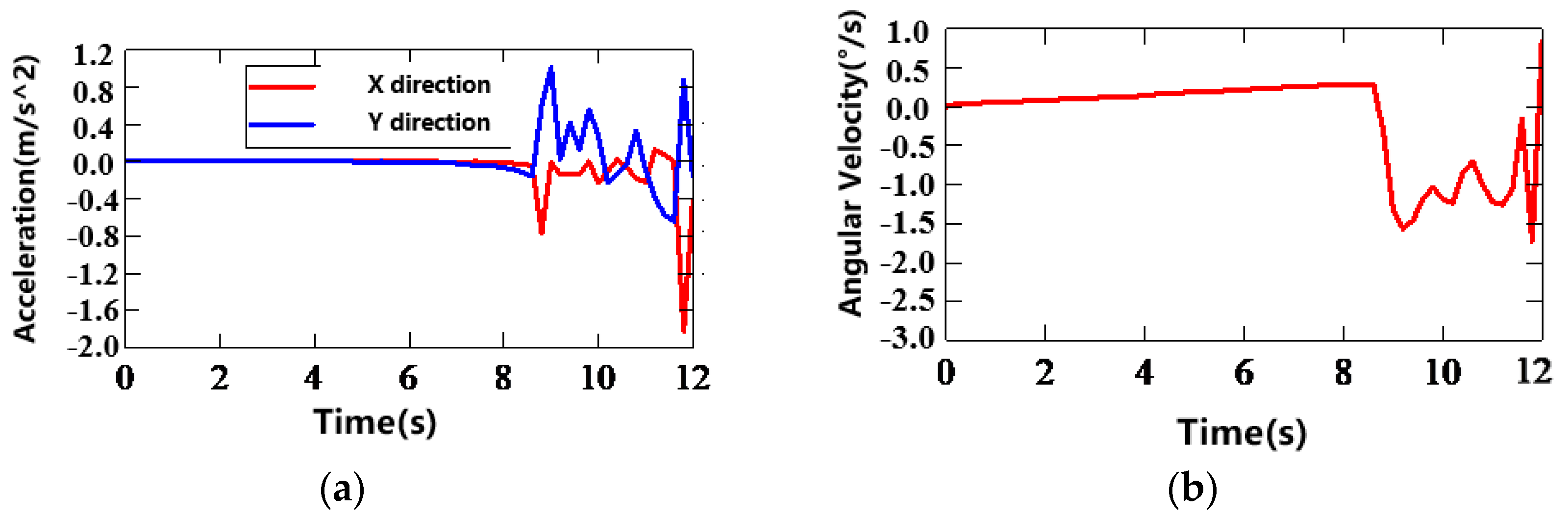
5.3.3. Test Results and Analysis
- Experimental Validation of the Electromagnetic Force Model
- 2.
- Analysis of Test Results and Phenomena
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPR | Heading, Pitch, Roll |
| DC | Direct Current |
References
- Orozco, M.L.; Giraldo, B.S. Attitude Determination and Control in Small Satellites: A Review. IEEE J. Miniatur. Air Space Syst. 2024, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevgas, G.; Lagkas, T.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Argyriou, V. Advances in Remote Sensing and Propulsion Systems for Earth Observation Nanosatellites. Future Internet 2025, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero-Montalvo, P.D.; Priest, J.C.P. CubeSat Imaging Payload Design for Environmental Monitoring of Greenland. Electronics 2025, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.A. Preliminary Trajectory Analysis of CubeSats with Electric Thrusters in Nodal Flyby Missions for Asteroid Exploration. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, S.; De Angelis, G.; Pontani, M.; Graziani, F. An Iterative Guidance and Navigation Algorithm for Orbit Rendezvous of Cooperating CubeSats. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumer, A.M.; Kim, D.-K. Real-Time Fuel Optimization and Guidance for Spacecraft Rendezvous and Docking. Aerospace 2022, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghali, A.; Zhu, Z.H. An introductory review of swarm technology for spacecraft on-orbit servicing. Int. J. Mech. Syst. Dyn. 2024, 4, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, C.; Pellegrino, S.; Lappas, J.V.; Bridges, C.; Baker, J. Using CubeSat/micro-satellite technology to demonstrate the Autonomous Assembly of a Reconfigurable Space Telescope. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 114, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, S. Tracking Model Predictive Control for Docking Maneuvers of a CubeSat with a Big Spacecraft. Aerospace 2021, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangtian, Z.; Shijie, Z. Adaptive saturated control for spacecraft rendezvous and docking under motion constraints. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 106739. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Li, K.; Cai, H.; Duan, J.; Zhi, J.; Wang, Y. Design and Analysis of Non-cooperative Target Space Docking Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2022 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2022; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, F.; Deng, Z. Research Progress of Space Non-Pyrotechnic Low-Shock Connection and Separation Technology (SNLT): A Review. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 113–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Liu, C.; Biggs, J.D.; Sun, Z.; Yue, X. Observer-based control for spacecraft electromagnetic docking. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branz, F.; Olivieri, L.; Sansone, F.; Francesconi, A. Miniature docking mechanism for CubeSats. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 176, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-del-Pulgar, C.J.; Palomeque, A.L.; Juli, J.; Madi, M. Extensible Hook System for Rendezvous and Docking of a CubeSat Swarm. Eng. Proc. 2025, 90, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.M.C.; Otero, A.S.; Nolet, S.; Berkovitz, D.S.; Miller, D.W.; Sell, S.W. SPHERES as a Formation Flight Algorithm Development and Validation Testbed: Current Progress and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Formation Flying Missions and Technologies, Paris, France, 19–21 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.; Forshaw, J.; Lindsay, M.; Brydon, G.; Lidtke, A.; Yarr, N. Space Situational Awareness (SSA) activities explored through the ELSA-d mission. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference (AMOS), Maui, HI, USA, 8–11 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, L.; Branz, F.; Duzzi, M.; Mantellato, R.; Grassi, G.; Sansone, F.; Francesconi, A. Technologies to Join Spacecraft Using a Tethered Electromagnetic Probe. In Proceedings of the XXIV International Conference of the Italian Association of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Palermo-Enna, Italy, 18–22 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Foust, R.C.; Lupu, E.S.; Nakka, Y.K.; Chung, S.-J.; Hadaegh, F.Y. Ultra-Soft Electromagnetic Docking with Applications to In-Orbit Assembly. In Proceedings of the 69th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), Bremen, Germany, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Duzzi, M.; Casagrande, R.; Mazzucato, M.; Moro, L.; Francesconiet, A. Electromagnetic Position and Attitude Control for PACMAN Experiment. In Proceedings of the 10th International ESA Conference on Guidance, Navigation & Control Systems, Salzburg, Austria, 5–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Han, R. Micro- and Nanosatellite Sensorless Electromagnetic Docking Control Based on the High-Frequency Injection Method. Aerospace 2023, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, G.; Wu, L.; Han, R.; Wang, B. Design of Electromagnetic Docking Device for Micro–Nanosatellite. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Han, R. A solution using only electromagnetic coils for relative pose control in satellite docking. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Chen, P.L. Self-Alignment Capability Analysis and Self-Attraction Dipole Solution of Spacecraft Electromagnetic Docking. AIAA J. 2023, 61, 3247–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilvanathan, V.; Raj, A.T.; Vance, L.D.; Eniko, E. Sequential Control of Electromagnets for CubeSat Docking Attitude Alignment. In Proceedings of the ASCEND 2023 Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–28 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, K. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Delayed Electromagnetic Docking of Spacecraft in Elliptical Orbits. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 58, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijian, W.; Guangzheng, R.; Runqi, H.; Bo, W.; Yaobing, W. Relative Roll Control of Satellite Docking Using Electromagnetic Coils. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2023, 36, 361–374. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, J.; Kong, N.; Ma, S.; Wang, B.; Han, R. Self-Docking Characteristics and Sliding Mode Control on Space Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism. Machines 2023, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Mechanical System Dynamics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 35–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wertz, J.R. Spacecraft Attitude Determination and Control; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; pp. 362–435. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 174–225. [Google Scholar]
- Knap, V.; Bonvang, G.A.P.; Fagerlund, F.R.; Krøyer, S.; Nguyen, K.; Thorsager, M.; Tan, Z.-H. Extending battery life in CubeSats by charging current control utilizing a long short-term memory network for solar power predictions. J. Power Sources 2024, 618, 235164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.O.E.; Abbaker, A.E.M.; Elfaki, S.E.E. Modeling, Simulation, and Implementation of the Electrical Power System of Cube Satellite Using Matlab and Simulink. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Control, Electrical, and Electronic Engineering (ICCCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 26 February–1 March 2021. [Google Scholar]









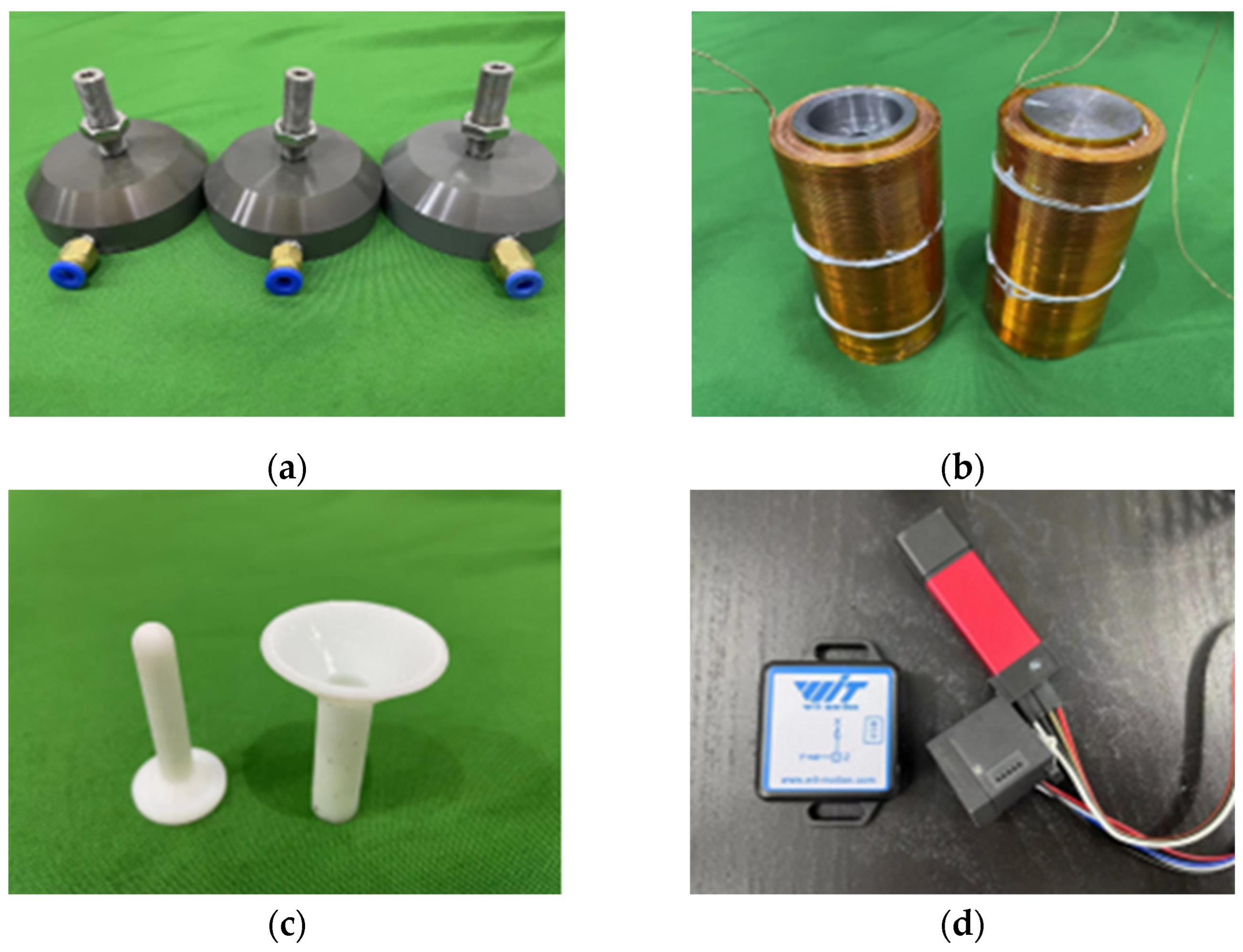

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Solenoid length | 100 mm |
| Coil outer diameter | 55 mm |
| Iron core diameter | 40 mm |
| Number of turns | 2000 turns |
| Current | 1 A |
| Dimensions of docking interface | 500 × 500 mm |
| Number | Distance d (mm) | Electromagnetic Force F (N) | Theoretical Electromagnetic Force (N) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 12.042 | 13.676 | 11.9% |
| 2 | 5 | 3.524 | 3.854 | 8.6% |
| 3 | 10 | 1.355 | 1.532 | 11.6% |
| 4 | 20 | 0.425 | 0.478 | 11.1% |
| 5 | 50 | 0.087 | 0.098 | 11.2% |
| 6 | 100 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 9.5% |
| Number | Experimental Parameters | Test Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Distance (mm) | Eccentricity (mm) | Deviation Angle θ | First Time | Second Time | Third Time | |
| 1 | 500 | 5 | 0° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0° | Succeeded 0.2 m/s, 0.1° | Succeeded 0.05 m/s, 0° |
| 2 | 500 | 5 | 5° | Succeeded 0.09 m/s, −0.1° | Succeeded 0.05 m/s, 0.2° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0° |
| 3 | 500 | 5 | 10° | Succeeded 0.18 m/s, 0.3° | Succeeded 0.21 m/s, −0.2° | Succeeded 0.08 m/s, 0.1° |
| 4 | 500 | 5 | 20° | Ejected | Collided | Succeeded 0.23 m/s, −0.1° |
| 5 | 600 | 5 | 20° | Succeeded 0.18 m/s, 0° | Succeeded 0.14 m/s, 1° | Succeeded 0.06 m/s, 0.2° |
| 6 | 600 | 5 | 25° | Succeeded 0.16 m/s, 0.2° | Ejected | Succeeded 0.21 m/s, 0.1° |
| 7 | 600 | 5 | 30° | Collided | Succeeded 0.2 m/s, −0.1° | Collided |
| Number | Experimental Parameters | Test Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Distance (mm) | Eccentricity (mm) | Deviation Angle θ | First Time | Second Time | Third Time | |
| 1 | 500 | 5 | 0° | No significant displacement occurred within 10 s after powering on. | ||
| 2 | 400 | 5 | 0° | Succeeded 0.03 m/s, 0.1° | Succeeded 0.15 m/s, −0.2° | Succeeded 0.04 m/s, 0.3° |
| 3 | 400 | 5 | 5° | Succeeded 0 m/s, 1° | Succeeded 0.2 m/s, 0.1° | Succeeded 0.02 m/s, 0.8° |
| 4 | 400 | 5 | 10° | Succeeded 0.09 m/s, 0° | Succeeded 0.12 m/s, −0.3° | Succeeded 0.05 m/s, 0.2° |
| 5 | 400 | 5 | 20° | Collided | Collided | Succeeded 0.13 m/s, 1° |
| 6 | 400 | 5 | 25° | Succeeded 0.23 m/s, 0.1° | Ejected | Succeeded 0.09 m/s, −0.5° |
| 7 | 400 | 5 | 30° | Both ends with N poles facing each other, resulting in repulsion | ||
| Number | Experimental Parameters | Test Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Distance (mm) | Eccentricity (mm) | Deviation Angle θ | First Time | Second Time | Third Time | |
| 1 | 500 | 5 | 0° | No significant displacement occurred within 10 s after powering on. | ||
| 2 | 400 | 5 | 0° | No significant displacement occurred within 10 s after powering on. | ||
| 3 | 300 | 5 | 0° | Succeeded 0.05 m/s, 0° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0.2° | Succeeded 0.04 m/s, 0.2° |
| 4 | 300 | 5 | 5° | Misaligned | Succeeded 0.15 m/s, −0.6° | Succeeded 0.11 m/s, 1° |
| 5 | 300 | 5 | 10° | Misaligned | Ejected | Succeeded 0.2 m/s, −0.2° |
| 6 | 300 | 5 | 15° | Both ends with N poles facing each other, resulting in repulsion | ||
| Number | Experimental Parameters | Test Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Distance (mm) | Eccentricity (mm) | Deviation Angle θ | First Time | Second Time | Third Time | |
| 1 | 500 | 5 | 0° | No significant displacement occurred within 10 s after powering on. | ||
| 2 | 400 | 5 | 0° | Succeeded 0.02 m/s, −0.2° | Succeeded 0.03 m/s, 0.2° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0.1° |
| 3 | 400 | 5 | 5° | Succeeded 0.01 m/s, 0.6° | Succeeded 0.19 m/s, 0.2° | Succeeded 0.03 m/s, 0.4° |
| 4 | 400 | 5 | 10° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 1° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0.5° | Succeeded 0.08 m/s, 0.3° |
| 5 | 400 | 5 | 20° | Succeeded 0.11 m/s, 0.5° | Succeeded 0.09 m/s, 0.1° | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, −0.2° |
| 6 | 400 | 5 | 25° | Ejected | Collided | Succeeded 0.1 m/s, 0.5° |
| 7 | 400 | 5 | 30° | Both ends with N poles facing each other, resulting in repulsion | ||
| Relative Distance (mm) | Maximum Deviation Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| 600 | ±30° |
| 400 | ±20° |
| 300 | ±10° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; He, C.; Hu, T.; Li, M.; Yue, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Analysis and Experiments of an Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism for Repeated Docking and Separation of the CubeSats. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081446
Yang X, Li C, Zhang L, Zhao Z, He C, Hu T, Li M, Yue H, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, et al. Analysis and Experiments of an Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism for Repeated Docking and Separation of the CubeSats. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(8):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081446
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaoze, Chenyuan Li, Lili Zhang, Zeming Zhao, Caiting He, Tao Hu, Mingyang Li, Honghao Yue, Yong Zhao, Yuhao Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Analysis and Experiments of an Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism for Repeated Docking and Separation of the CubeSats" Remote Sensing 17, no. 8: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081446
APA StyleYang, X., Li, C., Zhang, L., Zhao, Z., He, C., Hu, T., Li, M., Yue, H., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wei, Y. (2025). Analysis and Experiments of an Electromagnetic Docking Mechanism for Repeated Docking and Separation of the CubeSats. Remote Sensing, 17(8), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081446






