Extraction, Dynamics, and Driving Factors of Shallow Water Area in Hongze Lake Based on Landsat Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
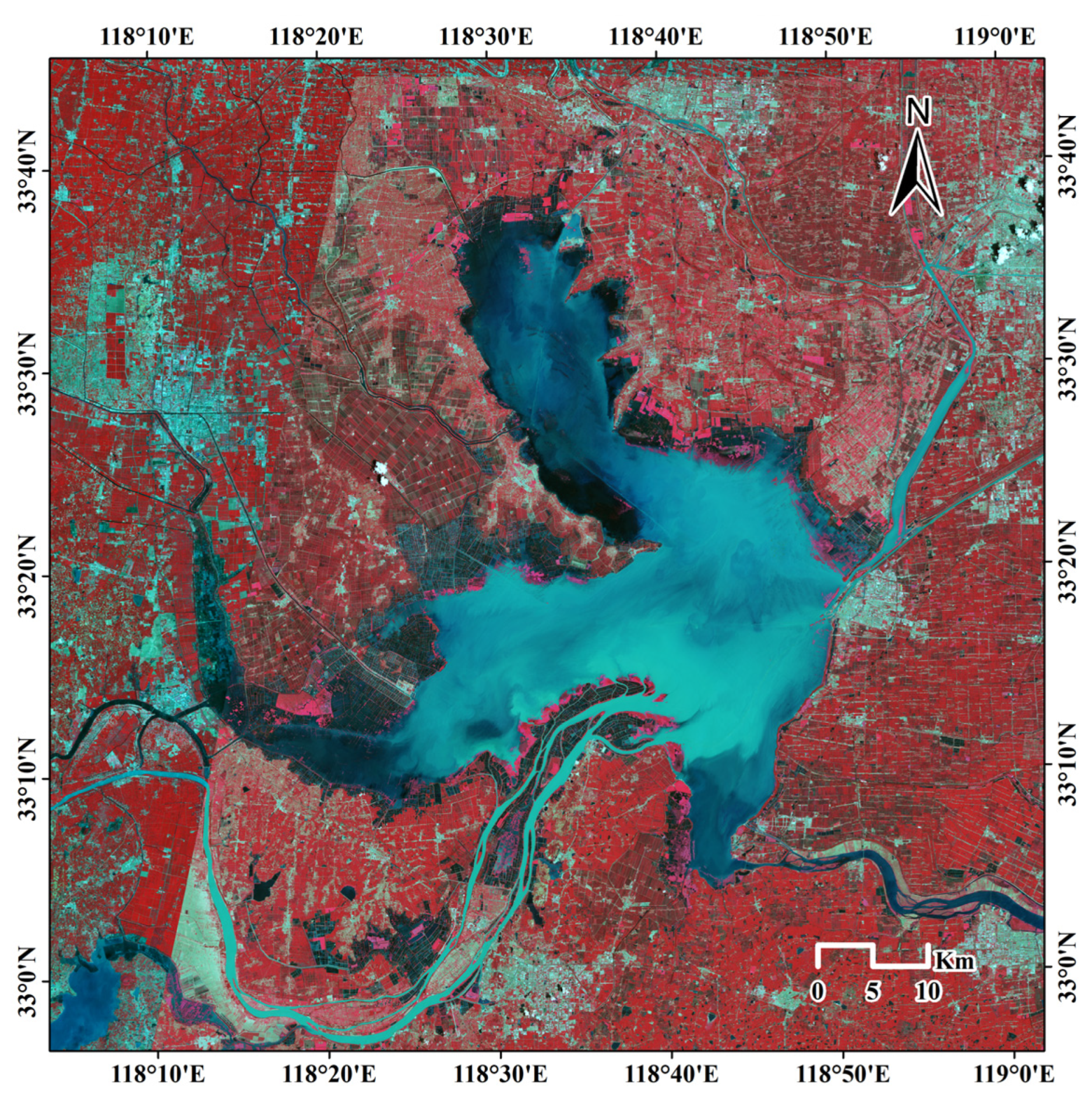
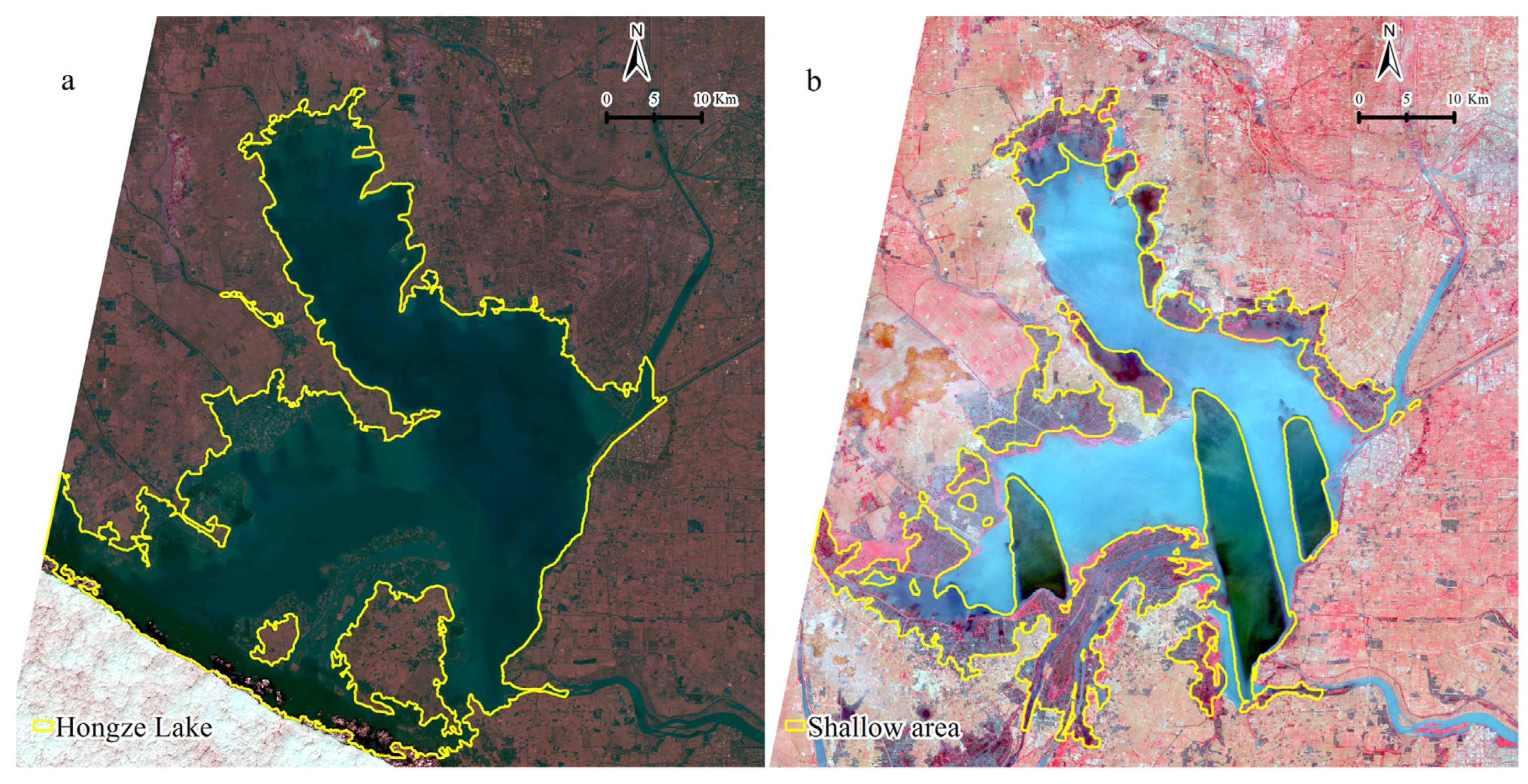
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Data and Upstream Water Supply
2.2.3. Humanistic Data
2.3. Methodology
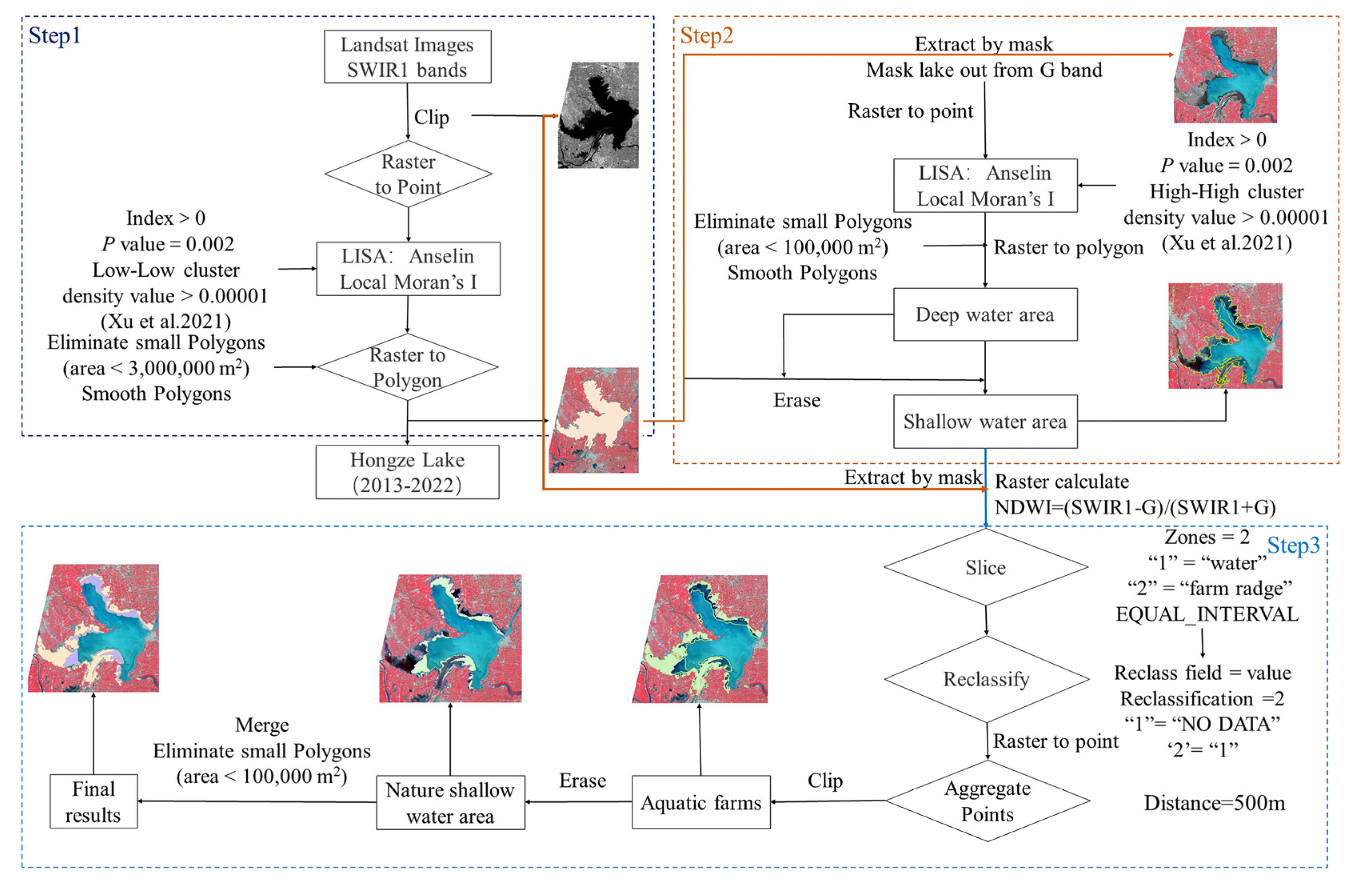
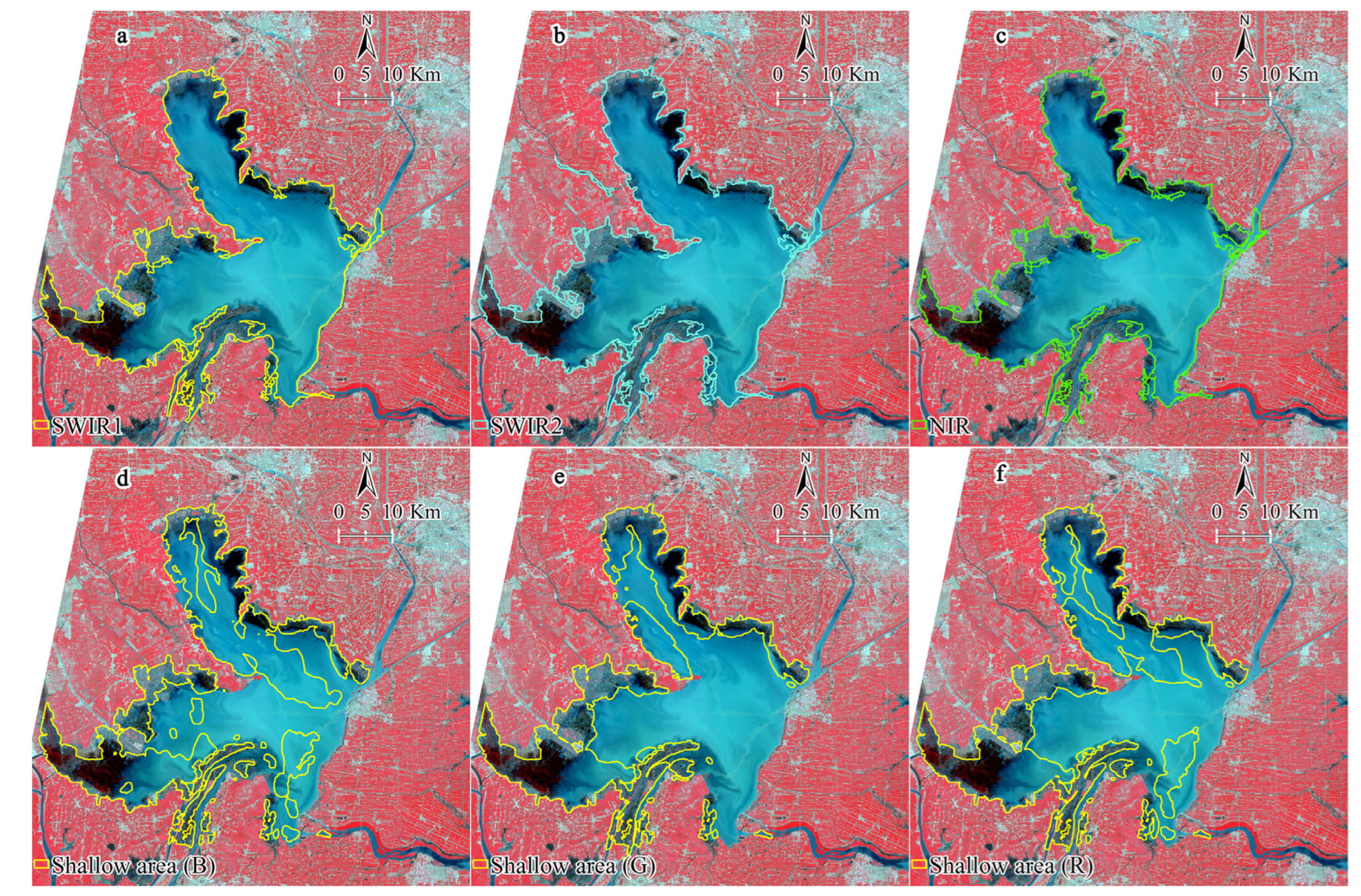
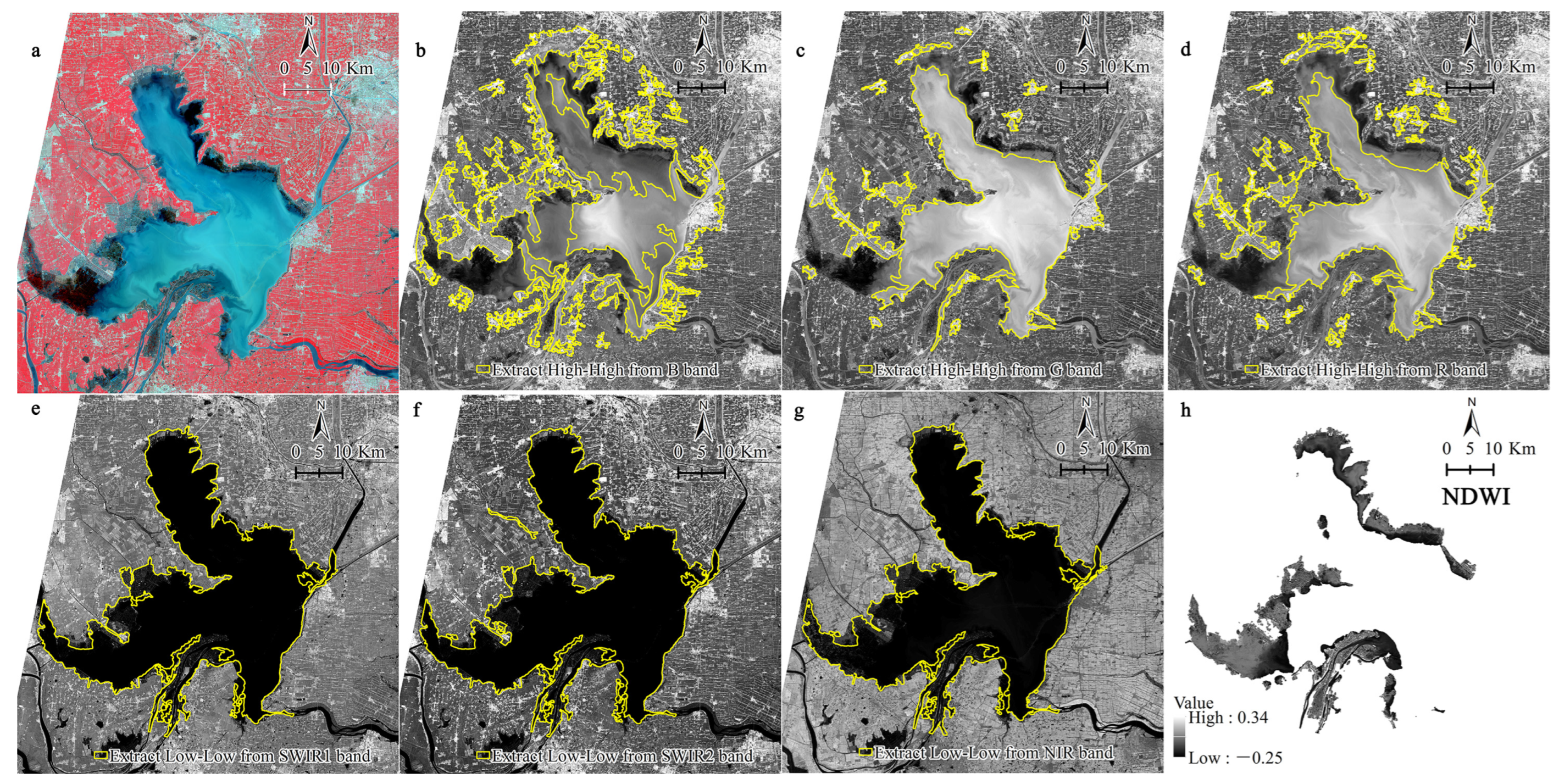
2.3.1. Automatic Extraction of Shallow Area in Hongze Lake
2.3.2. Time Series Analysis of Shallow Water Area
2.3.3. Segmented Linear Regression Analysis and Linear Regression
3. Results
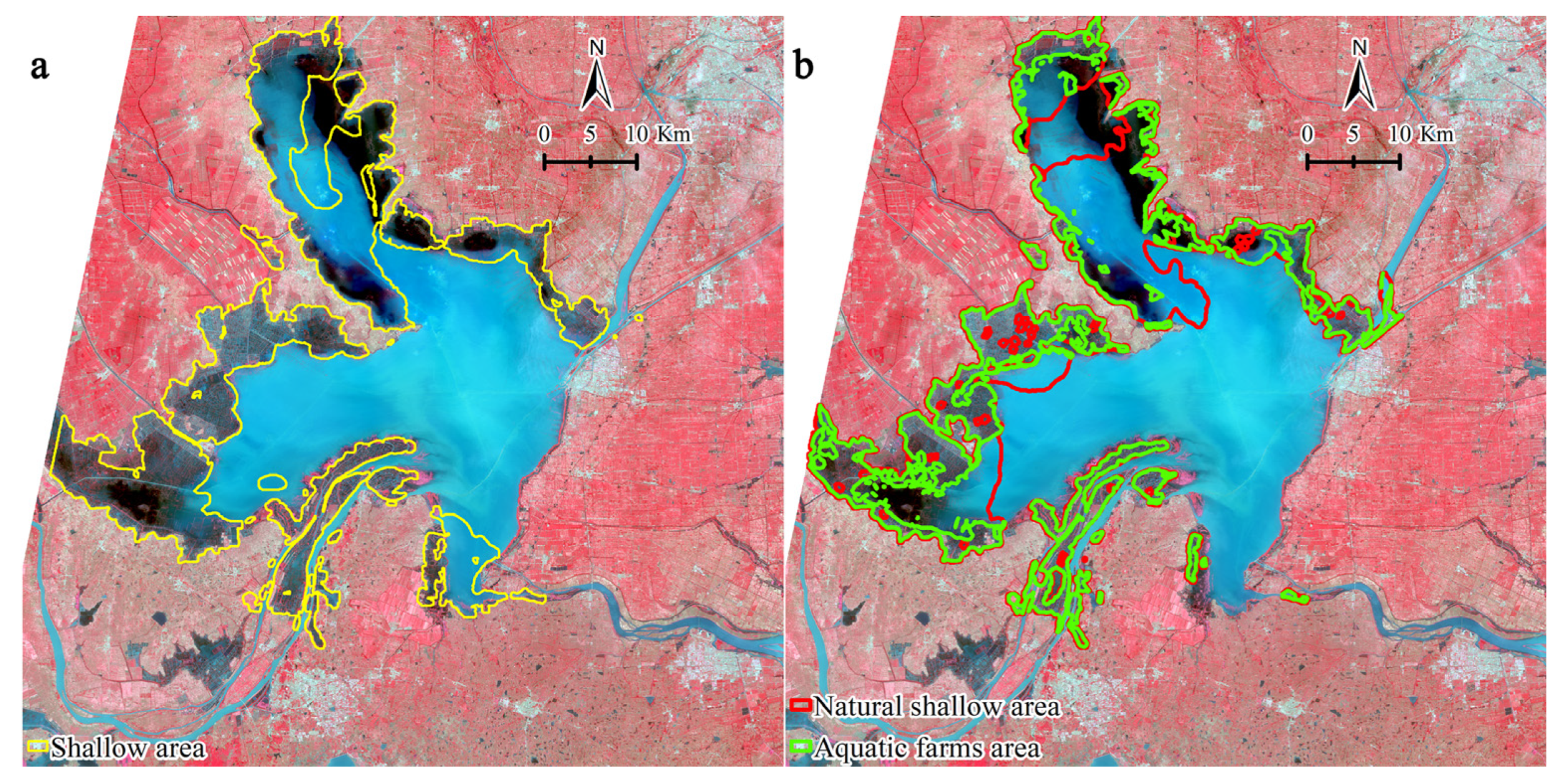
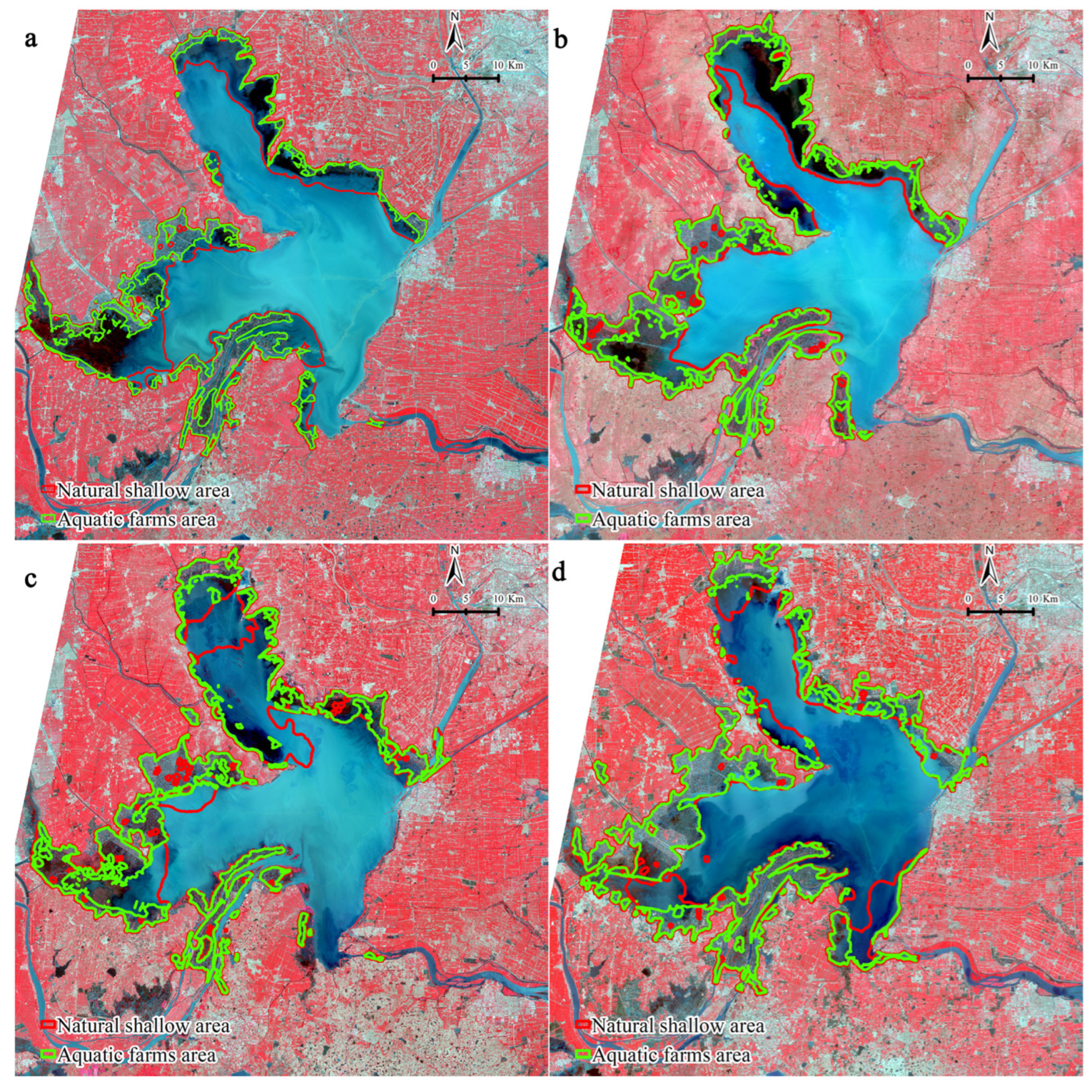
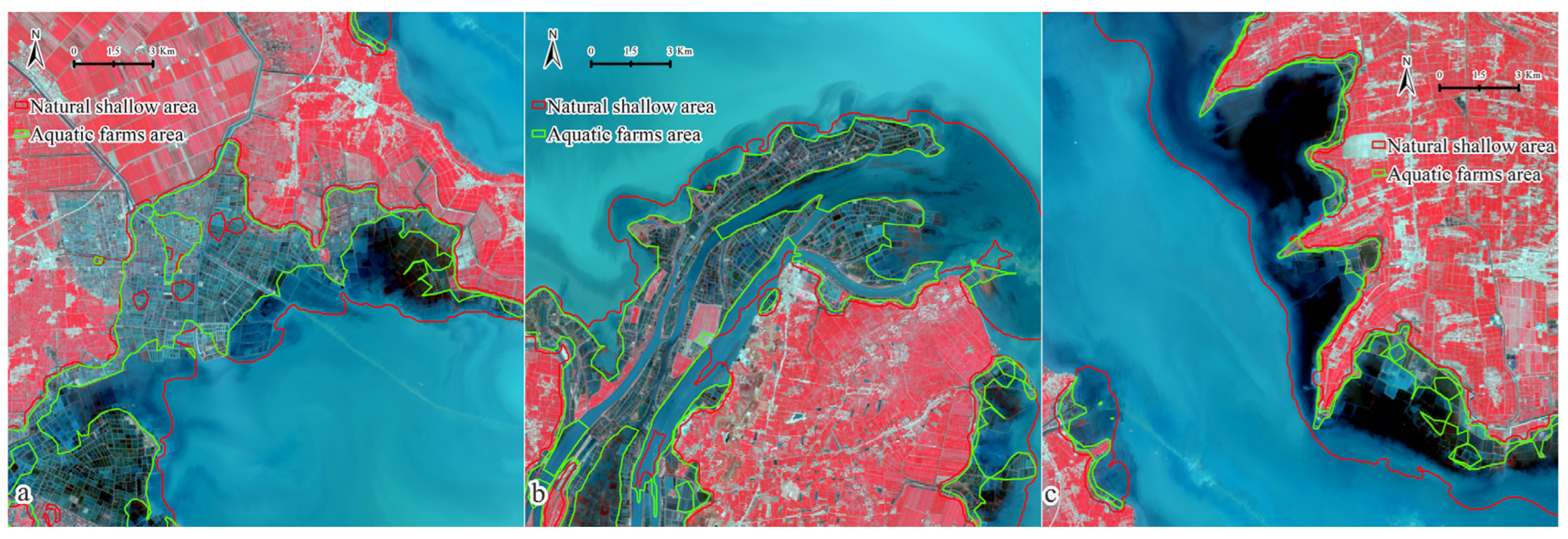
3.1. Extraction of Shallow Water Area
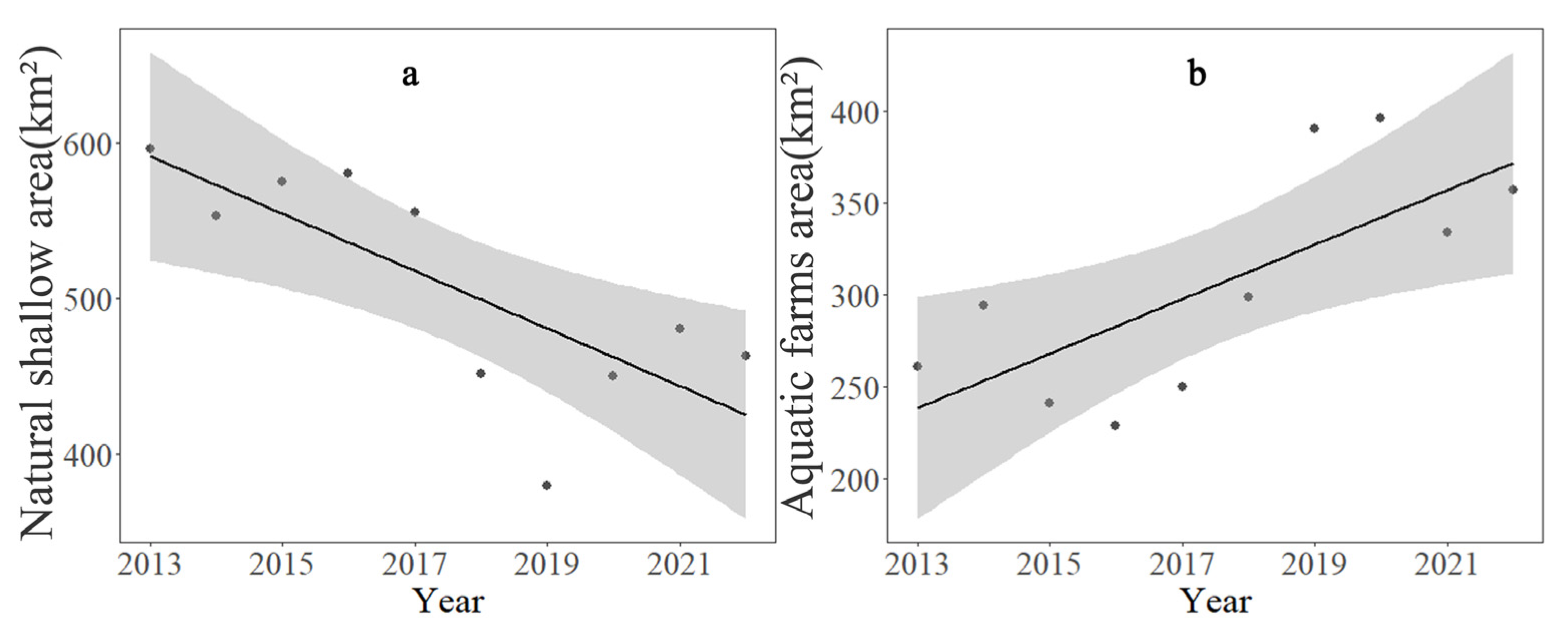
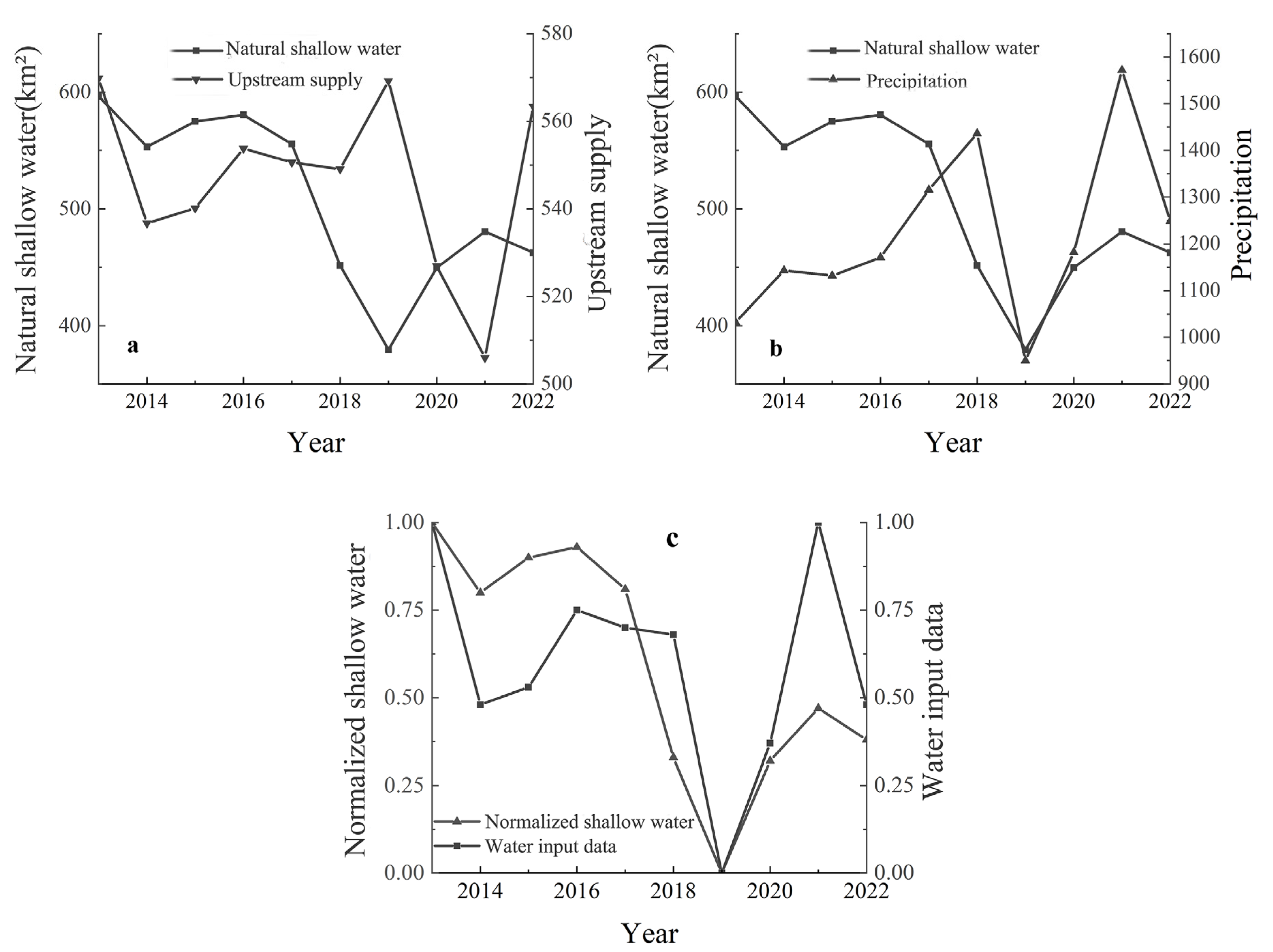
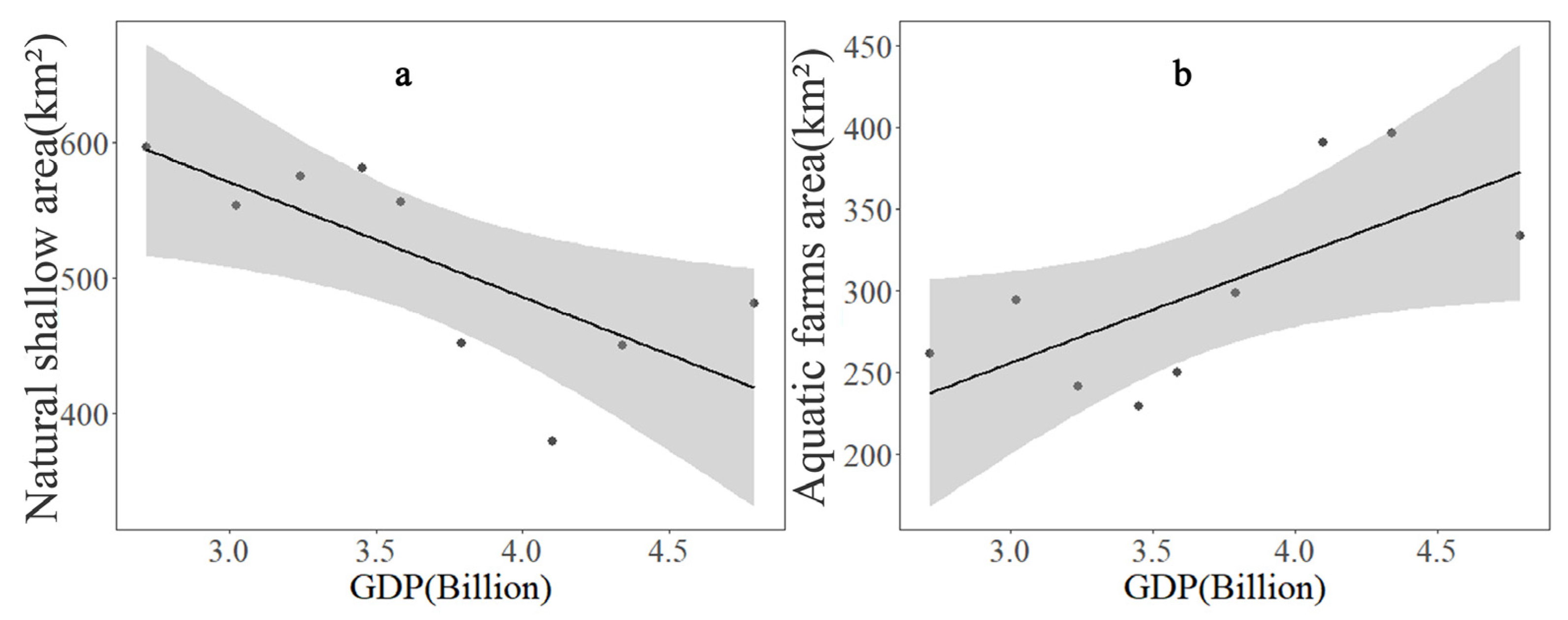
3.2. Temporal Changes in Shallow Water Area and the Driving Factors
3.3. Seasonal Changes in Shallow Water Area and the Driving Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Shallow Water Area Extraction
4.2. Dynamics of Shallow Water Area of Hongze Lake and Its Driving Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q. Water resource dynamics and protection strategies for inland lakes: A case study of hongjiannao lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Tu, Z.; Yu, G.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. Shrinkage and protection of inland lakes on the regional scale: A case study of hubei province, china. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T. The study of carbon in inland waters—From isolated ecosystems to players in the global carbon cycle. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2018, 3, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Gao, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhi, D.; Yao, J. Exploring the relationship between hydroclimate and lake area in source area of the yellow river: Implications for the paleoclimate studies. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, G.; Bo, Y.; Chen, G. Time series remote sensing data-based identification of the dominant factor for inland lake surface area change: Anthropogenic activities or natural events? Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Duan, S.Q. Lakes as sentinels of climate change on the tibetan plateau. All Earth 2021, 33, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nõges, T. Relationships between morphometry, geographic location and water quality parameters of european lakes. Hydrobiologia 2009, 633, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Xia, J.; Zhu, F.L.; Quan, J.; Wang, H. Response of hydrodynamics and water-quality conditions to climate change in a shallow lake. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4961–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.J.; Lin, C. Impacts of future climate change and different management scenarios on water-related ecosystem services: A case study in the jianghuai ecological economic zone, china. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.G.; Huang, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gutscher, H.; Bi, J. How do the chinese perceive ecological risk in freshwater lakes? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62486. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.D.; Geng, Q.H.; Jin, C.S.; Xu, Z.K.; Xu, X. Tree line identification and dynamics under climate change in wuyishan national park based on landsat images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Latif, A. Extraction of urban water bodies from high-resolution remote-sensing imagery using deep learning. Water 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.K.; Kumar, L.; Roy, C. Monitoring the coastline change of hatiya island in bangladesh using remote sensing techniques. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.R.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zang, S.Y. Lake wetland classification based on an svm-cnn composite classifier and high-resolution images using wudalianchi as an example. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezine, E.M.D.; Kyzivat, E.D.; Smith, L.C. Super-resolution surface water mapping on the canadian shield using planet cubesat images and a generative adversarial network. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 47, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hin, L.Z.; Othman, Z. Lake chini water level prediction model using classification techniques. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computational Science and Technology (ICCST), Spatial Explorer, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 29–30 August 2019; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.F.; Yao, Z.J.; Wang, R. Assessing methods of identifying open water bodies using landsat 8 oli imagery. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, H.; Yu, L.; Cracknell, A. Deep learning based oil palm tree detection and counting for high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdogan, F.; Bovik, A.C.; Passalacqua, P. Surface water mapping by deep learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, H.; Ptak, M.; Dai, J.; Ji, Q. Lake water-level fluctuation forecasting using machine learning models: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44807–44819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannasi Chakravarthy, S.R.; Bharanidharan, N.; Rajaguru, H. A systematic review on machine learning algorithms used for forecasting lake-water level fluctuations. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, L.S. Extraction of surface water bodies using optical remote sensing images: A review. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 893–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Ni, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, G. Multilayer perceptron neural network for surface water extraction in landsat 8 oli satellite images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; He, C.; Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Sun, F.; Gong, P. High-resolution remote sensing mapping of global land water. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.Y. Flood inundation extraction based on decision-level data fusion: A case in peru. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, X-3/W1-2022, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.K.; Feng, X.Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Ramadan, E. The methods of extracting water information from spot image. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Dong, T.; McNairn, H.; Champagne, C.; Liu, M.; Shang, J. Object-based crop classification using multi-temporal spot-5 imagery and textural features with a random forest classifier. Geocarto Int. 2017, 33, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (ndwi) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.D.; Pu, R.L.; Zhang, B.; Gao, L.R. A comparative study of coastline changes at tampa bay and xiangshan harbor during the last 30 years. In Proceedings of the 36th IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 5185–5188. [Google Scholar]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Mu, M.; Lyu, H.; Miao, S.; Xu, J. Optical classification of inland waters based on an improved fuzzy c-means method. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 34838–34856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—Lisa. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowe, P.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J.; Dube, T. Exploring the spatial patterns of vegetation fragmentation using local spatial autocorrelation indices. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 024523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.-P. A method for automatic and rapid mapping of water surfaces from sentinel-1 imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Diao, C.; Ji, W.; Yin, D. A survey of methods incorporating spatial information in image classification and spectral unmixing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3870–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Zhang, D.; Shi, D.; Luan, Z.Q. Automatic extraction of open water using imagery of landsat series. Water 2020, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Guo, Z.Y.; Dai, X.Y.; Li, X.D. Application of satellite remote sensing to coastal topography generation: Case study of chongming island in shanghai, china. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Shi, K.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.; Pan, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y. Characteristics of the total suspended matter concentration in the hongze lake during 1984–2019 based on landsat data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Shen, X.Y. Variations in water level, area and volume of hongze lake, china from 2003 to 2018. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.G.; Duan, H.T.; Feng, L.; Ma, R.H.; Xue, K. Climate- and human-induced changes in suspended particulate matter over lake hongze on short and long timescales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.; Li, H.P.; Yang, G.S.; Zhang, Q.; Diao, Y.Q. Assessing the hydrologic impacts of land use change in the taihu lake basin of china from 1985 to 2010. Water 2018, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Pu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Luan, Z.; Shi, K. Automatic detection of algal blooms using sentinel-2 msi and landsat oli images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8497–8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, S.; Carrer, D.; Planque, C.; Camacho, F.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.-C. Satellite leaf area index: Global scale analysis of the tendencies per vegetation type over the last 17 years. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Pu, Y.; Luan, Z. Shoreline dynamics of chongming island and driving factor analysis based on landsat images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, R.R.; Souza, C.T.; Vazquez, B.; Wickel, A.J.; Ressl, R. Analysis of optimal thresholds for identification of open water using modis-derived spectral indices for two coastal wetland systems in mexico. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 70, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, P.J.; Schwartzkopf, W.C.; Koehler, F.W. Robust automated thresholding of sar imagery for open-water detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.W.; Guo, Z.L.; Jiang, B.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.N.; Wang, D.A.; Zhang, M.Y.; Cui, L.J. Improving wetland ecosystem health in china. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, F.; Bozdag, A.; Durduran, S.S.; Gumus, M.G. Monitoring coastline change using remote sensing and gis technology: A case study of burdur lake, turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 7235–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, R.Z.; Zhang, L. Changes of hongze lake wetlands in the past three decades. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing (WICOM), Chengdu, China, 23–25 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, D.-B.; Zhang, W.-S.; Zhang, J.-S. Impacts of different dynamic factors on the saltwater intrusion in the northern branch of the yangtze estuary. China Ocean Eng. 2019, 33, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, X. Spatial distribution of penetration depth in taihu lake (China) during spring and autumn. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.S.F.; Costa, M.P.F.; Melack, J.M.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Remote sensing of aquatic vegetation: Theory and applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 140, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Hydroclimatological influences on recently increased droughts in china’s largest freshwater lake. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, K.M.; Hein, C.L.; Lottig, N.R.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Lake water level response to drought in a lake-rich region explained by lake and landscape characteristics. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Duan, H.T.; Hu, C.M.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, A.N.; Ju, W.M.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, G.S. A half-century of changes in china’s lakes: Global warming or human influence? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L24106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Zhu, L. Differences and cause analysis of changes in lakes of different supply types in the north-western tibetan plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2752–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Liu, Y.C.; Li, J.L.; Tian, P.; Zhang, H.T. Surface water changes in china’s yangtze river delta over the past forty years. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Chen, J.C.; Li, M.X.; Jia, J.W.; Fan, K.X.; Destech Publicat, I. Impact of water diversion of the south-to-north water diversion middle route project on the hydrological characteristics at the junction of yangtze river and poyang lake. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environment, Climate Change and Sustainable Development (ECCSD), Beijing, China, 28–29 May 2016; pp. 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, Y.-P.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-C. Incorporating the implementation intensity of returning farmland to lakes into policymaking and ecosystem management: A case study of the jianghuai ecological economic zone, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, W.; Mitchell, B. Evaluation of water quality and management of hongze lake and gaoyou lake along the grand canal in eastern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 176, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanari, N.; Schuler, R.; Kohler, T.; Liniger, H. The impact of commercial horticulture on river water resources in the upper ewaso ng’iro river basin, kenya. Mt. Res. Dev. 2018, 38, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yu, H. Human activities and climate variability affecting inland water surface area in a high latitude river basin. Water 2020, 12, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CORPrecipitation | CORTemperature | CORSupply | CORPrecipitation>2018&Supply≤2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural shallow water area | −0.188 | −0.455 | 0.212 | 0.720 * |
| The area of aquatic farms | 0.115 | 0.515 | −0.151 | −0.591 |
| Coefficient | Sum Sq 2 | F Value | p | Explained Variation (%) 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water input 1 | 37.9265 | 18,271.9 | 13.686 | <0.01 | 38.3 |
| Aquatic farms | −0.9443 | 20,140.7 | 15.085 | <0.01 | 42.2 |
| Residuals | 9345.9 | 19.6 | |||
| Total | 47,758.5 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Huang, J.; Xu, D.; Na, N.; Luan, Z. Extraction, Dynamics, and Driving Factors of Shallow Water Area in Hongze Lake Based on Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071128
Liu N, Huang J, Xu D, Na N, Luan Z. Extraction, Dynamics, and Driving Factors of Shallow Water Area in Hongze Lake Based on Landsat Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(7):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nianao, Jinhui Huang, Dandan Xu, Ni Na, and Zhaoqing Luan. 2025. "Extraction, Dynamics, and Driving Factors of Shallow Water Area in Hongze Lake Based on Landsat Imagery" Remote Sensing 17, no. 7: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071128
APA StyleLiu, N., Huang, J., Xu, D., Na, N., & Luan, Z. (2025). Extraction, Dynamics, and Driving Factors of Shallow Water Area in Hongze Lake Based on Landsat Imagery. Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17071128







