FI-MambaNet: A Feature Integration Network with Mamba and Multi-Head Self-Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection
Highlights
- The MSA-Mamba module is designed herein. By combining large-kernel convolution with a multi-directional structure-aware scanning strategy, it effectively captures local details and long-range spatial dependencies, significantly enhancing the modeling capability for multi-scale objects.
- The MCSA module is developed, which utilizes parallel convolution branches with different receptive fields to simultaneously model multi-granularity channel context information. This enhances semantic discriminative power and effectively alleviates feature confusion caused by similar textures or dense objects.
- The MSA-Mamba and MCSA modules are integrated in parallel to construct a dual-branch FIBlock architecture, which realizes the joint context modeling of spatial structure and channel semantics and forms complementary advantages.
- Extensive experiments on the DOTA-v1.0, DOTA-v1.5 and HRSC2016 datasets show that FI-MambaNet outperforms various advanced methods in terms of mAP (mean Average Precision) while maintaining high computational efficiency, demonstrating its effectiveness and practicality.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
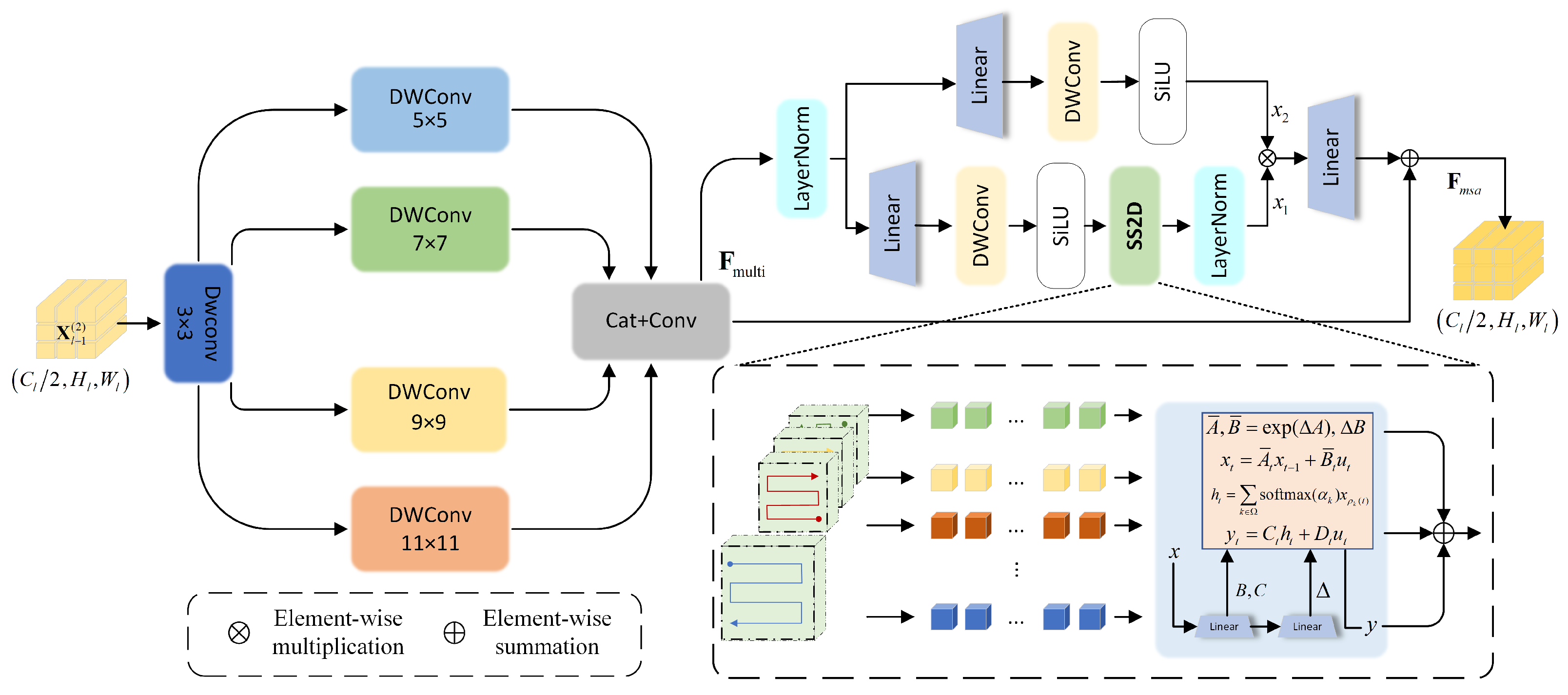
- To tackle the challenges posed by varying target scales and complex structures in remote sensing images, this work introduces the Multi-scale Structure-Aware Mamba (MSA-Mamba) module. By integrating multi-scale feature extraction with a multi-directional scanning strategy incorporating a normalized structure-aware state mechanism, this module significantly enhances the modeling capabilities for both local structures and global context in remote sensing images;
- 2.
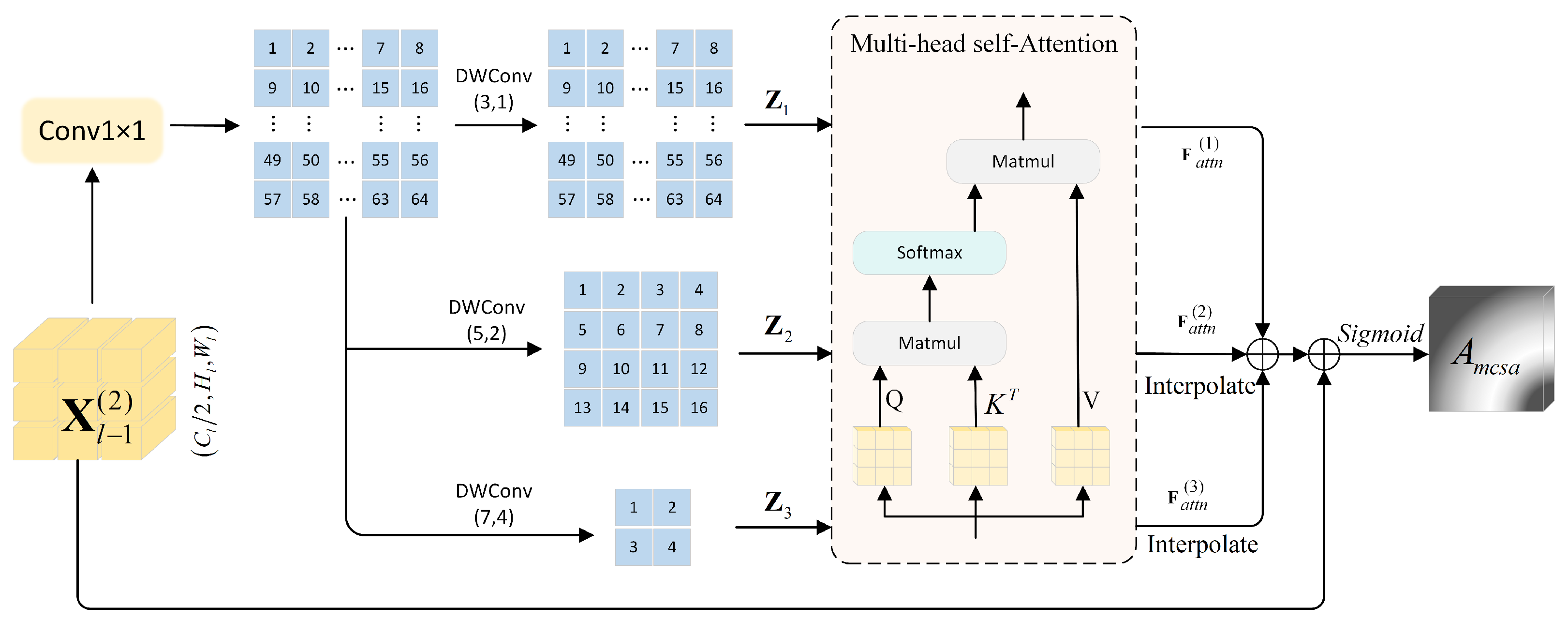
- To further enhance information interaction and discrimination across channel dimen- sions, a Multi-granularity Contextual Self-Attention (MCSA) Block is designed. This block employs deep convolutional branches, each configured with a distinct kernel size and stride, to concurrently model multi-granularity channel contextual information, effectively mitigating confusion caused by abundant similar textures or dense targets in remote sensing images;
- 3.
- Our FI-MambaNet model delivers leading detection performance. When evaluated on the DOTA-v1.0, DOTA-v1.5 and HRSC2016 remote sensing benchmarks, the model strikes an excellent balance between accuracy and inference speed, underscoring its significant potential for real-world applications.
2. Related Works
2.1. Remote Sensing Object Detection
2.2. State Space Model
2.3. Attention Mechanism
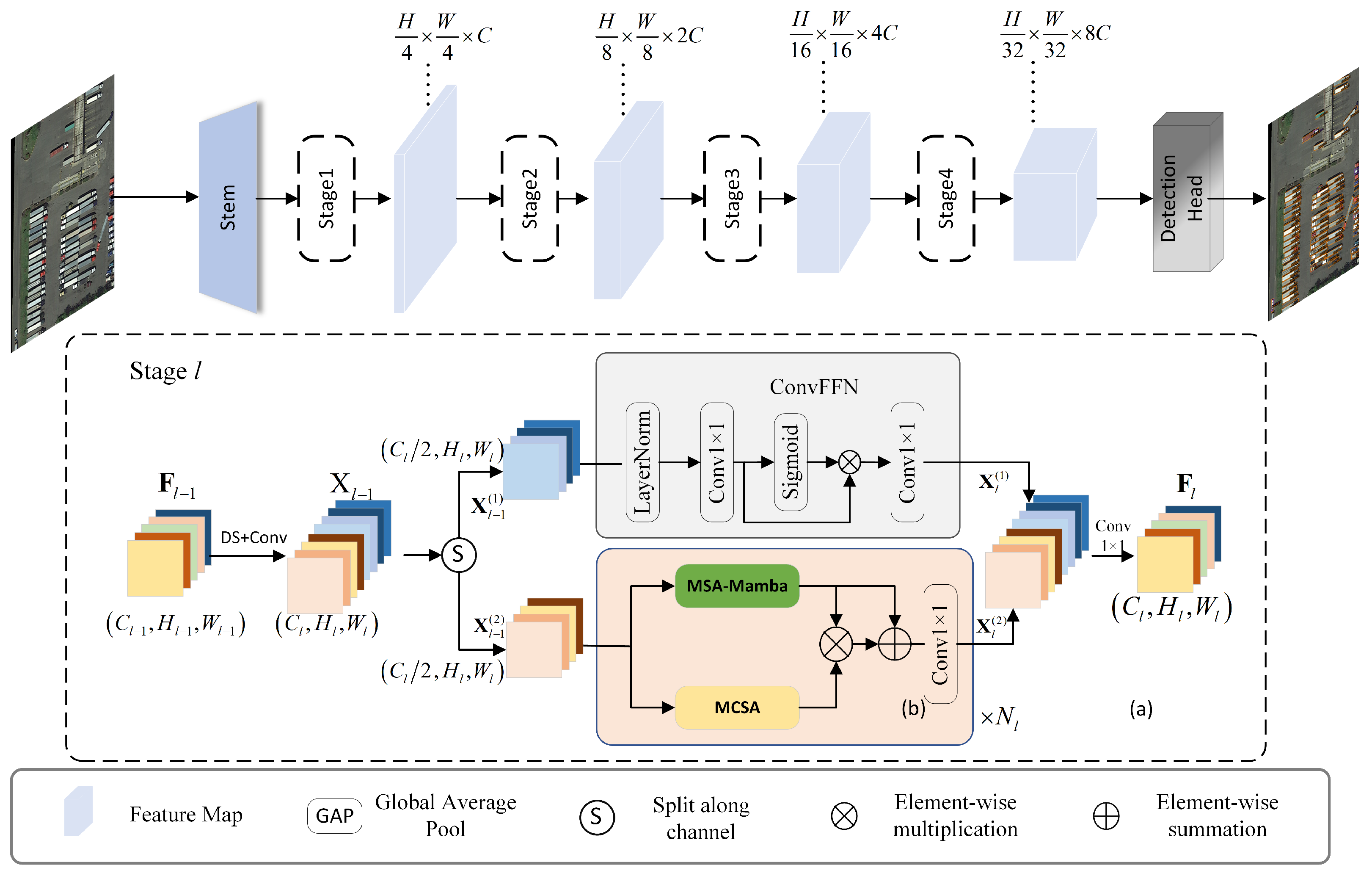
3. Methods
3.1. Multi-Scale Structure-Aware Mamba Block
3.2. Multi-Granularity Contextual Self-Attention Block
3.3. FI Stage
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Comparison
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Ablation Study on Multi-Scale Fusion in the MSA-Mamba Block
4.4.2. Analysis of Scanning Directions in the MSA-Mamba Block
4.4.3. Analysis of the MCSA Block
4.4.4. Collaborative Analysis of MSA-Mamba and MCSA
4.4.5. Performance Evaluation of FI-MambaNet Across Diverse Detection Frameworks
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- Focus on model lightweighting and inference optimization, such as simplifying redundant linear operations through module reparameterization, knowledge distillation, and network pruning to enhance deployment efficiency;
- 2.
- Exploring the extension of FI-MambaNet’s design principles to multi-source remote sensing data, such as SAR, hyperspectral, and lidar imagery, whilst investigating corresponding model adaptation adjustments to enhance robustness across broader application scenarios;
- 3.
- Conduct testing on larger and more diverse datasets, alongside comprehensive comparisons with the latest detection algorithms, to more thoroughly evaluate the model’s overall performance;
- 4.
- FI-MambaNet still faces limitations in dense small-sized targets and complex environments. Future research will focus on reducing missed detections through refined small-object feature modeling, adaptive attention mechanisms, and improved rotation-aware alignment strategies;
- 5.
- In the future, we will focus on enhancing the detection capability of extremely small and highly rotating targets. We plan to explore adaptive receptive field adjustment and rotation-aware feature encoding to improve robustness, reduce the missed detection rate, and further enhance performance in dense and complex scenes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; Xu, F.; Wang, R.; Diao, W.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Xu, T.; et al. FAIR1M: A benchmark dataset for fine-grained object recognition in high-resolution remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 184, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Weng, L.; Yang, Y. Ship rotated bounding box space for ship extraction from high-resolution optical satellite images with complex backgrounds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA:A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhu, J. Oriented reppoints for aerial object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Dense label encoding for boundary discontinuity free rotation detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15819–15829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, Q.; Yan, J. Learning high-precision bounding box for rotated object detection via kullback-leibler divergence. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 18381–18394. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. The KFIoU loss for rotated object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12558. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q. Learning RoI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Feng, Z.; He, T. R3det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. Rethinking rotated object detection with gaussian wasserstein distance loss. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 11830–11841. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, G.; Xiang, S.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Stitcher: Feedback-driven data provider for object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.12432. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsolmoali, P.; Zareapoor, M.; Chanussot, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J. Rotation equivariant feature image pyramid network for object detection in optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5608614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, W.; Jiao, L.; Chen, P.; Yang, S.; Hou, B. Multi-scale image block-level F-CNN for remote sensing images object detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43607–43621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lu, X. Hierarchical and robust convolutional neural network for very high-resolution remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5535–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Kuang, G. Squeeze and excitation rank faster R-CNN for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Large selective kernel network for remote sensing object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 16794–16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shen, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, F. Lightweight Ship Object Detection Algorithm for Remote Sensing Images Based on Multi-scale Perception and Feature Enhancement. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2025, 91, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mohamed, A.S.A. Gaussian-based R-CNN with large selective kernel for rotated object detection in remote sensing images. Neurocomputing 2025, 620, 129248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y. Poly kernel inception network for remote sensing detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 27706–27716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Talebi, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Milanfar, P.; Bovik, A.; Li, Y. Maxvit: Multi-axis vision transformer. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, B.; Lin, B.; He, X.; Liu, W. Crossformer++: A versatile vision transformer hinging on cross-scale attention. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ren, Y.; Sheng, K.; Dong, W.; Yuan, H.; Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Xu, C. Dynamic refinement network for oriented and densely packed object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11207–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabati, R.; Qi, H. Rrpn: Radar region proposal network for object detection in autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Xia, G.S. Redet: A rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2786–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, J. ARS-DETR: Aspect ratio-sensitive detection transformer for aerial oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Liu, H.; Tang, H.; Wu, Z.; Song, P. Ao2-detr: Arbitrary-oriented object detection transformer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 2342–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, W. FPNFormer: Rethink the method of processing the rotation-invariance and rotation-equivariance on arbitrary-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Warrington, A.; Linderman, S.W. Simplified state space layers for sequence modeling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.04933. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y. Vmamba: Visual state space model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 103031–103063. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Pun, M.O. Rs 3 mamba: Visual state space model for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6011405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Rsmamba: Remote sensing image classification with state space model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 8002605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X.; Dong, J.; Du, Q. MSFMamba: Multi-scale feature fusion state space model for multi-source remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5504116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, J.; Han, C.; Xia, J.; Yokoya, N. ChangeMamba: Remote sensing change detection with spatiotemporal state space model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4409720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, L.; Nguyen, A. Samba: Semantic segmentation of remotely sensed images with state space model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Vision mamba: Efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Z.; Espinosa, M.; Ericsson, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Crowley, E.J. Plainmamba: Improving non-hierarchical mamba in visual recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17695. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Pei, X.; You, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Xu, C. Localmamba: Visual state space model with windowed selective scan. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Q.; Chen, H.; Gan, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Tian, G.; Xie, L. Mambaad: Exploring state space models for multi-class unsupervised anomaly detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 71162–71187. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Ge, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, Y. Grootvl: Tree topology is all you need in state space model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.02395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Vedaldi, A. Gather-excite: Exploiting feature context in convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, F.; Hu, H. Gcnet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Spatial group-wise enhance: Improving semantic feature learning in convolutional networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Meng, Q.; Li, S.; Yuan, X. Improving transformers with dynamically composable multi-head attention. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.W.; Cao, J.L.; Cheng, M.M.; Hou, Q. Dformerv2: Geometry self-attention for rgbd semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 19345–19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, X. SCSA: A Plug-and-Play Semantic Continuous-Sparse Attention for Arbitrary Semantic Style Transfer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 13051–13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xia, X.; Liu, J.; Yi, Z.; He, T. Strengthening layer interaction via dynamic layer attention. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhu, R.J.; Chou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Deng, L.j.; Li, G. Gated attention coding for training high-performance and efficient spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yao, Y.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Dual-aligned oriented detector. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5618111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gan, W.; Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Huang, G. Adaptive rotated convolution for rotated object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 6589–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Da, F. Phase-shifting coder: Predicting accurate orientation in oriented object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 13354–13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K. Rtmdet: An empirical study of designing real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.07784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, C.; Dai, F. Rethinking boundary discontinuity problem for oriented object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 17406–17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, B.; Tao, D.; Zhang, L. Advancing plain vision transformer toward remote sensing foundation model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 61, 5607315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, S.B.; Li, H.D.; Shu, Q.L.; Ding, C.H.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. Legnet: Lightweight edge-Gaussian driven network for low-quality remote sensing image object detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14012. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Hybrid task cascade for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4974–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, A.S.M.S.; Zhang, X.; Shagar, M.M.B.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Meng, F. Cross Spatial Temporal Fusion Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection via Image Feature Matching. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.19118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M. Strip R-CNN: Large Strip Convolution for Remote Sensing Object Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.03775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Chu, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Shen, C. Fully convolutional one-stage 3d object detection on lidar range images. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 34899–34911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pei, Z.; Zhou, F.; Wang, G. Rotated faster R-CNN for oriented object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Robot Systems and Applications, Tokyo, Japan, 12–14 December 2020; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
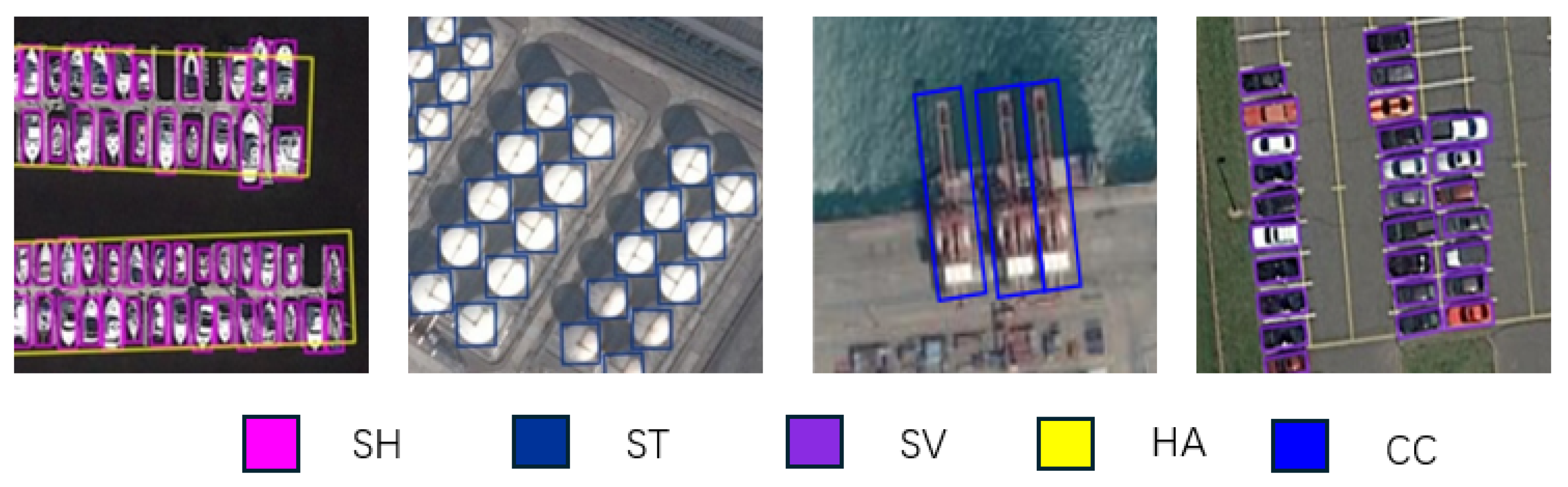
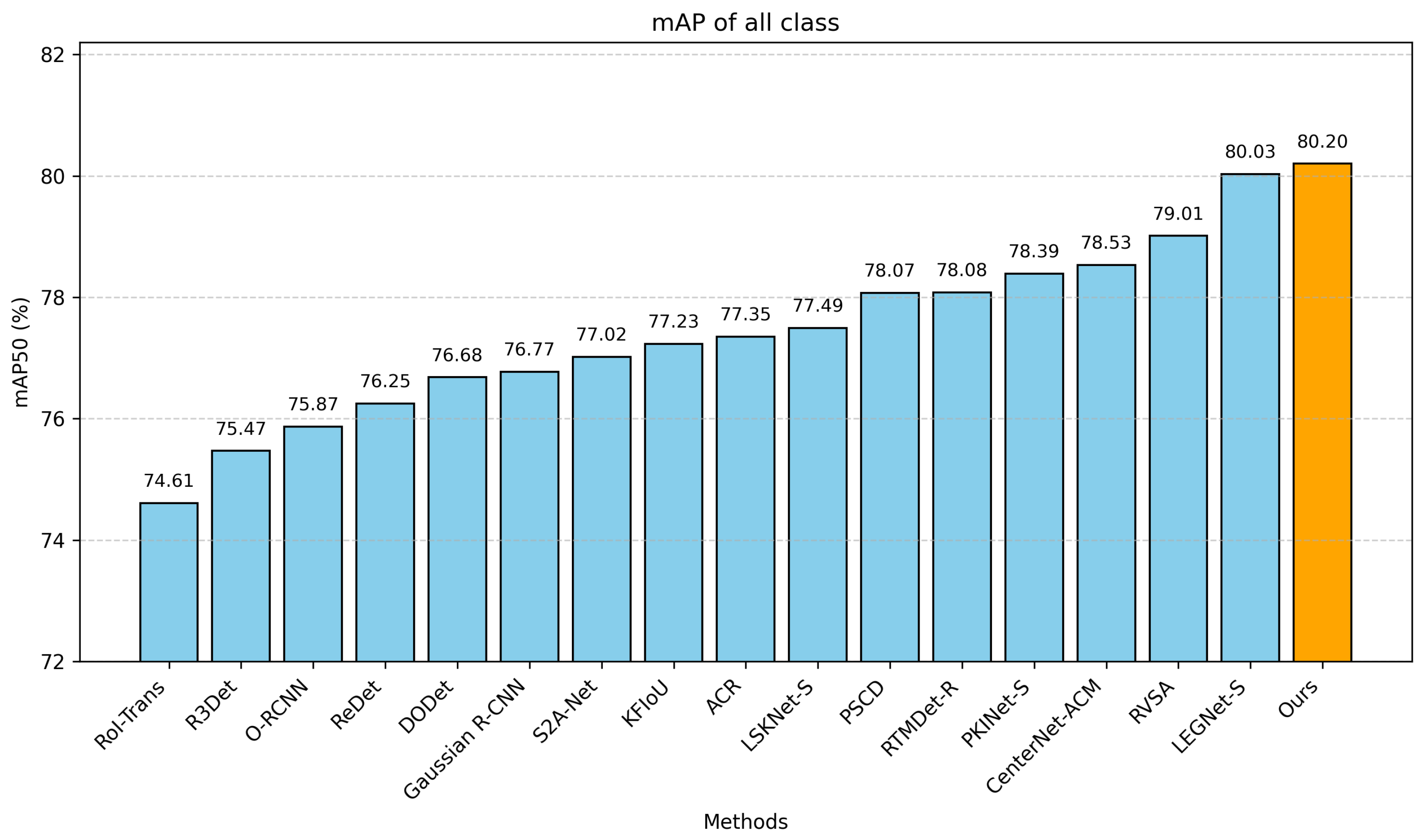
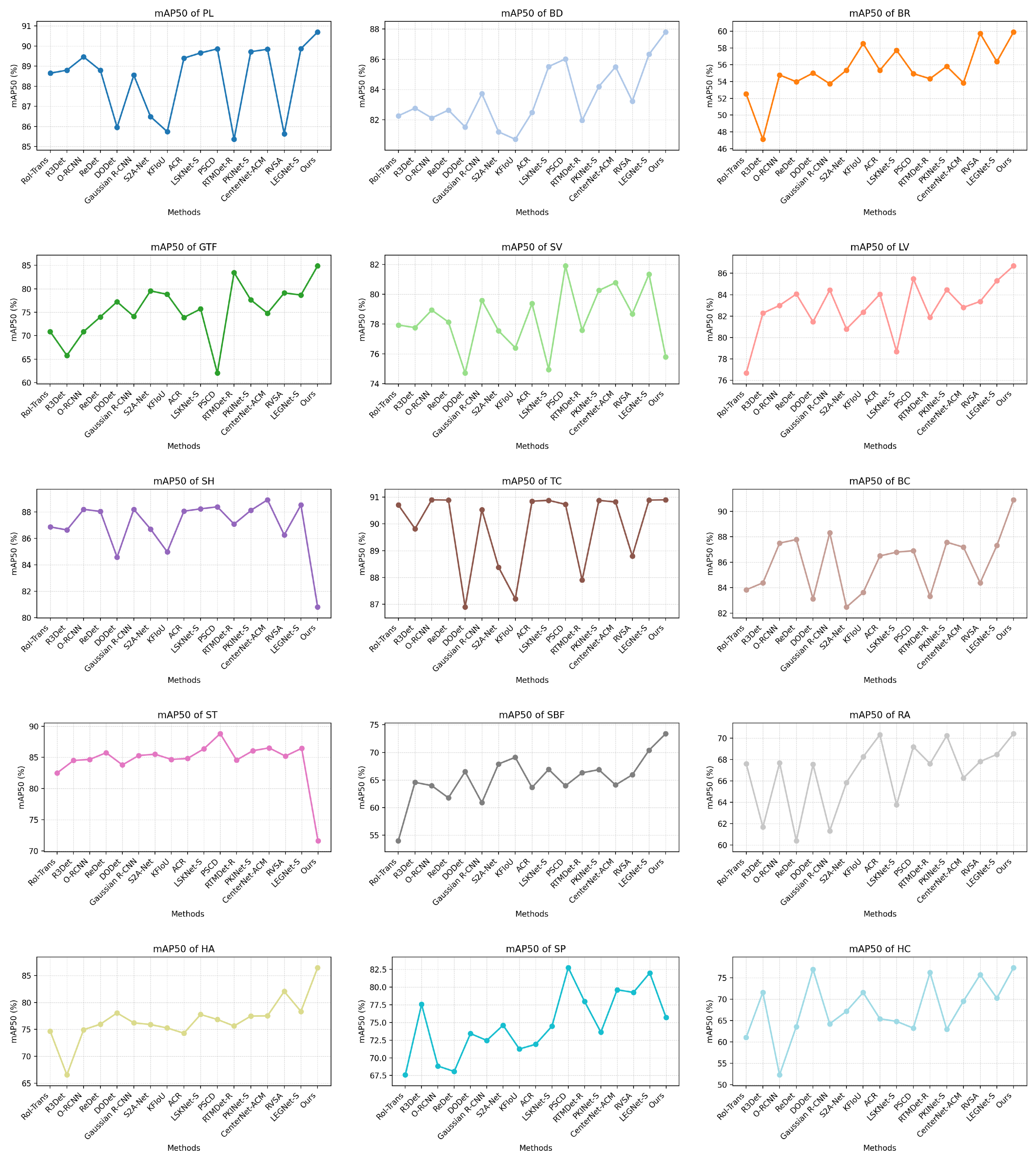
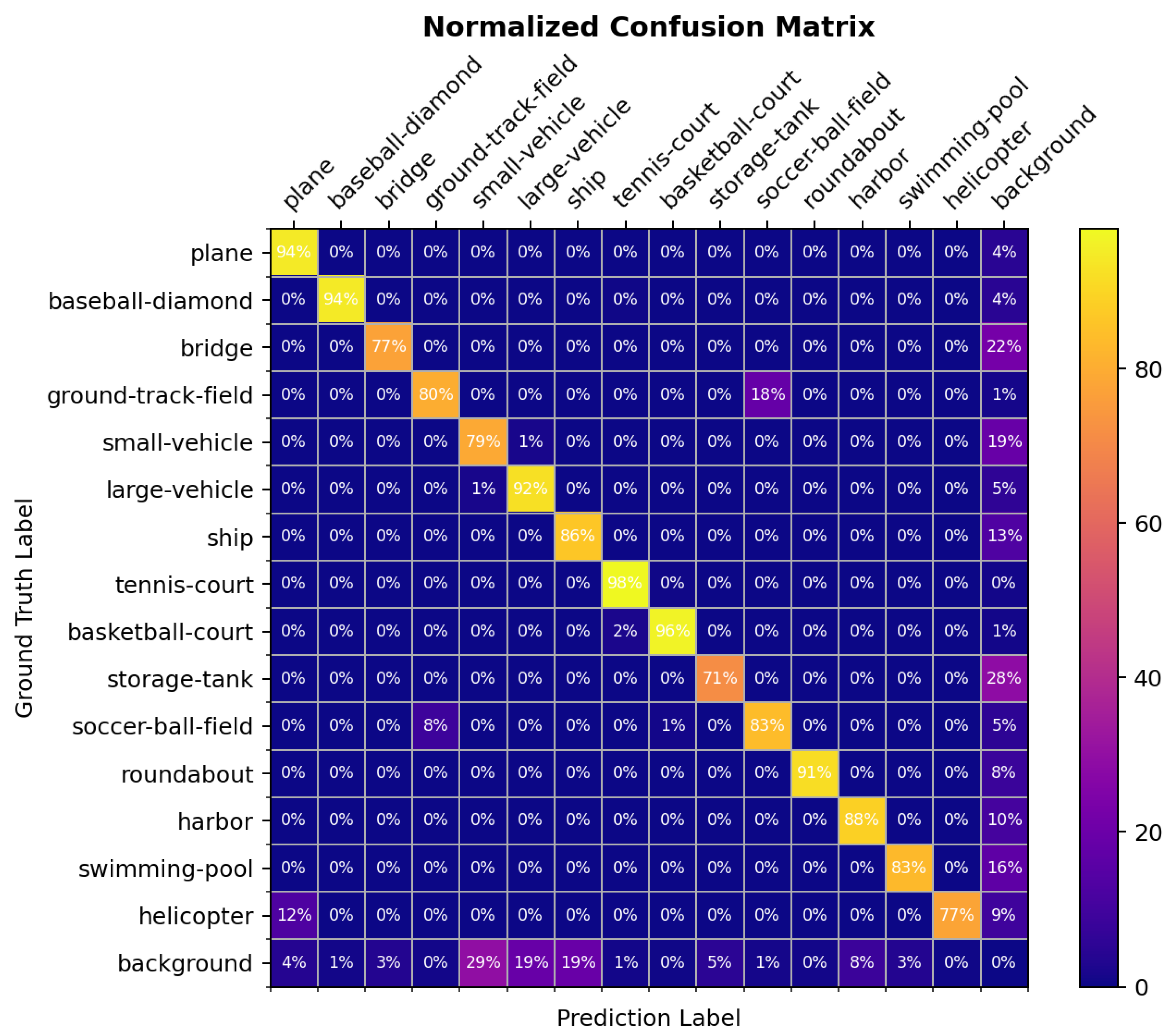
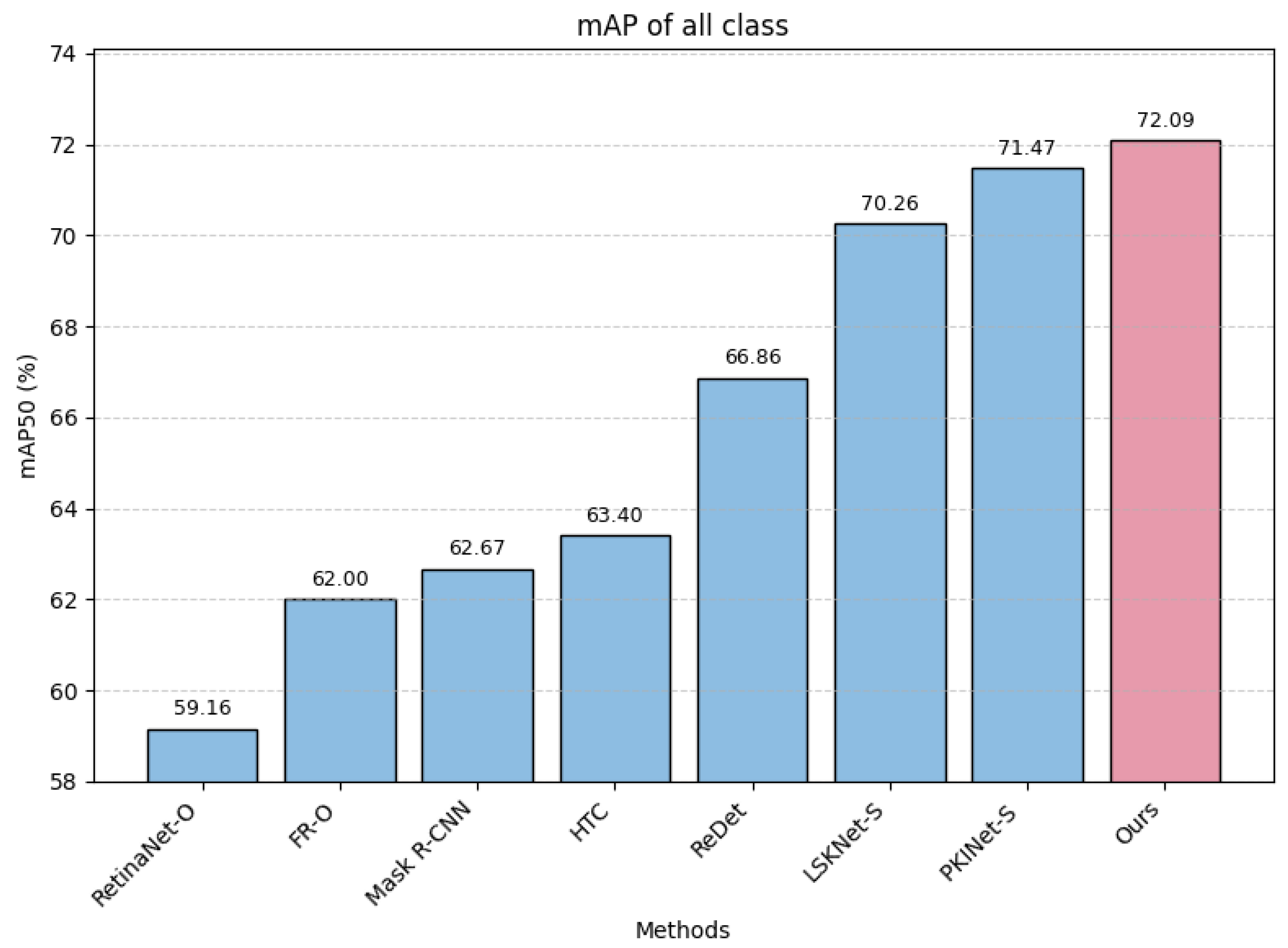
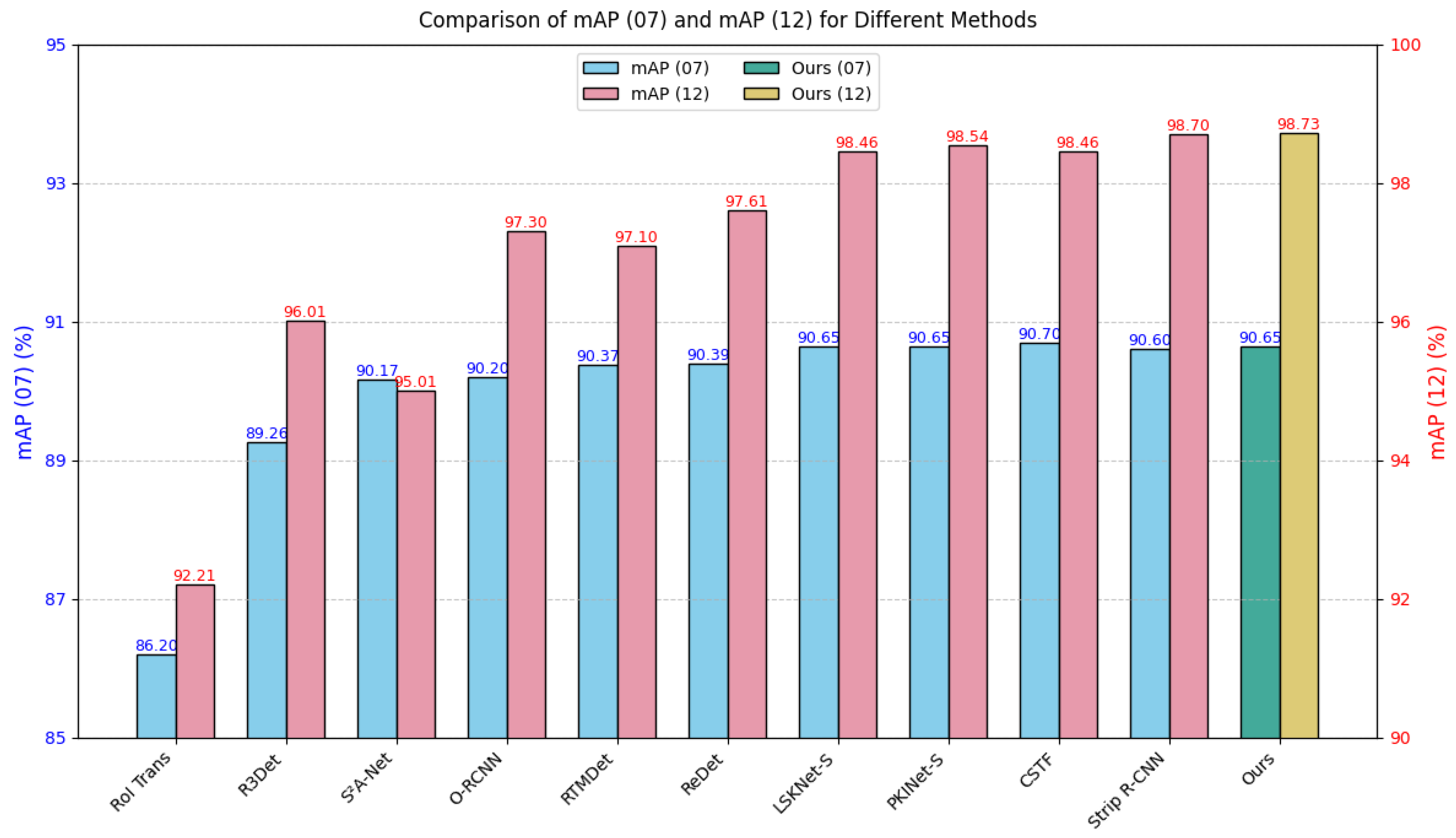
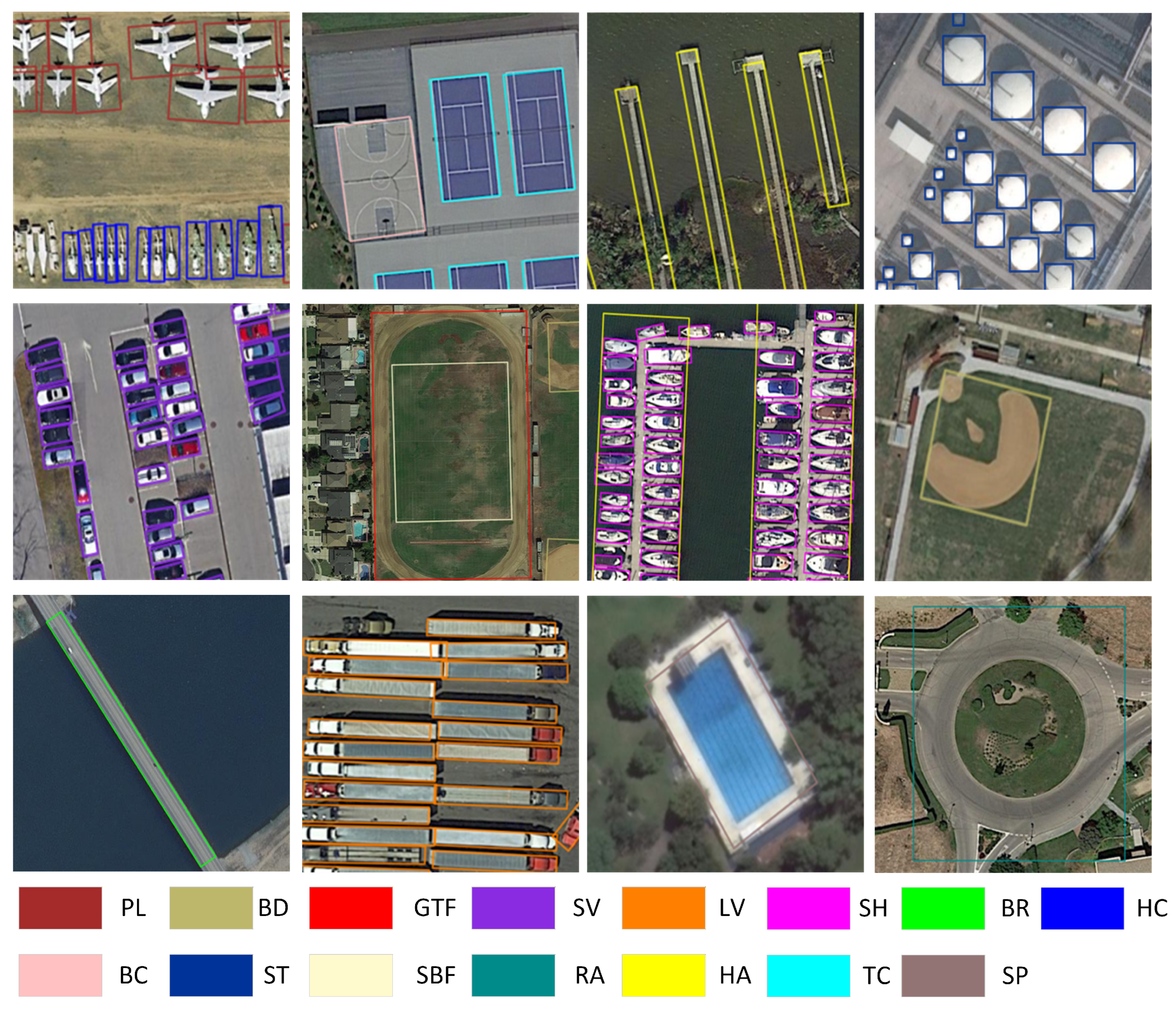

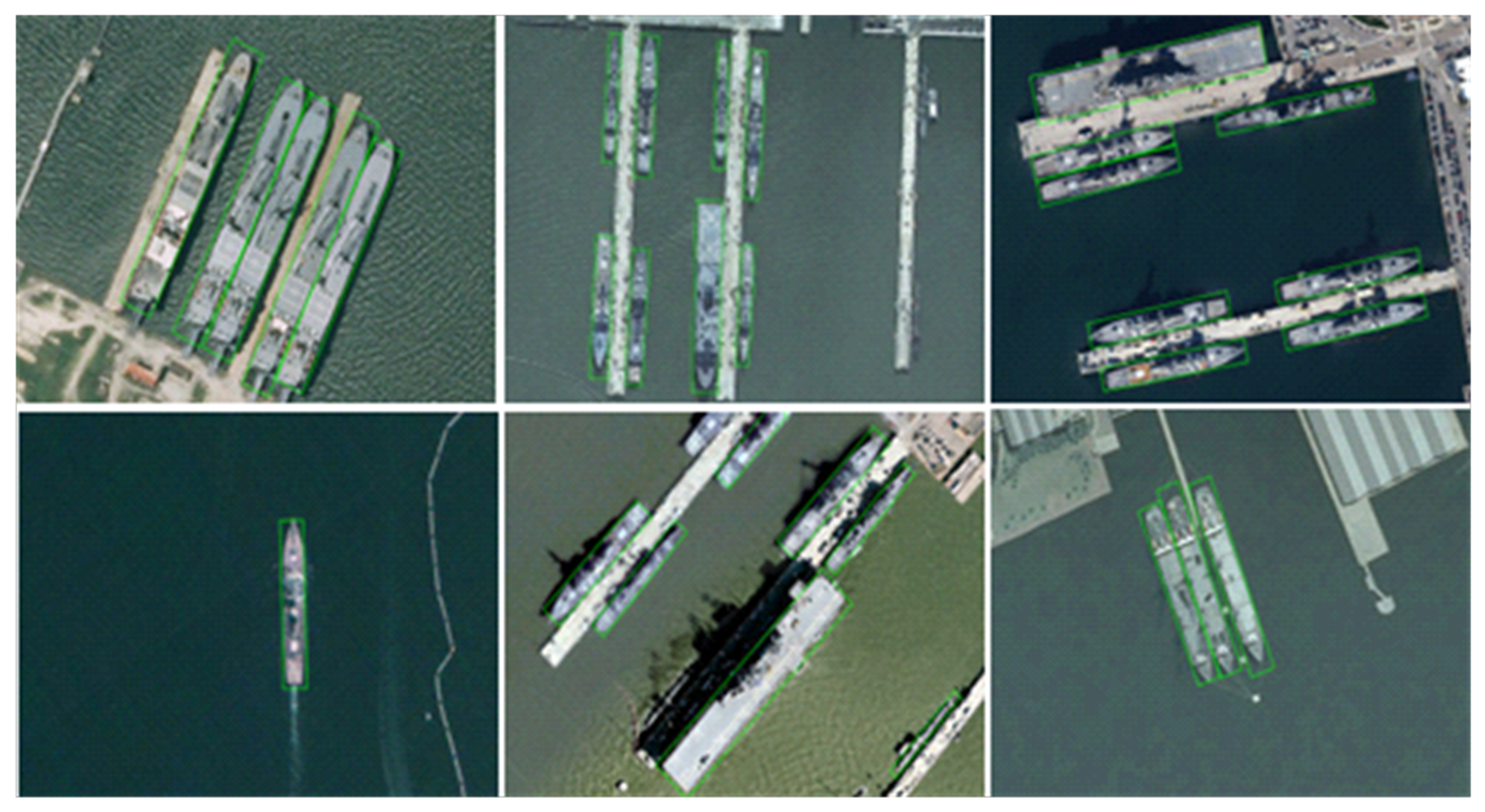
| Method | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC | BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | MAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RoI-Trans [10] | 88.65 | 82.26 | 52.53 | 70.87 | 77.93 | 76.67 | 86.87 | 90.71 | 83.83 | 82.51 | 53.95 | 67.61 | 74.67 | 67.58 | 61.03 | 74.61 |
| R3Det [12] | 88.8 | 82.77 | 47.11 | 65.77 | 77.76 | 82.27 | 86.64 | 89.82 | 84.38 | 84.51 | 64.57 | 61.68 | 66.53 | 77.56 | 71.62 | 75.47 |
| O-RCNN [11] | 89.46 | 82.12 | 54.78 | 70.86 | 78.93 | 83 | 88.2 | 90.9 | 87.5 | 84.68 | 63.97 | 67.69 | 74.94 | 68.84 | 52.28 | 75.87 |
| ReDet [30] | 88.79 | 82.64 | 53.97 | 74 | 78.13 | 84.06 | 88.04 | 90.89 | 87.78 | 85.75 | 61.76 | 60.39 | 75.96 | 68.07 | 63.59 | 76.25 |
| DODet [64] | 85.96 | 81.52 | 55.01 | 77.22 | 74.71 | 81.46 | 84.58 | 86.89 | 83.12 | 83.8 | 66.5 | 67.54 | 78.06 | 73.43 | 77.02 | 76.68 |
| Gauss R-CNN [21] | 89.4 | 82.48 | 55.33 | 73.88 | 79.37 | 84.05 | 88.06 | 90.85 | 86.49 | 84.83 | 63.63 | 70.32 | 74.29 | 71.91 | 65.43 | 77.35 |
| S2A-Net [5] | 86.49 | 81.2 | 55.34 | 79.55 | 77.54 | 80.79 | 86.71 | 88.38 | 82.47 | 85.51 | 67.9 | 65.85 | 75.9 | 74.61 | 67.18 | 77.02 |
| KFIoU [9] | 85.74 | 80.71 | 58.52 | 78.81 | 76.4 | 82.37 | 84.98 | 87.2 | 83.62 | 84.68 | 69.1 | 68.25 | 75.26 | 71.25 | 71.57 | 77.23 |
| ACR [65] | 89.4 | 82.48 | 55.33 | 73.88 | 79.37 | 84.05 | 88.06 | 90.85 | 86.49 | 84.83 | 63.63 | 70.32 | 74.29 | 71.91 | 65.43 | 77.35 |
| LSKNet-S [19] | 89.66 | 85.52 | 57.72 | 75.7 | 74.95 | 78.69 | 88.24 | 90.88 | 86.79 | 86.38 | 66.92 | 63.77 | 77.77 | 74.47 | 64.82 | 77.49 |
| PSCD [66] | 89.86 | 86.02 | 54.94 | 62.02 | 81.90 | 85.48 | 88.39 | 90.73 | 86.90 | 88.82 | 63.94 | 69.19 | 76.84 | 82.75 | 63.24 | 78.07 |
| RTMDet-R [67] | 85.36 | 81.96 | 54.33 | 83.46 | 77.58 | 81.88 | 87.08 | 87.9 | 83.32 | 84.57 | 66.29 | 67.61 | 75.63 | 77.97 | 76.24 | 78.08 |
| PKINet-S [22] | 89.72 | 84.2 | 55.81 | 77.63 | 80.25 | 84.45 | 88.12 | 90.88 | 87.57 | 86.07 | 66.86 | 70.23 | 77.47 | 73.62 | 62.94 | 78.39 |
| CenterNet [68] | 89.84 | 85.50 | 53.84 | 74.78 | 80.77 | 82.81 | 88.92 | 90.82 | 87.18 | 86.53 | 64.09 | 66.27 | 77.51 | 79.62 | 69.57 | 78.53 |
| RVSA [69] | 85.63 | 83.23 | 59.73 | 79.11 | 78.68 | 83.37 | 86.26 | 88.8 | 84.38 | 85.21 | 65.93 | 67.81 | 82.06 | 79.25 | 75.76 | 79.01 |
| LEGNet-S [70] | 89.87 | 86.32 | 56.36 | 78.67 | 81.34 | 85.29 | 88.53 | 90.89 | 87.31 | 86.46 | 70.38 | 68.48 | 78.34 | 82.00 | 70.25 | 80.03 |
| Ours | 90.7 | 87.8 | 59.9 | 84.9 | 75.8 | 86.7 | 80.8 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 71.6 | 73.4 | 70.42 | 86.48 | 75.7 | 77.4 | 80.2 |
| Method | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC | BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | CC | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet-O [71] | 71.43 | 77.64 | 42.12 | 64.65 | 44.53 | 56.79 | 73.31 | 90.84 | 76.02 | 59.96 | 46.95 | 69.24 | 59.65 | 64.52 | 48.06 | 0.83 | 59.16 |
| FR-O [72] | 71.89 | 74.47 | 44.45 | 59.87 | 51.28 | 68.98 | 79.37 | 90.78 | 77.38 | 67.5 | 47.75 | 69.72 | 61.22 | 65.28 | 60.47 | 1.54 | 62 |
| Mask R-CNN [73] | 76.84 | 73.51 | 49.9 | 57.8 | 51.31 | 71.34 | 79.75 | 90.46 | 74.21 | 66.07 | 46.21 | 70.61 | 64.46 | 64.46 | 57.81 | 9.42 | 62.67 |
| HTC [74] | 77.8 | 73.67 | 51.4 | 63.99 | 51.54 | 73.31 | 80.31 | 90.48 | 75.12 | 67.34 | 48.51 | 70.63 | 64.48 | 64.48 | 55.87 | 5.15 | 63.4 |
| ReDet [30] | 79.2 | 82.81 | 51.92 | 71.41 | 52.38 | 75.73 | 80.92 | 90.83 | 75.81 | 68.64 | 49.29 | 72.03 | 70.55 | 70.55 | 63.33 | 11.53 | 66.86 |
| LSKNet-S [19] | 72.05 | 84.94 | 55.41 | 74.93 | 52.42 | 77.45 | 81.17 | 90.85 | 79.44 | 69.00 | 62.1 | 73.72 | 77.49 | 75.29 | 55.81 | 42.19 | 70.26 |
| PKINet-S [22] | 80.31 | 85 | 55.61 | 74.38 | 52.41 | 76.85 | 88.38 | 90.87 | 79.04 | 68.78 | 67.47 | 72.45 | 76.24 | 74.53 | 64.07 | 37.13 | 71.47 |
| Ours | 80.64 | 85.21 | 55.64 | 76.32 | 52.41 | 77.47 | 88.26 | 90.87 | 79.45 | 68.79 | 67.47 | 73.74 | 78.38 | 74.53 | 65.03 | 39.21 | 72.09 |
| Method | mAP (07) | mAP (12) | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RoI-Trans [10] | 86.2 | 92.21 | 41.4 | 198 | 20.5 |
| R3Det [12] | 89.26 | 96.01 | 41.9 | 336 | 16.3 |
| S2A-Net [5] | 90.17 | 95.01 | 38.6 | 198 | 24.6 |
| O-RCNN [11] | 90.2 | 97.3 | 41.1 | 199 | 26.7 |
| RTMDet [67] | 90.37 | 97.1 | 52.3 | 205 | 17.3 |
| ReDet [30] | 90.39 | 97.61 | 31.6 | 205 | 17.2 |
| LSKNet-S [19] | 90.65 | 98.46 | 31 | 161 | 24.5 |
| PKINet-S [22] | 90.65 | 98.54 | 30.8 | 190 | 18.4 |
| CSTF [75] | 90.70 | 98.46 | 42.98 | 168 | 17.5 |
| Strip R-CNN [76] | 90.60 | 98.70 | 30.5 | 159 | 19.8 |
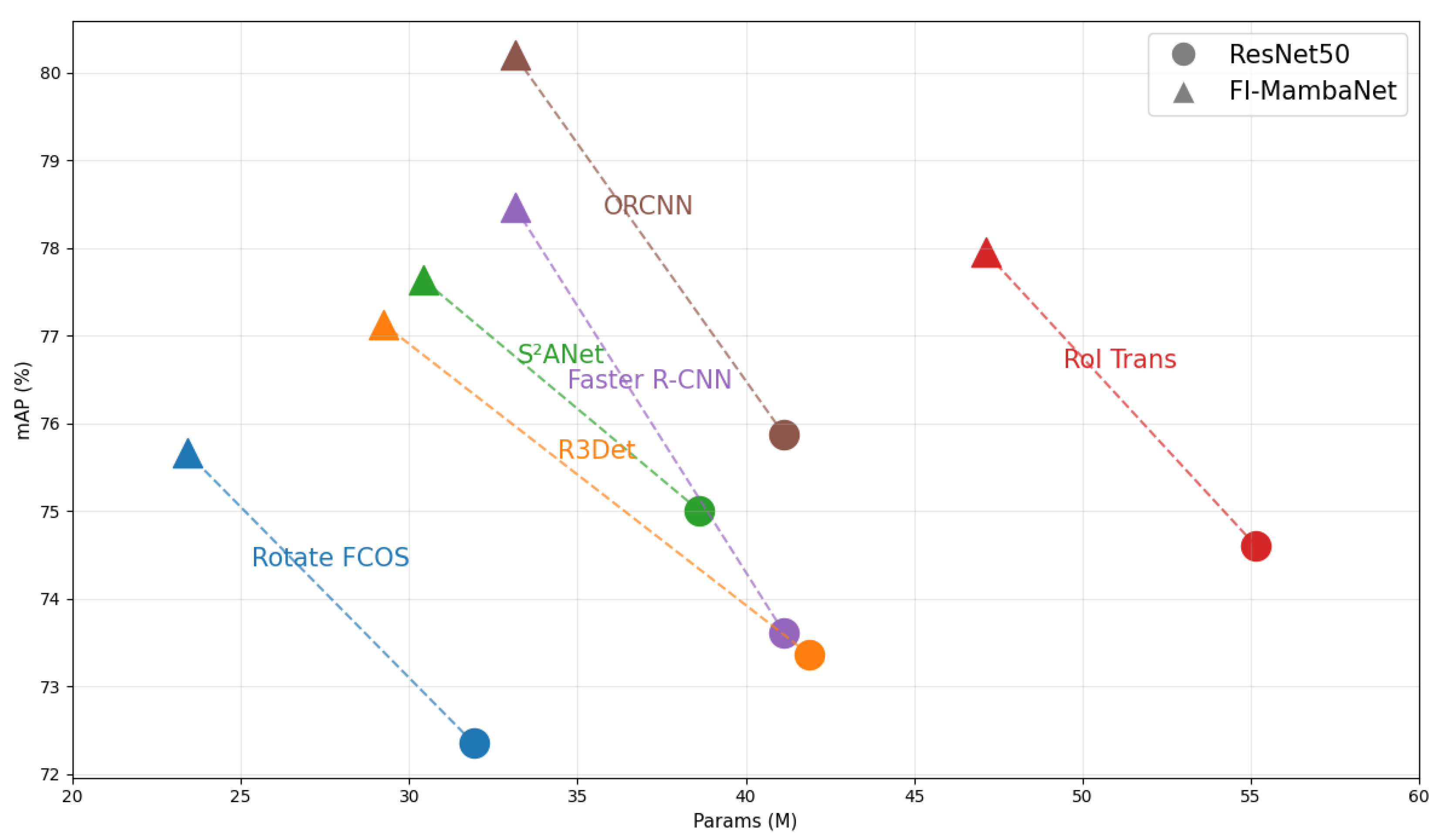
| Ours | 90.65 | 98.73 | 33.1 | 116 | 25.3 |
| Kernel Design | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | FPS | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1, 1, 3, 3) | 25.81 | 147 | 21.3 | 80.03 |
| (5, 7, 9, 11) | 26.44 | 150 | 20.5 | 80.20 |
| (5, 9, 13, 17) | 27.14 | 155 | 18.2 | 79.82 |
| (9, 13, 15, 17) | 27.62 | 159 | 17.3 | 79.65 |
| Number of Scanning Directions | Params (M) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 24.72 | 77.69 |
| 4 | 25.29 | 78.92 |
| 8 | 26.44 | 80.20 |
| Downsampling Frequency | Params (M) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 22.47 | 76.84 |
| 1 | 24.4 | 78.63 |
| 2 | 26.5 | 80.20 |
| 3 | 28.46 | 79.37 |
| Model | mAP (%) | FPS |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline(O-RCNN) | 75.87 | 25.4 |
| Baseline + MSA-Mamba | 78.73 | 21.7 |
| Baseline + MCSA | 79.05 | 22.6 |
| Ours | 80.20 | 20.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, L.; Tang, X. FI-MambaNet: A Feature Integration Network with Mamba and Multi-Head Self-Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233876
Liu J, Yang C, Wang J, Yan L, Tang X. FI-MambaNet: A Feature Integration Network with Mamba and Multi-Head Self-Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233876
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinhang, Chenxu Yang, Jing Wang, Lingyu Yan, and Xing Tang. 2025. "FI-MambaNet: A Feature Integration Network with Mamba and Multi-Head Self-Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233876
APA StyleLiu, J., Yang, C., Wang, J., Yan, L., & Tang, X. (2025). FI-MambaNet: A Feature Integration Network with Mamba and Multi-Head Self-Attention for Remote Sensing Object Detection. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233876









