Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Estimates Using High-Temporal Resolution Data from NEON and SMAP Missions
Highlights
- The τ-z model accurately estimates soil temperature sensing depth (zTeff), with best performance around 0.2 τ when monotonic conditions are met.
- Combining SMAP’s soil moisture, the τ-z model achieves high accuracy in estimating zTeff, with RMSD (0.05 m) and unRMSD (0.03 m), and correlations (0.67) between estimated and observed values.
- The τ-z model proves robust across diverse ecosystems, thereby enhancing confidence in the retrieval of soil moisture and temperature from passive microwave remote sensing.
- These results provide a solid foundation for advancing applications in agriculture, hydrology, and climate change monitoring.
Abstract
1. Introduction
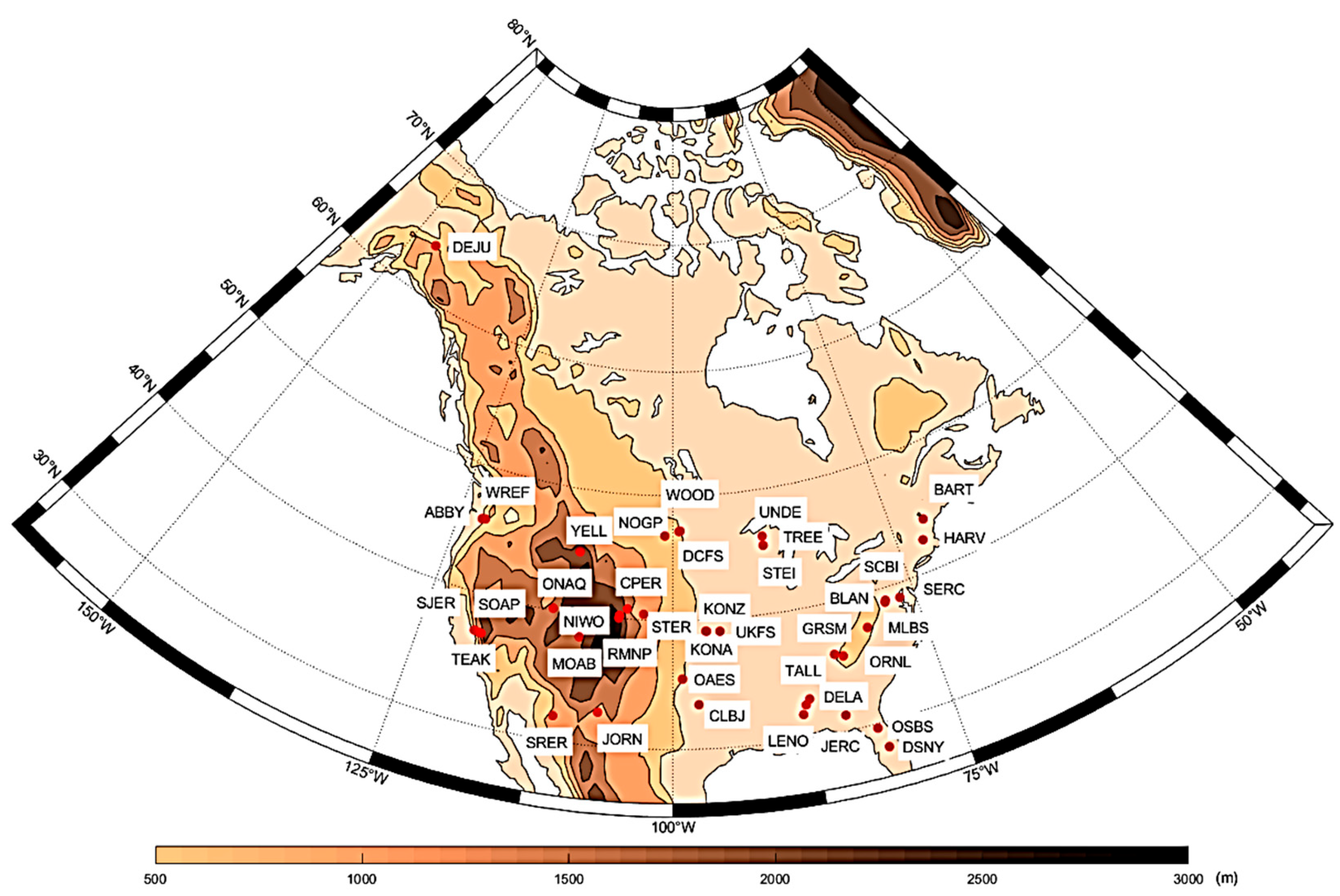
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Soil Effective Temperature (Teff)
3.2. The τ-z Model
3.3. The Statistics
4. Results
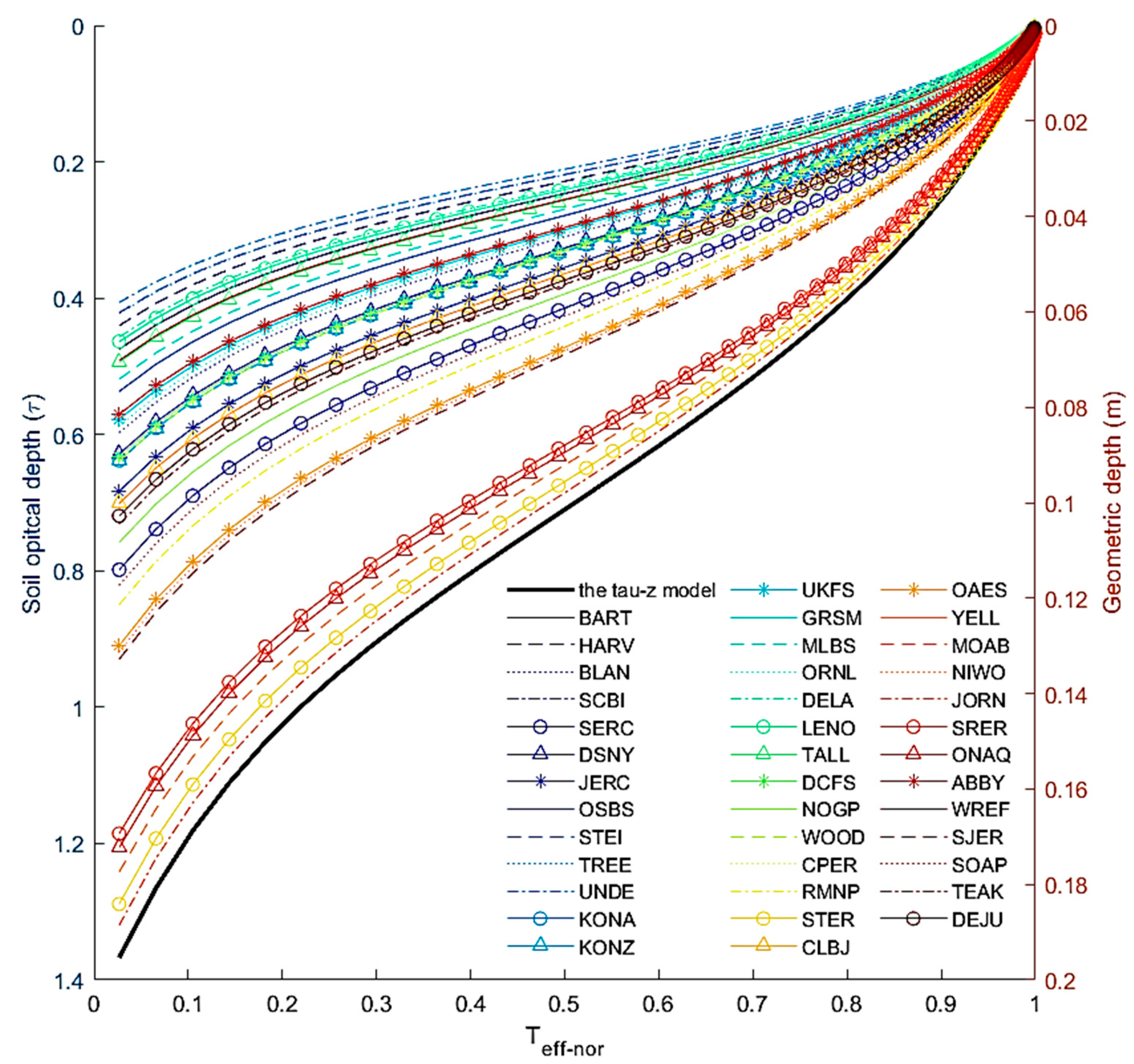
4.1. The τ-z and Its Assumption
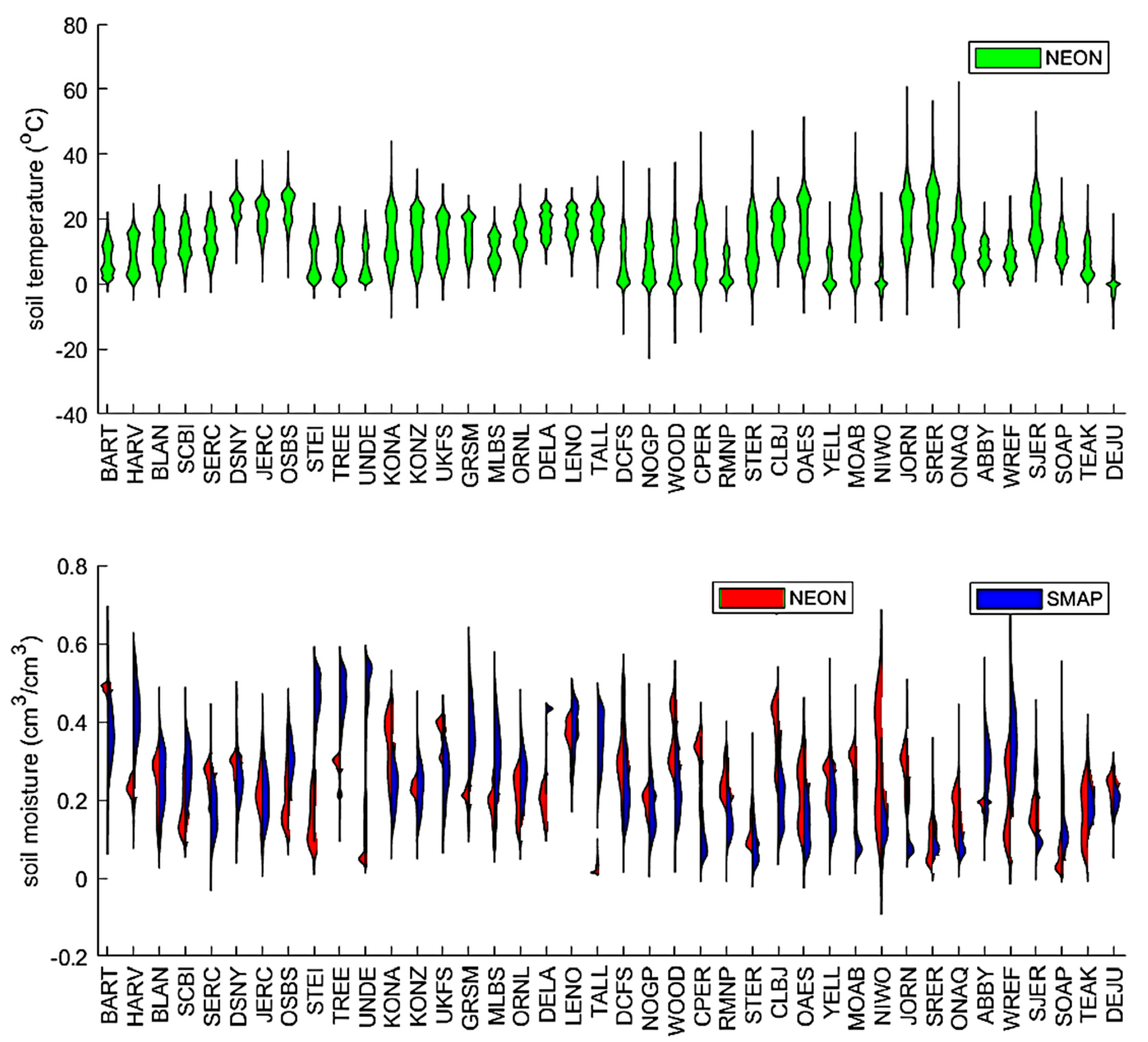
4.2. The Overall Performance
4.3. The Performance at Individual Sites
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wigneron, J.P.; Jackson, T.J.; O’Neill, P.; De Lannoy, G.; de Rosnay, P.; Walker, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mironov, V.; Bircher, S.; Grant, J.P.; et al. Modelling the passive microwave signature from land surfaces: A review of recent results and application to the L-band SMOS & SMAP soil moisture retrieval algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Jacobs, J.M.; Schroeder, R.; Tuttle, S.E.; Olheiser, C. Improvement of operational airborne gamma radiation snow water equivalent estimates using SMAP soil moisture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Fan, L.; Frappart, F.; Yueh, S.H.; Colliander, A.; Ebtehaj, A.; Gao, L.; Fernandez-Moran, R.; Liu, X.; et al. A new SMAP soil moisture and vegetation optical depth product (SMAP-IB): Algorithm, assessment and inter-comparison. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Montzka, C.; Baatz, R.; Vereecken, H.; Franssen, H.-J.H. The Importance of Subsurface Processes in Land Surface Modeling over a Temperate Region: An Analysis with SMAP, Cosmic Ray Neutron Sensing and Triple Collocation Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirmeyer, P.A.; Norton, H.E. Indications of Surface and Sub-Surface Hydrologic Properties from SMAP Soil Moisture Retrievals. Hydrology 2018, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS Mission: New Tool for Monitoring Key Elements of the Global Water Cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; Neill, P.E.O.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Xing, M.; Shang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J. Enhanced L-MEB Model for Soil Moisture Retrieval Over Soybean Fields During the Growing Season. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Cui, K.; Dong, T.; Ma, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Improved soil moisture retrieval during crop growing season using passive microwave data at L-band. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 143, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogapurapu, N.; Dey, S.; Mandal, D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Karthikeyan, L.; McNairn, H.; Rao, Y.S. Soil moisture retrieval over croplands using dual-pol L-band GRD SAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, J.; Li, X.; Fu, P.; Cosh, M.H.; Letu, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, N.; et al. Surface soil moisture from combined active and passive microwave observations: Integrating ASCAT and SMAP observations based on machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 308, 114197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Global multi-scale surface soil moisture retrieval coupling physical mechanisms and machine learning in the cloud environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 329, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Chan, S.K.; O’Neill, P.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Caldwell, T.; Walker, J.P.; Berg, A.; McNairn, H.; et al. An assessment of the differences between spatial resolution and grid size for the SMAP enhanced soil moisture product over homogeneous sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 207, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; O’Neill, P.E.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Colliander, A.; Chen, F.; Burgin, M.; Dunbar, S.; Piepmeier, J.; et al. Assessment of the SMAP Passive Soil Moisture Product. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhao, T.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J. Empirical Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Derived from the Tau-z Model Utilizing Data from the Soil Moisture Experiment in the Luan River (SMELR). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 14742–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macelloni, G.; Leduc-Leballeur, M.; Montomoli, F.; Brogioni, M.; Ritz, C.; Picard, G. On the retrieval of internal temperature of Antarctica Ice Sheet by using SMOS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakhasi, F.; Walker, J.P.; Ye, N.; Wu, X.; Shen, X.; Yeo, I.-Y.; Boopathi, N.; Kim, E.; Kerr, Y.; Jackson, T. Towards soil moisture profile estimation in the root zone using L- and P-band radiometer observations: A coherent modelling approach. Sci. Remote Sens. 2023, 7, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Active and Passive-Volume II: Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Advanced Book Program/World Science Division: Reading, MA, USA; Norwood, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bindlish, R. Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture; The Pennsylvania State University: University Park, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, M.; Schreiner, H.K.; Mohammadian, A.; Shirkhani, H.; Payeur, P.; Imanian, H.; Cobo, J.H. A Review of Machine Learning Approaches to Soil Temperature Estimation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zeng, Y.; Su, Z.; Wen, J. A Closed-Form Expression of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth at L-Band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.J.; Parker, S.M.; Edmonds, J.W.; Zeglin, L.H. Expanding the scale of aquatic sciences: The role of the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON). Freshw. Sci. 2015, 34, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, E.; Reichle, R.H.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Smith, L. Validation of Remotely Sensed and Modeled Soil Moisture at Forested and Unforested NEON Sites. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 14248–14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakhasi, F.; Walker, J.P.; Judge, J.; Liu, P.-W.; Shen, X.; Ye, N.; Wu, X.; Yeo, I.-Y.; Kim, E.; Kerr, Y.; et al. Soil moisture profile estimation under bare and vegetated soils using combined L-band and P-band radiometer observations: An incoherent modeling approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 307, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, E.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.H.; Roberti, J.A.; Simkin, S.; Genazzio, M.A. Validation of SMAP Soil Moisture at Terrestrial National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) Sites Show Potential for Soil Moisture Retrieval in Forested Areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 10903–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilheit, T.T. Radiative transfer in a plane stratified dielectric. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1978, 16, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, H.; Su, Z. An improved two-layer algorithm for estimating effective soil temperature in microwave radiometry using in situ temperature and soil moisture measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K., VII. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1997, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.R.H.; Owe, M.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Kooi, H. Estimating the soil temperature profile from a single depth observation: A simple empirical heatflow solution. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W02412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzman, L.D.; Goering, D.J.; Kane, D.L. A distributed thermal model for calculating soil temperature profiles and depth of thaw in permafrost regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 28975–28991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, V.L.; Kosolapova, L.G.; Fomin, S.V. Physically and Mineralogically Based Spectroscopic Dielectric Model for Moist Soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; El-rayes, M.A. Microwave Dielectric Behavior of Wet Soil-Part II: Dielectric Mixing Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lang, R.; Cosh, M. P-Band and L-Band Radiometry Retrieval of Soil Moisture and Temperature Profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwank, M.; Rautiainen, K.; Mätzler, C.; Stähli, M.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Pulliainen, J.; Vehviläinen, J.; Kontu, A.; Ikonen, J.; Ménard, C.B. Model for microwave emission of a snow-covered ground with focus on L band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J. Decadal-Scale Warming Signals in Antarctic Ice Sheet Interior Revealed by L-Band Passive Microwave Observations. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
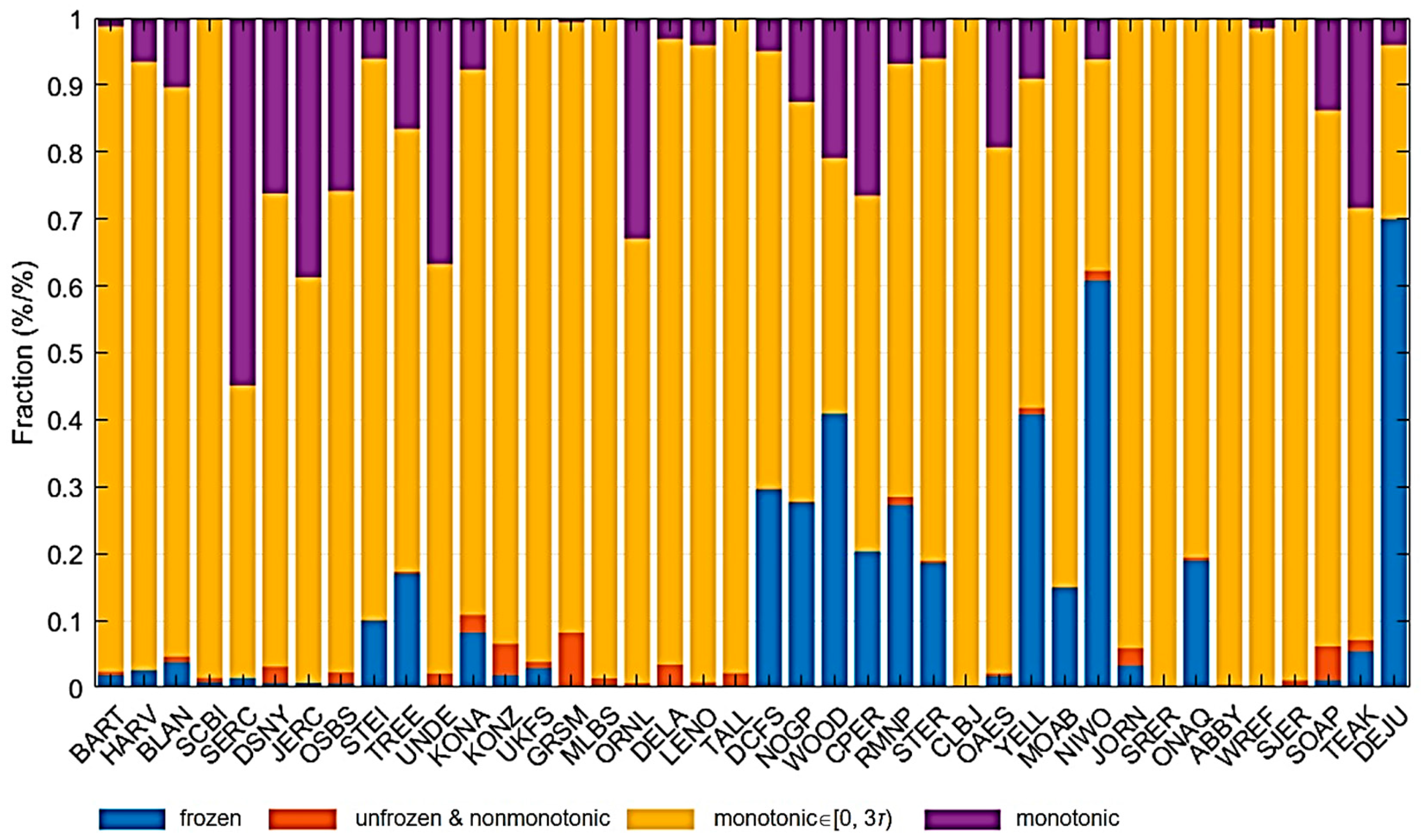
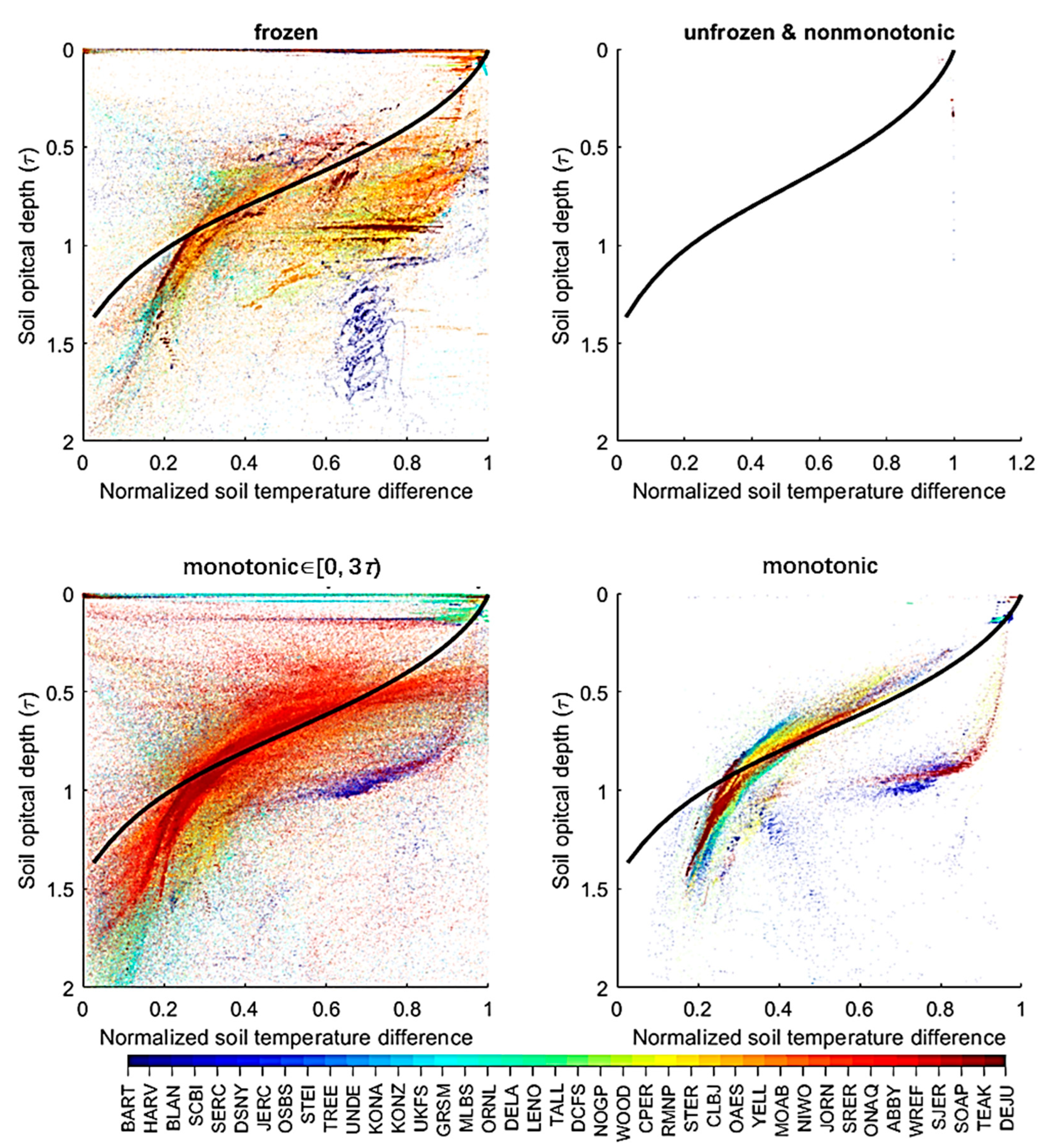
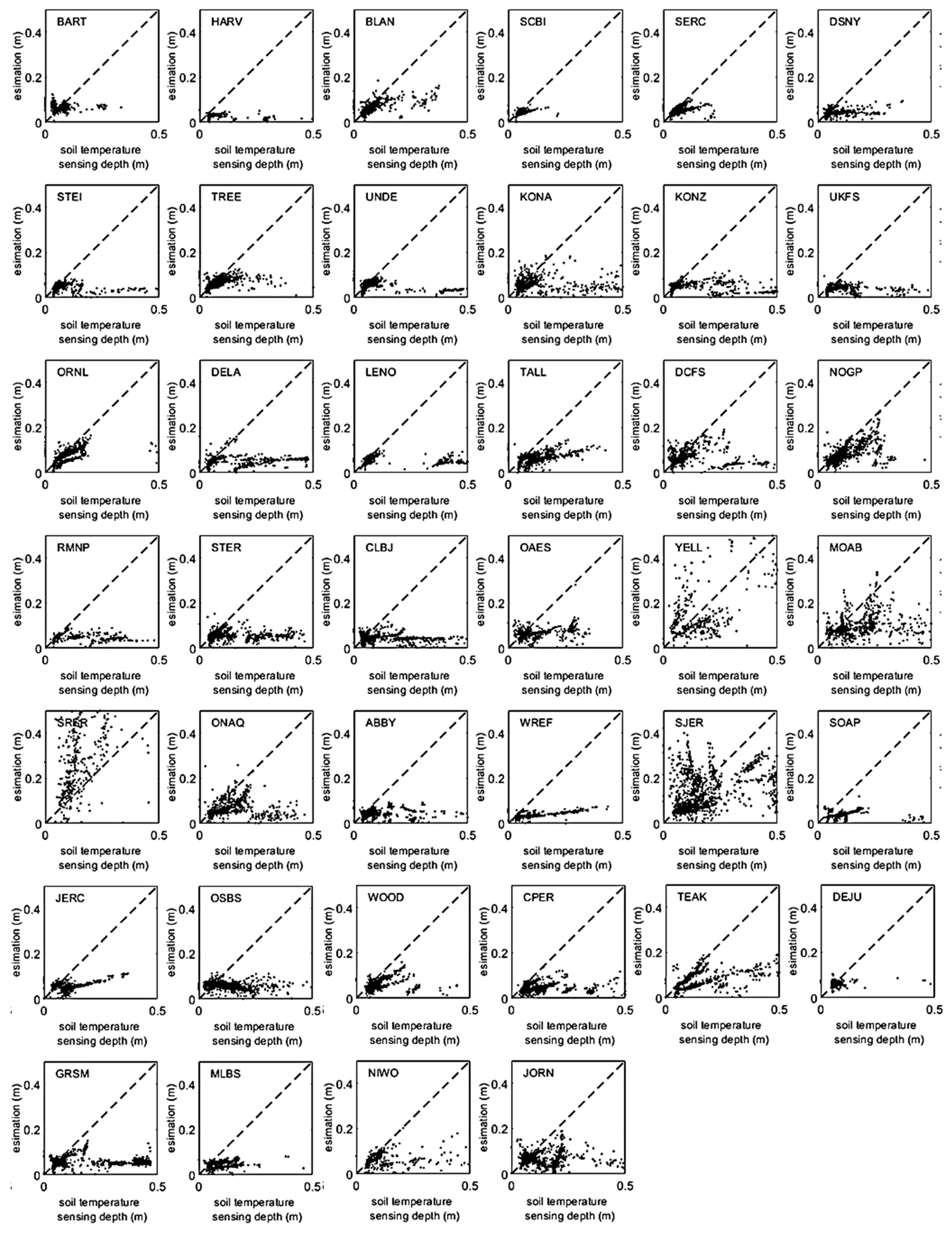
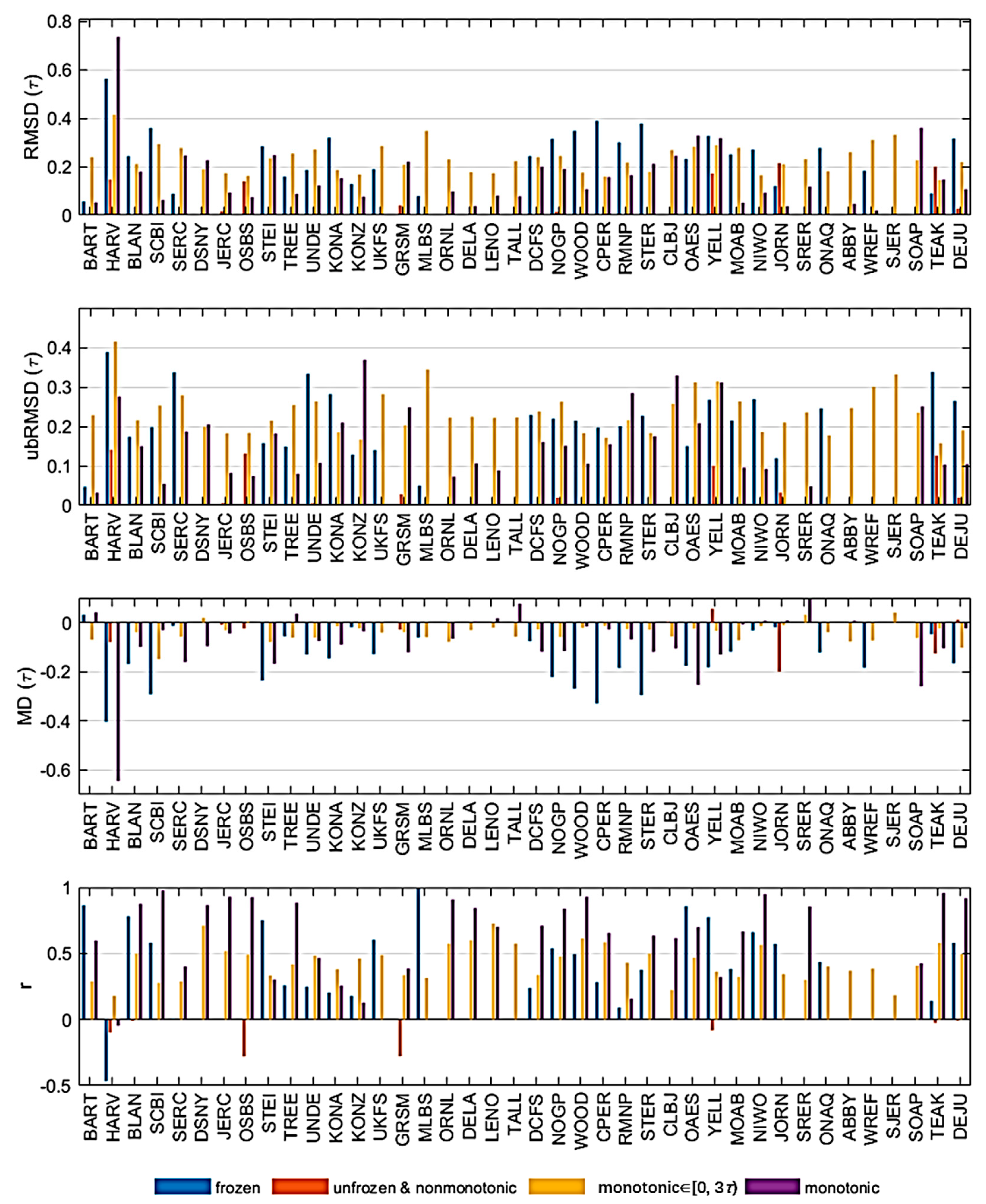
| Frozen | Unfrozen & Nonmonotonic | Monotonic ∈ [0, 3τ) | Monotonic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSD (τ) | 0.294 | 0.027 | 0.215 | 0.149 |
| unRMSD (τ) | 0.095 | 0.018 | 0.218 | 0.168 |
| MD (τ) Dobson | −0.094 | −0.012 | −0.040 | −0.064 |
| PearsonCC | 0.205 | −0.022 | 0.487 | 0.695 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, S.; Ayres, E.; Hu, Y. Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Estimates Using High-Temporal Resolution Data from NEON and SMAP Missions. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233845
Lv S, Ayres E, Hu Y. Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Estimates Using High-Temporal Resolution Data from NEON and SMAP Missions. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233845
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Shaoning, Edward Ayres, and Yin Hu. 2025. "Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Estimates Using High-Temporal Resolution Data from NEON and SMAP Missions" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233845
APA StyleLv, S., Ayres, E., & Hu, Y. (2025). Validation of Soil Temperature Sensing Depth Estimates Using High-Temporal Resolution Data from NEON and SMAP Missions. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3845. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233845






