Urban Informal Settlement Classification via Cross-Scale Hierarchical Perception Fusion Network Using Remote Sensing and Street View Images
Highlights
- We proposed PanFusion-Net, a cross-modal fusion framework that combines multi-scale remote sensing structures with fine-grained street-view information and employs dual multi-linear pooling to strengthen high-order interactions and deep semantic fusion across heterogeneous modalities.
- The proposed method achieved a consistently superior performance on the WuhanUIS dataset we constructed, as well as on the ChinaUIS and datasets.
- This work provides urban planners with automated and highly accurate tools for identifying informal settlements.
- The proposed approach establishes a new technical paradigm for cross-modal geospatial analyses and can be extended to a broader range of monitoring applications.
Abstract
1. Introduction
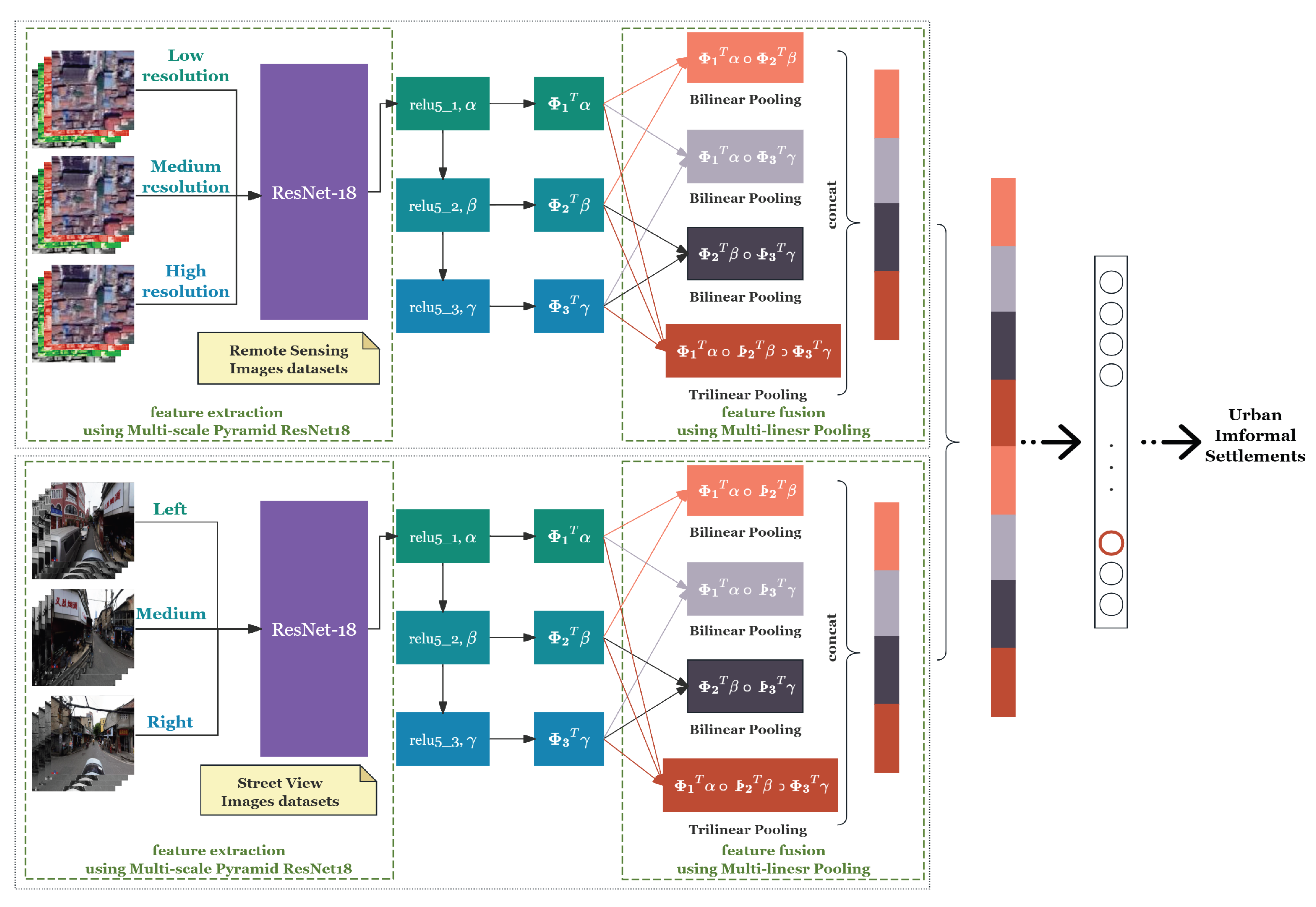
- For precise UIS classification, we proposed a novel multimodal PanFusion-Net designed to fully integrate multi-level and inter-level features from RSIs and SVIs.
- The proposed D-MLPH employs feature extraction using multi-scale pyramid ResNet18 to mimic the human eye’s coarse-to-fine progressive perspective from distant to near views and the panoramic perspective from left to right, efficiently extracting feature information from multi-resolution data sources.
- The proposed PanFusion-Net incorporates novel dual-feature fusion using a multi-linear pooling structure to jointly fuse and integrate modality-specific and cross-modality hierarchical features from both progressive RSIs and panoramic SVIs, dramatically boosting UIS mapping.
2. Panoramic Fusion Network (PanFusion-Net)
2.1. Network Architecture (PanFusion-Net)
2.2. Feature Extraction Using Multi-Scale Pyramid ResNet18 (FE-ResNet18-FPN)
2.3. Feature Fusion Using Multi-Linear Pooling (FF-MLP)
| Algorithm 1 Multi-linear pooling feature fusion. |
|
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Study Area
3.2. The Datasets
3.2.1. WuhanUIS Dataset
3.2.2. ChinaUIS Dataset
3.2.3. Dataset
3.3. Running Environment
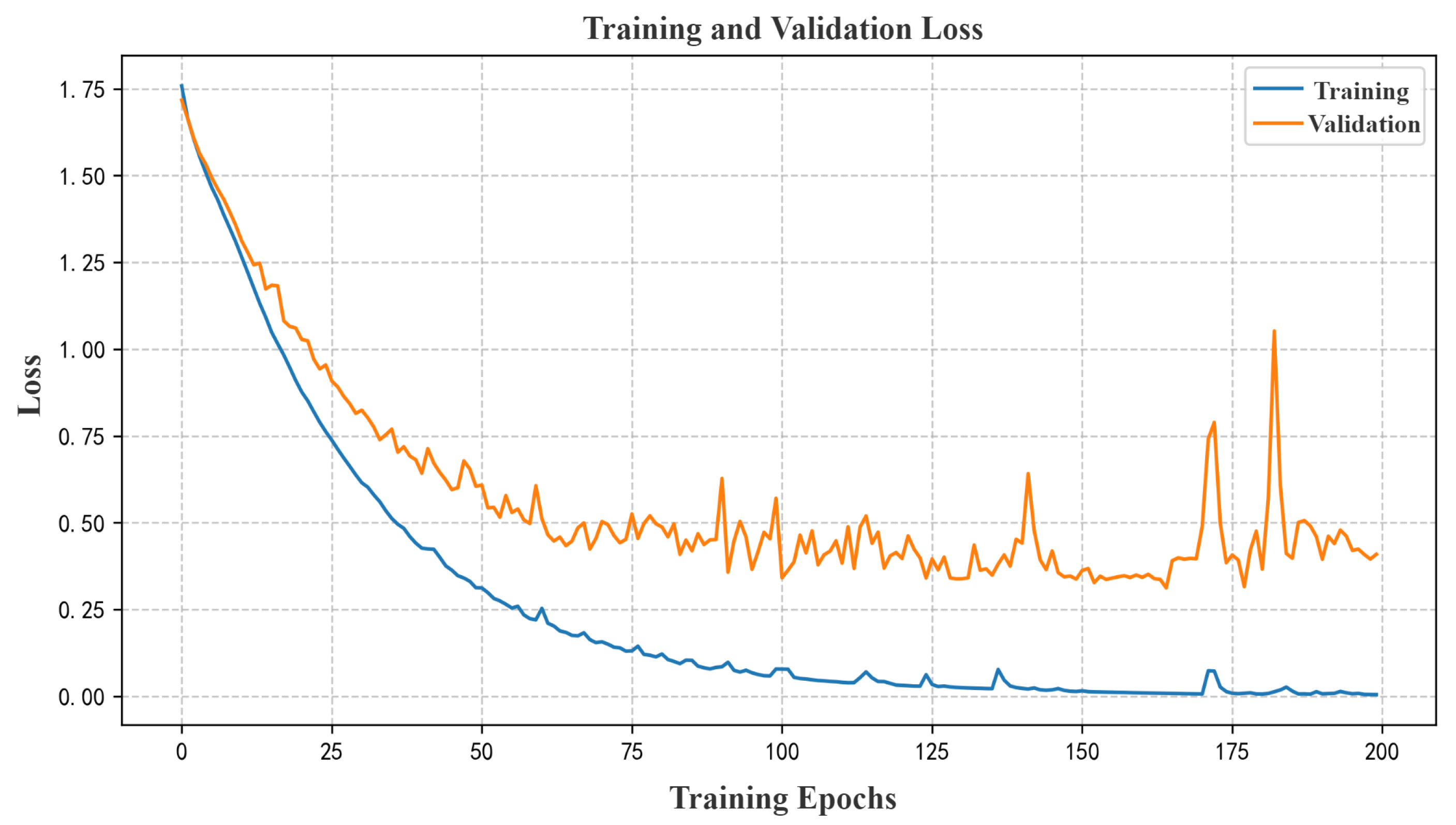
3.4. Experiment on WuhanUIS Dataset
3.4.1. Experimental Operation
- Only RSIs: Using only high-resolution RSIs.
- Only SVIs: Using only SVIs.
- RSIs and SVIs Merged: Combining high-resolution RSIs and SVIs to leverage complementary information.
3.4.2. Experimental Results
3.5. Experiment on ChinaUIS Dataset
3.5.1. Experimental Results
3.5.2. Experimental Validity
3.6. Experiment on Dataset
3.6.1. Experimental Results
3.6.2. Experimental Comparison with Multimodal Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Gains from Multimodal Integration
4.2. Mechanisms Behind the Performance Improvements
4.3. Cross-Dataset Robustness and Generalization
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, A. Informal settlements and urban sustainability in Bangladesh. Environ. Urban. 2010, 22, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mahabir, R.; Croitoru, A.; Crooks, A.T.; Agouris, P.; Stefanidis, A. A Review of Spatial Characteristics to Inform Slum Classification: The Case of Informal Settlements in Haiti. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD). The Sustainable Development Goals Report; United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD): New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, Z.R.M.A.; Sakil, A.H.; Baikady, R.; Deb, A.; Hossain, M.T. Building resilience in urban slums: Exploring urban poverty and policy responses amid crises. Discov. Glob. Soc. 2025, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Degbelo, A. An Empirical Analysis of AI Contributions to Sustainable Cities (SDG 11). In The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence for the Sustainable Development Goals; Mazzi, F., Floridi, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, J.; Shao, Y. A novel framework for leveraging geological environment big data to assess sustainable development goals. Innov. Geosci. 2025, 3, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Li, J.; Song, W.; Han, W.; Yan, J.; Wang, L. Urban informal settlements classification via a transformer-based spatial-temporal fusion network using multimodal remote sensing and time-series human activity data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Niu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, R. The first urban open space product of global 169 megacities using remote sensing and geospatial data. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, X. Advances in urban information extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ming, D.; Lv, X.; Zhou, K.; Bao, H. SO–CNN based urban functional zone fine division with VHR remote sensing image. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Stein, A.; Beurs, K.M.D. A Bayesian characterization of urban land use configurations from VHR remote sensing images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, Z.; Lin, J.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. UP-Diff: Latent Diffusion Model for Remote Sensing Urban Prediction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 22, 7502505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Tu, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Qiu, G. Deep learning-based remote and social sensing data fusion for urban region function recognition. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawode, G.L.; Oluwajuwon, T.V.; Hammed, R.A.; Olasuyi, K.E.; Krasovskiy, A.; Ogundipe, O.C.; Kraxner, F. Spatiotemporal assessment of land use land cover dynamics in Mödling district, Austria, using remote sensing techniques. Heliyon 2025, 11, e43454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dragicevic, S.; Castro, F.A.; Sester, M.; Winter, S.; Coltekin, A.; Pettit, C.; Jiang, B.; Haworth, J.; Stein, A.; et al. Geospatial big data handling theory and methods: A review and research challenges. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, T.; Gong, P.; Du, S.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Dai, Q. Mapping essential urban land use categories in Beijing with a fast area of interest (AOI)-based method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Dong, J.; Hamm, N.A.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Xing, H.; Fu, P. Integrating remote sensing and geospatial big data for urban land use mapping: A review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Niu, H.; Xu, Z.; Yan, J.; Song, W.; Feng, R. A unified multimodal learning method for urban functional zone identification by fusing inner-street visual–textual information from street-view and satellite images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 142, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, C.; Persello, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Vosselman, G. Informal settlement classification using point-cloud and image-based features from UAV data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Biljecki, F. Nighttime Street View Imagery: A new perspective for sensing urban lighting landscape. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fung, H.H.; Lin, H.; Ratti, C. Measuring human perceptions of a large-scale urban region using machine learning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 180, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ito, K. Street view imagery in urban analytics and GIS: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 215, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Niu, H.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Feng, R.; Wang, L. Refined Urban Informal Settlements’ Mapping at Agglomeration Scale With the Guidance of Background Knowledge From Easy-Accessed Crowdsourced Geospatial Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram-Hansen, B.J.; Helber, P.; Varatharajan, I.; Azam, F.; Coca-Castro, A.; Kopackova, V.; Bilinski, P. Mapping informal settlements in developing countries using machine learning and low resolution multi-spectral data. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–28 January 2019; pp. 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, Z. Artificial Intelligence Reshapes River Basin Governance. Sci. Bull. 2024, 70, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressick, R.D. Architecture & Legitimacy: Strategies for the Development of Urban Informal Settlements. Ph.D. Dissertation, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarira, D.; Mutanga, O.; Naidu, M.; Vizzari, M. Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Land 2022, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Multilevel spatial-channel feature fusion network for urban village classification by fusing satellite and streetview images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5630813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Fowlkes, C. Low-rank bilinear pooling for fine-grained classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sarlin, P.E.; Cadena, C.; Siegwart, R.; Dymczyk, M. From coarse to fine: Robust hierarchical localization at large scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12716–12725. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg, J.; Manning, C.D. Advances in natural language processing. Science 2015, 349, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charniak, E.; Johnson, M. Coarse-to-Fine n-Best Parsing and MaxEnt Discriminative Reranking. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL‘05), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; Knight, K., Ng, H.T., Oflazer, K., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Zhang, M.; Aw, A.; Tan, C.; Liu, T.; Li, S. Using a hybrid convolution tree kernel for semantic role labeling. ACM Trans. Asian Lang. Inf. Process. 2008, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, T.; Bruhn, A.; Papenberg, N.; Weickert, J. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, C.; Change Loy, C.; Tang, X. Face alignment by coarse-to-fine shape searching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4998–5006. [Google Scholar]
- Alrasheedi, K.G.; Dewan, A.; El-Mowafy, A. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabra, A.; Kumar, V. Neural Computing and Applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 34, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Park, D.H.; Yang, D.; Rohrbach, A.; Darrell, T.; Rohrbach, M. Multimodal Compact Bilinear Pooling for Visual Question Answering and Visual Grounding. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Algashaam, F.M.; Nguyen, K.; Alkanhal, M.; Chandran, V.; Boles, W.; Banks, J. Multispectral periocular classification with multimodal compact multi-linear pooling. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14572–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wen, J.R. Coarse-to-fine grained classification. In Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Paris, France, 21–25 July 2019; pp. 1033–1036. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, N.J.; Vurro, M.; Keith, S.B.; Kyada, M.J.; Pezaris, J.S. Perceptual learning in a non-human primate model of artificial vision. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.C.; Goebel, R.; Goffaux, V. From coarse to fine: Interactive feature processing precedes local feature analysis in human face perception. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 138, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, D.A.; Bondar, I.V.; Giese, M.A. Norm-based face encoding by single neurons in the monkey inferotemporal cortex. Nature 2006, 442, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.H.; Summerfield, C.; Morin, E.L.; Malecek, N.J.; Ungerleider, L.G. Encoding of Stimulus Probability in Macaque Inferior Temporal Cortex. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, B.E.; Koyano, K.W.; Day-Cooney, J.; Perwez, N.; Leopold, D.A. Temporal continuity shapes visual responses of macaque face patch neurons. Neuron 2023, 111, 903–914.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiwald, W.A.; Tsao, D.Y.; Livingstone, M.S. A face feature space in the macaque temporal lobe. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugase, Y.; Yamane, S.; Ueno, S.; Kawano, K. Global and fine information coded by single neurons in the temporal visual cortex. Nature 1999, 400, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An introduction to feature extraction. In Feature Extraction: Foundations and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Beijbom, O.; Zhang, N.; Darrell, T. Compact bilinear pooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Xiang, C.; Fan, J.; Tao, D. Beyond bilinear: Generalized multimodal factorized high-order pooling for visual question answering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 5947–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. A improved pooling method for convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; On, K.W.; Lim, W.; Kim, J.; Ha, J.W.; Zhang, B.T. Hadamard Product for Low-rank Bilinear Pooling. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.04325. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Belongie, S. Kernel pooling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2921–2930. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, X.; Feng, J.; Peng, Q.; Yan, S. Diversified visual attention networks for fine-grained object classification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 19, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, I.; Sevilla-Escoboza, R.; Sendiña-Nadal, I.; Gutiérrez, R.; Buldú, J.; Boccaletti, S. Inter-layer synchronization in non-identical multi-layer networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Gang, S.; Guan, C. FCIHMRT: Feature cross-layer interaction hybrid method based on Res2Net and transformer for remote sensing scene classification. Electronics 2023, 12, 4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lang, C.; Liew, J.H.; Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Feng, J. Cross-layer feature pyramid network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Zha, Z.J.; Luo, J. Looking for the devil in the details: Learning trilinear attention sampling network for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5012–5021. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Yuan, F.; Yu, J.; Wang, G.; Gu, X. Fine-grained image classification via multi-scale selective hierarchical biquadratic pooling. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2022, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Donahue, J.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T. Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part I 13. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 834–849. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; You, X. Hierarchical bilinear pooling for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 574–589. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ham, B. Network quantization with element-wise gradient scaling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 6448–6457. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, C.; Huang, J. Deep Co-Interaction for Multi-Granularity Feature Fusion in Fine-Grained Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 452–468. [Google Scholar]
- Boan Chen and Quanlong Feng and Bowen Niu and Fengqin Yan and Bingbo Gao and Jianyu Yang and Jianhua Gong and Jiantao Liu. Multi-modal fusion of satellite and street-view images for urban village classification based on a dual-branch deep neural network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 109, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Qian, L.; Gamba, P. Advances on Multimodal Remote Sensing Foundation Models for Earth Observation Downstream Tasks: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.K.; Han, K.; Lai, P.; Phan, K.T.; Xiang, W. RobSense: A Robust Multi-modal Foundation Model for Remote Sensing with Static, Temporal, and Incomplete Data Adaptability. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 7427–7436. [Google Scholar]
- Samadzadegan, F.; Toosi, A.; Dadrass Javan, F. A critical review on multi-sensor and multi-platform remote sensing data fusion approaches: Current status and prospects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 46, 1327–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
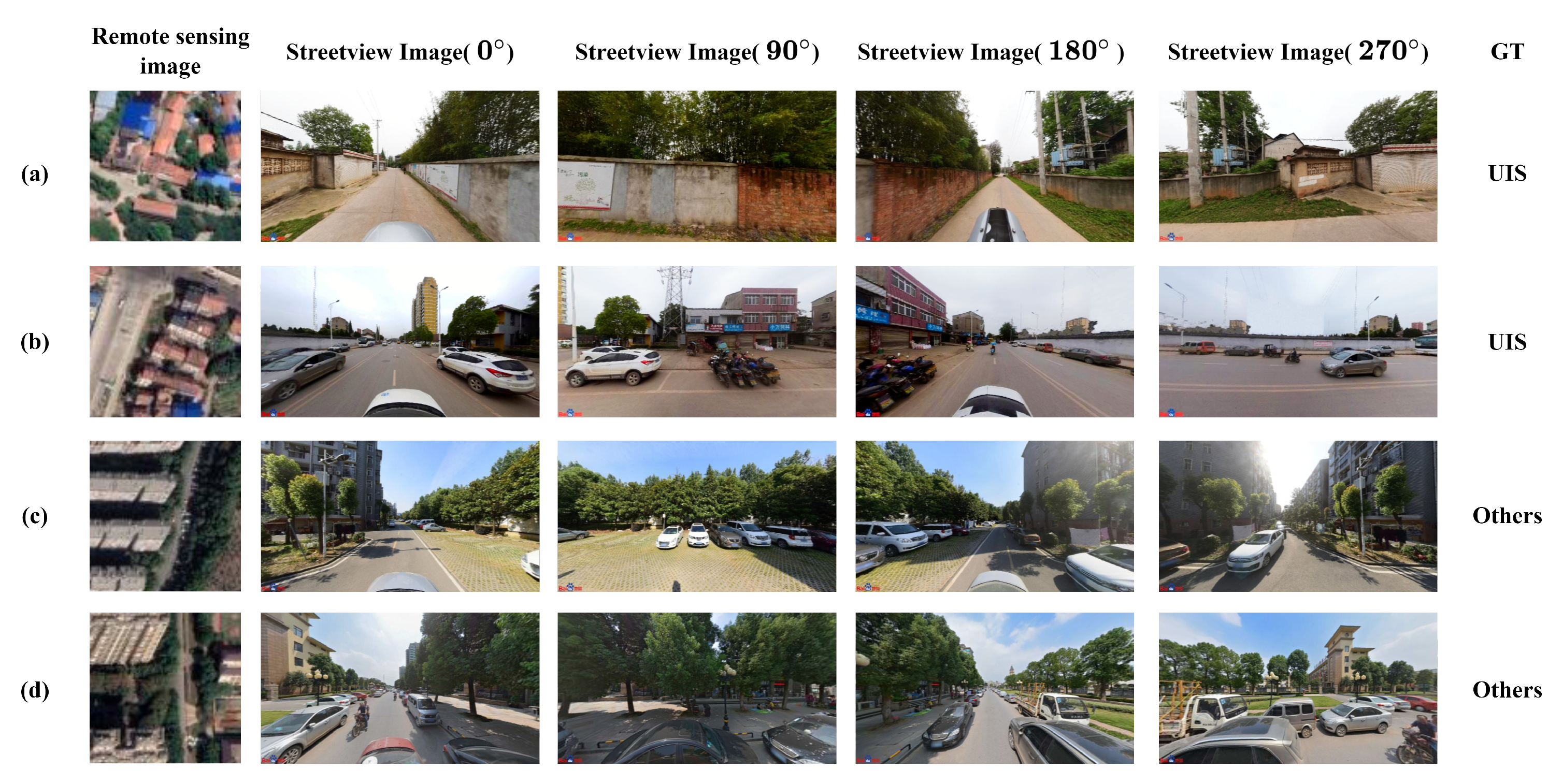
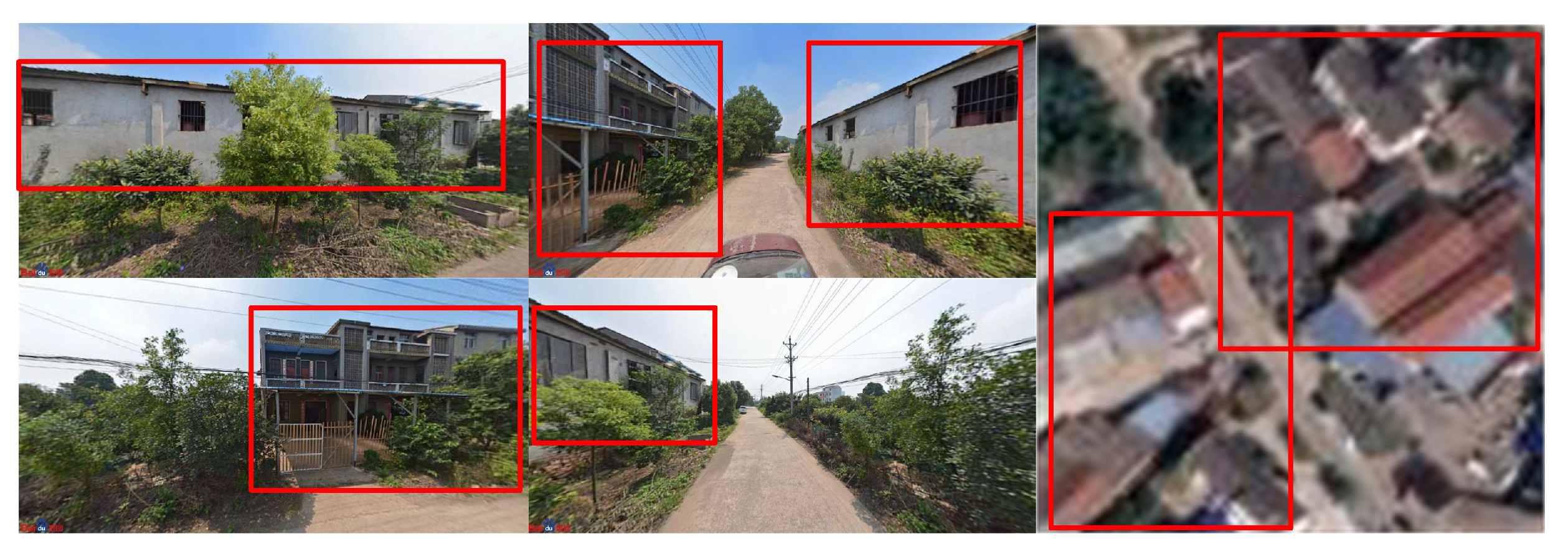
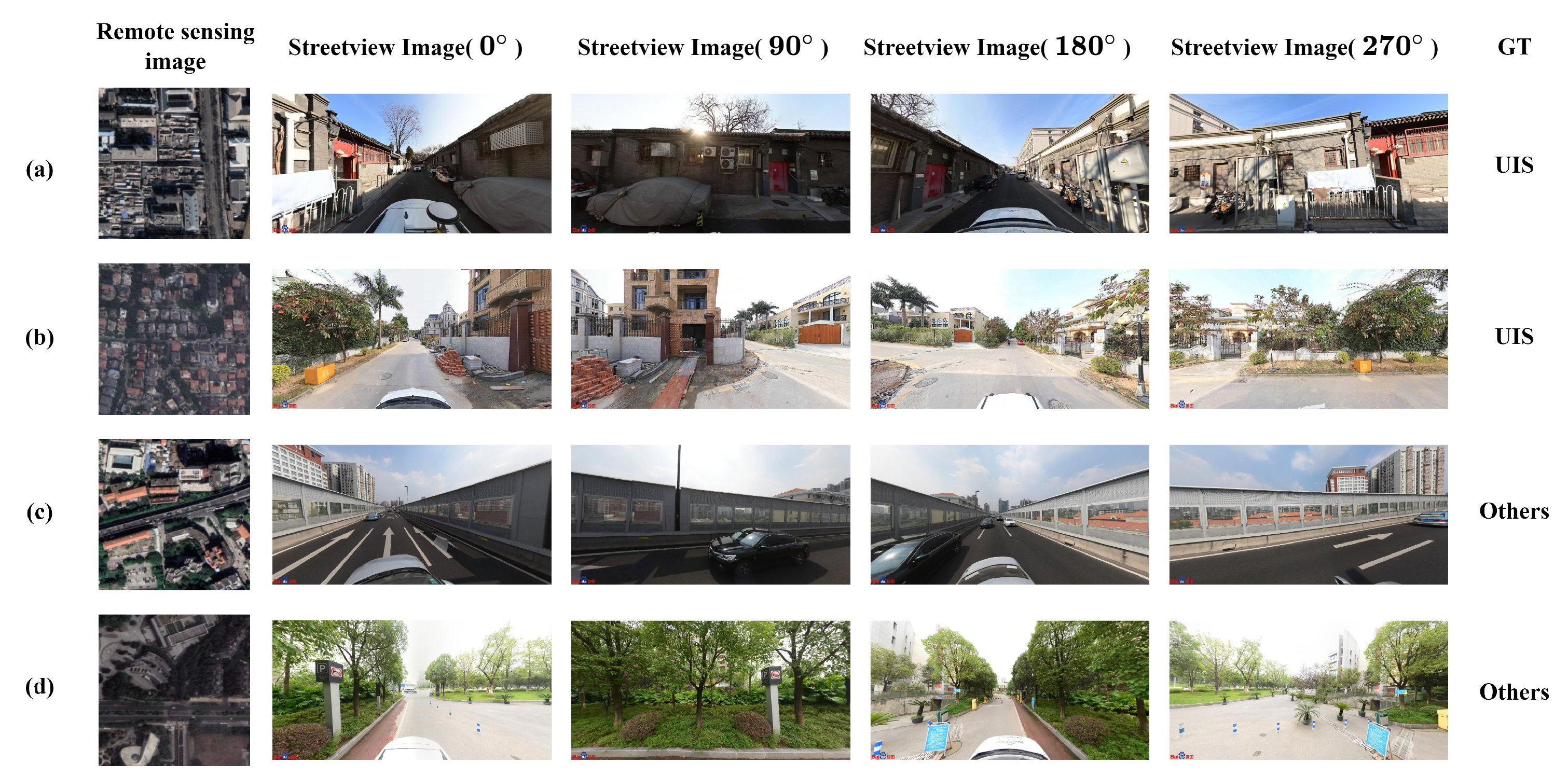
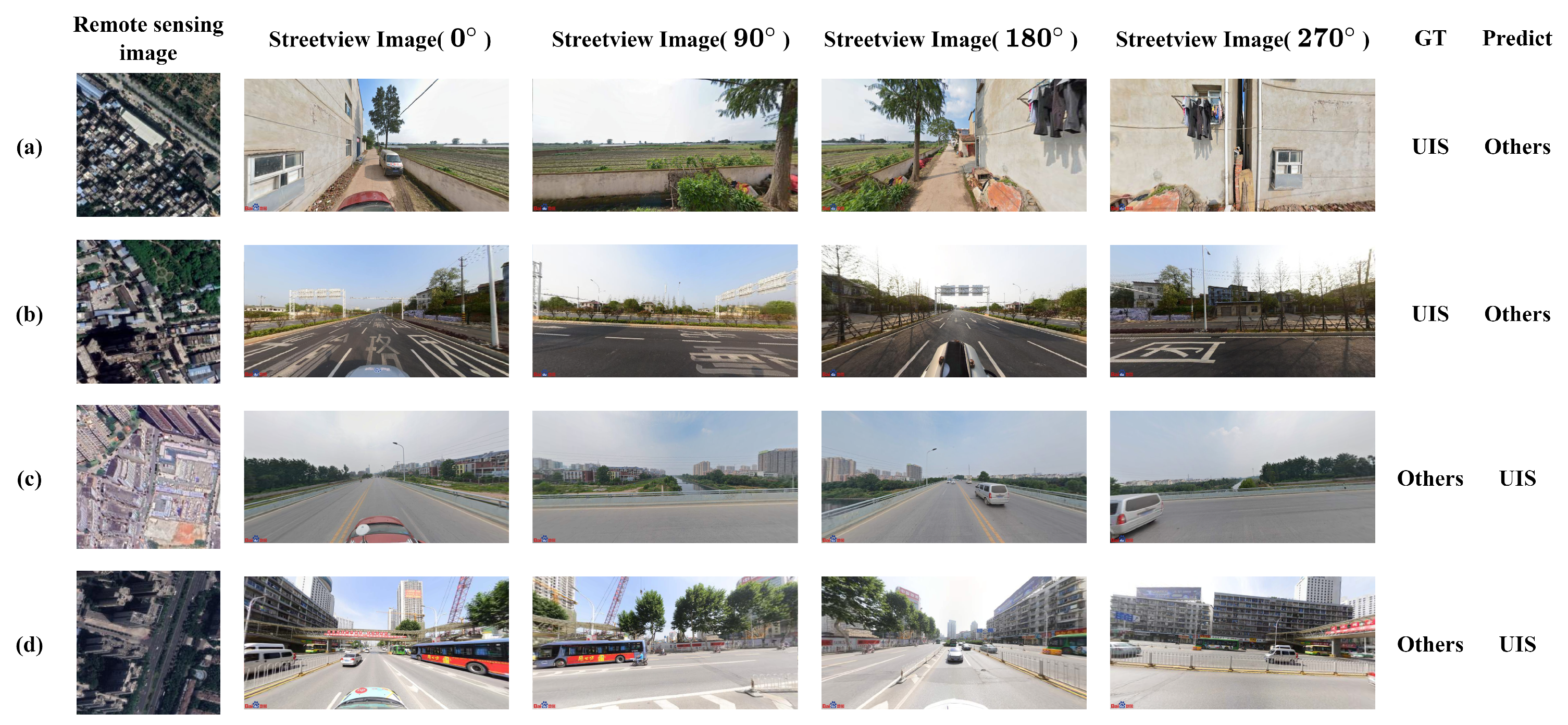
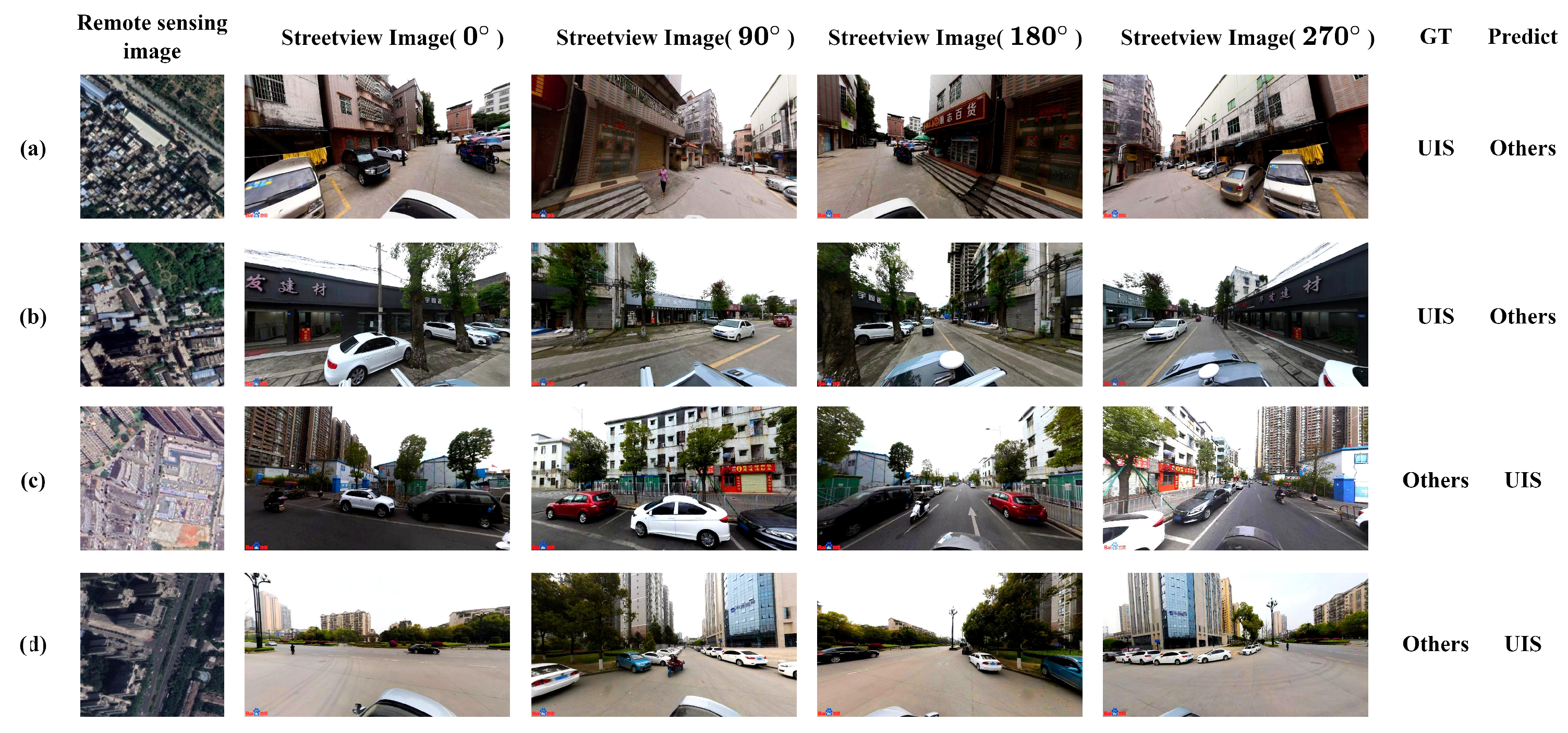
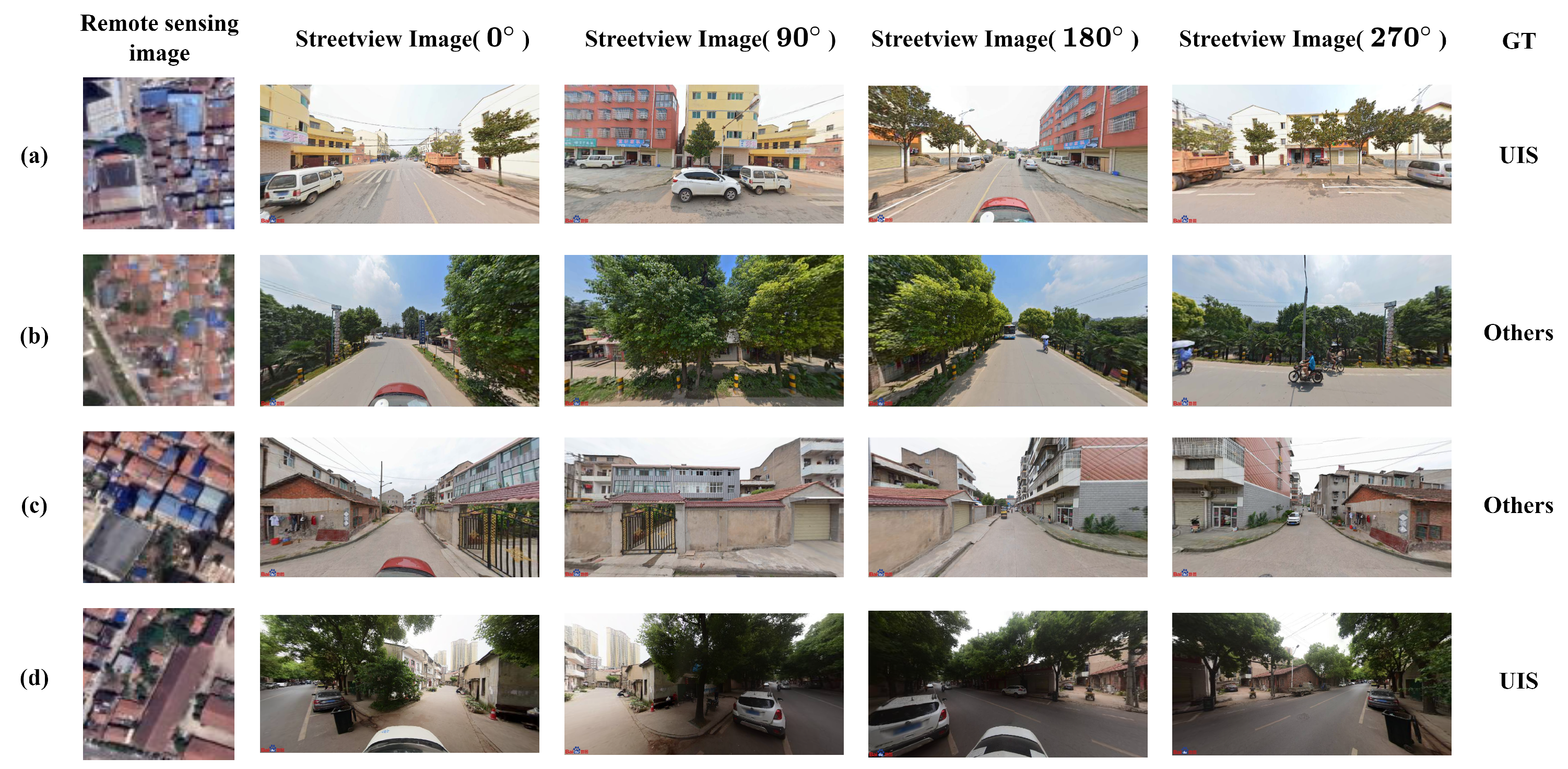






| Category | UIS | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 1500 | 2332 | 3832 |
| City | UIS | Others | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 127 | 136 | 263 |
| Shanghai | 90 | 151 | 241 |
| Guangzhou | 71 | 138 | 209 |
| Shenzhen | 44 | 153 | 197 |
| Tianjin | 100 | 157 | 257 |
| Chengdu | 77 | 156 | 233 |
| Chongqing | 53 | 156 | 209 |
| Wuhan | 81 | 143 | 224 |
| Total | 643 | 1190 | 1833 |
| Models | Input | Overall Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 [42] | RS | 94.72 |
| B-CNN [52] | RS | 95.85 |
| HBP [65] | RS | 95.95 |
| MLP [41] | RS | 95.85 |
| ResNet-18 [42] | SV | 82.66 |
| B-CNN [52] | SV | 82.76 |
| HBP [65] | SV | 84.84 |
| MLP [41] | SV | 82.92 |
| PanFusion-Net (ours) | RS + SV | 96.14 |
| Models | Input | Overall Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 [42] | RS + SV | 95.74 |
| HBP [65] | RS + SV | 95.54 |
| PanFusion-Net (ours) | RS + SV | 96.14 |
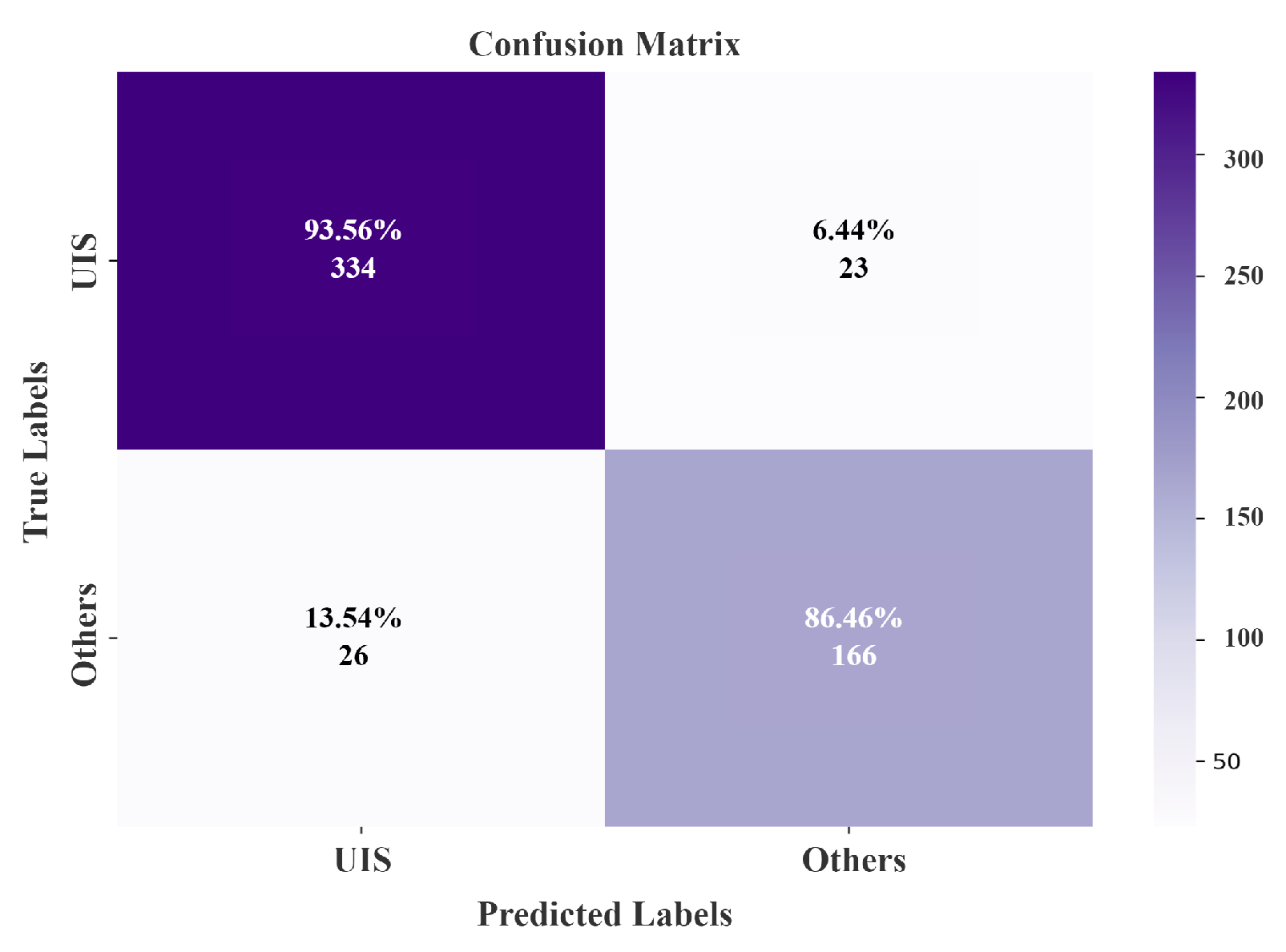
| Classification | UIS | Others | Total | P.A. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIS | 334 | 23 | 357 | 93.56 |
| Others | 26 | 166 | 192 | 86.46 |
| Total | 360 | 189 | 549 | |
| U.A. (%) | 92.78 | 87.83 | ||
| O.A. (%): | 91.07 | |||
| Kappa (%): | 80.31 | |||
| Models | Category Accuracy | OA (%) | Kappa (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIS (%) | Others (%) | |||
| Single-modal-sv-0° | 80.21 | 89.64 | 86.34 | 69.93 |
| Single-modal-sv-90° | 77.08 | 92.44 | 87.07 | 70.97 |
| Single-modal-sv-180° | 77.60 | 92.44 | 87.25 | 71.42 |
| Single-modal-sv-270° | 81.25 | 92.44 | 88.52 | 74.49 |
| Single-modal-sv-Comb. | 78.12 | 92.44 | 87.43 | 79.22 |
| Single-modal-rs | 85.40 | 91.62 | 89.44 | 77.37 |
| PanFusion-Net (ours) | 86.46 | 93.56 | 91.07 | 80.31 |
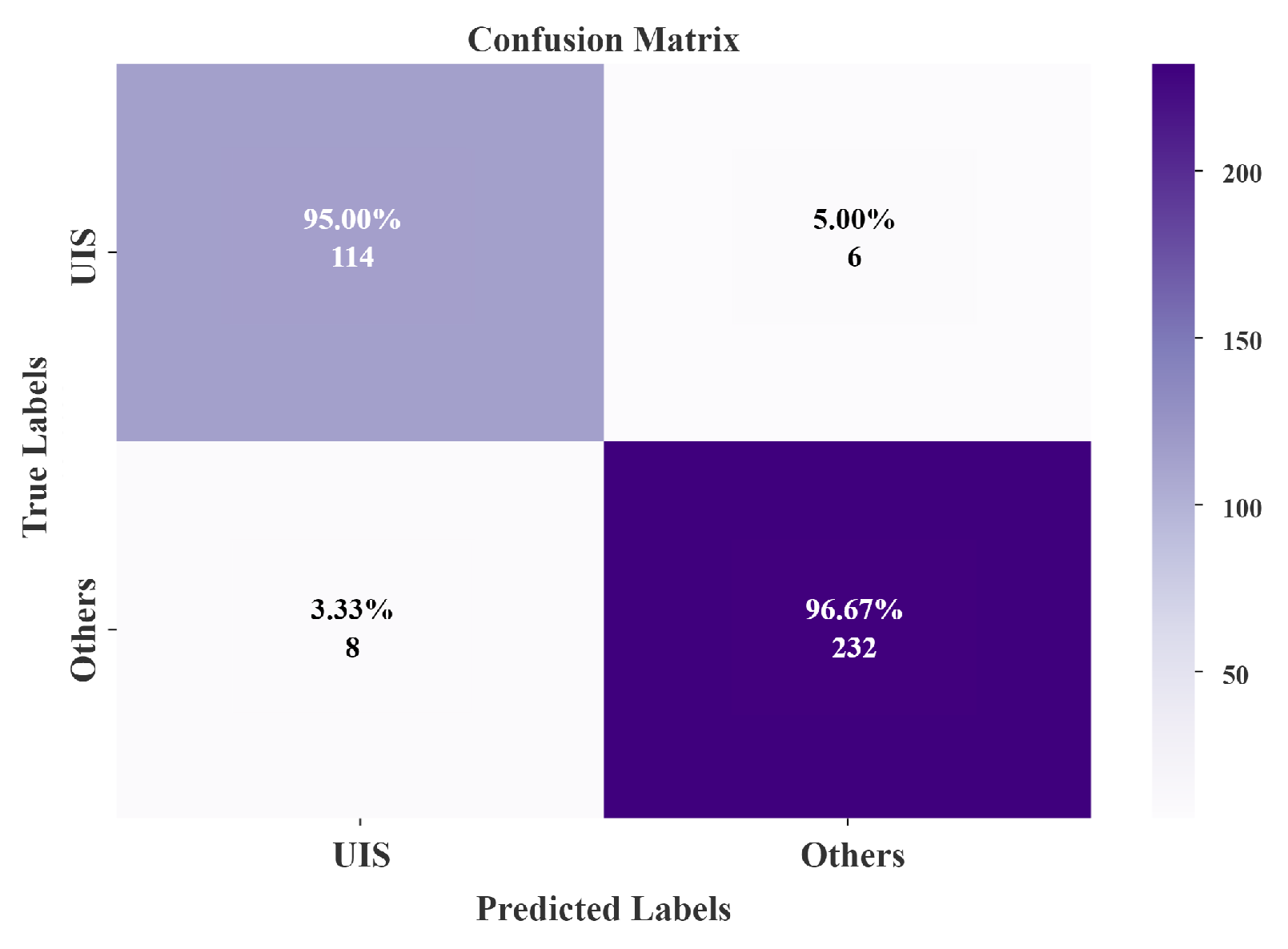
| Classification | UIS | Others | Total | P.A. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIS | 114 | 6 | 120 | 95.00 |
| Others | 8 | 232 | 240 | 96.67 |
| Total | 122 | 238 | 360 | |
| U.A. (%) | 93.44 | 97.48 | ||
| O.A. (%): | 96.11 | |||
| Kappa (%): | 91.29 | |||
| Model Name | OA (%) | Kappa (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Trans-MDCNN [68] | 92.61 | 83.52 |
| FusionMixer [28] | 94.30 | 87.34 |
| PanFusion-Net (ours) | 96.11 | 91.29 |
| Class | Trans-MDCNN | FusionMixer | PanFusion-Net (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UIS (%) | 86.05 | 93.12 | 95.00 |
| Others (%) | 94.28 | 93.56 | 96.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Huang, X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, L. Urban Informal Settlement Classification via Cross-Scale Hierarchical Perception Fusion Network Using Remote Sensing and Street View Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233841
Hu J, Huang X, Ren T, Zhang L. Urban Informal Settlement Classification via Cross-Scale Hierarchical Perception Fusion Network Using Remote Sensing and Street View Images. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jun, Xiaohui Huang, Tianyi Ren, and Liner Zhang. 2025. "Urban Informal Settlement Classification via Cross-Scale Hierarchical Perception Fusion Network Using Remote Sensing and Street View Images" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233841
APA StyleHu, J., Huang, X., Ren, T., & Zhang, L. (2025). Urban Informal Settlement Classification via Cross-Scale Hierarchical Perception Fusion Network Using Remote Sensing and Street View Images. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233841







