Speckle2Self: Learning Self-Supervised Despeckling with Attention Mechanism for SAR Images
Highlights
- A novel self-supervised despeckling framework, Speckle2Self, is proposed for SAR images, which learns directly from noisy inputs without requiring clean reference data or temporal image sequences.
- The method models despeckling as a masked pixel estimation problem using a Transformer backbone and attention-guided complementary masks, enabling effective noise suppression while preserving structural details.
- The proposed Speckle2Self achieves despeckling performance comparable to supervised approaches, significantly advancing the feasibility of reference-free SAR image restoration.
- This framework provides a robust and generalizable solution for SAR despeckling, facilitating improved image quality and enhanced performance in downstream remote sensing applications.
Abstract
1. Introduction
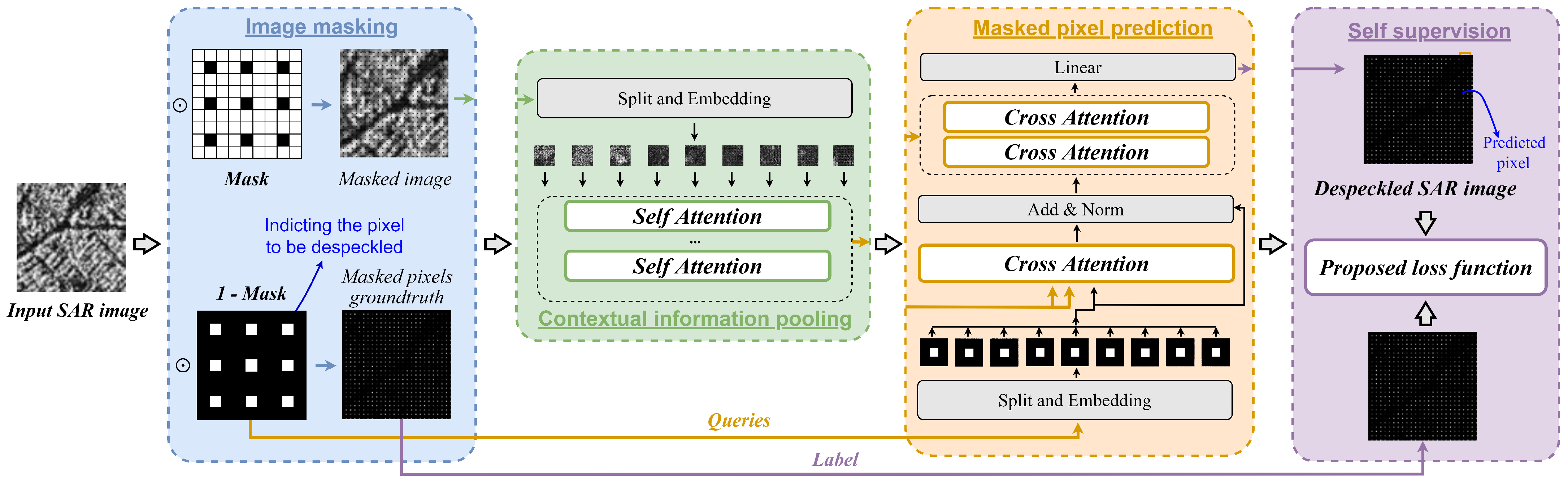
- We propose an end-to-end self-supervised despeckling approach named Speckle2Self for SAR images with Transformer architecture. The proposed Speckle2Self models the image despeckling as a masked-pixel estimation problem, where a set of masks is carefully designed. The final despeckled results are given by the Transformer queries indicating the positions of masked pixels, under the guidance of attention mechanism.
- We introduce a novel loss function that fully considers the statistical properties of SAR images, outperforming traditional and loss functions. Noise whitening is achieved through image downsampling, ensuring the validity of the white-noise assumption in our self-supervised method.
- The proposed Speckle2Self method achieves despeckling performance comparable to supervised methods, effectively suppressing noise while preserving structural details. Compared with the other self-supervised method, Speckle2Self also demonstrates significant advantages.
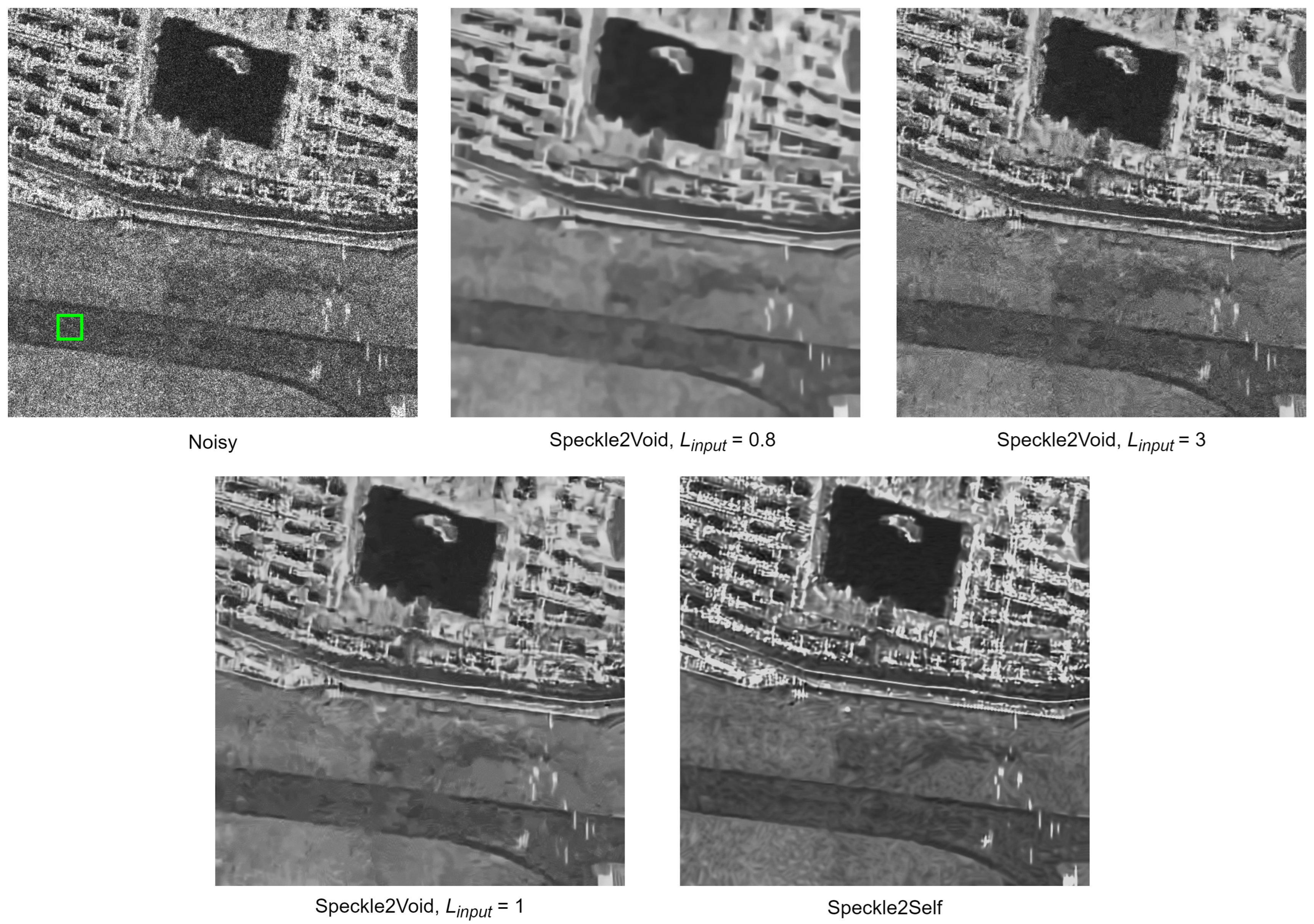
- They have different problem formulations. Speckle2Void employs NNs to estimate the parameters of the prior distribution of the noise, and generates despeckled results by combining the estimated parameters and a constructed MMSE estimator. On the contrary, in our method, the network operates directly on image data, taking the noisy image as input and outputting a denoised version.
- They use different loss functions and implementations of blind-spot network structures. The loss function of Speckle2Void is derived in the spatial domain, while ours is derived in the transform domain. And the blind-spot network is implemented by four convolutional neural network branches in Speckle2Void, while we choose a simpler way and implement such a structure through a series of carefully designed masks.
- They have different network architectures. The network mainbody of Speckle2Void is a CNN-based U-net [70], while we use Transformer architecture as the backbone.
- Speckle2Void relies on noise level priors and requires the noise level as an input parameter, while our proposed Speckle2Void is a blind filter, and has wider applications.
2. Background
2.1. Self-Supervised Denoising with NNs
2.2. Vanilla Transformer with Attention Mechanism
2.2.1. Attention Modules
- Self-attention. In Transformer encoder, we set in (7), where is the outputs of the previous layer.
- Masked Self-attention. To prevent leftward information flow in the decoder to preserve the auto-regressive property, the masking out (setting to ) of all values in the input of the softmax, which correspond to illegal connections, is implemented inside of scaled dot-product attention.
- Cross-attention. The queries come from the previous decoder layer, and the keys and values come from the output of the encoder.
2.2.2. Position-Wise FFN
2.2.3. Residual Connection and Normalization
3. Proposed Method
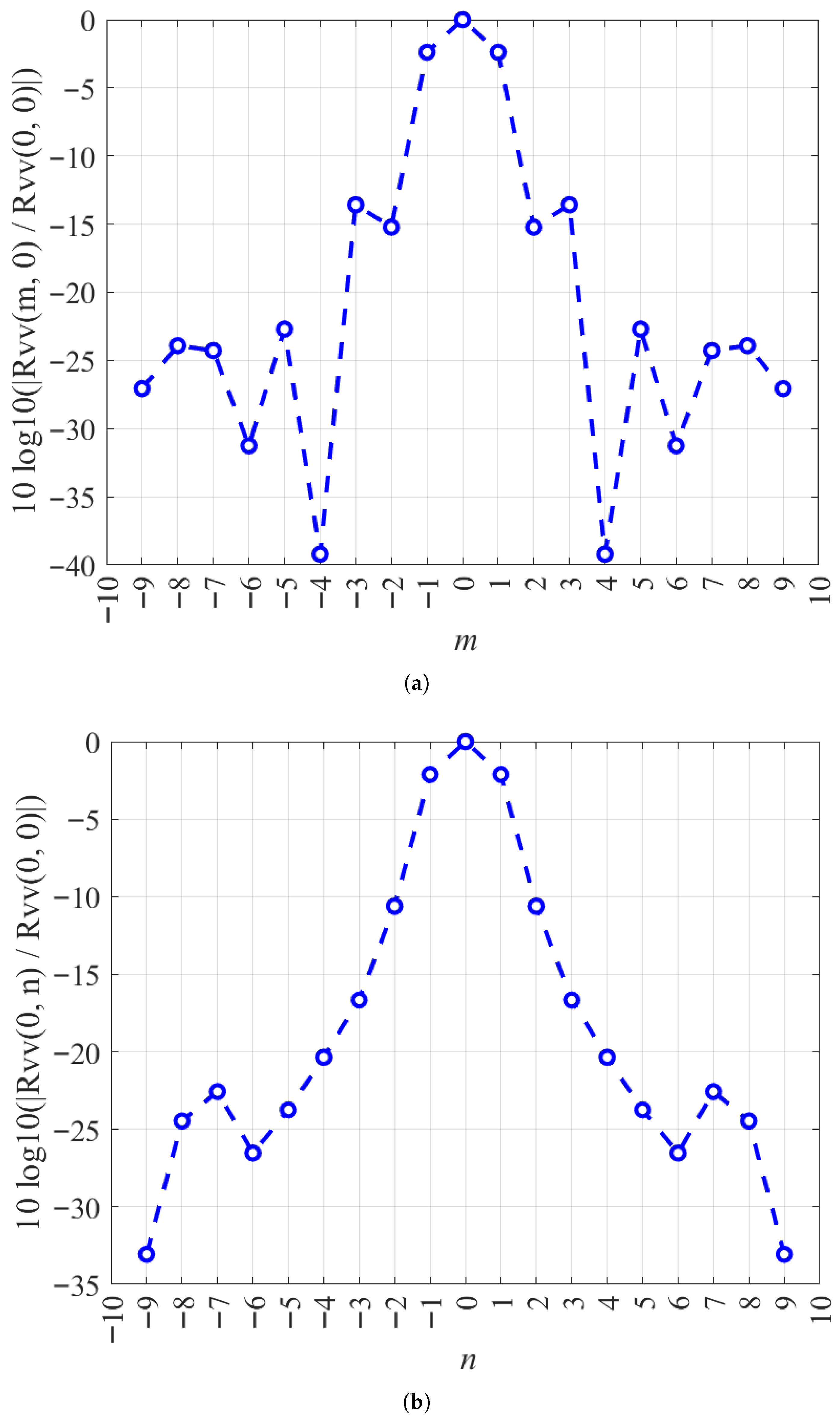
3.1. Statistics of SAR Images
3.2. Loss Function
3.3. Overall Architecture
3.4. Training Scheme
3.4.1. Image Downsampling
3.4.2. Mask Design
3.4.3. Masked Loss Function
3.5. Despeckling Scheme
| Algorithm 1 Speckle2Self Despeckling Scheme |
| Input: SAR image , mask step size and , |
| Downsampling rate r, trained NN . |
| Output: Despeckled result . |
|
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Parameter Settings and Experimental Details
4.2. Training Datasets and Test Images
4.3. Reference Methods and Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. Reference Methods
4.3.2. Evaluation Metrics
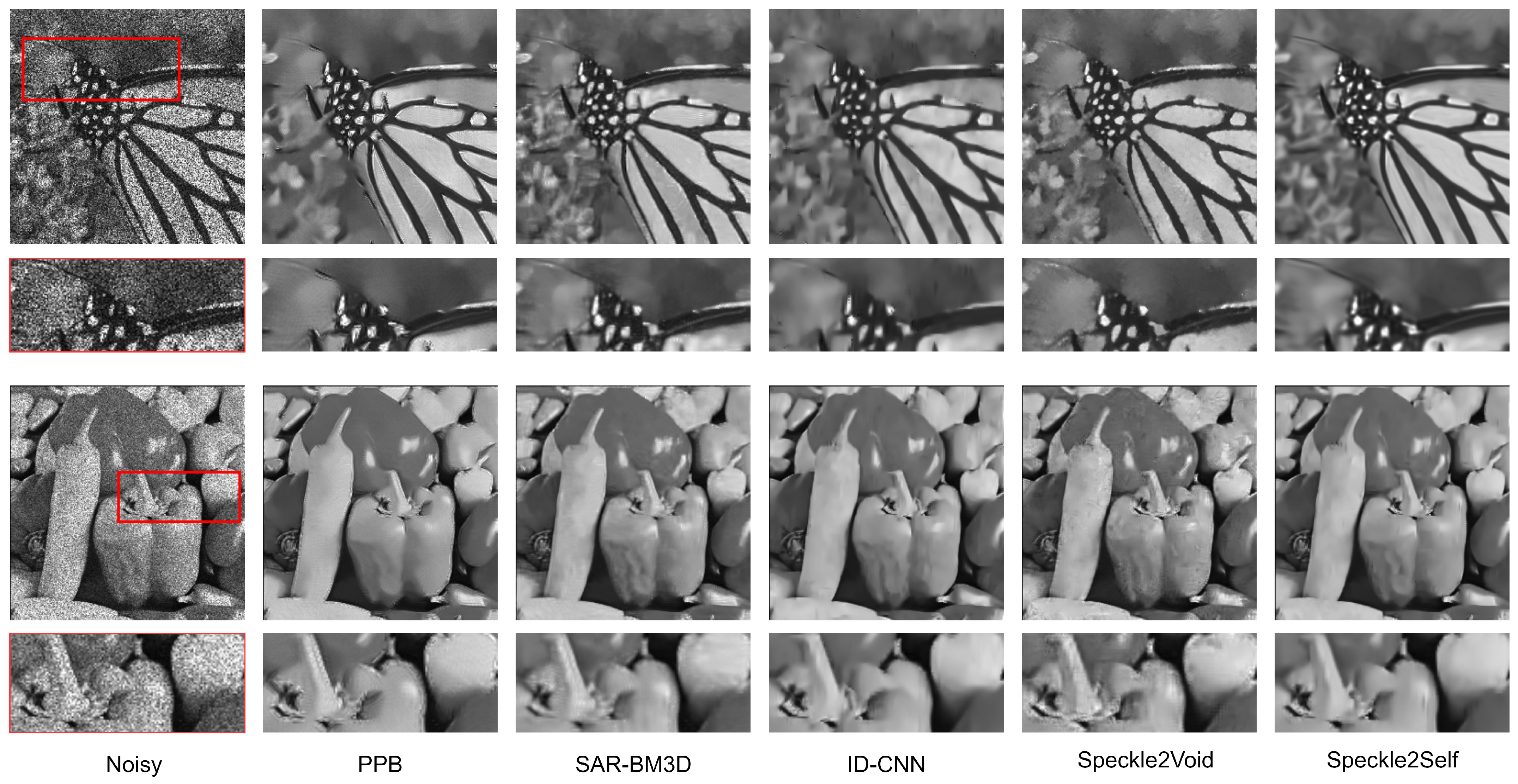
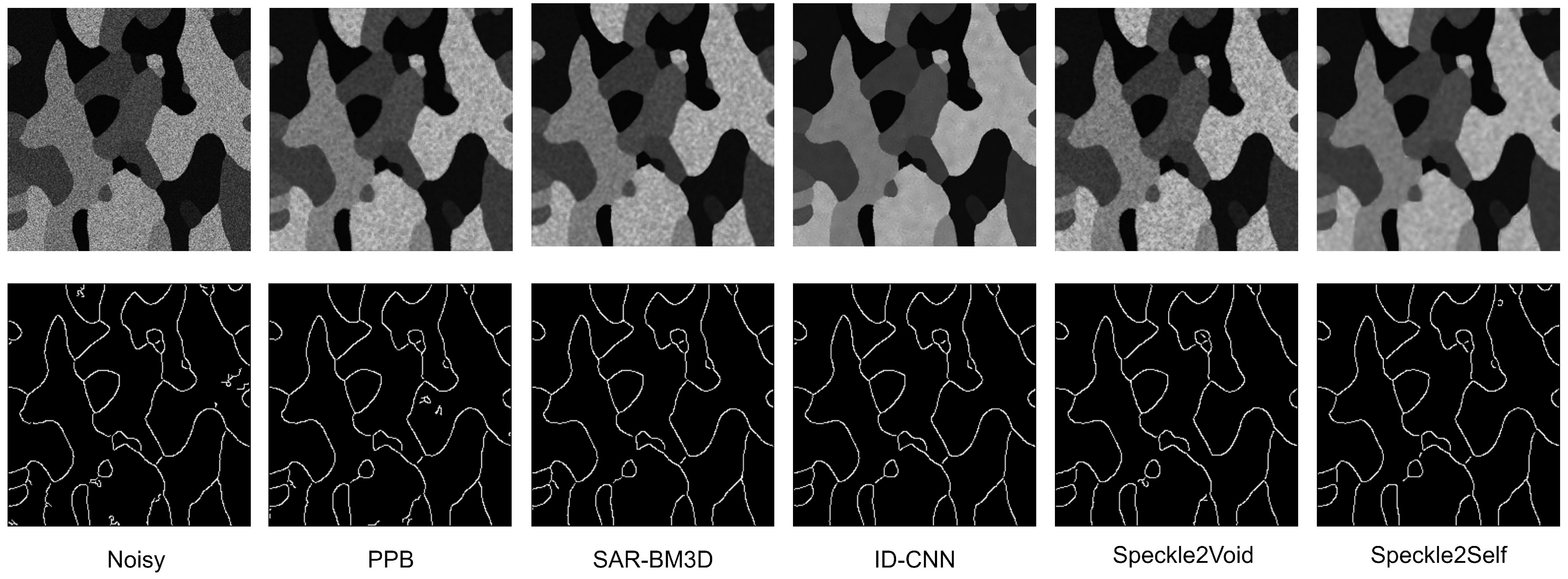
4.4. Results with Synthetic Images
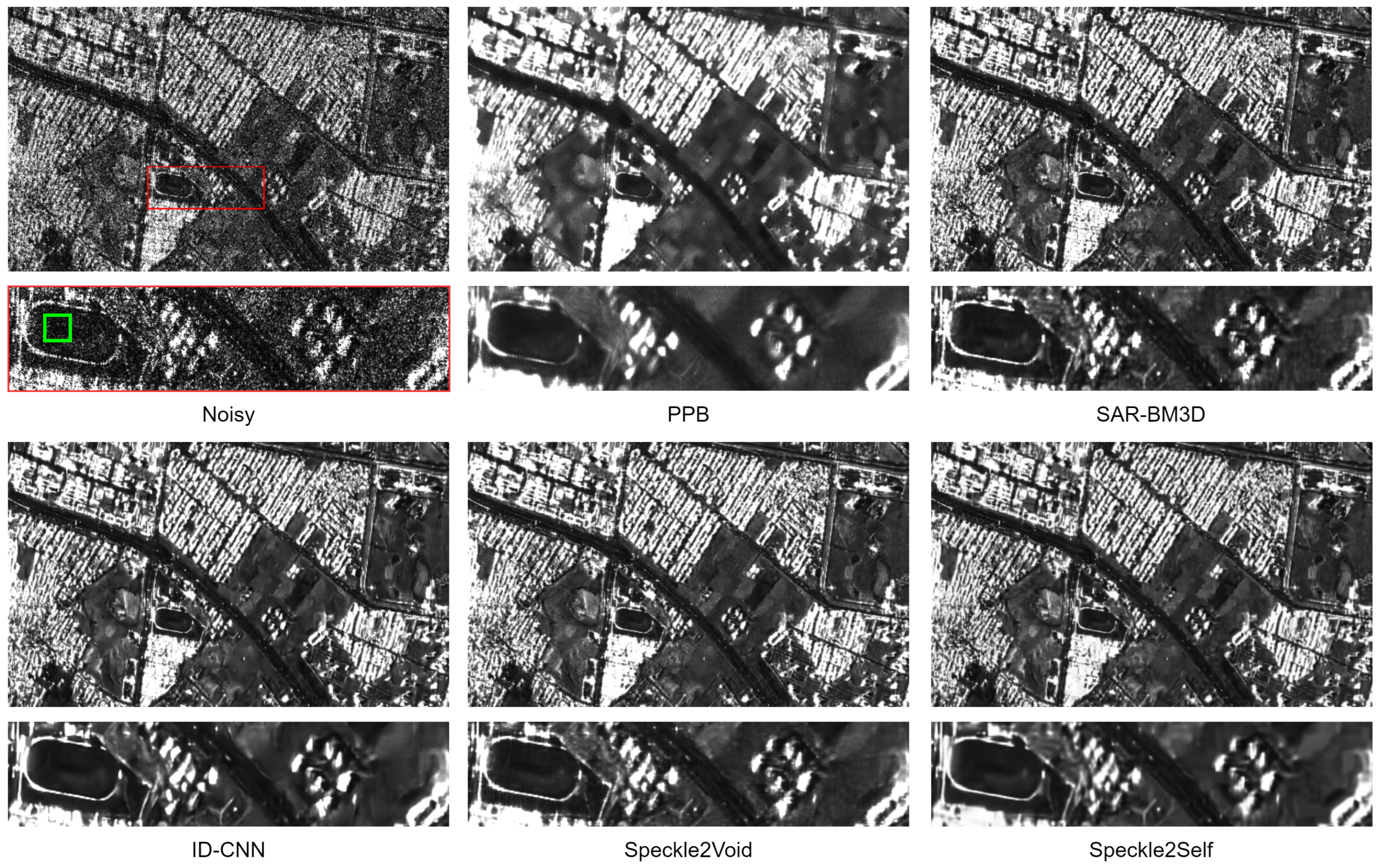
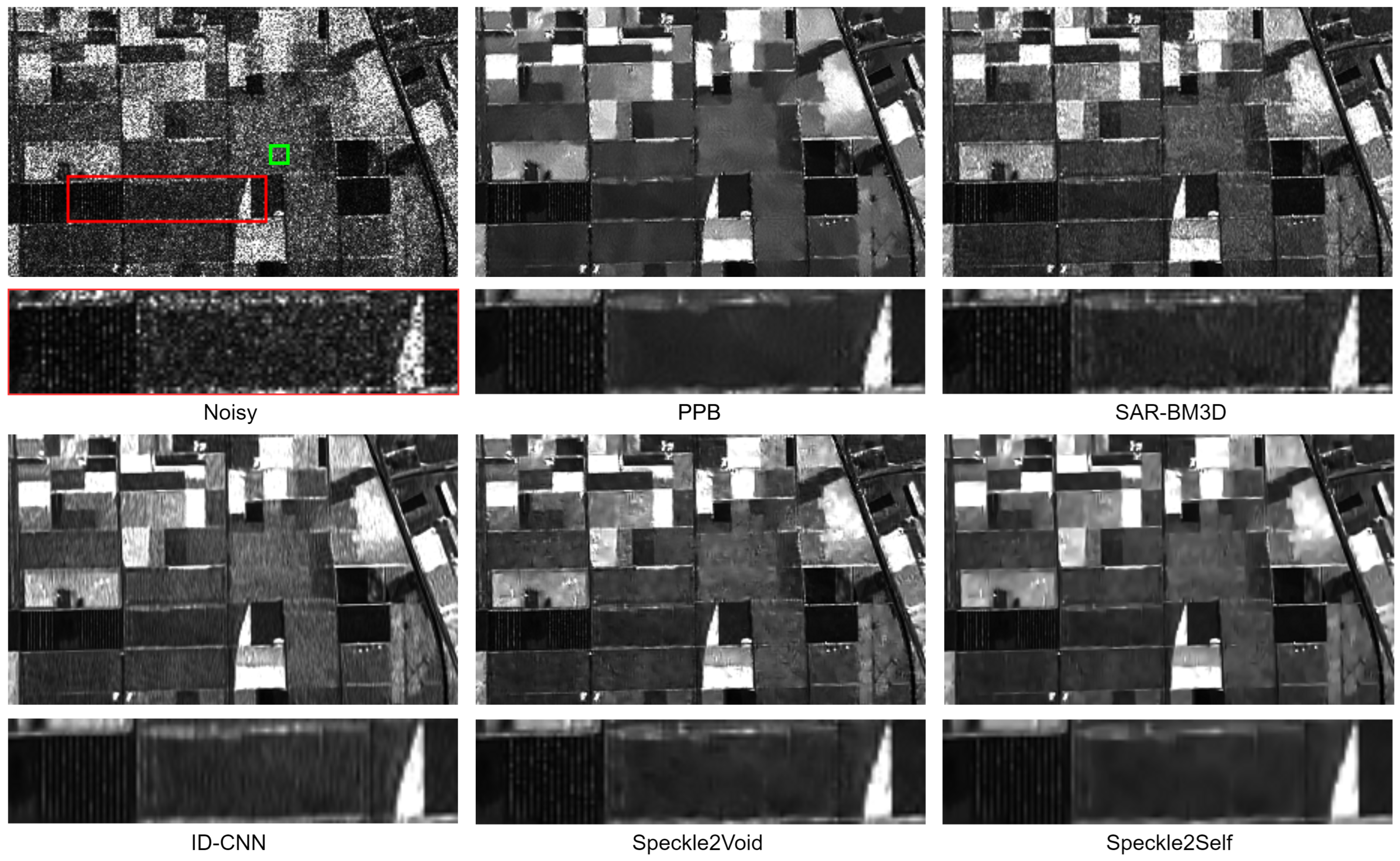
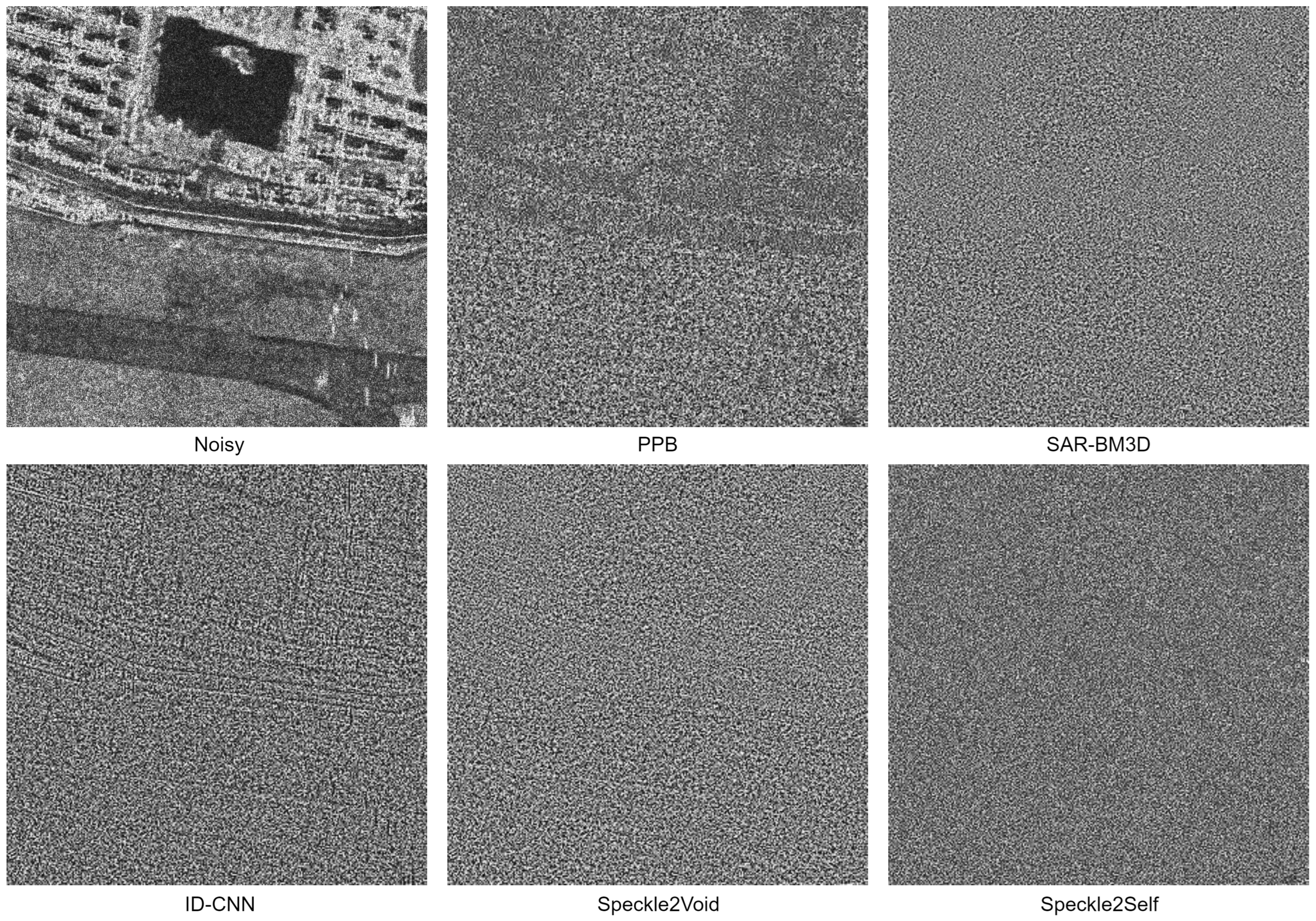
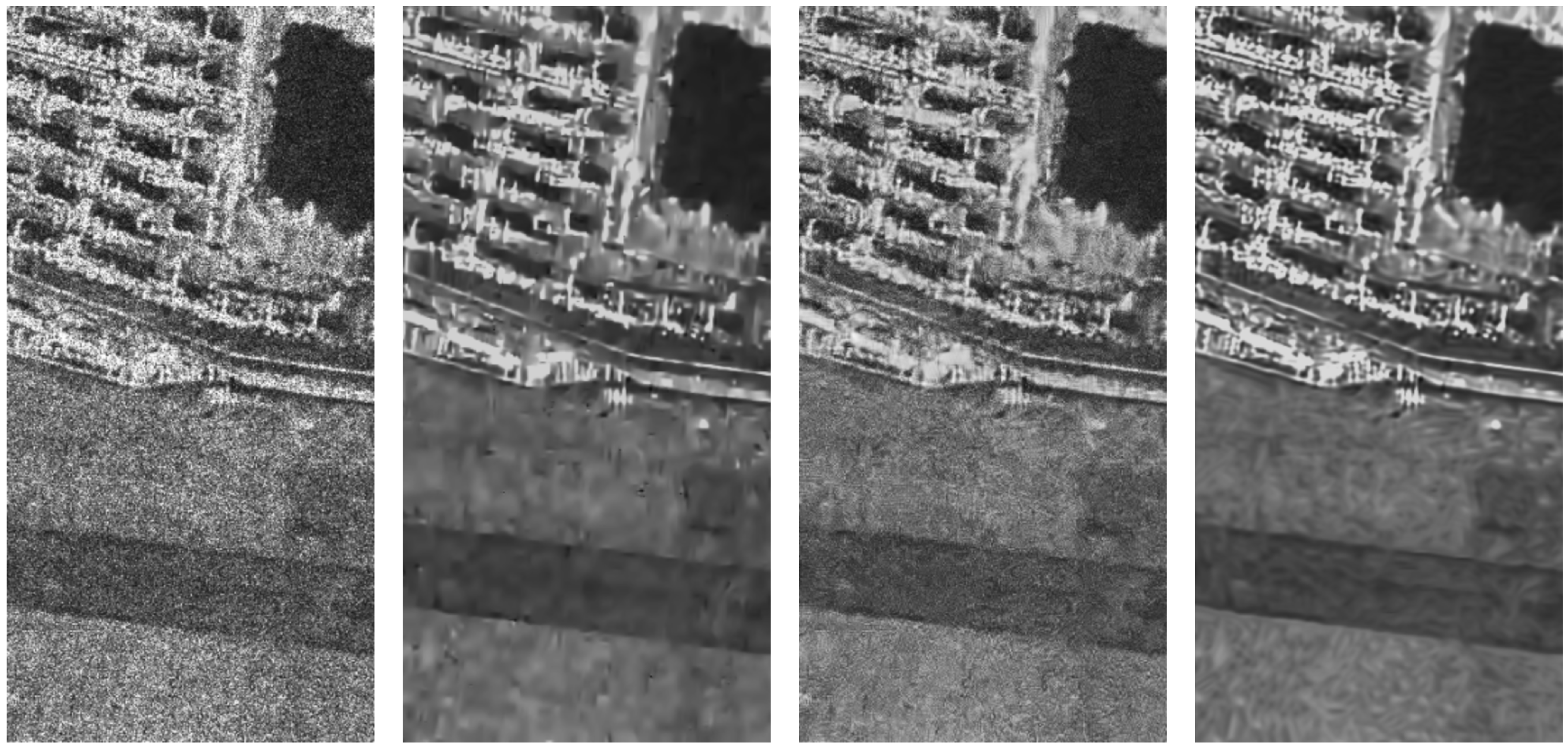
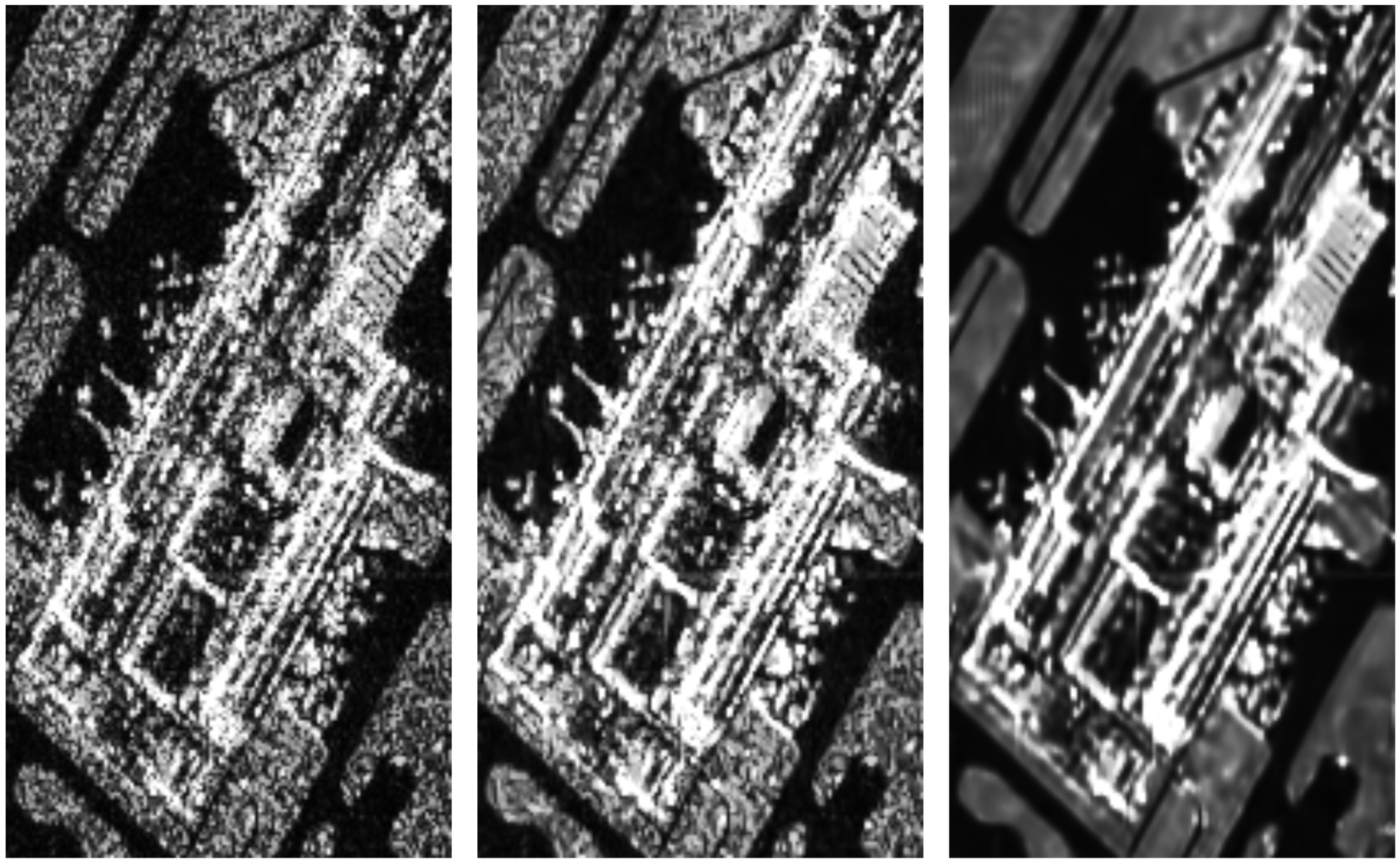
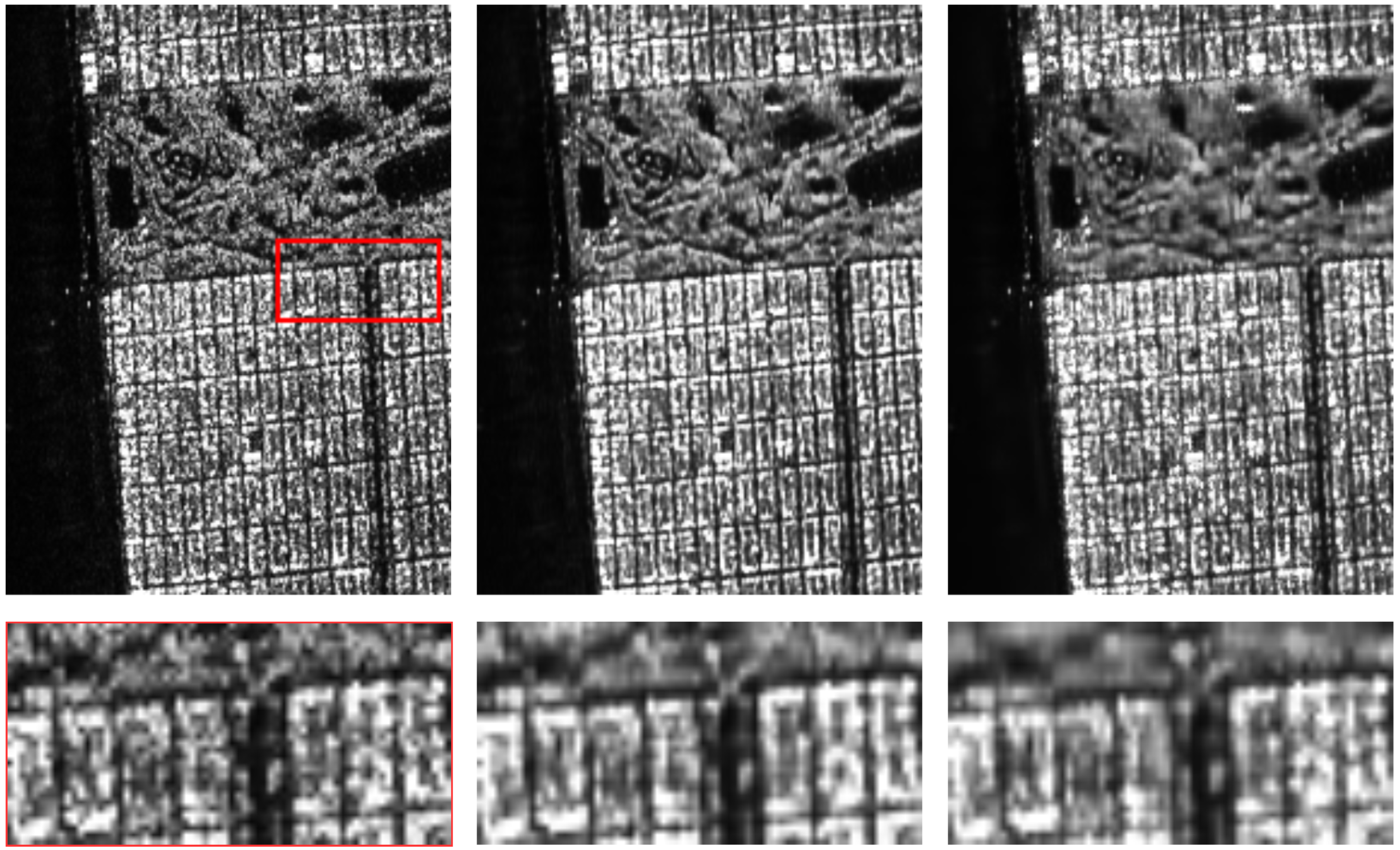
4.5. Results with Real Images
4.6. Model Complexity and Time Consumption
4.7. Comparison with Speckle2Void
4.8. Ablation Study
4.8.1. Loss Function
4.8.2. Image Downsampling
4.8.3. Regularizer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, C.; Quegan, S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bousquet, P. A statistical and geometrical edge detector for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; De Grandi, G. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, 30, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Speckle analysis and smoothing of synthetic aperture radar images. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1981, 17, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.K.; Thakur, R.K.; Yahia, H.M. SAR image denoising based on multifractal feature analysis and TV regularisation. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 4158–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, V.S.; Stiles, J.A.; Shanmugan, K.S.; Holtzman, J.C. A model for radar images and its application to adaptive digital filtering of multiplicative noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1982, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, D.T.; Sawchuk, A.A.; Strand, T.C.; Chavel, P. Adaptive noise smoothing filter for images with signal-dependent noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1985, 37, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.; Touzi, R.; Nezry, E. Adaptive speckle filters and scene heterogeneity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, D.; Sawchuk, A.; Strand, T.; Chavel, P. Adaptive restoration of images with speckle. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1987, 35, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.; Nezry, E.; Touzi, R.; Laur, H. Maximum a posteriori speckle filtering and first order texture models in SAR images. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, College Park, MD, USA, 20–24 May 1990; pp. 2409–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.; Nezry, E.; Touzi, R.; Laur, H. Structure detection and statistical adaptive speckle filtering in SAR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Grunes, M.R.; Schuler, D.L.; Pottier, E.; Ferro-Famil, L. Scattering-model-based speckle filtering of polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 44, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Argenti, F.; Lapini, A.; Bianchi, T.; Alparone, L. A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A. Multiplicative noise removal using variable splitting and constrained optimization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Odegard, J.E.; Lang, M.; Gopinath, R.A.; Selesnick, I.W.; Burrus, C.S. Wavelet based speckle reduction with application to SAR based ATD/R. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 November 1994; Volume 1, pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Solbo, S.; Eltoft, T. Homomorphic wavelet-based statistical despeckling of SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, S. SAR image filtering via learned dictionaries and sparse representations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008—2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; Volume 1, pp. 1–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, L.; Sang, N. Non-local sparse models for SAR image despeckling. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing, Xiamen, China, 16–18 December 2012; pp. 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, B.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Patch ordering-based SAR image despeckling via transform-domain filtering. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, J. An iterative SAR image filtering method using nonlocal sparse model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1635–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2005, 4, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.A.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. Iterative weighted maximum likelihood denoising with probabilistic patch-based weights. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jojy, C.; Nair, M.S.; Subrahmanyam, G.R.S.; Riji, R. Discontinuity adaptive non-local means with importance sampling unscented Kalman filter for de-speckling SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; An, W.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J. Nonlocal filtering for polarimetric SAR data: A pretest approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Cozzolino, D.; Scarpa, G.; Verdoliva, L.; Poggi, G. Guided patchwise nonlocal SAR despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6484–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, S.; Poderico, M.; Angelino, C.V.; Verdoliva, L. A nonlocal SAR image denoising algorithm based on LLMMSE wavelet shrinkage. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierchia, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5438–5441. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Xue, L.; Li, X. SAR image despeckling using a dilated densely connected network. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Peng, D.; Yang, W.; Li, H.C. A filter for SAR image despeckling using pre-trained convolutional neural network model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Ferraioli, G.; Pascazio, V. Multi-objective cnn-based algorithm for sar despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 9336–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledalle, C.A.; Denis, L.; Tabti, S.; Tupin, F. MuLoG, or how to apply Gaussian denoisers to multi-channel SAR speckle reduction? IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4389–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. SAR image despeckling using a convolutional neural network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelaez, P.; Maire, M.; Fowlkes, C.; Malik, J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Residual encoder-decoder network introduced for multisource SAR image despeckling. In Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C. Convolutional neural network and guided filtering for SAR image denoising. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Jiao, L. SAR image specle reduction based on a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. Generative adversarial network-based restoration of speckled SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th international workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing (CAMSAP), Curacao, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraioli, G.; Pascazio, V.; Vitale, S. A novel cost function for despeckling using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, S.; Ferraioli, G.; Pascazio, V. A new ratio image based CNN algorithm for SAR despeckling. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 9494–9497. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, D.X.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. SAR despeckling neural network with logarithmic convolutional product model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 7483–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y. HDRANet: Hybrid dilated residual attention network for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y. SAR image despeckling using multiconnection network incorporating wavelet features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Scarpa, G.; Poggi, G. Nonlocal SAR image despeckling by convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 5117–5120. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Scarpa, G.; Poggi, G. Nonlocal CNN SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Du, Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, B. A CNN-Based Self-Supervised Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Denoising Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X. SAR image despeckling with a multilayer perceptron neural network. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracastoro, G.; Magli, E.; Poggi, G.; Scarpa, G.; Valsesia, D.; Verdoliva, L. Deep learning methods for synthetic aperture radar image despeckling: An overview of trends and perspectives. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.; Ospina, R.; Frery, A.C. Unassisted quantitative evaluation of despeckling filters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, J.; Munkberg, J.; Hasselgren, J.; Laine, S.; Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Aila, T. Noise2Noise: Learning image restoration without clean data. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2965–2974. [Google Scholar]
- Krull, A.; Buchholz, T.O.; Jug, F. Noise2void-learning denoising from single noisy images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2129–2137. [Google Scholar]
- Batson, J.; Royer, L. Noise2self: Blind denoising by self-supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 524–533. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Y.; Chen, M.; Pang, T.; Ji, H. Self2self with dropout: Learning self-supervised denoising from single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1890–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, S.; Karras, T.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. High-quality self-supervised deep image denoising. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Guan, J.; Feng, P.; Wu, Y. A practical solution for SAR despeckling with adversarial learning generated speckled-to-speckled images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravani, K.; Saboo, S.; Bhatt, J.S. A practical approach for SAR image despeckling using deep learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 2957–2960. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Guan, J.; Sun, J. Blind SAR image despeckling using self-supervised dense dilated convolutional neural network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.01608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Learning synthetic aperture radar image despeckling without clean data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 026518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Cha, S.; Moon, T. DoPAMINE: Double-sided masked CNN for pixel adaptive multiplicative noise despeckling. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 4031–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.W.; Li, M.D.; Chen, S.W. Sublook2Sublook: A Self-Supervised Speckle Filtering Framework for Single SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5211613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molini, A.B.; Valsesia, D.; Fracastoro, G.; Magli, E. Towards deep unsupervised SAR despeckling with blind-spot convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2507–2510. [Google Scholar]
- Dalsasso, E.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. SAR2SAR: A semi-supervised despeckling algorithm for SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullissa, A.G.; Marcos, D.; Tuia, D.; Herold, M.; Reiche, J. DeSpeckNet: Generalizing deep learning-based SAR image despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molini, A.B.; Valsesia, D.; Fracastoro, G.; Magli, E. Speckle2Void: Deep self-supervised SAR despeckling with blind-spot convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, X. A survey of transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapini, A.; Bianchi, T.; Argenti, F.; Alparone, L. Blind speckle decorrelation for SAR image despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.B.; Krim, H. A variational approach to maximum a posteriori estimation for image denoising. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Sophia Antipolis, France, 3–5 September 2001; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, G.; Yang, J.; Yamaguchi, Y. Unsupervised estimation of the equivalent number of looks in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Anfinsen, S.N.; Doulgeris, A.P.; Eltoft, T. Estimation of the equivalent number of looks in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3795–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jin, K.; Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Residual In Residual Scaling Networks for Polarimetric SAR Image Despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5207717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
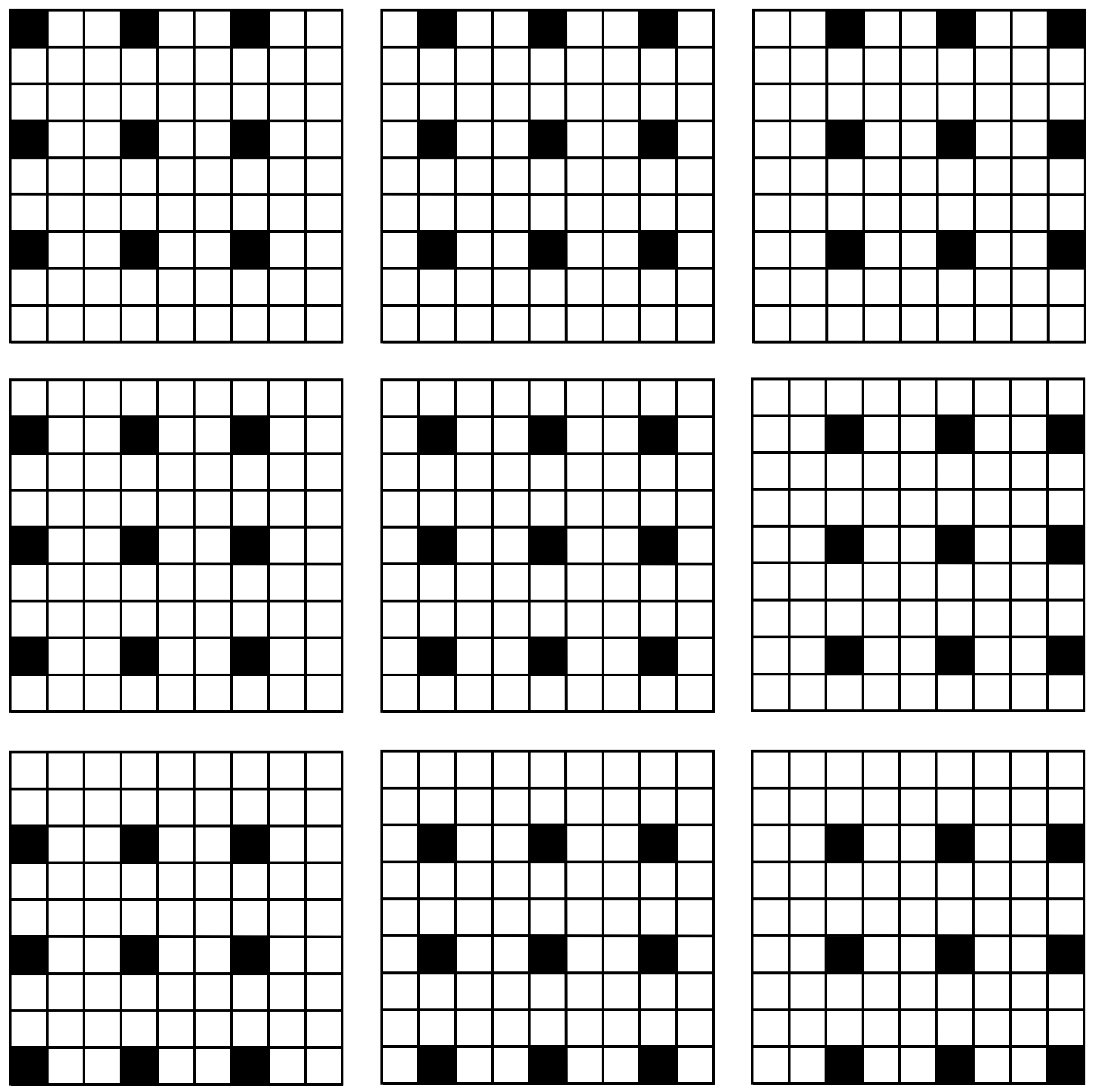
| Algorithm Parameters | Symbols | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Full Image Size | ||
| Downsampling Rate | r | 2 |
| Downsampled Image Size | ||
| Patch size | P | 16 |
| Number of Patches | N | 196 |
| Embedding Feature Dimension | D | 768 |
| Encoder Depth | 12 | |
| Decoder Depth | 2 | |
| Mask Interval in Row Direction | 3 | |
| Mask Interval in Column Direction | 3 |
| PPB | SAR-BM3D | ID-CNN | Speckle2Void | Speckle2Self | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monarch | 22.74 | 24.58 | 23.23 | 23.15 | 24.26 | |
| 24.27 | 26.29 | 26.35 | 25.67 | 26.07 | ||
| 26.02 | 28.63 | 28.70 | 27.96 | 28.41 | ||
| 27.39 | 29.73 | 29.27 | 28.94 | 29.91 | ||
| 28.93 | 30.35 | 30.02 | 29.97 | 30.60 | ||
| Peppers | 23.86 | 24.91 | 24.06 | 23.24 | 24.58 | |
| 25.50 | 26.56 | 26.40 | 25.71 | 26.93 | ||
| 26.95 | 27.90 | 28.27 | 27.36 | 28.11 | ||
| 28.43 | 29.72 | 29.04 | 28.88 | 30.67 | ||
| 29.86 | 31.37 | 30.63 | 30.62 | 31.33 | ||
| PPB | SAR-BM3D | ID-CNN | Speckle2Void | Speckle2Self | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monarch | 0.713 | 0.790 | 0.752 | 0.754 | 0.787 | |
| 0.778 | 0.843 | 0.845 | 0.819 | 0.841 | ||
| 0.837 | 0.891 | 0.890 | 0.874 | 0.904 | ||
| 0.871 | 0.915 | 0.914 | 0.905 | 0.925 | ||
| 0.903 | 0.922 | 0.920 | 0.912 | 0.917 | ||
| Peppers | 0.678 | 0.747 | 0.698 | 0.626 | 0.737 | |
| 0.739 | 0.798 | 0.779 | 0.725 | 0.788 | ||
| 0.790 | 0.824 | 0.830 | 0.796 | 0.838 | ||
| 0.831 | 0.872 | 0.843 | 0.839 | 0.877 | ||
| 0.865 | 0.897 | 0.901 | 0.873 | 0.896 | ||
| PPB | SAR-BM3D | ID-CNN | Speckle2Void | Speckle2Self |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 92.93 | 94.55 | 94.87 | 93.48 | 95.12 |
| Image-5 [69] () | Dalian () | Flevoland () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENL | ENL | ENL | |||||||
| PPB | 22.93 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 42.49 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 148.91 | 0.97 | 0.25 |
| SAR-BM3D | 16.24 | 0.89 | 0.55 | 8.98 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 40.83 | 0.95 | 0.19 |
| ID-CNN | 16.61 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 22.27 | 0.92 | 1.69 | 79.22 | 0.89 | 0.31 |
| Speckle2Void | 18.90 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 31.46 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 92.85 | 0.93 | 0.29 |
| Speckle2Self | 19.03 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 46.83 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 133.08 | 0.99 | 0.34 |
| Method | PPB | SAR-BM3D | ID-CNN | Speckle2Void | Speckle2Self |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters (M) | - | - | 2.03 | 5.34 | 7.95 |
| Execution Time per Sample | |||||
| for Training (s) | - | - | 0.084 | 0.096 | 0.097 |
| Execution Time per Sample | |||||
| for Inference (s) | 13.39 | 38.47 | 0.076 | 0.088 | 0.090 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.; Su, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xing, C.; Yin, J. Speckle2Self: Learning Self-Supervised Despeckling with Attention Mechanism for SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233840
Lin H, Su X, Zeng Z, Xing C, Yin J. Speckle2Self: Learning Self-Supervised Despeckling with Attention Mechanism for SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233840
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Huiping, Xin Su, Zhiqiang Zeng, Cheng Xing, and Junjun Yin. 2025. "Speckle2Self: Learning Self-Supervised Despeckling with Attention Mechanism for SAR Images" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233840
APA StyleLin, H., Su, X., Zeng, Z., Xing, C., & Yin, J. (2025). Speckle2Self: Learning Self-Supervised Despeckling with Attention Mechanism for SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233840







