Automated 3D Building Model Reconstruction from Satellite Images Using Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Adaptive Roof Fitting
Highlights
- This study developed a two-stage polygon decomposition and adaptive roof fitting method for automatic 3D building model reconstruction.
- By integrating polygon decomposition with adaptive roof parameter modeling, the proposed approach effectively decomposed building footprints and achieved accu-rate reconstruction of both flat roofs and common non-flat roof types.
- The developed approach is capable of reliably reconstructing buildings with complex connection structures and produces 3D building models with high geometric accu-racy and a high degree of standardization.
- The two-stage polygon decomposition and adaptive roof fitting framework demon-strates strong potential to handle footprints with intricate connectivity and to model buildings with complex flat roofs.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
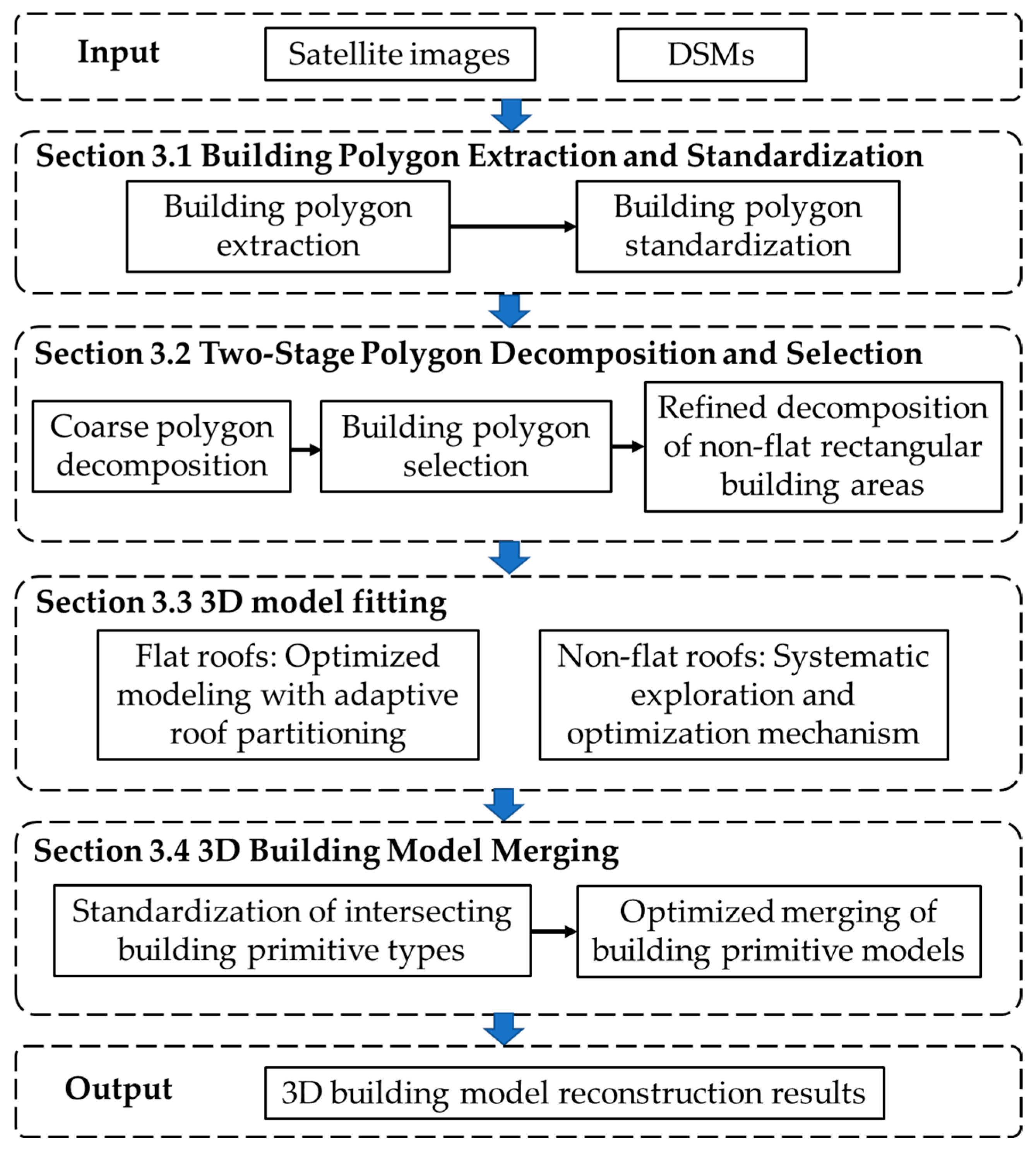
3. Methodology
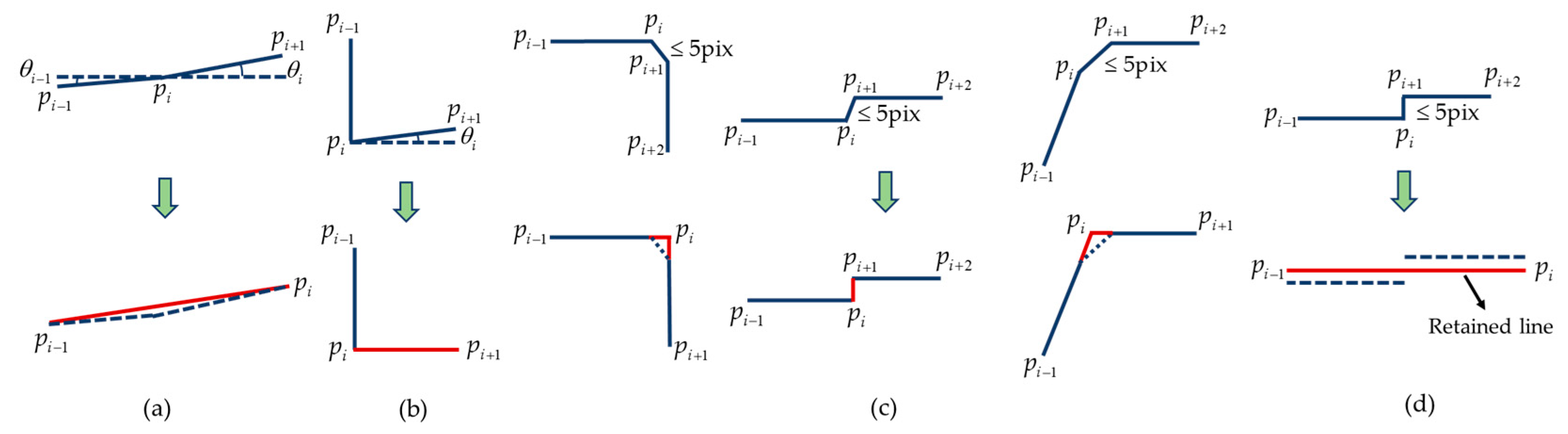
3.1. Building Polygon Extraction and Standardization
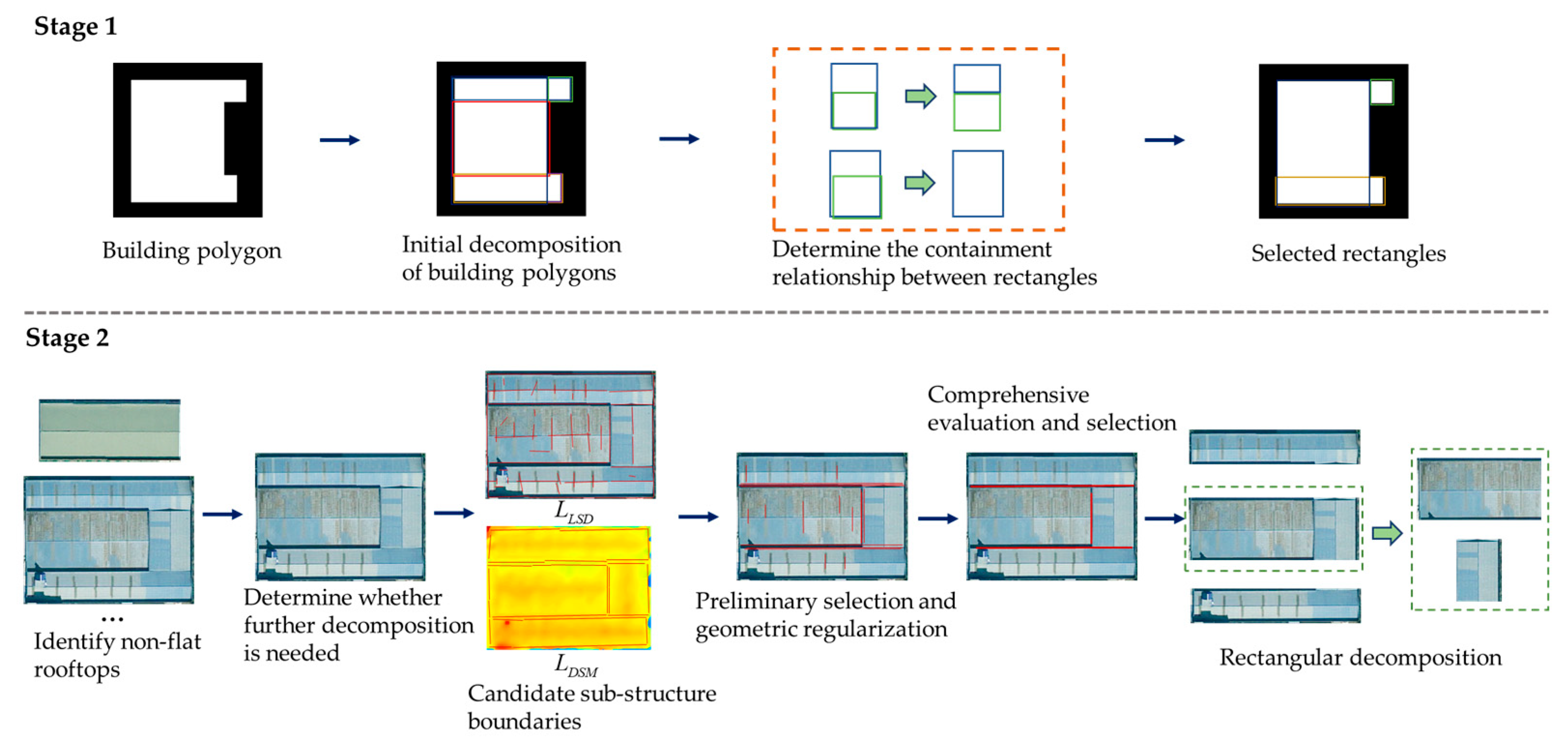
3.2. Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Selection
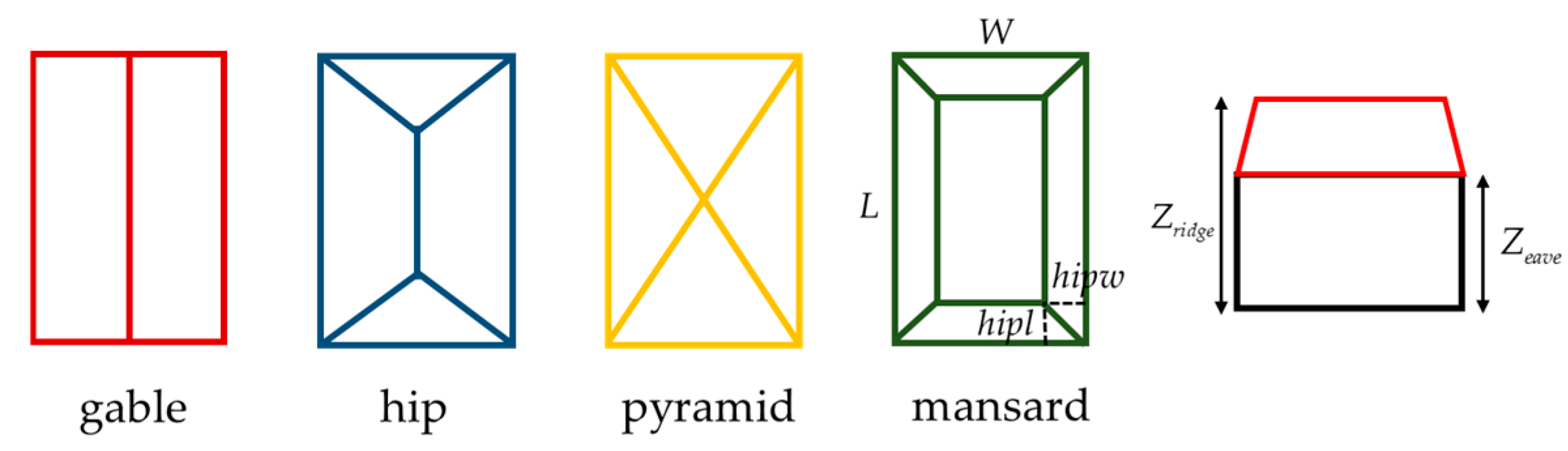
3.3. 3D Model Fitting
3.4. 3D Model Merging
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Data and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Parameter Setting
4.3. Experimental Parameter Analysis
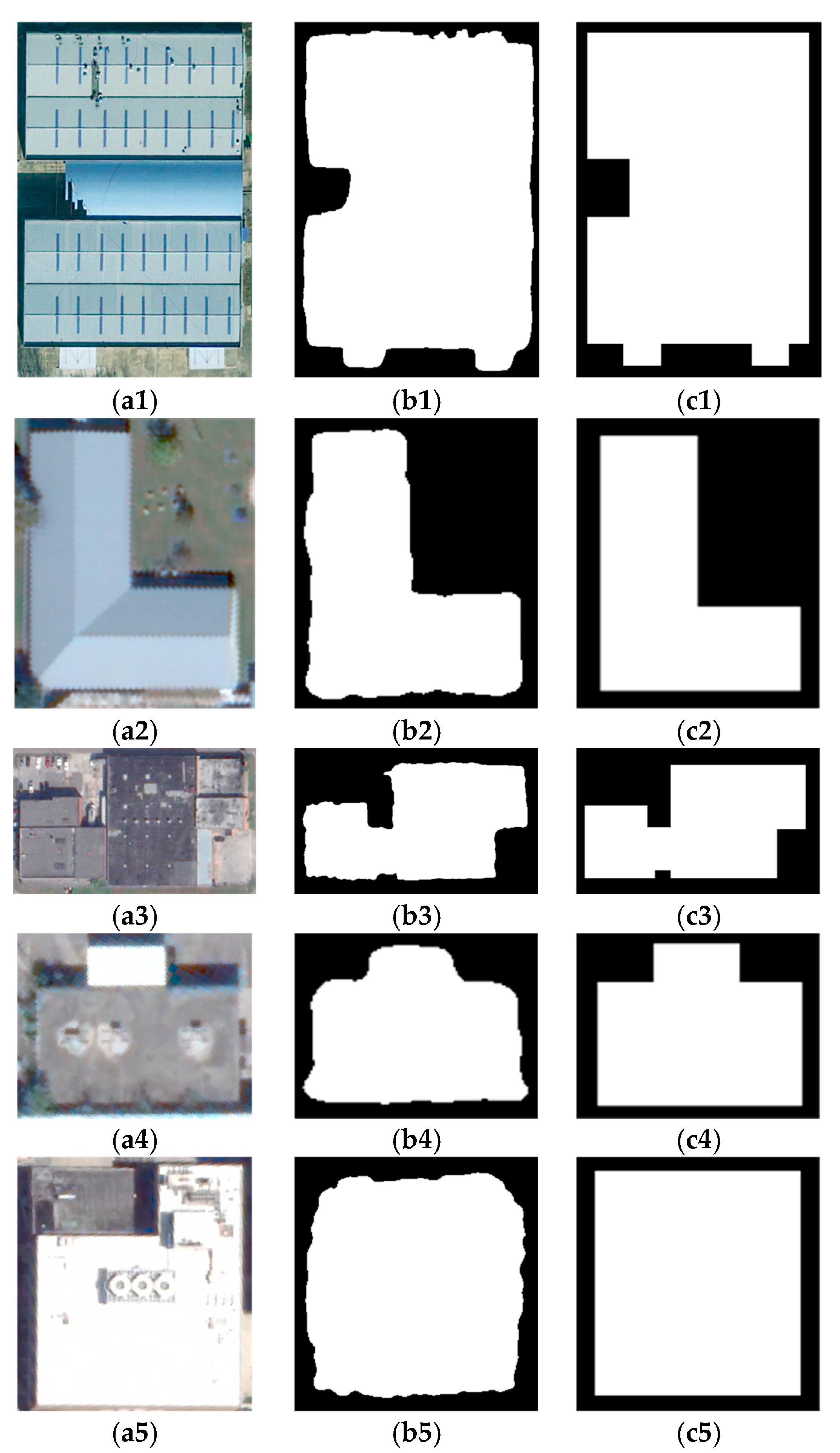
4.4. Standardization Results of Building Polygons
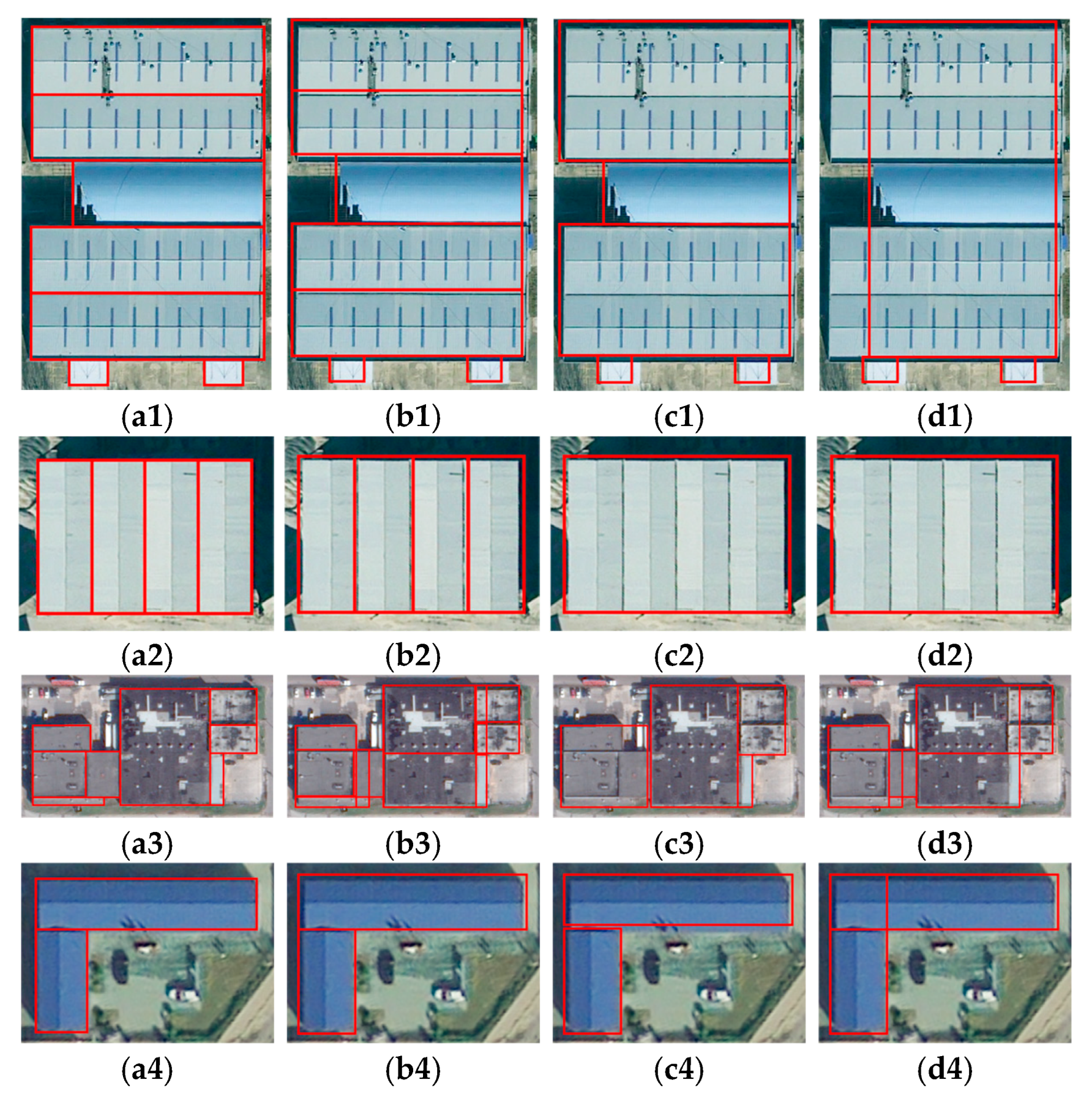
4.5. Analysis of Building Polygon Decomposition
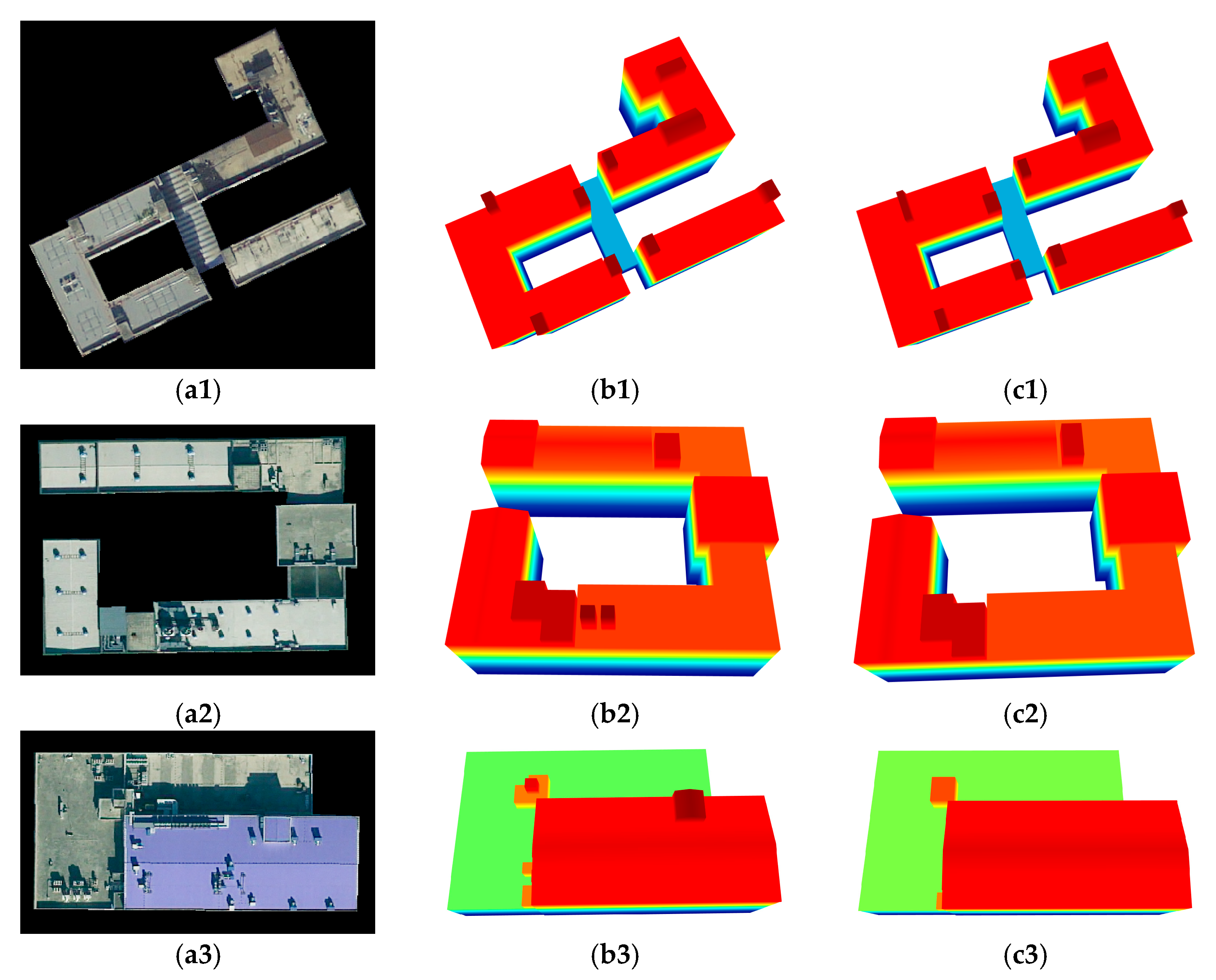
4.6. Comparison to State-of-the-Art Methods
5. Discussion
5.1. Method Applicability Analysis
5.2. Computational Efficiency Analysis
5.3. Applicability, Limitations, and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wu, B. Relation-constrained 3D reconstruction of buildings in metropolitan areas from photogrammetric point clouds. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Y.; Lee, S. Sat2map: Reconstructing 3D building roof from 2D satellite images. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostikolaei, F.S.; Jabari, S. Automated LoD2 building reconstruction using bimodal segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 23289–23305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shan, J. RANSAC-based multi primitive building reconstruction from 3D point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 185, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Goldberg, H.; Foster, K.; Leichtman, A.; Wang, S.; Hagstrom, S.; Bosch, M.; Almes, S. Large-Scale Public Lidar and Satellite Image Data Set for Urban Semantic Labeling. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense + Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 154–167. [Google Scholar]
- Leotta, M.J.; Long, C.; Jacquet, B.; Zins, M.; Lipsa, D.; Shan, J.; Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chang, S.-F.; et al. Urban semantic 3D reconstruction from multiview satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Khoshelham, K. 3-D building instance extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images and DSM with an end-to-end deep neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4406019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, S. 3D model extraction network based on RFM constrained deformation inference and self-similar convolution for satellite stereo images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 11877–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, N.; Mourshed, M. A shadow-overlapping algorithm for estimating building heights from VHR satellite images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, K.; Korner, M. Automatic large-scale 3d building shape refinement using conditional generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1887–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, S.; Qin, R. Automated LoD-2 model reconstruction from very-high-resolution satellite-derived digital surface model and orthophoto. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 181, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthuber, E.; Avbelj, J. 3D building reconstruction from lidar point clouds by adaptive dual contouring. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, II-3/W4, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, R.Q.; Sadeq, H. LoD2 building reconstruction from stereo satellite imagery using deep learning and model-driven approach. Zanco J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2025, 37, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Furukawa, Y. Roof-GAN: Learning to Generate Roof Geometry and Relations for Residential Houses. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2796–2805. [Google Scholar]
- Schuegraf, P.; Shan, J.; Bittner, K. PLANES4LOD2: Reconstruction of LoD-2 building models using a depth attention-based fully convolutional neural network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 211, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partovi, T.; Fraundorfer, F.; Bahmanyar, R.; Huang, H.; Reinartz, P. Automatic 3-D building model reconstruction from very high resolution stereo satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Schuegraf, P.; Bittner, K.; Qin, R. Unit-level LoD2 building reconstruction from satellite-derived digital surface model and orthophoto. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, X-2-2024, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Qin, R.; Tang, Y. SAT2LOD2: A software for automated lod-2 building reconstruction from satellite-derived orthophoto and digital surface model. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, XLIII-B2-2022, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, A.; Gröger, G.; Stroh, V.; Plümer, L. Model driven reconstruction of roofs from sparse LiDAR point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 76, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Weng, Q. Model-driven reconstruction of 3-D buildings using LiDAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girindran, R.; Boyd, D.S.; Rosser, J.; Vijayan, D.; Long, G.; Robinson, D. On the reliable generation of 3D city models from open data. Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Brenner, C.; Sester, M. A generative statistical approach to automatic 3D building roof reconstruction from laser scanning data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Mei, Z. Computational methods of acquisition and processing of 3D point cloud data for construction applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 27, 479–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuegraf, P.; Gui, S.; Qin, R.; Fraundorfer, F.; Bittner, K. Sat2building: LoD-2 building reconstruction from satellite imagery using spatial embeddings. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2025, 91, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidoost, F.; Arefi, H.; Tombari, F. 2D image-to-3D model: Knowledge-based 3D building reconstruction (3DBR) using single aerial images and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Yan, K. Semantic decomposition and reconstruction of compound buildings with symmetric roofs from LiDAR data and aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13945–13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partovi, T.; Bahmanyar, R.; Krauß, T.; Reinartz, P. Building outline extraction using a heuristic approach based on generalization of line segments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the Reduction of the Number of Points Required to Represent a Digitized Line or Its Caricature. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovis. 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Kibbe, W.A.; Lin, S.M. Improved peak detection in mass spectrum by incorporating continuous wavelet transform-based pattern matching. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Using Kernel Density Estimates to Investigate Multimodality. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1981, 43, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, B.; Karaboga, D. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm for real–parameter optimization. Inf. Sci. 2012, 192, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Akay, B. A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 214, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, H.; He, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, T.; He, J. A learning-based dual-scale enhanced confidence for DSM fusion in 3D reconstruction of multi-view satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 11767–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, H.; Li, T.; Ji, M.; He, Y. SuperView-1 satellite image-based winter wheat spatial distribution information refined extraction using the fusion of machine learning and deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Remote Sensing, Surveying, and Mapping (RSSM 2024), Wuhan, China, 12–14 January 2024; pp. 296–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, M.; Foster, K.; Christie, G.; Wang, S.; Hager, G.D.; Brown, M. Semantic Stereo for Incidental Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1524–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Generalized Stereo Matching Method Based on Iterative Optimization of Hierarchical Graph Structure Consistency Cost for Urban 3D Reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.; Randall, G.; Facciolo, G.; von Gioi, R.G. An experimental comparison of multi-view stereo approaches on satellite images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 844–853. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Ji, S. A general deep learning based framework for 3D reconstruction from multi-view stereo satellite images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 195, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, F.; Koz, A.; Bahmanyar, R.; Azimi, S.M.; Süzen, M.L. Fusing Convolution and Vision Transformer Encoders for Object Height Estimation from Monocular Satellite and Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 19–23 October 2025; pp. 3709–3718. [Google Scholar]
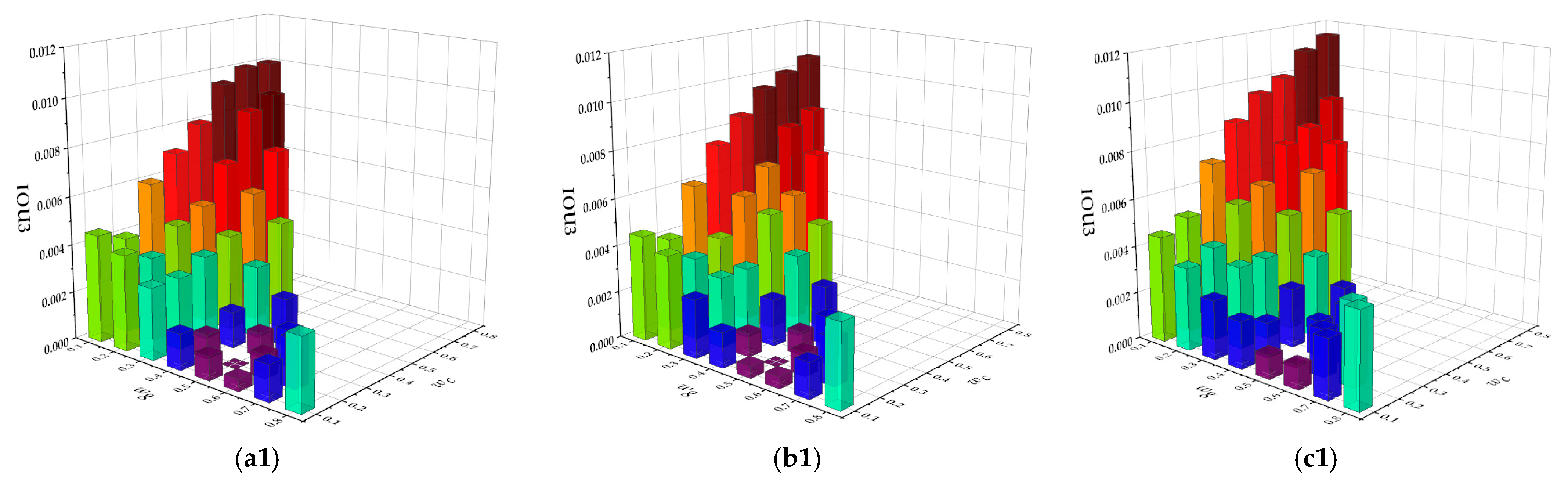
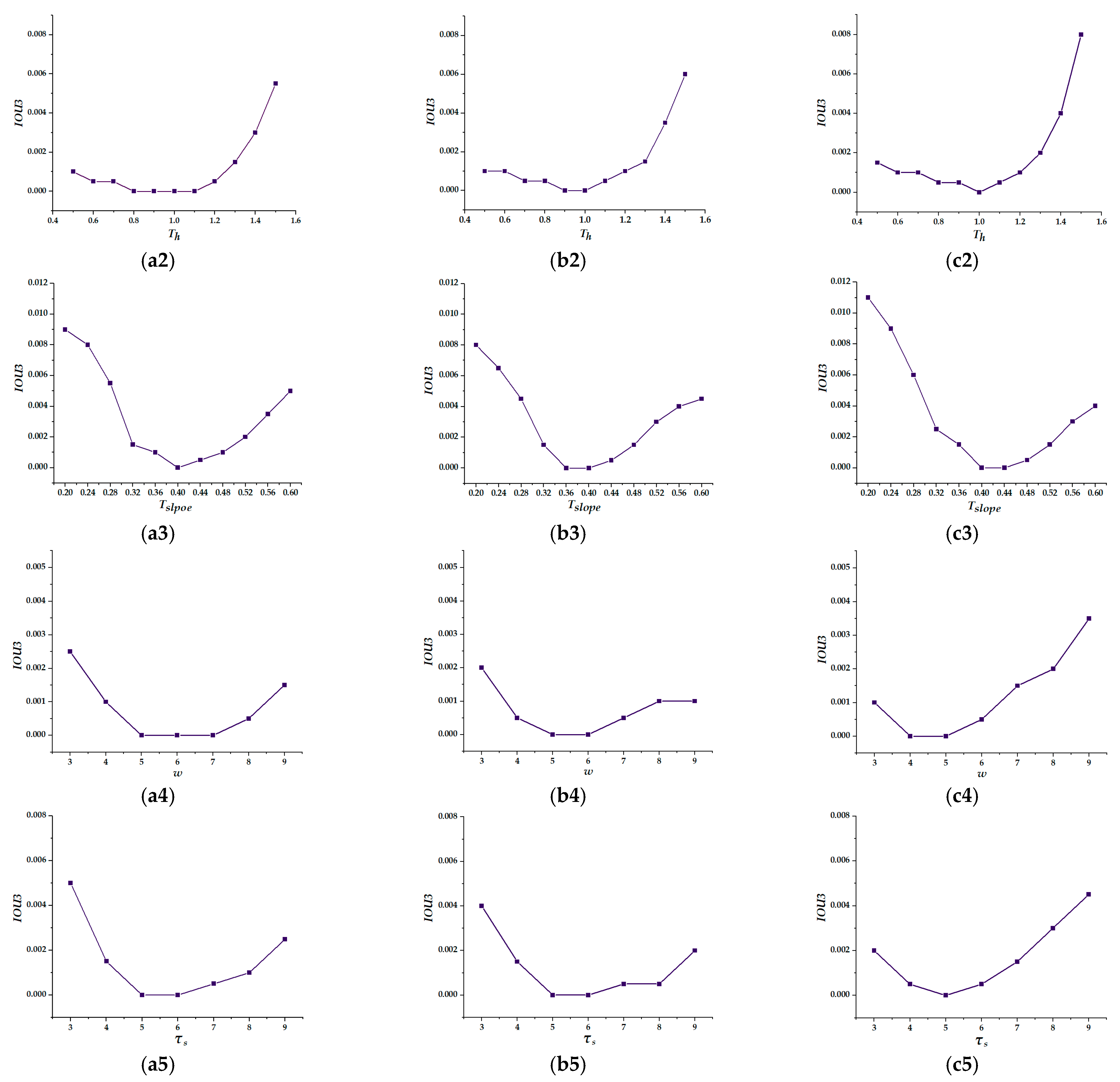

| Parameter | Search Range | Step Size |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | ||
| 0.2 | ||
| 0.4 | ||
| 0.4 |
| Method/ Building Target | Partovi | Gui | Our | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IOU2 | 0.8022 | 0.9033 | 0.9067 |
| IOU3 | 0.7733 | 0.9023 | 0.9284 | |
| 2 | IOU2 | 0.9190 | 0.9190 | 0.9190 |
| IOU3 | 0.8913 | 0.8913 | 0.8991 | |
| 3 | IOU2 | 0.9224 | 0.8937 | 0.9224 |
| IOU3 | 0.8939 | 0.8428 | 0.9140 | |
| 4 | IOU2 | 0.8962 | 0.8519 | 0.8962 |
| IOU3 | 0.8547 | 0.8284 | 0.8609 | |
| Method/ Building Target | Our | ALOD2MR | ABMR | PLANES4 LOD2 | SAT2LOD2 | RDISCMR | FusedSeg-HE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IOU3 (%) | 86.09 | 79.51 | 83.62 | 80.28 | 77.35 | 78.68 | 78.42 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.51 | 1.22 | 0.61 | 1.36 | 1.49 | 1.29 | 1.34 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.30 | |
| 2 | IOU3 (%) | 92.47 | 85.44 | 80.35 | 91.82 | 83.80 | 88.16 | 86.87 |
| RMSE (m) | 1.67 | 3.57 | 3.68 | 3.26 | 3.59 | 2.74 | 3.09 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.40 | 1.44 | 1.60 | 0.72 | 1.51 | 0.69 | 0.75 | |
| 3 | IOU3 (%) | 89.91 | 86.00 | 84.36 | 87.31 | 86.09 | 86.41 | 86.24 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.47 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.28 | |
| 4 | IOU3 (%) | 91.40 | 79.77 | 86.27 | 87.65 | 81.78 | 86.74 | 87.19 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.54 | 1.29 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 1.30 | 1.03 | 0.96 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.25 | |
| 5 | IOU3 (%) | 91.00 | 86.67 | 85.41 | 87.95 | 86.21 | 87.22 | 87.63 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.58 | 1.45 | 1.59 | 1.24 | 1.48 | 1.29 | 1.27 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.42 | |
| 6 | IOU3 (%) | 92.84 | 90.11 | 76.22 | 92.29 | 86.55 | 89.42 | 88.36 |
| RMSE (m) | 1.19 | 1.43 | 3.41 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 1.34 | 1.48 | |
| MHE (m) | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.33 |
| Method | Our | ALOD2MR | ABMR | PLANES4 LOD2 | SAT2LOD2 | RDISCMR | FusedSeg-HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOU3 (%) | 91.26 | 85.54 | 83.17 | 88.36 | 83.68 | 86.32 | 85.89 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.78 | 1.49 | 1.71 | 1.35 | 1.60 | 1.37 | 1.41 |
| MHE (m) | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
| Metric | Original Data | Resolution Reduction | Noise Injection | Occlusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOU3 (%) | 91.42 | 90.87 | 91.23 | 91.34 |
| RMSE (m) | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.77 |
| MHE (m) | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Huang, P. Automated 3D Building Model Reconstruction from Satellite Images Using Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Adaptive Roof Fitting. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233832
Yang S, Chen H, Huang P. Automated 3D Building Model Reconstruction from Satellite Images Using Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Adaptive Roof Fitting. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233832
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuting, Hao Chen, and Puxi Huang. 2025. "Automated 3D Building Model Reconstruction from Satellite Images Using Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Adaptive Roof Fitting" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233832
APA StyleYang, S., Chen, H., & Huang, P. (2025). Automated 3D Building Model Reconstruction from Satellite Images Using Two-Stage Polygon Decomposition and Adaptive Roof Fitting. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233832





