Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Sparse R-CNN with Wavelet Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism
Highlights
- A novel wavelet deformable convolution (WDC) module is proposed, which incorporates wavelet-domain information and adaptively models multi-scale ship targets with improved edge and boundary representation.
- A position-encoded multi-head attention mechanism (PEMA) is introduced to replace the original dynamic head in Sparse R-CNN, enabling more effective focus on spatially and semantically relevant regions for sparse target detection.
- The proposed method significantly improves detection accuracy for sparse, multi-scale, and irregularly distributed ships in SAR images, particularly under complex background conditions.
- By combining wavelet-domain representation, deformable convolution, and attention mechanisms, the framework provides a robust solution that advances SAR-based maritime surveillance and monitoring applications.
Abstract
1. Introduction
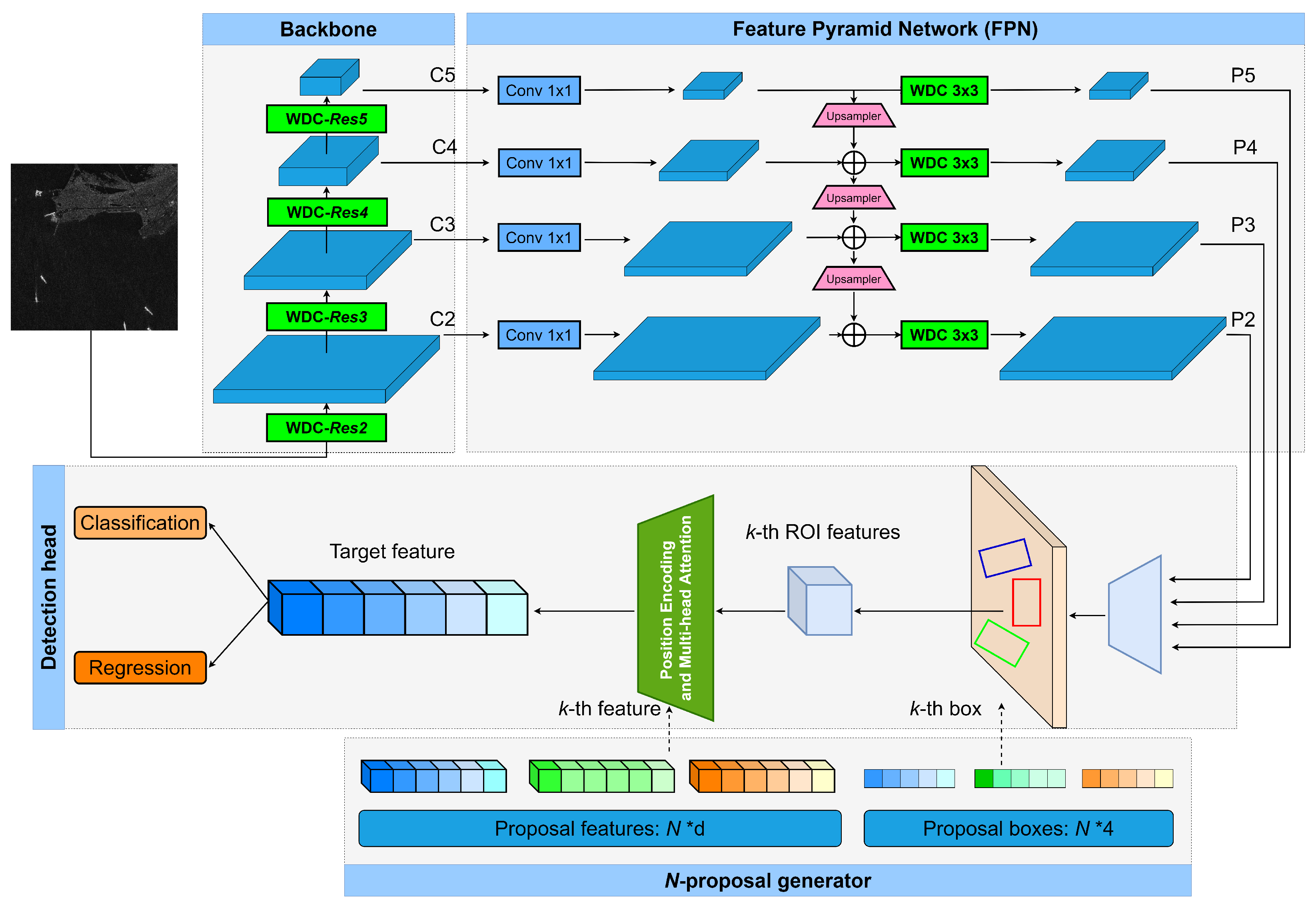
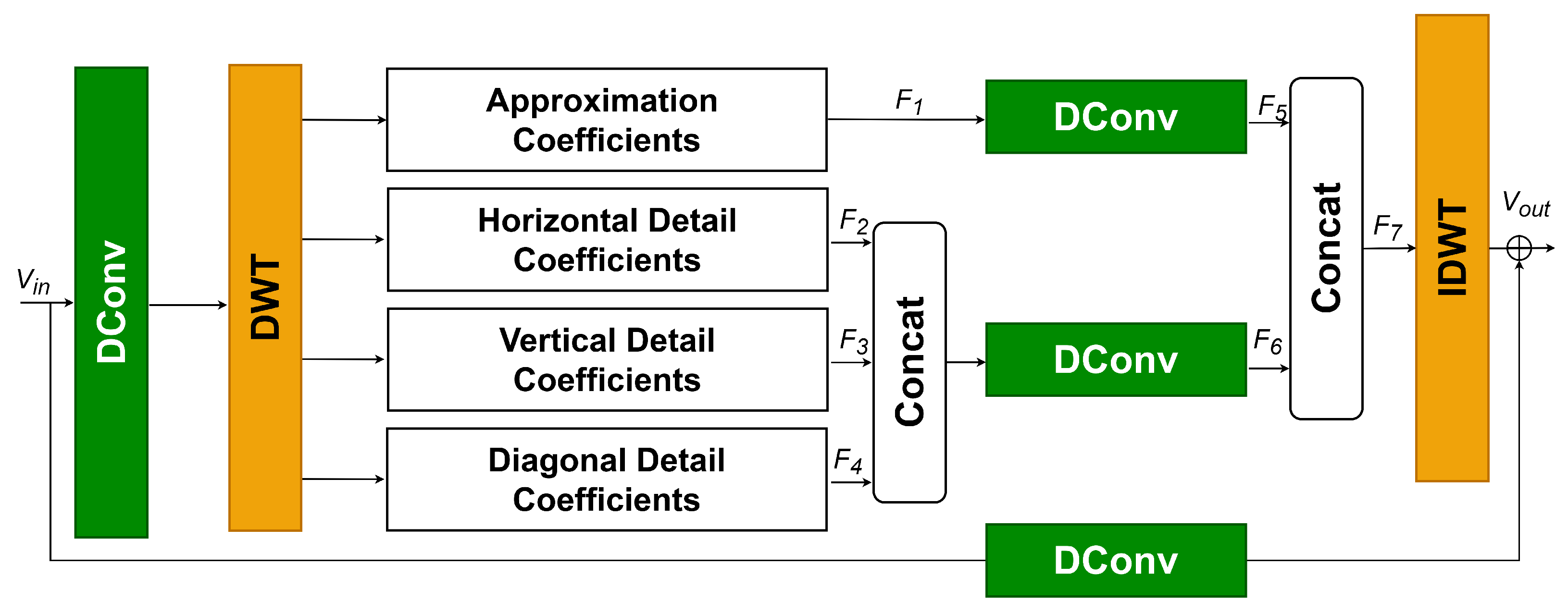
- We propose a novel wavelet deformable convolution (WDC) module that extracts wavelet-domain information while capturing geometric transformations of multi-scale targets. Specifically, the WDC module applies discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to project input data into the wavelet domain, performs subband-based deformable convolution, and reconstructs features in the spatial domain using inverse DWT (IDWT).
- We introduce a position-encoded multi-head attention (PEMA) mechanism to replace the original dynamic convolution module. PEMA enables the model to focus more accurately on regions with spatial and semantic relevance to target areas, thereby improving discrimination of sparse targets.
- Extensive experiments on two public datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms baseline approaches. In particular, it achieves higher detection accuracy in challenging scenarios involving multi-scale targets, complex backgrounds, and sparse ship distributions.
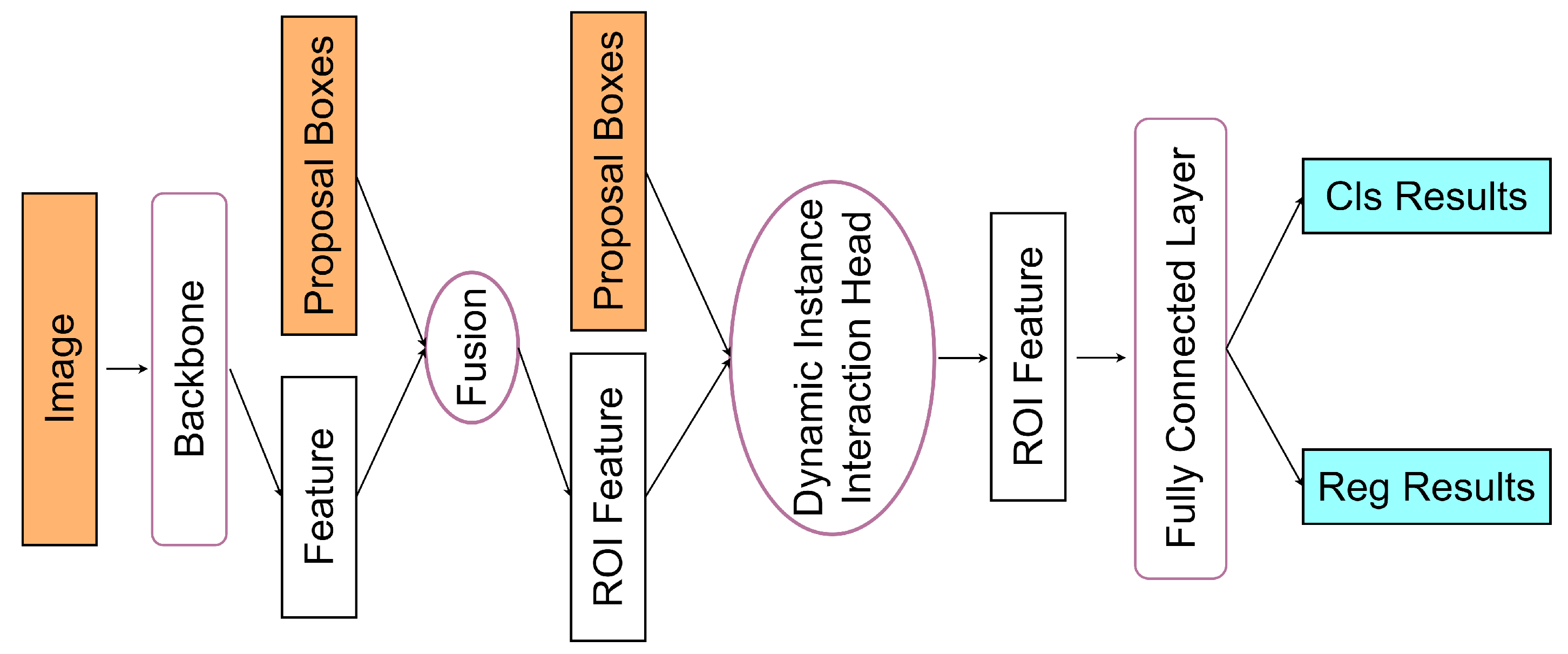
2. Overview of the Sparse R-CNN Framework
- Backbone and Feature Pyramid Network: The backbone (usually a ResNet) extracts hierarchical feature maps from the input image, while the FPN fuses multi-scale features through lateral connections and upsampling operations. This combination enables effective detection of objects with large scale variations.
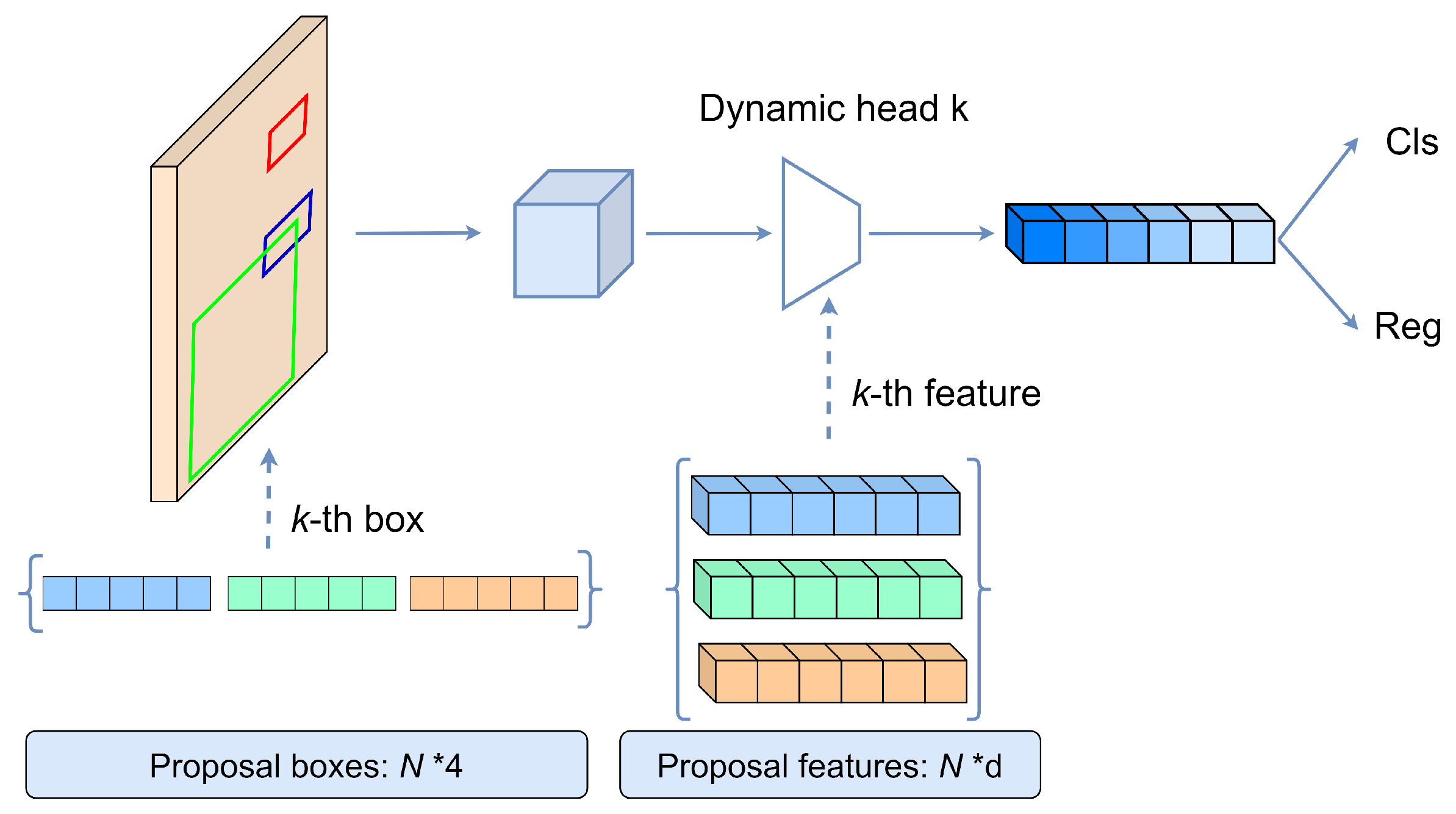
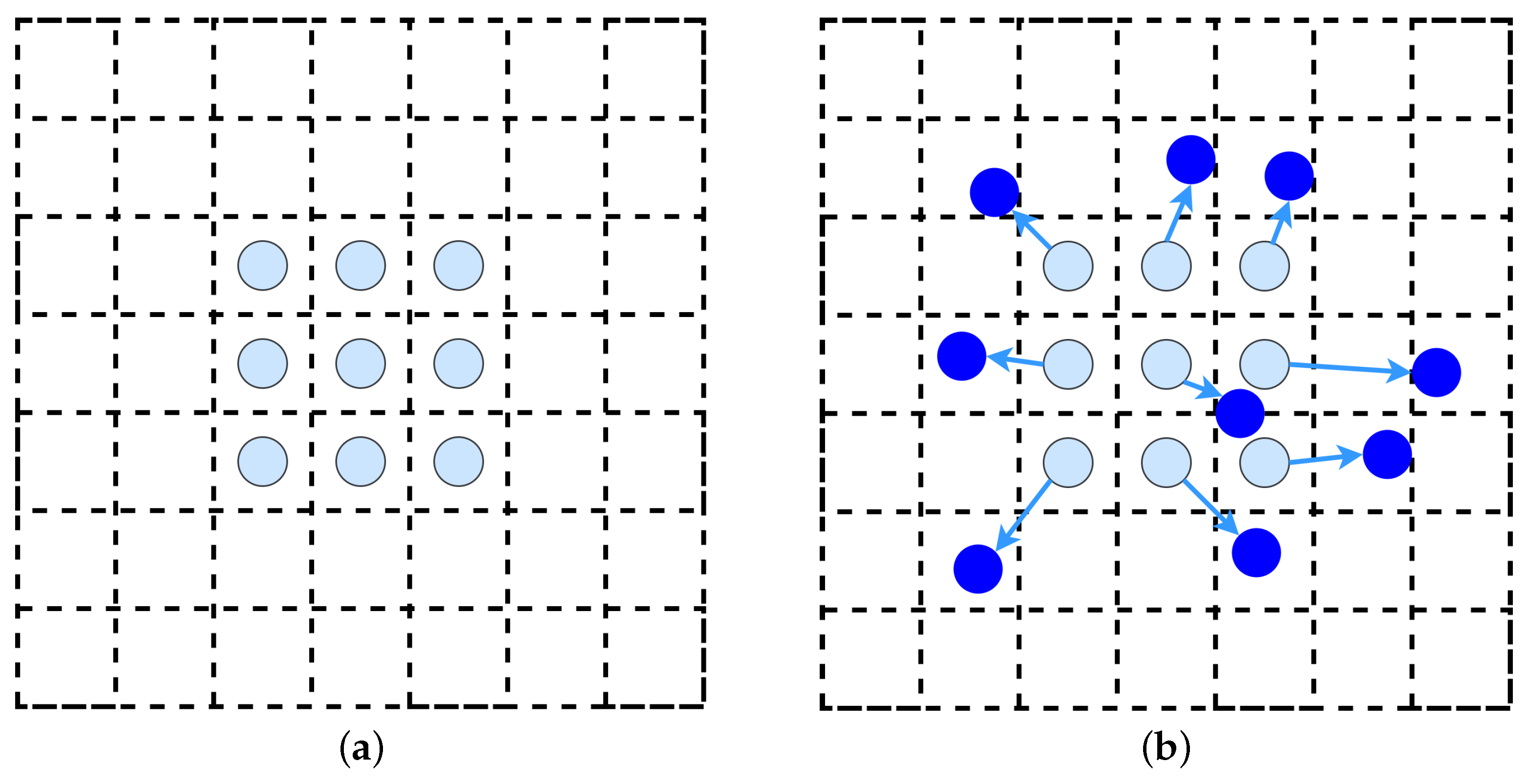
- Dynamic Instance Interaction Head: Each learnable proposal is associated with a proposal feature vector that encodes instance-specific information such as appearance, shape, and context. During training and inference, the proposal feature interacts dynamically with the region of interest (ROI) features through attention mechanisms. This dynamic interaction allows the network to refine both classification and bounding-box regression results iteratively.
- Set-Based Matching and Loss Function: Sparse R-CNN replaces the conventional dense assignment of anchors with Hungarian matching, which establishes a one-to-one correspondence between predicted and ground-truth boxes. This set-based supervision avoids duplicate predictions and simplifies label assignment.
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Wavelet Deformable Convolution
3.2. Position-Encoded Multi-Head Attention
3.2.1. Position Encoding Integrated into ROI Features
3.2.2. Multi-Head Attention-Based Feature Fusion
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
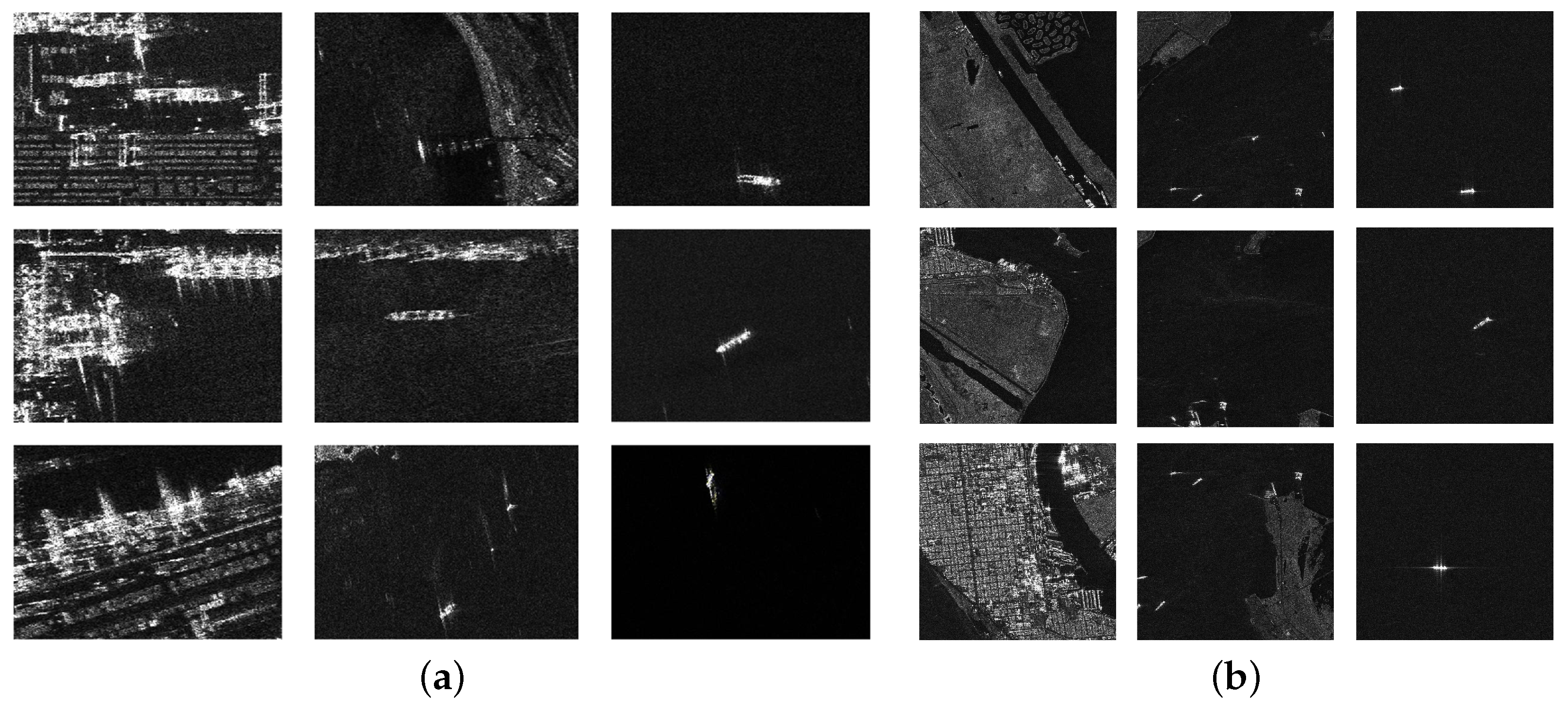
4.1.1. SAR Ship Detection Datasets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Settings
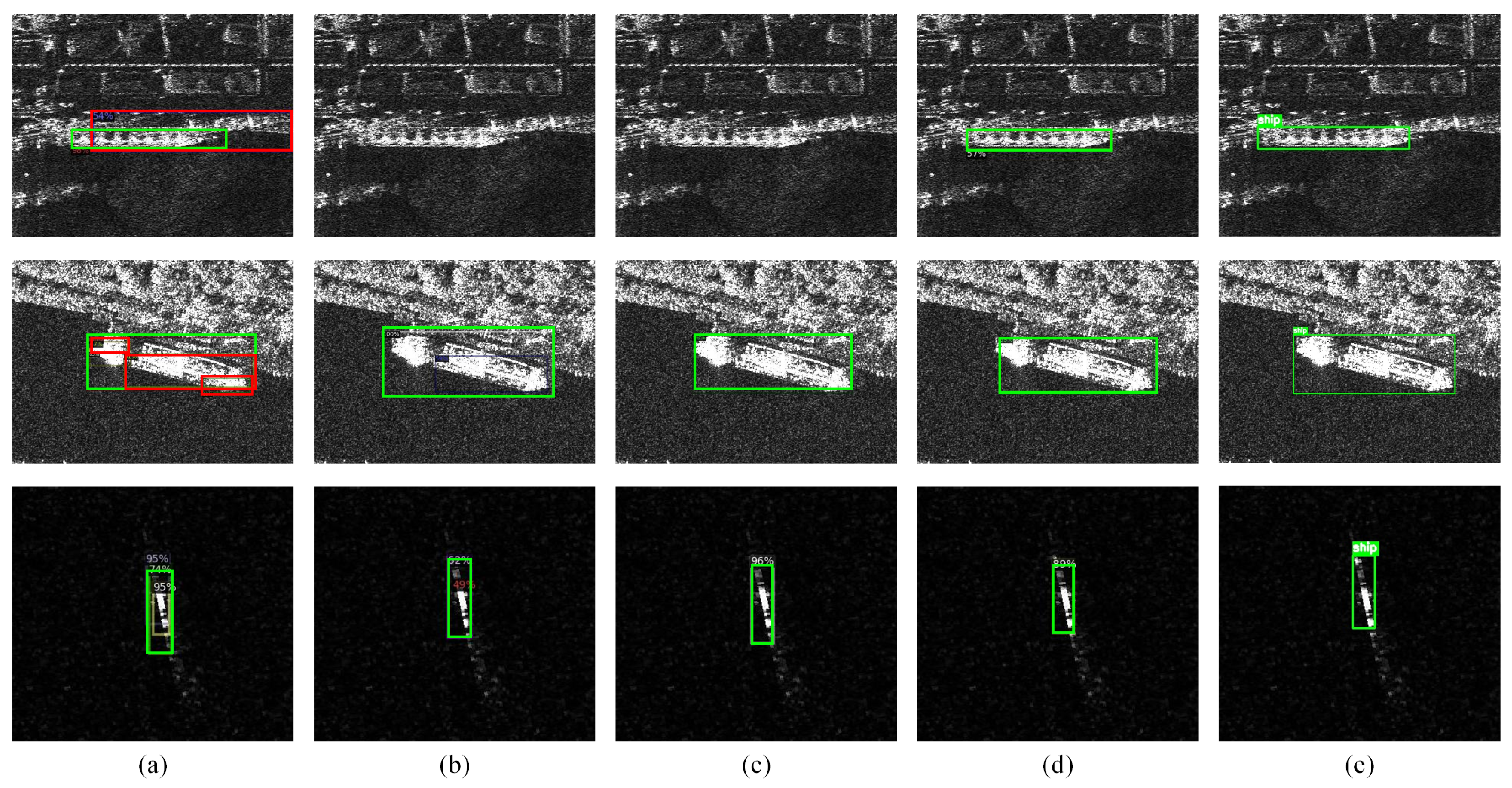
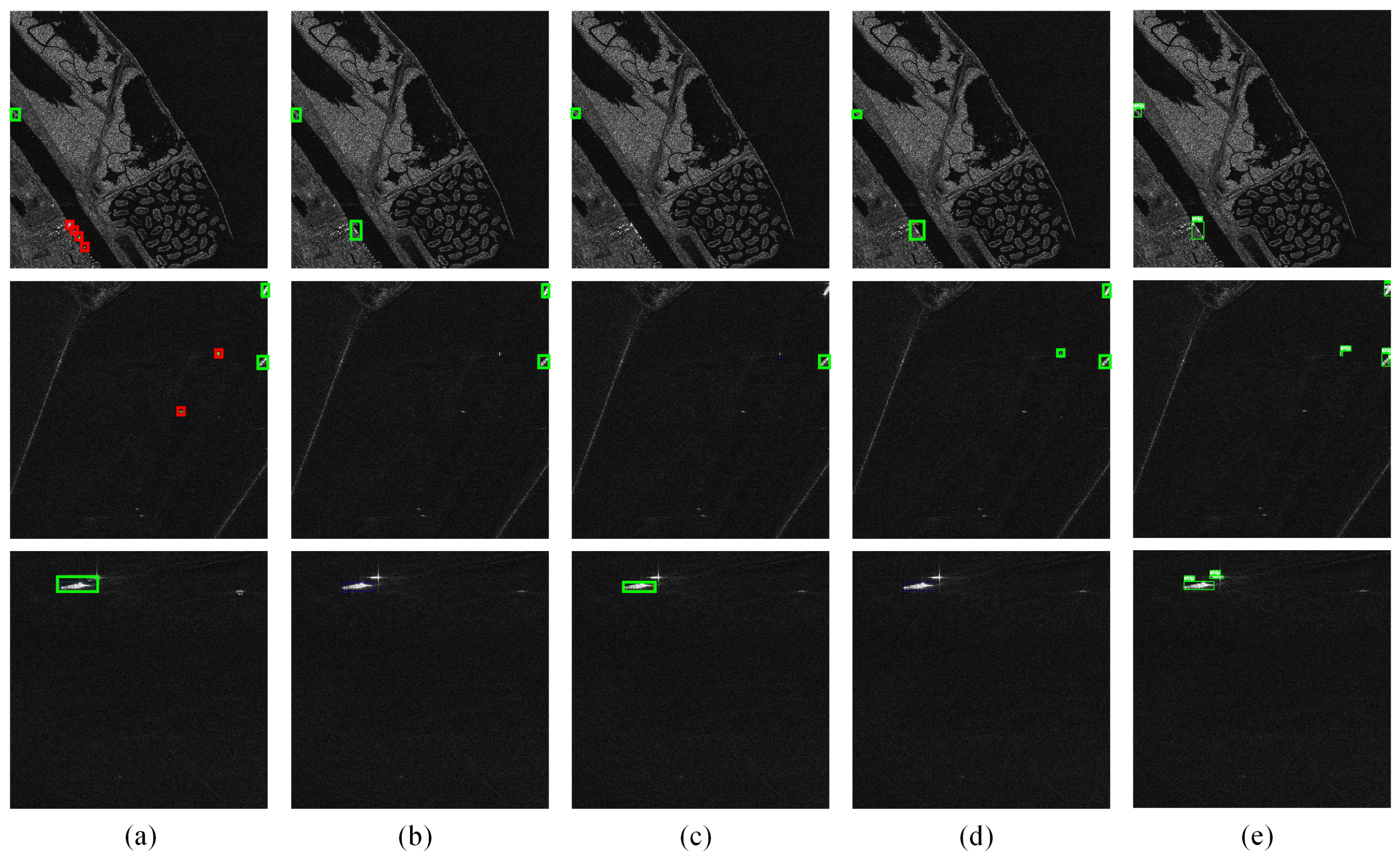
4.3. Performance Comparison with Reference Methods
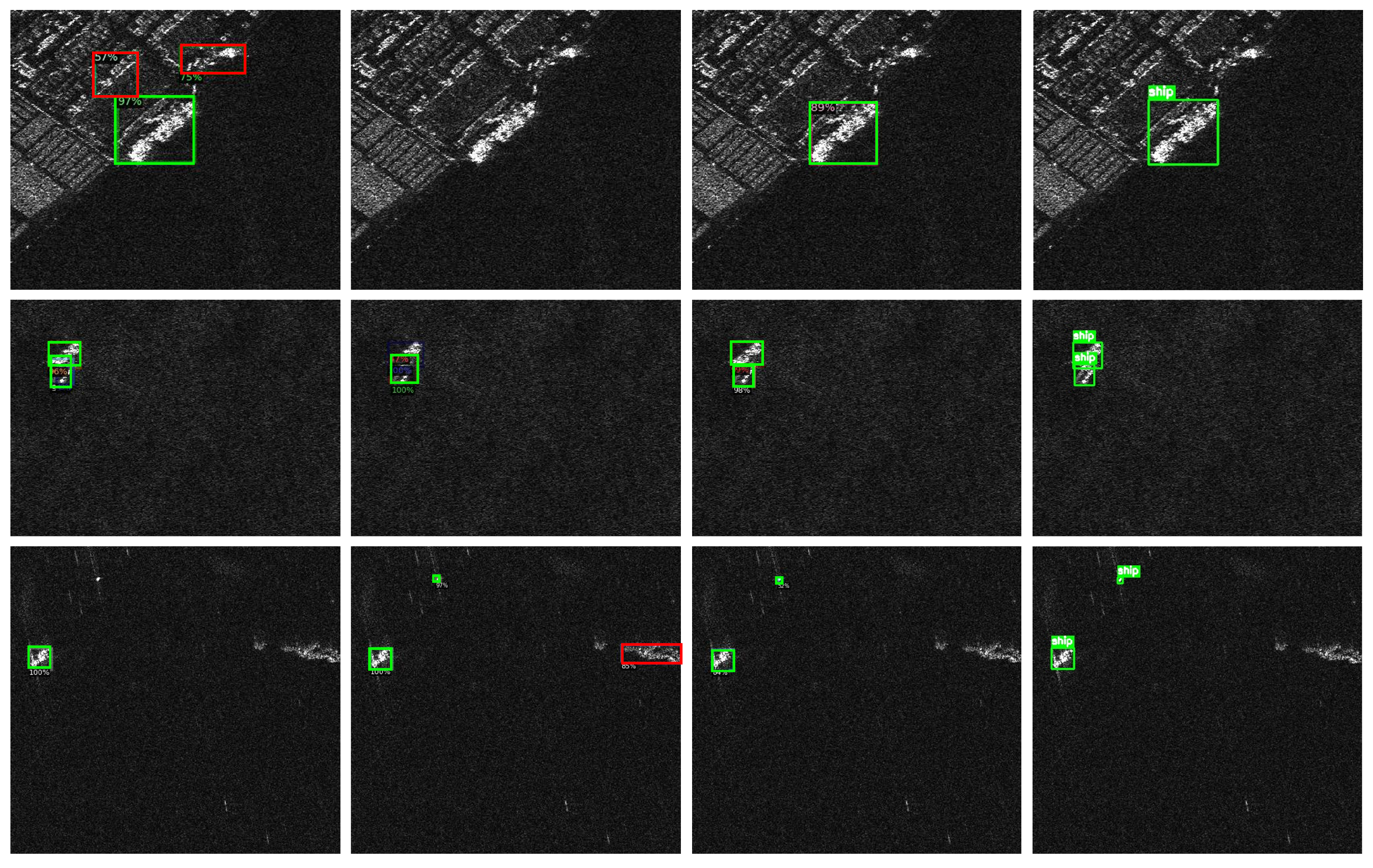
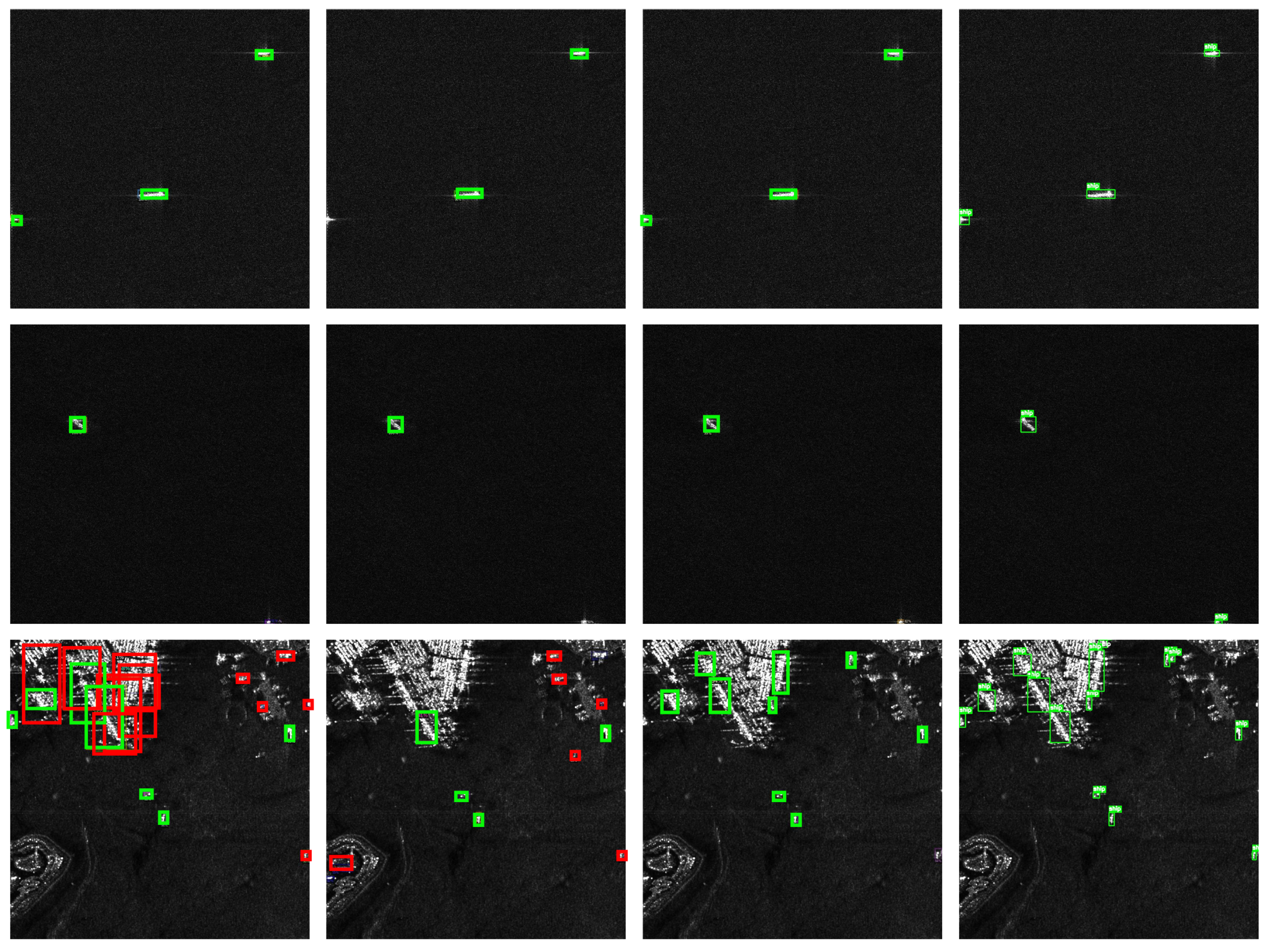
4.3.1. Comparative Experimental Results on SSDD
4.3.2. Comparative Experimental Results on HRSID
4.4. Ablation Study
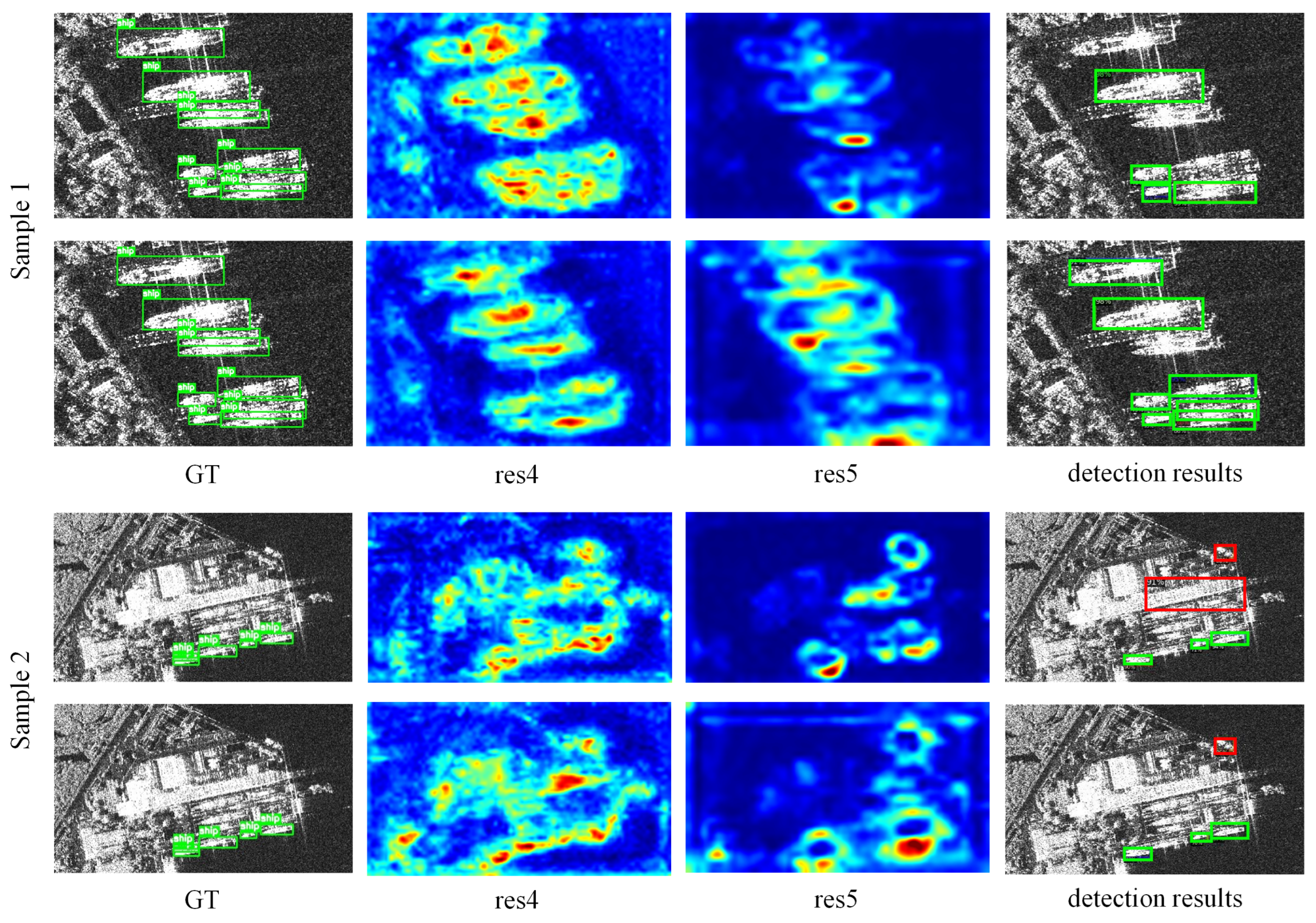
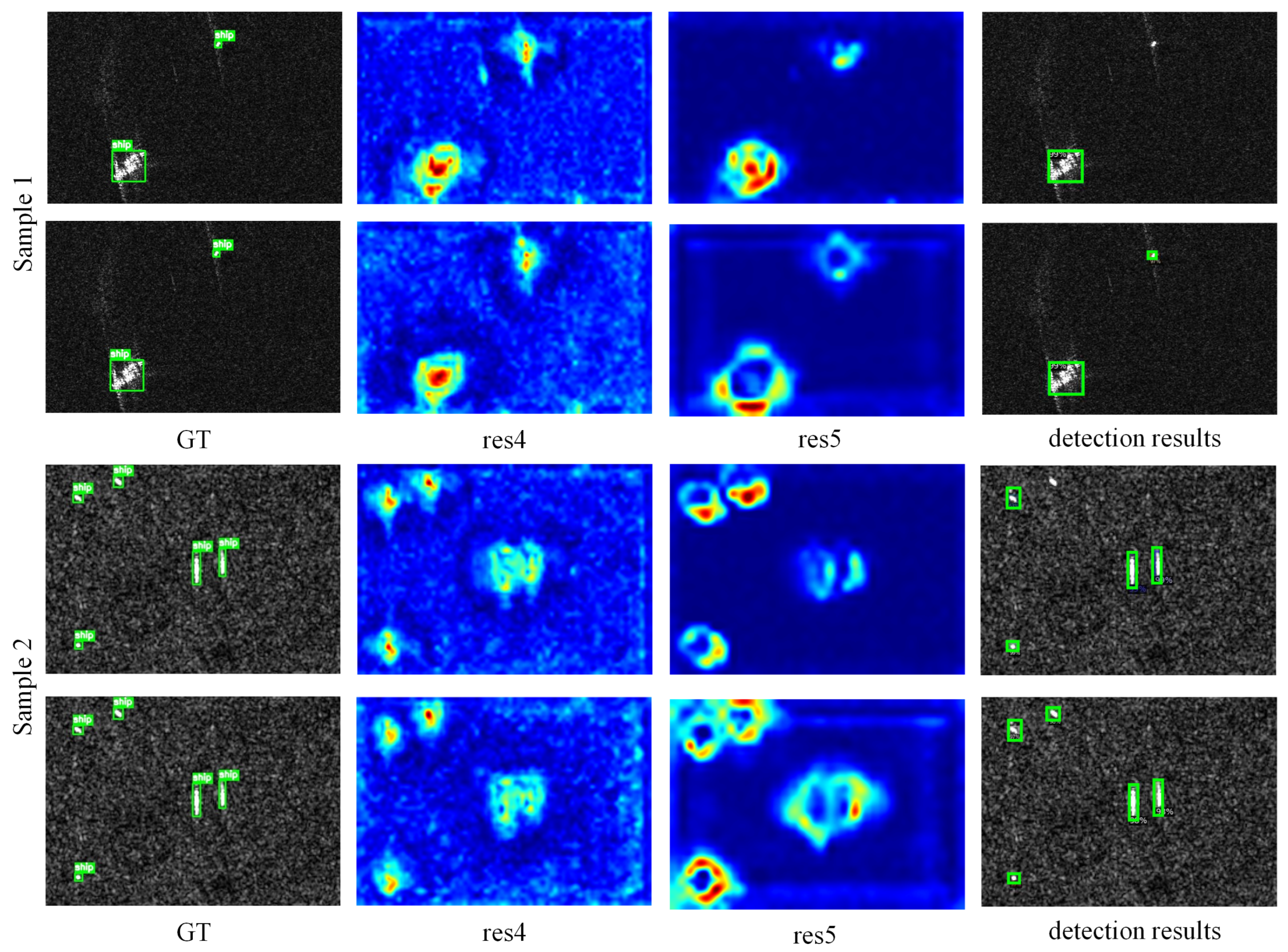
4.5. Discussion on Sparse and Multi-Scale Ship Detection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, G.; Lang, H.; Liu, G.; Cao, C.; Song, Y.; Guan, Y.; Dai, Y. Development and application of ship detection and classification datasets: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 12, 12–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Gao, G.; Yang, J.; Marino, A. CFAR ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on whitening filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 58–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Gao, G. A CFAR detection algorithm for generalized gamma distributed background in high-resolution SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 806–810. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X. CFAR-DP-FW: A CFAR-guided dual-polarization fusion framework for large-scene SAR ship detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 7242–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.D.; Cui, X.C.; Chen, S.W. Adaptive superpixel-level CFAR detector for SAR inshore dense ship detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4010405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ji, J.; Li, X.; Yu, W.; Xiong, H. Ship detection from PolSAR imagery using the complete polarimetric covariance difference matrix. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2824–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. PolSAR Ship Detection Based on Superpixel-Level Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4008805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Quan, S.; Xing, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Meng, W. PSO-based fine polarimetric decomposition for ship scattering characterization. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 220, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ji, K.; Zou, H.; Chen, W.; Sun, J. Ship classification in TerraSAR-X images with feature space based sparse representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Song, S.; Yang, J. Ship classification based on MSHOG feature and task-driven dictionary learning with structured incoherent constraints in SAR images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Yin, J.; Yang, J. Ship detection for PolSAR images via task-driven discriminative dictionary learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B. Ship detection in synthetic aperture radar imagery based on discriminative dictionary learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 26–29 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Jin, K.; Zeng, L.; Yang, J. Ship detection with superpixel-level Fisher vector in high-resolution SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Plaza, A.; He, Y. Ship detection in SAR images via enhanced nonnegative sparse locality-representation of Fisher vectors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9424–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. A patch-to-pixel convolutional neural network for small ship detection with PolSAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6623–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Gong, S.; Xing, M. CANet: An unsupervised deep convolutional neural network for efficient cluster-analysis-based multibaseline InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5212315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Lan, Y.; Xing, M. Deep learning-based branch-cut method for InSAR two-dimensional phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5209615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mei, S.; Ma, M.; Han, Z. Adaptive composite feature generation for object detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5631716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, F.; Yu, W. VLF-SAR: A Novel Vision-Language Framework for Few-shot SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 9530–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, K.; Song, X.; Shen, Y.; Liu, S. Weighted pseudo-labels and bounding boxes for semisupervised SAR target detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 5193–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Shao, J. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, W. R-CNN-based ship detection from high resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yin, C.; Wang, D.; Han, W. Fast ship detection combining visual saliency and a cascade CNN in SAR images. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.Q. A lightweight faster R-CNN for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 4006105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Nie, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X. Enhanced cascade R-CNN for multiscale object detection in dense scenes from SAR images. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 20143–20153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Fan, H.; Du, B.; Liu, S. Mask R-CNN for object detection in multitemporal SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (MultiTemp), Shanghai, China, 5–7 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X. Quad-FPN: A novel quad feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Z. Deform-FPN: A novel FPN with deformable convolution for multi-scale SAR ship detection. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 5273–5276. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Ye, W.; Li, J.; Ran, D. Small ship detection in SAR images based on modified SSD. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wei, S. Automatic ship detection based on RetinaNet using multi-resolution Gaofen-3 imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, T.; Zeng, H.; Yang, W.; Chu, B.; Zou, F.; Ren, W.; Chen, J. An improved lightweight RetinaNet for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhu, M.; He, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, G. Ship detection with SAR based on YOLO. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1647–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.M.; Yunze, C. Ship detection in SAR Image using YOLOv2. In Proceedings of the 2018 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Wuhan, China, 25–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 9495–9499. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Yang, T.; Tong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, R.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, S. Multi-scale ship detection from SAR and optical imagery via a more accurate YOLOv3. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6083–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Fu, X.; Qin, R.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z. High-speed lightweight ship detection algorithm based on YOLO-v4 for three-channels RGB SAR image. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shin, Y. SAR ship detection based on improved YOLOv5 and BiFPN. ICT Express 2024, 10, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y. CSS-YOLO: A SAR Image Ship Detection Method for Complex Scenes. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 20636–20654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Wen, G.; Tan, Y.; Shi, C. SHIP-YOLO: A lightweight synthetic aperture radar ship detection model based on YOLOv8n algorithm. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 37030–37041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. SAR Small Ship Detection Based on Enhanced YOLO Network. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, P. LHSDNet: A Lightweight and High-Accuracy SAR Ship Object Detection Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Han, M.; Liao, G.; Yang, L.; Shao, R.; Li, Y. SFFNet: A ship detection method using scattering feature fusion for sea surface SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4018305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, S. Scattering information fusion network for oriented ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4013105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Duan, D. Scattering characteristic-aware fully polarized SAR ship detection network based on a four-component decomposition model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5222722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Wei, Y.; Chai, S. Study on ship Kelvin wake detection in numerically simulated SAR images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qi, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Identifiability of Kelvin wakes in SAR imageries: The role of time-varying characteristics and decoherence effect of wake. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 20197–20213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Yang, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Ni, K.; Zhou, Q. Towards real-time detection of ships and wakes with lightweight deep learning model in Gaofen-3 SAR images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Fu, X.; Dong, J.; Yang, H.; Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Martorella, M. Recent Advances in Deep Learning Based SAR Image Targets Detection and Recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 6884–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, J. Inshore ship detection based on convolutional neural network in optical satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4005–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K. Oriented ship detection based on strong scattering points network in large-scale SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5218018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Chen, F.; Cheng, M.; Lou, S.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Ship detection using a fully convolutional network with compact polarimetric SAR images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Hong, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 20881–20892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, F.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, F. A sidelobe-aware small ship detection network for synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5205516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Min, R.; Cui, Z.; Pi, Y.; Xu, Z. Multiscale ship detection based on dense attention pyramid network in SAR images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xia, R.; Wu, B.; Sun, L.; Yao, B.; Liu, X.; Xing, M. AFSar: An anchor-free SAR target detection algorithm based on multiscale enhancement representation learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5219514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; An, W.; Li, S.; Wei, G.; Zou, B. An improved FCOS method for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8910–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, G. An oriented ship detection method of remote sensing image with contextual global attention mechanism and lightweight task-specific context decoupling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4200918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Sparse r-cnn: End-to-end object detection with learnable proposals. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14454–14463. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wu, F.; Xu, J.; Gao, G.; Ge, Q.; Jing, X.Y. Adaptive deformable convolutional network. Neurocomputing 2021, 453, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liang, J.; Fang, Z.; Han, J.; Liang, F.; Zhang, G. Weconvene: Learned image compression with wavelet-domain convolution and entropy model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, N.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J. Ship detection in large-scale SAR images via spatial shuffle-group enhance attention. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2738–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, P.; Ebrahimi, T. Learning-Based Image Compression using Convolutional Autoencoder and Wavelet Decomposition. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Iliopoulou, S.; Tsinganos, P.; Ampeliotis, D.; Skodras, A. Learned Image Compression with Wavelet Preprocessing for Low Bit Rates. In Proceedings of the 2023 24th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Rhodes, Greece, 11–13 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Dai, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Hu, X.; Lu, T.; Lu, L.; Li, H.; et al. Internimage: Exploring large-scale vision foundation models with deformable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 14408–14419. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhai, G.; Chen, J. Dehazedct: Towards effective non-homogeneous dehazing via deformable convolutional transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 6405–6414. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Centernet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 6569–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: A simple and strong anchor-free object detector. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test Methods | AP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 59.7 | 94.5 | 68.7 | 55.9 | 66.7 | 48.2 |
| Cascade R-CNN | 60.4 | 93.8 | 68.3 | 55.5 | 67.8 | 58.5 |
| Mask R-CNN | 59.6 | 94.1 | 67.3 | 56.0 | 65.6 | 50.3 |
| RetinaNet | 56.3 | 91.0 | 62.9 | 51.9 | 63.3 | 46.1 |
| YOLOv5s | 73.5 | 98.3 | 80.0 | 66.8 | 74.9 | 67.6 |
| YOLOv8s | 74.7 | 98.2 | 82.6 | 66.9 | 75.7 | 73.1 |
| YOLOv9s | 74.2 | 98.4 | 86.7 | 66.7 | 76.3 | 70.8 |
| YOLOv11s | 74.0 | 98.3 | 85.5 | 66.6 | 74.6 | 73.8 |
| CSS-YOLO | 73.0 | 98.6 | 87.2 | 65.9 | 73.6 | 65.5 |
| Sparse R-CNN | 70.8 | 95.9 | 86.6 | 69.1 | 76.8 | 66.7 |
| Proposed | 74.5 | 98.7 | 89.9 | 73.4 | 80.5 | 70.8 |
| Test Methods | AP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 63.5 | 86.8 | 73.3 | 64.4 | 65.1 | 16.4 |
| Cascade R-CNN | 66.6 | 87.9 | 76.4 | 67.6 | 67.7 | 28.8 |
| Mask R-CNN | 65.0 | 88.0 | 75.2 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 17.3 |
| LHSDNet | 60.7 | 87.0 | 70.3 | 60.9 | 69.1 | 12.1 |
| RetinaNet | 60.0 | 84.8 | 67.2 | 60.9 | 60.9 | 26.8 |
| YOLOv5n | 61.7 | 86.3 | 71.6 | 61.3 | 69.1 | 8.3 |
| YOLOv8n | 62.7 | 87.7 | 73.0 | 62.1 | 71.3 | 11.5 |
| YOLOv10n | 58.8 | 83.7 | 66.8 | 59.2 | 61.7 | 7.4 |
| YOLOv11n | 61.7 | 86.3 | 67.9 | 60.9 | 69.9 | 9.0 |
| SHIP-YOLO | 61.3 | 86.0 | 71.5 | 62.5 | 70.2 | 7.7 |
| Enhanced YOLOv8 | 63.4 | 88.4 | 72.7 | 62.9 | 72.4 | 15.4 |
| CenterNet | 56.8 | 85.7 | 64.1 | 57.7 | 35.2 | 14.4 |
| FCOS | 41.5 | 69.9 | 50.2 | 43.0 | 7.6 | 2.8 |
| Sparse R-CNN | 66.5 | 88.6 | 77.4 | 67.5 | 67.7 | 49.1 |
| Proposed | 68.7 | 90.5 | 79.7 | 69.9 | 68.8 | 55.2 |
| WDC | PEMA | AP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sparse R-CNN | ✗ | ✗ | 70.8 | 95.9 | 86.6 | 69.1 | 76.8 | 66.7 |
| Sparse R-CNN + WDC | ✔ | ✗ | 73.9 | 97.4 | 89.8 | 72.1 | 80.3 | 69.9 |
| Sparse R-CNN + PEMA | ✗ | ✔ | 72.2 | 96.6 | 87.8 | 70.4 | 78.6 | 67.6 |
| Proposed | ✔ | ✔ | 74.5 | 98.7 | 89.9 | 73.4 | 80.5 | 70.8 |
| WDC | PEMA | AP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sparse R-CNN | ✗ | ✗ | 66.5 | 88.6 | 77.4 | 67.5 | 67.7 | 49.1 |
| Sparse R-CNN + WDC | ✔ | ✗ | 67.8 | 89.7 | 78.9 | 68.9 | 68.2 | 51.9 |
| Sparse R-CNN + PEMA | ✗ | ✔ | 67.4 | 89.3 | 78.5 | 68.6 | 68.0 | 52.3 |
| Proposed | ✔ | ✔ | 68.7 | 90.5 | 79.7 | 69.9 | 68.8 | 55.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yin, J.; Lin, H. Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Sparse R-CNN with Wavelet Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233794
Zeng Z, Chen Z, Yin J, Lin H. Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Sparse R-CNN with Wavelet Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233794
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Zhiqiang, Zongsi Chen, Junjun Yin, and Huiping Lin. 2025. "Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Sparse R-CNN with Wavelet Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233794
APA StyleZeng, Z., Chen, Z., Yin, J., & Lin, H. (2025). Ship Detection in SAR Images Using Sparse R-CNN with Wavelet Deformable Convolution and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233794







