Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Integrating GNSS and LEO observations can significantly reduce the convergence time and improve the precision of time links.
- Using 1 s observations, the time link errors can converge to 1 ns within 1 min.
What are the implications of the main findings?
- With LEO augmentation, time links can achieve high precision with less time.
- Not only fast, but also high-performance time links can be achieved with LEO augmentation.
Abstract
GNSS Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technology has been applied to the time transfer for a long time, enabling time synchronization between two arbitrary stations on a global scale. Over the past decade, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations have been developed to enhance GNSS, offering rapid geometry configuration variations that can accelerate PPP convergence and enhance the time link performance. In this contribution, LEO observations are integrated into GNSS to enhance the real-time PPP time transfer. Simulated LEO constellations with varying numbers of satellites are used to assess their impact on real-time PPP time transfer performance. One week of observation data from 11 globally distributed stations is used to generate 10 time links, and five experimental schemes are designed: (1) GPS/BDS-3/Galileo solution (GCE), (2) GCE with 120 LEO satellites (GCE+120L), (3) GCE with 180 LEO satellites (GCE+180L), (4) GCE with 240 LEO satellites (GCE+240L), and (5) GCE with 300 LEO satellites (GCE+300L). Results showed that compared to the GCE solution, integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites increases the average number of observed satellites from 23.4 to 30.6, 34.1, 37.7, and 41.3, respectively, while reducing Time Dilution of Precision (TDOP) values from 0.547 to 0.424, 0.391, 0.363, and 0.342, respectively. Using 30 s observations, the average convergence time to STD of time link errors better than 0.1 ns is reduced from 7.95 to 5.94, 4.83, 4.46, and 4.45 min in static mode, with improvements of 25.3%, 39.2%, 43.9%, and 44.0%, respectively, and from 8.75 to 6.18, 5.17, 4.89, and 4.72 min in kinematic mode, with improvements of 29.3%, 40.8%, 44.1%, and 46.0%, respectively. Using 1 s observations, Scenarios GCE+120L, GCE+180L, GCE+240L, and GCE+300L can achieve 1 ns convergence within 1 min. The time link precision was also found to be significantly improved, i.e., from 0.337 to 0.243 ns in static mode with improvements of 27.9%, and from 0.377 to 0.253 ns in kinematic mode with improvements of 32.9%. The time link stability is significantly enhanced for averaging times between 60 and 20,000 s in both static and kinematic modes, with a maximum improvement of nearly 50%. These results have demonstrated that integrating LEO satellites can significantly enhance real-time PPP time transfer performance.
1. Introduction
Time transfer is the transmission of high-precision time information between two or more locations, enabling clocks in different sites to achieve time synchronization [1]. Precise time transfer is essential for various fields, such as communication networks and power transmission [2].
GPS Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technology has been utilized by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) for International Atomic Time (TAI) comparison since 2008 [3] due to its high precision, low cost, and global scale coverage. Multi-GNSS observations were afterward incorporated into time transfer to enhance redundancy and robustness [4,5]. Despite the convenience brought by PPP time transfer, the large altitude difference (about 20,000 km or more) between the GNSS Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites and the ground stations results in slow satellite geometry changes and strong temporal correlations in estimated parameters. Consequently, PPP time transfer requires nearly 10 min (or more) to converge [6], during which the time link stability is degraded. This is especially crucial for kinematic PPP time transfer.
In recent years, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) navigation satellite constellations have been widely developed [7], such as Xona Space [8], Centispace [9], and Geely [10]. Some LEO satellites will broadcast GNSS-like navigation signals to ground users, enabling LEO-enhanced GNSS ground Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) services. The LEO satellite orbit altitude is about 400–1500 km [11]. The lower altitudes compared to those of GNSS satellites imply faster motion and geometry change, which also helps to decrease the correlation among the estimated parameters between adjacent epochs and shorten the convergence time.
Simulated LEO constellations have been investigated for augmenting Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) [12], GNSS PPP [13], PPP-Ambiguity Resolution (AR) [14], and PPP-RTK [15]. Compared to the multi-GNSS solutions, the convergence time, the positioning accuracy, and the Time To First Fix (TTFF) in AR are remarkably improved after using LEO-enhanced GNSS. Real LEO observations from CENTISPACETM LEO mission [16,17] have been used for LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP, confirming both the improved convergence time and positioning performance.
In the PPP time transfer, the receiver clocks are simultaneously estimated with the station coordinates. The LEO-enhanced GPS PPP time transfer was investigated by Liu et al. [6], in which one-day observation data with 160 LEO satellites in fixed station mode was used, showing that the short-term stability and the convergence time can be improved. Nowadays, the fixed station coordinates mode is not sufficient considering applications in kinematic scenarios, such as autonomous driving. The LEO enhancement in time transfer is worthwhile to investigate in multi-GNSS cases under both static and kinematic scenarios across multiple days, with varying LEO constellation sizes, considering the different phases of the constellation development. The performance of LEO-enhanced PPP time transfer under different observation sampling intervals, e.g., 30 s and 1 s, can also be compared.
This contribution focuses on LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer. One week of observation data from 11 Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) stations [18] were selected to generate 10 time links, and the LEO constellations with 120, 180, 240, and 300 satellites were simulated and used to conduct the experiments. After this introduction, the LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer methods are introduced. Next, the LEO constellation simulation, data and processing strategies are presented. Thereafter, the performance of LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP time transfer is evaluated in terms of the number of satellites and Time Dilution of Precision (TDOP), convergence time, time link precision and stability in both the static and kinematic scenarios. Finally, the conclusion is provided.
2. Methods
This section first introduces the time transfer model based on multi-GNSS PPP. The LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP model is then presented. The time transfer method is given at the end.
2.1. Multi-GNSS-Based PPP Model
The dual-frequency Ionospheric-Free (IF) observation equations from a GNSS satellite to receiver for system (GPS, BDS-3, Galileo) can be expressed as:
where and represents the code and carrier phase IF observations, respectively. is the geometric distance between the GNSS satellite and the receiver. denotes the speed of light. and are the receiver and satellite clocks containing the corresponding IF code biases [19], respectively. is the slant troposphere delay, and is the IF wavelength. is the IF combined ambiguity in cycles, the carrier phase and code delay on the satellite and receiver end were absorbed by ambiguity [20]. and represent the measurement noise for code and carrier phase observations, respectively. The antenna Phase Center Offsets (PCOs) and Variations (PCVs) on the satellite and receiver end, the relativistic effects, the tidal loadings, and the phase windup were corrected using the existing models in Equations (1) and (2) [21]. Note that in addition to the traditional IF form, the PPP can also be formed in the Undifferenced and Uncombined (UDUC) form [22].
The observation equations can be transformed into error equations for PPP, expressed as:
where and indicate the code and phase IF combination, respectively. and represent the posterior and the Observed-Minus-Computed (OMC) terms, respectively. is the unit direction vector from the satellite to the receiver. is the vector of the coordinate increments relative to their a priori positions. is the estimated receiver clock, and are the tropospheric mapping function, and the estimated Zenith Wet Delay (ZWD) of the troposphere.
By integrating GPS, BDS-3, and Galileo observations, the multi-GNSS-based PPP models can be formed and expressed as:
where and stand for the Inter-System Biases (ISB) between GPS and BDS, and between GPS and Galileo, respectively.
2.2. LEO-Enhanced Multi-GNSS PPP Model
The LEO observations are integrated into the multi-GNSS observations to enhance the PPP time transfer, which can be expressed as:
where indicates the observations from LEO satellites. is the estimated receiver ISB between GPS and LEO signals. The estimated parameters can be expressed:
2.3. Time Transfer Method
The estimated receiver clock is used to conduct precise time transfer. The time difference between the receiver clocks of two stations can be expressed as [23]:
where and are the estimated receiver clocks at stations A and B, and represents the time reference, which depends on the GNSS satellite clocks used in the PPP. The time reference of and is the same because the same satellite clocks were applied when estimating the receiver clocks.
3. Data and Processing Strategies
This section first introduces the simulation of the LEO satellite constellations to be used in the processing. The experimental settings are then briefly explained.
3.1. LEO Satellite Constellations
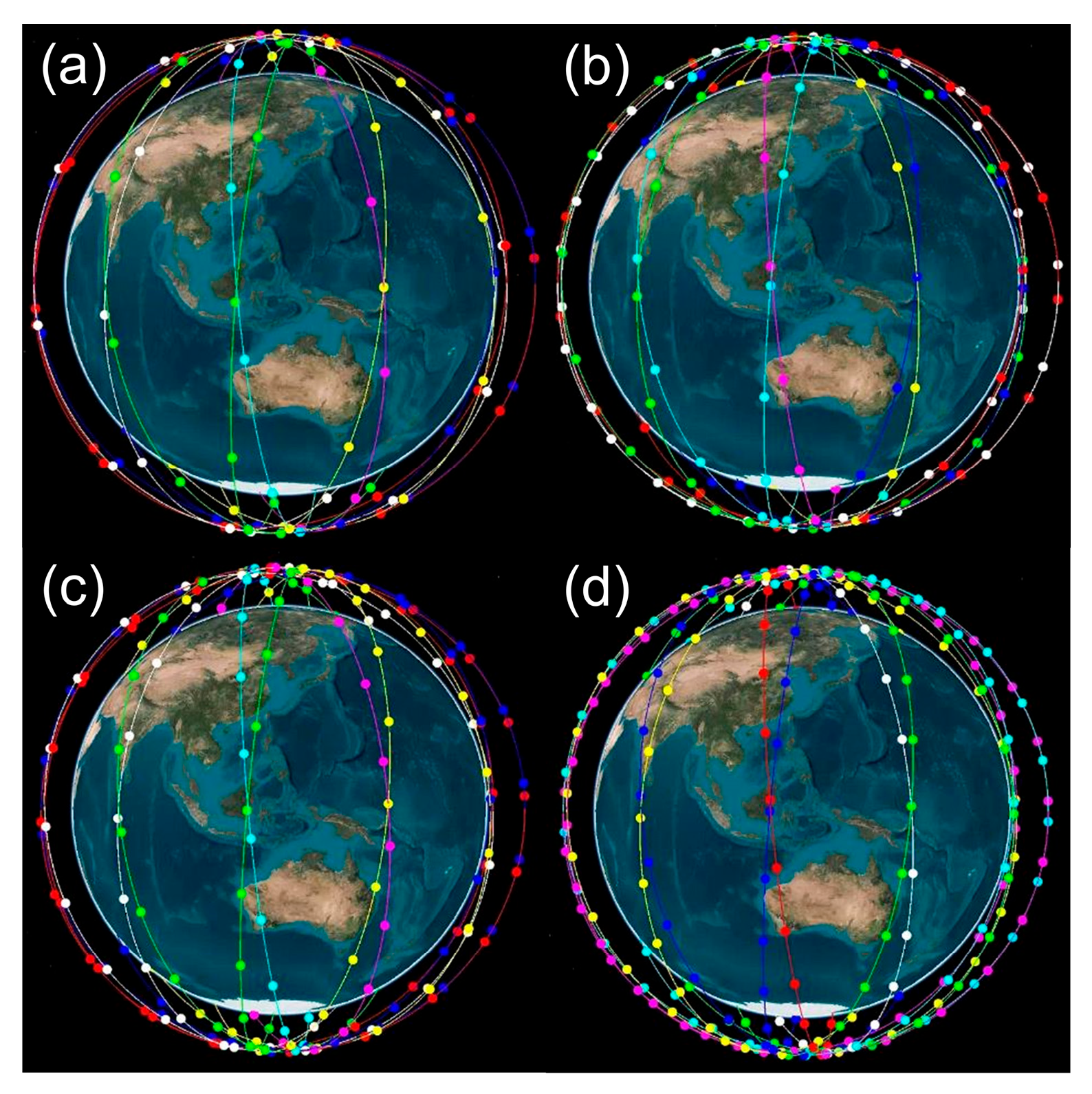
Due to the limited availability of public LEO satellite navigation signals, navigation signals from LEO satellites are simulated for the PPP processing. The Walker constellation is applied in this contribution due to the uniform coverage of its geometric distribution to the Earth [24,25]. As shown in Figure 1, the Walker constellations 120/12/1, 180/12/1, 240/12/1, and 300/12/1 are to be used, with the number of LEO satellites amounting to 120, 180, 240, and 300, respectively. The satellite orbits have an altitude of 1175 km and an inclination of 85° [24,25]. In this study, only the near-polar orbit configuration is employed to simulate a relatively conservative situation at the beginning phase of the LEO constellation development, while adding more LEO satellites with inclined orbits should further improve the overall geometry for the LEO PNT services.
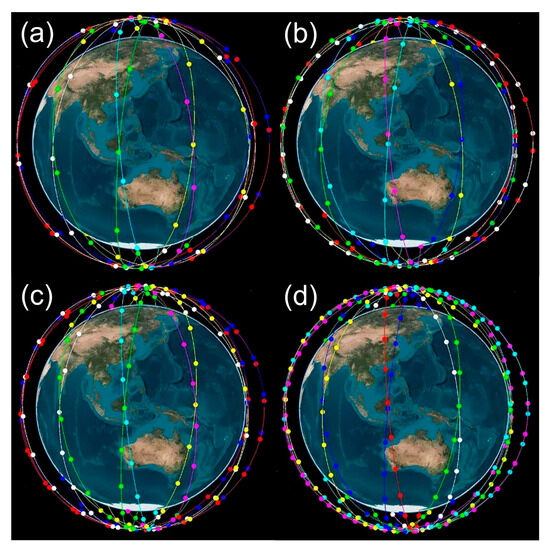
Figure 1.
Simulated LEO satellite constellations with 120 (a), 180 (b), 240 (c), and 300 satellites (d).
The initial orbits of the LEO satellites are calculated using the six Keplerian parameters, and the satellite orbits can then be numerically integrated to the desired time points. Because the variations in GNSS satellite clocks present nearly linear characteristics [26], the LEO satellite clocks are simulated using a linear model and random noise [27], which can be expressed as:
where is the LEO satellite clock at the epoch for satellite . , and represent the clock bias and clock drift for satellite , respectively. and indicate the time at epoch and reference epoch, respectively. is the random noise term with the Standard Deviation (STD) of 0.001 ns [28]. The real LEO satellite clocks contain other systematic effects as described in [29,30,31,32]. For LEO-enhanced PPP, however, only the differences between the simulated and the used ones (in the PPP), i.e., the real-time LEO satellite orbital/clock estimation errors, are of concern. Their influences on the PPP are investigated in detail in our other work [33], and are not further studied in this contribution.
For the observation simulations, the downlink signal frequencies are assumed to be the same as the BDS B1I (1575.42 MHz) and B3I (1268.52 MHz) [24,25], with a sampling of 30 s. The observation noise is set to 3 mm for the carrier phase and 0.3 m for the code observations. The relativistic effects [34,35], the phase windups [36], and the Earth rotation corrections are simulated using the existing models and are assumed to be corrected in the PPP processing. The PCOs and PCVs of the LEO satellite are set to 0 considering they are known and corrected. The ionospheric delay is simulated using the Global Ionosphere Map (GIM) provided by the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) [37]. The slant tropospheric delay consists of hydrostatic and wet components [38], both calculated using the Saastamoinen model [39] and the Global Mapping Function (GMF) [40]. The station coordinates are obtained from International GNSS Services (IGS) weekly solutions, and the receiver PCO and PCV for LEO signals are also set to 0. The receiver clocks are applied using values from European Space Agency Multi-GNSS (ESM) final products [41], with the ISBs between LEO and GPS signals set to zeros.
3.2. Experimental Settings
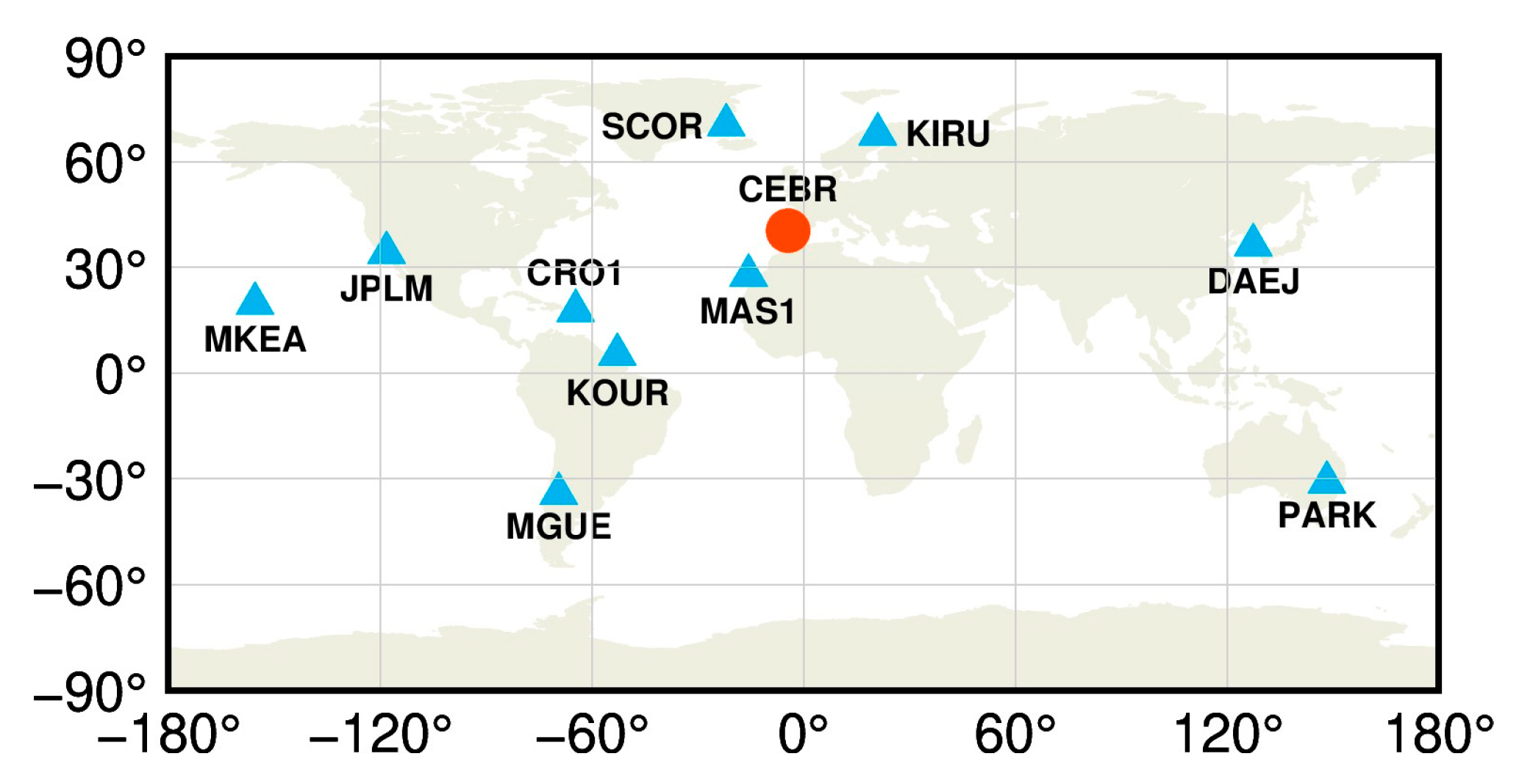
A total of 11 MGEX stations [18] were selected to perform the LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer experiments, as shown in Figure 2. The details of these stations are listed in Table 1, in which all stations are equipped with high-performance atomic clocks. The station CEBR, equipped with an external H-Maser, is selected as the central node (red dot in Figure 2), while the other stations (blue triangles in Figure 2) are used to conduct the time transfer experiments. The time link distance ranges from 1741.1 to 12,484.1 km, i.e., long to very long baselines.
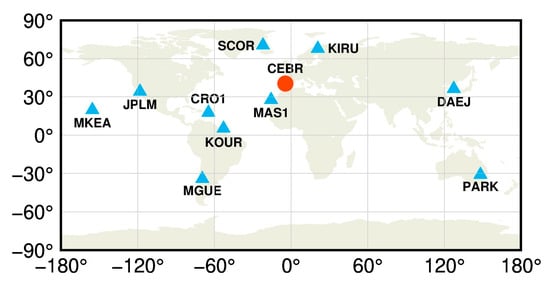
Figure 2.
Station distribution of the 11 MGEX stations used for the time transfer experiments.

Table 1.
Station information used for LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP real-time transfer.
Real GNSS and simulated LEO observations from DOY 119 to 125, 2024, were used. The dual-frequency signals from GPS L1/L2, BDS-3 B1I/B3I, Galileo E1/E5a, and LEO B1I/B3I, sampled at 30 s, were employed to generate the IF combination. Real-time GNSS satellite orbits and clocks released from the Centre national d’études spatiales (CNES) [42], and simulated LEO satellite orbits and clocks were applied and fixed. The GNSS satellite PCOs and PCVs were corrected using values from IGS antenna files, while the LEO satellite PCOs and PCVs were not corrected, as they are set to zeros in LEO signal simulations. Relativistic effects [34], phase-windup [36], and Earth rotation are calculated by applying the existing models as mentioned before. The tropospheric slant hydrostatic delay is corrected using the Saastamoinen model [39] and the GMF [40]. Receiver PCOs and PCVs were only corrected for GNSS observations, as those for LEO signals are simulated to be zeros. The Kalman filter [43,44] was used for estimating the parameters epoch-by-epoch, and the station coordinates were estimated as constants in the static mode [45] and white noise in the kinematic mode [45]. Both the receiver clocks and ISBs are estimated as white noise [46]. The variance setting is 60 × 60 m2 for both kinematic positioning and ISBs parameters. The ZWD is estimated using a random walk model with the process noise standard deviation of m [45]. Ambiguities were treated as constants unless a cycle slip or loss of lock occurred. The simulated LEO satellite orbits and clocks are directly used in the PPP, with their errors not considered in this study.
Five schemes were designed with different numbers of LEO satellites: (1) GPS+BDS-3+Galileo solution (GCE), and (2) GPS+BDS-3+Galileo solution with 120 (GCE+120L), (3) 180 (GCE+180L), (4) 240 (GCE+240L), and (5) 300 LEO satellites (GCE+300L). The program was initialized every 3 h to collect more samples to investigate the performance of the convergence time and the time link precision. Additionally, daily solutions were applied to evaluate the time link stability.
4. Experimental Results
The experimental results were evaluated in terms of the number of satellites and TDOP, the convergence time, the time link precision, and the time link stability in this section.
4.1. Number of Satellites and TDOP
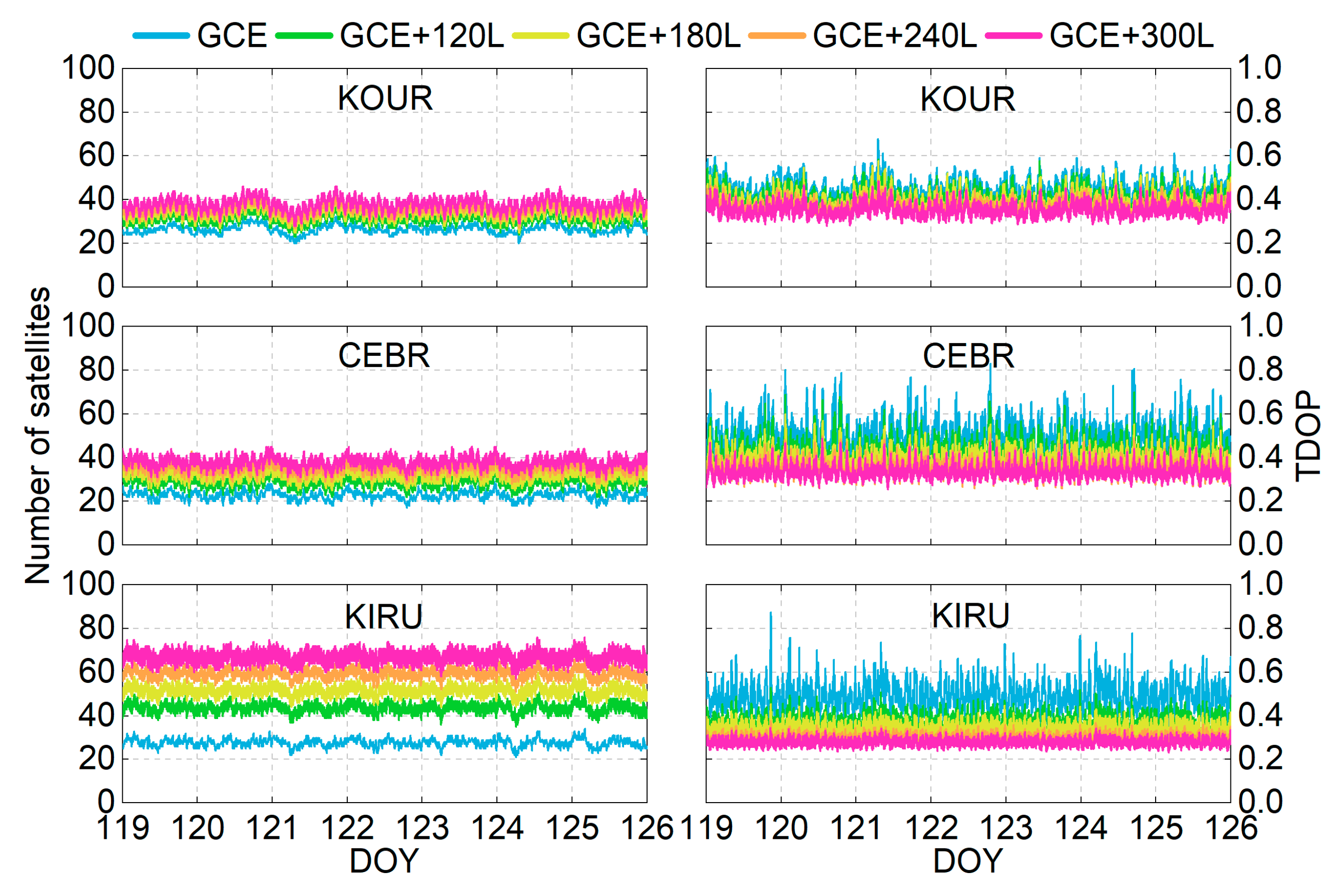
The performance of the PPP time transfer is directly influenced by the number of observed satellites and the TDOP values. Figure 3 presents the time series of satellite visibility and TDOP variations using different schemes over 7 days for three representative stations at different latitudes: KOUR (low latitude), CEBR (mid-latitude), and KIRU (high latitude). Under the GCE solution (blue lines), the number of visible satellites ranges from 20 to 32 for KOUR, 17 to 29 for CEBR, and 21 to 34 for KIRU. The integration of LEO constellations (120, 180, 240, and 300 satellites) significantly enhances satellite visibility. When incorporating 300 LEO satellites (magenta lines), the number of observed satellites can be remarkably increased to 28–46 for KOUR, 30–45 for CEBR, and 57–76 for KIRU. Notably, high-latitude stations exhibit significantly more satellite visibility compared to those of low- and mid-latitude counterparts. This spatial disparity is caused by two factors: First, the near-polar orbital configuration of the used Walker constellations results in satellites frequently passing over high-latitude regions. Second, high-latitude areas serve as intersection zones for multiple orbital planes, thereby increasing satellite visibility.
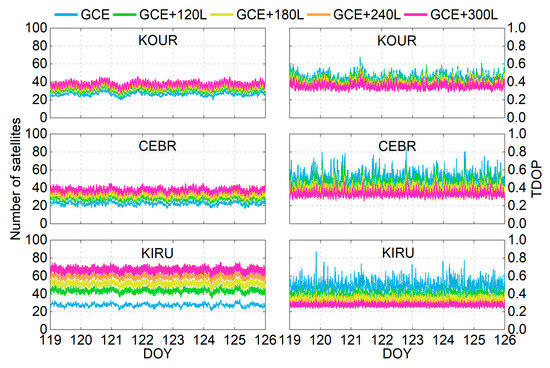
Figure 3.
Number of observed satellites and TDOP time series for stations KOUG, CEBR, and KIRU from DOY 119 to 125, 2024.
For the TDOP time series (see the right panel of Figure 3), the values range from 0.354 to 0.677 for KOUR, 0.341 to 0.830 for CEBR, and 0.355 to 0.875 for KIRU under the GCE solution. These values exhibit a significant reduction after integrating LEO observations. Notably, distinct spikes in the TDOP time series are observed in the GCE solution, particularly at the mid- and high-latitude stations (CEBR and KIRU). However, these phenomena are mitigated when integrating LEO observations. A clear inverse relationship is observed between satellite visibility and TDOP values, i.e., the larger the number of observed satellites, the smaller the TDOPs. A higher number of observed satellites can improve the geometric configuration and enhance the observation model. These factors collectively reduce uncertainties in receiver clock estimation, thereby lowering the TDOP values. The integration of LEO satellites into GNSS observations is expected to significantly enhance time transfer performance based on the model strength improvement.
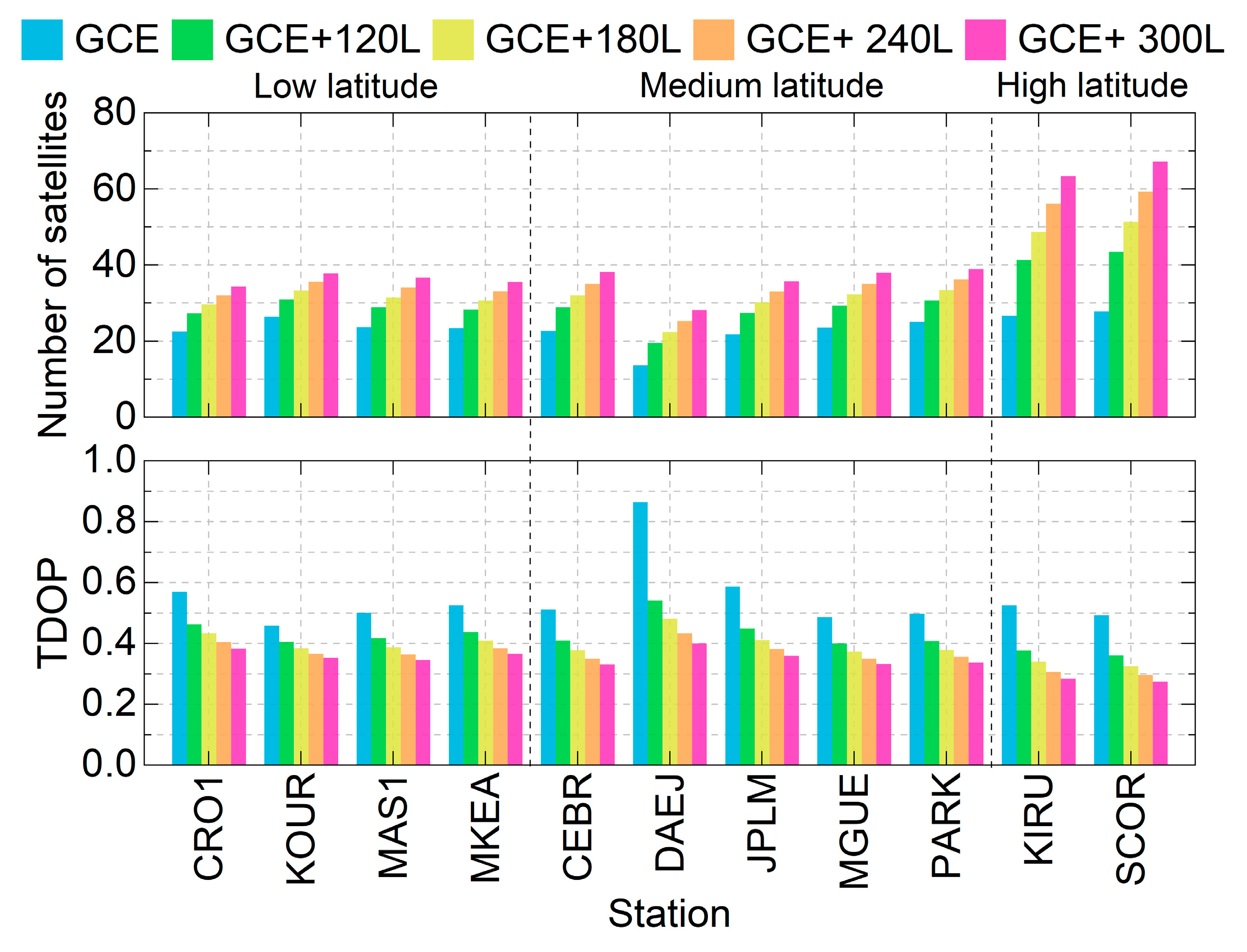
The average number of observed satellites and the TDOP values across all stations are presented in Figure 4. For the GCE solution (blue bars), the number of observed satellites ranges from 13.7 to 27.8 for different stations, while the TDOP values vary between 0.459 and 0.865. After integrating 120, 180, 240, and 360 LEO satellites, the number of observed satellites increases to 19.5–43.5, 22.4–51.4, 25.3–59.3, and 28.2–67.2, respectively. Correspondingly, TDOP values can significantly decrease to 0.360–0.541, 0.325–0.481, 0.296–0.433, and 0.275–0.400, owing to the increased number of observed satellites and the enhanced observation model strength. The two high-latitude stations, KIRU and SCOR, exhibit significantly higher satellite visibility compared to stations located at mid- and low latitudes. Notably, the number of observed satellites at station DAEJ is lower than that of other stations, with only 13.7 satellites being observed for GCE solutions, resulting in a higher TDOP value of 0.865. By checking observation files, the BDS-3 satellite Pseudorange Random Noise (PRN) larger than C32 cannot be received by this station, which may be related to hardware or software updates to be performed. However, its TDOP is reduced to 0.400 when integrating 300 LEO satellites, demonstrating the effectiveness of LEO-enhanced GNSS observations in improving time transfer performance, especially for stations not tracking enough GNSS observations, or in single- or dual-system situations.
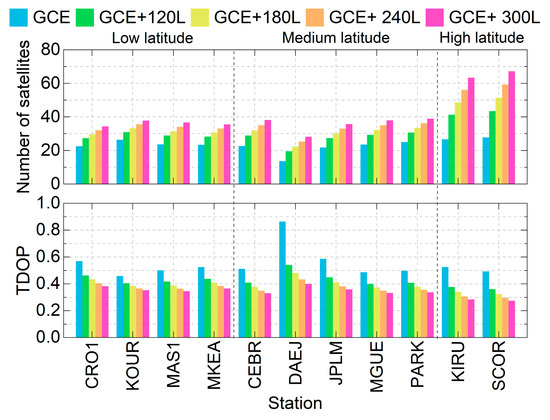
Figure 4.
Average numbers of satellites (top) and TDOPs (bottom) for ground stations.
The average number of observed satellites and the TDOPs of all stations are listed in Table 2. Under the GCE solutions, the average number of satellites amounts to 23.4, with a corresponding TDOP of 0.547. After integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites, the number of observed satellites is increased to 30.6, 34.1, 37.7, and 41.3, with improvements of 30.8%, 45.7%, 61.1%, and 76.5%, respectively, Meanwhile, the TDOP values decrease to 0.424, 0.391, 0.363, and 0.342, with a reduction rate of 22.5%, 28.5%, 33.6%, and 37.5%, respectively.

Table 2.
Average numbers of satellites and TDOPs for all stations from DOY 119 to 125, 2024.
4.2. Convergence Time
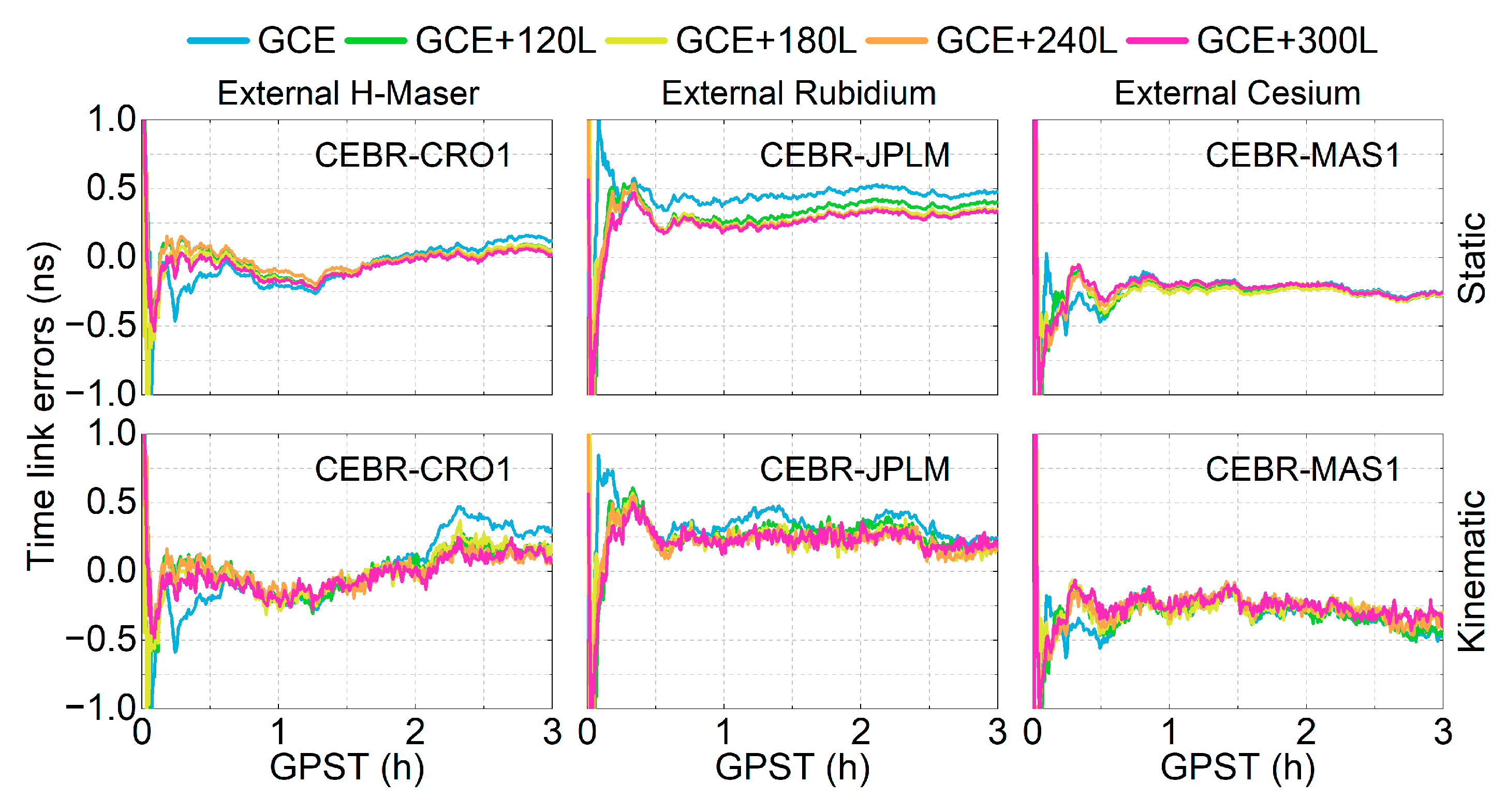
The time link error is defined as the time link difference between the estimated values and those based on the European Space Agency Multi-GNSS (ESM) final products. Figure 5 presents the time series of time link errors for three time links using the five schemes without or with different LEO constellations over the first three hours on DOY 122, 2024. The top and bottom panels represent the static and kinematic modes, respectively. The time series of the time link errors for the GCE solutions (blue lines) exhibits larger fluctuations than the other schemes in both the static and kinematic modes, particularly for the CEBR-CRO1 and CEBR-JPLM time links during the convergence period. After incorporating LEO observations, these fluctuations are significantly reduced or sometimes even eliminated. The improvements are especially significant for the kinematic mode (bottom panels) with weaker observation models.
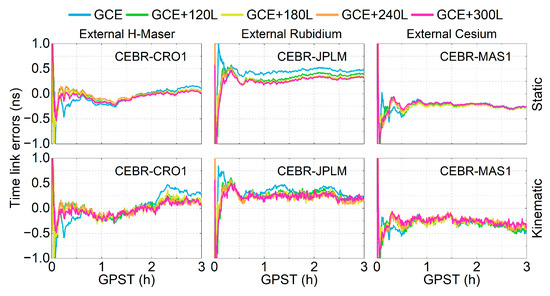
Figure 5.
Time link errors of three time links in static (top) and kinematic modes (bottom) for the first 3 h on DOY 122, 2024.
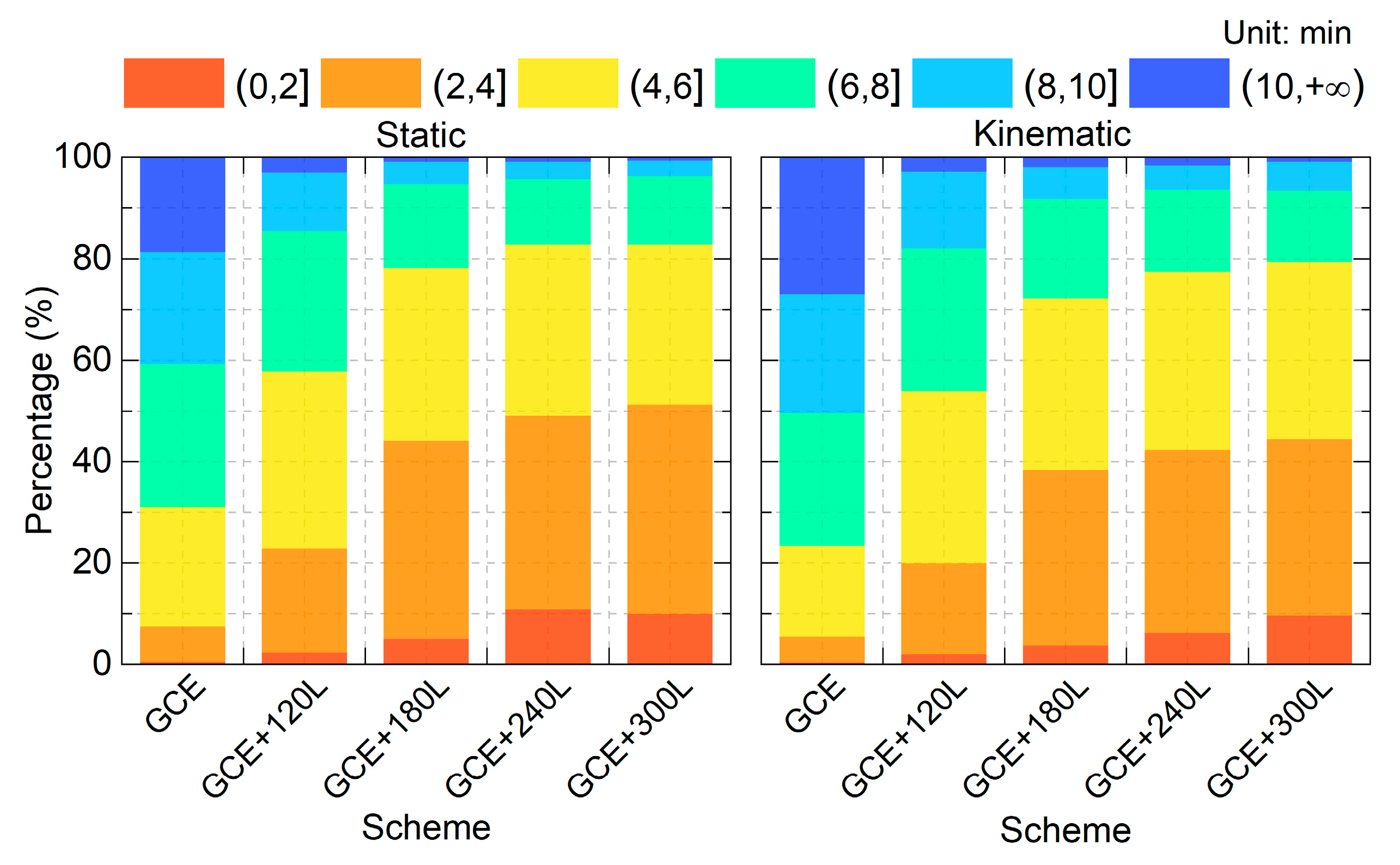
Also observed in Figure 5 is the accelerated convergence process after integrating LEO observations. When the time link errors STD between the current and the next 10 epochs can be kept within 0.1 ns (approximately 3 cm), the time elapsed from the start of data processing to the current epoch is regarded as the convergence time [47]. To evaluate the convergence performances, the program is restarted every 3 h, resulting in a total of 560 solution pieces. The percentage distribution of the convergence times at 2 min intervals for all pieces is presented in Figure 6 for both the static and kinematic modes. For the GCE solutions, the percentage of the convergence times within 6 min amounts to 31.1% for the static mode, and 23.4% for the kinematic mode. After integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites, it can be improved to 57.9%, 78.2%, 82.9%, and 82.9% in the static mode, and 53.9%, 72.3%, 77.5%, and 79.5% in the kinematic mode, respectively. For convergence times within 8 min, the percentage increases from 59.3% (static) and 49.6% (kinematic) in the GCE solutions to over 90% after integrating 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites in both modes. Furthermore, the percentage of solutions with convergence times exceeding 10 min is 18.6% for the static mode and 27.0% for the kinematic mode in the GCE solutions. They are reduced to below 4% after integrating LEO observations. The convergence performance in the static mode is overall better than that of the kinematic mode, adding or not adding the LEO observations.
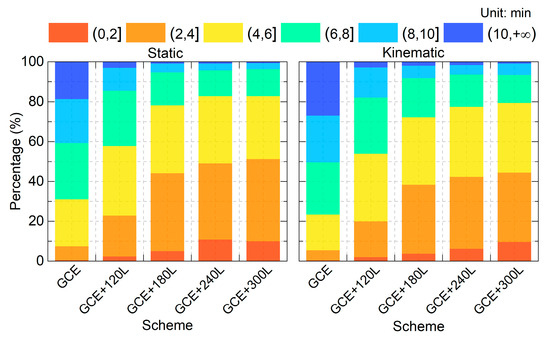
Figure 6.
Percentage of the convergence times across each 2 min interval for different schemes.
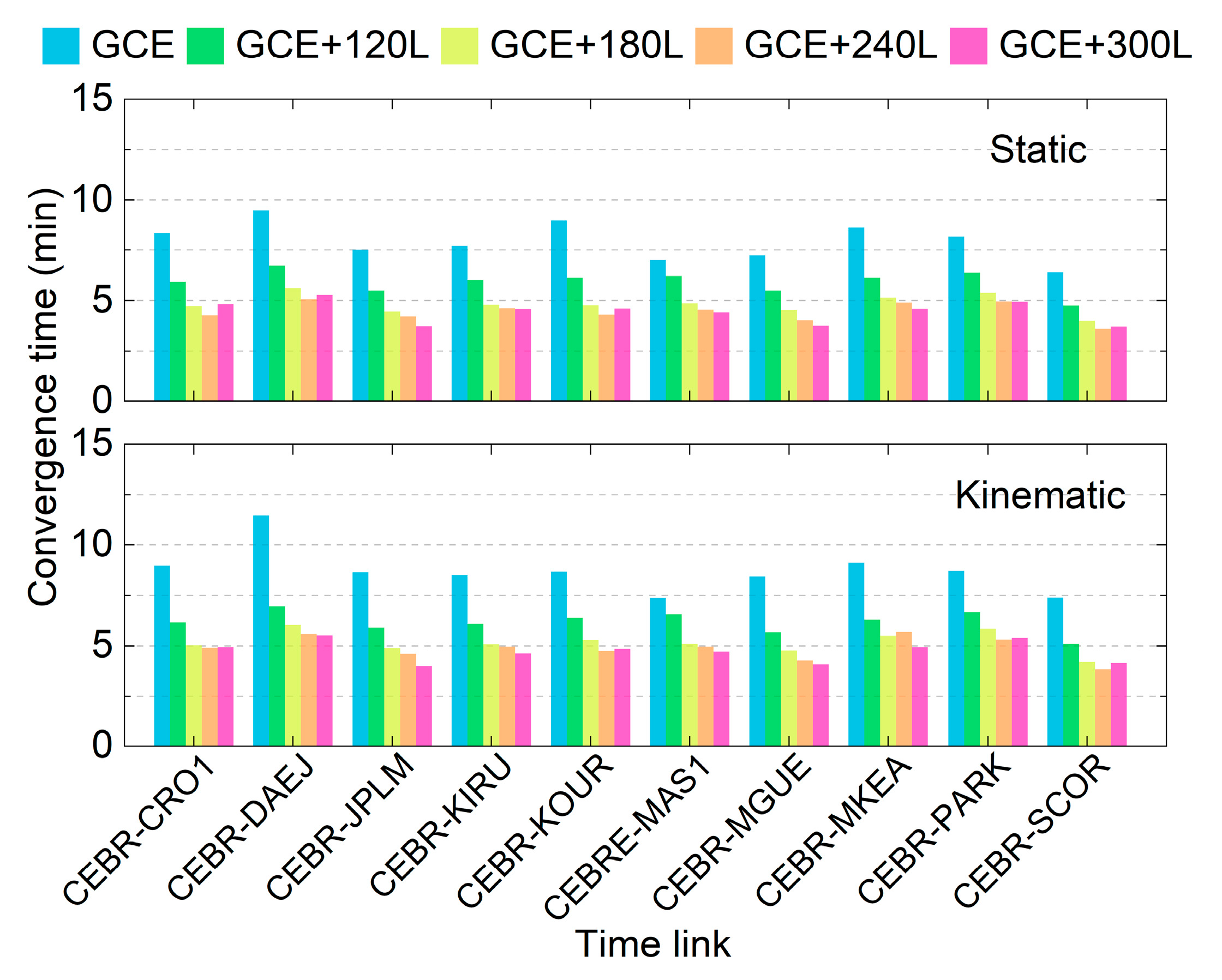
Figure 7 presents the average convergence times for each time link in both the static and kinematic modes across different schemes. It can be observed that the GCE solutions require at least 7 min to achieve convergence in both modes, with the longest convergence time observed for the CEBR-DAEJ time link, which may be attributed to the lower number of observed satellites and their poor TDOPs (see Figure 4). After integrating LEO observations, the convergence time is significantly reduced for all time links in both the static and kinematic modes. Specifically, the average convergence time decreases to approximately 5 min when utilizing a LEO constellation with at least 180 satellites. As the number of LEO satellites further increases, the improvement becomes marginal. The convergence time differences among the GCE+180L, GCE+240L, and GCE+300L schemes are negligible in both static and kinematic modes.
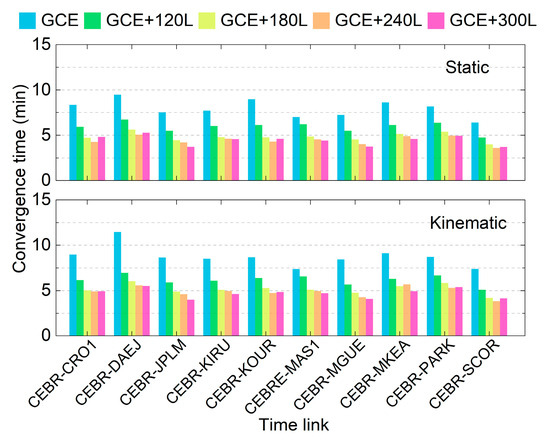
Figure 7.
Average convergence times of different time links applying the five schemes.
The average convergence times of all time links are listed in Table 3. When using the GCE solutions, the average convergence time amounts to 7.95 min in static and 8.74 min in kinematic mode. By integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites, the convergence time is reduced to 5.94, 4.83, 4.46, and 4.45 min in the static mode, and to 6.18, 5.17, 4.89, and 4.72 min in the kinematic mode, with improvements of 25.3%, 39.2%, 43.9%, and 44.0% in static mode, and 29.3%, 40.8%, 44.1%, and 46.0% in kinematic mode, respectively.

Table 3.
Average convergence times of different schemes for static and kinematic mode (unit: min).
The convergence times presented in this section were derived from observations with a 30 s sampling interval. Further reducing the sampling interval, i.e., to 1 s, should shorten the convergence time for all schemes. This will be discussed in Section 5.
4.3. Time Link Precision
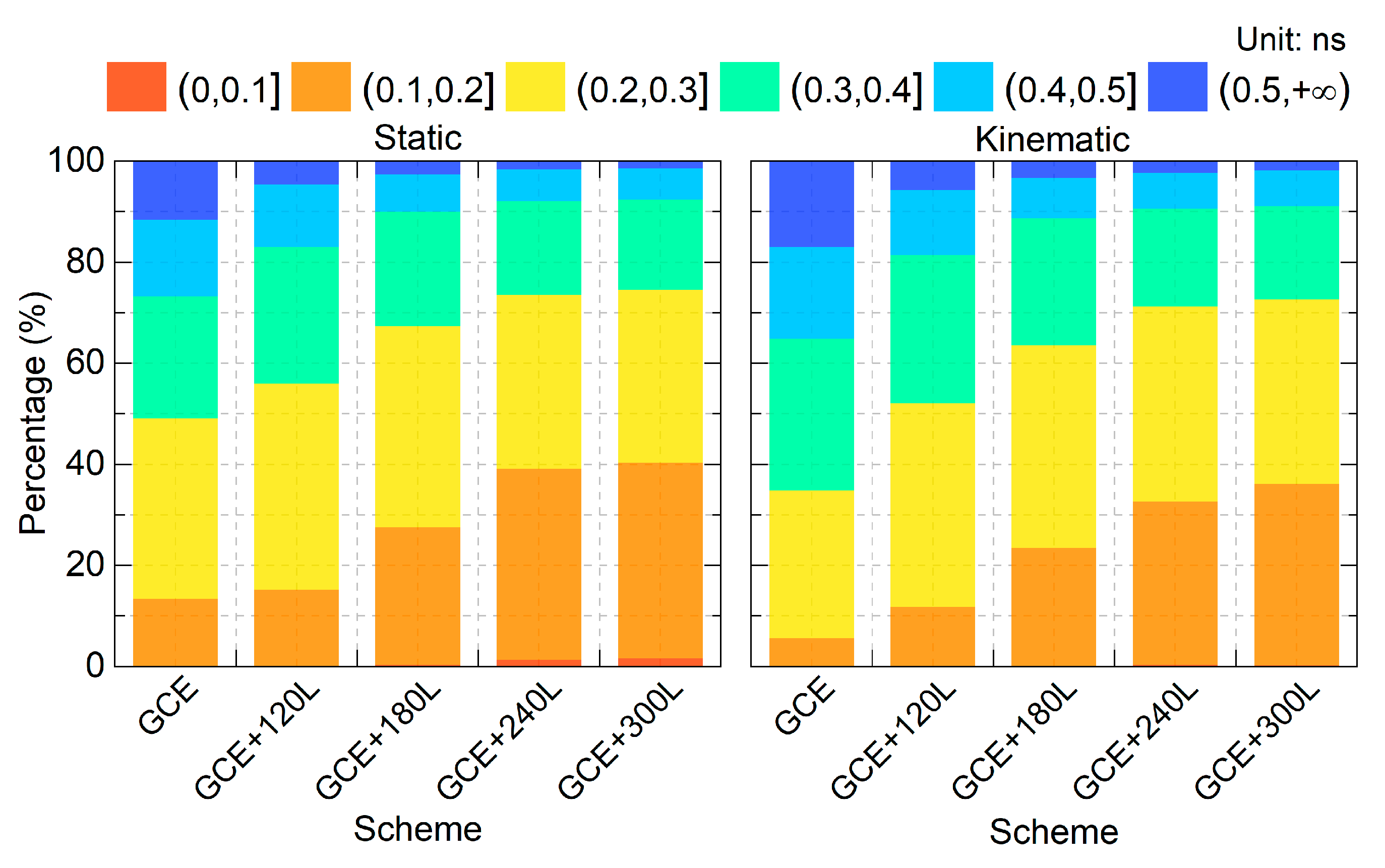
The time link precision is evaluated using the Standard Deviation (STD) of the time link errors (including the convergence period). Consistent with the convergence time analysis, a total of 560 solution instances were examined. Figure 8 presents the percentage distribution of the STD values in 0.1 ns increments from 0 to 0.5 ns, and those exceeding 0.5 ns. The percentage of solutions within the 0–0.4 ns range is 73.2%, 82.9%, 89.8%, 92.1%, and 92.3% for the static GCE, GCE+120L, GCE+180L, GCE+240L, and GCE+300L solutions, respectively. In the kinematic mode, the corresponding percentages are 64.8%, 81.4%, 88.64%, 90.5%, and 91.1%. The improvement in STD percentages confirms that integrating LEO observations can significantly enhance the time link precision.
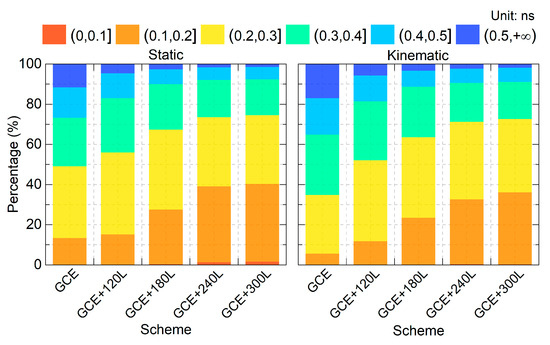
Figure 8.
STD percentage across each 0.1 ns interval for the static (left) and the kinematic mode (right).
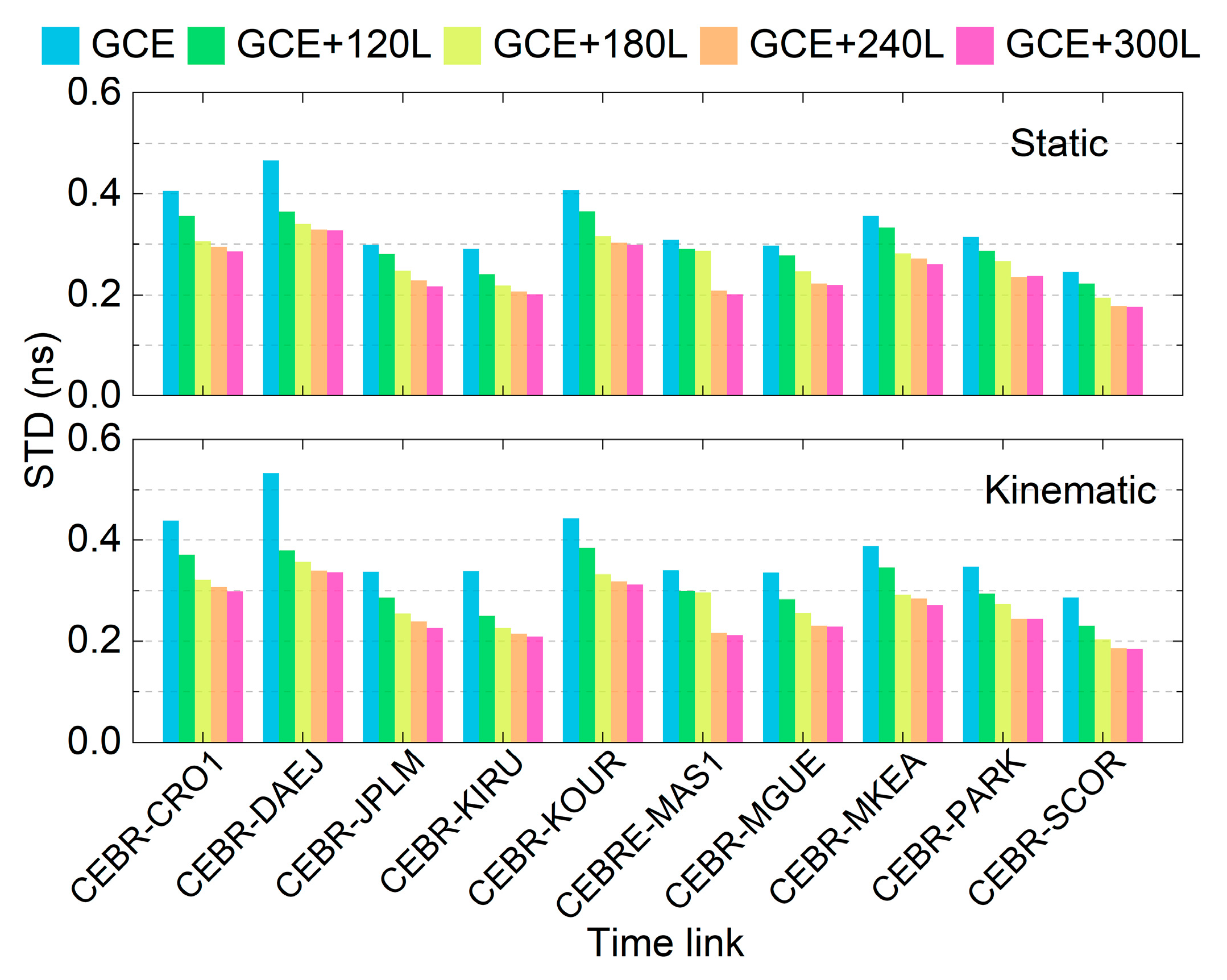
Figure 9 presents the STD of each time link under different schemes for both the static and kinematic modes. Compared to the GCE solutions, the integration of LEO observations can significantly improve the time link STD, particularly for links with sub-optimal precision, e.g., the CEBR-DAEJ time link. The difference in time link STD between the GCE+240L and GCE+300L solutions is marginal.
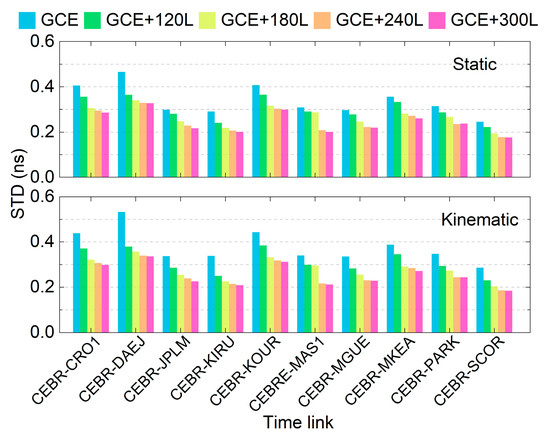
Figure 9.
STD of each time link across different schemes for the static and kinematic modes.
The average time link precision of each scheme for the static and kinematic modes is listed in Table 4, including and excluding the first hour. Having the convergence period included, the STDs of the static and kinematic GCE solutions are 0.337 and 0.377 ns. After integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites, the STD is reduced to 0.302, 0.266, 0.248, and 0.243 ns in the static mode, and 0.313, 0.277, 0.259, and 0.253 ns in the kinematic mode. This implies improvements of 10.4%, 21.1%, 26.4%, and 27.9% in the static mode, and 17.0%, 26.5%, 31.3%, and 32.9% in the kinematic mode. After removing the first hour of the time link errors, i.e., excluding the convergence period, the time link STDs amount to 0.064 ns for the GCE solution in the static mode, and are improved to 0.058, 0.055, 0.055, and 0.054 ns after integrating 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites, with improvements of 9.4% to 15.6%. For the kinematic mode, the STDs amount to 0.092, 0.084, 0.081, 0.080, and 0.079 ns for the five schemes, with the improvements amounting to 8.7% to 14.1%. This demonstrated that even after convergence, the improvements are still significant after integrating LEO satellites in the multi-GNSSS time link performances.

Table 4.
Average time link precision across each scheme for the static and kinematic modes, including and excluding the first processing hour (unit: ns).
4.4. Time Link Stability
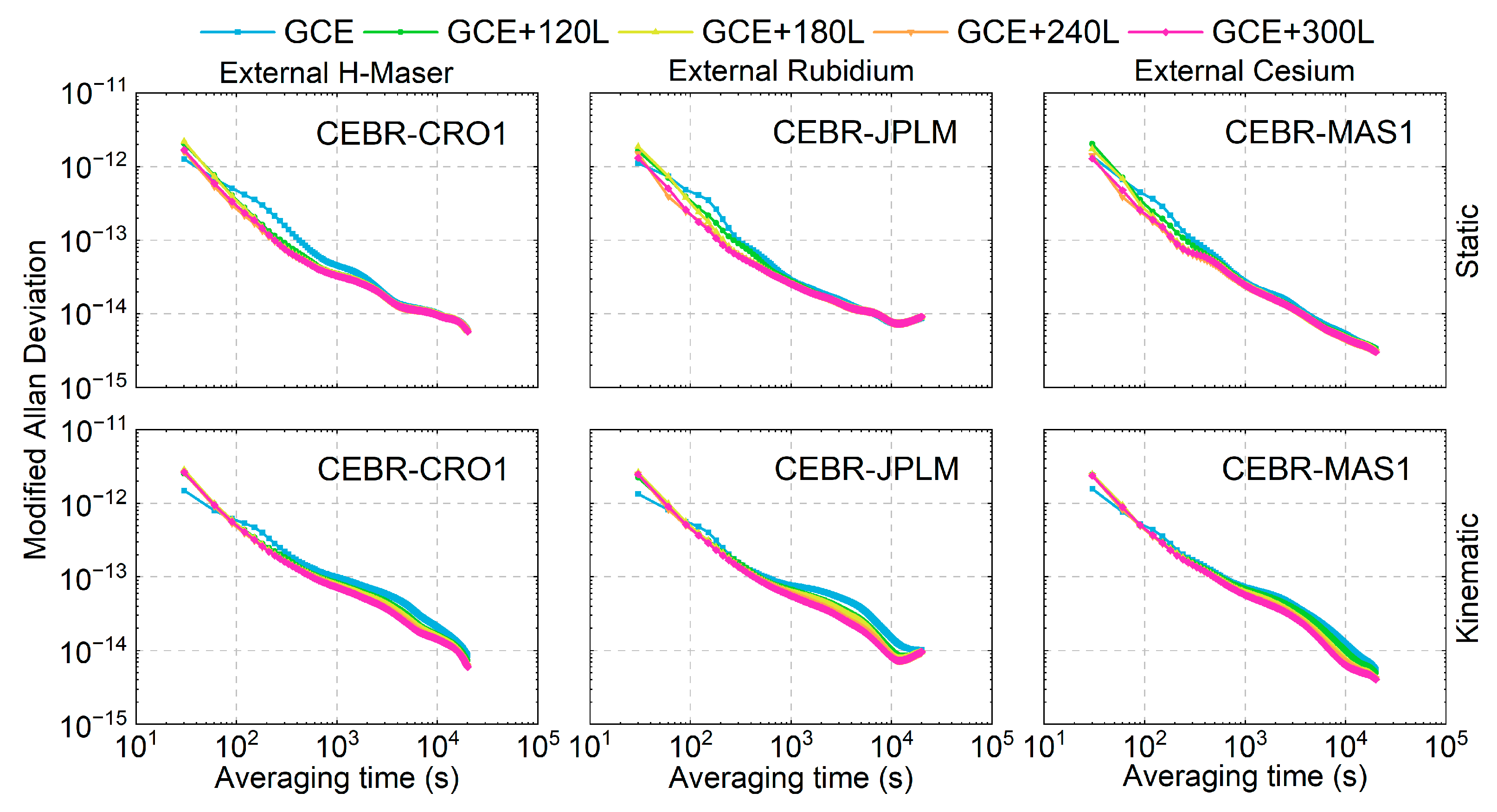
To further evaluate the performance of the estimated time links, the Modified Allan Deviation (MDEV) [48] is applied to evaluate the time link stability. The average time link stability (considering also the convergence period) of three time links equipped with different types of clocks is presented in Figure 10 for both the static and kinematic modes. The LEO-enhanced solutions exhibit poorer short-term stabilities, i.e., at an averaging time of 30 s in the static mode and 30–60 s in the kinematic mode. This can be attributed to the increased number of estimated parameters after integrating LEO observations, leading to higher short-term noise. However, a notable improvement was observed for averaging times between 60 and approximately 1000 s in the static mode. For the kinematic mode, improvements are observed for averaging times ranging from 90 to 10,000 s, with the most significant enhancements occurring between 1000 and 10,000 s. Since the kinematic PPP model strength is weaker than its static counterpart, a longer convergence time is required. As a result, the improvements in the 1000–10,000 s range are more pronounced.
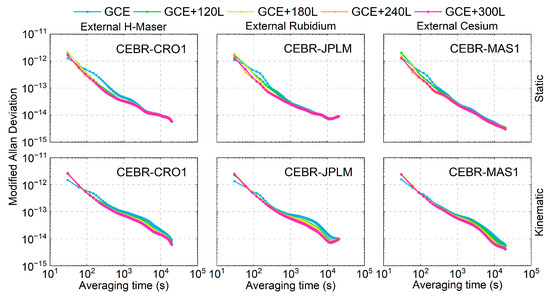
Figure 10.
Average MDEVs of three time links in the static (top) and kinematic modes (bottom).
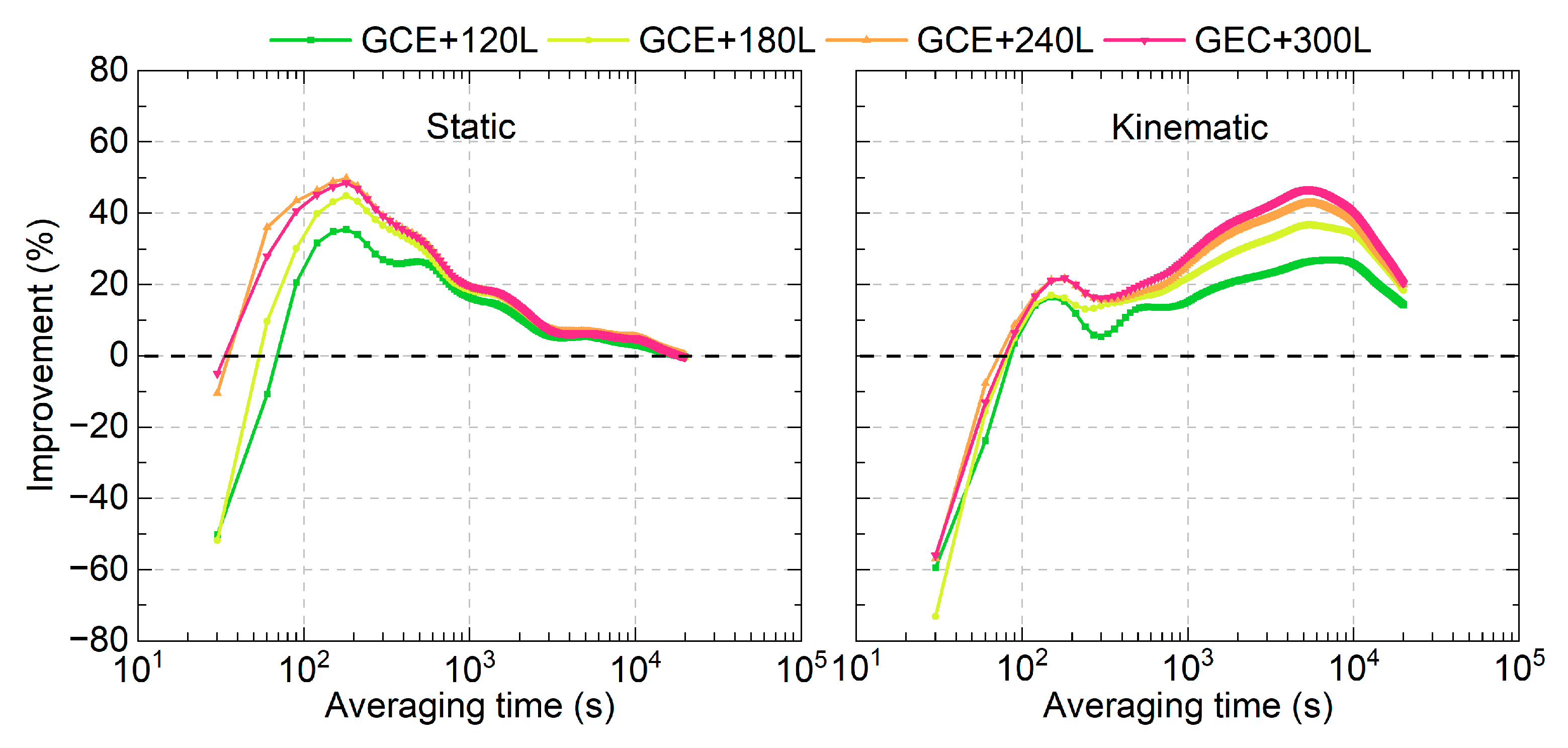
The average improvements in the MDEV for all time links at different averaging times are presented in Figure 11 for both the static and kinematic modes. Similar to Figure 10, the time link stability improvement is not observed for averaging times of 30 s in static mode and 30–60 s in the kinematic mode after integrating LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS observations. However, positive improvements are evident for averaging times longer than 90 s. The maximum improvement occurs at an averaging time of approximately 210 s, with improvements of 35.3%, 45.0%, 49.8%, and 48.6% for the GCE+120L, GCE+180L, GCE+240L, and GCE+300L solutions, respectively. For the kinematic mode, the maximum improvement is observed at an averaging time of approximately 5600 s, with improvements of 27.0%, 36.7%, 42.8%, and 46.8% for GCE+120L, GCE+180L, GCE+240L, and GCE+300L schemes, respectively. The time link stability improvements achieved with GCE+240L and GCE+300L solutions are superior to those of GCE+120L and GCE+180L. Similar to the time link STD results, the difference between the GCE+240L and GCE+300L solutions is marginal in both the static and kinematic modes.
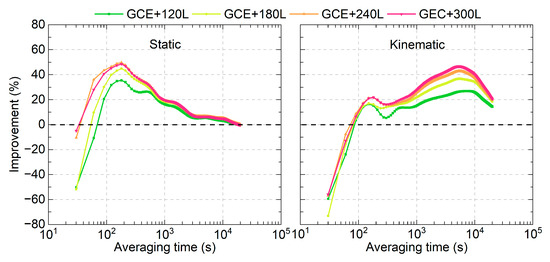
Figure 11.
Average improvements in the time link stabilities after integrating LEO observations in multi-GNSS PPP time transfer.
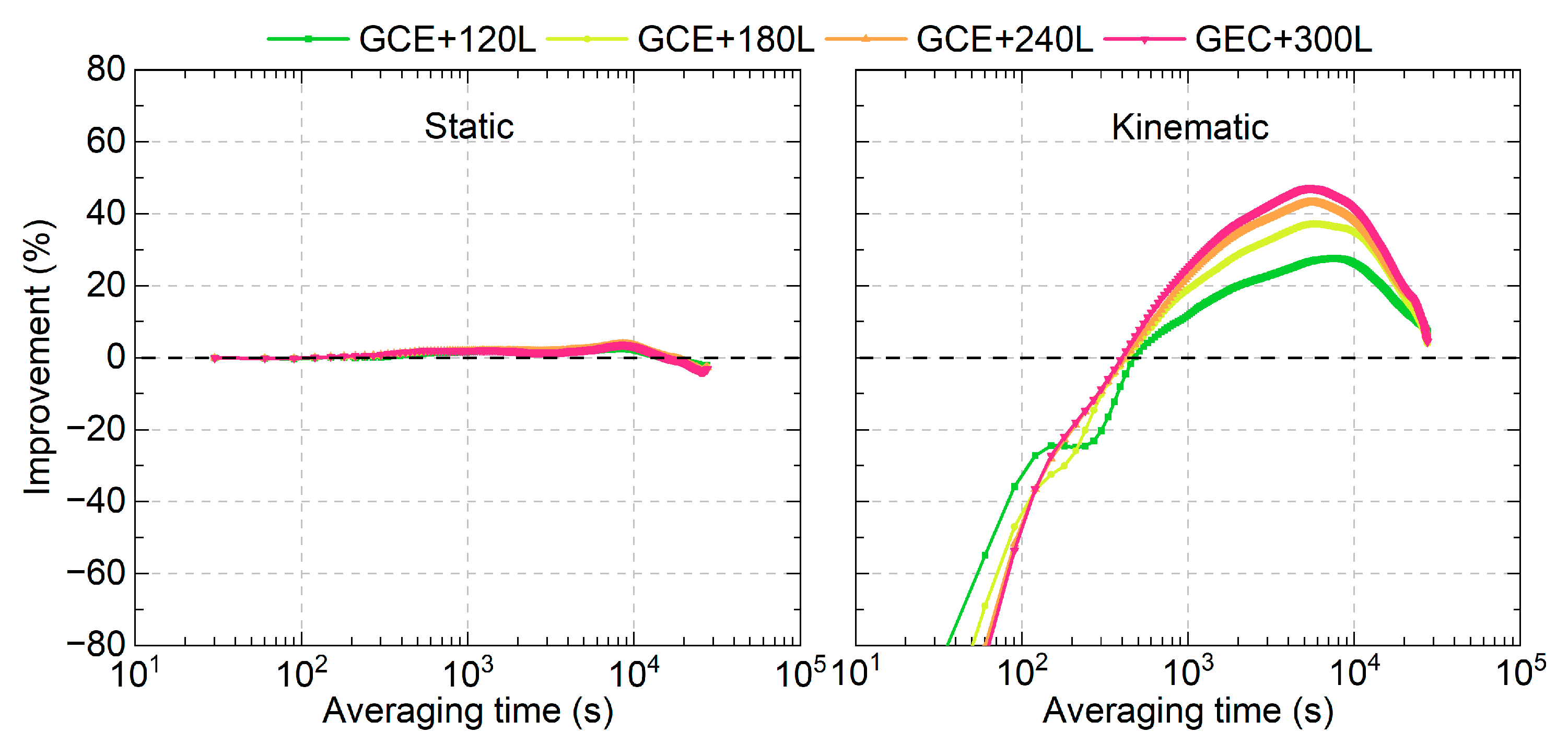
The time link stabilities were also evaluated using the time link errors after removing the first convergence hour. The time link stability improvements in the LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS solutions compared to those of GNSS-only solutions are presented in Figure 12. It can be observed that the improvements are less than 5% and can be ignored for the static mode. For the kinematic mode, the improvements can be observed when the averaging time becomes longer than 480 s. The maximum improvement is about 45% for the GCE+300L solutions.
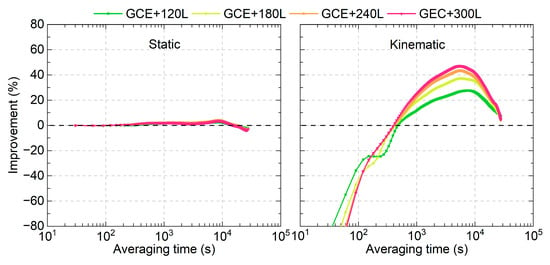
Figure 12.
Average time link stability improvements in the LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer compared to those of multi-GNSS solutions.
5. Discussions
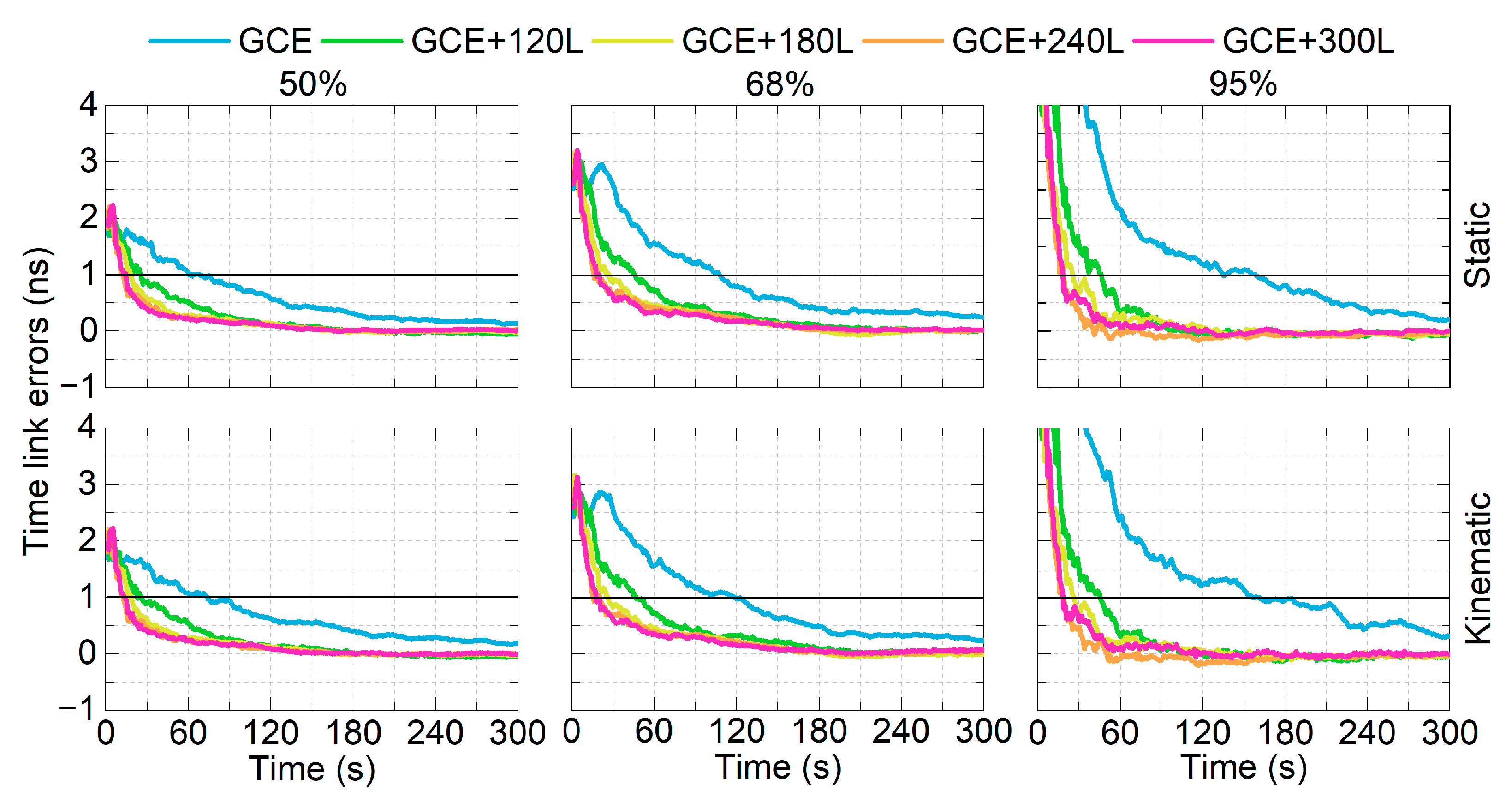
In this study, the sampling interval was set to 30 s, as often used in GNSS-based PPP [1,2]. Compared to using 30 s observations, it was reported that the PPP convergence can be shortened from 7.9, 5.3, and 6.9 min to 4.4, 3.1 and 3.7 min in the east, north and up coordinates, respectively, after using 1 s observations in LEO-enhanced GPS/BDS PPP [49], which concluded that a higher sampling rate is beneficial for further shorten the convergence time. Therefore, in this contribution, we have additionally conducted LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP time transfer using 1 s observations to evaluate the impacts. One-day observations on DOY 124, 2024, were processed with the program restarted every 30 min, resulting in 480 PPP pieces for the assessment. The continuous network solutions from DOY 118 to 125, 2024, were processed using the ESM final GPS satellite orbits, in which the receiver clocks on DOY 124 were used as references. The detailed clock estimation strategy can be found in [50,51,52].
With the mean offsets removed, the 50%, 68%, and 95% percentile lines of the time link errors are shown in Figure 13. The GCE solutions require 68, 108 and 159 s to converge to 1 ns in the static mode for the three percentile lines, and 74, 119 and 162 s for the kinematic mode. After integrating 120, 180, 240 and 300 LEO satellites, the required times are shortened to 13–26, 18–46, 19–47 s for the static mode, and 13–26, 18–47, and 19–46 s in the kinematic mode. The results show that the 1-sigma (68%) percentile line of the time link errors can converge to 1 ns within 1 min in using LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer.
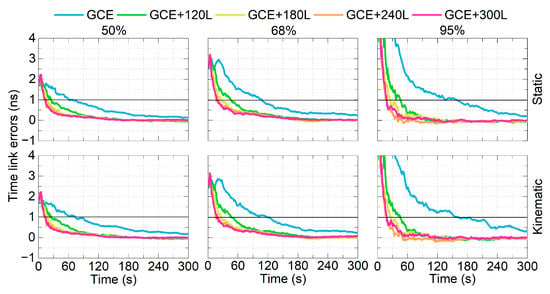
Figure 13.
Percentile lines of time link errors of LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS PPP time transfer with different numbers of LEO satellites for the static (top) and kinematic mode (bottom).
6. Conclusions
GNSS PPP time transfer suffers from a long initialization time due to the slow geometry change in GNSS satellites. The fast motion of LEO satellites helps accelerate changes in satellite geometry, thereby improving the convergence speed. This contribution investigates the performance of LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer. Simulated LEO constellations consisting of different numbers of LEO satellites (120, 180, 240, and 300) are integrated into the multi-GNSS scenario to perform time transfer in both the static and kinematic modes. The analysis is based on one week of observations from 11 globally distributed stations. 3 h solutions are used to assess the convergence times and the time link precision, while the MDEVs are evaluated using a daily based solution.
Compared to the GCE solutions, the integration of 120, 180, 240, and 300 LEO satellites can increase the average number of observed satellites from 23.4 to 30.6, 34.1, 37.7, and 41.3, respectively, while reducing the TDOP values from 0.547 to 0.424, 0.391, 0.363, and 0.342. Using 30 s observations, the average convergence times for all time links are shortened from 7.95 to 5.94, 4.83, 4.46, and 4.45 min for the static mode, and from 8.75 to 6.18, 5.17, 4.89, and 4.72 min in the kinematic mode. Additionally, the time link precision in the static mode is improved from 0.337 to 0.302, 0.266, 0.248, and 0.243 ns, while it is from 0.377 to 0.313, 0.277, 0.259, and 0.253 for the kinematic mode. The time link stabilities (MDEVs) are enhanced in both the static and kinematic modes compared to the GCE solutions. Using 1 s observations, the 1-sigma percentile line of the time link errors can converge to 1 ns within 1 min after using LEO-enhanced multi-GNSS real-time PPP time transfer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.X. and K.W.; methodology, W.X.; software, W.X., W.L. and M.W.; validation, W.X., W.L. and M.W. writing—original draft preparation, W.X.; writing—review and editing, K.W., W.L., M.W., M.L. and X.Y.; supervision, K.W.; funding acquisition, W.X. and K.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42404033, 12473078), the International Partnership Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (Grant No. 021GJHZ2023010FN), and the Special Research Assistant Funding Project, CAS (No. 110400T0XW).
Data Availability Statement
The observations can be found at ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/ (accessed on 25 September 2025). The DCB files can be found at https://data.bdsmart.cn/pub/product/bias/ (accessed on 25 September 2025). The GNSS satellite orbits and clocks can be found at http://www.ppp-wizard.net/products/REAL_TIME/ (accessed on 25 September 2025). The receive clocks can be found at the http://navigation-office.esa.int/products/gnss-products/ (accessed on 25 September 2025).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of the international GNSS monitoring and assessment system (iGMAS) at the National Time Service Center, and the National Space Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.nssdc.ac.cn (accessed on 25 September 2025)). Wuhan University is acknowledged for providing the Multi-GNSS observation data. The CAS is acknowledged for providing the Multi-GNSS DCB products. The CNES is acknowledged for providing the Multi-GNSS real-time orbits and clocks. The ESM is acknowledged for providing the receiver clocks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ge, Y.; Qin, W.; Su, K.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, X. A new approach to real-time precise point positioning timing with International GNSS Service real-time service products. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Lu, X. Modeling and assessment of precise time transfer by using BeiDou navigation satellite system triple-frequency signals. Sensors. 2018, 18, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, G.; Jiang, Z. Precise Point Positioning for TAI Computation. Int. J. Navig. Obs. 2008, 2008, 562878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Baire, Q. Combining GPS and GLONASS for time and frequency transfer. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Lu, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, R. Performance of Multi-GNSS Real-Time UTC(NTSC) Time and Frequency Transfer Service Using Carrier Phase Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tu, R.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Lu, X. Study of fast and reliable time transfer methods using low Earth orbit enhancement. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, T.G.R.; Neish, A.M.; Walter, T.; Enge, P.K. Broadband LEO constellations for navigation. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2018, 65, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikbilek, K.; Saleem, Z.; Ferre, R.M.; Praks, J.; Lohan, S. Survey on Optimization Methods for LEO-Satellite-Based Networks with Applications in Future Autonomous Transportation. Sensors 2022, 22, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L. The CentiSpace-1: A leo satellite-based augmentation system. In Proceedings of the 14th meeting of the international committee on global navigation satellite systems, Beijing, China, 10 December 2019; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Qian, C.; Shu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, Y. Real-Time Estimation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Clock Based on Ground Tracking Stations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Lv, H.; Bian, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X. LEO constellation-augmented multi-GNSS for rapid PPP convergence. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, H.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z. GNSS RTK Positioning Augmented with Large LEO Constellation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, M.; Lv, J.; Chang, J.; Dai, W.; Tong, K.; Zhu, M. Integrating GPS and LEO to accelerate convergence time of precise point positioning. In Proceedings of the 7th international conference on wireless communications and signal, Nanjing, China, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ma, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, X. Improved PPP Ambiguity Resolution with the Assistance of Multiple LEO Constellations and Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Fu, Y. Toward wide-area and high-precision positioning with LEO constellation augmented PPP-RTK. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5500213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Q.; Du, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Qin, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Y.; Qin, G. LEO augmented precise point positioning using real observations from two CENTISPACE™ experimental satellites. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yang, Q.; Du, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Qin, Y.; Guo, J. Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning enhanced by the real navigation signals from CENTISPACETM LEO mission. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)-achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Li, P.; Cui, B. An efficient clock offset datum switching compensation method for BDS real-time satellite clock offset estimation. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Dang, Y. M_FCB: An open-source software for multi-GNSS fractional cycle bias estimation. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Lu, X. Modeling performance analysis of precise time transfer based on BDStriple-frequency un-combined observations. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, D.; Cao, X.; Shen, F.; Meng, X. A new receiver clock model to enhance BDS-3 real-time PPP time transfer with the PPP-B2b service. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, Z.; Li, R.; Xie, S.; She, H. Precise orbit determination of integrated BDS-3 and LEO satellites with ambiguity fixing under regional ground stations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 116305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Xie, S.; She, H. Beidou UPD estimation and assessment based on LEO-assisted regional stations observations. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luojie, D.; Ding, H. Real-time service performances of BDS-3 and Galileo constellations with a linear satellite clock correction models. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G. Real-time clock offset prediction with an improved model. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, G.; Xie, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, H. Assessment and comparison of satellite clock offset between BeiDou-3 and other GNSSs. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2021, 56, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Zou, M.; Yang, X. Influencing factors on real-time determination of LEO satellite clocks. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 066315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Xie, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Ge, Y.; El-Mowafy, A.; Yang, X. Impact of latency and continuity of GNSS products on filter-based real-tTime LEO satellite clock determination. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, M.; Zou, M.; El-Mowafy, A.; Yang, X. Real-time LEO satellite clock estimation with predicted LEO satellite orbits constrained. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Wu, M.; El-Mowafy, A.; Yang, X. Impact of ISB stochastic models on LEO satellite clock estimation with onboard multi-GNSS observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 046313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, K.; Wei, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, M. The impact of LEO satellite hardware delays on LEO-augmented precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2025. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J. Relativity effects of galileo passive hydrogen maser satellite clocks. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y. Relativistic effects of LEO satellite and its impact on clock prediction. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Lichten, S.M. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Brockmann, E.; Schaer, S.; Beutler, G.; Meindl, M.; Prange, L.; Bock, H.; Jäggi, A.; Ostini, L. GNSS processing at CODE: Status report. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Herring, T.A.; Shapiro, I.I.; Rogers, A.E.E.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction—Part II Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull. Géod. 1973, 47, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenemann, E.; Gini, F.; Mayer, V.; Springer, T. ESOC MGNSS Processing Strategy. Available online: http://navigation-office.esa.int/products/gnss-products/esm.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2025).
- Laurichesse, D.; Privat, A. An open-source PPP client implementation for the CNES PPP-WIZARD demonstrator. In Proceedings of the 28th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2015), Tampa, FL, USA, 14–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Bertolesi, E.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, W.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Predicting Accelerometer Baseline Correction and Nondivergent Deformation Velocity Based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) During GNSS Downgrade. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 11982–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X. Integrating GPS and GLONASS to accelerate convergence and initialization times of precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, K.; Cui, B.; Yang, X. Regional multi-station real-time time transfer using an undifferenced multi-GNSS network solution. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Han, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, T. Combined BDS-2/BDS-3 real-time satellite clock estimation with the overlapping B1I/B3I signals. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4470–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.W.; Barnes, J.A. A modified ‘Allan variance’ with increased oscillator characterization ability. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Frequency Control Symposium, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 27–29 May 1981; pp. 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.; Li, B.; Ge, M.; Zang, N.; Nie, L.; Shen, Y.; Schuh, H. Initial assessment of precise point positioning with LEO enhanced Global Navigation Satellite Systems (LeGNSS). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, S.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Multi-GNSS real-time clock estimation using sequential least square adjustment with online quality control. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Du, S.; Cui, B.; Li, M.; Tan, Y. Rapid estimation of undifferenced multi-GNSS real-time satellite clock offset using partial observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, K.; Fu, W.; Xie, S.; Cui, B.; Li, M. Real-time estimation of BDS-3 satellite clock offset with ambiguity resolution using B1C/B2a signals. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).