Dehazing of Panchromatic Remote Sensing Images Based on Histogram Features
Abstract
Highlights
- A correlation exists between the histogram features of panchromatic remote sensing images and the transmission. The relation equation between the average occurrence differences between the adjacent gray levels (AODAG) feature of the plain image patch and the transmission, and the relation equation between the average distance to the gray-level gravity center (ADGG) feature of the mixed image patch and the transmission are established, respectively.
- The atmospheric light of different regions in the remote sensing image may be different. The threshold segmentation method is applied to calculate the atmospheric light of each image patch based on the maximum gray level of the patch separately.
- The transmission map is obtained according to the statistical relation equation without relying on the color information, which is beneficial for the dehazing of panchromatic remote sensing images.
- A refined atmospheric light map is obtained, resulting in a more uniform brightness distribution in the dehazed image.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
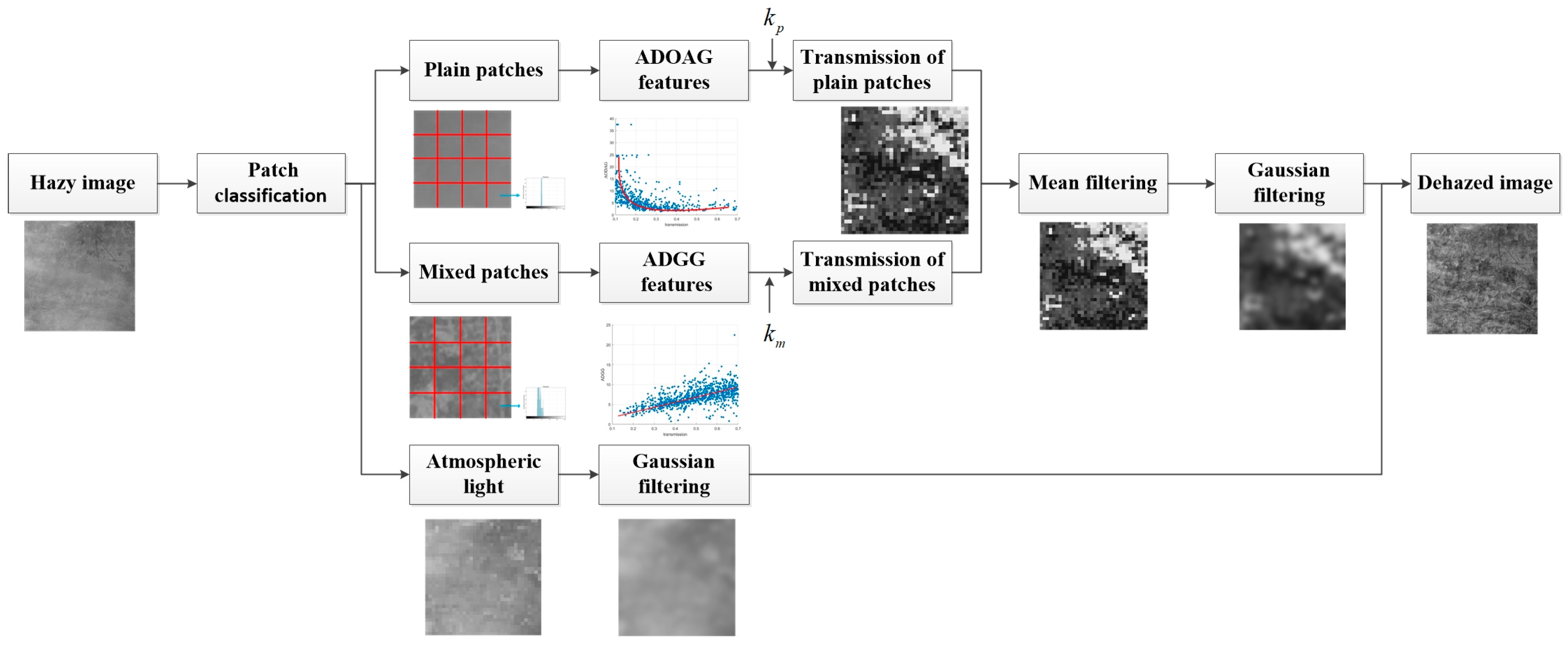
- Without relying on the color information of the image, dehazing is achieved by extracting histogram features of the panchromatic remote sensing image. According to the histogram features, the hazy image is divided into plain image patches and mixed image patches, and the dehazing is carried out, respectively.
- (2)
- The relation equation between the AODAG feature of the plain image patch and the transmission, and the relation equation between the ADGG feature of the mixed image patch and the transmission are established, respectively. Eight-neighborhood mean filtering and Gaussian filtering are applied to smooth the original transmission map.
- (3)
- According to the characteristics of atmospheric light distribution in remote sensing images, the threshold segmentation method is applied to calculate the atmospheric light of each image patch based on the maximum gray level of the patch separately, which makes the intensity of the dehazed images more uniform.
2. Materials and Methods
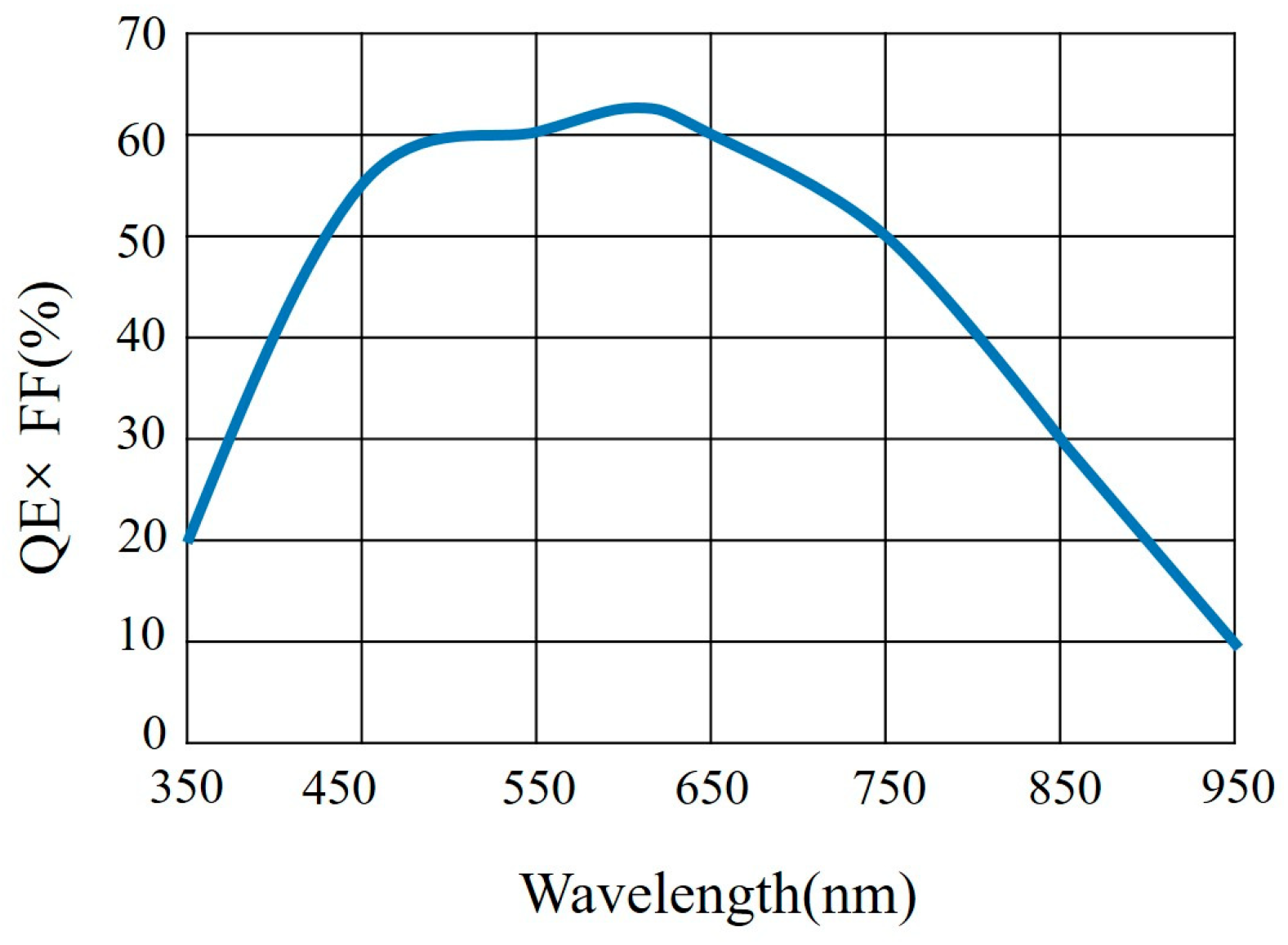
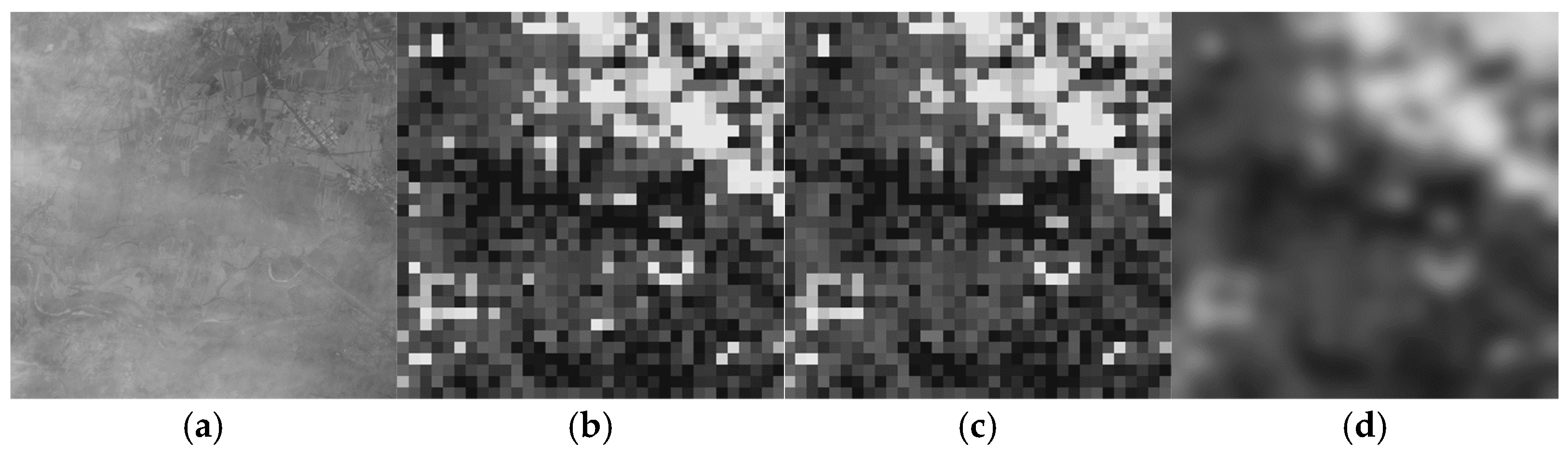
2.1. Histogram Features
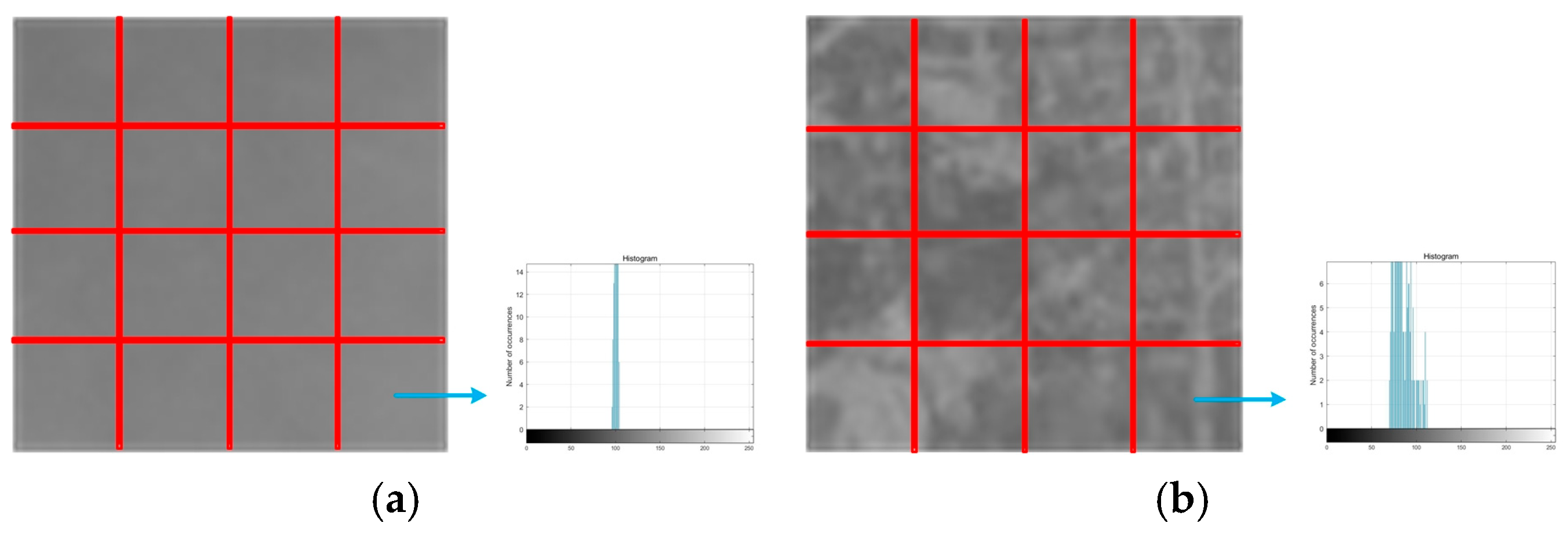
2.1.1. Patch Classification
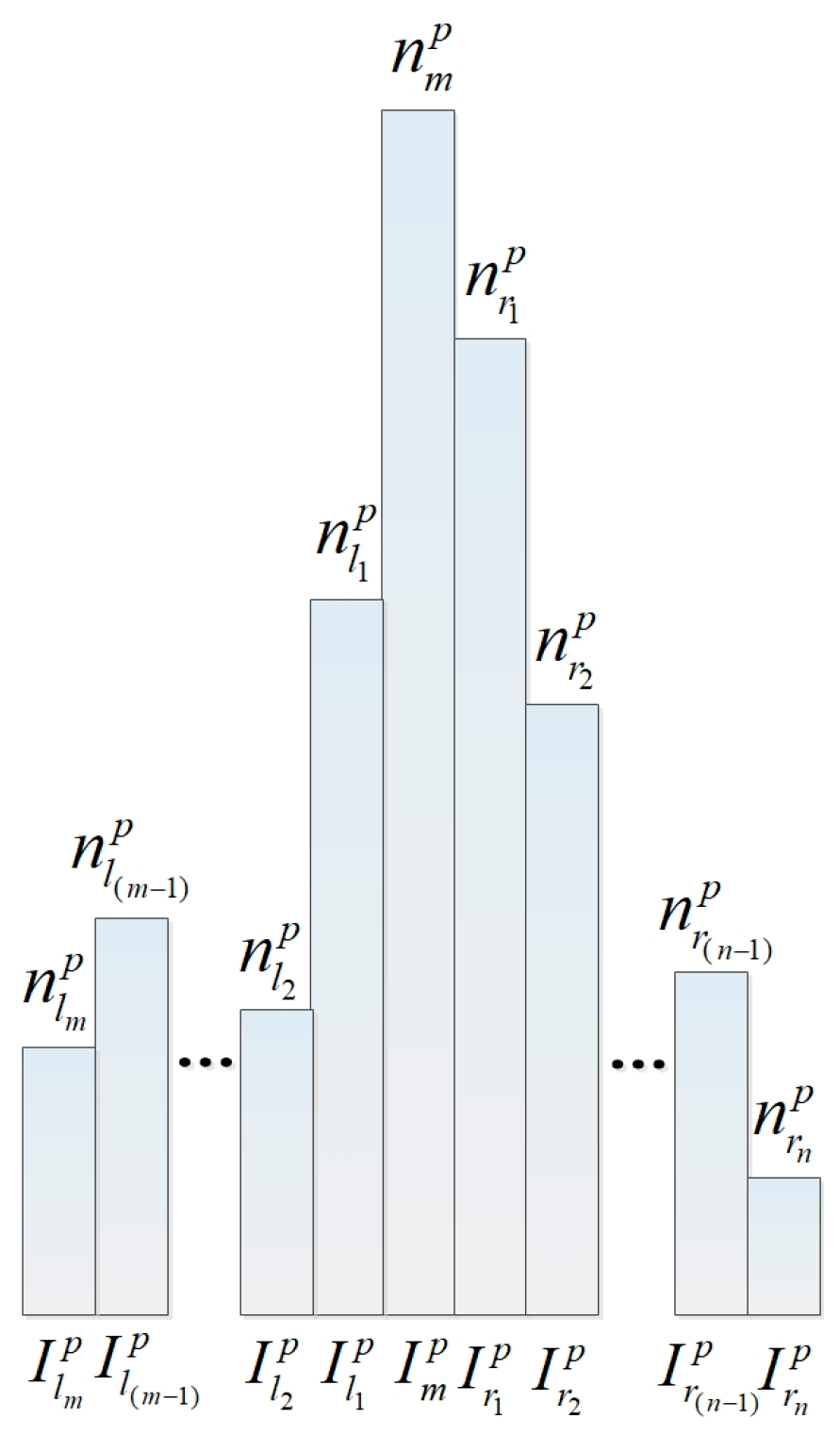
2.1.2. Plain Patch Feature
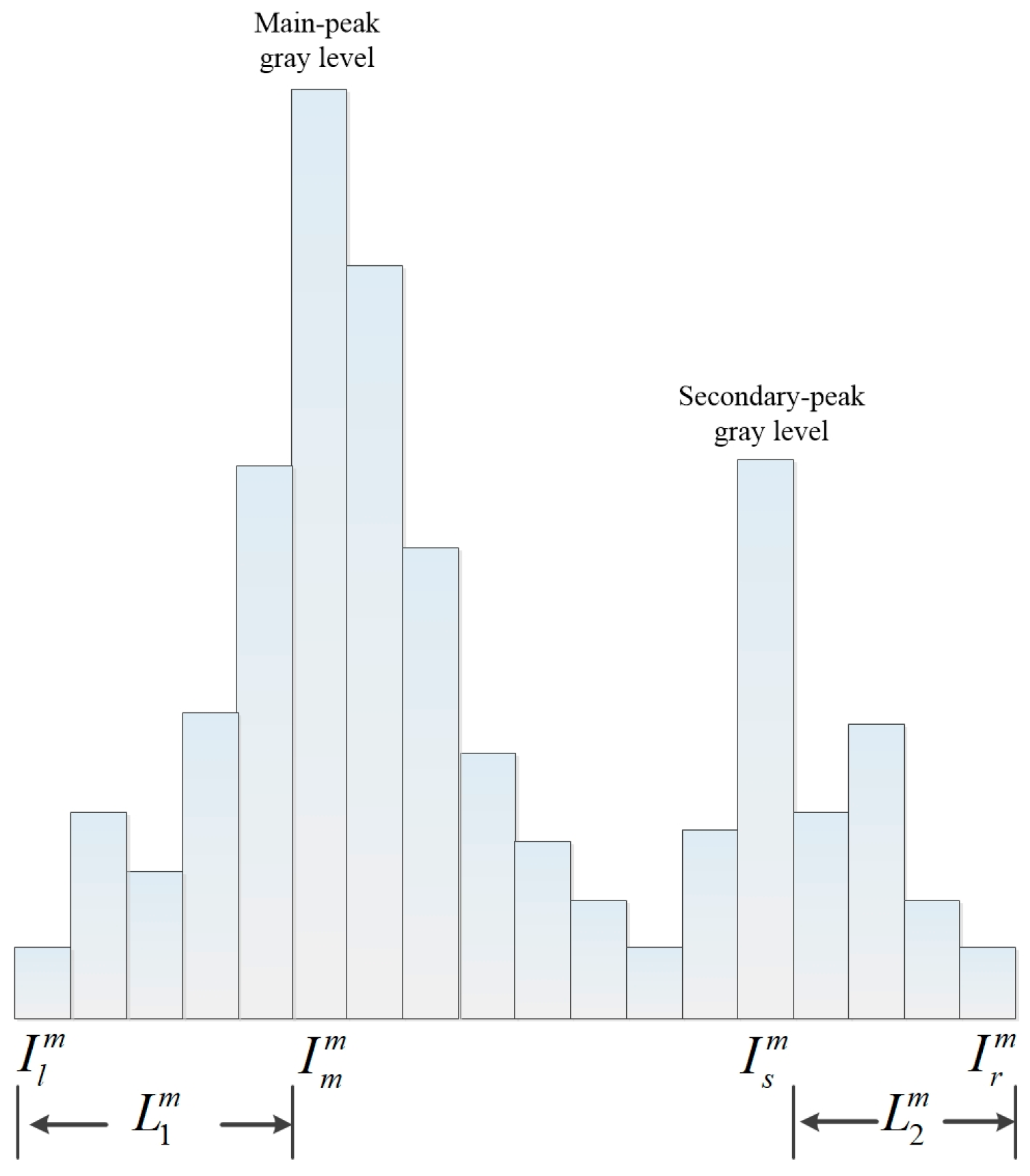
2.1.3. Mixed Patch Feature
2.2. Statistical Relation Equation
2.2.1. Hazy Image Synthesis
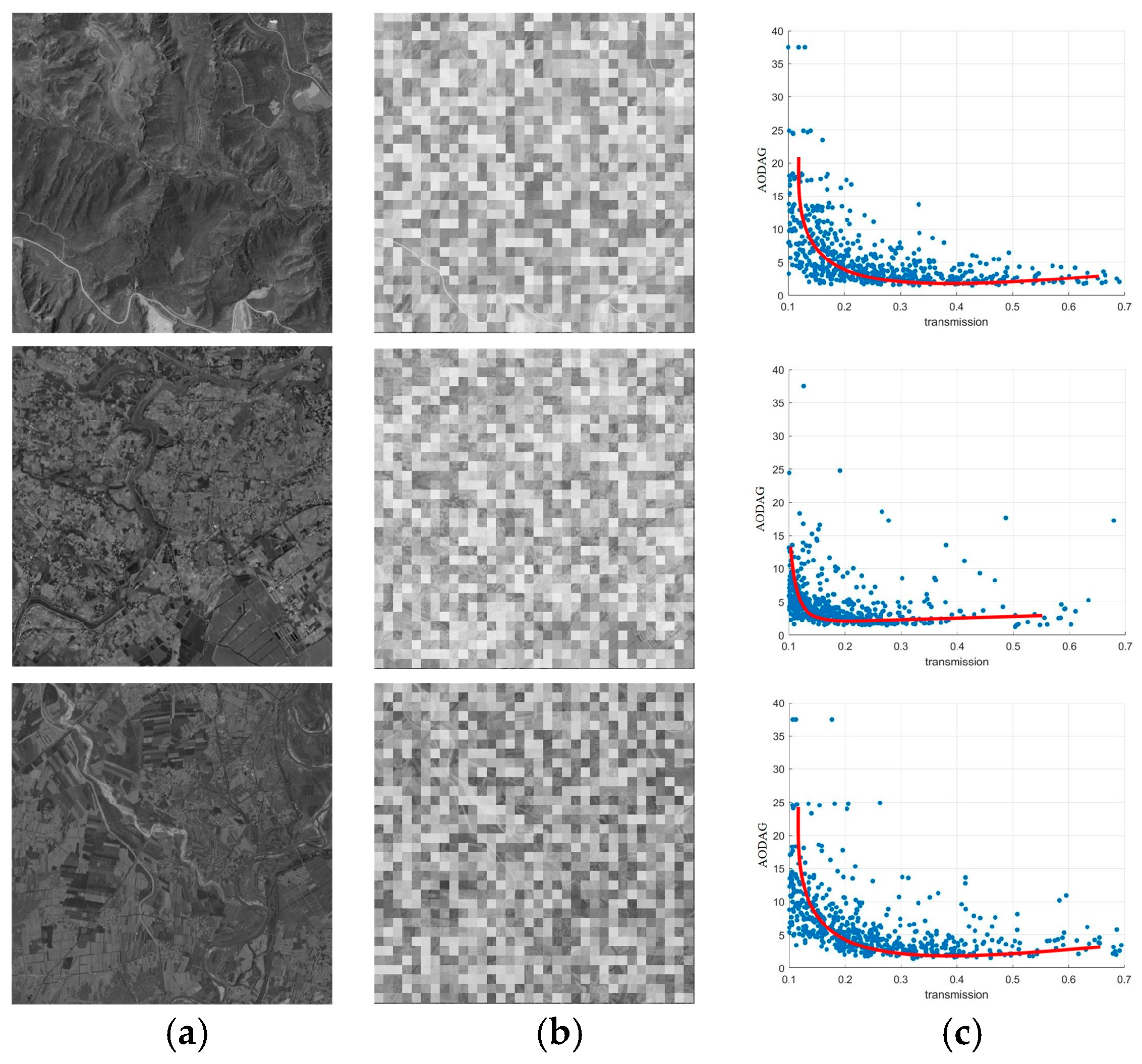
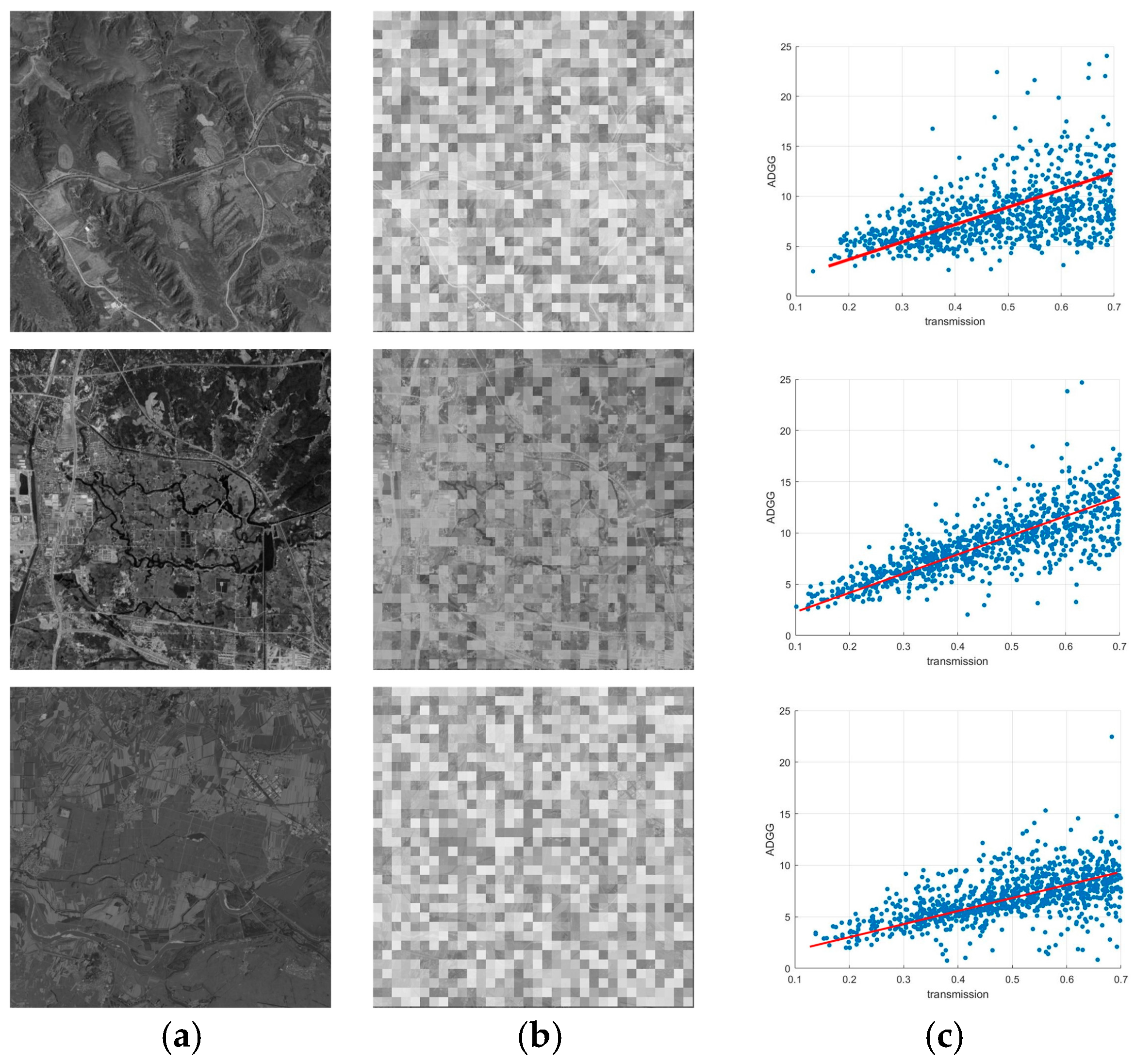
2.2.2. AODAG Relation Equation
2.2.3. ADGG Relation Equation
2.2.4. Relation Equation Fitting
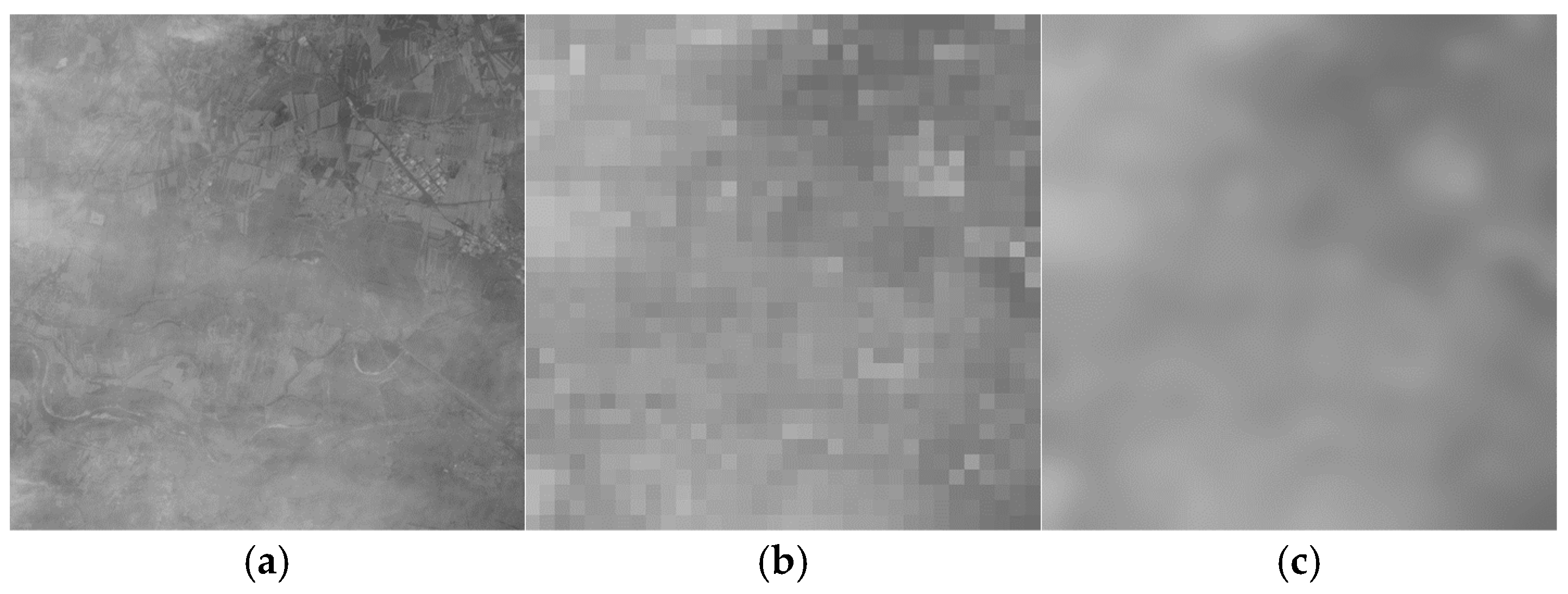
2.3. Atmospheric Light Calculation
2.4. Transmission Calculation
2.4.1. Initial Transmission Map
2.4.2. Transmission Map Smoothing
2.5. Image Restoration
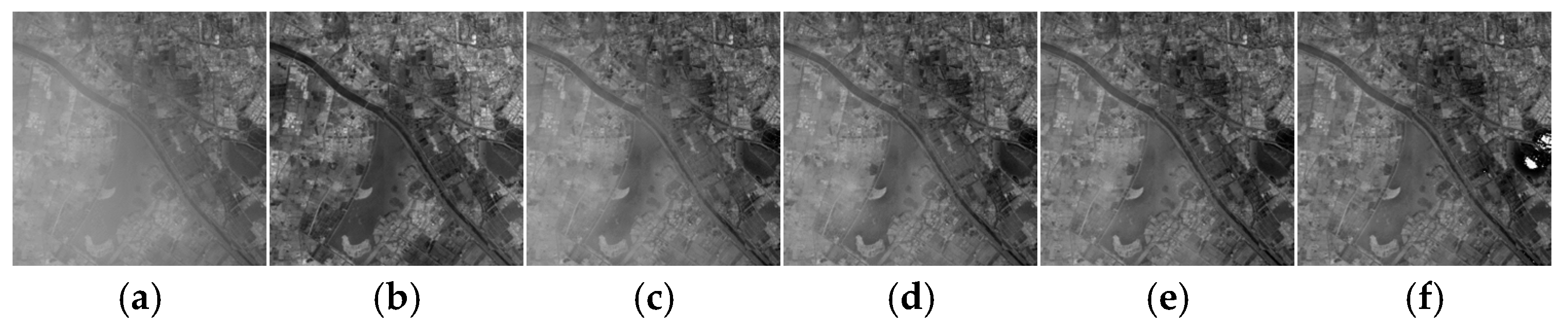
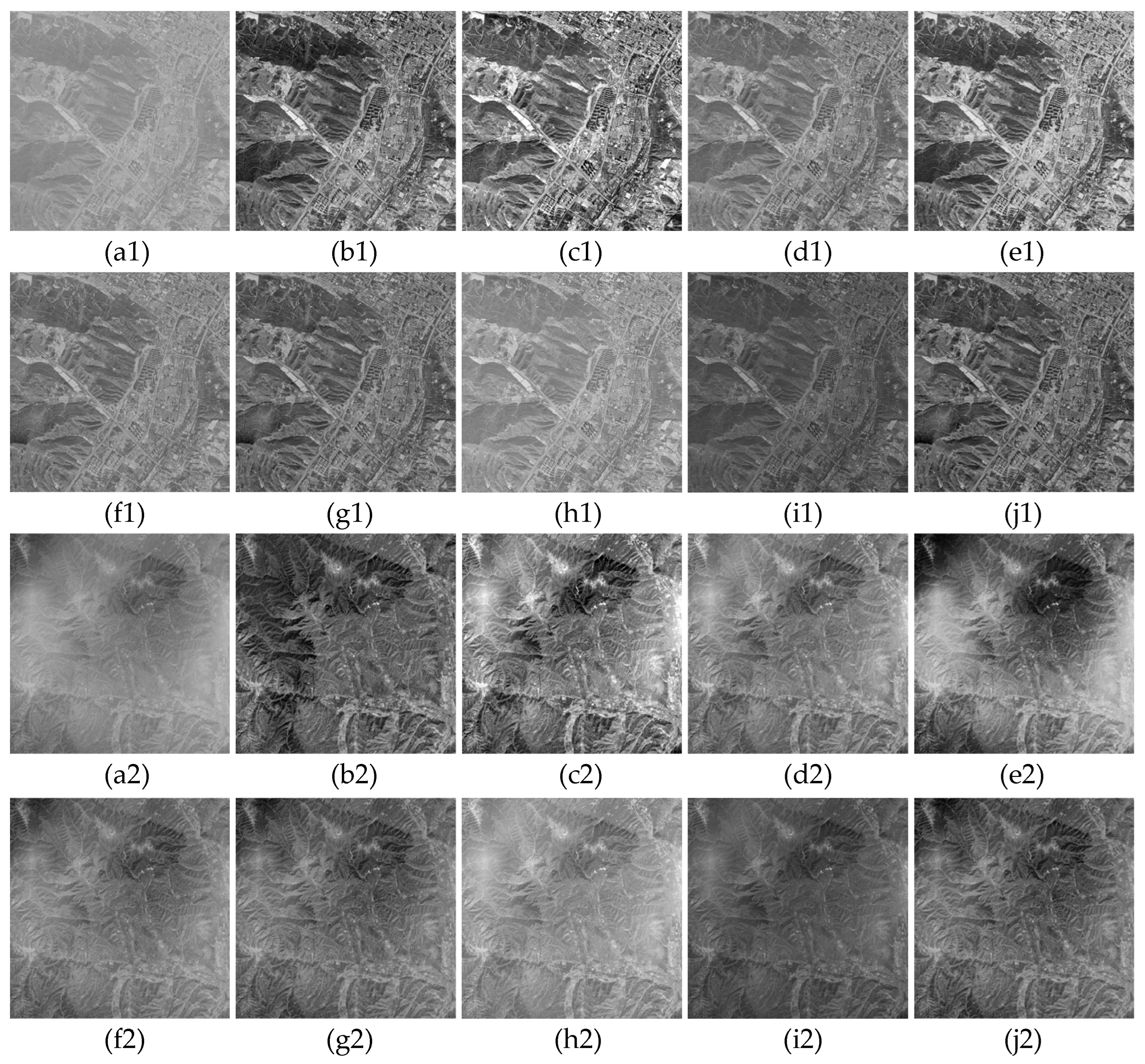
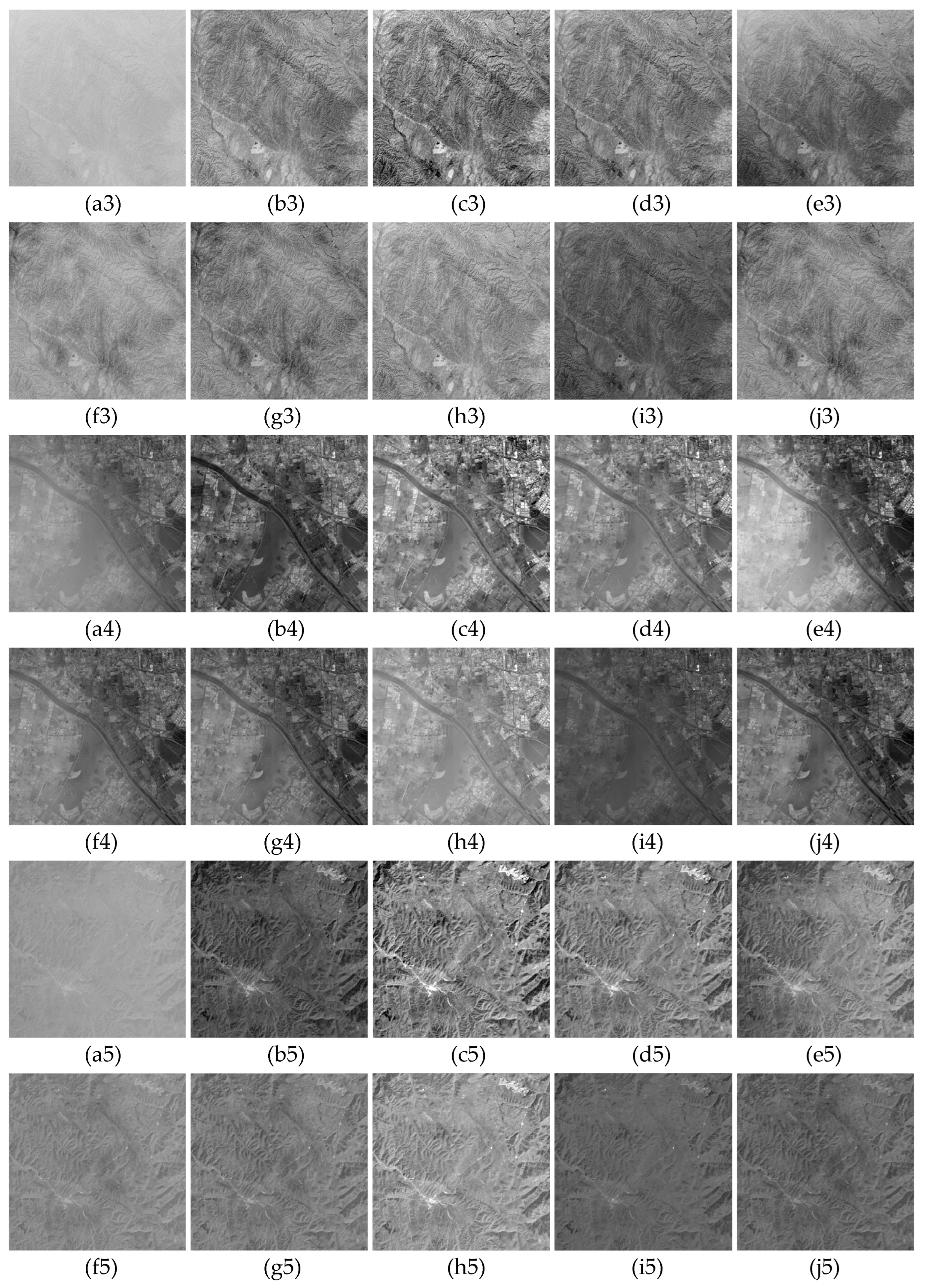
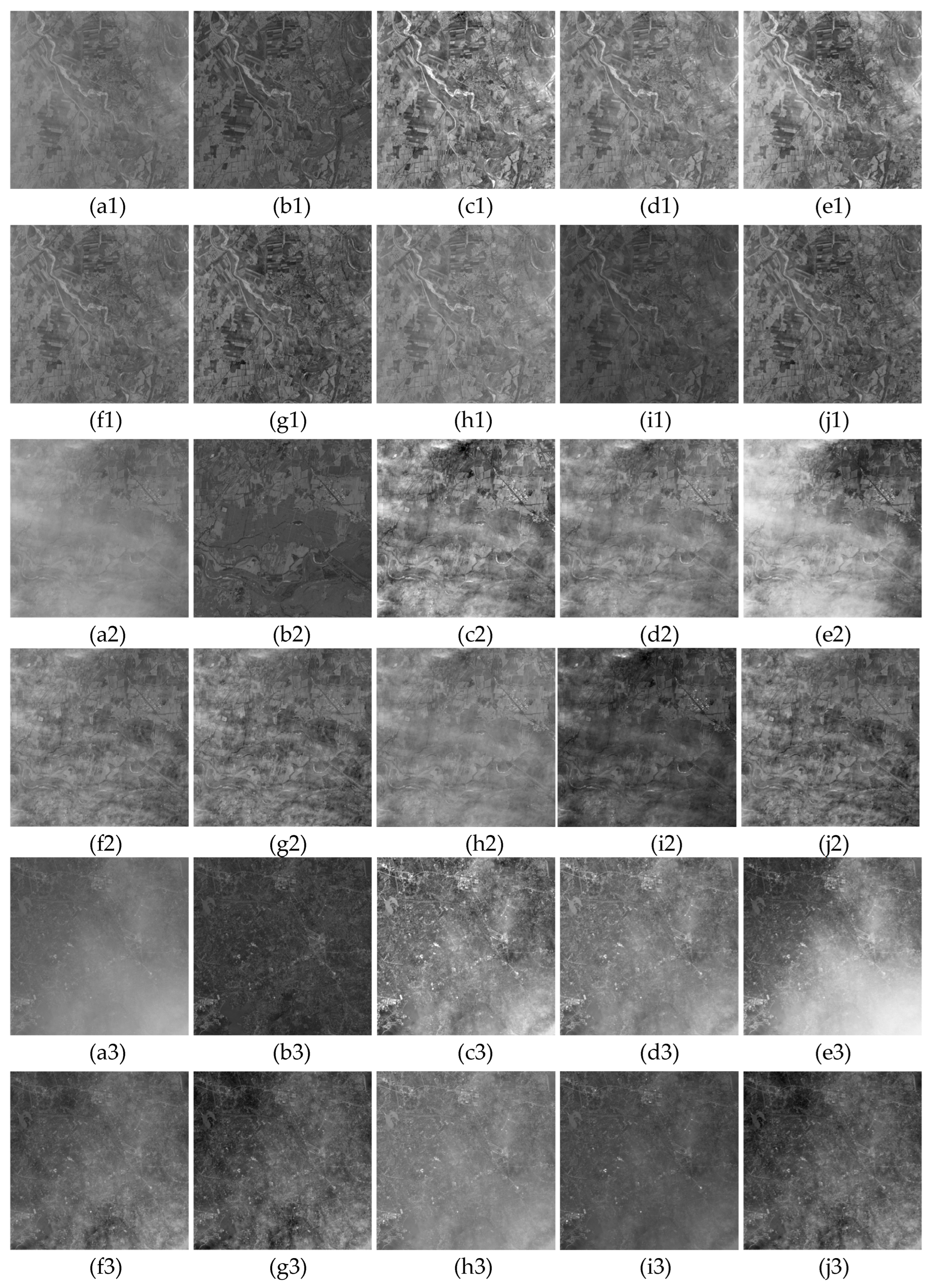
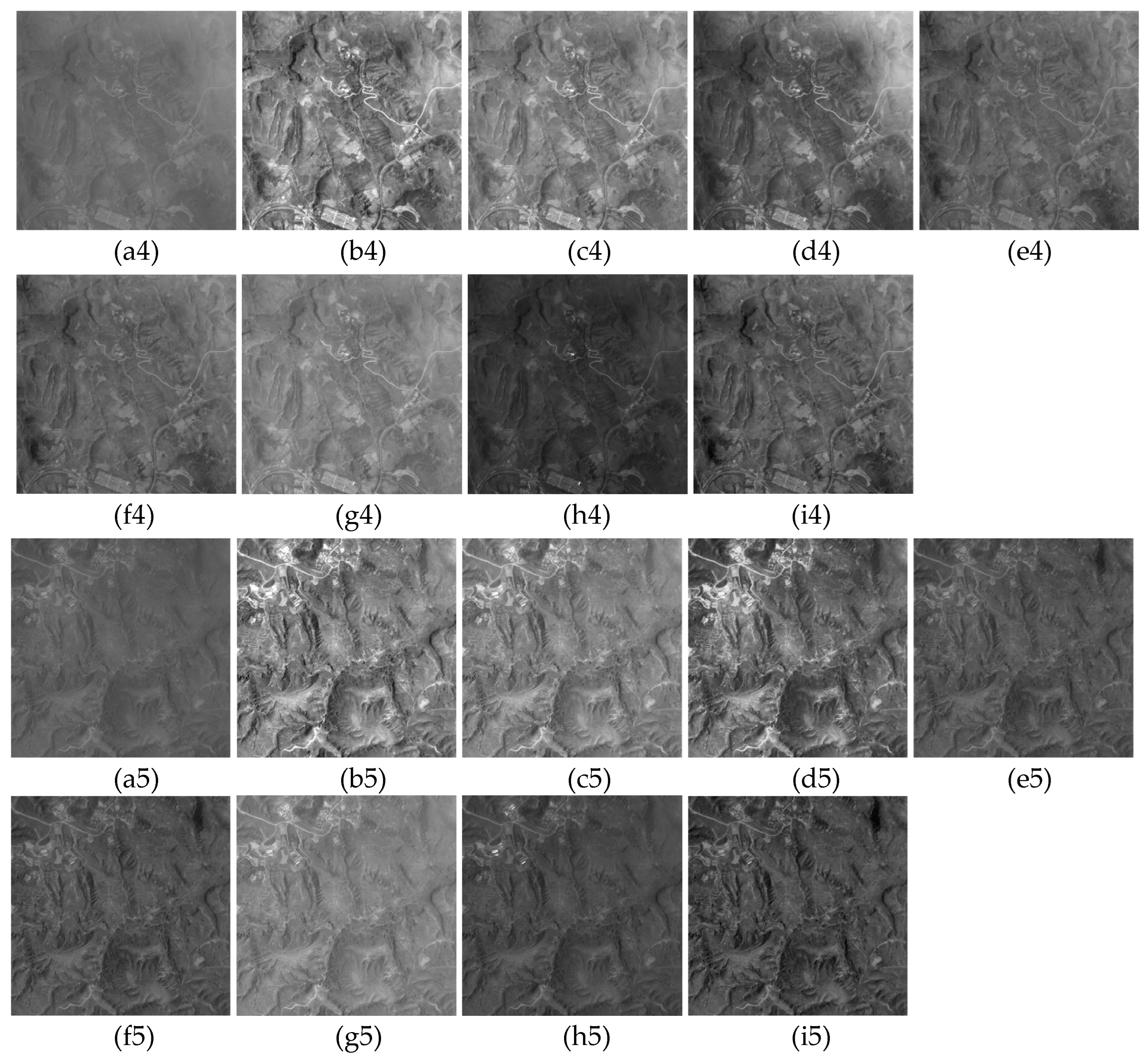
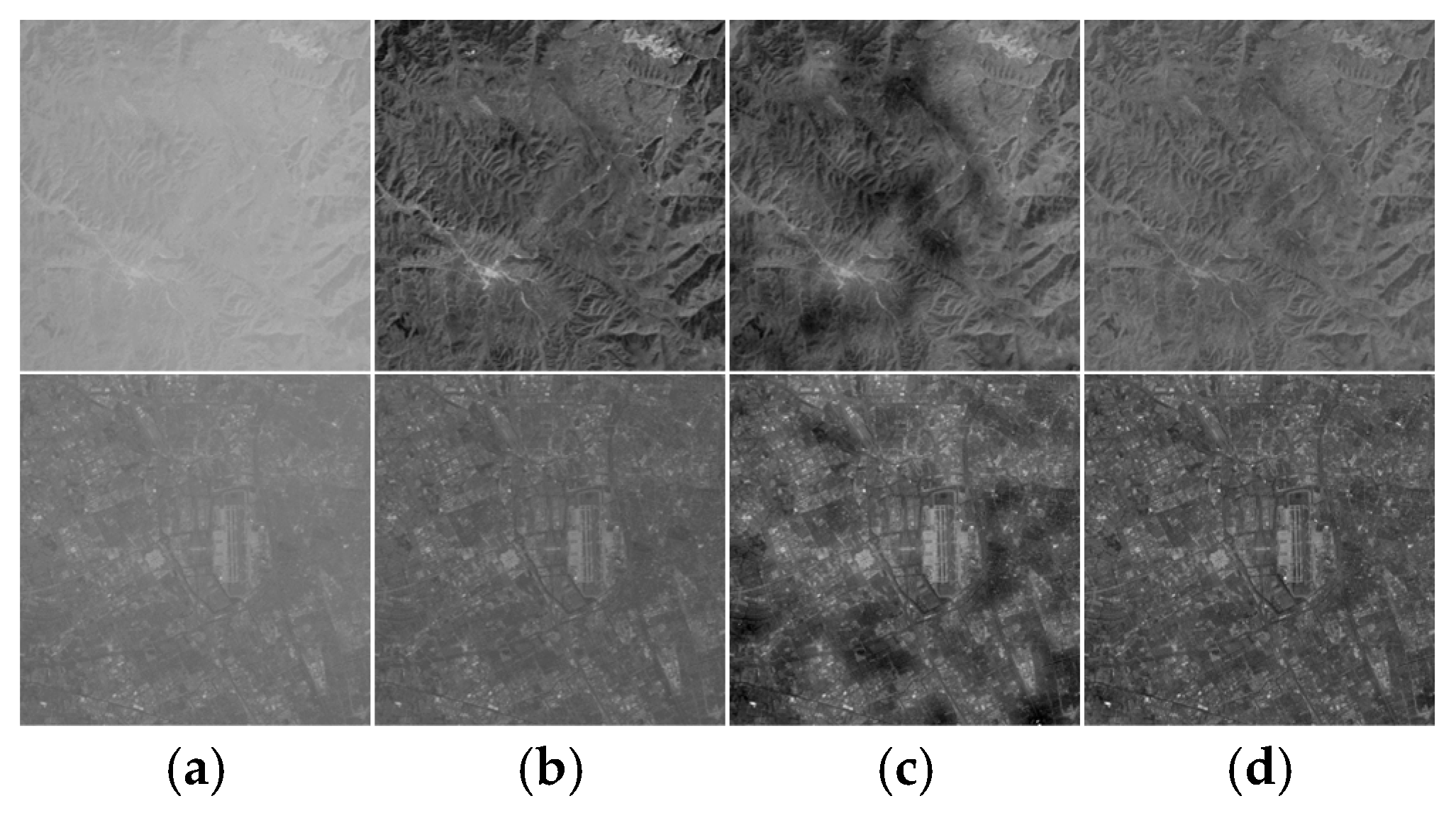
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Evaluation
3.2. Quantitative Evaluation
3.3. Ablation Experiment
3.3.1. Validity of Atmospheric Light Calculation
3.3.2. Influence of Patch Classification Threshold
3.4. Running Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Leung, H. Fusion of multispectral and panchromatic images using a restoration-based method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, H. Remote Sensing Image Dehazing via a Local Context-Enriched Transformer. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ngo, D.; Choi, Y.; Kang, B. Autonomous Single-Image Dehazing: Enhancing Local Texture with Haze Density-Aware Image Blending. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1956–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Gu, N. AIPNet: Image-to-image single image dehazing with atmospheric illumination prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Gong, T.; Liang, Z.; Chen, T.; Cong, R.; Bai, H.; Zhao, Y. Perception-oriented UAV image dehazing based on super-pixel scene prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5913519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, A.; Liu, C. Variational single nighttime image haze removal with a gray haze-line prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, P.; Chen, H.; Tan, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, E. Single image dehazing using saturation line prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3238–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Mai, J.; Shao, L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Si, G.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, B.; Lv, H. Haze removal for a single remote sensing image using low-rank and sparse prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5615513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wen Liu, R.; Sun, J.; Zeng, T. Rank-one prior: Toward real-time scene recovery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 10–25 June 2021; pp. 14797–14805. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Tang, G.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.; Maybank, S. Single image haze removal based on a simple additive model with haze smoothness prior. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 3490–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tan, H.; Li, K. MAPD: An FPGA-based real-time video haze removal accelerator using mixed atmosphere prior. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2023, 42, 4777–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Xu, X.; Jia, K.; Qing, C.; Tao, D. Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, D. AOD-Net: All-in-one dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Internation Conference Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4780–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B. Multi-stream fusion network with generalized smooth L1 loss for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7620–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J. GriddehazeNet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Internation Conference Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7313–7322. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Pan, Z.; Tang, H.; Hu, Y. Cloudformer: A cloud-removal network combining self-attention mechanism and convolution. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.; Huang, C.; Kang, L. Multi-scale deep residual learning-based single image haze removal via image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 3153–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Deng, F.; Jia, S.; Jia, X.; Plaza, A. Attention mechanism-based generative adversarial networks for cloud removal in Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, K.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Ren, P. Cloudy image arithmetic: A cloudy scene synthesis paradigm with an application to deep-learning-based thin cloud removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5612616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Luo, Z.; Ren, D.; Du, B.; Chang, L.; Wan, J. Unsupervised multi-branch network with high-frequency enhancement for image dehazing. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 156, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, C.; Dai, L. Unpaired image dehazing with physical-guided restoration and depth-guided refinement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, S.; Tao, M.; Wang, L. Dehaze-AGGAN: Unpaired remote sensing image dehazing using enhanced attention-guide generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5630413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Muhammad, K.; Irfan, M.; Anwar, S.; Sajjad, M.; Imran, A.; Albuquerque, V. Light-DehazeNet: A novel lightweight CNN architecture for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8968–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Tao, D. A light dual-task neural network for haze removal. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Kung, S. PSRNet: A progressive self-refine network for lightweight optical remote sensing image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5648413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Ning, J.; Ding, Z.; Duo, B. Additional self-attention transformer with adapter for thick haze removal. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6004705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Fan, S.; Li, P.; Jin, J.; Jin, G.; Fan, L. Learning an effective transformer for remote sensing satellite image dehazing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 8002305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Yin, J.; Deng, F.; Xie, L. MABDT: Multi-scale attention boosted deformable transformer for remote sensing image dehazing. Signal Process. 2024, 229, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Song, T.; Qi, X.; Jin, G.; Jin, J.; Ma, L. Prompt-guided sparse transformer for remote sensing image dehazing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 8003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Ding, H.; Yan, S.; Shi, Z. Proxy and cross-stripes integration transformer for remote sensing image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5640315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhong, Q.; Du, B.; Tu, Z.; Wan, J.; Wang, W.; Ren, D. Bidirectional-modulation frequency-heterogeneous network for remote sensing image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xie, F.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z. Robust haze and thin cloud removal via conditional variational autoencoders. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5604616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Q.; Tong, X. Nighttime light remote sensing image haze removal based on a deep learning model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fang, H.; Ding, J.; Kuo, S. PMHLD: Patch map-based hybrid learning DehazeNet for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 6773–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. RefineDNet: A weakly supervised refinement framework for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, H. Depth information assisted collaborative mutual promotion network for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference Computer Vision Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 2846–2855. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ward, R. Fast image/video contrast enhancement based on weighted thresholded histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 1997, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Spatial entropy-based global and local image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5298–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, X.; Jia, R.; Cheung, Y. Reversible data hiding with brightness preserving contrast enhancement by two-dimensional histogram modification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 7605–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; You, J.; Jeong, J. Contrast enhancement using histogram equalization based on logarithmic mapping. Opt. Eng. 2012, 51, 067002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Dai, S. Adaptive histogram equalization framework based on new visual prior and optimization model. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2025, 132, 117246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Peng, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; An, F. FPGA-based low-visibility enhancement accelerator for video sequence by adaptive histogram equalization with dynamic clip-threshold. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2020, 67, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kawanishi, T.; Kashino, K. Reflectance-guided histogram equalization and comparametric approximation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Syue, J.; Radzicki, V.; Lee, H. An efficient fusion-based defogging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, M.; Kang, M. Single image dehazing via atmospheric scattering model-based image fusion. Signal Process. 2020, 178, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Parihar, A. Variational optimization based single image dehazing. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 79, 103241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X. Depth-aware total variation regularization for underwater image dehazing. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 98, 116408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Internation Conference Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, E.; Wang, A.; Shiri, B.; Lin, W. VNDHR: Variational single nighttime image dehazing for enhancing visibility in intelligent transportation systems via hybrid regularization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 10189–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Tan, J.; Li, Y. Multi-purpose oriented single nighttime image haze removal based on unified variational Retinex model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, X.; He, L.; Lu, W. Single image dehazing with depth-aware non-local total variation regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 5178–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kim, S.; Ra, J. Enhancement of optical remote sensing images by subband-decomposed multiscale Retinex with hybrid intensity transfer function. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Sharif, M.; Bibi, N.; Usman, M.; Haider, S.; Zainab, S.; Shah, J.; Bashir, Y.; Muhammad, N. Localization of radiance transformation for image dehazing in wavelet domain. Neurocomputing 2019, 381, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Narasimhan, S. Vision in bad weather. In Proceedings of the IEEE Internation Conference Computer Vision (ICCV), Corfu, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, L. Single remote sensing image dehazing using a prior-based dense attentive network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Dense haze removal based on dynamic collaborative inference learning for remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5631016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. A remote sensing image dataset for cloud removal. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.00600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, Z.; Qian, H.; Du, X. Vision transformers for single image dehazing. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.03883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilanci, M.; Arikan, O.; Pinar, M. Structured least squares problems and robust estimators. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Yu, C. Perceptual learning of Vernier discrimination transfers from high to zero noise after double training. Vision Res. 2019, 156, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautiere, N.; Tarel, J.P.; Aubert, D.; Dumont, E. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges. Image Anal. Stereol. 2008, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | RICE-1 | RSHaze | Jilin-1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | RMSC | e | PSNR | SSIM | RMSC | e | RMSC | e | |
| Jang et al. [55] | 19.53 | 0.76 | 25.69 | 0.11 | 17.42 | 0.72 | 24.05 | 0.13 | 22.61 | 0.07 |
| Khan et al. [56] | 23.79 | 0.80 | 19.46 | 0.13 | 20.77 | 0.78 | 17.16 | 0.12 | 17.83 | 0.09 |
| Singh et al. [49] | 16.83 | 0.71 | 22.18 | 0.08 | 15.97 | 0.67 | 15.71 | 0.07 | 19.42 | 0.06 |
| DehazeNet [14] | 27.04 | 0.85 | 17.93 | 0.19 | 25.29 | 0.83 | 19.86 | 0.15 | 16.08 | 0.13 |
| Ding et al. [34] | 28.51 | 0.87 | 20.59 | 0.24 | 27.62 | 0.85 | 21.19 | 0.19 | 16.94 | 0.16 |
| AMGAN-CR [20] | 19.26 | 0.78 | 19.84 | 0.10 | 18.61 | 0.74 | 16.86 | 0.09 | 16.62 | 0.11 |
| MS-GAN [21] | 22.74 | 0.82 | 20.18 | 0.15 | 26.57 | 0.81 | 18.37 | 0.12 | 17.16 | 0.12 |
| Proposed | 31.73 | 0.91 | 23.74 | 0.32 | 29.48 | 0.89 | 23.94 | 0.26 | 20.96 | 0.19 |
| Method | RICE-1 | RSHaze | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| HE_a1 | 20.92 | 0.81 | 19.24 | 0.78 |
| Proposed | 31.73 | 0.91 | 29.48 | 0.89 |
| RICE-1 | RSHaze | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| 0.45 | 26.93 | 0.83 | 26.31 | 0.82 |
| 0.55 | 27.38 | 0.86 | 27.19 | 0.84 |
| 0.65 | 31.73 | 0.91 | 29.48 | 0.89 |
| 0.75 | 25.39 | 0.82 | 24.57 | 0.79 |
| Methods | Time |
|---|---|
| Jang et al. [55] | 0.25 (C) |
| Khan et al. [56] | 0.48 (C) |
| Singh et al. [49] | 0.32 (C) |
| DehazeNet [14] | 0.29 (G) |
| Ding et al. [34] | 0.36 (G) |
| AMGAN-CR [20] | 0.38(G) |
| MS-GAN [21] | 0.27(G) |
| Proposed | 0.21 (C) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, C. Dehazing of Panchromatic Remote Sensing Images Based on Histogram Features. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203479
Wang H, Ding Y, Zhou X, Yuan G, Sun C. Dehazing of Panchromatic Remote Sensing Images Based on Histogram Features. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(20):3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203479
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Yalin Ding, Xiaoqin Zhou, Guoqin Yuan, and Chao Sun. 2025. "Dehazing of Panchromatic Remote Sensing Images Based on Histogram Features" Remote Sensing 17, no. 20: 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203479
APA StyleWang, H., Ding, Y., Zhou, X., Yuan, G., & Sun, C. (2025). Dehazing of Panchromatic Remote Sensing Images Based on Histogram Features. Remote Sensing, 17(20), 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17203479





