Local Surface Environmental Changes in a Basin in the Permafrost Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Affected by Lake Outburst Event
Abstract
Highlights
- A “hot zone” with higher surface temperatures and reduced vegetation cover emerged around Zonag Lake following its outburst.
- Downstream areas (from Kusai Lake to Salt Lake) exhibited significantly higher dryness levels compared to the upstream region.
- The outburst-induced surface changes drive contrasting permafrost processes: desertification enhances permafrost development upstream, while wetting accelerates degradation downstream.
- This study provides critical insights for assessing environmental impacts and engineering safety in high-altitude permafrost regions under lake outburst events.
Abstract
1. Introduction
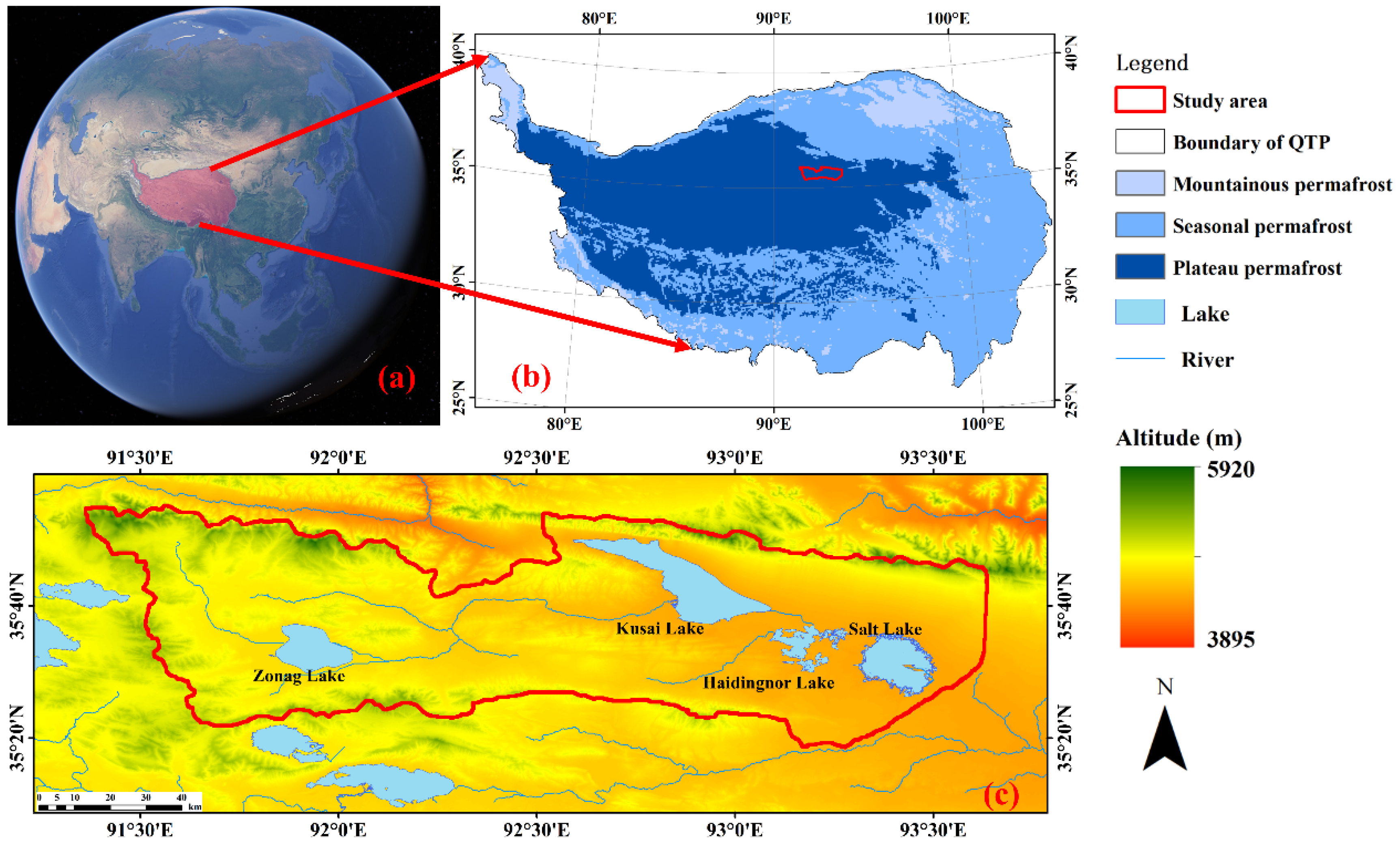
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
3. Methods
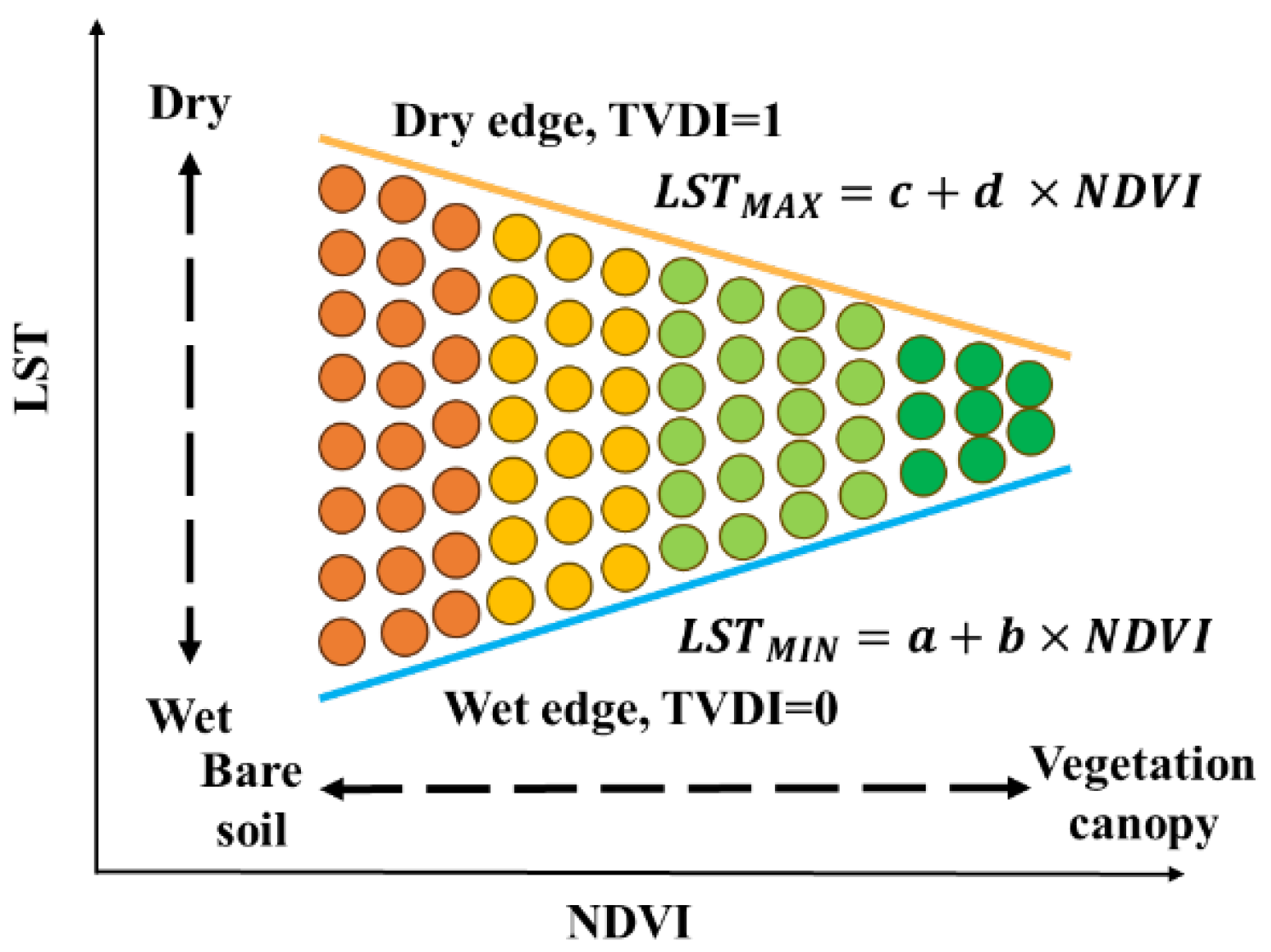
3.1. Environmental Indexes: LST, NDVI and TVDI
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.3. Research Workflow
4. Results
4.1. The Changes in the Environmental Indexes
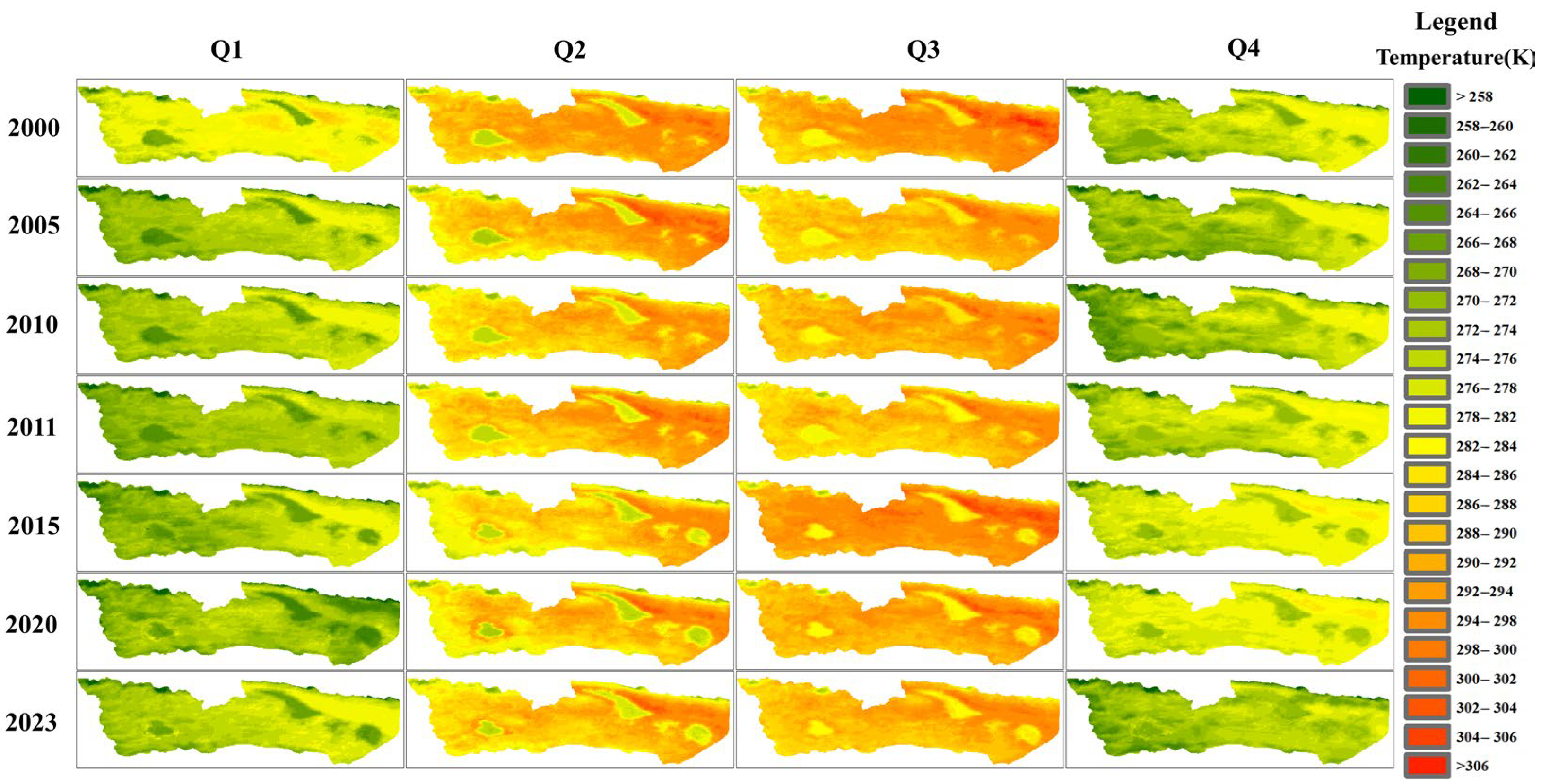
4.1.1. Changes in LST and NDVI
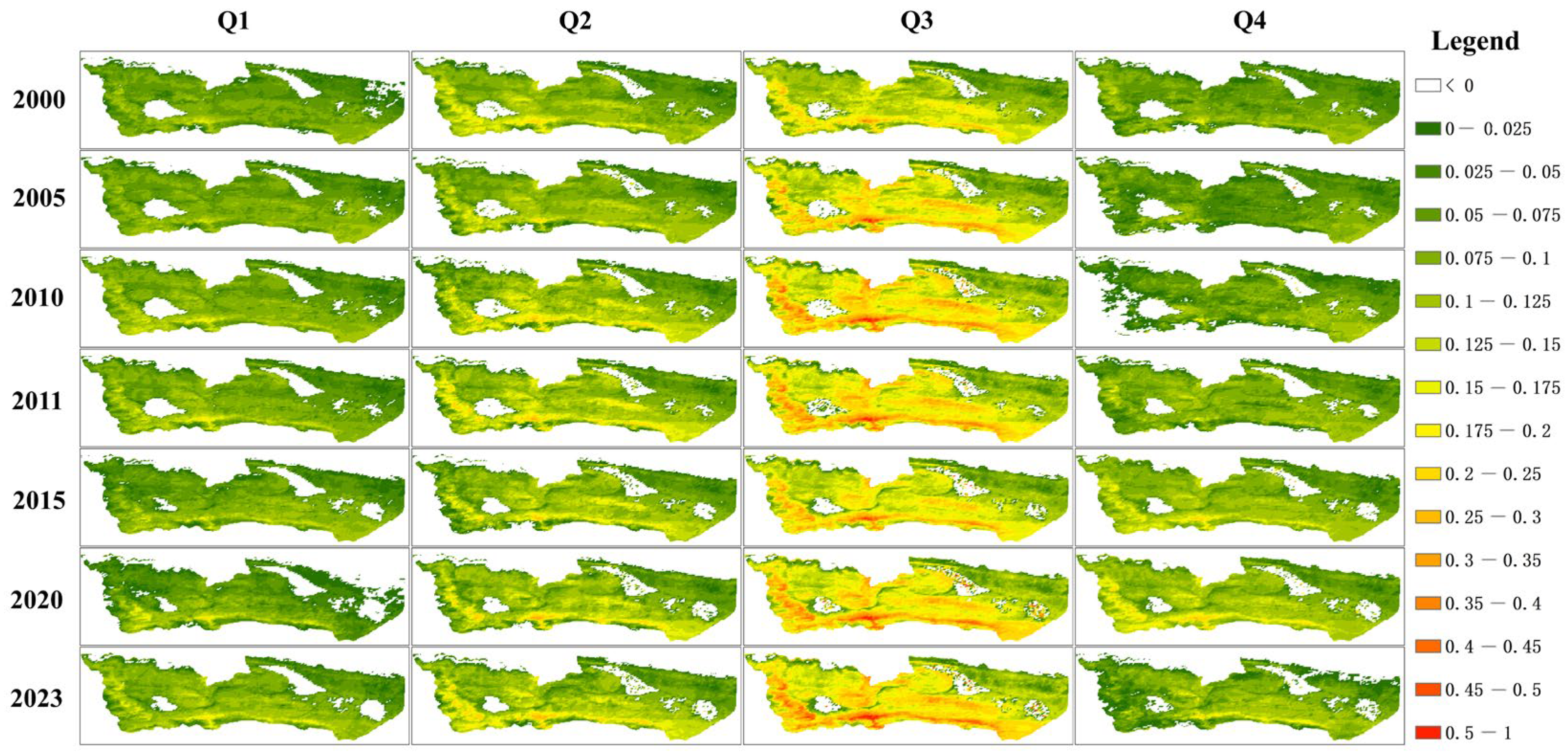
4.1.2. Changes in TVDI
4.2. Temporal and Spatial Analysis of the Environmental Indexes
4.2.1. Temporal Analysis of the Mean Value
4.2.2. Spatially Analysis
5. Discussion
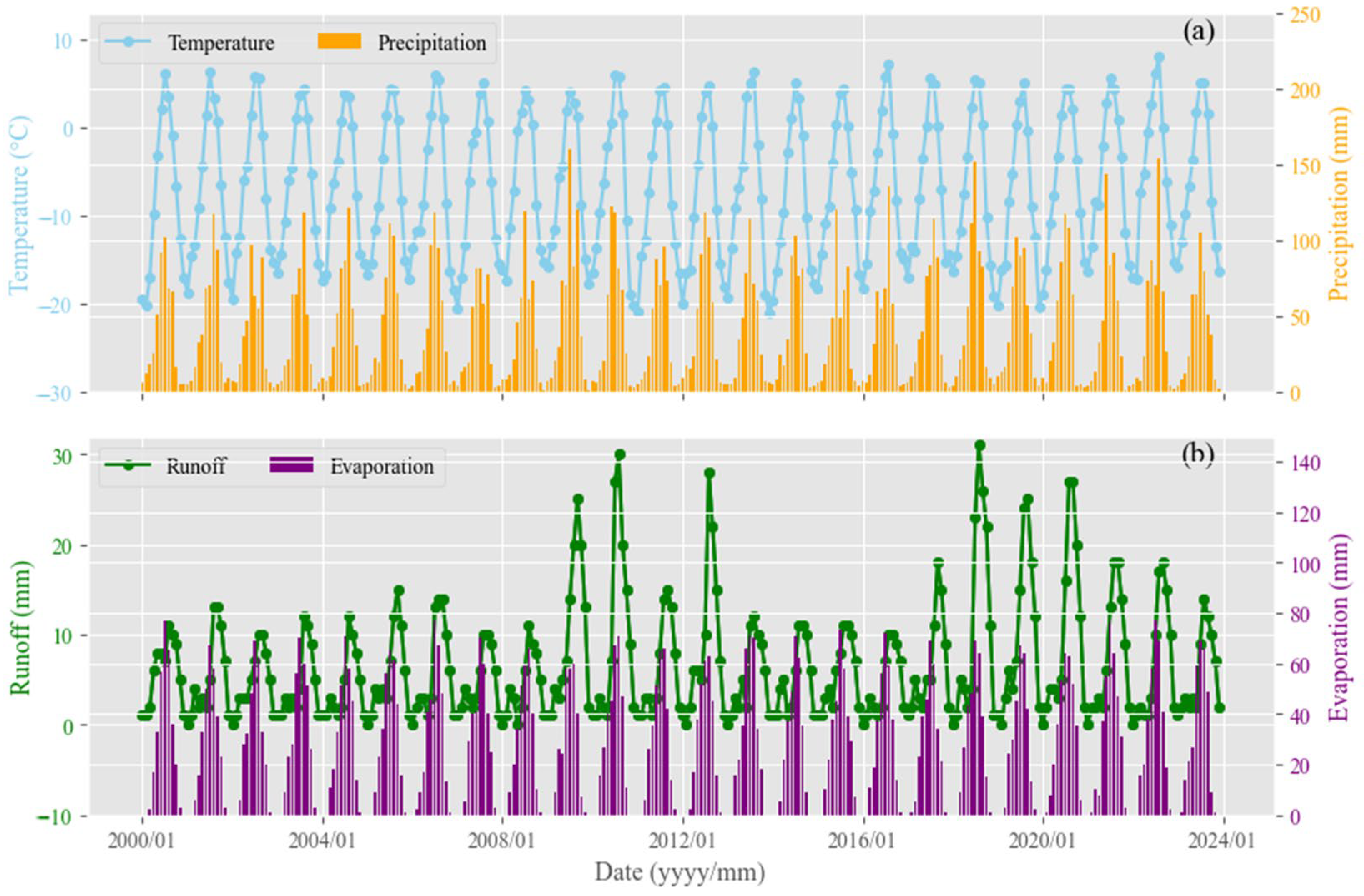
5.1. The Climate Conditions Triggered the Surface Environmental Changes
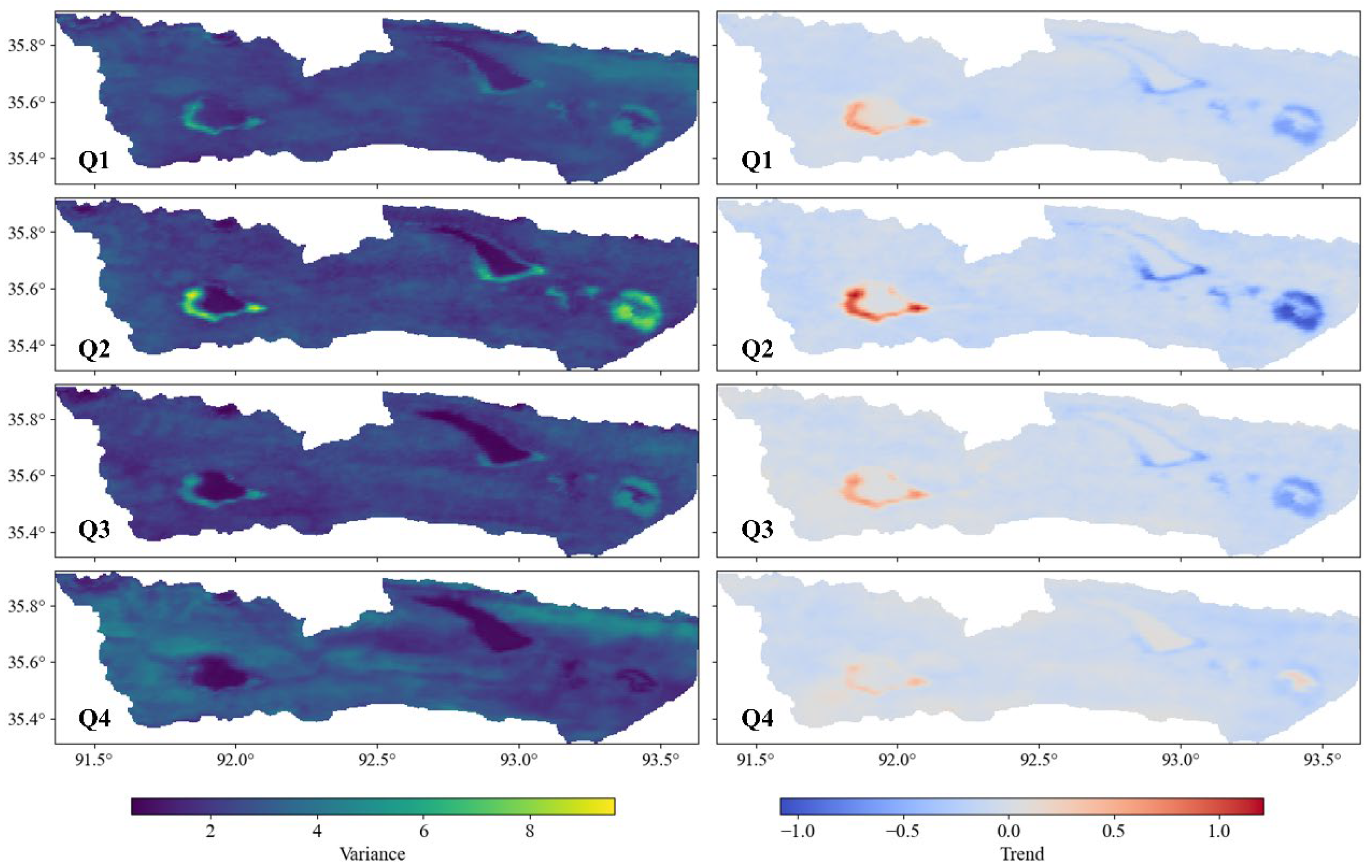
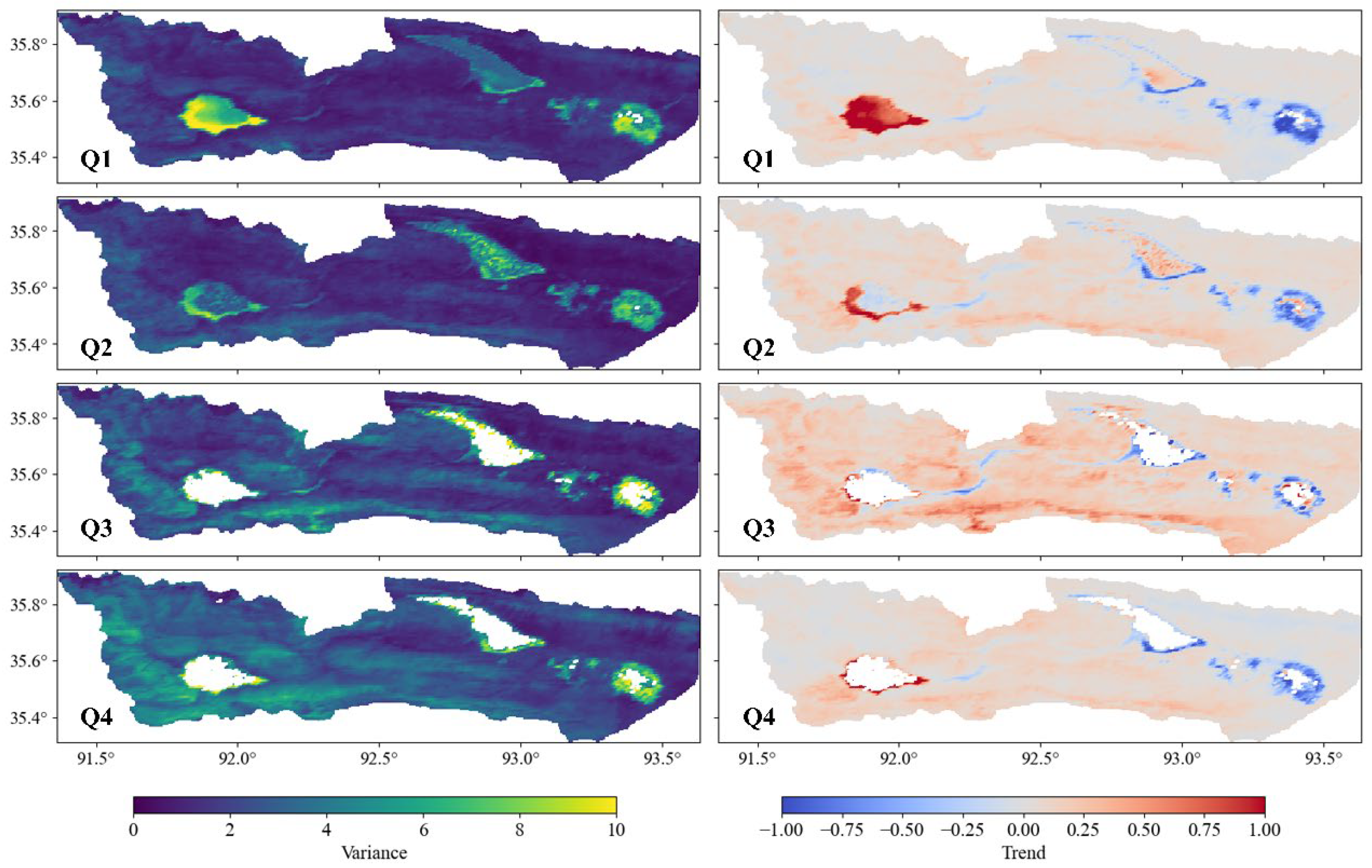
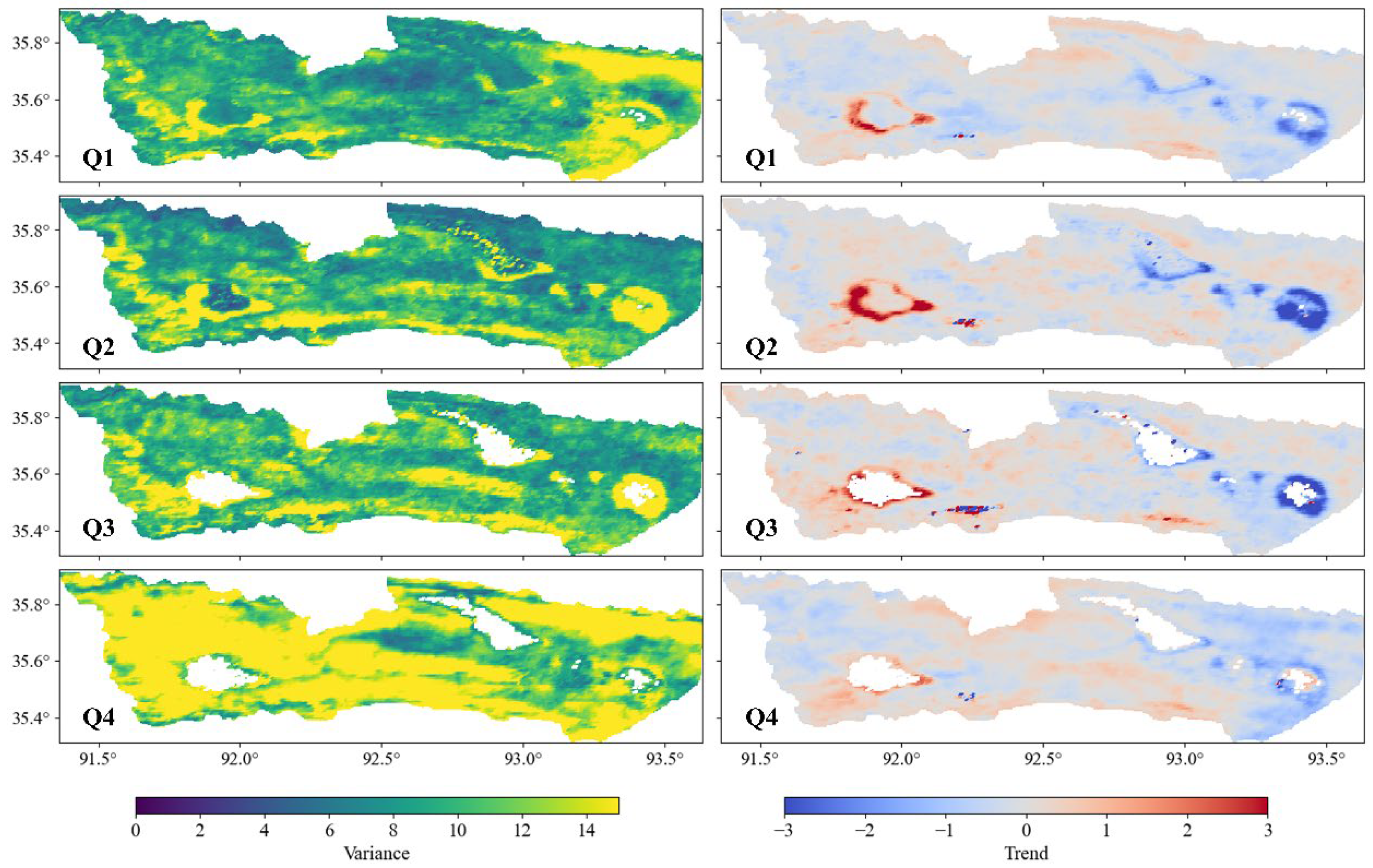
5.2. The Variance and Trend of Surface Environmental Changes in the Basin
5.3. Broader Ecological, Climatic, and Engineering Implications
6. Conclusions
- Analysis of LST and NDVI extracted from satellite data revealed the emergence of a “hot zone” in the post-outburst Zonag Lake area, indicating higher surface temperatures compared to surrounding land. Additionally, reduced vegetation cover due to the exposed lakebed negatively impacted vegetation development in this region.
- Calculation of the TVDI showed significantly higher dryness indexes in downstream areas of Zonag Lake, such as from Kusai Lake to Salt Lake, compared to the upstream Zonag Lake area.
- Temporal analysis indicated a declining trend in average LST despite seasonal fluctuations, while NDVI values showed an increasing trend from 2000 to 2023, indicating an improvement in vegetation conditions in the region.
- Analysis of geographical centroid shifts in environmental indexes across different seasons revealed varying migration directions and distances during specific time periods, which are linked to seasonal climate changes and the outburst event.
- The surface environmental changes could lead to different variations in permafrost. The local desertification around Zonag Lake accelerates permafrost development, while the wetting environment around Salt Lake could cause permafrost degradation.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.Q.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.F.; Zheng, G.X. A robust but variable lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Piao, S.; Bolch, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; et al. Extensive and drastically different alpine lake changes on Asia’s high plateaus during the past four decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.M.; Wang, W.; Niu, F.j.; Gao, Z.Y.; Huang, W.K.; Cao, H.K. Thermokarst lakes disturb the permafrost structure and stimulate through-talik formation in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China: A hydrogeophysical investigation. EGUsphere, 2025; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Bolch, T.; Chen, W.F.; Crétaux, J.F. Comprehensive estimation of lake volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau during 1976–2019 and basin-wide glacier contribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Ohata, T.; Kadota, T. Land-surface hydrological processes in the permafrost region of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2003, 283, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, A.; Yao, T. Rapid expansion of glacial lakes caused by climate and glacier retreat in the central Himalayas. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Reynolds, J.M. An overview of glacial hazards in the Himalayas. Quat. Int. 2000, 65–66, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugar, D.H.; Burr, A.; Haritashya, U.K.; Kargel, J.S.; Watson, C.S.; Kennedy, M.C.; Bevington, A.R.; Betts, R.A.; Harrison, S.; Strattman, K. Rapid worldwide growth of glacial lakes since 1990. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Tian, J.C.; Zhang, Z.B.; Qiang, B. Debris flow induced by glacial-lake break in southeast Tibet. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Dang, C.; Cheng, Z.L.; Scott, K.M. Debris flows resulting from glacial-lake outburst floods in Tibet, China. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 31, 508–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Tang, C.; Cheng, Z.L.; Liu, Y. Impact of temperature on glacier-lake outbursts in Tibet. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2011, 41, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Preliminary study on debris flow induced by glacier lake outburst in Tibet. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2006, 3, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Feng, Q.H. Dangerous glacial lake and outburst features in Xizang Himalayas. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1989, 3, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D. Characteristics of debris flow caused by outburst of glacial lake in Boqu River, Xizang, China, 1981. GeoJournal 1988, 17, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.L.; Jin, H.J.; Du, H.Q.; Li, C.; Ma, Q.; Duan, S.Q.; Li, G.S. Variation of alpine lakes from 1986 to 2019 in the headwater area of the Yellow River, Tibetan Plateau using Google Earth Engine. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 11, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Liu, H.; Lu, J. Hydrothermal processes of alpine tundra lakes, Beiluhe Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Niu, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, G. Thermal regime at bottom of thermokarst lakes along Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor. Earth Sci. 2015, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Niu, F.J.; Xu, Z.Y.; Wang, P. Thermal regime of a thermokarst lake and its influence on permafrost, Beiluhe Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2010, 21, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Zhelezniak, M.; Wang, D.Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhirkov, A.; Gao, Q. Thermal interaction between a thermokarst lake and a nearby embankment in permafrost regions. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 155, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.J.; Cheng, G.D.; Shi, Y.Y.; Yin, G.A.; Luo, J. Permafrost and stability of the major linear engineering in the pan-Arctic region. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2021, 43, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, G.Q.; Niu, F.J.; Mu, Y.H. Progress and prospect of the basic research on the major permafrost projects in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. China Basic Sci. 2016, 18, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.H.; Ma, W.; Li, G.Y.; Niu, F.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y. Impacts of supra-permafrost water ponding and drainage on a railway embankment in continuous permafrost zone. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.J.; Dong, S.; Lin, Z.J.; Lu, J.; Luo, J. Distribution of thermokarst lakes and its thermal influence on permafrost along Qinghai-Tibet Highway. Adv. Earth Sci. 2013, 28, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.K.; Niu, F.J.; Li, G.Y.; Mu, Y.; Chai, M.; He, P. The outburst of a lake and its impacts on redistribution of surface water bodies in high-altitude permafrost region. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Xie, C.W.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yang, G.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Yue, G.Y. Dynamic changes in lakes in the Hoh Xil region before and after the 2011 outburst of Zonag Lake. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.K.; Niu, F.J.; Mu, Y.H.; Li, G.; Chai, M.; Gao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, K.; Mao, Y. Dynamic variations in thermal regime and surface deformation along the drainage channel for an expanding lake on the Tibetan Plateau. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2266661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, G.; Pang, Q.; Zou, D.; Liu, H. The Impact of Permafrost Degradation on Lake Changes in the Endorheic Basin on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, G. Analysis on expansion trend and outburst risk of the Yanhu Lake in Hoh Xil region, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2019, 41, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.K.; Niu, F.J.; Mu, Y.H.; He, P.; Gao, Z.; Fan, X. Primarily investigation with multiple methods on permafrost state around a rapid change lake in the interior of the Tibet Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.X.; Xing, Z.; Zou, D.; Hu, G.; Xie, C.; Pang, Q.; Liu, G.; Du, E.; et al. Characteristics of freeze–thaw cycles in an endorheic basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Pang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. The formation of permafrost in the bottom of the Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau after an outburst: Monitoring and simulation. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.; Wu, T.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Hu, G.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; et al. New permafrost is forming on the exposed bottom of Zonag Lake on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xie, C.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Pang, Q.; Liu, G.; et al. Permafrost characteristics and potential influencing factors in the lake regions of Hoh Xil, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.H.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Jin, H.; Jin, R. Distribution of permafrost in China: An overview of existing permafrost maps. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2012, 23, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, S.; Duguay, C.R.; Allard, M. Comparison of MODIS-derived land surface temperatures with ground surface and air temperature measurements in continuous permafrost terrain. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of surface moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, D. Does summer precipitation trend over and around the Tibetan Plateau depend on elevation? Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.G.; Yao, T.D.; Davis, M.E.; Mosley-Thompson, E.; Wu, G.; Porter, S.E.; Xu, B.; Lin, P.N.; Wang, N.; Beaudon, E.; et al. Ice core records of climate variability on the Third Pole with emphasis on the Guliya ice cap. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 188, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Jin, J.M.; Zhou, J.F.; Li, X.; Ju, J.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Q.; et al. Drainage basin reorganization and endorheic–exorheic transition triggered by climate change and human intervention. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2021, 201, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Liu, A.B.; Cheng, X. Vegetation grows more luxuriantly in Arctic permafrost drained lake basins. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5865–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Grosse, G.; Arp, C.D.; Jones, M.C.; Anthony, K.M.W.; Romanovsky, V.E. Modern thermokarst lake dynamics in the continuous permafrost zone, northern Seward Peninsula, Alaska. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, Artn G00m03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Grosse, G.; Farquharson, L.M.; Roy-Léveillée, P.; Veremeeva, A.; Kanevskiy, M.Z.; Gaglioti, B.; Breen, A.L.; Parsekian, A.D.; Ulrich, M.; et al. Lake and drained lake basin systems in lowland permafrost regions. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liljedahl, A.K.; Burn, C.R.; Grosse, G.; Noetzli, J.; Goetz, S.J.; Douglas, T.A.; Yang, Y.H. Permafrost vulnerability to climate change: Understanding thaw dynamics and climate feedback of permafrost degradation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

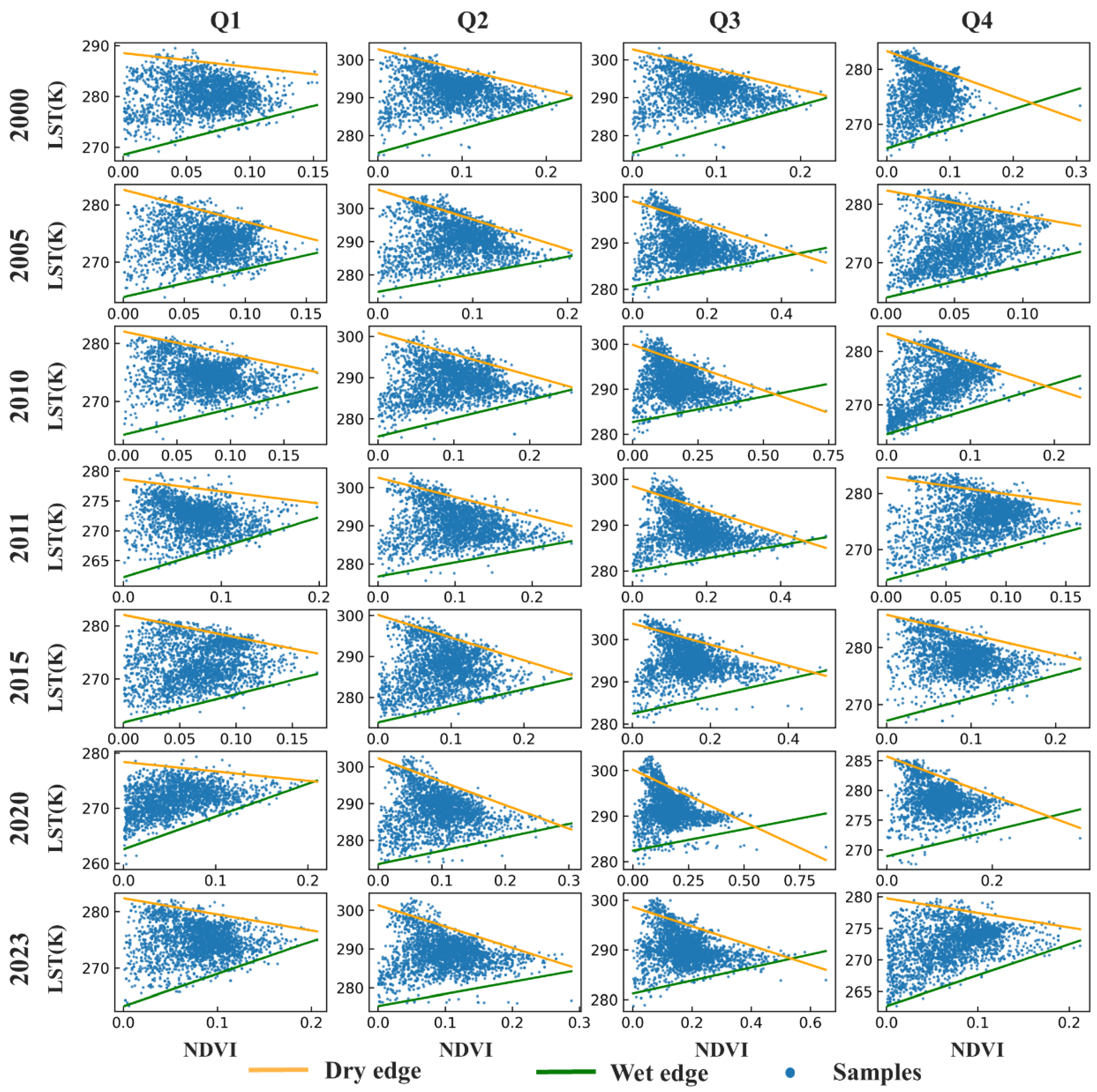
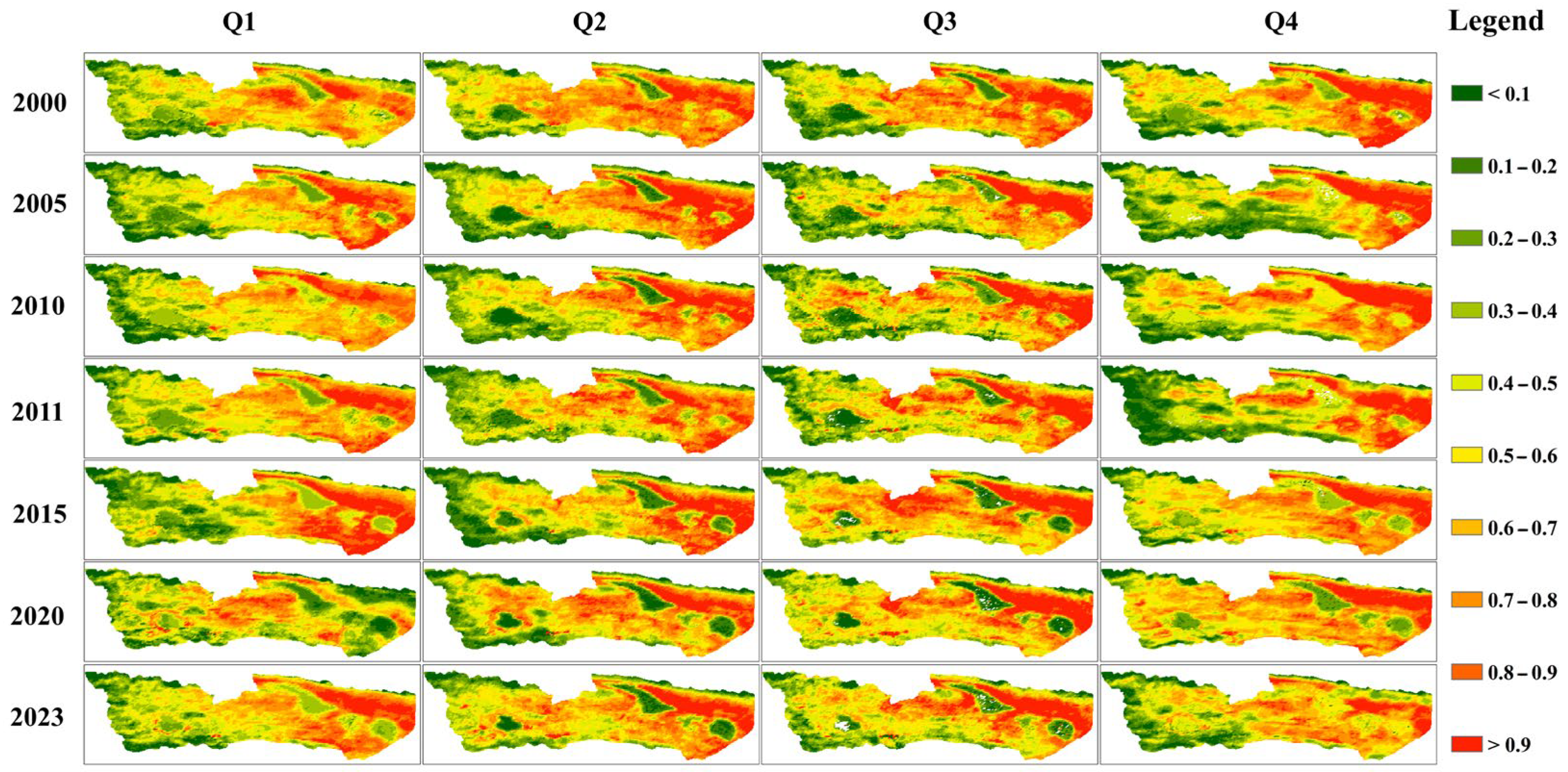
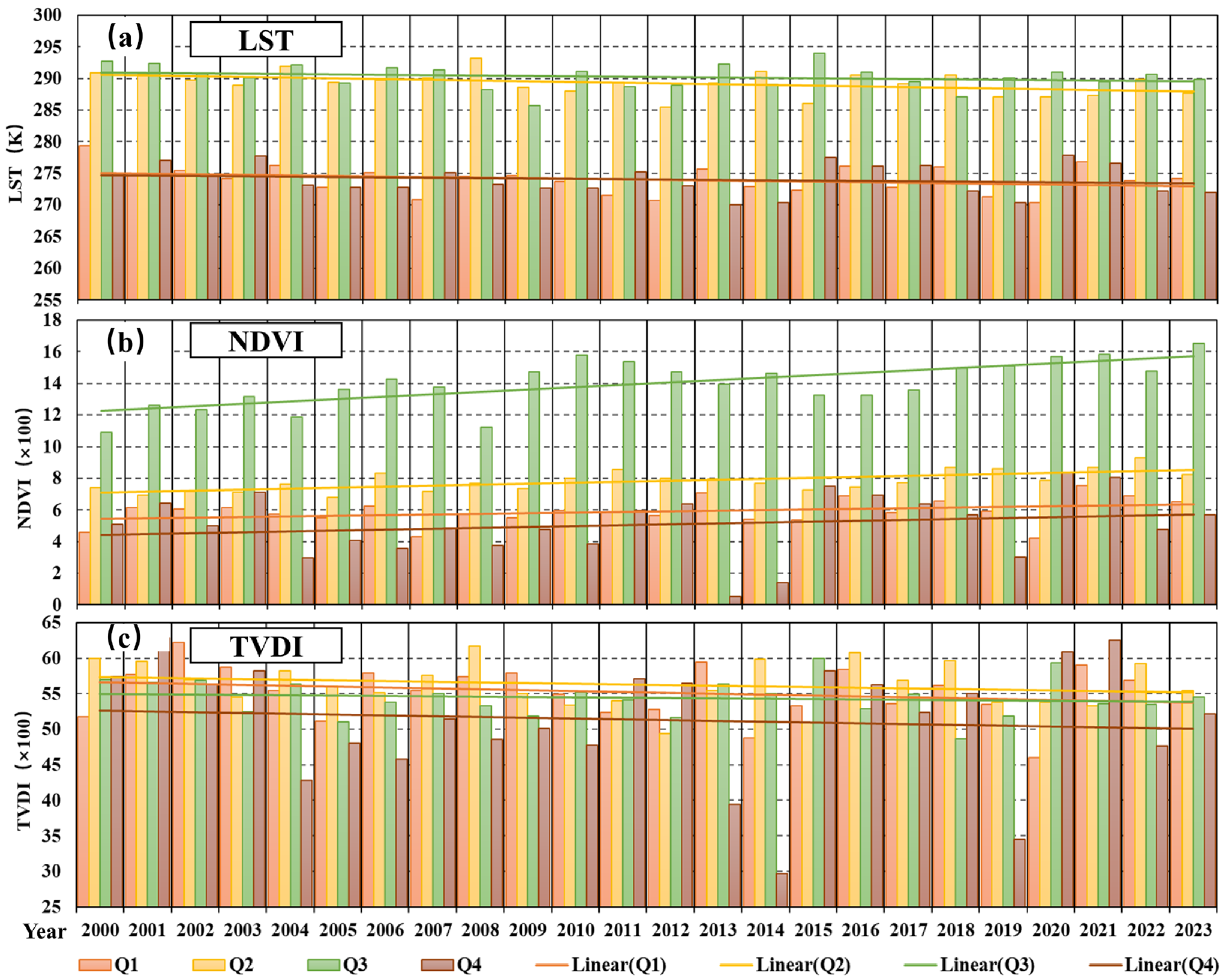



| Year | Q | a | b | c | d | Year | Q | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 1 | 268.5 | 64.0 | 288.5 | −27.7 | 2011 | 3 | 279.9 | 14.3 | 298.5 | −25.8 |
| 2000 | 2 | 275.4 | 62.8 | 302.7 | −53.1 | 2011 | 4 | 264.5 | 57.2 | 282.9 | −30.0 |
| 2000 | 3 | 275.4 | 62.8 | 302.7 | −53.1 | 2015 | 1 | 261.8 | 53.1 | 282.1 | −42.3 |
| 2000 | 4 | 265.6 | 35.6 | 283.3 | −41.2 | 2015 | 2 | 273.9 | 40.4 | 300.1 | −55.4 |
| 2005 | 1 | 263.9 | 48.8 | 282.7 | −55.9 | 2015 | 3 | 282.4 | 20.6 | 303.8 | −24.9 |
| 2005 | 2 | 274.9 | 53.0 | 305.7 | −90.0 | 2015 | 4 | 267.2 | 39.9 | 285.7 | −34.3 |
| 2005 | 3 | 280.6 | 16.1 | 299.1 | −25.7 | 2020 | 1 | 262.5 | 59.3 | 278.4 | −17.0 |
| 2005 | 4 | 264.0 | 55.1 | 282.4 | −42.7 | 2020 | 2 | 273.5 | 36.4 | 302.3 | −63.8 |
| 2010 | 1 | 264.2 | 45.1 | 282.1 | −39.0 | 2020 | 3 | 282.4 | 9.4 | 300.2 | −22.9 |
| 2010 | 2 | 275.7 | 44.5 | 300.8 | −51.5 | 2020 | 4 | 268.9 | 21.5 | 285.7 | −32.8 |
| 2010 | 3 | 282.7 | 11.3 | 299.9 | −20.2 | 2023 | 1 | 263.3 | 57.3 | 282.4 | −28.6 |
| 2010 | 4 | 264.5 | 47.4 | 283.3 | −51.6 | 2023 | 2 | 275.3 | 31.0 | 301.3 | −55.1 |
| 2011 | 1 | 262.2 | 50.2 | 278.6 | −20.2 | 2023 | 3 | 281.2 | 13.1 | 298.6 | −19.4 |
| 2011 | 2 | 276.7 | 36.9 | 302.6 | −50.5 | 2023 | 4 | 262.7 | 48.8 | 279.8 | −23.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Ding, Z.; Niu, F.; Mu, Y. Local Surface Environmental Changes in a Basin in the Permafrost Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Affected by Lake Outburst Event. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193392
Zhang S, Wu S, Ding Z, Niu F, Mu Y. Local Surface Environmental Changes in a Basin in the Permafrost Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Affected by Lake Outburst Event. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193392
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Saize, Shifen Wu, Zekun Ding, Fujun Niu, and Yanhu Mu. 2025. "Local Surface Environmental Changes in a Basin in the Permafrost Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Affected by Lake Outburst Event" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193392
APA StyleZhang, S., Wu, S., Ding, Z., Niu, F., & Mu, Y. (2025). Local Surface Environmental Changes in a Basin in the Permafrost Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Affected by Lake Outburst Event. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193392







