Phenological Shifts of Vegetation in Seasonally Frozen Ground and Permafrost Zones of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
Highlights
- A delayed start of the growing season, an advanced end of the growing season, and a shortened length of the growing season were observed during certain sub-periods.
- The end of the growing season showed opposite trends both in permafrost versus seasonally frozen ground regions and between alpine meadow and alpine steppe.
- Vegetation phenology was likely to show new changes amid current climate change.
- When studying changes in vegetation phenology, the impacts of permafrost changes and differences in vegetation types should be considered.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Method
4. Results
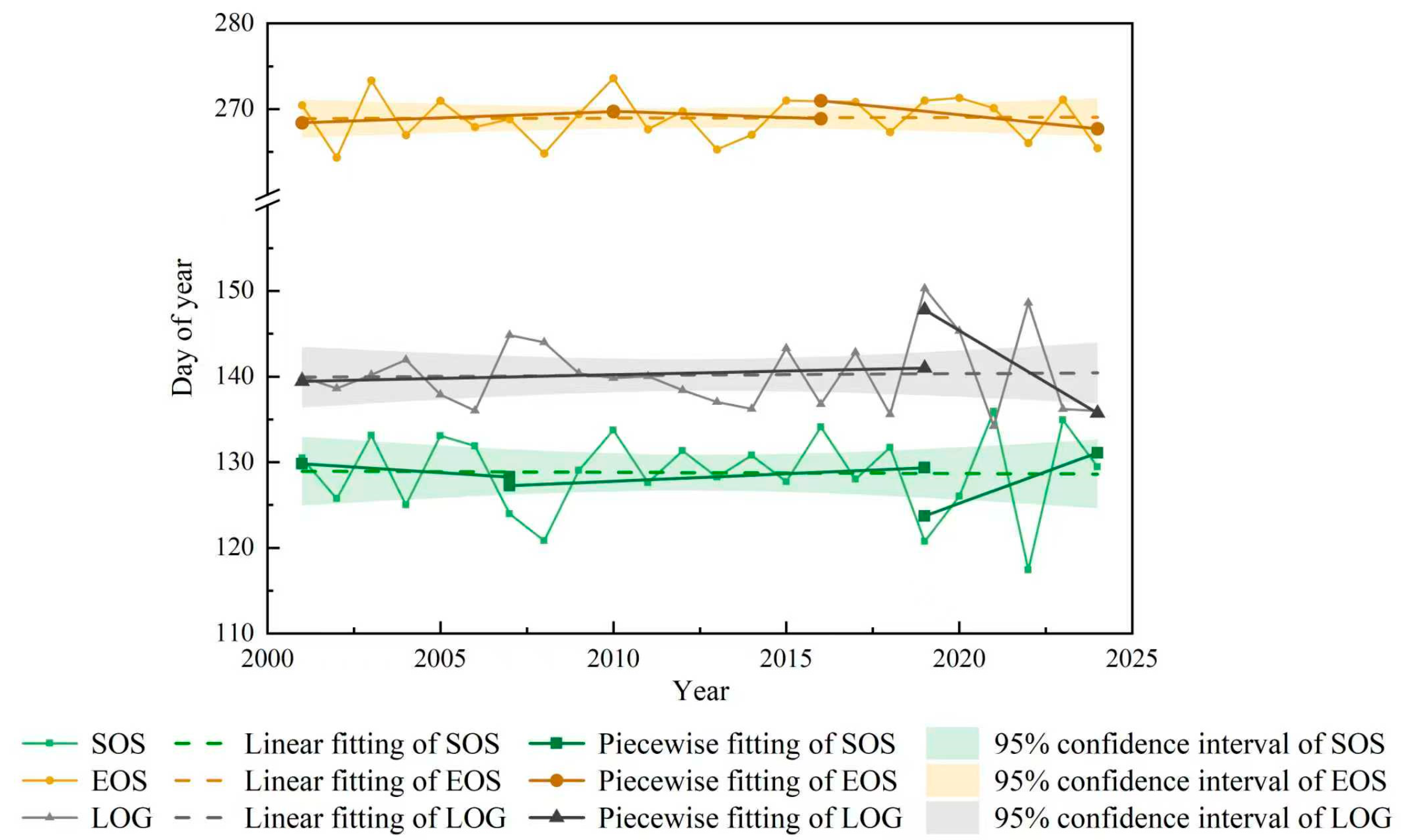
4.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Vegetation Phenological Indicators
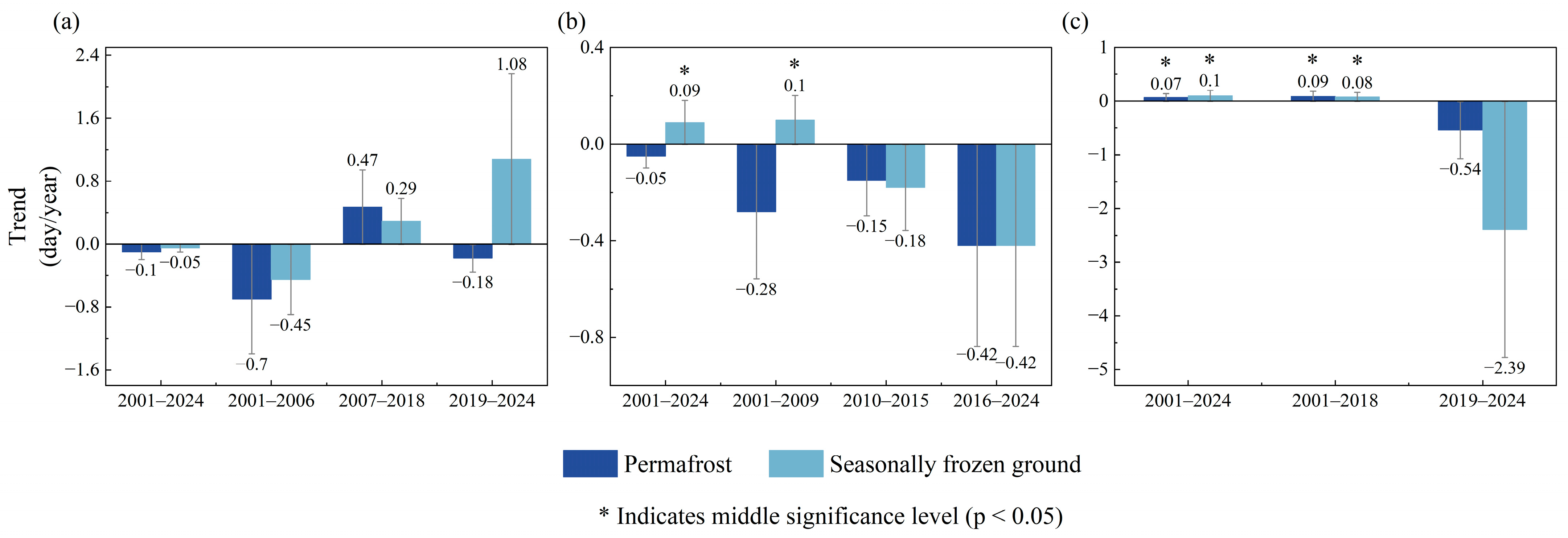
4.2. Phenological Characteristics Across Different Frozen Soil Regions
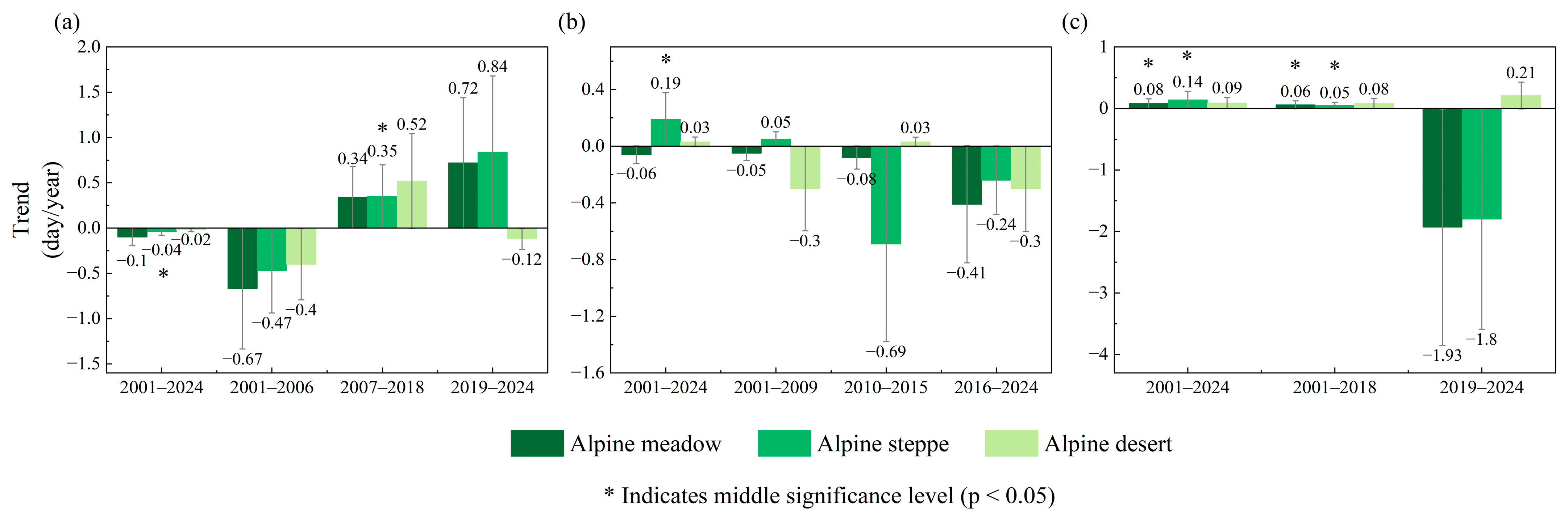
4.3. Phenological Characteristics Among Different Vegetation Types
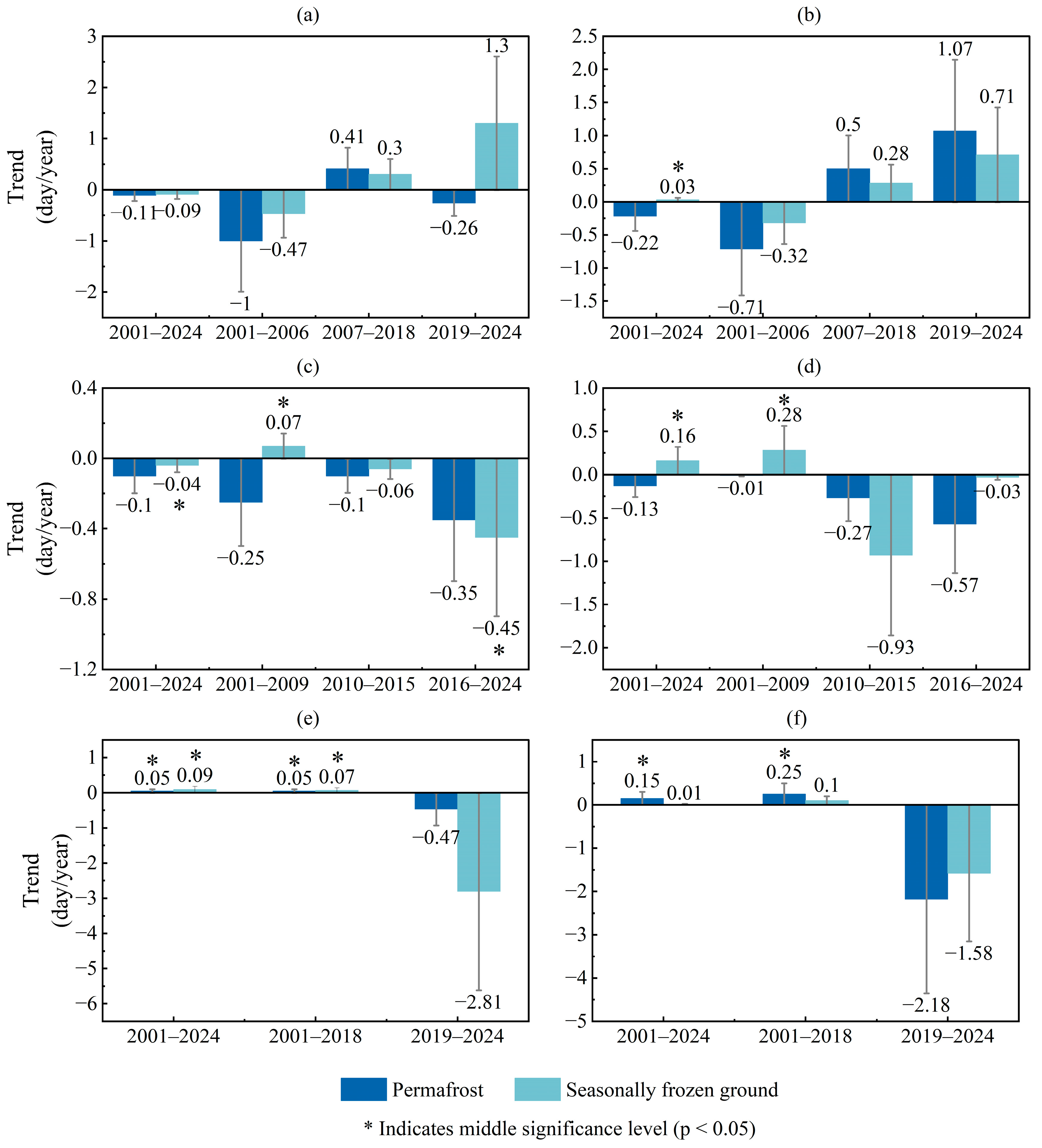
4.4. Analysis of Phenological Change Among Different Frozen Soils and Various Vegetation Types
4.5. Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Greenness
5. Discussion
5.1. Vegetation Phenological Changes
5.2. Comparison of Vegetation Phenology Between Permafrost and Seasonally Frozen Soil Regions
5.3. The Correlation Between the Variation in Vegetation Greenness and Frozen Ground
5.4. Limits and Future Works
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, J.; Körner, C.; Muraoka, H.; Piao, S.; Shen, M.; Thackeray, S.J.; Yang, X. Emerging Opportunities and Challenges in Phenology: A Review. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B.; Running, S.W. Climate-Driven Increases in Global Terrestrial Net Primary Production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Zhang, H.; Wan, L. Spatial Distribution of Permafrost Degradation and Its Impact on Vegetation Phenology from 2000 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, D. Vegetation Green-up Date Is More Sensitive to Permafrost Degradation than Climate Change in Spring across the Northern Permafrost Region. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, D.; Shi, P.; Singh, V.P.; Sun, P. Vegetation Phenology on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and Its Response to Climate Change (1982–2013). Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 248, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Wu, T.; Wu, J.; Xie, C.; Wu, X.; Pang, Q.; et al. A New Map of Permafrost Distribution on the Tibetan Plateau. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 2527–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and Temperature Dependence of Change in the Spring Vegetation Green-up Date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Luedeling, E.; Xu, J. Winter and Spring Warming Result in Delayed Spring Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22151–22156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, D.; Zheng, G.; Shi, R. Possible Negative Effects of Earlier Thaw Onset and Longer Thaw Duration on Vegetation Greenness over the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 326, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Sun, J.; Cao, R.; Ling, X.; Fang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; et al. Plant Phenology Changes and Drivers on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Env. 2022, 3, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; McVicar, T.R.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Schellekens, J.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Global Evaluation of Four AVHRR-NDVI Data Sets: Intercomparison and Assessment against Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2547–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Band, L.E.; Sun, G.; Li, J. Reanalysis of Global Terrestrial Vegetation Trends from MODIS Products: Browning or Greening? Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Cong, N.; Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Piao, S. Increasing Altitudinal Gradient of Spring Vegetation Phenology during the Last Decade on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, X. Effects of Climate Change and Ozone on Vegetation Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; He, M.; Shishov, V.; Tychkov, I.; Vaganov, E.; Rossi, S.; Ljungqvist, F.C.; Bräuning, A.; Grießinger, J. New Perspective on Spring Vegetation Phenology and Global Climate Change Based on Tibetan Plateau Tree-Ring Data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6966–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhu, W.; Chen, G.; Jiang, N.; Fan, D.; Zhang, D. Continuous but Diverse Advancement of Spring-Summer Phenology in Response to Climate Warming across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, S. Asymmetric Impacts of Surface Thaw Onset Change on Seasonal Vegetation Growth in Arctic Permafrost. Glob. Ecol Biogeogr 2024, 33, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Fluegel, W.-A.; Pepin, N.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J. Decreasing Wind Speed and Weakening Latitudinal Surface Pressure Gradients in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Res. 2010, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, H. Permafrost and Groundwater on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in Northeast China. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.M.; Baughman, C.A.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Parsekian, A.D.; Babcock, E.L.; Stephani, E.; Jones, M.C.; Grosse, G.; Berg, E.E. Presence of Rapidly Degrading Permafrost Plateaus in South-Central Alaska. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2673–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-Y.; Jin, H.-J.; Iwahana, G.; Marchenko, S.S.; Luo, D.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Liang, S.-H. Impacts of Climate-Induced Permafrost Degradation on Vegetation: A Review. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y. Impacts of Permafrost Changes on Alpine Ecosystem in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T. Changes in Active Layer Thickness over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1995 to 2007. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, D09107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Han, Z. Management Practices Should Be Strengthened in High Potential Vegetation Productivity Areas Based on Vegetation Phenology Assessment on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Adu, B.; Li, C.; Wu, J. Diverse Responses of Phenology in Multi-Grassland to Environmental Factors on Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau in China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2022, 148, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. Spatio-temporal Analysis of Vegetation Phenology with Multiple Methods over the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS NDVI Data. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2018, 33, 486–498. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Sique, D.; Cui, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, S. Changes of Plant Phenophases and Their Effects on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Nat. 2017, 39, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Huang, K.; Zu, J.; Chen, N.; Cong, N.; Stegehuis, A.I. Warming Slowdown over the Tibetan Plateau in Recent Decades. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Ren, H.; Zhou, G. The 30 m Vegetation Maps from 1990 to 2020 in the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; et al. Variation of the Start Date of the Vegetation Growing Season (SOS) and Its Climatic Drivers in the Tibetan Plateau. Plants 2024, 13, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, N.; Shen, M.; Piao, S. Spatial Variations in Responses of Vegetation Autumn Phenology to Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 10, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Ju, Q.; Chen, X. Analysis of the Spatial Distribution of Precipitation and Topography with GPM Data in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, X. Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, S.; Wu, Q.; Yang, K.; Ding, Y. The Role of Permafrost and Soil Water in Distribution of Alpine Grassland and Its NDVI Dynamics on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2016, 147, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, R.; Ma, D.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Yin, G. Tracking Autumn Photosynthetic Phenology on Tibetan Plateau Grassland with the Green-Red Vegetation Index. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 339, 109573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, C.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Q. Dynamics of Vegetation Autumn Phenology and Its Response to Multiple Environmental Factors from 1982 to 2012 on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the Radiometric and Biophysical Performance of the MODIS Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tucker, C.J.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Slayback, D.; Shabanov, N.V.; Myneni, R.B. Variations in Northern Vegetation Activity Inferred from Satellite Data of Vegetation Index during 1981 to 1999. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 20069–20083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal Change and Trend Analysis of Potential Evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.C. Assessment of Climate Change Trends over the Loess Plateau in China from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A Simple Method for Reconstructing a High-Quality NDVI Time-Series Data Set Based on the Savitzky–Golay Filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; De BEURS, K.M.; Didan, K.; Inouye, D.W.; Richardson, A.D.; Jensen, O.P.; O’keefe, J.; Zhang, G.; Nemani, R.R.; Van LEEUWEN, W.J.D.; et al. Intercomparison, Interpretation, and Assessment of Spring Phenology in North America Estimated from Remote Sensing for 1982–2006. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 2335–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zan, M. Driving Forces of the Changes in Vegetation Phenology in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, Y.; You, H.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Alpine Vegetation Phenology and Its Response to Climatic and Topographic Factors on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in the Sensitivity of Vegetation Growth to Typical Climate Factors on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: Oxford, England, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Bai, K.; Shu, S.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of Vegetation Indexes and Green-Up Date Extraction Methods on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Green-up Dates in the Tibetan Plateau Have Continuously Advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjurjav, H.; Gornish, E.; Hu, G.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Q. Phenological Changes Offset the Warming Effects on Biomass Production in an Alpine Meadow on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhou, X. Change in Autumn Vegetation Phenology and the Climate Controls From 1982 to 2012 on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, B.; Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Yuan, W. Drier August and Colder September Slow down the Delaying Trend of Leaf Senescence in Herbaceous Plants on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, M.; Chen, B.; Innes, J.L.; Wang, G.; Dou, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, H. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the End Date of the Vegetation Growing Season throughout the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2011. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fu, Y.H.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, M.; Li, X.; Piao, S. Temperature, Precipitation, and Insolation Effects on Autumn Vegetation Phenology in Temperate China. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R. Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Phenology of Different Land-Cover Types on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 470–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Lu, L. Spring Phenology Outweighed Climate Change in Determining Autumn Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3725–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N.; Cong, N. Biological and Climate Factors Co-Regulated Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Vegetation Autumn Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-N.; Wang, X.-F.; Luo, D.-L.; Wei, Y.-Q.; Cui, X.; Wu, N.; Bagaria, P. Phenological Changes in Alpine Grasslands and Their Influencing Factors in Seasonally Frozen Ground Regions Across the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 797928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, G.; Sun, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Liang, S. Monitoring Grassland Variation in a Typical Area of the Qinghai Lake Basin Using 30 m Annual Maximum NDVI Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Xiao, X.; Shao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Climate Change and Livestock Management Drove Extensive Vegetation Recovery in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniwaer, N.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Hong, S. Shifts in the Trends of Vegetation Greenness and Photosynthesis in Different Parts of Tibetan Plateau over the Past Two Decades. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 345, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, S.M.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Rubin, R.L. Increased Plant Productivity in Alaskan Tundra as a Result of Experimental Warming of Soil and Permafrost. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Penuelas, J.; Liu, L.; Ge, Q. Weakening Warming on Spring Freeze-Thaw Cycle Caused Greening Earth’s Third Pole. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319581121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Kang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yong, B.; Guo, F. Grassland Production in Response to Changes in Biological Metrics over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.F.; Gray, J.; Friedl, M.A.; Toomey, M.; Bohrer, G.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Munger, J.W.; O’Keefe, J.; Schmid, H.P.; SueWing, I.; et al. Net Carbon Uptake Has Increased through Warming-Induced Changes in Temperate Forest Phenology. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkaz, T.; Çetin, M.; Tülücü, K. The Impact of Water Resources Development Projects on Water Vapor Pressure Trends in a Semi-Arid Region, Turkey. Clim. Change 2007, 82, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Q.-Q.; Yu, H. Response of Vegetation Productivity to Greening and Drought in the Loess Plateau Based on VIs and SIF. Forests 2024, 15, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Deng, Y.; Tan, H.; Du, Y.; Gu, S.; Tang, Y.; Cui, X. Comprehensive Assessments of Root Biomass and Production in a Kobresia Humilis Meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Cong, N.; Tang, Z. Effects of Data Temporal Resolution on Phenology Extractions from the Alpine Grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kross, A.; Fernandes, R.; Seaquist, J.; Beaubien, E. The Effect of the Temporal Resolution of NDVI Data on Season Onset Dates and Trends across Canadian Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Avirmed, B.; Bayanmunkh, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q. Unveiling Drivers and Projecting Future Risks of Desertification Vulnerability in the Mongolian Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


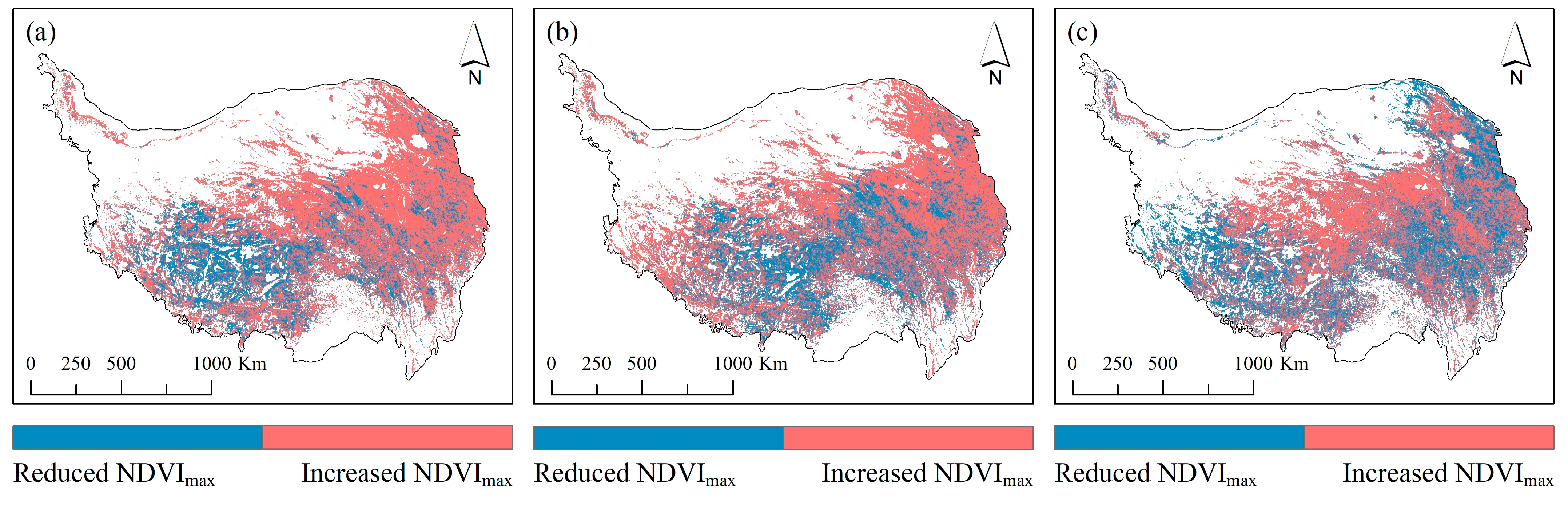
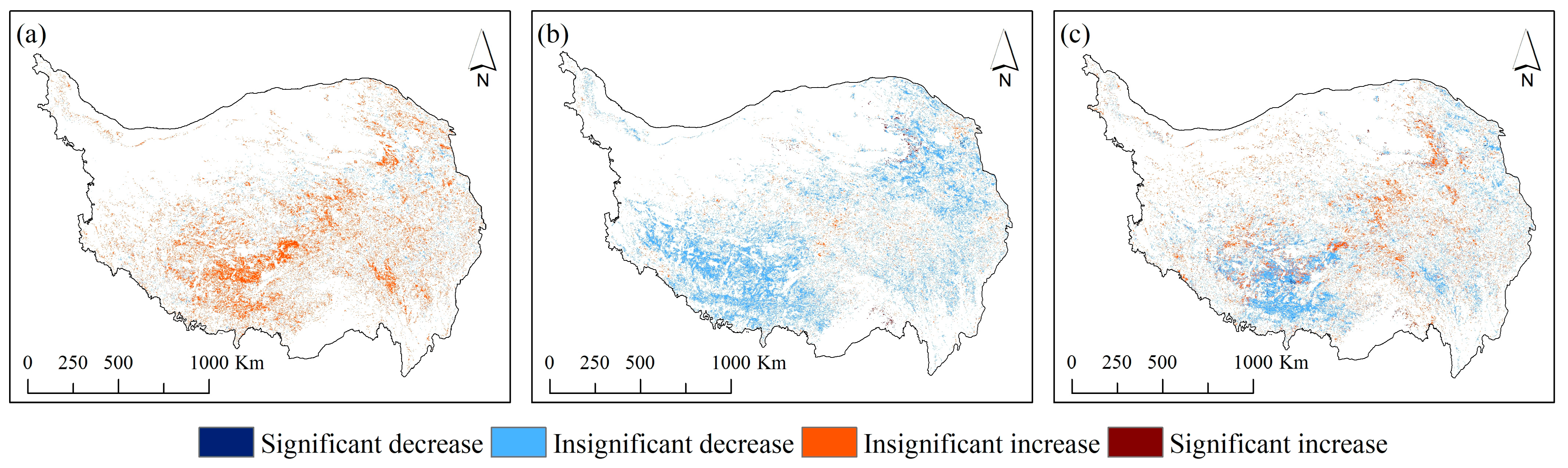
| Periods | Precipitation | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| 2001–2023 | 0.378 | −0.151 |
| 2001–2006 | 0.365 | −0.195 * |
| 2007–2018 | 0.375 * | −0.132 * |
| 2019–2023 | 0.396 | −0.148 |
| Periods | Precipitation | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| 2001–2023 | −0.286 | 0.353 |
| 2001–2009 | −0.281 | 0.333 |
| 2010–2015 | −0.309 * | 0.394 * |
| 2016–2023 | −0.277 | 0.348 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, T.; Zhong, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Z. Phenological Shifts of Vegetation in Seasonally Frozen Ground and Permafrost Zones of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193391
Fan T, Zhong X, Wang C, Zhou L, Zhou Z. Phenological Shifts of Vegetation in Seasonally Frozen Ground and Permafrost Zones of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193391
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Tianyang, Xinyan Zhong, Chong Wang, Lingyun Zhou, and Zhinan Zhou. 2025. "Phenological Shifts of Vegetation in Seasonally Frozen Ground and Permafrost Zones of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193391
APA StyleFan, T., Zhong, X., Wang, C., Zhou, L., & Zhou, Z. (2025). Phenological Shifts of Vegetation in Seasonally Frozen Ground and Permafrost Zones of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193391






