Cloud Mask Detection by Combining Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
Highlights
- A transfer learning-based model for cloud detection by combining CALIOP active remote sensing data and MODIS passive remote sensing data.
- A consistency analysis of cloud mask detection across FY-4A/AGRI, FY-4B/AGRI and Himawari-8/9 AHI.
- Cross-validation of multi-source datasets shows that the cloud mask algorithm in this study is highly accurate and stable.
- Results revealed that the cloud mask results of different satellite maintain high consistency, providing a robust foundation for the development of cloud datasets integrated.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Study Area
2.1. Geostationary Satellite Data
2.2. CALIPSO VFM
2.3. MOD35/MYD35
2.4. Land Cover Type Data
3. Methods
3.1. Random Forest
- Bootstrap sampling: From a total of N training samples, n bootstrap samples are drawn with replacement to form n training sets. The remaining unsampled data in each set, called out-of-bag data, are used to estimate prediction error.
- Feature selection: At each node of a decision tree, randomly select m features (m < M, where M is the total number of input variables), and determine the optimal split based on these m features. Each tree is grown to its maximum depth without pruning.
- Prediction aggregation: A random forest is formed from the generated multiple decision trees, and the random forest is used to do regression analysis, and the average of the output results of each decision tree is used as the prediction value, as shown in the following equation:where is each decision tree and is the number of decision trees.
3.2. TrAdaBoost
- Initialize the weights in the source domain and the target domain:where is the number of samples in the source domain, is the number of samples in the target domain, and w is the weight in the source domain and the target domain. These are unnormalized initial weights, and the sum of the weights within the source and target domains is 1.
- Normalize weights of all samples and call a learner (basic machine learning algorithms):where is the normalized weight of the sample in the source domain and target domain, is the number of iterations, t is the iteration index, and is the unnormalized weight of sample i in round t.
- Calculate the error rate () of in the target domain:where is the classifier learned in the step. 2, is an input variable, is the prediction of the weak classifier (or base learner) on sample in the t round, and is the actual label of in the target domain. Note that must be less than 0.5.
- Calculate the weight adjustment rate in the source domain and the weight adjustment rate in the target domain:where is constant during each iteration.
- Update the weights of all samples:where is the unnormalized weight of sample i in round t+1.
- Output the hypothesis:where is the decision function used to predict the label of sample x.
3.3. Constructing the Cloud Mask Model
3.4. Validation Metrics
3.5. SHAP Interpretability Analysis
4. Results
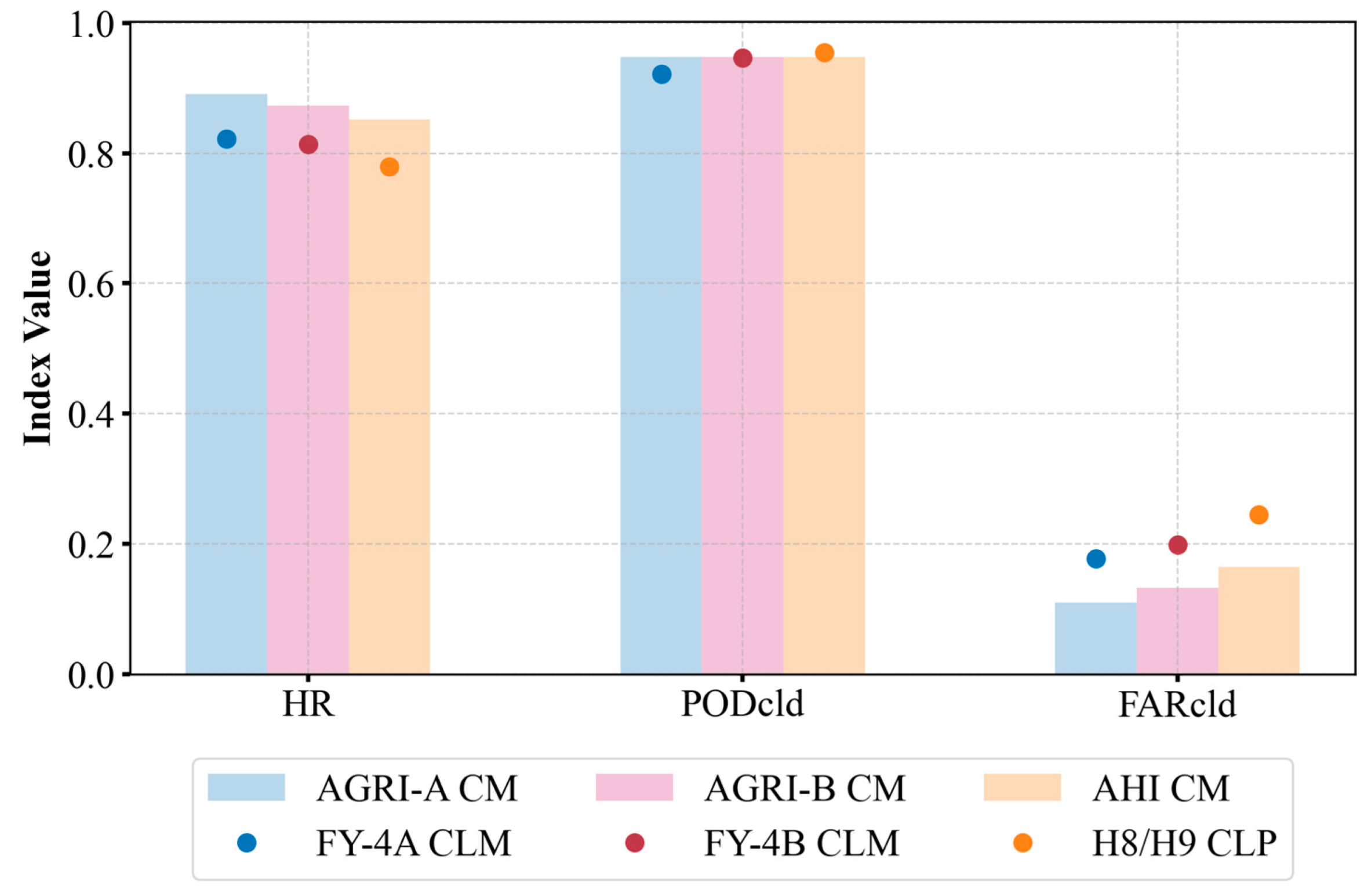
4.1. Cloud Mask Algorithm Validation
4.2. Case Studies for Intercomparisons
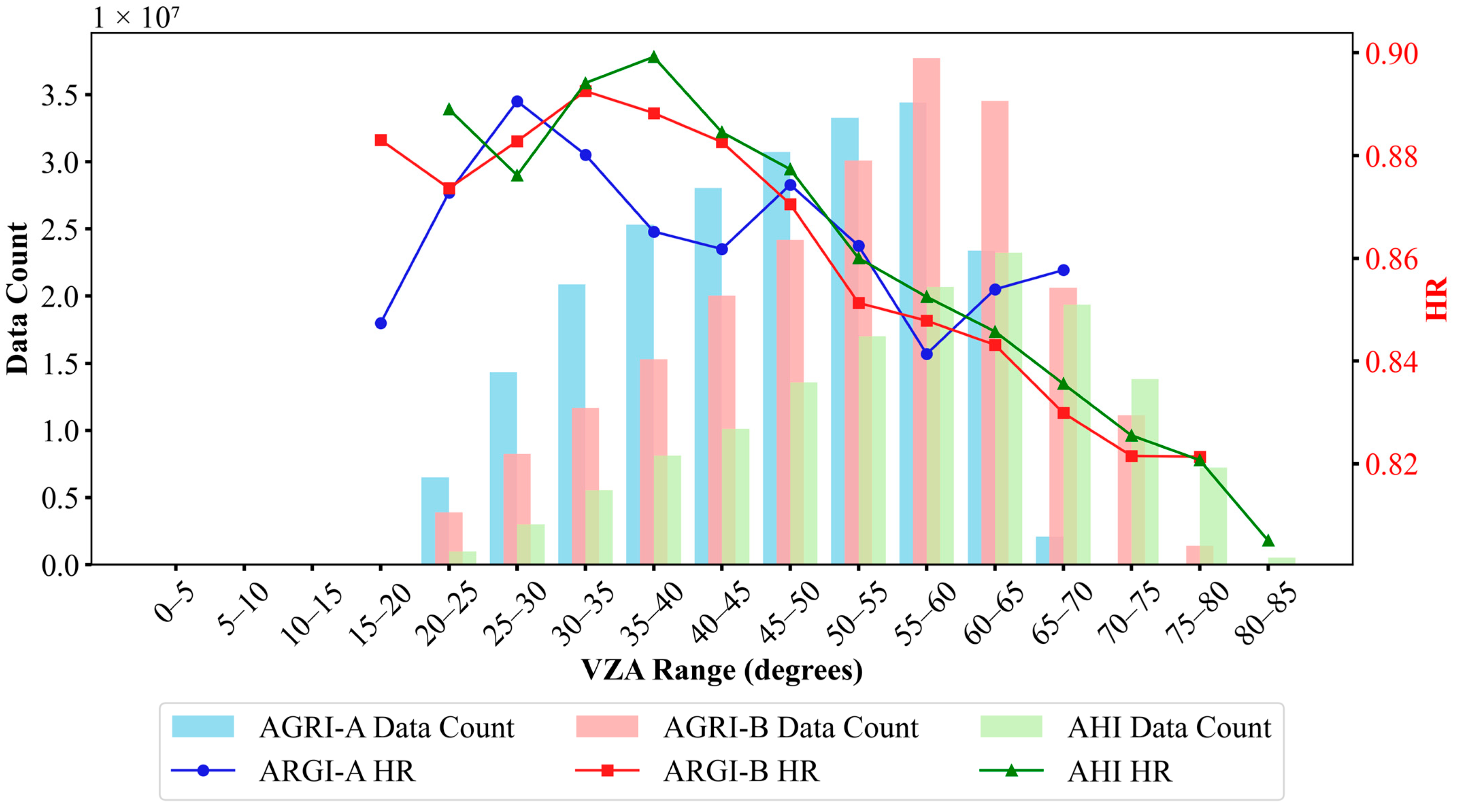
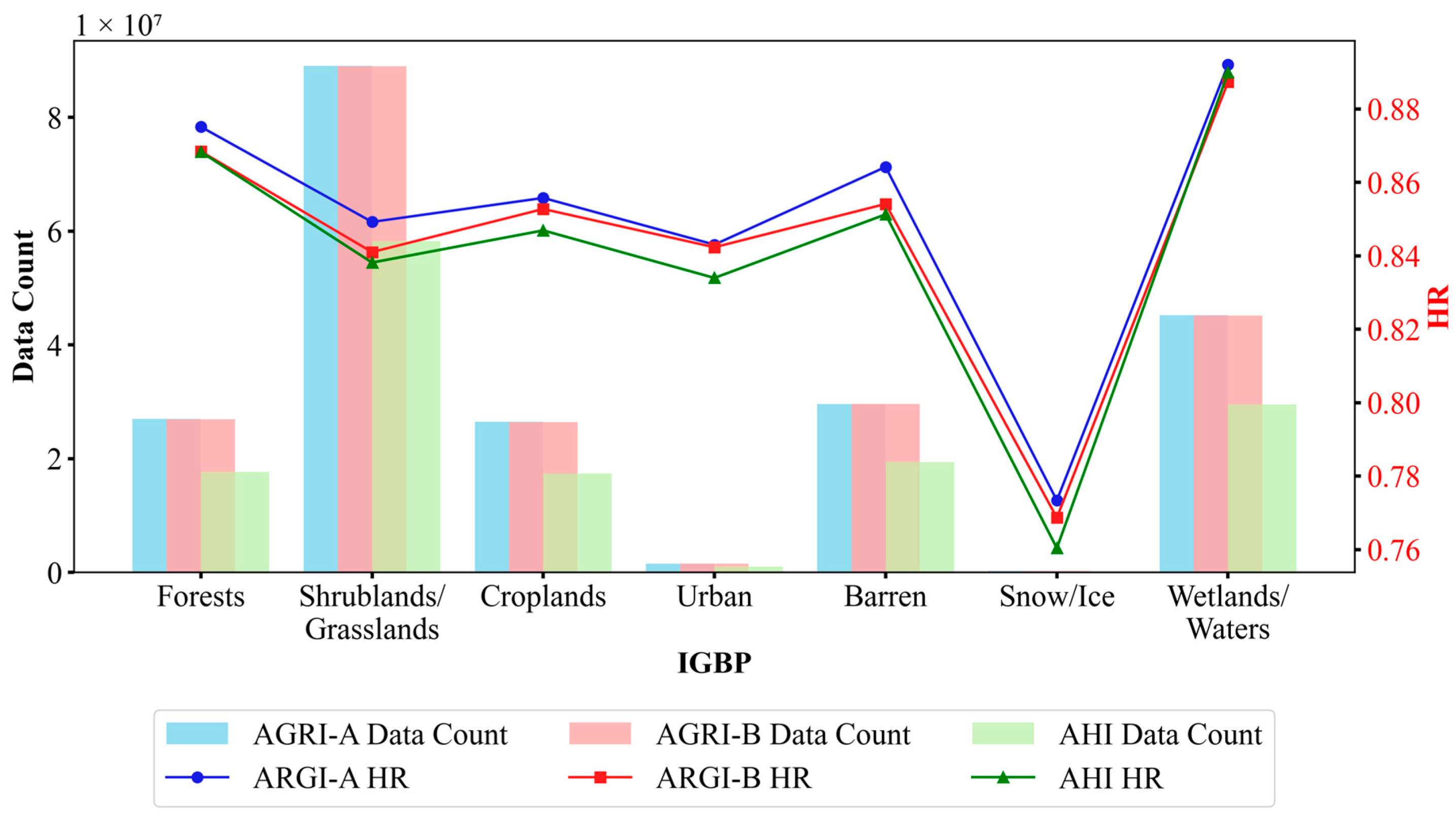
4.3. Consistency Analysis
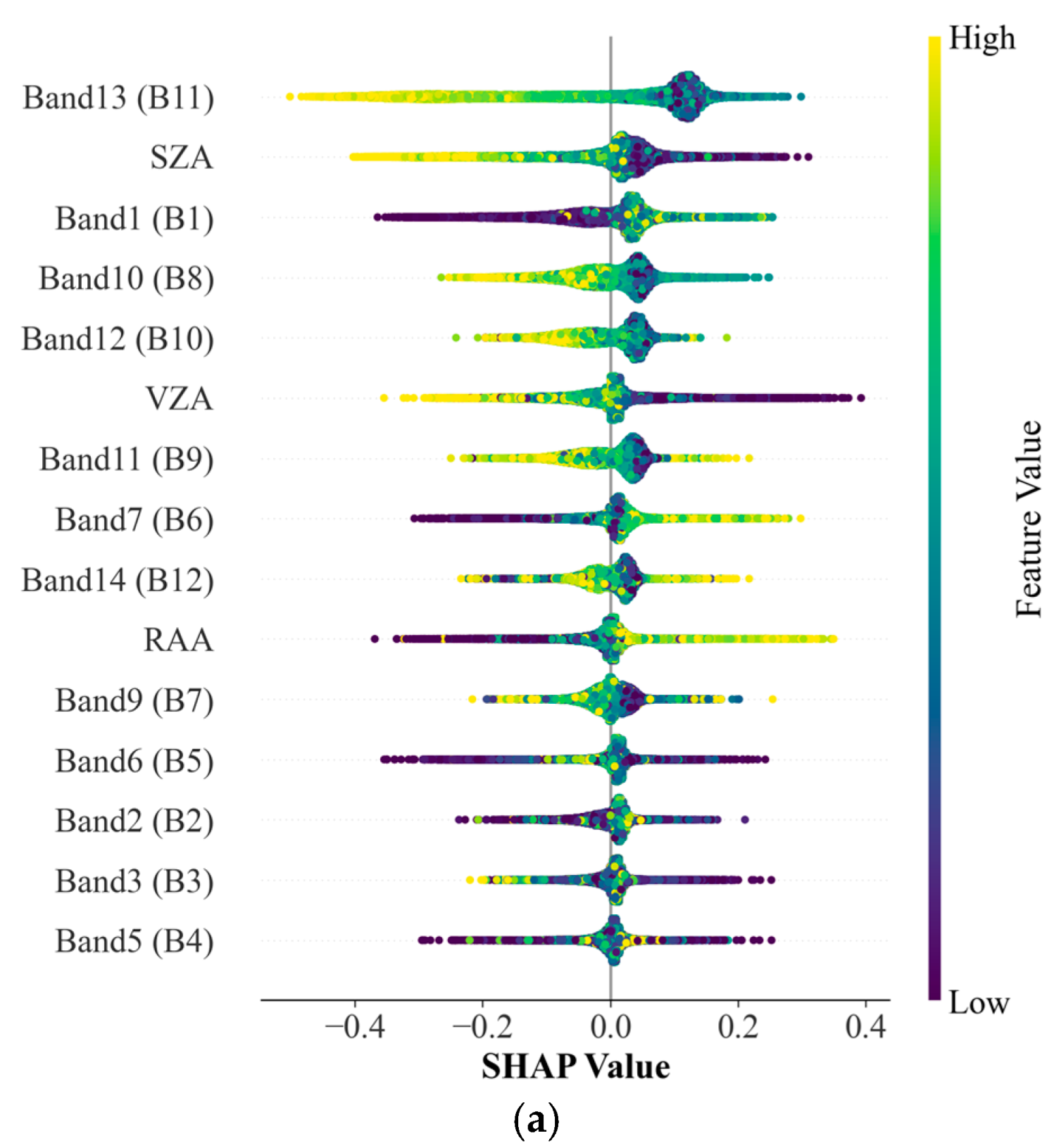
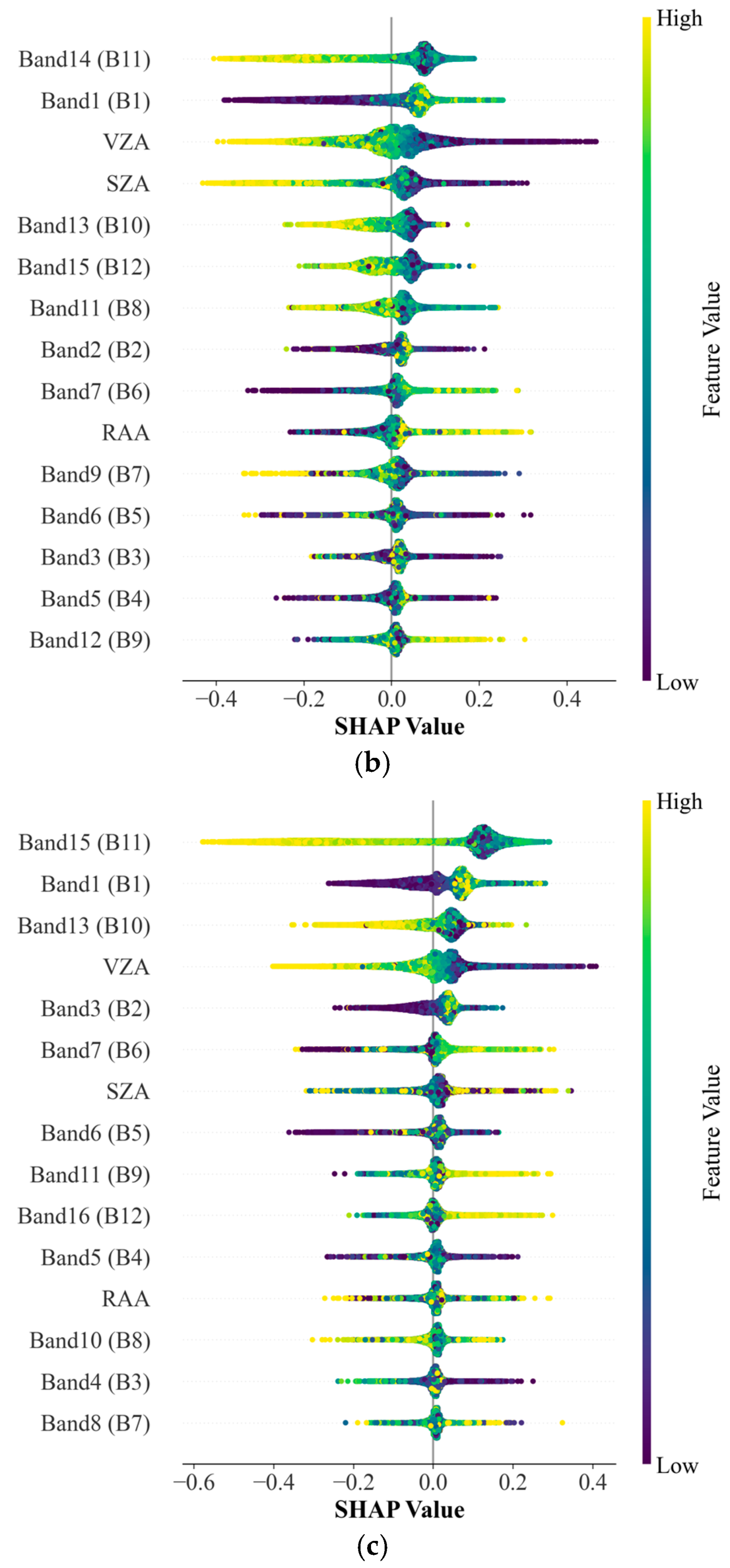
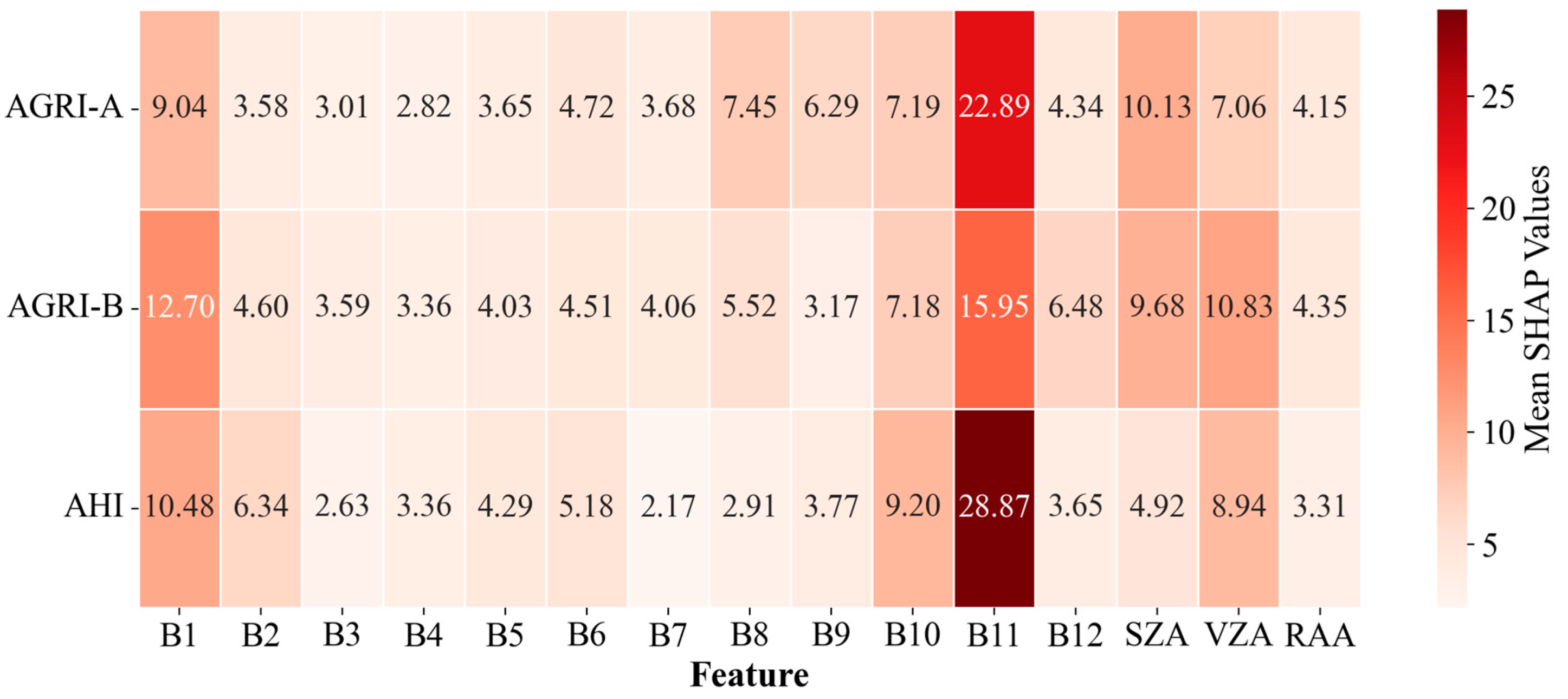
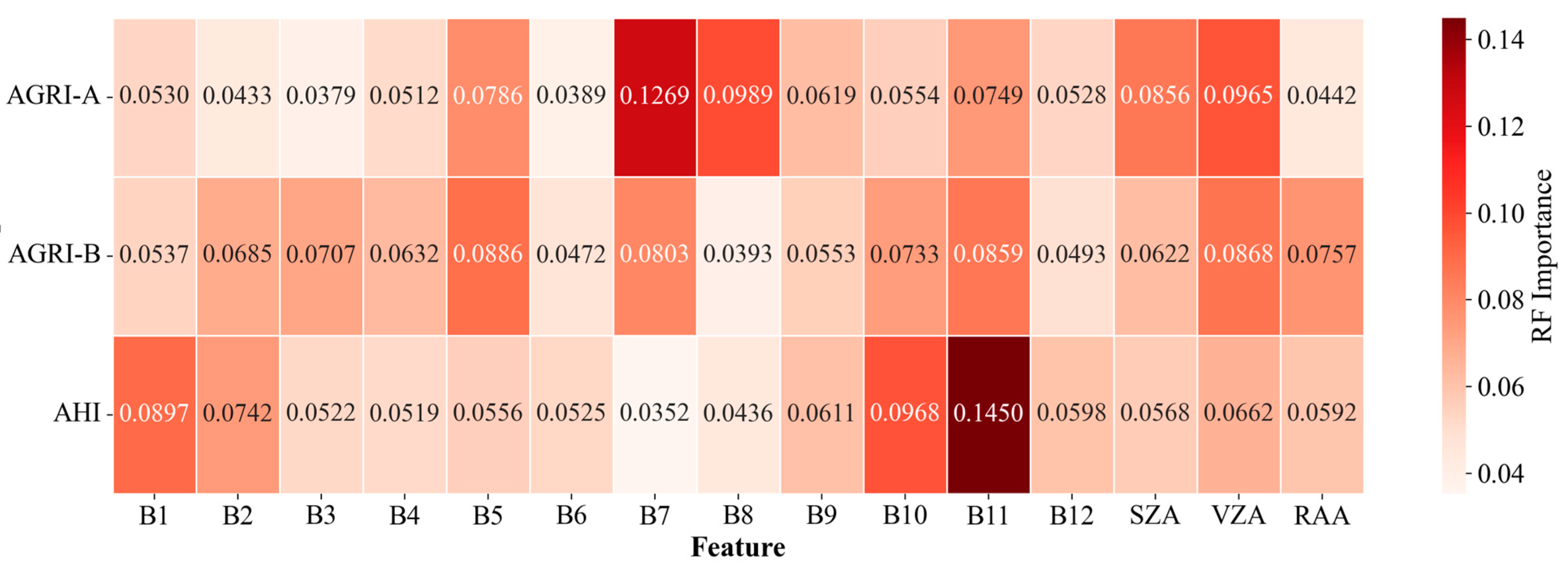
4.3.1. Variable Importance Analysis
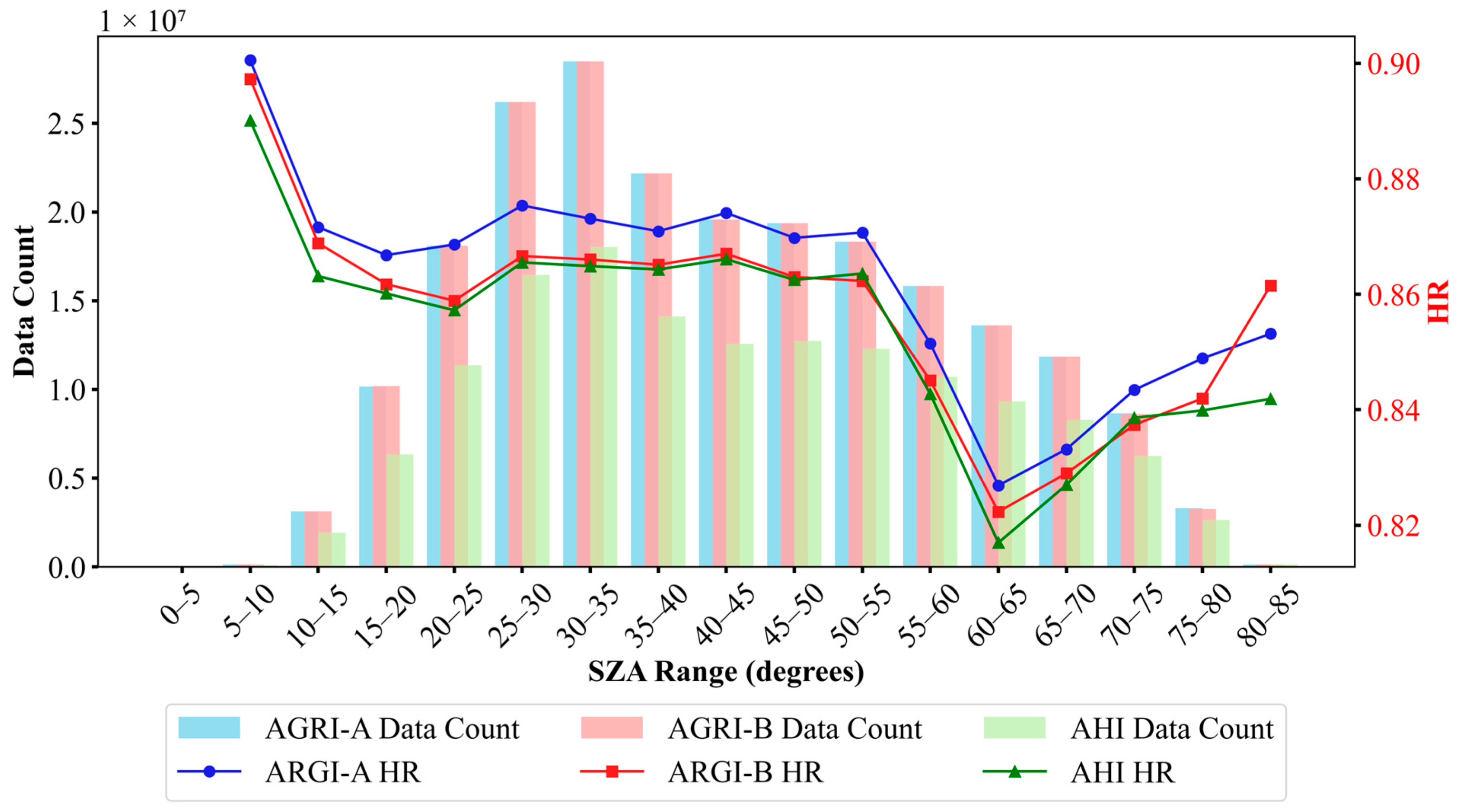
4.3.2. Variability Analysis
5. Discussion
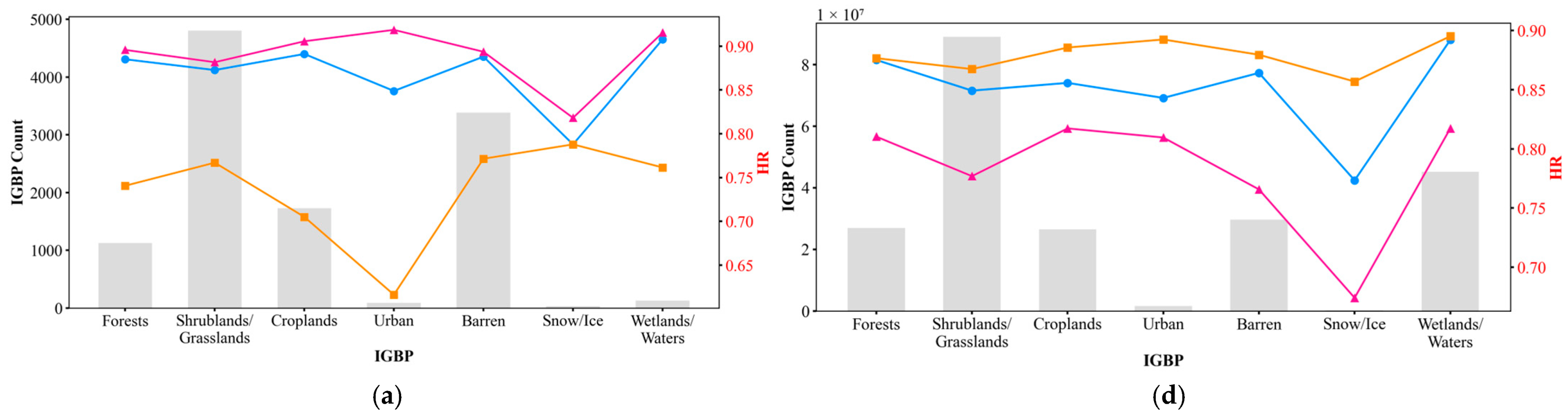
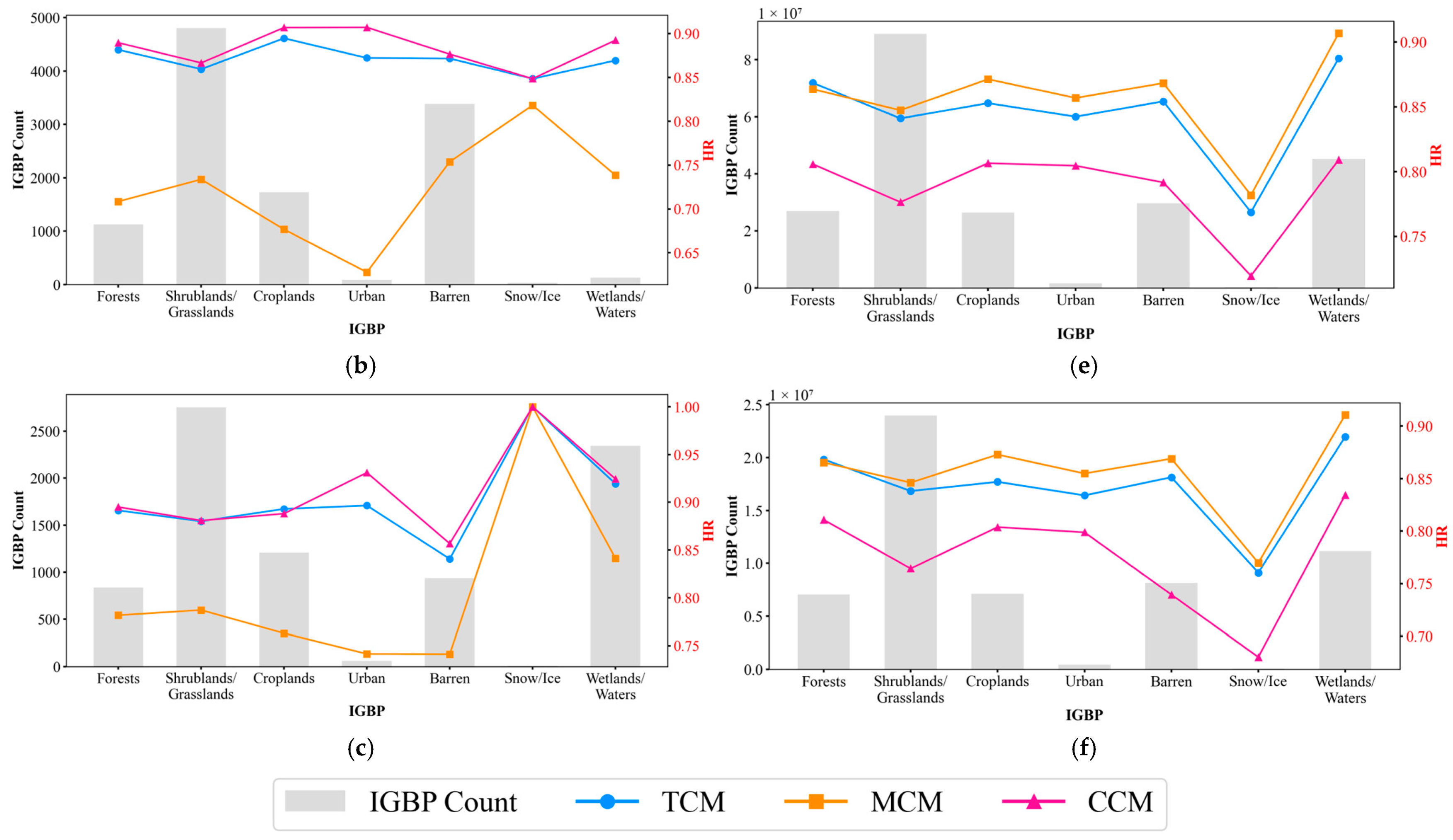
5.1. Performance of TCM, MCM, and CCM by IGBP Class
5.2. Comparison of Mean SHAP Values and RF Feature Importance Scores
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCM | TrAdaBoost cloud mask algorithm |
| MCM | MODIS-based cloud mask algorithm |
| CCM | CALIOP-based cloud mask algorithm |
| TCM-CM | Cloud mask results generated by the TCM algorithm from each sensor |
| AGRI-A | FY-4A/AGRI |
| AGRI-B | FY-4B/AGRI |
| AHI | Himawair-8 AHI and Himawair-9 AHI |
| AGRI-A CM | Cloud mask results generated by the TCM algorithm from AGRI-A |
| AGRI-B CM | Cloud mask results generated by the TCM algorithm from AGRI-B |
| AHI CM | Cloud mask results generated by the TCM algorithm from AHI |
| B1 | 0.47 μm band of AGRI-A, AGRI-B and AHI |
| B2 | 0.65 μm band of AGRI-A and AGRI-B; 0.64 μm band of AHI |
| B3 | 0.83 μm band of AGRI-A; 0.825 μm band of AGRI-B; 0.86 μm band of AHI |
| B4 | 1.61 μm band of AGRI-A and AGRI-B; 1.6 μm band of AHI |
| B5 | 2.22 μm band of AGRI-A; 2.225 μm band of AGRI-B; 2.3 μm band of AHI |
| B6 | 3.72 μm band of AGRI-A; 3.75 μm band of AGRI-B; 3.9 μm band of AHI |
| B7 | 6.25 μm band of AGRI-A and AGRI-B; 6.2 μm band of AHI |
| B8 | 7.10 μm band of AGRI-A; 7.42 μm band of AGRI-B; 7.3 μm band of AHI |
| B9 | 8.50 μm band of AGRI-A; 8.55 μm band of AGRI-B; 8.6 μm band of AHI |
| B10 | 10.80 μm band of AGRI-A and AGRI-B; 10.4 μm band of AHI |
| B11 | 12.0 μm band of AGRI-A and AGRI-B; 12.4 μm band of AHI |
| B12 | 13.5 μm band of AGRI-A; 13.3 μm band of AGRI-B and AHI |
| SZA | Solar zenith angle |
| VZA | Satellite zenith angle |
| RAA | Relative azimuthal angle |
| POD | Probability of detection |
| FAR | False alarm ratio |
| HR | Hit rate |
| KSS | Kuiper’s skill score |
References
- Baker, M.B. Cloud Microphysics and Climate. Science 1997, 276, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Shen, L. An Uneven Illumination Correction Algorithm for Optical Remote Sensing Images Covered with Thin Clouds. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11848–11862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapakis, R.; Charalambides, A.G. Equipment and methodologies for cloud detection and classification: A review. Sol. Energy 2013, 95, 392–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, P.; Gan, W.; Fang, L. Cloud removal in remote sensing images using nonnegative matrix factorization and error correction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 148, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Q. An effective thin cloud removal procedure for visible remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 96, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.G.; King, M.D.; Wind, G.; Amarasinghe, N.; Marchant, B.; Arnold, G.T.; Zhang, Z.; Hubanks, P.A.; Holz, R.E. The MODIS cloud optical and microphysical products: Collection 6 updates and examples from Terra and Aqua. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 502–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection in multitemporal Landsat data: An algorithm designed specifically for monitoring land cover change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepfer, H.; Bony, S.; Winker, D.; Chiriaco, M.; Dufresne, J.L.; Sèze, G. Use of CALIPSO lidar observations to evaluate the cloudiness simulated by a climate model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L15704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarba, A.Z. Calibration of global MODIS cloud amount using CALIOP cloud profiles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4995–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, W.; Gatebe, C.; Tanikawa, T.; Hori, M.; Shimada, R.; Aoki, T.; Stamnes, K. New neural network cloud mask algorithm based on radiative transfer simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; He, Z. Deep learning based cloud detection for medium and high resolution remote sensing images of different sensors. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y. A machine-learning-based cloud detection and thermodynamic-phase classification algorithm using passive spectral observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2257–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D.; Haß, E.; Uhl, A.; Stoffels, J.; Hill, J. Improvement of the Fmask algorithm for Sentinel-2 images: Separating clouds from bright surfaces based on parallax effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Letu, H.; Xu, R.; Wei, L.; Wu, L.; Shao, J.; Nagao, T.M.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Riedi, J.; He, J. A hybrid cloud detection and cloud phase classification algorithm using classic threshold-based tests and extra randomized tree model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Cribb, M. Cloud detection for Landsat imagery by combining the random forest and superpixels extracted via energy-driven sampling segmentation approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 112005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Hong, S. A daytime cloud detection method for advanced meteorological imager using visible and near-infrared bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yu, J.; Han, L. Research on PWV calculation combining MODIS and ERA5. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Geology, Mapping, and Remote Sensing (ICGMRS 2023), Wuhan, China, 14–16 April 2023; pp. 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, B.; Rapp, A.D.; Yang, P.; Baum, B.A.; King, M.D. A comparison of Aqua MODIS ice and liquid water cloud physical and optical properties between collection 6 and collection 5.1: Pixel-to-pixel comparisons. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4528–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Rapp, A.D.; Yang, P.; Baum, B.A.; King, M.D. A comparison of Aqua MODIS ice and liquid water cloud physical and optical properties between collection 6 and collection 5.1: Cloud radiative effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4550–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Teng, S.; Yi, B.; Letu, H.; Min, M.; Tang, S.; Liu, C. Comparison of cloud properties from Himawari-8 and FengYun-4A geostationary satellite radiometers with MODIS cloud retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, R.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Holz, R.E.; Dutcher, S.; Griffith, Z. The continuity MODIS-VIIRS cloud mask. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Min, M.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Tang, S. Intercomparisons of cloud mask products among Fengyun-4A, Himawari-8, and MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8827–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Menzel, W.P.; Ackerman, S.A.; Hubanks, P.A. Spatial and temporal distribution of clouds observed by MODIS onboard the Terra and Aqua satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3826–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q. A novel cloud detection algorithm based on simplified radiative transfer model for aerosol retrievals: Preliminary result on Himawari-8 over eastern China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 2550–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Lu, Q.; Liu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Ni, Z.; Liu, X. Algorithm for detecting ice overlaying water multilayer clouds using the infrared bands of FY-4A/AGRI. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1001205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Oreopoulos, L. Enhancing a simple MODIS cloud mask algorithm for the Landsat data continuity mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, G. MODIS cloud detection evaluation using CALIOP over polluted eastern China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Mauro, F.; Raza, R.A.; Mazzara, M.; Distefano, S.; Khan, A.M.; Ullo, S.L. Transformer-Driven Active Transfer Learning for Cross-Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 19635–19648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmanis, D.; Datcu, M.; Esch, T.; Stilla, U. Deep Learning Earth Observation Classification Using ImageNet Pretrained Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissaee, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Xia, G.-S.; Khan, F.S. Transformers in Remote Sensing: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Pang, S.; Wei, J. Unveiling diurnal aerosol layer height variability from space using deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 229, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Tong, X.; Pan, B.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Letu, H.; Mustafa, F. Transfer-learning-based approach to retrieve the cloud properties using diverse remote sensing datasets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Chhipa, P.C.; Mengi, G.; Gupta, V.; Liwicki, M. Domain Adaptable Self-supervised Representation Learning on Remote Sensing Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo-Garcia, G.; Laparra, V.; López-Puigdollers, D.; Gómez-Chova, L. Cross-Sensor Adversarial Domain Adaptation of Landsat-8 and Proba-V Images for Cloud Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Khoshelham, K.; Fraser, C. A multiclass TrAdaBoost transfer learning algorithm for the classification of mobile lidar data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan Ser. II 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J., Jr.; Ackerman, S.; Charlson, R.; Colarco, P.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.; Kittaka, C. The CALIPSO mission: A global 3D view of aerosols and clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1211–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Qin, W. Quantifying and mitigating errors in estimating downward surface shortwave radiation caused by cloud mask data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A.; Strabala, K.I.; Menzel, W.P.; Frey, R.A.; Moeller, C.C.; Gumley, L.E. Discriminating clear sky from clouds with MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32141–32157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Menzel, W.P.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Gao, B.-C.; Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.A.; Remer, L.A.; Pincus, R.; Hubanks, P.A. Cloud and aerosol properties, precipitable water, and profiles of temperature and water vapor from MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MODIS/Terra+Aqua Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 500m SIN Grid V061 [Data Set]. NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5067/MODIS/MCD12Q1.061 (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yang, Q.; Xue, G.-R.; Yu, Y. Boosting for transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm. In Proceedings of the Icml, Bari, Italy, 3–6 July 1996; pp. 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T. A cloud type classification with NOAA 7 split-window measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 3991–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; King, M.D.; Ackerman, S.A.; Menzel, W.P.; Baum, B.A.; Riedi, J.C.; Frey, R.A. The MODIS cloud products: Algorithms and examples from Terra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorutti, B.; Michel, B.; Saint-Pierre, P. Correlation and variable importance in random forests. Stat. Comput. 2017, 27, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Bias in random forest variable importance measures: Illustrations, sources and a solution. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
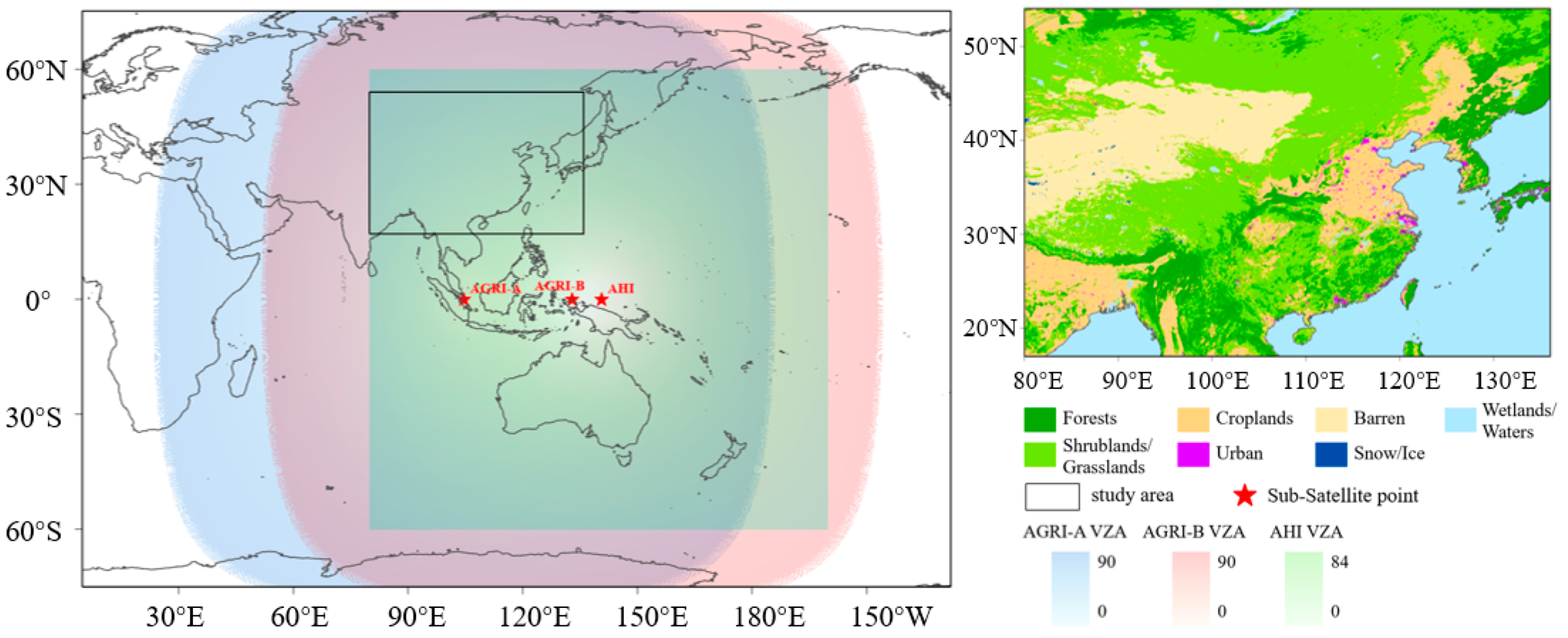
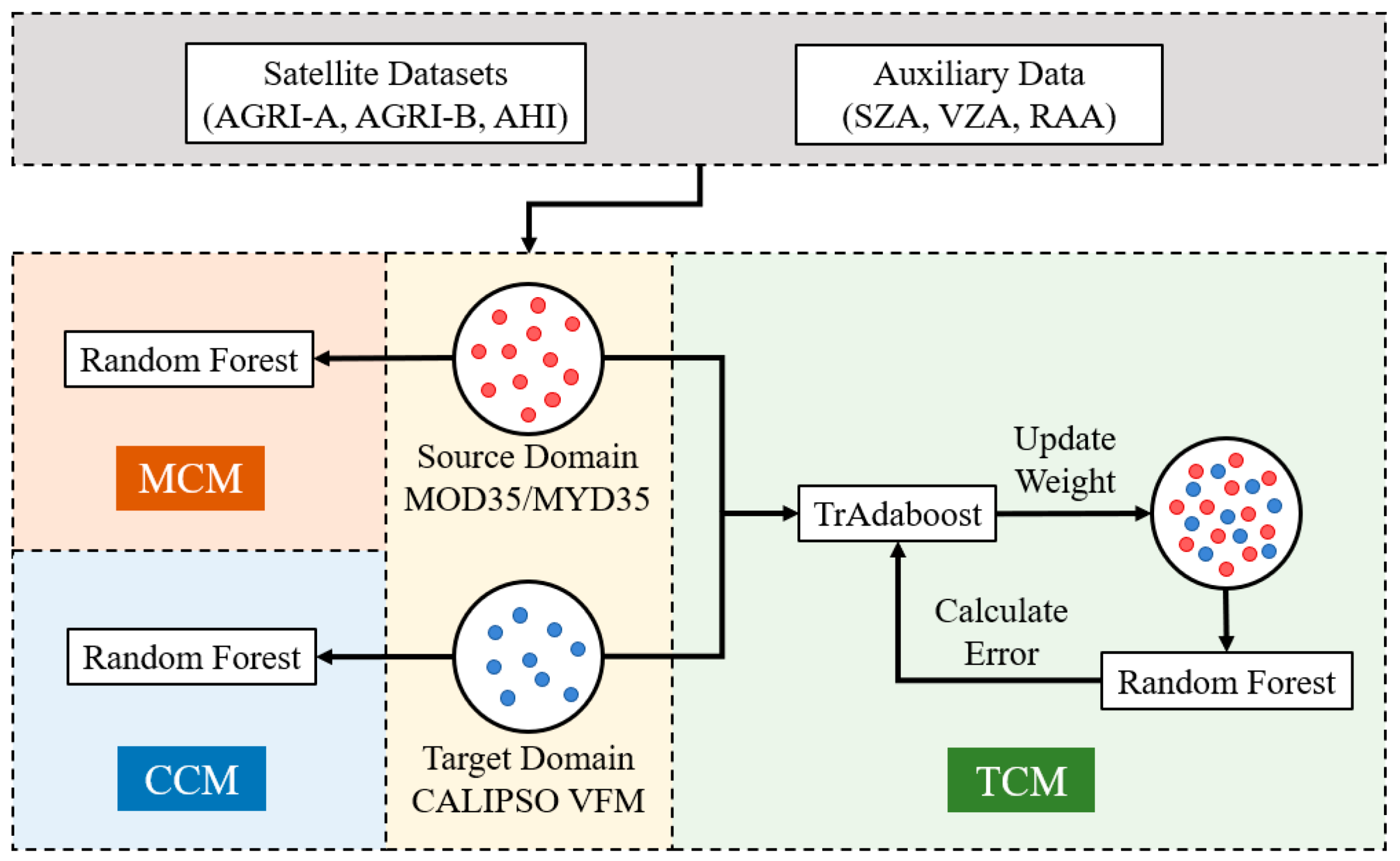
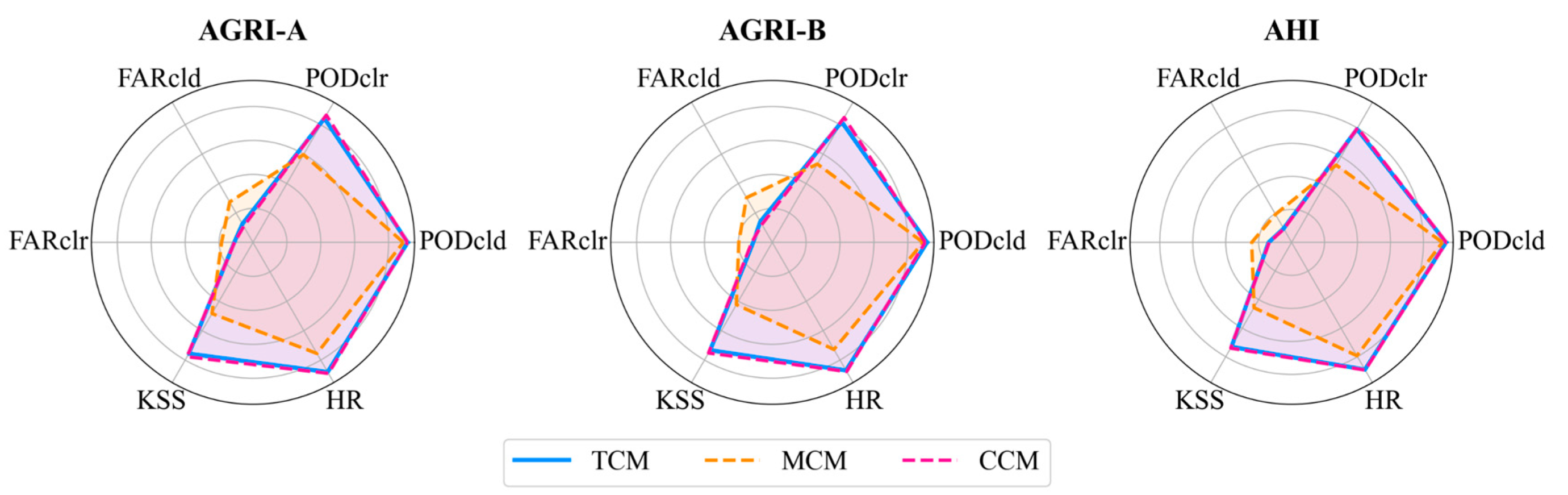

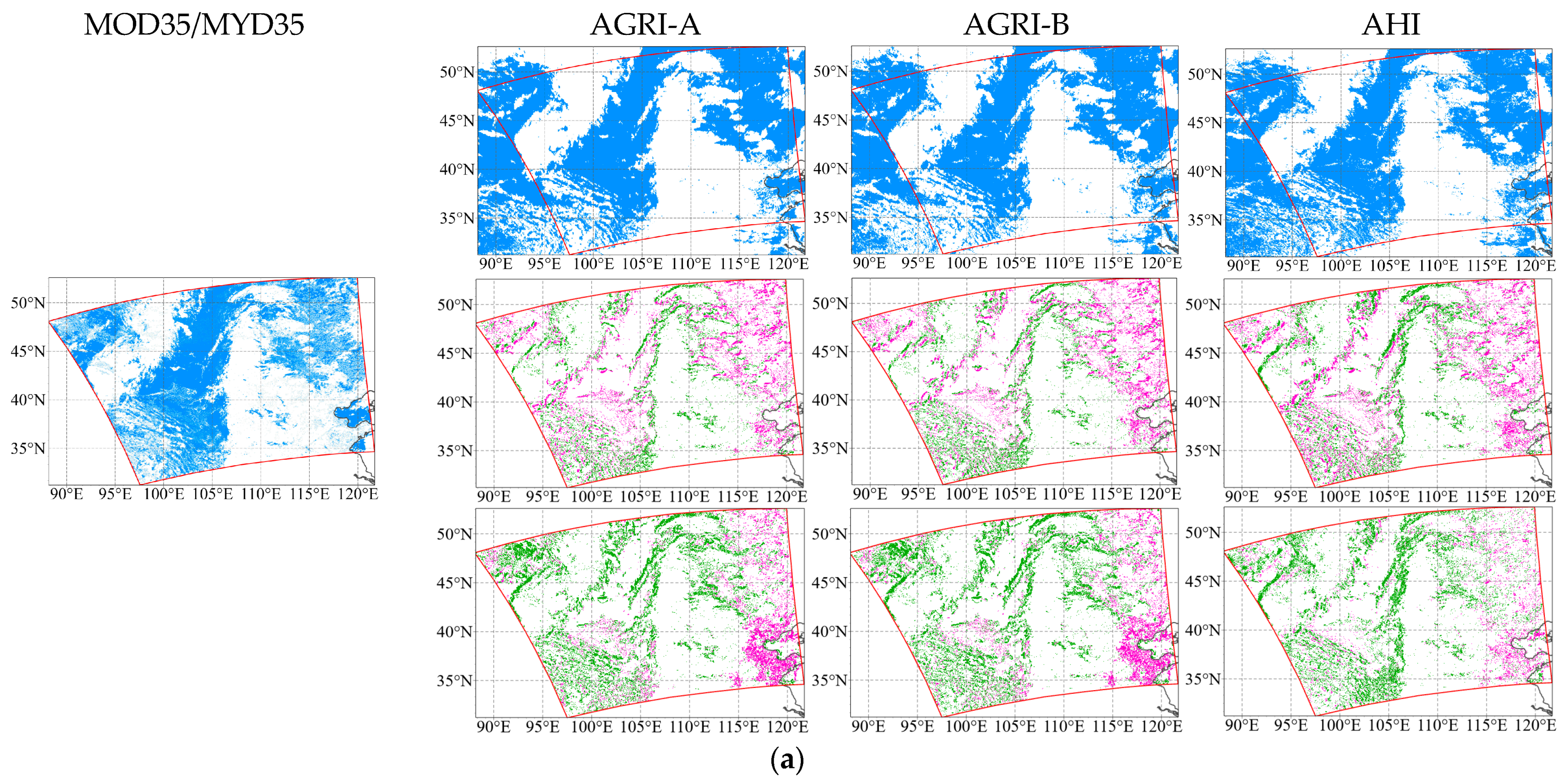
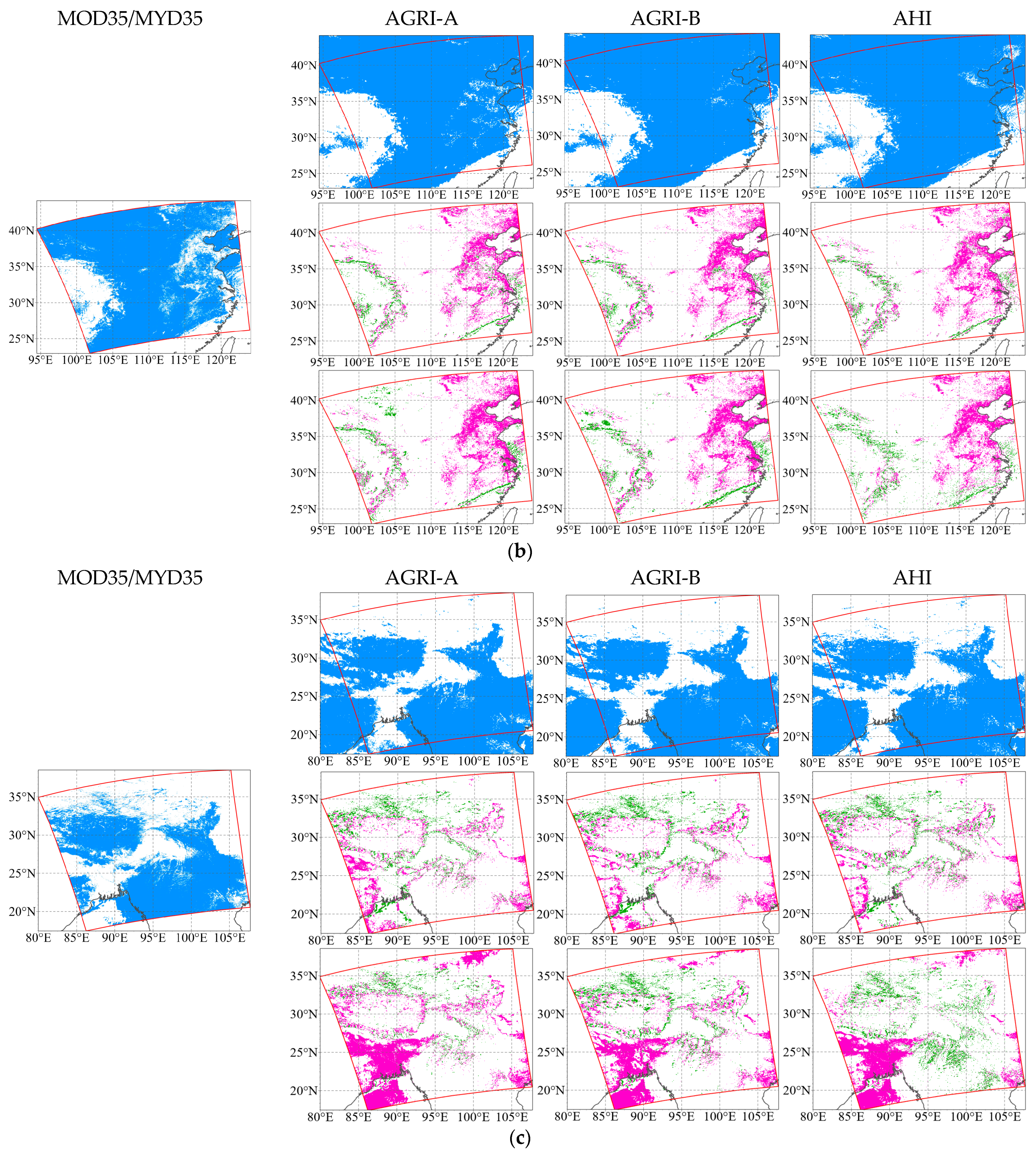
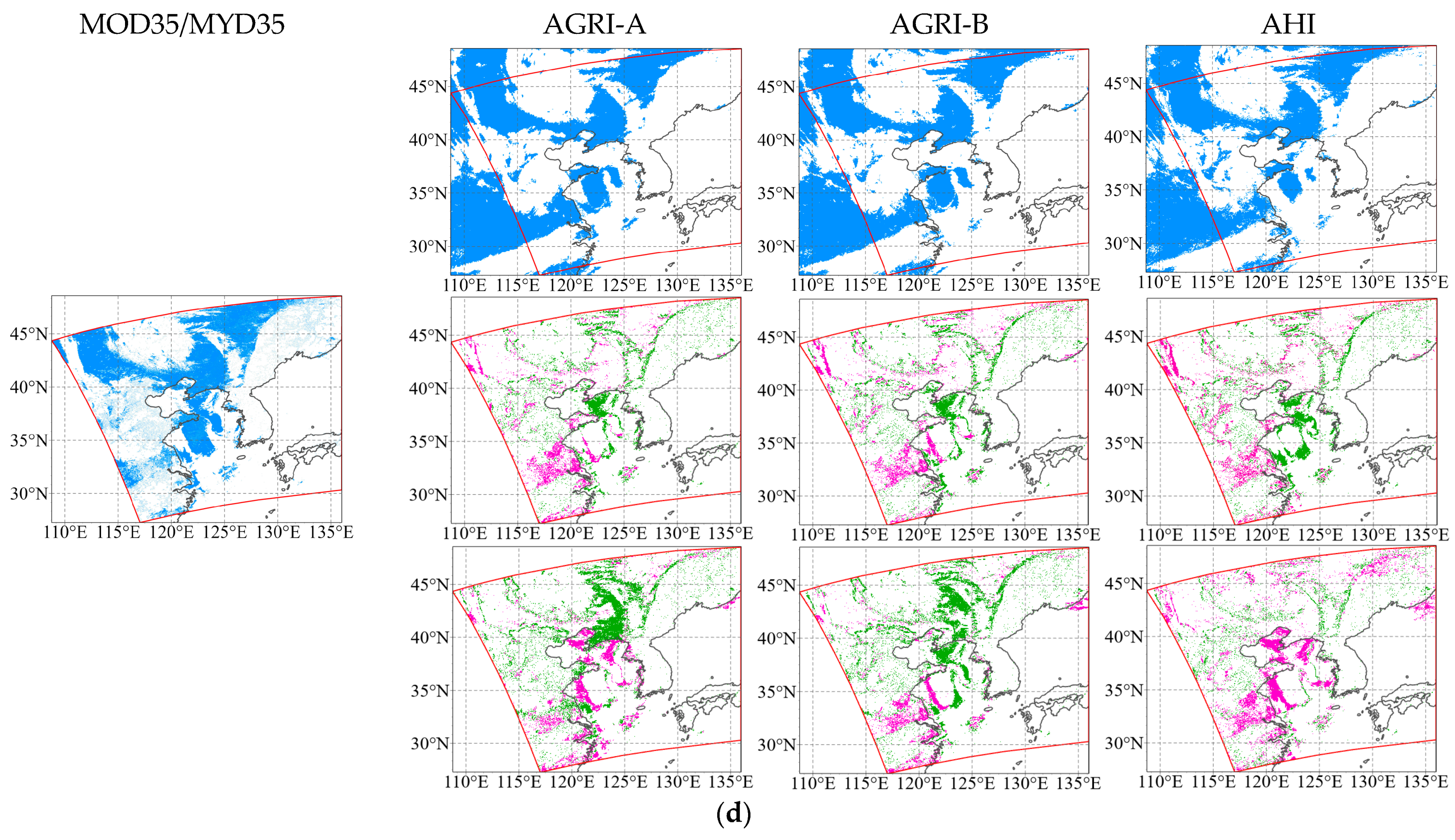
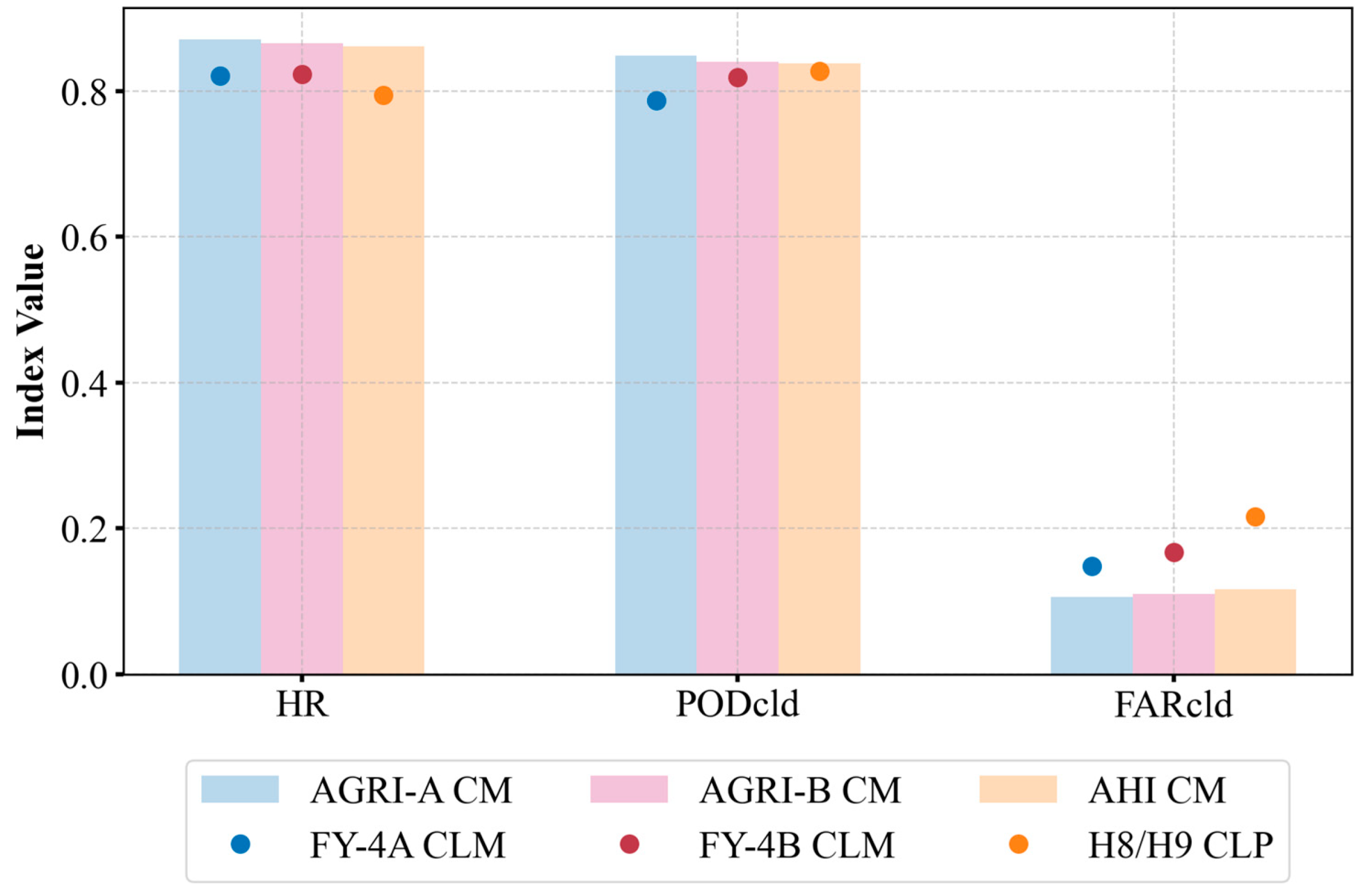
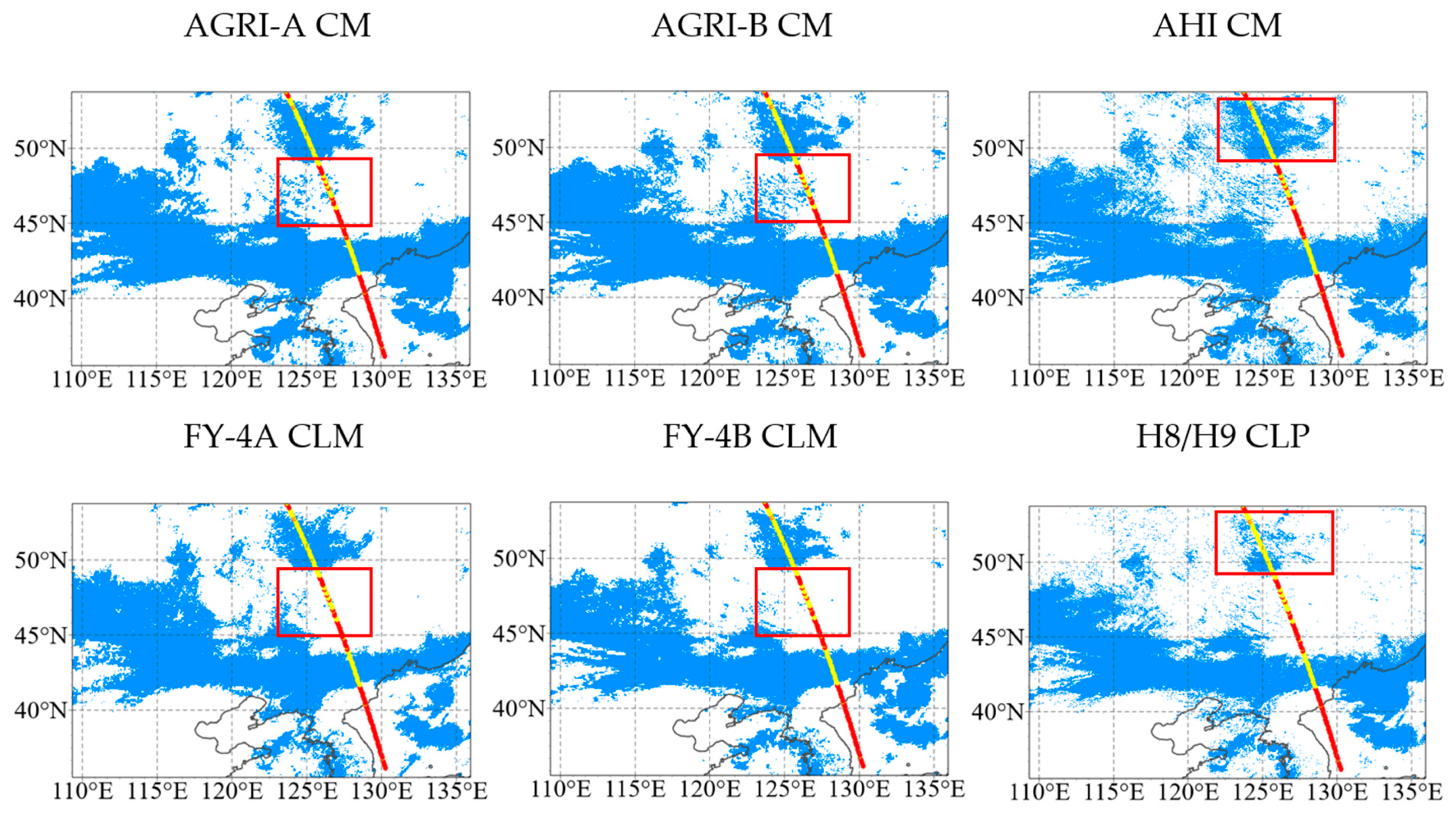
| Sensor | Satellite | Short Name | Sub-Satellite Point | Spatial Resolution (km) | Temporal Resolution (min) | Scanning Continuity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGRI | FY-4A | AGRI-A | 105.0°E | 4 | 15 | incomplete continuity |
| FY-4B | AGRI-B | 133.0°E | 4 | 15 | completely continuous | |
| AHI | H-8/H-9 | AHI | 140.7°E | 5 | 10 | completely continuous |
| Rename | AGRI-A | AGRI-B | AHI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Band (μm) | No | Band (μm) | No | Band (μm) | |
| B1 | 1 | 0.47 | 1 | 0.47 | 1 | 0.47 |
| - | - | - | - | 2 | 0.51 | |
| B2 | 2 | 0.65 | 2 | 0.65 | 3 | 0.64 |
| B3 | 3 | 0.83 | 3 | 0.825 | 4 | 0.86 |
| 4 | 1.37 | 4 | 1.379 | - | - | |
| B4 | 5 | 1.61 | 5 | 1.61 | 5 | 1.6 |
| B5 | 6 | 2.22 | 6 | 2.225 | 6 | 2.3 |
| B6 | 7 | 3.72 (high) | 7 | 3.75 (high) | 7 | 3.9 |
| 8 | 3.72 (low) | 8 | 3.75 (low) | - | - | |
| B7 | 9 | 6.25 | 9 | 6.25 | 8 | 6.2 |
| - | - | 10 | 6.95 | 9 | 6.9 | |
| B8 | 10 | 7.10 | 11 | 7.42 | 10 | 7.3 |
| B9 | 11 | 8.50 | 12 | 8.55 | 11 | 8.6 |
| - | - | - | - | 12 | 9.6 | |
| B10 | 12 | 10.80 | 13 | 10.80 | 13 | 10.4 |
| - | - | - | - | 14 | 11.2 | |
| B11 | 13 | 12.0 | 14 | 12.0 | 15 | 12.4 |
| B12 | 14 | 13.5 | 15 | 13.3 | 16 | 13.3 |
| IGBP Class Name | IGBP Class Value | Reclassification Types |
|---|---|---|
| Evergreen Needleleaf Forests | 1 | Forests |
| Evergreen Broadleaf Forests | 2 | Forests |
| Deciduous Needleleaf Forests | 3 | Forests |
| Deciduous Broadleaf Forests | 4 | Forests |
| Mixed Forests | 5 | Forests |
| Closed Shrublands | 6 | Shrublands/Grasslands |
| Open Shrublands | 7 | Shrublands/Grasslands |
| Woody Savannas | 8 | Shrublands/Grasslands |
| Savannas | 9 | Shrublands/Grasslands |
| Grasslands | 10 | Shrublands/Grasslands |
| Permanent Wetlands | 11 | Wetlands/Waters |
| Croplands | 12 | Croplands |
| Urban and Built-up Lands | 13 | Urban |
| Cropland/Natural Vegetation Mosaics | 14 | Croplands |
| Permanent Snow and Ice | 15 | Snow/Ice |
| Barren | 16 | Barren |
| Water Bodies | 17 | Wetlands/Waters |
| Cloudy (Predicted Values) | Clear (Predicted Values) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudy (true values) | a | b |
| Clear (true values) | c | d |
| Sensor | Matched Pixels | HR | KSS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGRI-A | 11,287 | 0.9128 | 0.8435 | 0.1250 | 0.1104 | 0.8813 | 0.7563 |
| AGRI-B | 11,287 | 0.9133 | 0.8197 | 0.1413 | 0.1127 | 0.8707 | 0.7330 |
| AHI | 8139 | 0.9373 | 0.7933 | 0.0970 | 0.1395 | 0.8902 | 0.7307 |
| Sensor | Matched Pixels 108) | HR | KSS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGRI-A | 2.19011756 | 0.9046 | 0. 7946 | 0.1176 | 0.1699 | 0.8639 | 0.6992 |
| AGRI-B | 2.18914853 | 0.8998 | 0. 7842 | 0.1234 | 0.1788 | 0.8571 | 0.6840 |
| AHI | 1.43243702 | 0.8956 | 0. 7861 | 0.1224 | 0.1852 | 0.8553 | 0.6817 |
| Case | Value | AGRI-A CM | FY-4A CLM | AGRI-B CM | FY-4B CLM | AHI CM | H8/H9 CLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | HR | 0.8369 | 0.7879 | 0.8265 | 0.7706 | 0.8079 | 0.7542 |
| 0.8541 | 0.8890 | 0.8455 | 0.9087 | 0.8293 | 0.9338 | ||
| 0.1374 | 0.2234 | 0.1468 | 0.2443 | 0.1629 | 0.2776 | ||
| b | HR | 0.8753 | 0.8542 | 0.8671 | 0.8569 | 0.8686 | 0.8351 |
| 0.6439 | 0.5728 | 0.6005 | 0.5971 | 0.6087 | 0.6485 | ||
| 0.1350 | 0.1569 | 0.1266 | 0.1682 | 0.1282 | 0.2798 | ||
| c | HR | 0.8771 | 0.7904 | 0.8767 | 0.8039 | 0.8803 | 0.7410 |
| 0.8577 | 0.6584 | 0.8595 | 0.7209 | 0.8693 | 0.7442 | ||
| 0.0949 | 0.0764 | 0.0972 | 0.1126 | 0.0990 | 0.2389 | ||
| d | HR | 0.9022 | 0.8636 | 0.8977 | 0.8729 | 0.8923 | 0.8718 |
| 0.9458 | 0.9378 | 0.9455 | 0.9540 | 0.9424 | 0.9053 | ||
| 0.0731 | 0.1112 | 0.0781 | 0.1124 | 0.0820 | 0.0755 | ||
| Mean (all cases) | HR | 0.8711 | 0.8213 | 0.8653 | 0.8233 | 0.8611 | 0.7950 |
| 0.8486 | 0.7873 | 0.8400 | 0.8193 | 0.8386 | 0.8276 | ||
| 0.1058 | 0.1478 | 0.1095 | 0.1673 | 0.1161 | 0.2161 |
| Case | Value | AGRI-A | FY-4A CLM | AGRI-B | FY-4B CLM | AHI | H8/H9 CLP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e | HR | 0.9151 | 0.8270 | 0.9119 | 0.8239 | 0.8985 | 0.7331 |
| 0.9822 | 1.0000 | 0.9822 | 0.9882 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.1263 | 0.2455 | 0.1309 | 0.2443 | 0.1617 | 0.3365 | ||
| f | HR | 0.8455 | 0.8073 | 0.8206 | 0.7625 | 0.8090 | 0.7639 |
| 0.9071 | 0.9098 | 0.9153 | 0.9372 | 0.9437 | 0.9683 | ||
| 0.1509 | 0.1995 | 0.8131 | 0.2592 | 0.2232 | 0.2782 | ||
| g | HR | 0.9302 | 0.8357 | 0.9138 | 0.8706 | 0.8730 | 0.8307 |
| 0.9704 | 0.8978 | 0.9651 | 0.9355 | 0.9255 | 0.9184 | ||
| 0.0599 | 0.1117 | 0.0747 | 0.1008 | 0.0938 | 0.1367 | ||
| Mean (all cases) | HR | 0.8905 | 0.8216 | 0.8735 | 0.8138 | 0.8515 | 0.7790 |
| 0.9471 | 0.9217 | 0.9482 | 0.9460 | 0.9476 | 0.9547 | ||
| 0.1098 | 0.1772 | 0.1322 | 0.1989 | 0.1637 | 0.2444 |
| Model | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | B10 | B11 | B12 | SZA | VZA | RAA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM for ARGI-A | 9.04 | 3.58 | 3.01 | 2.82 | 3.65 | 4.72 | 3.68 | 7.45 | 6.29 | 7.19 | 22.89 | 4.34 | 10.13 | 7.06 | 4.15 |
| TCM for AGRI-B | 12.80 | 4.60 | 3.59 | 3.36 | 4.03 | 4.51 | 4.06 | 5.52 | 3.17 | 7.18 | 15.95 | 6.48 | 9.68 | 10.83 | 4.35 |
| TCM for AHI | 10.48 | 6.34 | 2.63 | 3.36 | 4.29 | 5.18 | 2.17 | 2.91 | 3.77 | 9.20 | 28.87 | 3.65 | 4.92 | 8.94 | 3.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Wang, Z.; Lang, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Qin, W.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Cloud Mask Detection by Combining Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193315
He C, Wang Z, Lang Q, Feng L, Zhang M, Qin W, Tao M, Wang Y, Wang L. Cloud Mask Detection by Combining Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193315
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chenxi, Zhitong Wang, Qin Lang, Lan Feng, Ming Zhang, Wenmin Qin, Minghui Tao, Yi Wang, and Lunche Wang. 2025. "Cloud Mask Detection by Combining Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193315
APA StyleHe, C., Wang, Z., Lang, Q., Feng, L., Zhang, M., Qin, W., Tao, M., Wang, Y., & Wang, L. (2025). Cloud Mask Detection by Combining Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193315









