Improved Pixel Offset Tracking Method Based on Corner Point Variation in Large-Gradient Landslide Deformation Monitoring
Abstract
Highlights
- A novel corner point change normalization cross-correlation pixel offset tracking method is proposed.
- The method demonstrates improved landslide delineation and offset calculation using VV and VH polarization data.
- The proposed method ensures high reliability in evaluating landslide displacement.
- It provides an effective solution for monitoring large-gradient landslides and overcoming feature-matching challenges.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
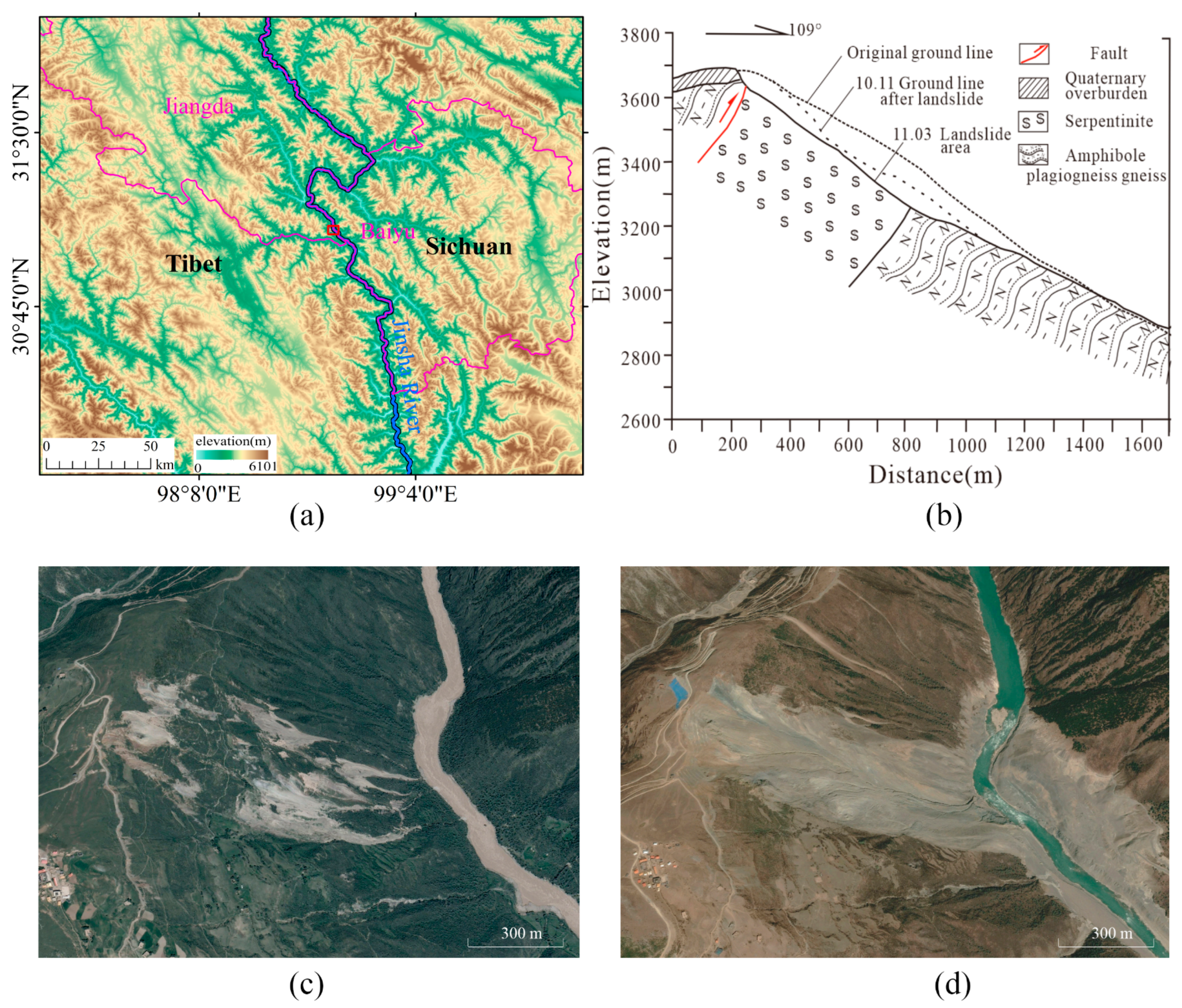
2.1. Jinsha River Baige Landslide
2.2. SAR Data and Auxiliary Data
2.3. Methods
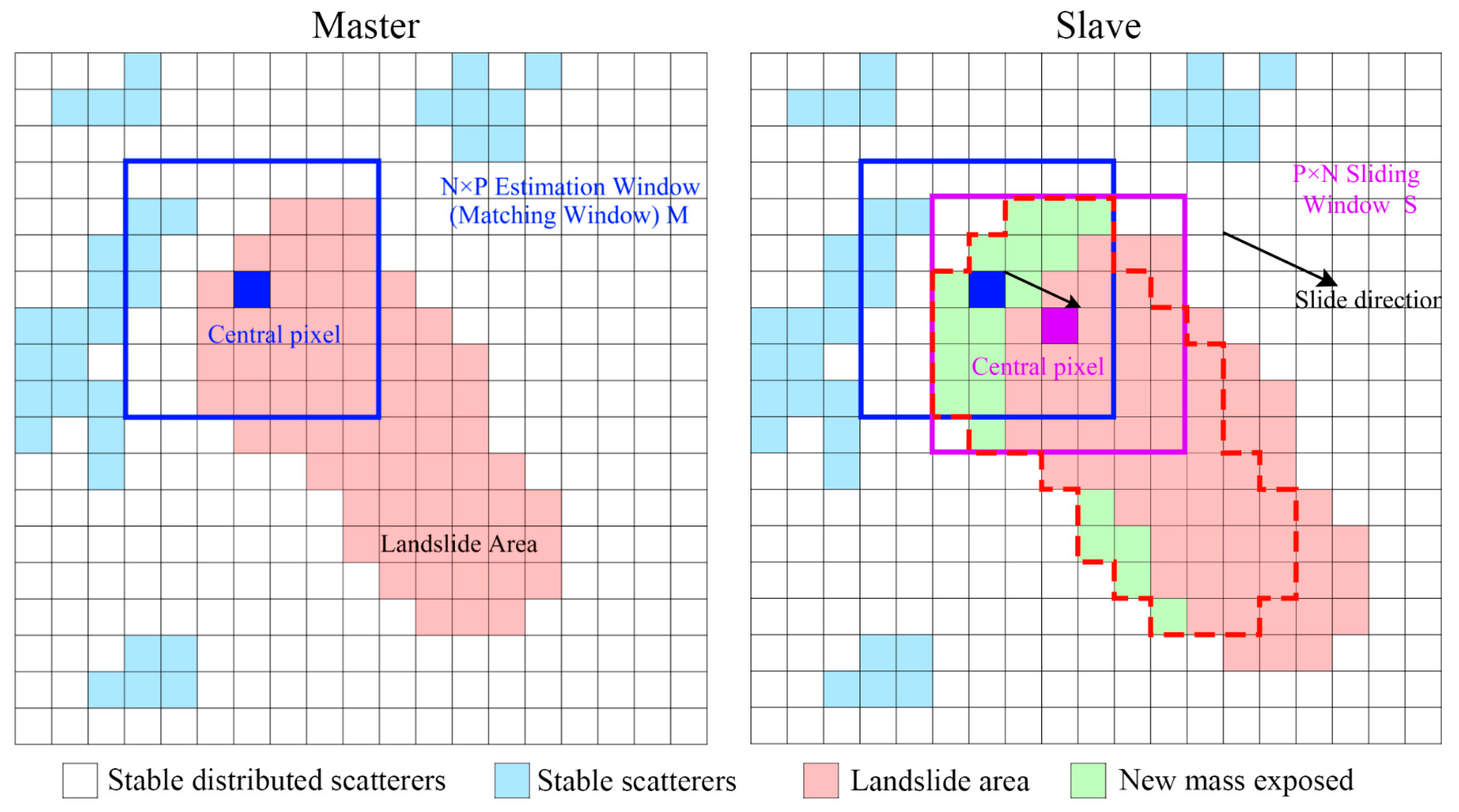
2.3.1. Traditional Normalized Cross-Correlation Tracking Methods
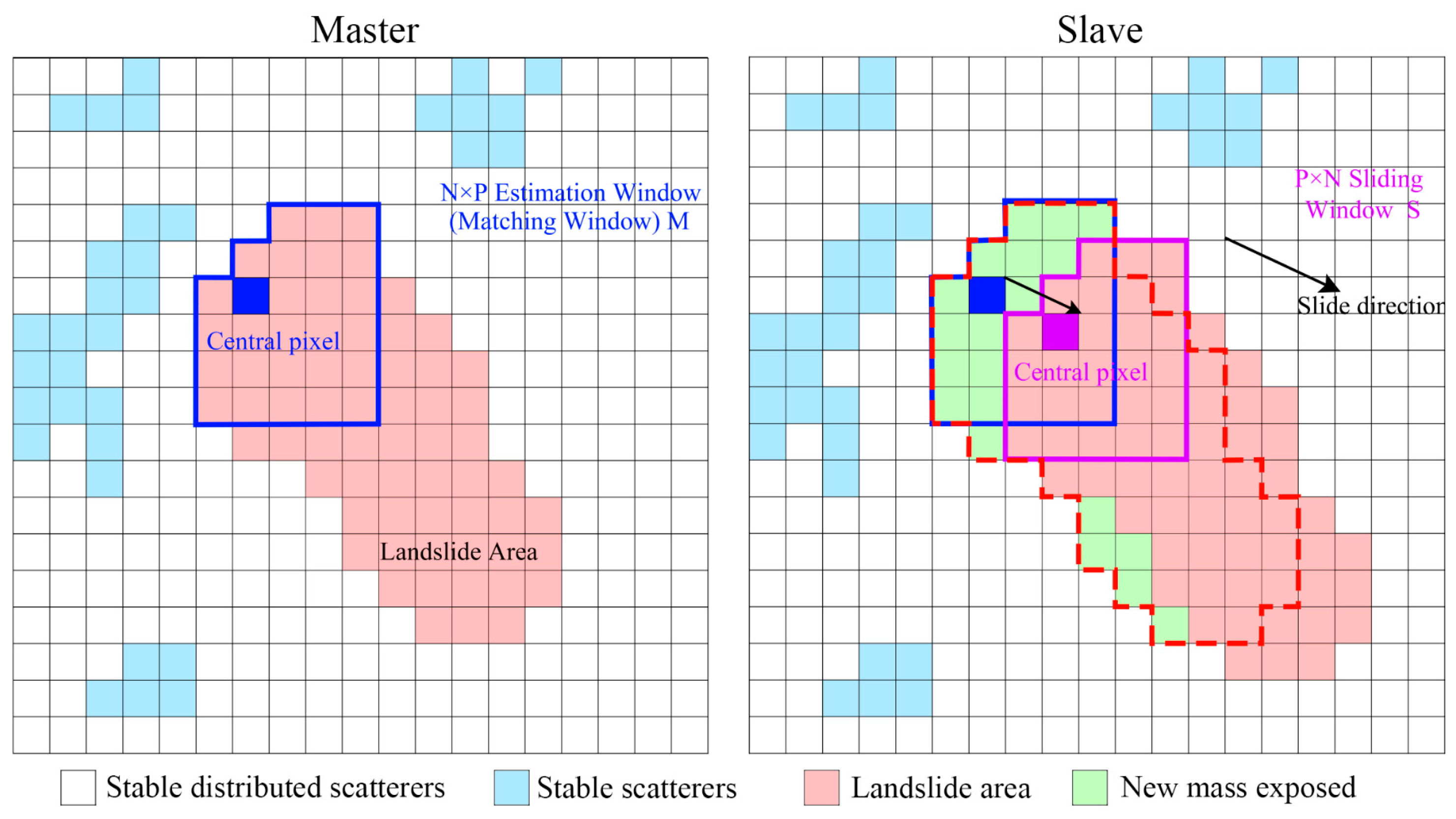
2.3.2. Adaptive Window Normalized Cross-Correlation Tracking Method
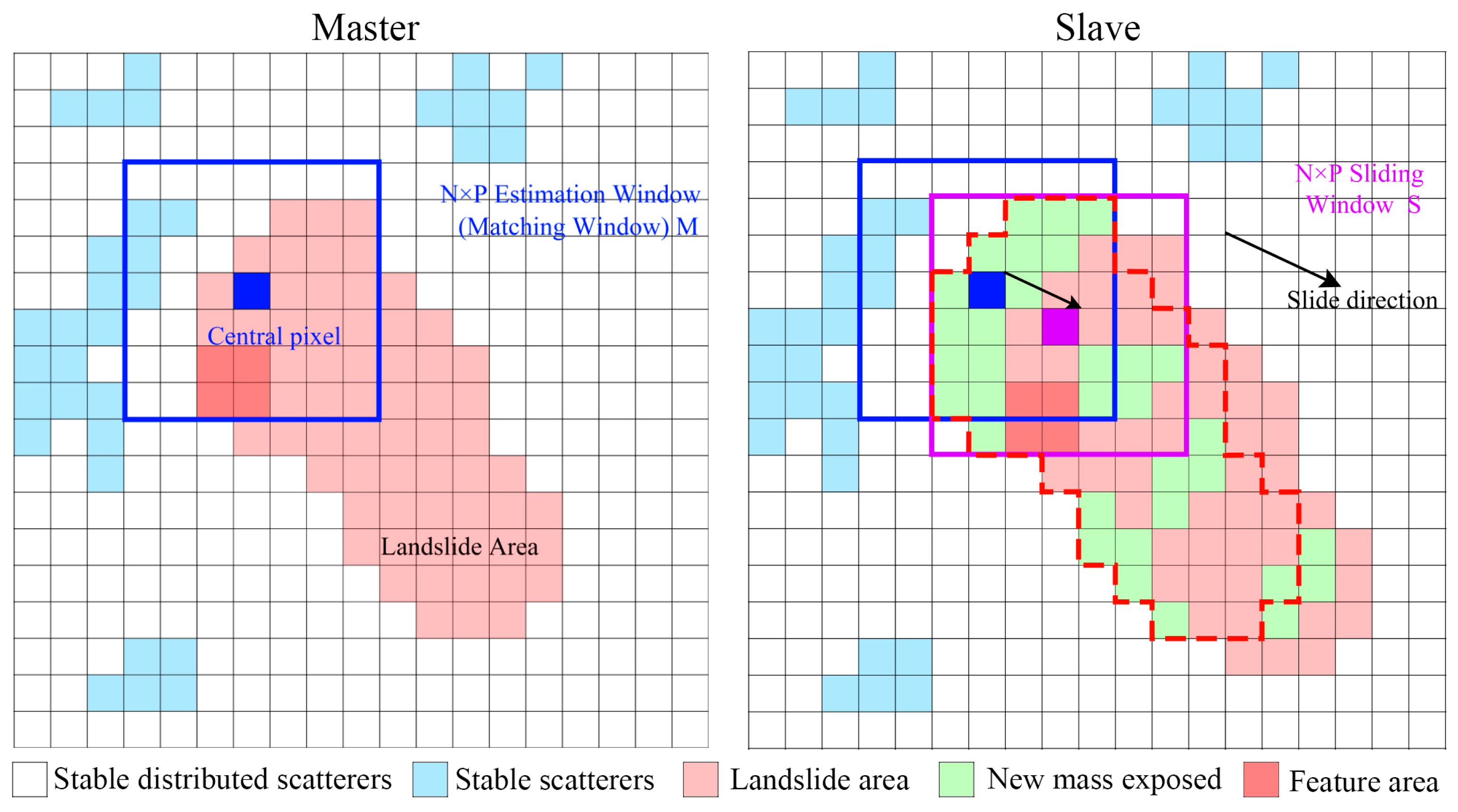
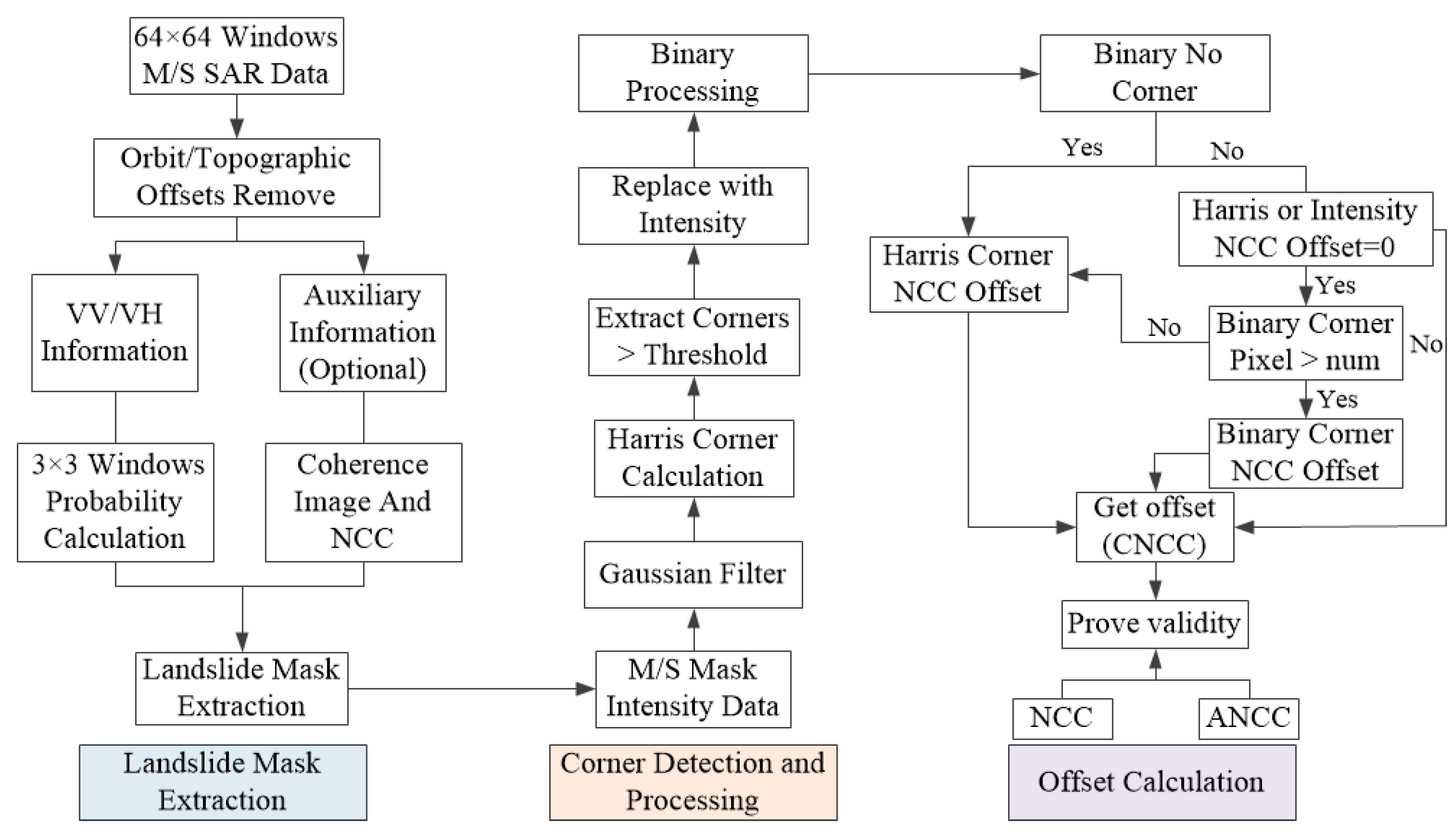
2.3.3. Corner Point Change Normalized Cross-Correlation Tracking Method
- Landslide mask extraction
- Corner detection and handling
- Corner detection and handling offset calculation and comparison
3. Results
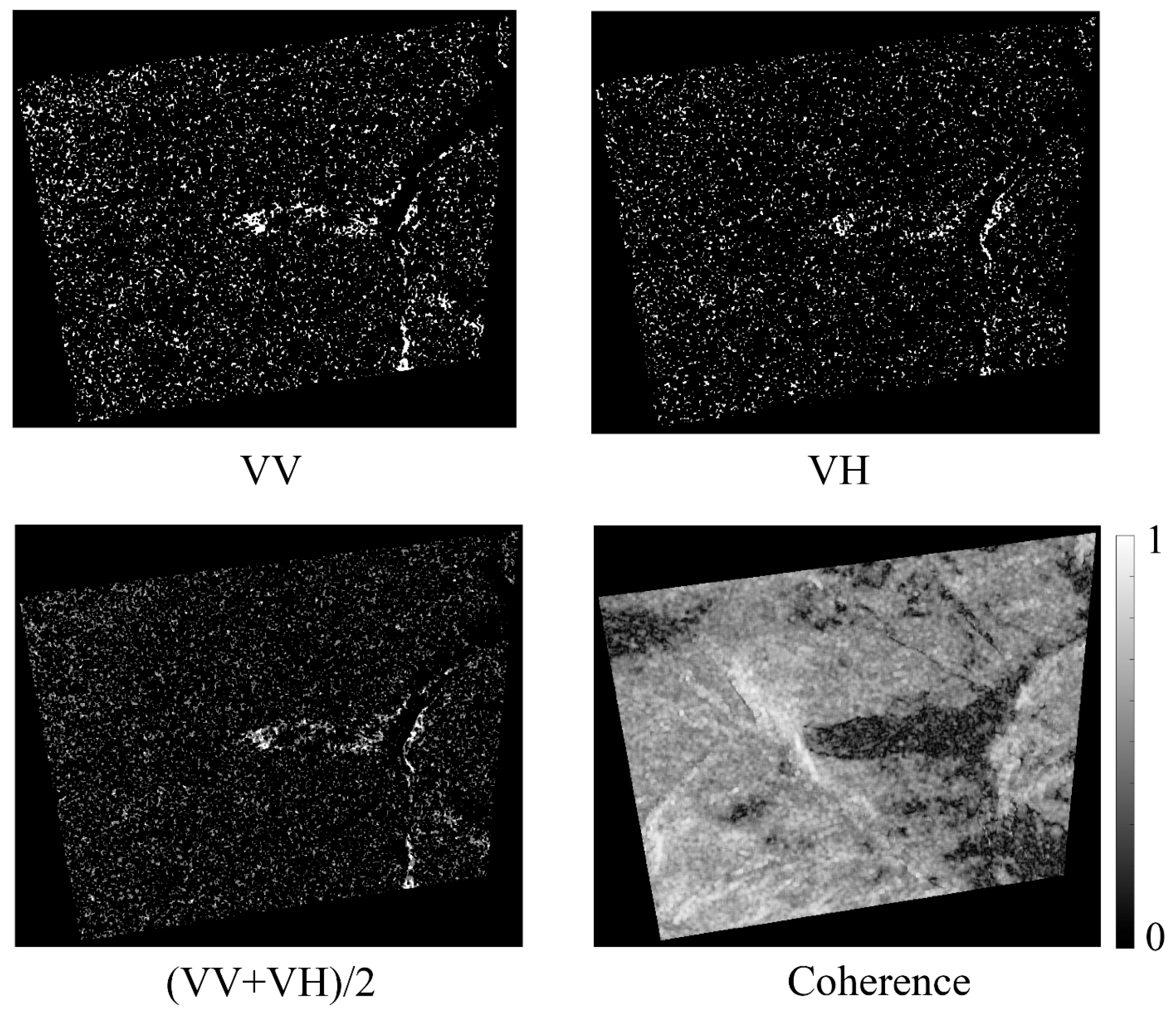
3.1. Landslide Mask Extraction Results
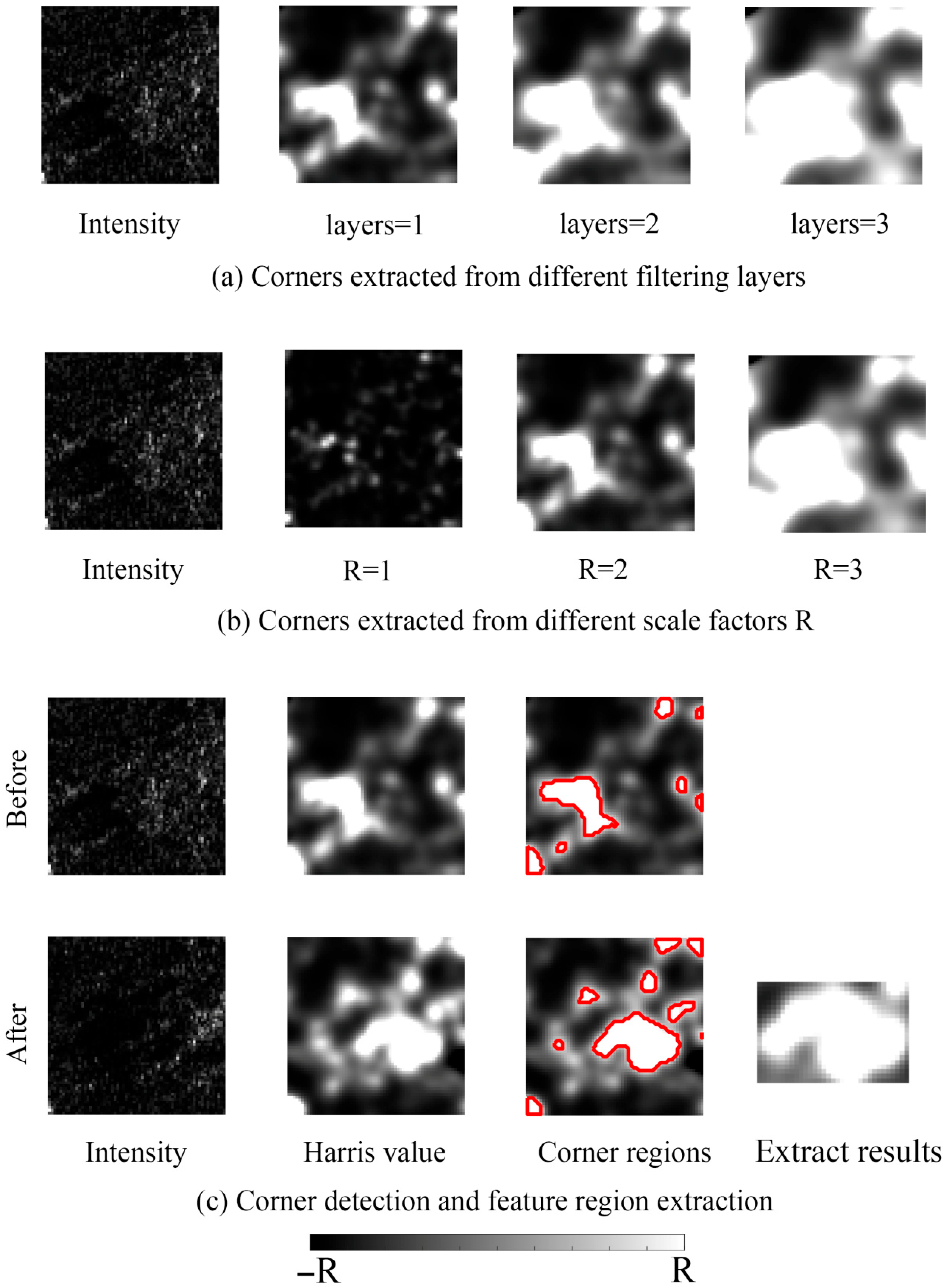
3.2. Corner Detection and Extraction Results
3.3. Offset Calculation Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of This Paper’s Method over Existing Methods
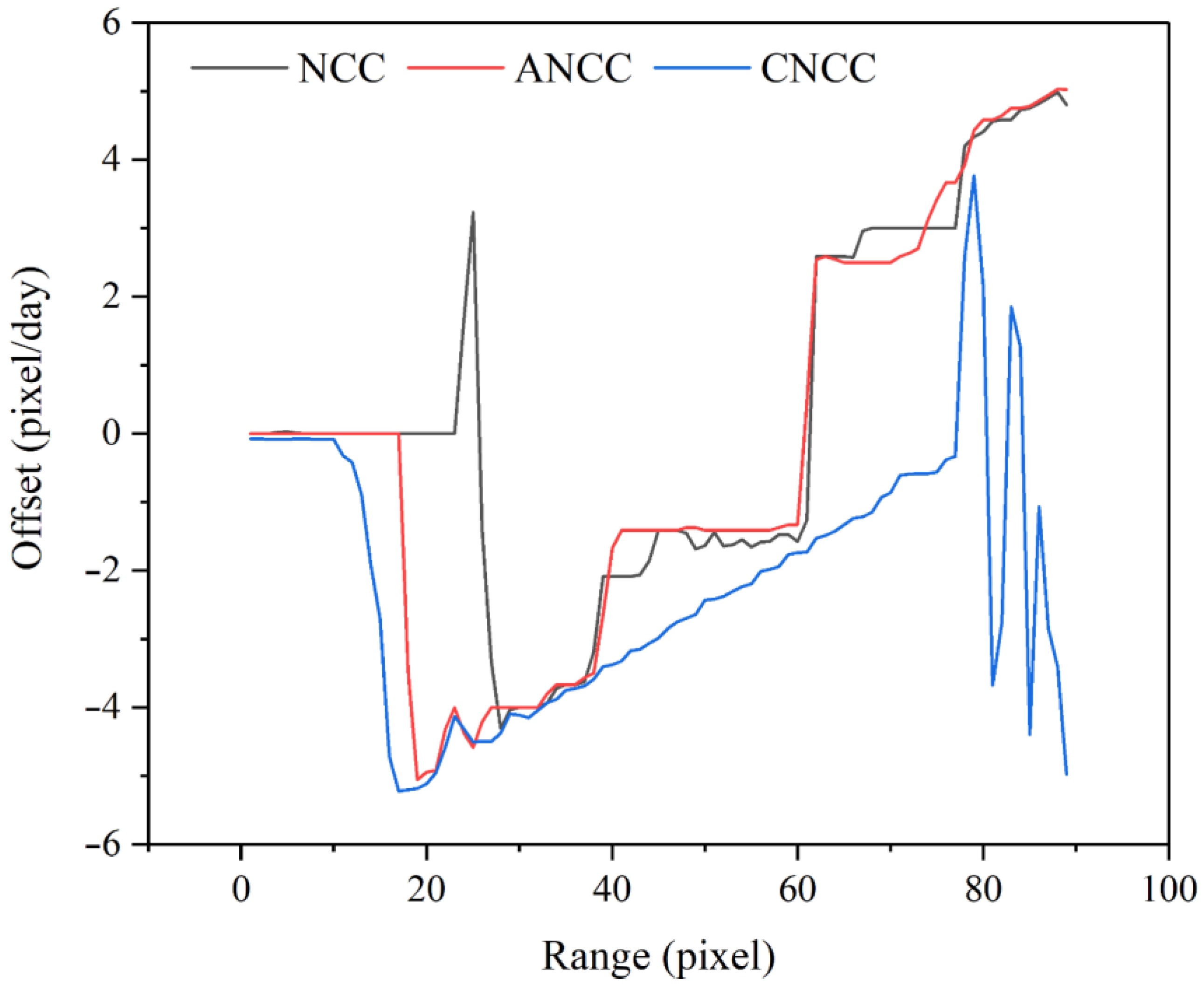
4.2. Validation of the Accuracy of the Offset Results Obtained by Different Methods
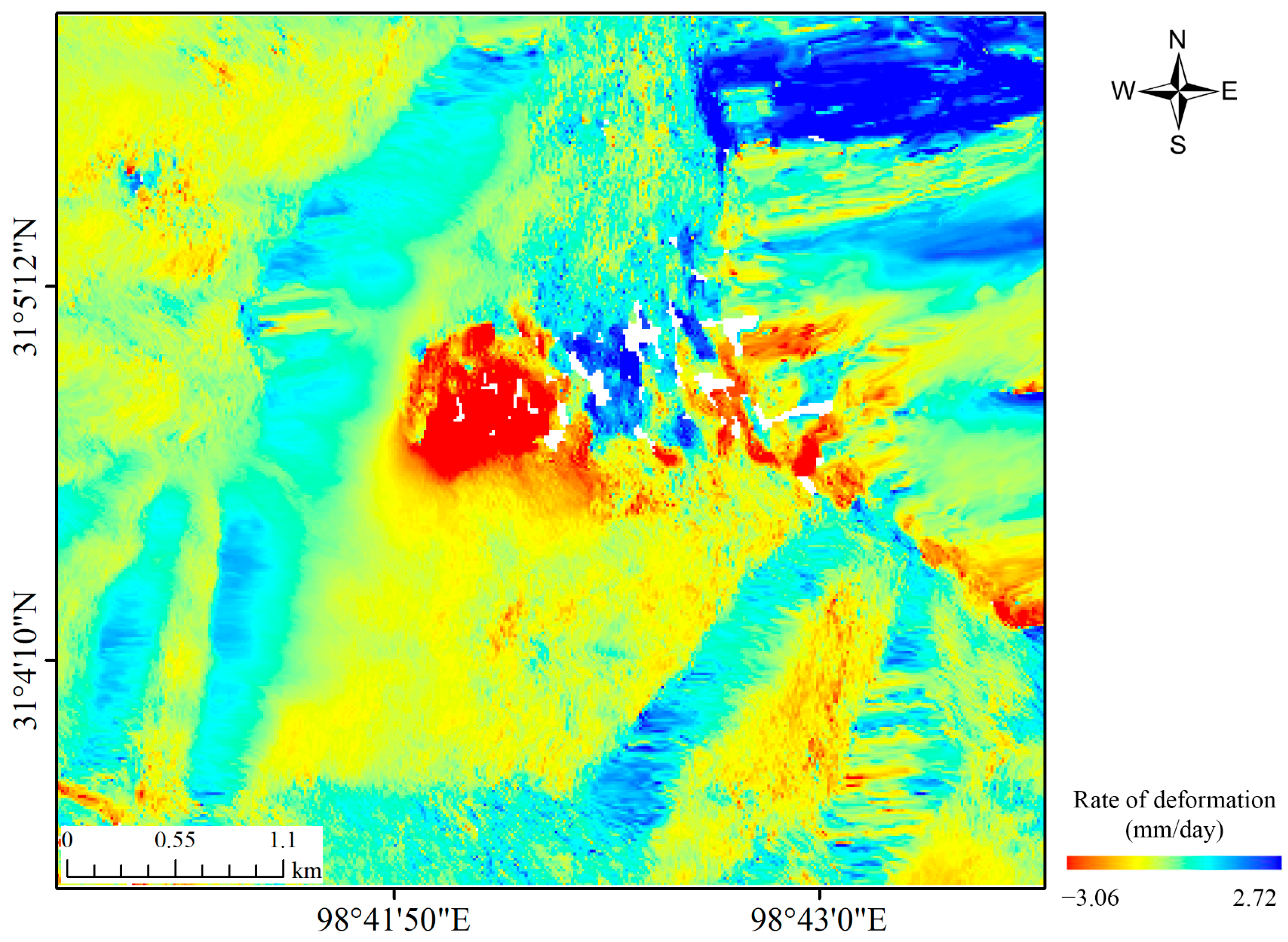
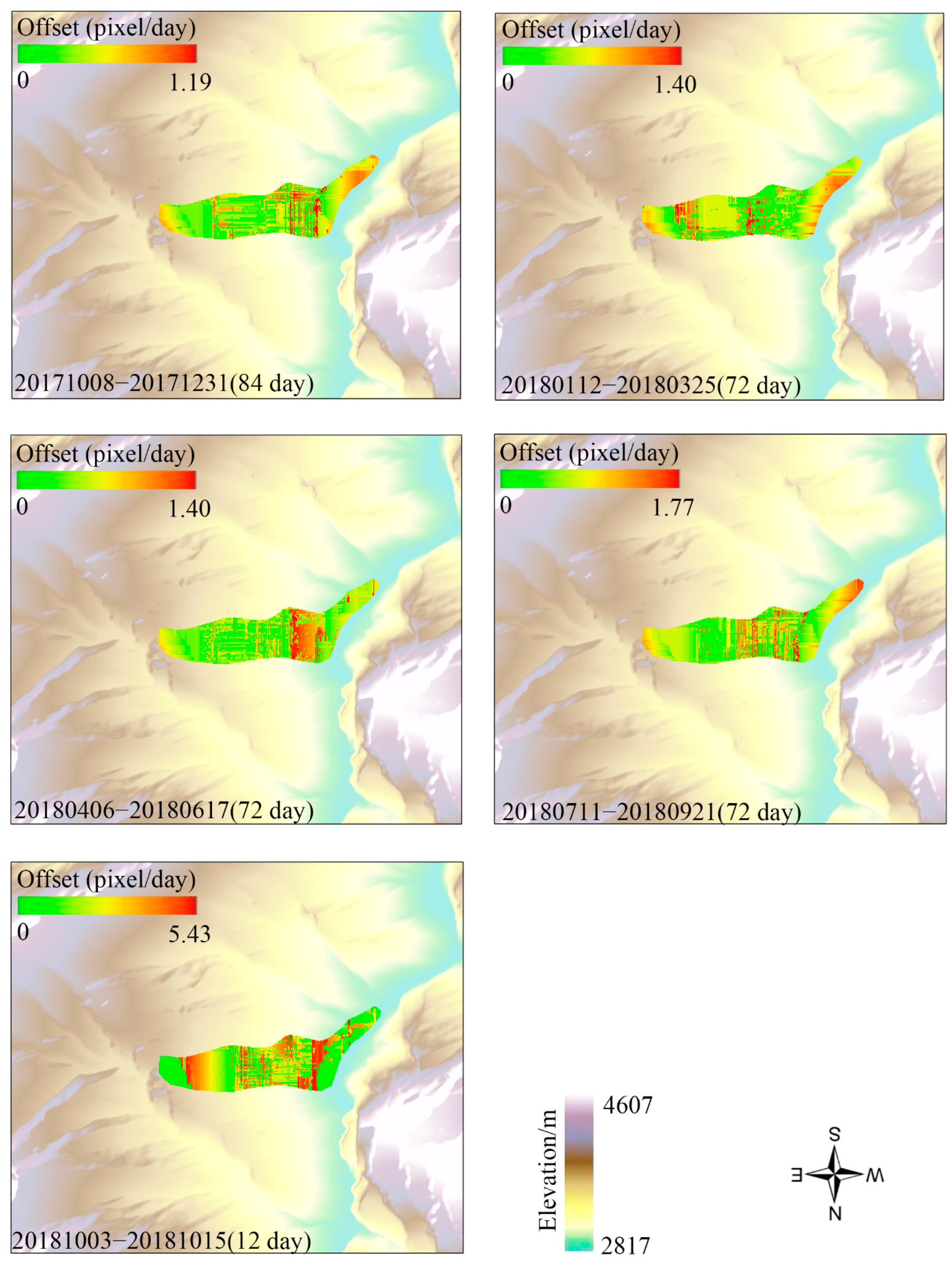
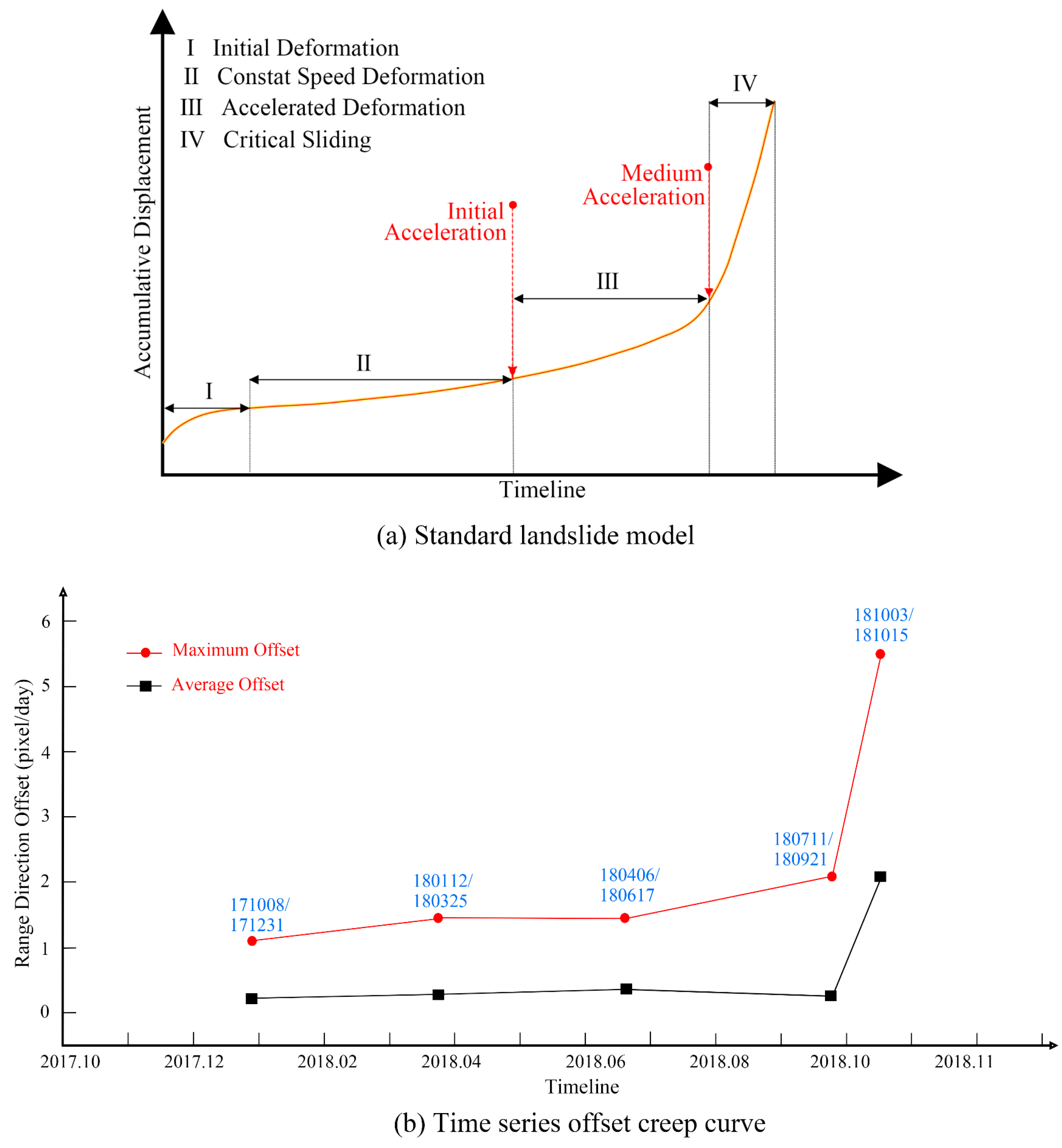
4.3. Pre-Disaster Deformation Monitoring and Evolution Process of Landslides
4.4. Offset Validity and Noise Control
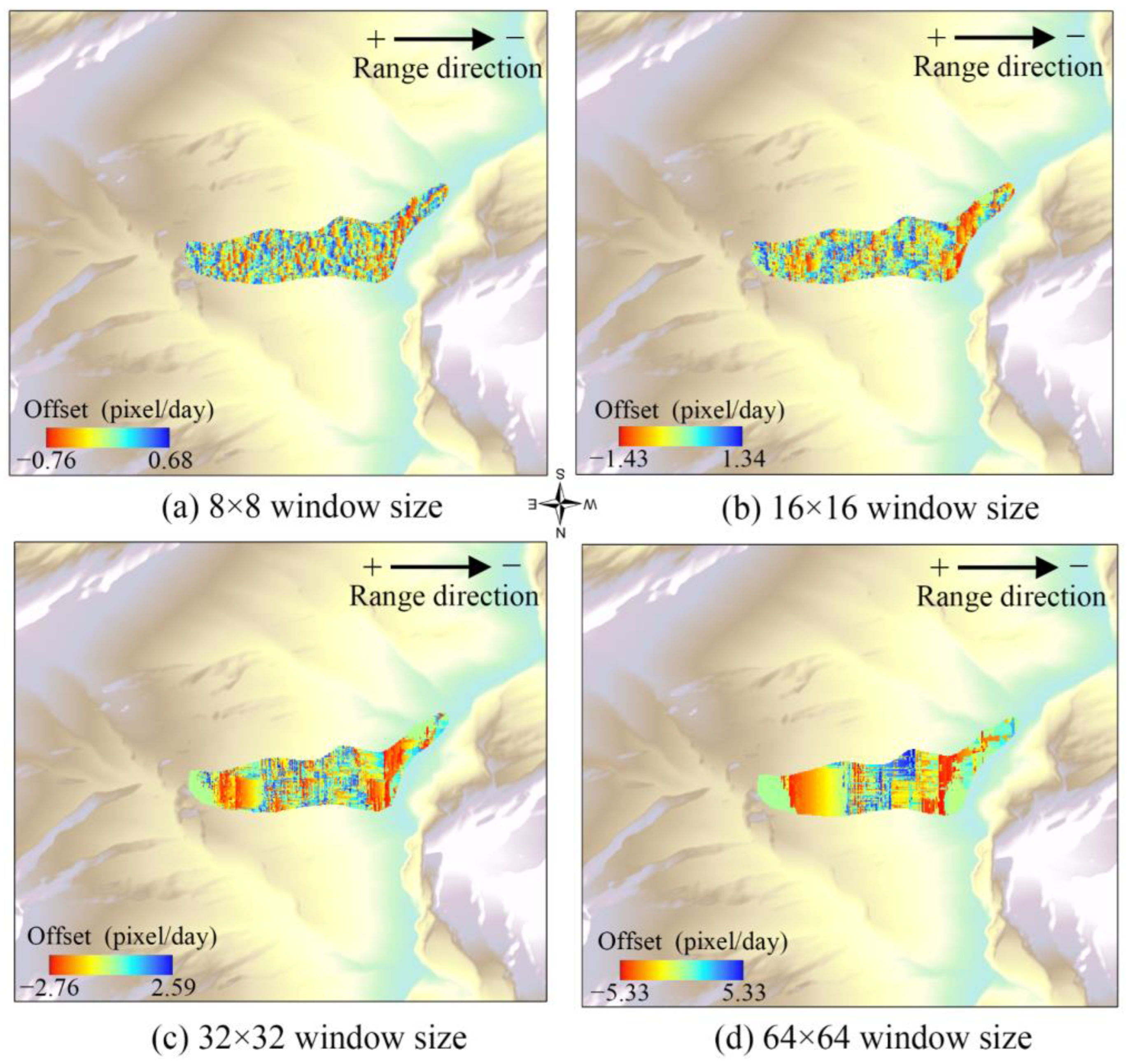
4.5. Effect of Different Matrix Windows on the Calculation of Offsets for the Method in This Paper
4.6. Limitations of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kc, R.; Sharma, K.; Dahal, B.K.; Aryal, M.; Subedi, M. Study of the spatial distribution and the temporal trend of landslide disasters that occurred in the Nepal Himalayas from 2011 to 2020. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 83, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D. Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology 2012, 40, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Motagh, M.; Xia, Z.; Plank, S.; Li, Z.; Orynbaikyzy, A.; Zhou, C.; Roessner, S. A framework for automated landslide dating utilizing SAR-Derived Parameters Time-Series, An Enhanced Transformer Model, and Dynamic Thresholding. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2024, 129, 103795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Schulz, W.H.; Lu, Z.; Kim, J.; Baxstrom, K. Geologic controls of slow-moving landslides near the US West Coast. Landslides 2021, 18, 3353–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, Z.; Xi, W.; Zhao, X.; Chao, J. New method for landslide susceptibility evaluation in alpine valley regions that considers the suitability of InSAR monitoring and introduces deformation rate grading. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2025, 28, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, D.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R. Improved offset tracking for predisaster deformation monitoring of the 2018 Jinsha River landslide (Tibet, China). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, C.; Liao, M. Polarimetric SAR pixel offset tracking for large-gradient landslide displacement mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2022, 112, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Feng, Y.; Zhuo, G.; Tie, Y.; Deng, J.; Balz, T.; Li, Z. Applicability Analysis of Potential Landslide Identification by InSAR in Alpine-Canyon Terrain—Case Study on Yalong River. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Ding, C.; Li, W.; Luo, H.; Liao, M.; Xu, Q. Retrieval of historical surface displacements of the Baige landslide from time-series SAR observations for retrospective analysis of the collapse event. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.; Zheng, M. Research on ground deformation monitoring method in mining areas using the probability integral model fusion D-InSAR, sub-band InSAR and offset-tracking. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2020, 85, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Motagh, M.; Li, T.; Peng, M.; Roessner, S. A methodology to characterize 4D post-failure slope instability dynamics using remote sensing measurements: A case study of the Aniangzhai landslide in Sichuan, Southwest China. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, S.; Zhang, G.; Liao, M.; Gong, J. Automatic detection and update of landslide inventory before and after impoundments at the Lianghekou reservoir using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2023, 118, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; de la Fuente, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS/PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, Q. An Adaptive Offset Tracking Method with SAR Images for Landslide Displacement Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Luckman, A.; Murray, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Werner, C.L. Glacier motion estimation using SAR offset-tracking procedures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 40, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Zhao, F. Patch-Like Reduction (PLR): A SAR Offset Tracking amplitude filter for deformation monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2022, 113, 102976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Guo, S. Reducing patch-like Errors in SAR offset tracking displacements using logarithmic transformation and a weighted NCC algorithm. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 14, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, Q. Landslide Displacement Monitoring by a Fully Polarimetric SAR Offset Tracking Method. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Muller, J.-P. Evaluating sub-pixel offset techniques as an alternative to D-InSAR for monitoring episodic landslide movements in vegetated terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, Q.; Alonso-Rodriguez, A.; Subramanian, S.S.; Li, W.; Zheng, G.; Dong, X.; Huang, R. Successive landsliding and damming of the Jinsha River in eastern Tibet, China: Prime investigation, early warning, and emergency response. Landslides 2019, 16, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.; An, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, P.; Wang, D.; Cheng, D.; She, J. Insights from the failure and dynamic characteristics of two sequential landslides at Baige village along the Jinsha River, China. Landslides 2019, 16, 1397–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C. Using Sentinel-2 time series to detect slope movement before the Jinsha River landslide. Landslides 2019, 16, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitová, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Allinson, N.M. A comprehensive review of current local features for computer vision. Neurocomputing. 2008, 71, 1771–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.; Monzón, N.; Salgado, A. An Analysis and Implementation of the Harris Corner Detector. Image Process. Line 2018, 8, 305–328. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, Q.; He, P. An Improved Corner Detection Algorithm Based on Harris. Adv. Eng. Forum 2012, 6–7, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, F.; Delon, J.; Gousseau, Y.; Michel, J.; Tupin, F. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-Like Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Gong, M.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L. Remote Sensing Image Registration With Modified SIFT and Enhanced Feature Matching. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; Stephens, M. A Combined Corner and Edge Detector. In Proceedings of the 4th Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 31 August–2 September 1988; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Radar Band | C-band |
| Orbit | Ascending |
| Imaging Mode | IW |
| Polarization Mode | VV, VH |
| Incidence Angle (°) | 36.62 |
| Range Pixel | 6.99 |
| Azimuth Pixel | 13.99 |
| Pre-landslide Image Date | 3 October 2018 |
| Post-landslide Image Date | 15 October 2018 |
| Additional Images for Pre-disaster Monitoring | 8 scenes from October 2017 to September 2018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, F. Improved Pixel Offset Tracking Method Based on Corner Point Variation in Large-Gradient Landslide Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193292
Zhou D, Zhao Z, Zhao F. Improved Pixel Offset Tracking Method Based on Corner Point Variation in Large-Gradient Landslide Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193292
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dingyi, Zhifang Zhao, and Fei Zhao. 2025. "Improved Pixel Offset Tracking Method Based on Corner Point Variation in Large-Gradient Landslide Deformation Monitoring" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193292
APA StyleZhou, D., Zhao, Z., & Zhao, F. (2025). Improved Pixel Offset Tracking Method Based on Corner Point Variation in Large-Gradient Landslide Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193292







