Fine-Scale Mapping and Uncertainty Quantification of Intertidal Sediment Grain Size Using Geostatistical Simulation Integrated with Machine Learning and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery
Abstract
Highlights
- Incorporating satellite-derived features into the random forest model improved the accuracy of grain size prediction compared to using field samples alone.
- The proposed geostatistical simulation framework enabled explicit quantification of prediction uncertainty.
- Satellite-derived features, when integrated with machine learning and multivariate geostatistics, can be used to complement limited field data in tidal flats.
- The proposed approach provides fine-scale grain-size maps with associated uncertainty information to support coastal management.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
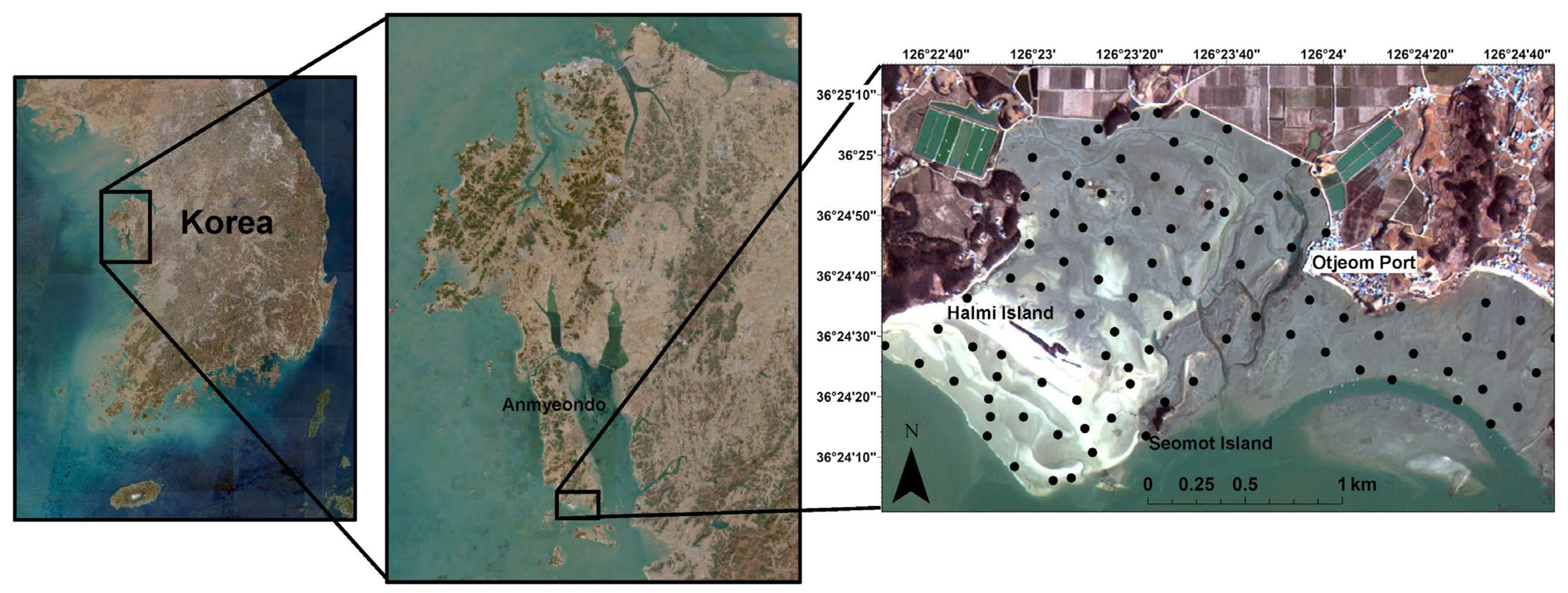
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Field Survey Data
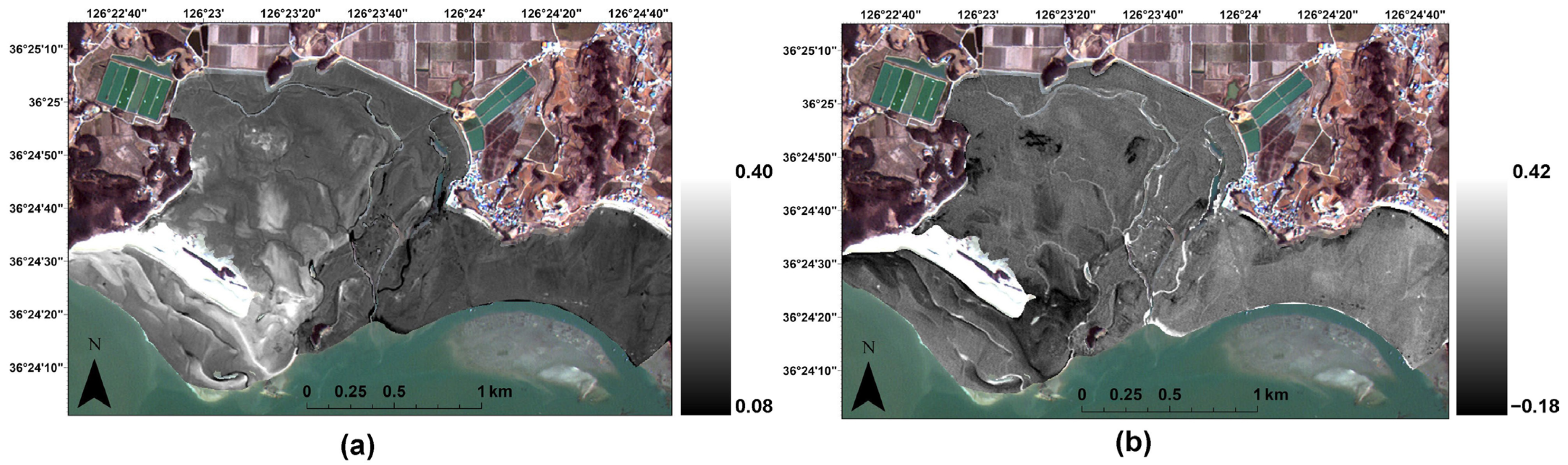
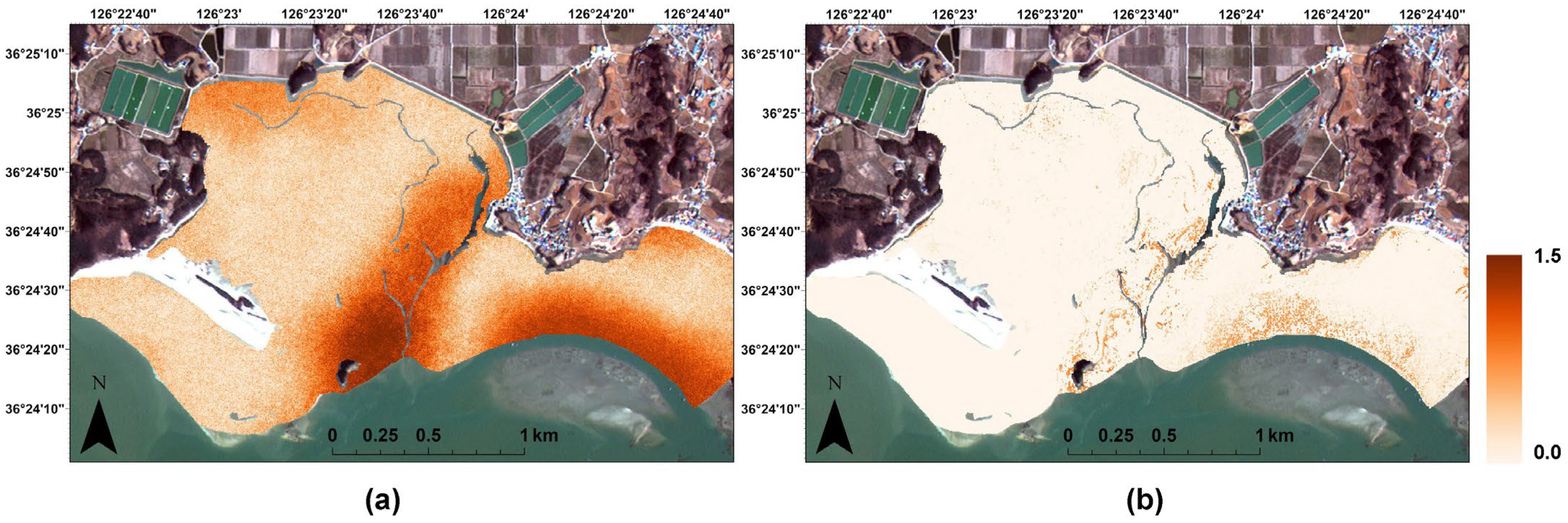
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Imagery
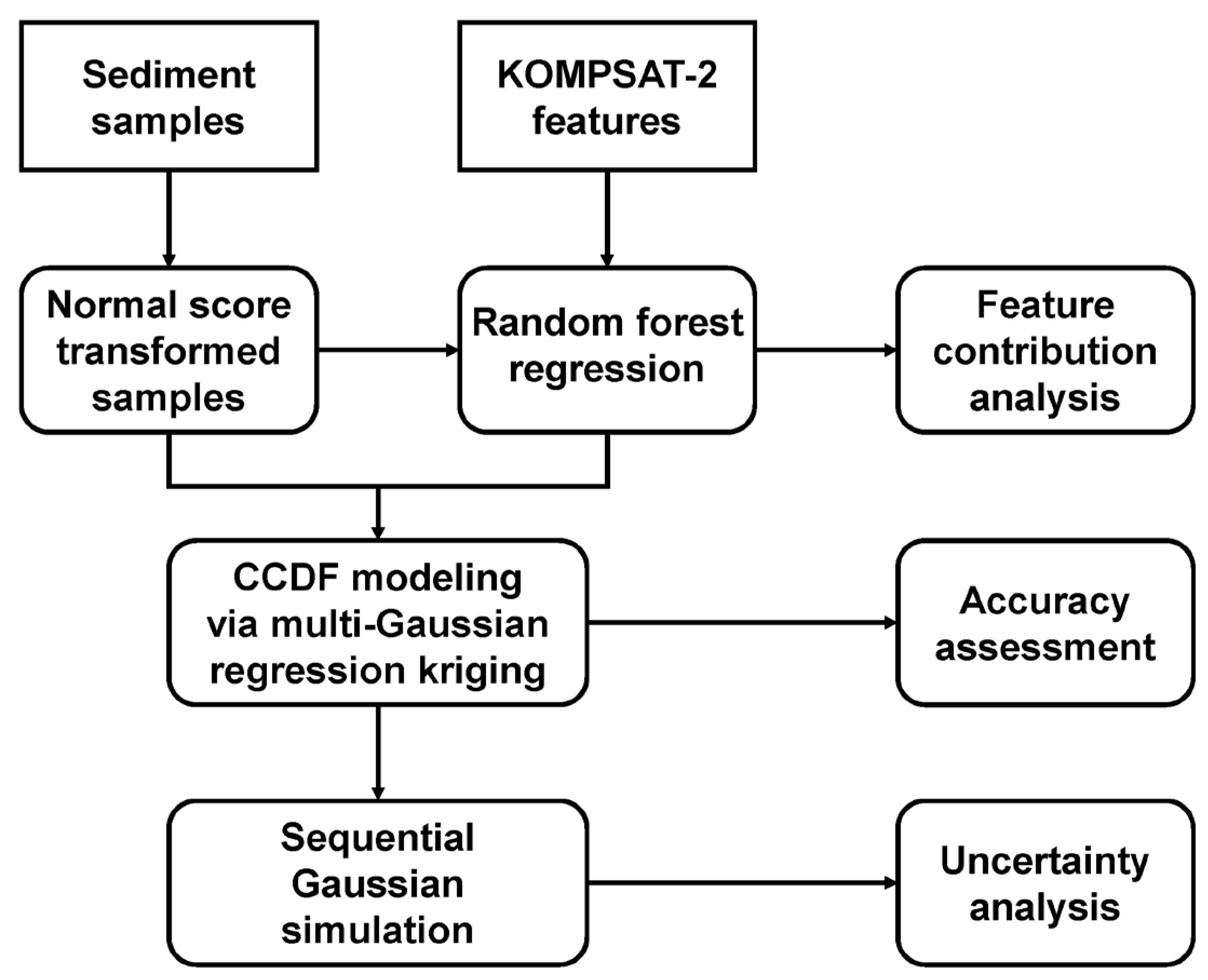
2.3. Geostatistical Methods
2.3.1. CCDF Modeling
2.3.2. Multi-Gaussian Regression Kriging with Random Forest Regression
2.3.3. Sequential Gaussian Simulation
2.4. Evaluation
2.5. Implementation
3. Results
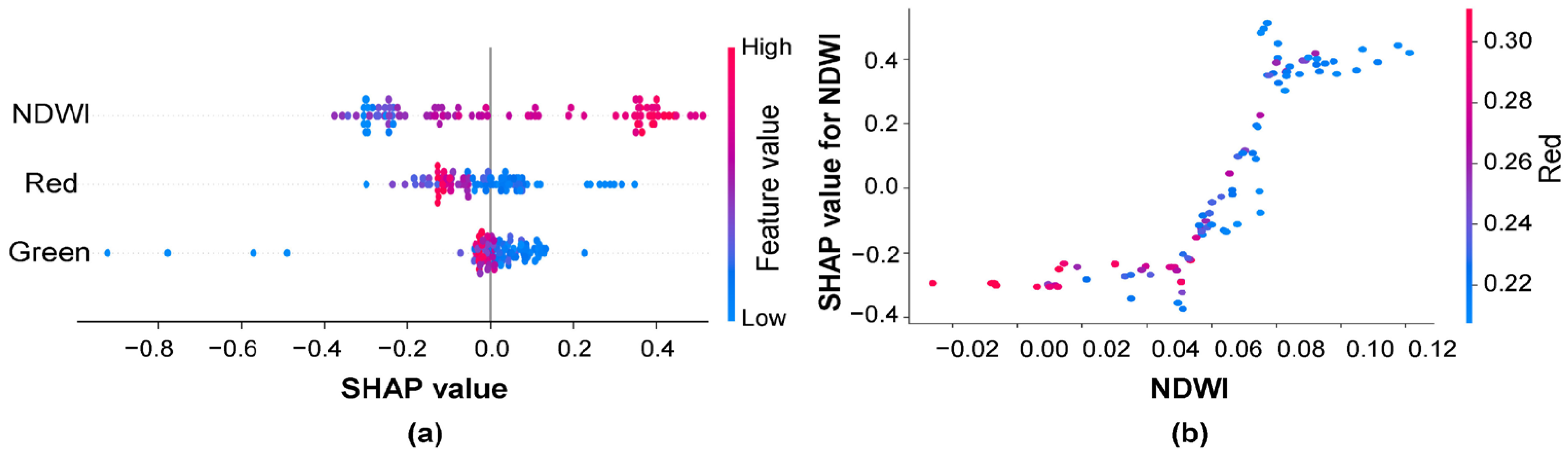
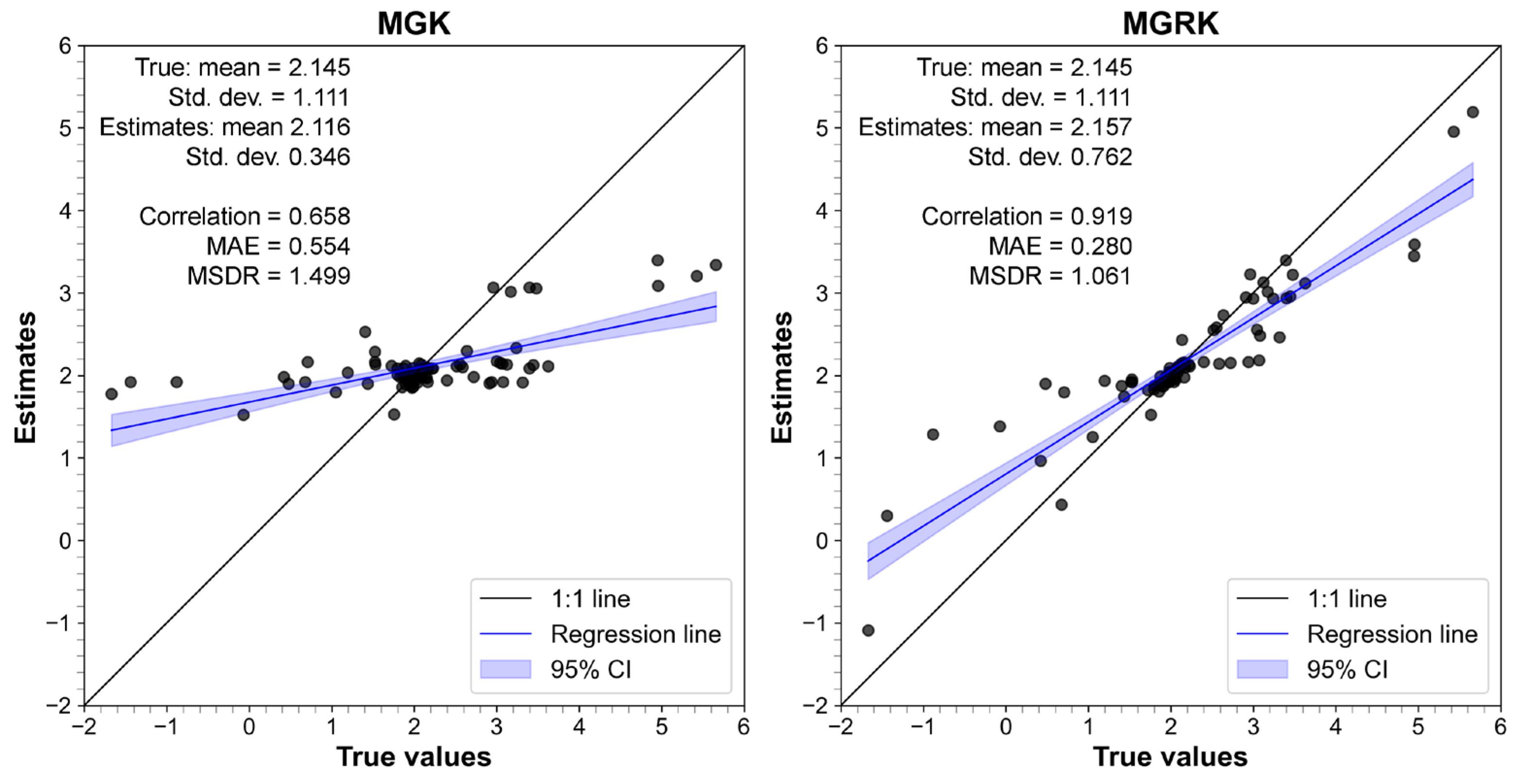
3.1. RF Regression Modeling Results
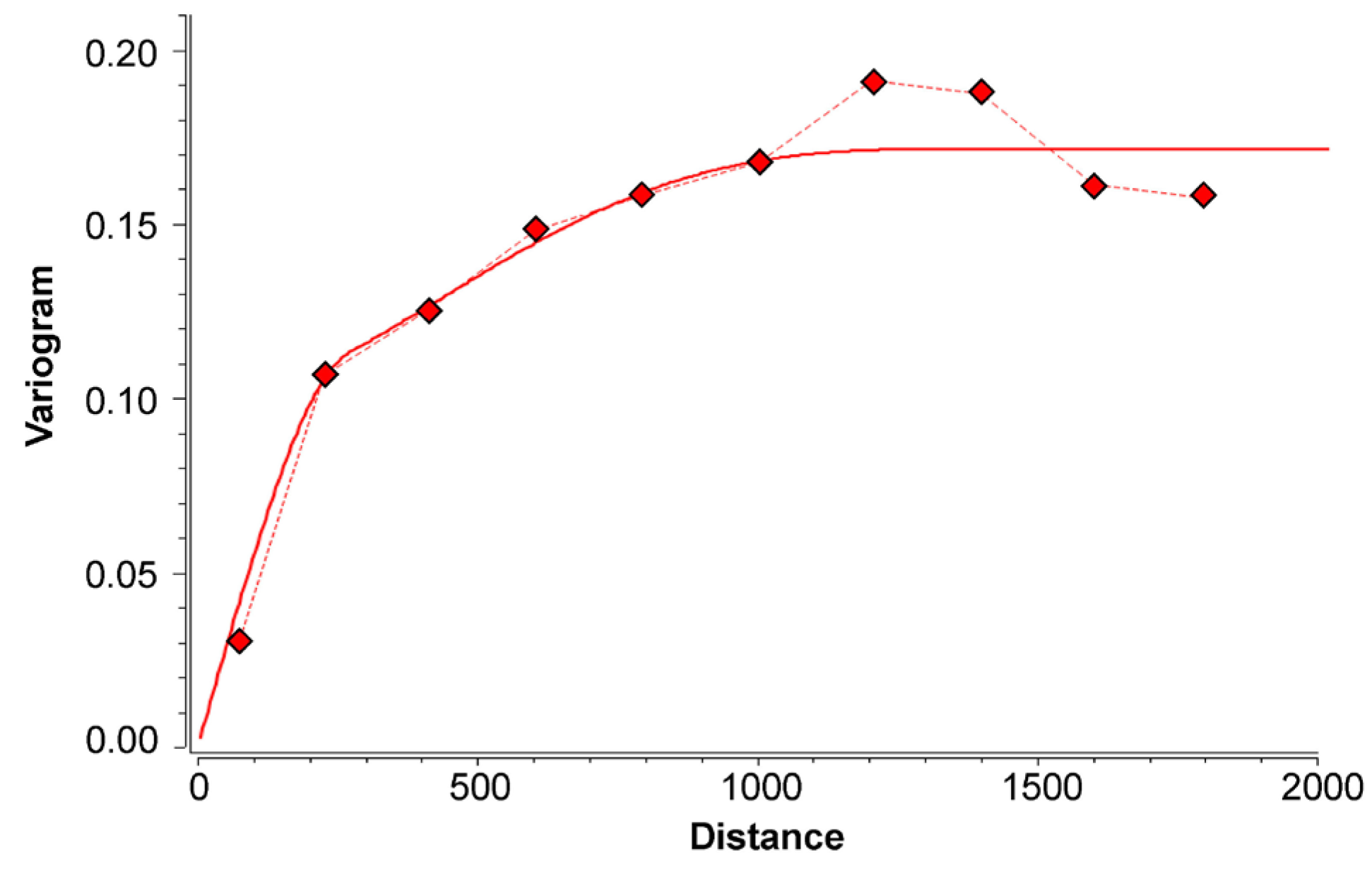
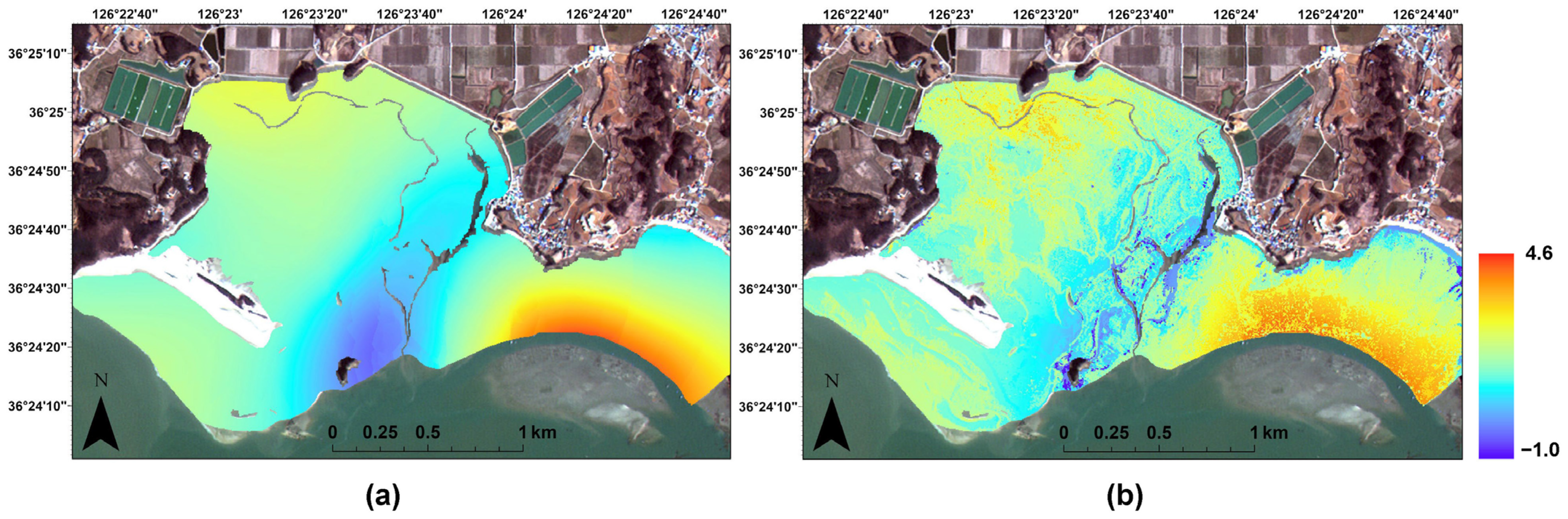
3.2. Geostatistical Modeling Results
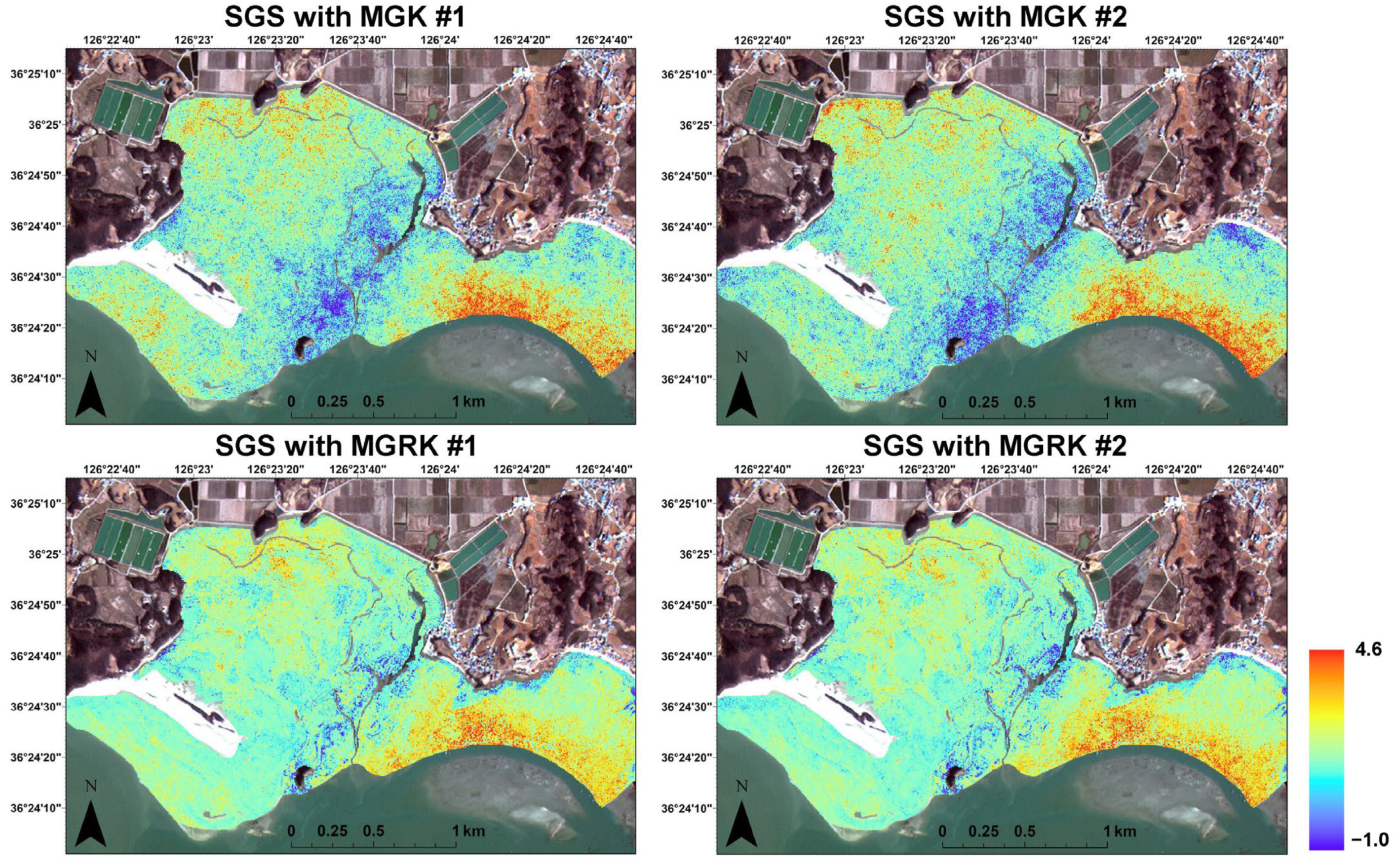
3.3. Simulation Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Contribution of the Study
4.2. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, J.-K.; Lee, Y.-K. Potential of remote sensing in management of tidal flats: A case study of thematic mapping in the Korean tidal flats. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijvershof, R.A.; Van Maren, D.S.; Van der Wegen, M.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Land reclamation controls on multi-centennial estuarine morphodynamics. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF005080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.R.; Lingbeek, J.; Weisscher, S.A.; Kleinhans, M.G. Effects of sea-level rise on dredging and dredged estuary morphology. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, e2022JF006790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Impacts of tidal flat reclamation on suspended sediment dynamics in the tidal-dominated Wenzhou Coast, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1097177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, M.P.; Tyler, A.N.; Givear, D.J.; Bryant, R.G.; McDonald, P. Mapping intertidal estuarine sediment grain size distributions through airborne remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J.; Wielemaker-Van Den, D. Characterisation of surface roughness and sediment texture of intertidal flats using ERS SAR imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J. Regression-based synergy of optical, shortwave infrared and microwave remote sensing for monitoring the grain-size of intertidal sediments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Baek, W.-K.; Jung, H.S.; Ryu, J.-H. Analysis of micro-sedimentary structure characteristics using ultra-high resolution UAV imagery: Hwangdo tidal flat, South Korea. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2024, 40, 295–305, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yates, M.G.; Jones, A.R.; McGroty, S.; Goss-Custard, J.D. The use of satellite imagery to determine the distribution of intertidal surface sediments of The Wash, England. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1993, 36, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-L.; Kim, B.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Ryu, J.-H. Generation of a large-scale surface sediment classification map using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data: A case study at the Hwang-do tidal flat, Korea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, J.; Hyun, C.-U. Evaluating changes in blue carbon storage by analyzing tidal flat areas using multi-temporal satellite data in the Nakdong River estuary, South Korea. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2024, 40, 191–202, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.-W. Geostatistical integration of field measurements and multi-sensor remote sensing images for spatial prediction of grain size of intertidal surface sediments. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 90, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing techniques for studying coastal ecosystems: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.-W.; Jang, D.-H.; Chi, K.-H. Integration of IKONOS imagery for geostatistical mapping of sediment grain size at Baramarae beach, Korea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5703–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; Heuyvelink, G.B.M.; Rossiter, D.G. About regression-kriging: From equations to case studies. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A.; Ping, J.L. Geostatistical integration of yield monitor data and remote sensing improves yield maps. Agron. J. 2004, 9, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, R.; Goovaerts, P.; Rawlins, B.G.; Marchant, B.P. Disaggregation of legacy soil data using area to point kriging for mapping soil organic carbon at the regional scale. Geoderma 2012, 170, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, G.-H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Ryu, J.-H. Unmanned aerial vehicles images based tidal flat surface sedimentary facies mapping using regression kriging. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2023, 39, 537–549, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutengs, C.; Vohland, M. Downscaling land surface temperatures at regional scales with random forest regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilès, J.-P.; Delfiner, P. Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, N.-W. Characteristics variation of the sedimentary environment in winter season around the Baramarae Beach of Anmyeondo using surface sediment analysis. J. Korean Geomroph. Assoc. 2010, 17, 15–27, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Khodada, S.; Jang, D.-H. Analysis of landform changes and sedimentary environment characteristics during winter season around the Baramarae Beach, Anmyeondo in Korea’s west coast. J. Korean Geomroph. Assoc. 2014, 21, 95–109, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Jang, D.-H.; Park, N.-W.; Yoo, H.Y. Assessment of landform changes in Baramarae tidal flat, Korea using combined analysis of multi-temporal remote sensing images and grain size measurement data. J. Mar. Sci. Tech. 2016, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, W.; Le Hir, P.; Whitehouse, R.J.S. Investigation using simple mathematical models of the effect of tidal currents and waves on the profile shape of intertidal mudflats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 10–11, 1079–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.-W.; Jang, D.-H. Geostatistical classification of intertidal surface sediments using log-ratio transformation and high-resolution remote sensing imagery. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 102, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.V.; Journel, A.G. GSLIB: Geostatistical Software Library and User’s Guide, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. Catena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- SHAP Documentation. Available online: https://shap.readthedocs.io (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Choi, J.-K.; Oh, H.-J.; Koom, B.J.; Lee, S.; Ryu, J.-H. Macrobenthos habitat mapping in a tidal flat using remotely sensed data and a GIS-based probabilistic model. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, W.; Van Bernem, K.-H.; Eppel, D.; Kapitza, H.; Pleskachevsky, A.; Riethmüller, R.; Vaessen, B. Prediction of benthic community structure from environmental variables in a soft-sediment tidal basin (North Sea). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2012, 66, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Carlin, B.P.; Gelfand, A.E. Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Blangiardo, M.; Cameletti, M. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Bayesian Models with R-INLA; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- PyMC. Available online: https://www.pymc.io/welcome.html (accessed on 9 September 2025).[Green Version]
- Stan: Software for Bayesian Data Analysis. Available online: https://mc-stan.org/ (accessed on 9 September 2025).[Green Version]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, N.-W.; Jang, D.-H. Fine-Scale Mapping and Uncertainty Quantification of Intertidal Sediment Grain Size Using Geostatistical Simulation Integrated with Machine Learning and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183230
Park N-W, Jang D-H. Fine-Scale Mapping and Uncertainty Quantification of Intertidal Sediment Grain Size Using Geostatistical Simulation Integrated with Machine Learning and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183230
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, No-Wook, and Dong-Ho Jang. 2025. "Fine-Scale Mapping and Uncertainty Quantification of Intertidal Sediment Grain Size Using Geostatistical Simulation Integrated with Machine Learning and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183230
APA StylePark, N.-W., & Jang, D.-H. (2025). Fine-Scale Mapping and Uncertainty Quantification of Intertidal Sediment Grain Size Using Geostatistical Simulation Integrated with Machine Learning and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183230







