Time-Series 3D Modeling of Tunnel Damage Through Fusion of Image and Point Cloud Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Digital Transformation in Tunnel Inspection
2.2. TLS-Based Approaches for Geometric Analysis
2.3. Image-Based Approaches for Defect Detection and 3D Modeling
2.4. Data Fusion of Imagery and Point Clouds for SHM
3. Materials and Methods
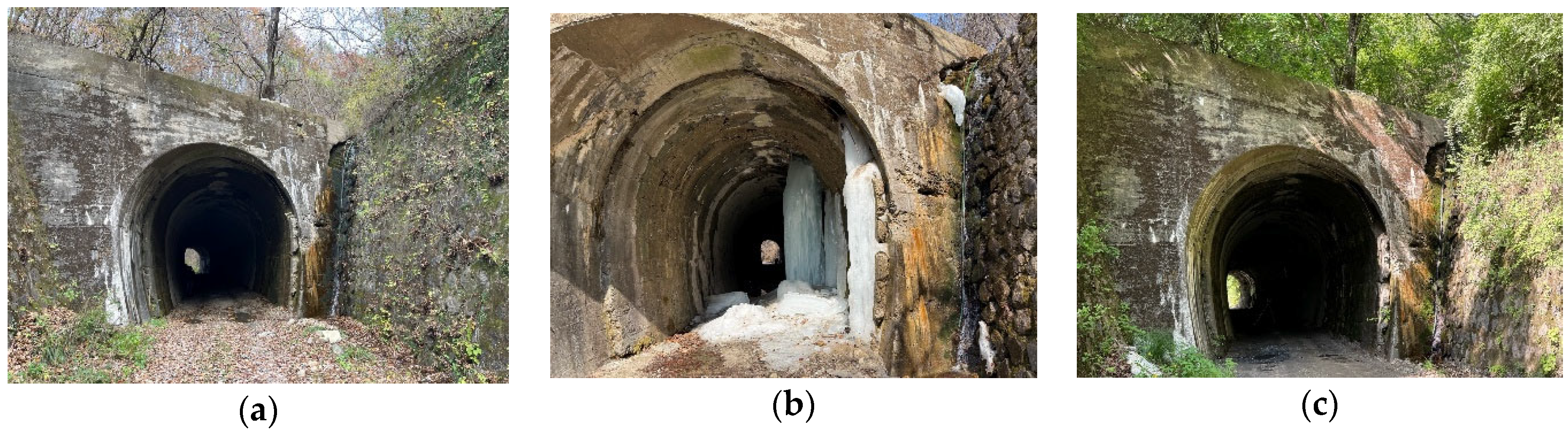
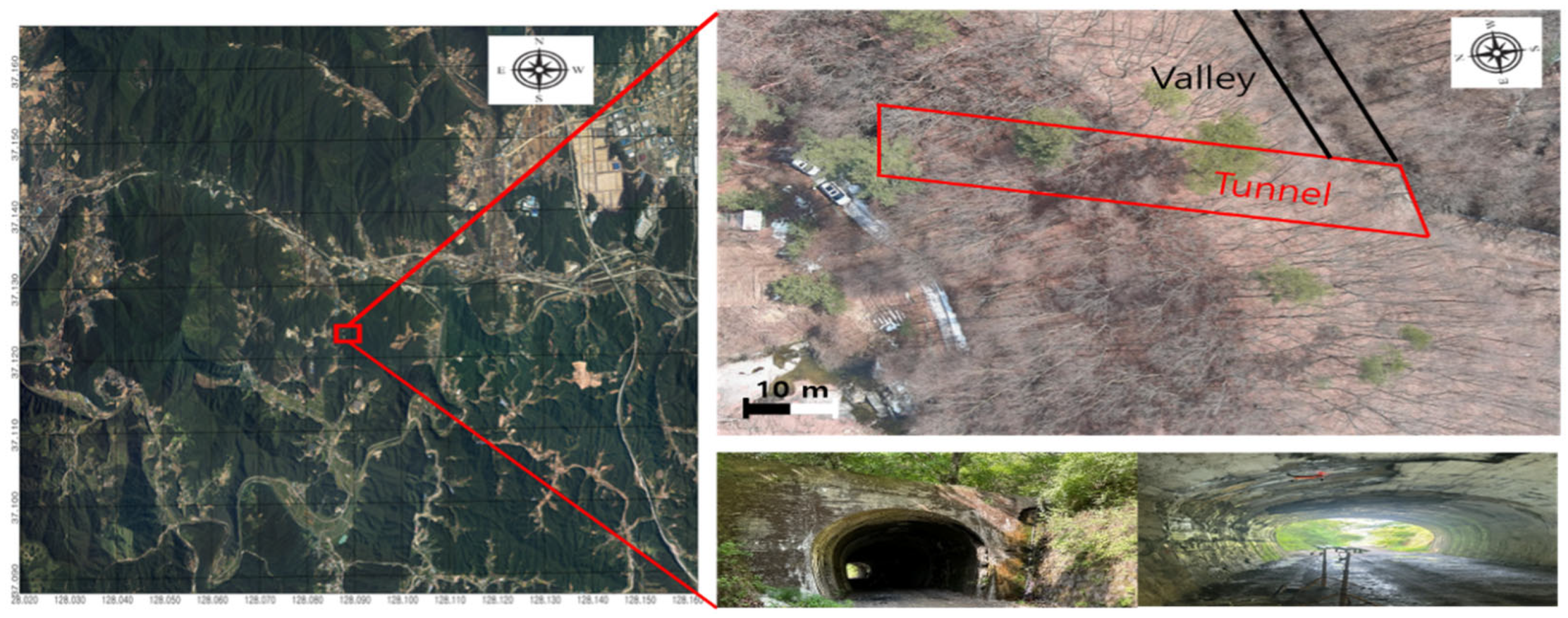
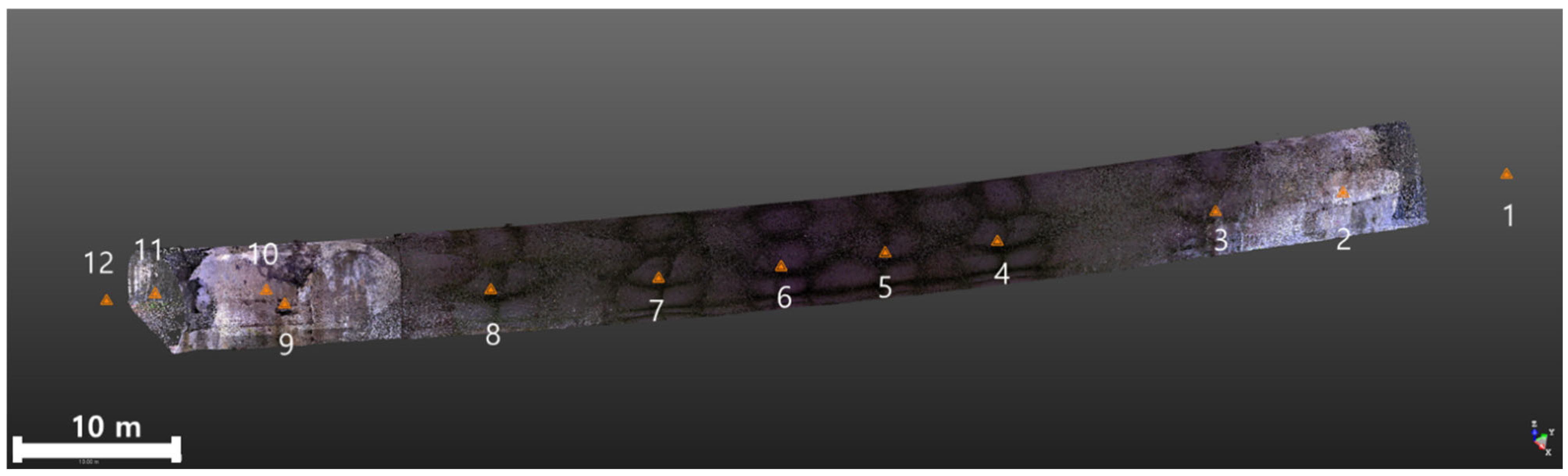
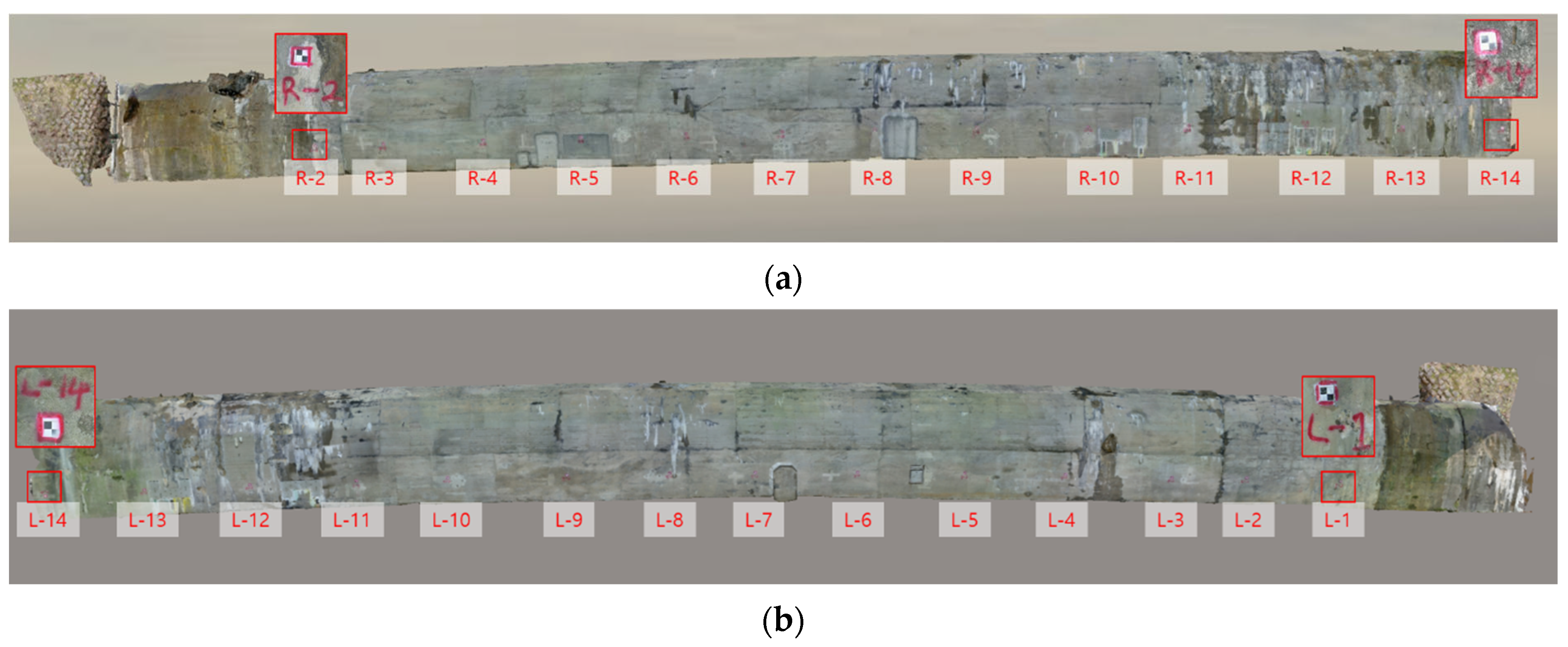
3.1. Description of the Testbed
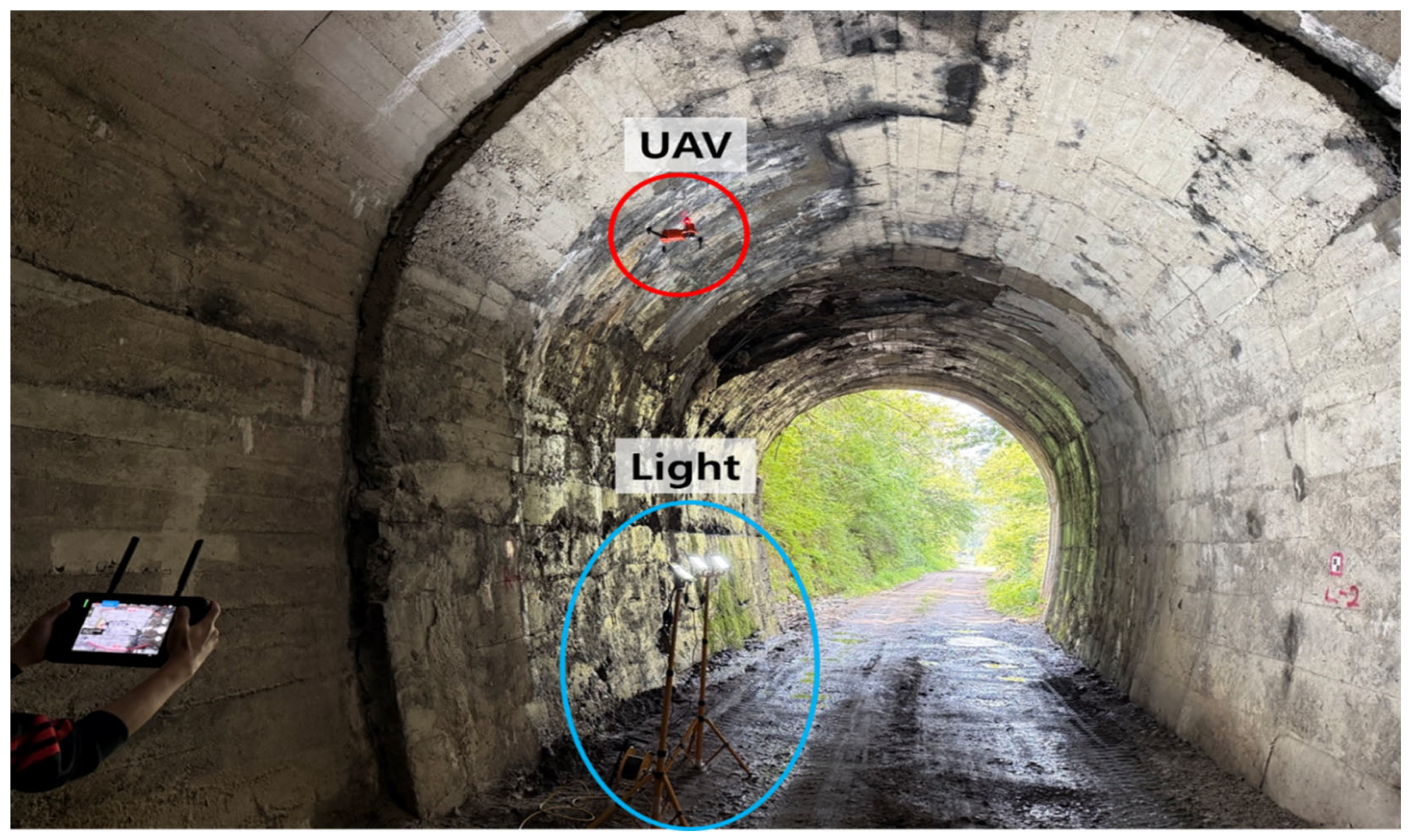
3.2. Data Acquisition
3.2.1. Terrestrial LiDAR Scanning
3.2.2. High-Resolution Image Acquisition
3.2.3. Time-Series Data Collection
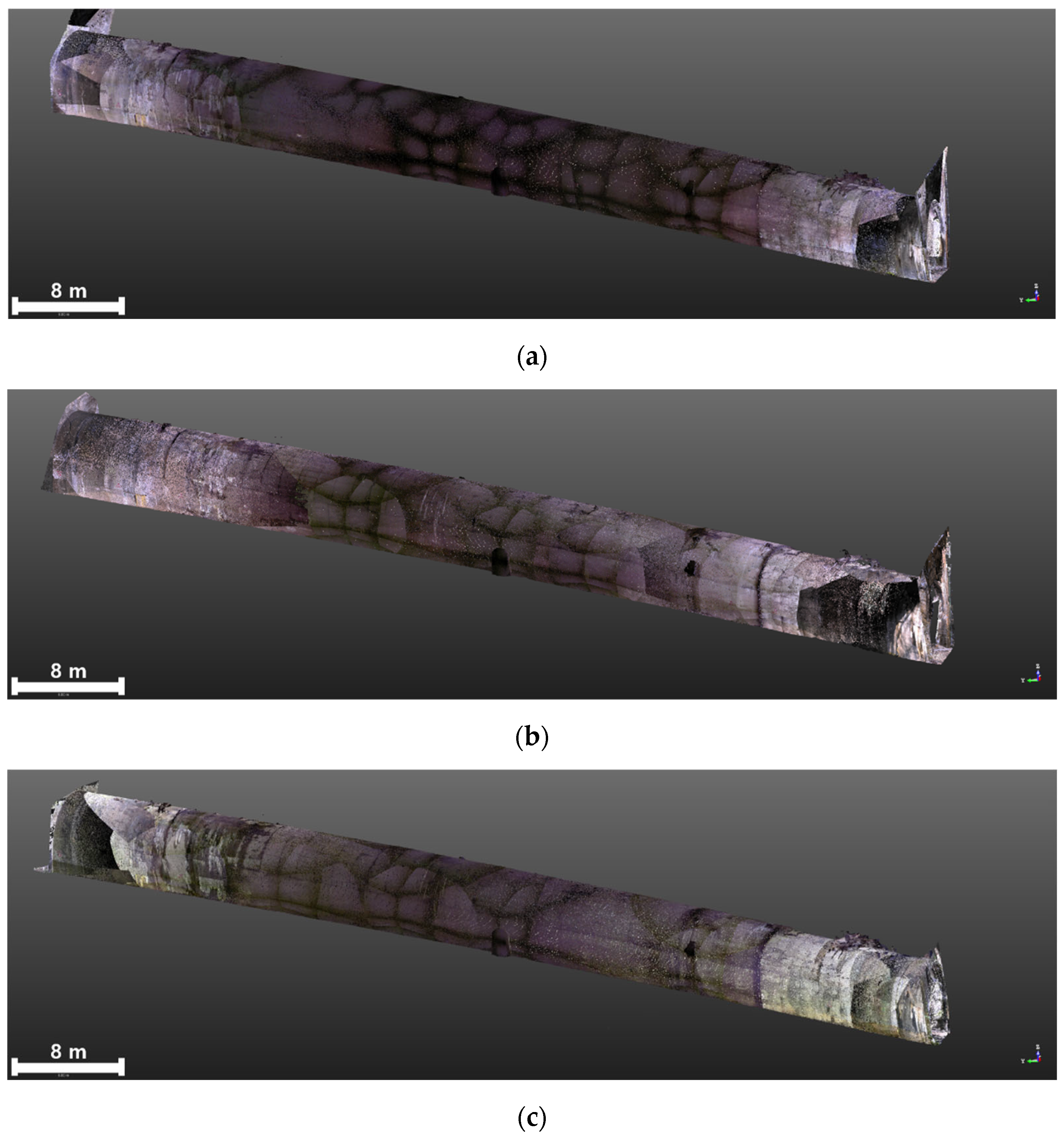
3.3. Generation of 3D Models
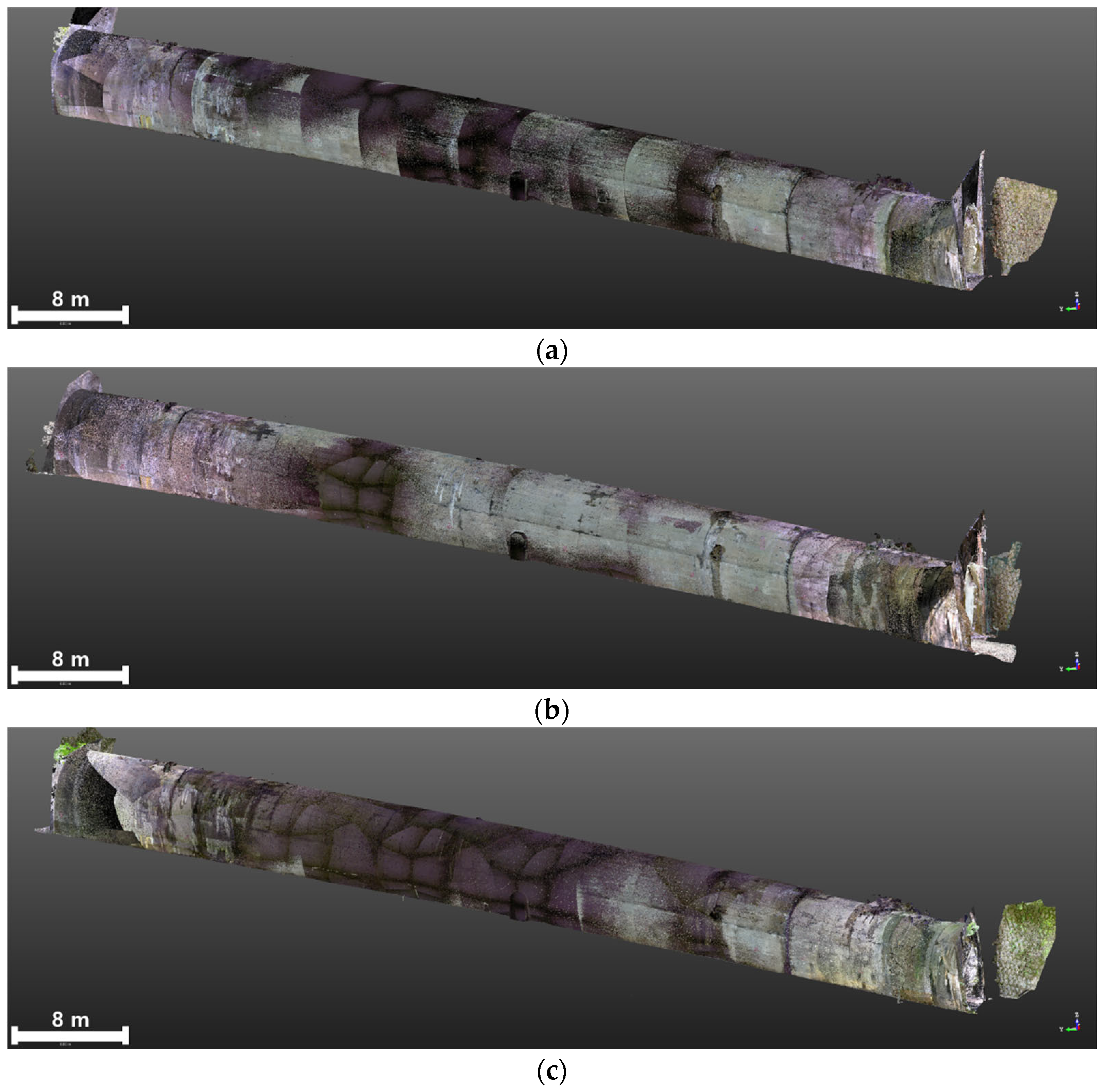
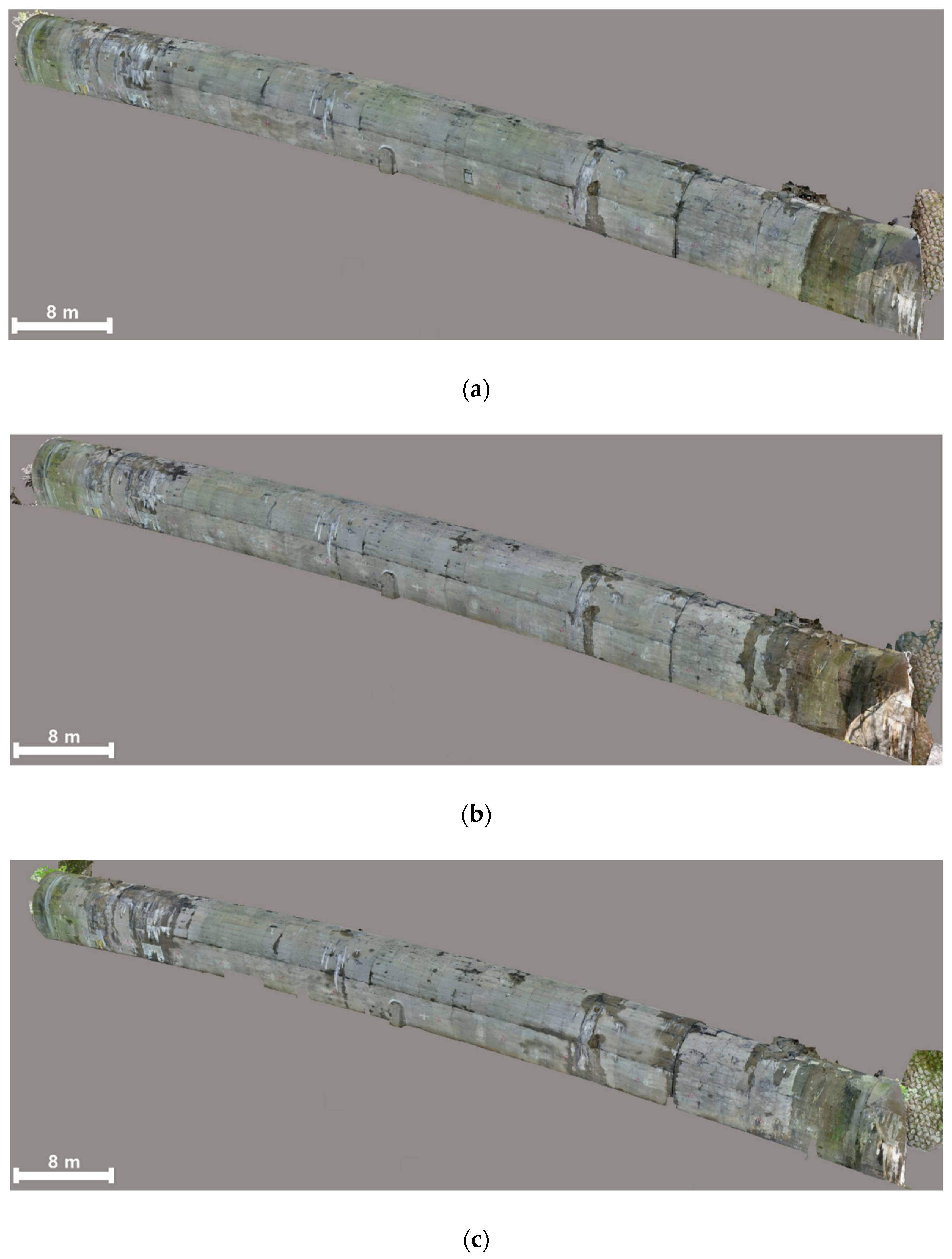
3.3.1. TLS-Based PCD Generation
3.3.2. Image-Based PCD Generation
3.3.3. Fusion-Based 3D Model Generation
3.4. Framework for Comparative Analysis
3.4.1. Assessment of Geometric Precision and Location
3.4.2. Assessment of Damage Representation and Visualization Quality
3.4.3. Assessment of Time-Series Change Detection Capability
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Geometric Performance Assessment
4.1.1. Geometric Accuracy Assessment
4.1.2. Resolution and Level of Detail (LOD) Analysis
4.2. Damage Representation and Visualization Assessment
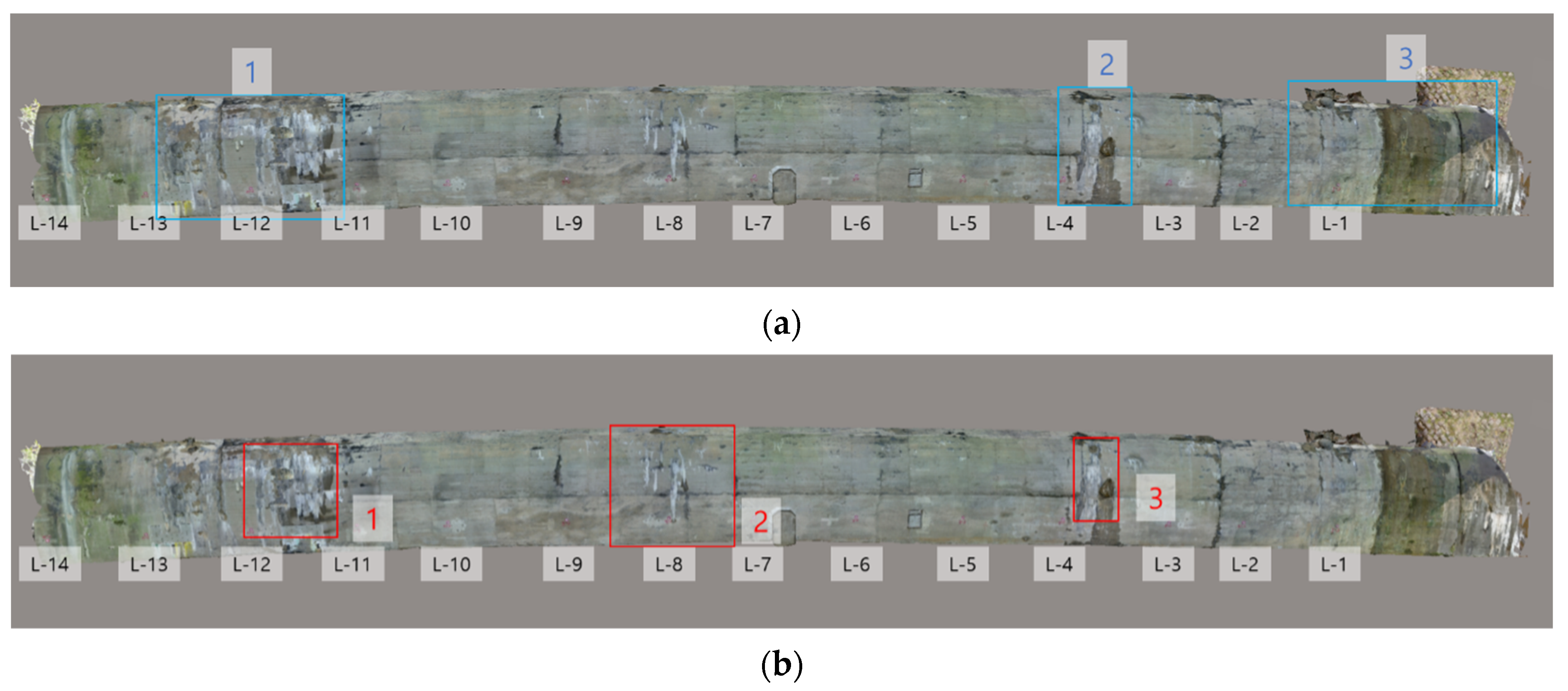
4.2.1. Analysis of Spalling and Damage
4.2.2. Analysis of Leakage and Efflorescence
4.2.3. Analysis of Cracks
4.2.4. Overall Assessment of Damage Representation
4.3. Time-Series Change Detection Assessment
4.3.1. Geometric Change Detection
4.3.2. Visual Change Detection
4.3.3. Integrated Analysis of Damage Progression
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of Comparative Performance
5.2. Practical Implications for Tunnel Asset Management
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Dai, X.; Ye, J.; Sun, B.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Tunnel lining detection and retrofitting. Autom. Constr. 2023, 152, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncetti, B.L.; Ruiz, D.V.; Assis, L.S.; Machado, L.B.; Silva, T.B.; Akinlalu, A.A.; Futai, M.M. Tunnel inspection review: Normative practices and non-destructive method advancements for tunnels with concrete cover. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, Y. Study of structural deterioration behavior of mining method tunnels under steel reinforcement corrosion. Buildings 2025, 15, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Liu, T.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y. recent progress in the cracking mechanism and control measures of tunnel lining cracking under the freeze–thaw cycle. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liang, N.; Mao, J.; Chen, H. Study of the damage characteristics and corrosion mechanism of tunnel lining in a sulfate environment. Front. Mater. 2024, 10, 1323274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Du, X.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, G. Structural Damage Assessment of Shallow Buried Tunnel Subjected to Multiple Slip Surfaces and Blind Reverse Fault: A Numerical Study. Smart Constr. Sustain. Cities 2025, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, L.; Debono, C.J.; Valentino, G.; Di Castro, M. Tunnel inspection using photogrammetric techniques and image processing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2018, 144, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Ren, X.; Zheng, L. Alternating interaction fusion of image-point cloud for multi-modal 3D object detection. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Georgieva, K.; Kasireddy, V.; Akinci, B.; Fieguth, P. A review on computer vision based defect detection and condition assessment of concrete and asphalt civil infrastructure. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, H. Intelligent recognition of tunnel lining defects based on deep learning: Methods, challenges and prospects. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 170, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Xie, J.; Wang, B.; Guo, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Z. Lightweight defect detection algorithm of tunnel lining based on knowledge distillation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Qi, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhu, J. Efficient detection of apparent defects in subway tunnel linings based on deep learning methods. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chu, X.; Lin, F.; Wu, F.; Jin, S.; Zhang, K. A highly efficient tunnel lining crack detection model based on Mini-Unet. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, X. Tunnel crack detection method and crack image processing algorithm based on improved Retinex and deep learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Wang, B.; Xie, J.; Ma, C. MFF-YOLO: An accurate model for detecting tunnel defects based on multi-scale feature fusion. Sensors 2023, 23, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Shi, P.; Jia, F.; Huang, H. 3D reconstruction and automatic leakage defect quantification of metro tunnel based on sfm-deep learning method. Undergr. Space 2022, 7, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xue, F.; Wang, T.; Lin, Z.; Cai, M.; Shou, F. Combining SfM and deep learning to construct 3D point cloud models of shield tunnels and realize spatial localization of water leakages. Measurement 2025, 250, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewski, M.; Torkan, M.; Uotinen, L.; Rinne, M. Rapid photogrammetry with a 360-degree camera for tunnel mapping. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Large-scale 3D reconstruction from multi-view imagery: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Xue, Y. 3D Tunnel reconstruction and visualization through multi-smartphone measurement. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104177. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, H. Novel SfM-DLT method for metro tunnel 3D reconstruction and visualization. Undergr. Space. 2021, 6, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Cai, X.; Shadabfar, M.; Shao, H.; Zhang, S. Deep learning-based automatic recognition of water leakage area in shield tunnel lining. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 104, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S. Towards automated 3D inspection of water leakages in shield tunnel linings using mobile laser scanning data. Sensors 2020, 20, 6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Shao, H.; Li, Q.; Thansirichaisree, P. Automated 3D defect inspection in shield tunnel linings through integration of image and point cloud data. AI Civ. Eng. 2025, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hong, Q.; Jiang, D.; Fu, J.; Xu, S. Automated tunnel point cloud segmentation and extraction method. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, S. A state-of-the-practice review of three-dimensional laser scanning technology for tunnel distress monitoring. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2021, 35, e04021085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Lu, D.; Xie, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Tunnel deformation inspection via global spatial axis extraction from 3D raw point cloud. Sensors 2020, 20, 6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Sheil, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, B.; Wang, C.; Xie, X. Seg2Tunnel: A hierarchical point cloud dataset and benchmarks for segmentation of segmental tunnel linings. Tunnelling Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 147, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, F.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. An enhanced segmentation method for 3D point cloud of tunnel support system using PointNet++ and coverage-voted strategy algorithms. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ren, X.; Mao, Q.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W. Shield subway tunnel deformation detection based on mobile laser scanning. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stałowska, P.; Suchocki, C.; Rutkowska, M. Crack detection in building walls based on geometric and radiometric point cloud information. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Aparicio, L.J.; del Blanco-García, F.L.; Mencías-Carrizosa, D.; Villanueva-Llauradó, P.; Aira-Zunzunegui, J.R.; Sanz-Arauz, D.; Pierdicca, R.; Pinilla-Melo, J.; Garcia-Gago, J.; Pinilla-Melo, J.; et al. Detection of damage in heritage constructions based on 3D point clouds. A systematic review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Fuentes, W.; Trujillo-Hernández, G.; Alba-Corpus, I.Y.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Mirada-Vega, J.E.; Hernández-Balbuena, D.; Murrieta-Rico, F.N.; Sergiyenko, O.; Sergiyenko, O. 3D spatial measurement for model reconstruction: A review. Measurement 2023, 207, 112321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Koundal, D.; Kadyan, V. Image fusion techniques: A survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 4425–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Qiu, W.; Huang, W.; Meng, G.; Huang, J.; Xu, S. A multi-source information fusion approach in tunnel collapse risk analysis based on improved d–s evidence theory. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Li, L. Structural damage identification of shield tunnels using distributed fiberoptic sensors and information fusion. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 131, 104761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mu, E. A review of intelligent subway tunnels based on digital twin technology. Buildings 2024, 14, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Digital twin-based rapid risk assessment for urban utility tunnels. Autom. Constr. 2023, 140, 104451. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, F. Inspection equipment study for subway tunnel defects by grey-scale image processing. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2017, 32, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Kojima, Y. Tunnel maintenance in Japan. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2003, 18, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Bi, X. Acquiring sectional profile of metro tunnels using charge-coupled device cameras. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 12, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W.; Li, Q.T.; Zhang, D.M. Deep learning based image recognition for crack and leakage defects of metro shield tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 77, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, Y.; Siringoringo, D.M. Recent research and development programs for infrastructures maintenance, renovation and management in Japan. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 16, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer, C.; Montero, R.; Victores, J.G.; Martínez, S.; Jardón, A. Towards fully automated tunnel inspection: A survey and future trends. In Proceedings of the 31st International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining, Sydney, Australia, 9–11 July 2014; Volume 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukai, M. Advanced inspection system of tunnel wall deformation using image processing. Q. Rep. RTRI 2007, 48, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, D.; Liu, Y. Automatic crack detection and classification method for subway tunnel safety monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 19307–19328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Enomoto, M.; Nitta, Y. Smart tunnel inspection and assessment using mobile inspection vehicle, non-contact radar and AI. In Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC 2020): From Demonstration to Practical Use to New Stage of Construction Robot, Kitakyushu, Japan, 21–28 October 2020; pp. 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z. Automatic subway tunnel crack detection system based on a line scan camera. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhai, J.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Zhou, B.; Cai, J.; Lei, Y. Design of fast acquisition system and analysis of geometric feature for highway tunnel lining cracks based on machine vision. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Qi, T.; Lei, B.; Li, Z. Rapid and automatic image acquisition system for structural surface defects of high-speed rail tunnels. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 967–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hao, G.; Zhang, K.; Xu, G.; Gao, M.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. Reactive UAV-based automatic tunnel surface defect inspection with a field test. Autom. Constr. 2024, 163, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.B.; Futai, M.M. Tunnel performance prediction through degradation inspection and digital twin construction. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 144, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Li, H. Identification framework for cracks on a steel structure surface by a restricted Boltzmann machines algorithm based on consumer-grade camera images. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, W.; Huang, L.; Vimarlund, V.; Wang, Z. Applications of terrestrial laser scanning for tunnels: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2014, 1, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.Y.; Qiu, W.G.; Cheng, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.C.; Lu, F. Reconstruction of shield tunnel lining using point cloud. Autom. Constr. 2021, 130, 103860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y. Point cloud registration for excavation tunnels based on concave–convex extraction and encoding. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 157, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, C.; Sun, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y. Research on fitting and denoising subway shield-tunnel cross-section point-cloud data based on the huber loss function. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishida, T.; Nagata, Y.; Kawamura, H.; Tokuno, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Automatic detection of delamination on tunnel lining surfaces from laser 3D point cloud data by 3D features and a support vector machine. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, 14, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, M.; Wang, L.; You, Z. Tunnel cross-section deformation monitoring based on mobile laser scanning point cloud. Sensors 2024, 24, 7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Li, M.; Mao, S.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, B. A Coal mine tunnel deformation detection method using point cloud data. Sensors 2024, 24, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, C.J.; Gräbe, P.J. Water leakage mapping in concrete railway tunnels using LiDAR generated point clouds. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Pei, Y.; He, P. Automated extraction of tunnel leakage location and area from 3D laser scanning point clouds. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 178, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panella, F.; Roecklinger, N.; Vojnovic, L.; Loo, Y.; Boehm, J. Cost–benefit analysis of rail tunnel inspection for photogrammetry and laser scanning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII–B2, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölander, A.; Belloni, V.; Ansell, A.; Nordström, E. Towards automated inspections of tunnels: A review of optical inspections and autonomous assessment of concrete tunnel linings. Sensors 2023, 23, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Liu, L.; Shi, C.; Tan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W. A novel tunnel-lining crack recognition system based on digital image technology. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X. Calibration of a 3D laser rangefinder and a camera based on optimization solution. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2021, 17, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Pang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H. A Novel calibration board and experiments for 3D LiDAR and camera calibration. Sensors 2020, 20, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Zhang, D. Image-range stitching and semantic-based crack detection methods for tunnel inspection vehicles. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Cheng, W.; Huang, H.; Chen, J. A novel approach to automated 3D spalling defects inspection in railway tunnel linings using laser intensity and depth information. Sensors 2021, 21, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Hu, X.; Tan, K.; Wang, L.; Yang, L. Automatic detection of shield tunnel leakages based on terrestrial mobile lidar intensity images using deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55300–55310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Tang, L.; Sun, F.; Chen, X.; Niu, L.; Ren, C.; Li, Q. Defect detection for a vertical shaft surface based on multimodal sensors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8109–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, T. Integrating vision and laser point cloud data for shield tunnel digital twin modeling. Autom. Constr. 2024, 157, 105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Trimble’s GNSS R8 | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Weight | 1.52 kg | Channels | 440 Channel |
| Stop Positioning Vertical | 3.5 mm + 0.4 ppm RMS | Input | CMR+, CMRx, RTCM2.1~3.1 | |
| Stop Positioning Horizontal | 3 mm + 0.1 ppm RMS | Output | 24 NVEA | |
| VRS Vertical | 15 mm + 0.5 ppm RMS | Radio Modem | 403 MHz | |
| VRS Horizontal | 8 mm + 0.5 ppm RMS | Signal Update Cycle | 1 Hz~20 Hz | |
| HITARGET’s HTS 420R | Parameters | |||
 | Angle Accuracy | 2″ | Compensator Range | Dual axis ±3′ |
| Accuracy | Prism: 2 mm + 2 ppm Reflectorless, mode: 3 mm + 2 ppm | Setting Accuracy | 1″ | |
| Range | Prism: 3000 m Reflectorless Mode: 600 m | Graphics | LCD 240 × 320 | |
| Trimble’s SX10 | Parameters | |||
 | Angle Accuracy | 1″ | Range Noise | 1.5 mm |
| Accuracy | Prism: 1 mm + 1.5 ppm DR mode: 2 mm + 1.5 | EDM | Laser: 1550 mm Laser spot size at 100 m: 14 mm | |
| Scanning | Band Scanning | Point Spacing | 6.25~50 mm | |
| Measurement Rate | 26.6 kHz | Camera | 5 MP (84×) | |
| Range | Prism: 5500 m DR Mode: 800 m | Communication | Wi-fi, USB, Cable, Long range radio | |
| SMATO SWTE50-2 | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Power consumption | 50 W | ||
| Correlated color temperature | 6500 K (daylight white) | |||
| Luminous flux | ~4000 lx | |||
| AUTEL EVO2 RTK | Parameters | Camera | ||
 | Weight | 1237 g | Resolution | 5472 × 3648 |
| Satellite system | GPS/GLONASS/Galileo | Image Sensor | 1/2″CMOS | |
| Max flight time | 42 min | ISO | 100–12,800 (auto) | |
| Angular vibration range | ±0.005° | F-Stop | F/2.8 | |
| IMU sensor | Gyroscope Acceleration Compass Distance | FOV | 82° | |
| RMSE | X | Y | Z | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time-series | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 1st | 2nd | 3rd |
| TLS-based model | 0.022 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.019 |
| Image-based model | 0.200 | 0.285 | 0.497 | 0.186 | 0.176 | 0.443 | 0.218 | 0.20 | 0.481 |
| Fusion-based model | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.014 |
| Point Density (Points/m2) | TLS | Image | Fusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 81,595 | 1,784,477 | 1,866,072 |
| 2nd | 81,890 | 1,390,254 | 1,472,144 |
| 3rd | 81,625 | 1,385,682 | 1,467,307 |
| Classification | TLS-Based PCD | Image-Based PCD | Fusion-Based PCD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd | 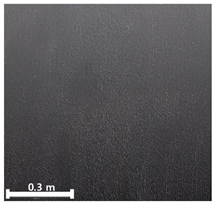 | 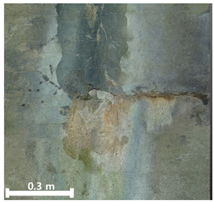 |  | |
| 3rd |  | 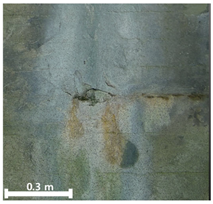 |  | |
| 2 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| 3 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| 4 | 1st | 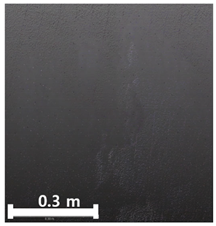 |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| Classification | TLS-Based PCD | Image-Based PCD | Fusion-Based PCD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st |  | 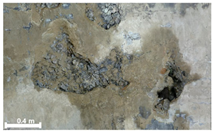 |  |
| 2nd |  | 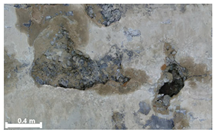 | 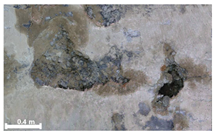 | |
| 3rd |  | 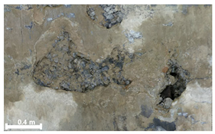 | 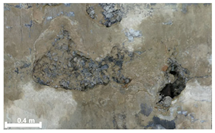 | |
| 2 | 1st | 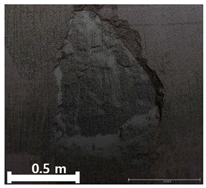 |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd | 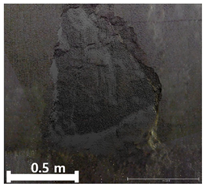 |  |  | |
| 3 | 1st | 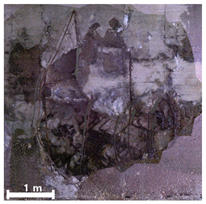 | 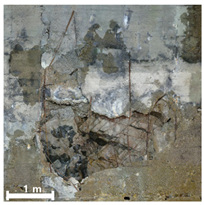 | 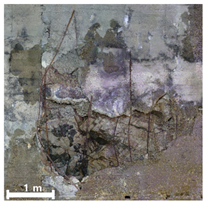 |
| 2nd | 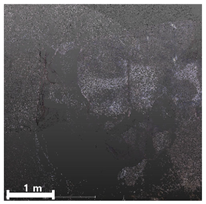 | 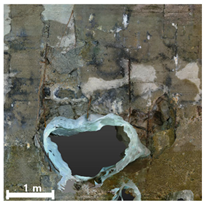 |  | |
| 3rd | 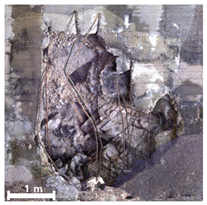 | 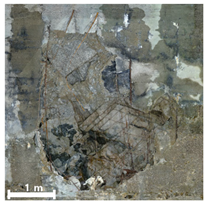 | 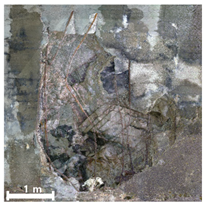 | |
| Classification | TLS-Based PCD | Image-Based PCD | Fusion-Based PCD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st | 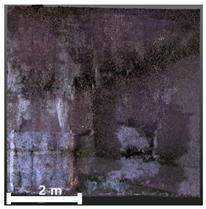 | 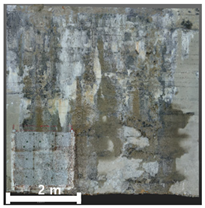 |  |
| 2nd | 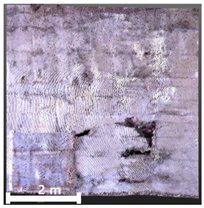 | 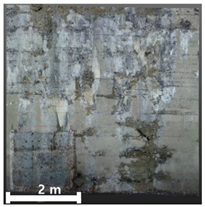 |  | |
| 3rd | 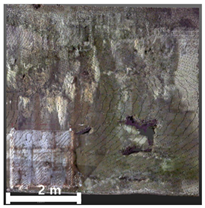 | 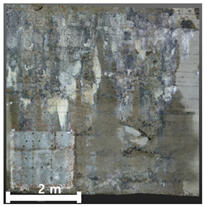 | 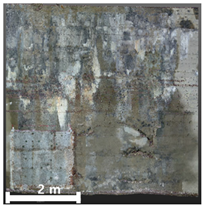 | |
| 2 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd | 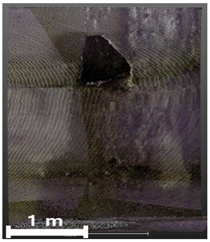 |  |  | |
| 3 | 1st | 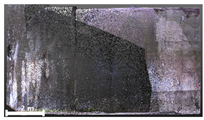 |  |  |
| 2nd | 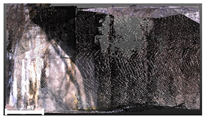 |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| Classification | TLS-Based PCD | Image-Based PCD | Fusion-Based PCD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st | 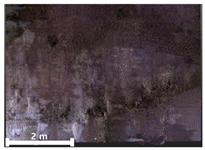 | 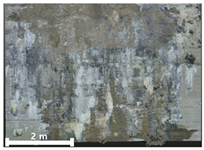 | 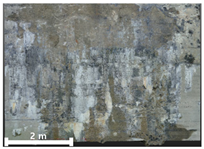 |
| 2nd |  | 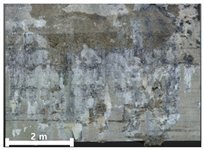 | 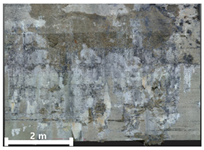 | |
| 3rd | 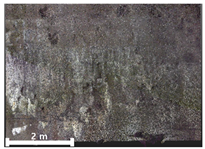 | 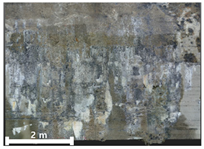 | 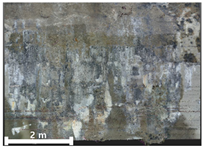 | |
| 2 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| 3 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| Classification | TLS-Based PCD | Image-Based PCD | Fusion-Based PCD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st | 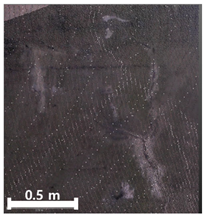 |  |  |
| 2nd |  | 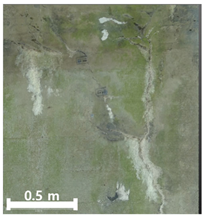 | 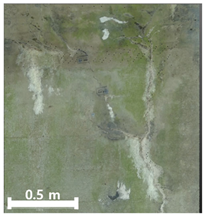 | |
| 3rd | 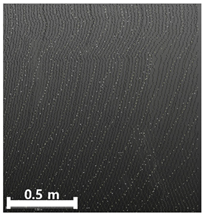 | 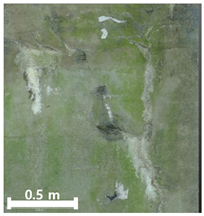 |  | |
| 2 | 1st |  |  |  |
| 2nd |  |  |  | |
| 3rd |  |  |  | |
| 3 | 1st | 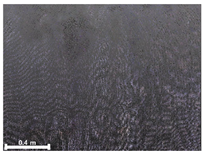 | 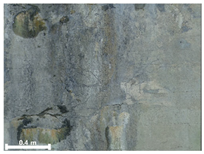 | 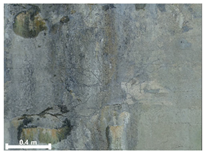 |
| 2nd | 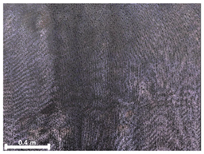 | 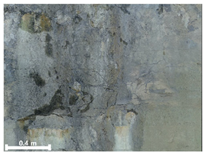 | 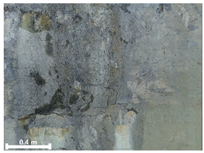 | |
| 3rd |  |  | 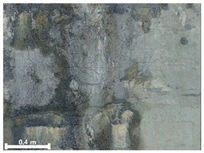 | |
| Damage Type | TLS-Based Model | Image-Based Model | Fusion-Based Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spalling | Geometric shape representation (O) Visual identification impossible (X) | Visual identification (O) Geometric shape distortion (Δ) | Integrated representation of shape and visual information (O) |
| Damage | Geometric shape representation (O) Limitation in visual expression (Δ) | Visual identification (O) Limitation in expressing the depths (Δ) | Integrated representation of shape and visual information (O) |
| Leakage | Identification impossible (X) | Visual identification and pattern representation (O) | Identification and specification of the exact location (O) |
| Efflorescence | Identification impossible (X) | Visual identification and pattern representation (O) | Identification and specification of the exact location (O) |
| Crack | Impossible to identify fine cracks (X) | Visual identification (O) Limitation in the accuracy of 3D position (Δ) | Identification and specification of the exact 3D location (O) |
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 0.0061 m2 | 0.0061 m2 | 0.0061 m2 | |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| 0.18 m2 | 0.18 m2 | 0.18 m2 | |
| 3 |  |  |  |
| 0.39 m2 | 0.39 m2 | 0.39 m2 | |
| 4 |  |  |  |
| 0.0741 m2 | 0.0741 m2 | 0.0741 m2 |
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3D model |  |  | 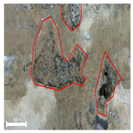 |
| Inspection map | 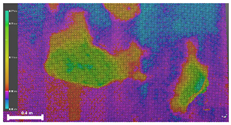 | 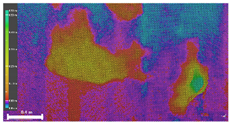 | 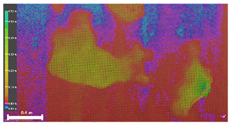 | |
| Area | 0.57 m2 | 0.57 m2 | 0.60 m2 | |
| Volume | 0.07 m3 | 0.07 m3 | 0.09 m3 | |
| 2 | 3D model |  |  |  |
| Inspection map | 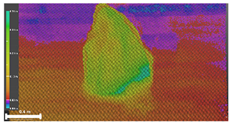 |  | 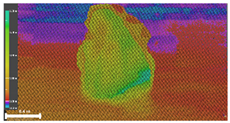 | |
| Area | 0.57 m2 | 0.57 m2 | 0.60 m2 | |
| Volume | 0.16 m3 | 0.16 m3 | 0.18 m3 | |
| 3 | 3D model | 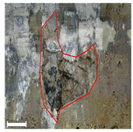 |  |  |
| Inspection map | 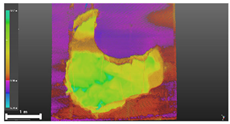 | 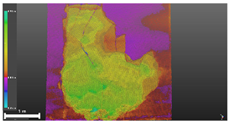 | ||
| Area | 5.77 m2 | Impossible to analyze | 8.99 m2 | |
| Volume | 2.47 m3 | Impossible to analyze | 3.38 m3 |
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 25.41 m2 | 6.36 m2 | 38.82 m2 | |
| 2 | 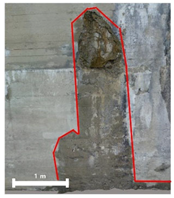 |  | 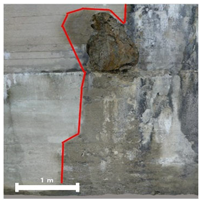 |
| 3.71 m2 | 2.65 m2 | 10.26 m2 | |
| 3 |  |  |  |
| 37.02 m2 | 50.65 m2 | 43.32 m2 |
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 16.37 m2 | 16.37 m2 | 16.37 m2 | |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| 4.17 m2 | 4.17 m2 | 4.17 m2 | |
| 3 |  |  |  |
| 2.59 m2 | 2.59 m2 | 2.59 m2 |
| 1 |  |  |  |
| Width 0.002 m Length 0.371 m | Width 0.002 m Length 0.371 m | Width 0.002 m Length 0.371 m | |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| Width 0.002 m Length 1.94 m | Width 0.002 m Length 1.94 m | Width 0.002 m Length 1.94 m | |
| 3 |  |  |  |
| Width 0.002 m Length 0.82 m | Width 0.002 m Length 0.82 m | Width 0.002 m Length 0.82 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Kang, J. Time-Series 3D Modeling of Tunnel Damage Through Fusion of Image and Point Cloud Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183173
Lee C, Kim D, Kim D, Kang J. Time-Series 3D Modeling of Tunnel Damage Through Fusion of Image and Point Cloud Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183173
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chulhee, Donggyou Kim, Dongku Kim, and Joonoh Kang. 2025. "Time-Series 3D Modeling of Tunnel Damage Through Fusion of Image and Point Cloud Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183173
APA StyleLee, C., Kim, D., Kim, D., & Kang, J. (2025). Time-Series 3D Modeling of Tunnel Damage Through Fusion of Image and Point Cloud Data. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183173






