Effects of Atmospheric Tide Loading on GPS Coordinate Time Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
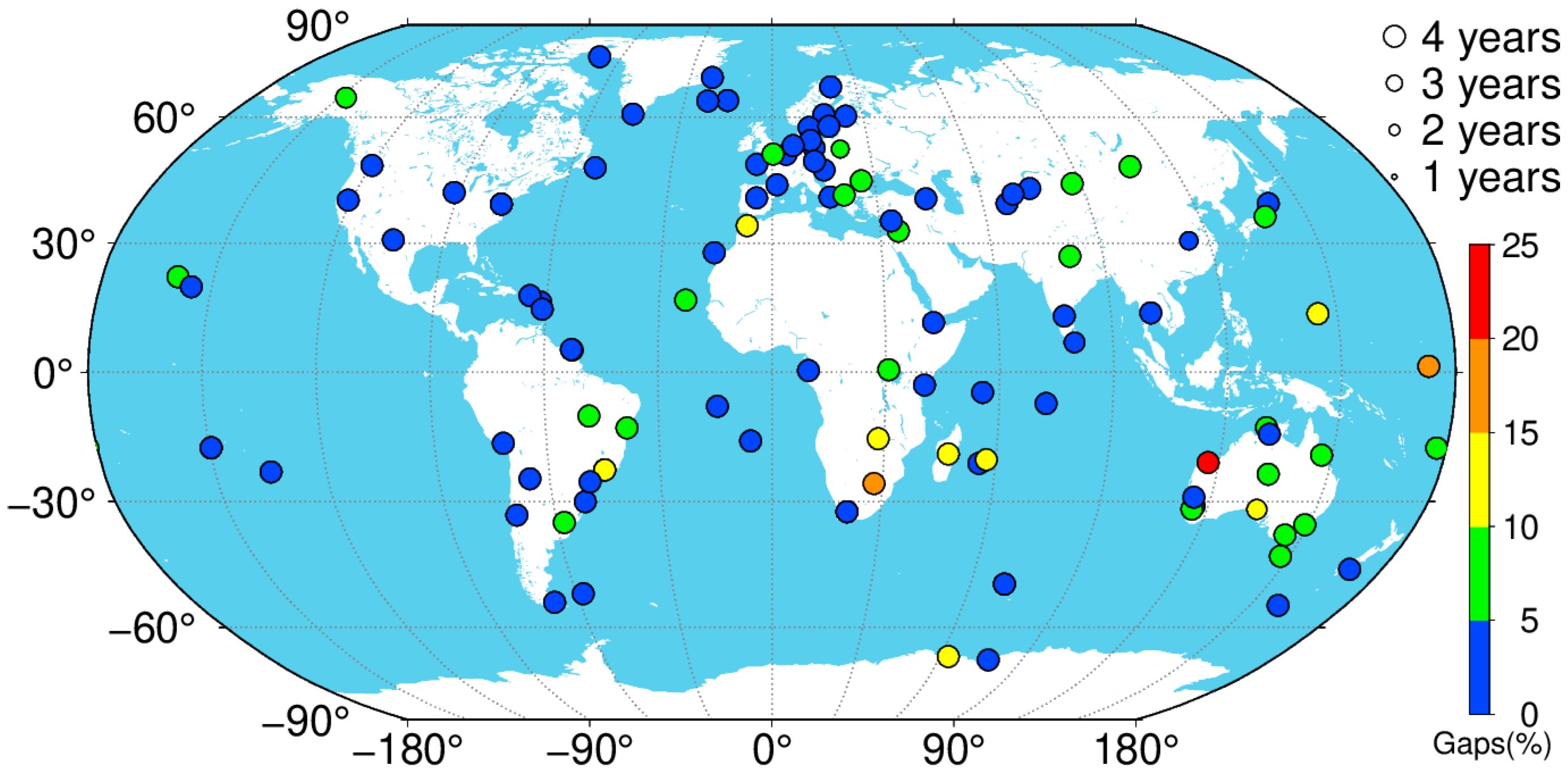
2. Data Sets
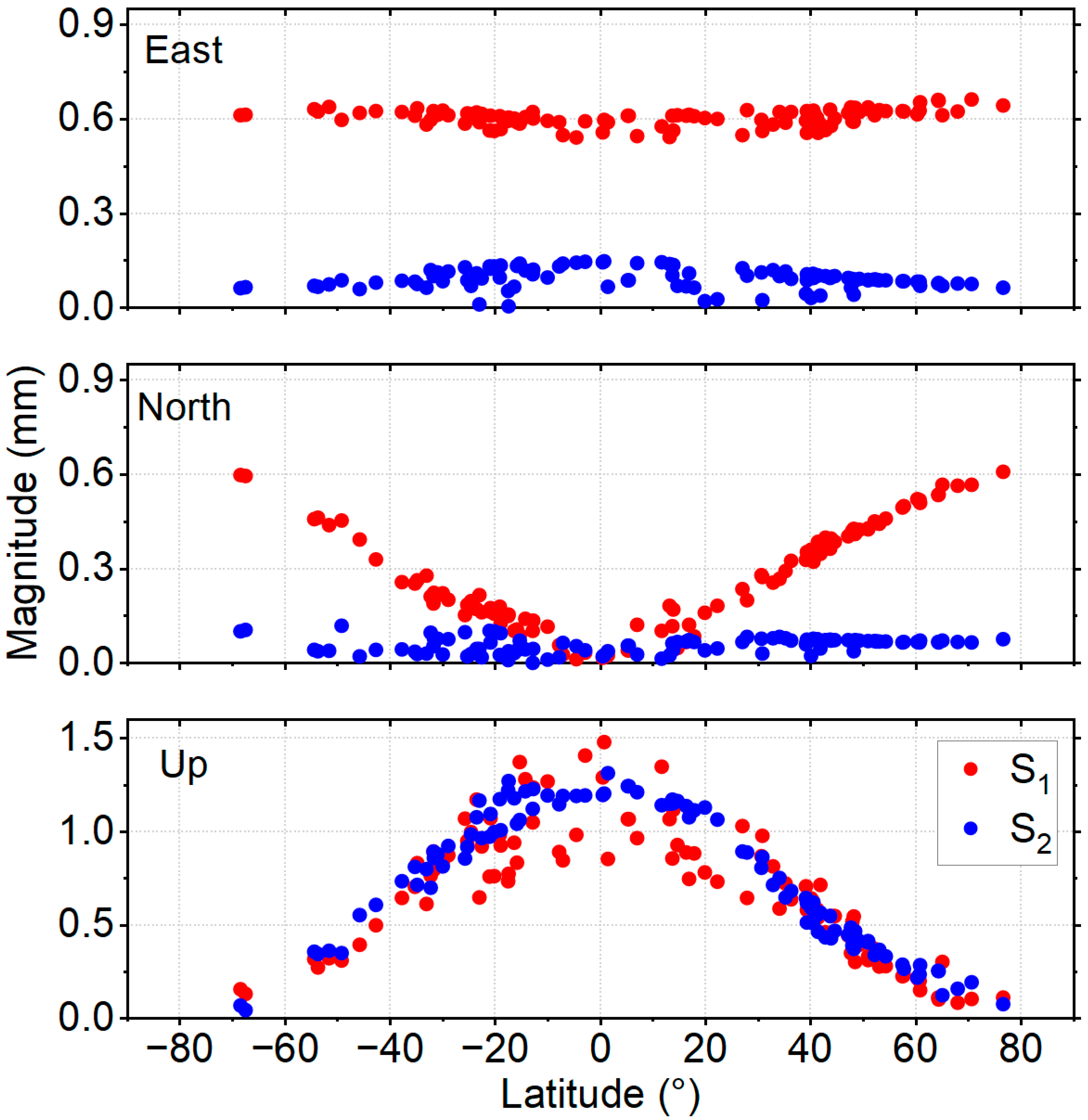
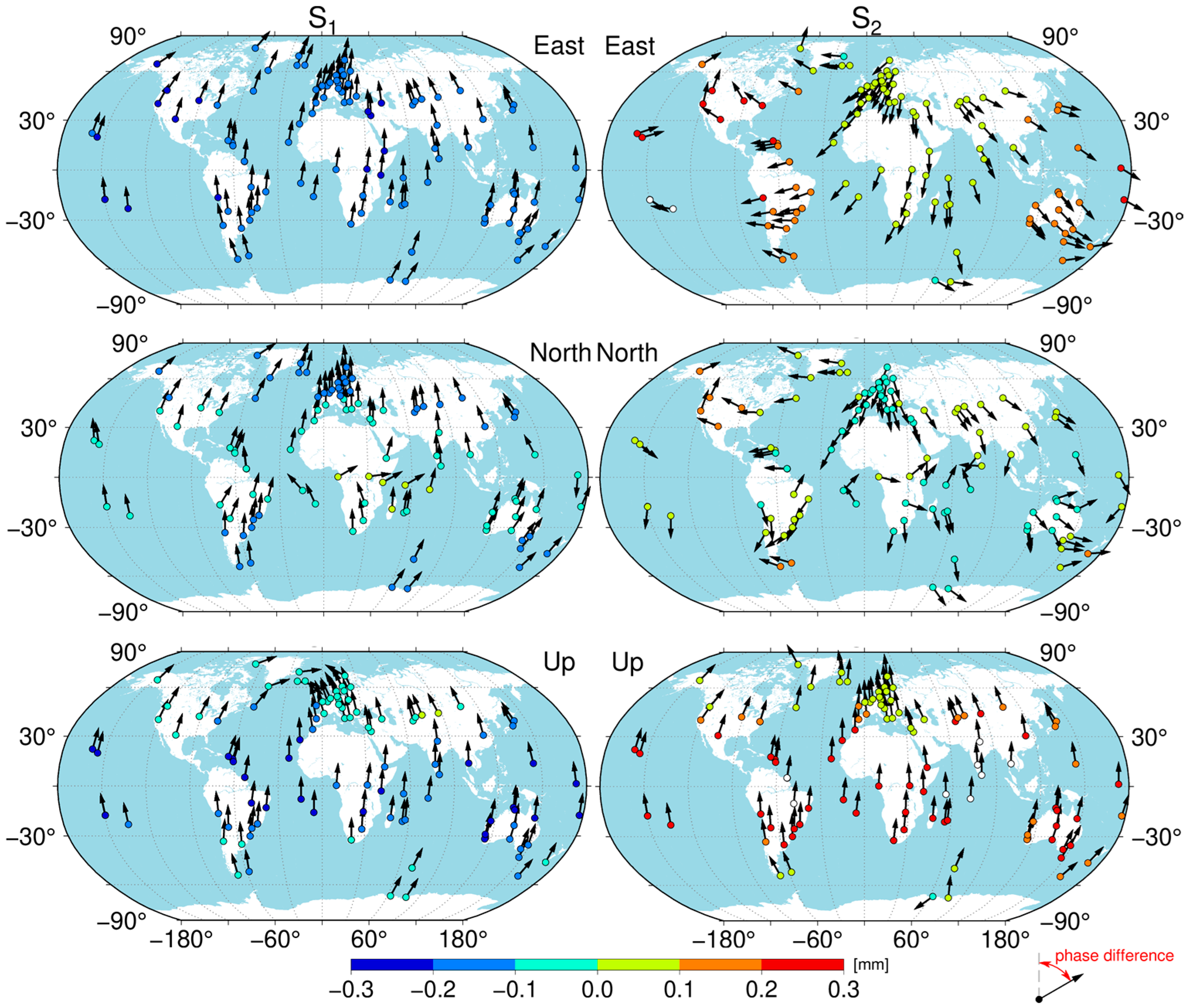
2.1. S1-S2 Atmospheric Tide Loading
2.2. GPS Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
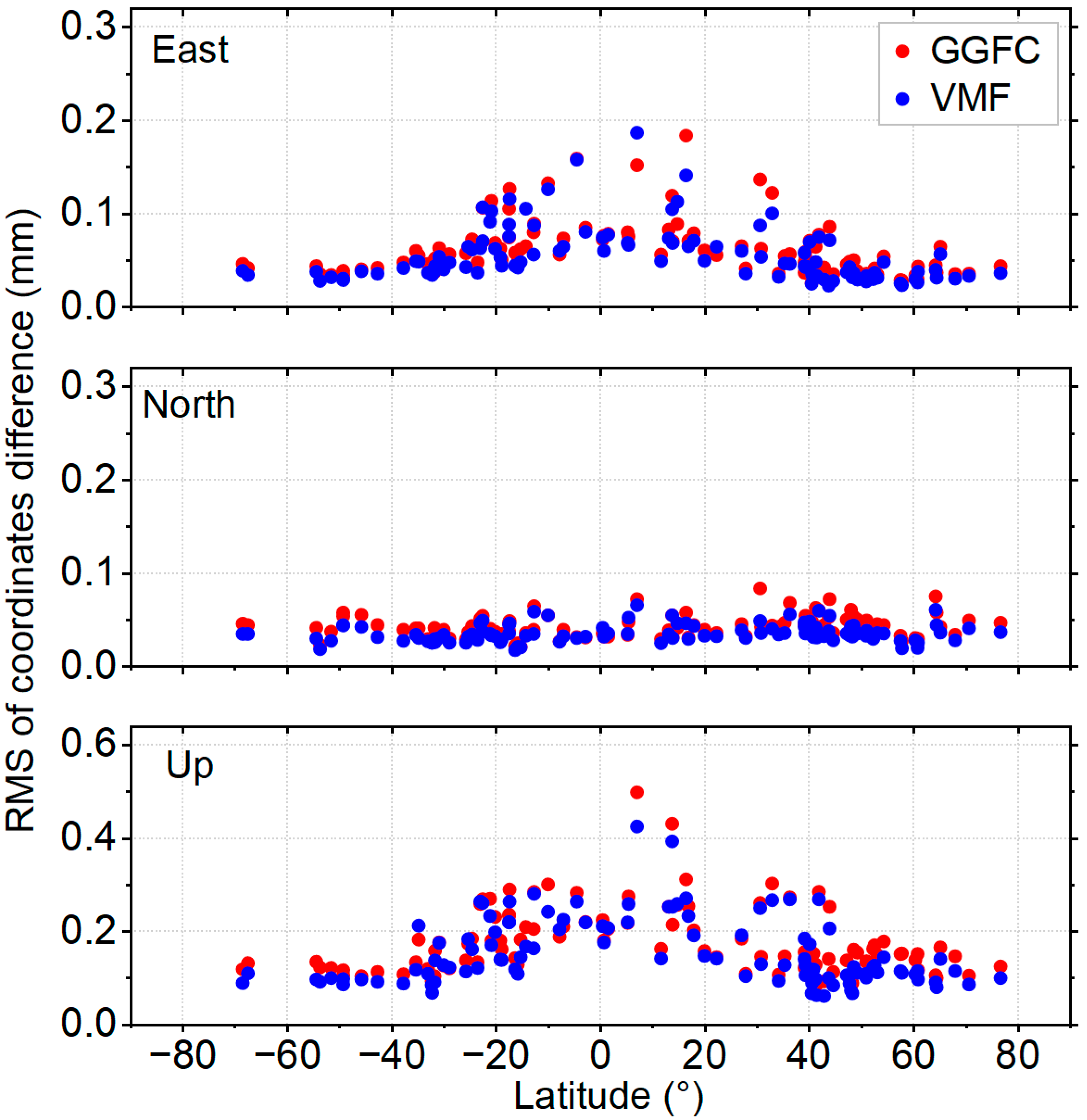
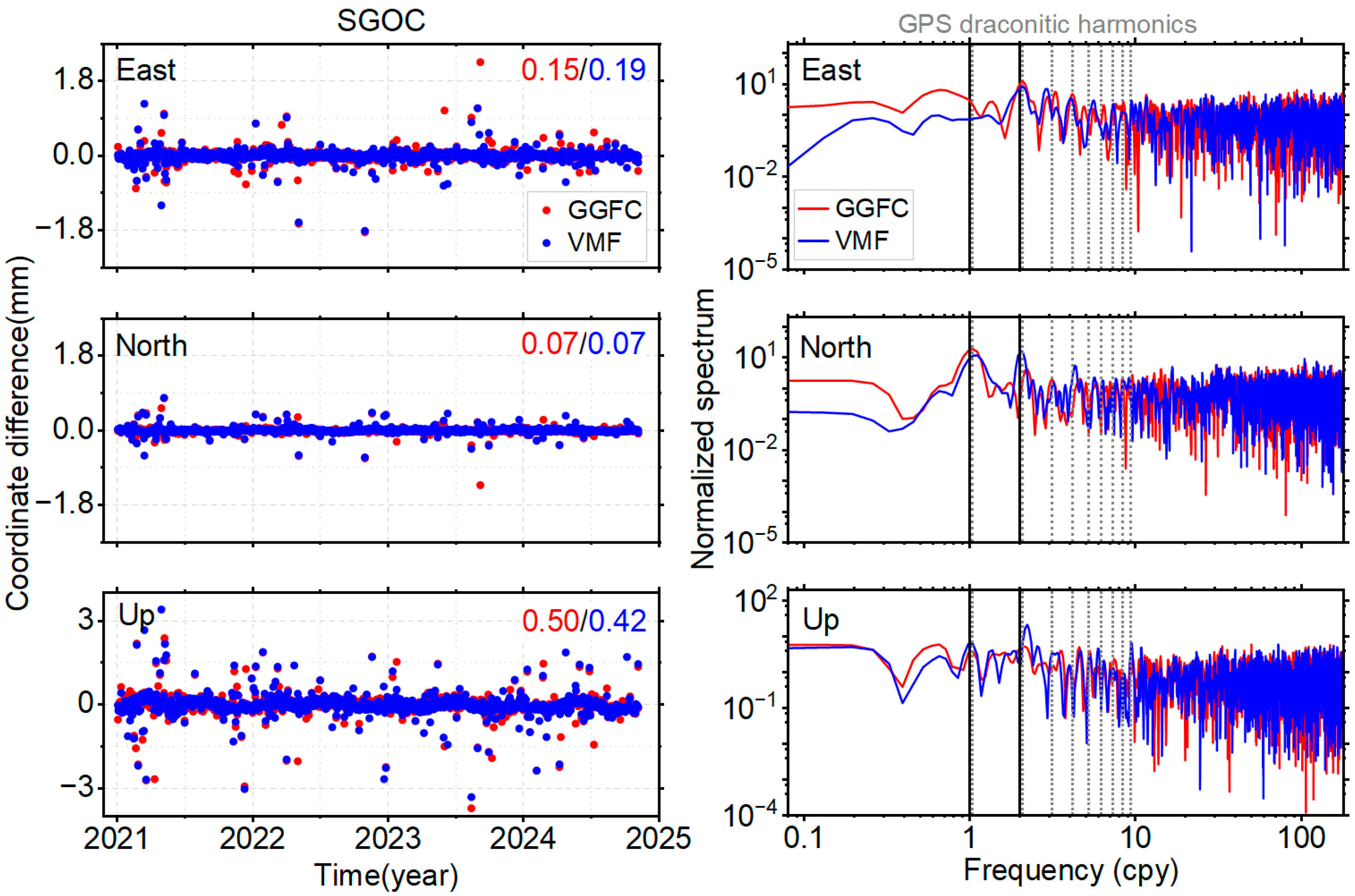
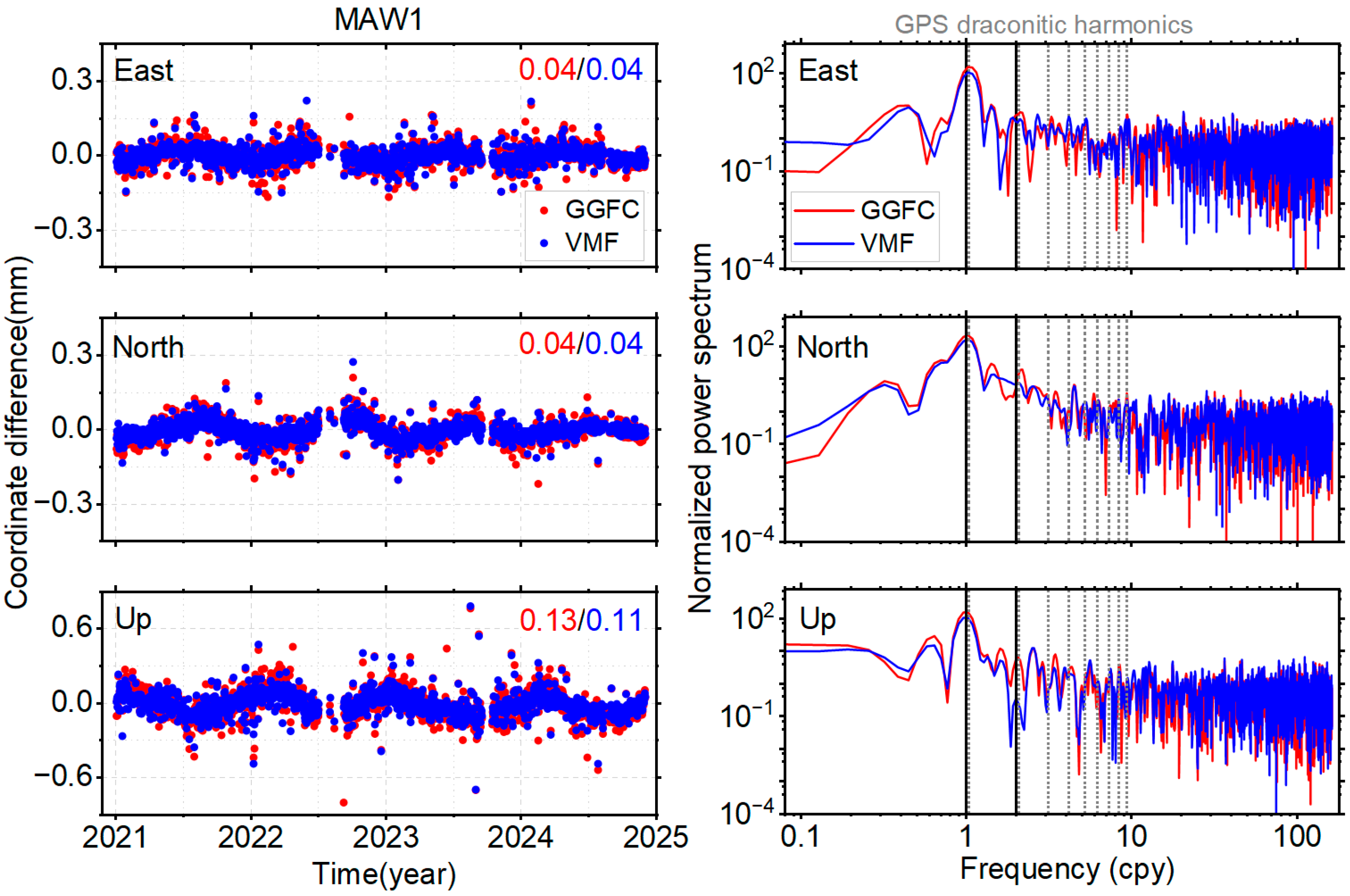
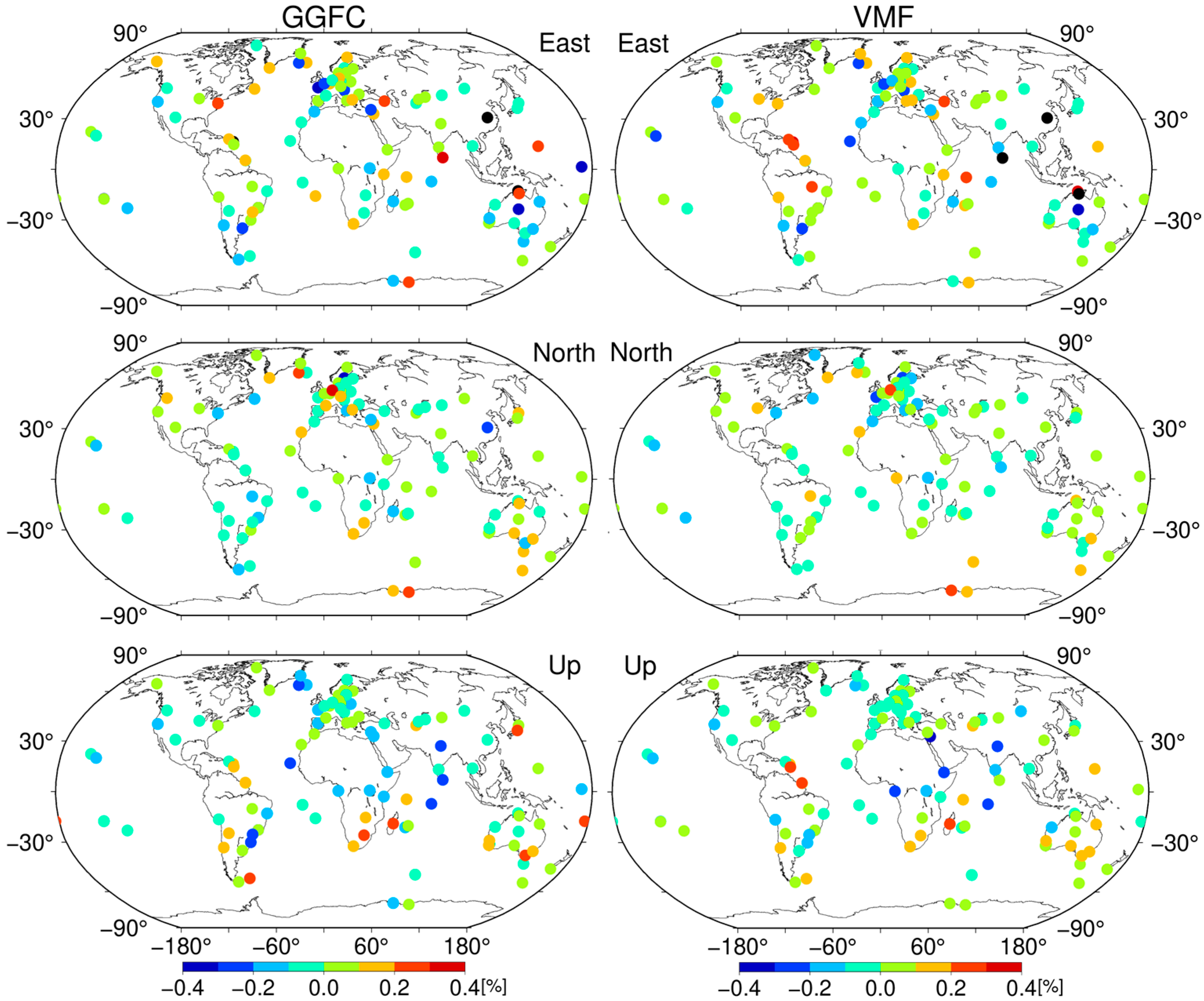
3.1. Station Coordinates Differences
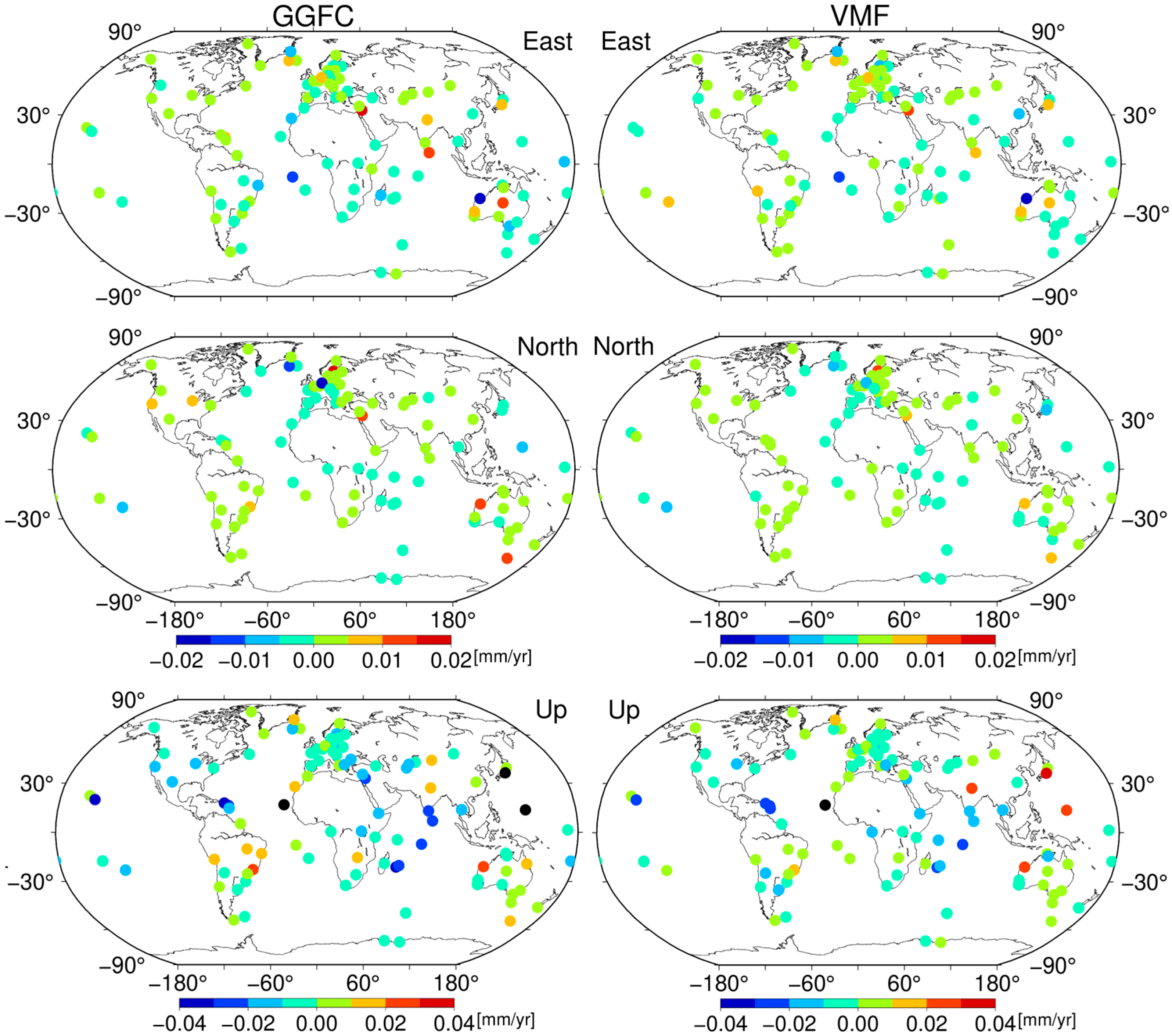
3.2. Linear Velocity
3.3. Periodical Variations
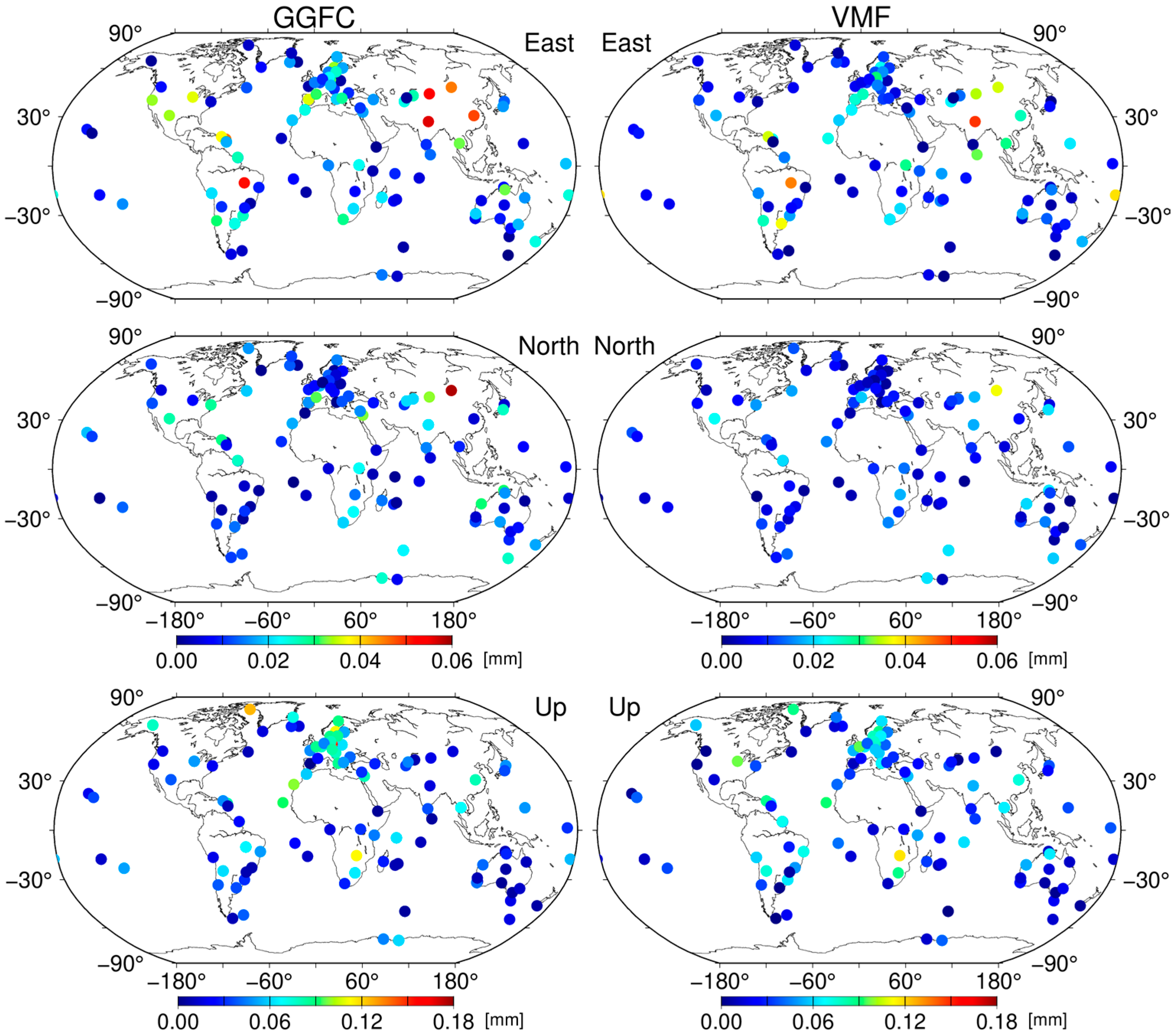
3.4. WRMS Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Han, S.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Benefits of Tidal Admittance Functions for Refining GNSS-Observed Solar and Lunisolar Tidal Constituents. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, Z.; Rebischung, P.; Collilieux, X.; Métivier, L.; Chanard, K. ITRF2020: An Augmented Reference Frame Refining the Modeling of Nonlinear Station Motions. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Haines, B.J.; Heflin, M.B.; Landerer, F.W. Improved Global Nonlinear Surface Mass Variation Estimates from Geodetic Displacements and Reconciliation with GRACE Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Song, S.; He, L. Recommendations for Construction of a Nonlinear International Terrestrial Reference Frame. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 54, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranchi, R.; Moghtased-Azar, K.; Safari, A. Fast Approximation Algorithm to Noise Components Estimation in Long-Term GPS Coordinate Time Series. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría Gómez, A.; Ray, J.R. Chameleonic Noise in GPS Position Time Series. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB019541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, J.; Klos, A. On the Significance of Periodic Signals in Noise Analysis of GPS Station Coordinates Time Series. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Deser, C. Diurnal and Semidiurnal Variations in Global Surface Wind and Divergence Fields. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1999, 104, 31109–31125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.T.; King, M.A.; Stewart, M.P. GPS Height Time Series: Short-Period Origins of Spurious Long-Period Signals. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 2005JB004047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchuk, S.; Doskich, S.; Gołda, P.; Rurak, A. The Seasonal Variations Analysis of Permanent GNSS Station Time Series in the Central-East of Europe. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifa, S. Correlation Study of the Annual Signal in GPS and DORIS Station Positions with Atmospheric and Hydrology Loading Effects. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, L.; Boy, J.P. Study of the Atmospheric Pressure Loading Signal in Very Long Baseline Interferometry Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2004, 109, 2003JB002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregoning, P.; van Dam, T. Atmospheric Pressure Loading Corrections Applied to GPS Data at the Observation Level. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 2005GL024104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K.; Jin, S. Geodetic Study On Earth Surface Loading with GNSS and GRACE. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.T.; Stewart, M.P. Aliased Tidal Signatures in Continuous GPS Height Time Series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2003GL018828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Yang, P.; He, L.; Xia, Y.; Luan, W. Research On the Refinement Algorithm of Surface Loading Deformation Based On Green’S Function. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2025, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregoning, P.; Watson, C. Atmospheric Effects and Spurious Signals in GPS Analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114, 2009JB006344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebischung, P.; Altamimi, Z.; Métivier, L.; Collilieux, X.; Gobron, K.; Chanard, K. Analysis of the IGS Contribution to ITRF2020. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J. Combined Orbits and Clocks From IGS Second Reprocessing. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.D.; Ponte, R.M. Barometric Tides From ECMWF Operational Analyses. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, W.E. Deformation of the Earth by Surface Loads. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 761–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z.; He, L. Impacts of Local Green’s Functions On Modeling Atmospheric Loading Effects for GNSS Reference Stations. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2023EA003113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Self-Consistency in Reference Frames, Geocenter Definition, and Surface Loading of the Solid Earth. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2002JB002082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, C.; Stammer, D. Atmospheric Loading and the Oceanic “Inverted Barometer” Effect. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, T.; Ray, R. Updated October 2010. S1 and S2 Atmospheric Tide Loading Effects for Geodetic Applications. 2010. Available online: https://geophy.uni.lu/atmosphere/tide-loading-calculator/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Wijaya, D.D.; Böhm, J.; Karbon, M.; Kràsnà, H.; Schuh, H. Atmospheric Pressure Loading. In Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Jiang, W.; Deng, L.; Yang, R. The Magnitude of Diurnal/Semidiurnal Atmospheric Tides (S1/S2) and their Impacts On the Continuous GPS Coordinate Time Series. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re3Data.Org: VMF Data Server; Editing Status 2020-12-14; Re3Data.Org-Registry of Research Data Repositories. Available online: https://www.re3data.org/repository/r3d100012025 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Dach, R.; Böhm, J.; Lutz, S.; Steigenberger, P.; Beutler, G. Evaluation of the Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Loading Modeling On GNSS Data Analysis. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Dool, H.M.; Saha, S.; Schemm, J.; Huang, J. A Temporal Interpolation Method to Obtain Hourly Atmospheric Surface Pressure Tides in Reanalysis 1979-1995. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 22013–22024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions. 2010. Available online: https://iers-conventions.obspm.fr/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise Point Positioning for the Efficient and Robust Analysis of GPS Data From Large Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Mao, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, K. PRIDE PPP-AR: An Open-Source Software for GPS PPP Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, D.; Böhm, J. VMF3/GPT3: Refined Discrete and Empirical Troposphere Mapping Functions. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.H.; Allain, D.J.; Cancet, M.; Carrère, L.; Picot, N. FES2014 Global Ocean Tide Atlas: Design and Performance. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Shi, C.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Fan, L.; Wang, C.; Zheng, F. Helmert Transformation Strategies in Analysis of GPS Position Time-Series. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 223, 973–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.P.; Penna, N.T.; Lichti, D.D. Investigating the Propagation Mechanism of Unmodelled Systematic Errors On Coordinate Time Series Estimated Using Least Squares. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Shi, C.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Fan, L.; Zhang, D. Effect of Ambiguity Resolution On the Draconitic Errors in Sub-Daily GPS Position Estimates. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; van Dam, T. Anomalous Harmonics in the Spectra of GPS Position Estimates. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; van Dam, T.; Ding, W. Comparative Analysis of Different Environmental Loading Methods and their Impacts On the GPS Height Time Series. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Description |
|---|---|
| Software | PRIDE PPP-AR (version 3.1.4) |
| Model | Ionosphere-free combination model |
| Frequencies | GPS: L1/L2 |
| Elevation cut-off angle | 7° |
| Sampling rate | 30 s |
| Tropospheric delay model | VMF3 |
| Orbits/clocks/bias products | Rapid products of Wuhan University |
| Receiver antenna calibration | igs14.atx: 3 January 2021 to 26 November 2022 igs20.atx: 27 November 2022 to 1 December 2024 |
| Tidal corrections | Atmospheric tides: RP03 (GGFC or VMF grid model) Ocean tidal loading: FES2014b Solid earth tides and pole tides: IERS 2010 conventions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wei, N.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Atmospheric Tide Loading on GPS Coordinate Time Series. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183147
Li Y, Wei N, Xiao K, Zhang Q. Effects of Atmospheric Tide Loading on GPS Coordinate Time Series. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(18):3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183147
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanlin, Na Wei, Kaiwen Xiao, and Qiyuan Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Atmospheric Tide Loading on GPS Coordinate Time Series" Remote Sensing 17, no. 18: 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183147
APA StyleLi, Y., Wei, N., Xiao, K., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Effects of Atmospheric Tide Loading on GPS Coordinate Time Series. Remote Sensing, 17(18), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17183147






